Diagnosis and Management of Fetal and Neonatal Thyrotoxicosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
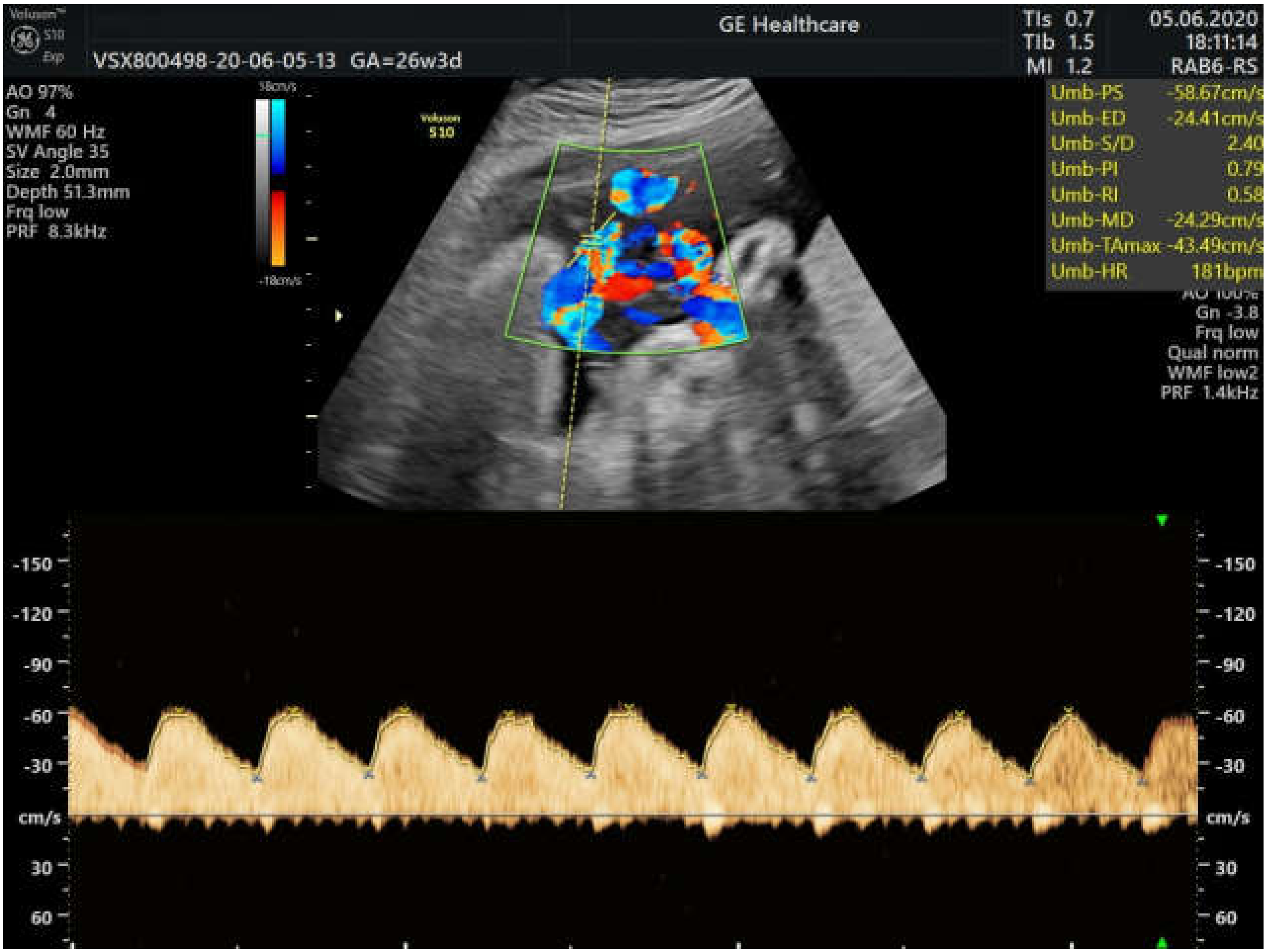
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Polak, M.; Legac, I.; Vuillard, E.; Guibourdenche, J.; Castanet, M.; Luton, D. Congenital Hyperthyroidism: The Fetus as a Patient. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2006, 65, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duprez, L.; Parma, J.; Van Sande, J.; Allgeier, A.; Leclère, J.; Schvartz, C.; Delisle, M.J.; Decoulx, M.; Orgiazzi, J.; Dumont, J.; et al. Germline mutations in the thyrotropin receptor gene cause non–autoimmune autosomal dominant hyperthyroidism. Nat. Genet. 1994, 7, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzapfel, H.-P.; Wonerow, P.; Von Petrykowski, W.; Henschen, M.; Scherbaum, W.A.; Paschke, R. Sporadic Congenital Hyperthyroidism due to a Spontaneous Germline Mutation in the Thyrotropin Receptor Gene. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 3879–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastorakos, G.; Mitsiades, N.S.; Doufas, A.G.; Koutras, D.A. Hyperthyroidism in McCune-Albright Syndrome with a Review of Thyroid Abnormalities Sixty Years After the First Report. Thyroid 1997, 7, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogilvy-Stuart, A.L. Neonatal thyroid disorders. Arch. Dis. Child.—Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2002, 87, 165F–171F. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, F.H.; Burrow, G.N.; Fisher, D.A.; Larsen, P.R. Maternal and Fetal Thyroid Function. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 331, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vulsma, T.; Gons, M.H.; de Vijlder, J.J. Maternal-Fetal Transfer of Thyroxine in Congenital Hypothyroidism Due to a Total Organification Defect or Thyroid Agenesis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1989, 321, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, G.W.; Mandel, S.J. Therapy Insight: Management of Graves’ disease during pregnancy. Nat. Clin. Pract. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 3, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbesino, G.; Tomer, Y. Clinical Utility of TSH Receptor Antibodies. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 2247–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Jiménez, A.; Fernández-Soto, M.L.; Escobar-Jiménez, F.; Glinoer, D.; Navarrete, L. Thyroid function parameters and TSH-receptor antibodies in healthy subjects and Graves’ disease patients: A sequential study before, during and after pregnancy. Thyroidology 1993, 5, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Laurberg, P.; Wallin, G.; Tallstedt, L.; Abraham-Nordling, M.; Lundell, G.; Tørring, O. TSH-receptor autoimmunity in Graves’ disease after therapy with anti-thyroid drugs, surgery, or radioiodine: A 5-year prospective randomized study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2008, 158, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, C.M. Fetal and neonatal thyrotoxicosis. