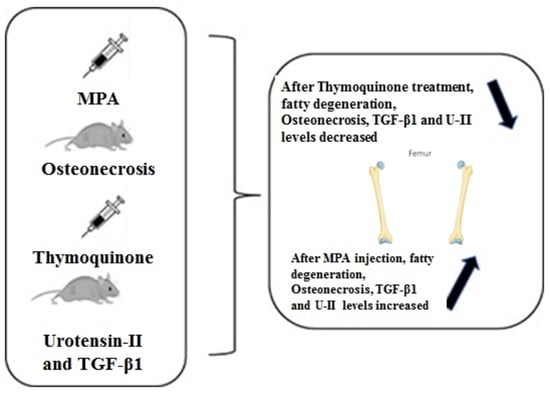
Effects of Thymoquinone on Urotensin-II and TGF-β1 Levels in Model of Osteonecrosis in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement and Experimental Design
2.2. Biochemical Analyses
2.3. Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Histopathological Examination
3.2. Oxidative Evaluations
3.3. Expression of U-II and TGF-β1
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Microsurgery Department of the Orthopedics Branch of the Chinese Medical Doctor Association; Group from the Osteonecrosis and Bone Defect Branch of the Chinese Association of Reparative and Reconstructive Surgery; Microsurgery and Reconstructive Surgery Group of the Orthopedics Branch of the Chinese Medical Association. Chinese Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head in Adults. Orthop. Surg. 2017, 9, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, R.S. Glucocorticoids, osteocytes, and skeletal fragility: The role of bone vascularity. Bone 2010, 46, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlRowis, R.; Aldawood, A.; AlOtaibi, M.; Alnasser, E.; AlSaif, I.; Aljaber, A.; Natto, Z. Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (MRONJ): A Review of Pathophysiology, Risk Factors, Preventive Measures and Treatment Strategies. Saudi Dent. J. 2022, 34, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Kumagai, K.; Osaki, M.; Murata, M.; Tomita, M.; Miyata, N.; Hozumi, A.; Niwa, M. Osteonecrosis of femoral head in the stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats, especially old rats. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2008, 30, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanasekararaja, P.; Soundarrajan, D.; Kumar, K.S.; Pushpa, B.T.; Rajkumar, N.; Rajasekaran, S. Aggressive Presentation and Rapid Progression of Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head After COVID-19. Indian J. Orthop. 2022, 56, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, R.E.; Reis, I.G.N.; Waldolato, G.S.; Pires, D.D.; Bidolegui, F.; Giordano, V. What Do We Need to Know About Musculoskeletal Manifestations of COVID-19?: A Systematic Review. JBJS Rev. 2022, 10, e22.00036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Disser, N.P.; De Micheli, A.J.; Schonk, M.M.; Konnaris, M.A.; Piacentini, A.N.; Edon, D.L.; Toresdahl, B.G.; Rodeo, S.A.; Casey, E.K.; Mendias, C.L. Musculoskeletal Consequences of COVID-19. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2020, 102, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koca, I.; Ucar, M.; Arik, H.O.; Yilmaz, M.; Dokuyucu, R. Alpha-lipoic acid could be a promising treatment in steroid-induced osteonecrosis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 7404–7412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koca, I.; Dokuyucu, R.; Tas, Z.; Gokce, H.; Ozcan, O. Effects of Alpha-Lipoic Acid on TGF-beta 1 and Urotensin-II Levels in Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteonecrosis in Rats. Iran. Red Crescent Med. J. 2020, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uruc, V.; Duman, I.G.; Davul, S.; Özden, R.; Gonenci, R.; Gokce, H.; Dokuyucu, R.; Akdag, A. The Effect of Cape on Steroid Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head in Rat Model. J. Hard Tissue Biol. 2018, 27, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darakhshan, S.; Bidmeshki Pour, A.; Hosseinzadeh Colagar, A.; Sisakhtnezhad, S. Thymoquinone and its therapeutic potentials. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 95–96, 138–