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 17, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneman, D.; Howard, N.J. Neonatal thyrotoxicosis: Intellectual impairment and craniosynostosis in later years. J. Pediatr. 1980, 97, 257–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempers, M.J.E.; Van Tijn, D.A.; Van Trotsenburg, A.S.P.; De Vijlder, J.J.M.; Wiedijk, B.M.; Vulsma, T. Central Congenital Hypothyroidism due to Gestational Hyperthyroidism: Detection Where Prevention Failed. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 5851–5857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, E.K.; Pearce, E.N.; Brent, G.A.; Brown, R.S.; Chen, H.; Dosiou, C.; Grobman, W.A.; Laurberg, P.; Lazarus, J.H.; Mandel, S.J.; et al. 2017 Guidelines of the American Thyroid Association for the Diagnosis and Management of Thyroid Disease During Pregnancy and the Postpartum. Thyroid 2017, 27, 315–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahaly, G.J.; Bartalena, L.; Hegedüs, L.; Leenhardt, L.; Poppe, K.; Pearce, S.H. 2018 European Thyroid Association Guideline for the Management of Graves’ Hyperthyroidism. Eur. Thyroid J. 2018, 7, 167–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurberg, P.; Bournaud, C.; Karmisholt, J.; Orgiazzi, J. Management of Graves’ hyperthyroidism in pregnancy: Focus on both maternal and foetal thyroid function, and caution against surgical thyroidectomy in pregnancy. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2009, 160, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohiltea, R.E.; Zugravu, C.-A.; Neacsu, A.; Navolan, D.; Berceanu, C.; Nemescu, D.; Bodean, O.; Turcan, N.; Baros, A.; Cirstoiu, M.M. The Prevalence of Vitamin D Defficiency and its Obstetrical Effects. A prospective study on Romanian patients. Rev. Chim. 2019, 70, 1228–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshihara, A.; Noh, J.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ohye, H.; Sato, S.; Sekiya, K.; Kosuga, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Kunii, Y.; et al. Treatment of Graves’ Disease with Antithyroid Drugs in the First Trimester of Pregnancy and the Prevalence of Congenital Malformation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 2396–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, S.L.; Olsen, J.; Wu, C.S.; Laurberg, P. Birth Defects After Early Pregnancy Use of Antithyroid Drugs: A Danish Nationwide Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 4373–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahn, R.S.; Burch, H.S.; Cooper, D.S.; Garber, J.R.; Greenlee, C.M.; Klein, I.L.; Laurberg, P.; McDougall, I.R.; Rivkees, S.A.; Ross, D.; et al. The Role of Propylthiouracil in the Management of Graves’ Disease in Adults: Report of a Meeting Jointly Sponsored by the American Thyroid Association and the Food and Drug Administration. Thyroid 2009, 19, 673–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, N.; Narimatsu, H.; Noh, J.Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Kami, M.; Kunii, Y.; Mukasa, K.; Ito, K. Antithyroid drug-induced hematopoietic damage: A retrospective cohort study of agranulocytosis and pancytopenia involving 50, 385 patients with Graves’ disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, E49–E53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel, S.J.; Cooper, D.S. The Use of Antithyroid Drugs in Pregnancy and Lactation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 2354–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milham, S.J.; Elledge, W. Maternal methimazole and congenital defects in children. Teratology 1972, 5, 125–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clementi, M.; Di Gianantonio, E.; Cassina, M.; Leoncini, E.; Botto, L.D.; Mastroiacovo, P.; SAFE-Med Study Group. Treatment of Hyperthyroidism in Pregnancy and Birth Defects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, E337–E341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeverhaus, M.; Koenen, J.; Bechrakis, N.; Stöhr, M.; Herrmann, K.; Fendler, W.P.; Eckstein, A.; Weber, M. Radioiodine ablation of thyroid remnants in patients with Graves’ orbitopathy. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, jnumed.122.264660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moleti, M.; Violi, M.A.; Montanini, D.; Trombetta, C.; Di Bella, B.; Sturniolo, G.; Presti, S.; Alibrandi, A.; Campennì, A.; Baldari, S.; et al. Radioiodine Ablation of Postsurgical Thyroid Remnants After Treatment with Recombinant Human TSH (rhTSH) in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Graves’ Orbitopathy (GO): A Prospective, Randomized, Single-Blind Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 1783–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, C.M.; Gupta, V.; Gupta, N.; Menon, P.S.N. Fetal Hyperthyroidism: Intrauterine Treatment with Carbimazole in Two Siblings. Indian J. Pediatr. 2015, 82, 962–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Murata, M.; Sasahara, J.; Hayashi, S.; Ishii, K.; Mitsuda, N. A case of fetal hyperthyroidism treated with maternal administration of methimazole. J. Perinatol. 2014, 34, 945–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, S.L.; Olsen, J.; Wu, C.S.; Laurberg, P. Severity of Birth Defects After Propylthiouracil Exposure in Early Pregnancy. Thyroid 2014, 24, 1533–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bohîlțea, R.-E.; Mihai, B.-M.; Szini, E.; Șucaliuc, I.-A.; Badiu, C. Diagnosis and Management of Fetal and Neonatal Thyrotoxicosis. Medicina 2023, 59, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59010036
Bohîlțea R-E, Mihai B-M, Szini E, Șucaliuc I-A, Badiu C. Diagnosis and Management of Fetal and Neonatal Thyrotoxicosis. Medicina. 2023; 59(1):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59010036
Chicago/Turabian StyleBohîlțea, Roxana-Elena, Bianca-Margareta Mihai, Elena Szini, Ileana-Alina Șucaliuc, and Corin Badiu. 2023. "Diagnosis and Management of Fetal and Neonatal Thyrotoxicosis" Medicina 59, no. 1: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59010036
APA StyleBohîlțea, R.-E., Mihai, B.-M., Szini, E., Șucaliuc, I.-A., & Badiu, C. (2023). Diagnosis and Management of Fetal and Neonatal Thyrotoxicosis. Medicina, 59(1), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59010036





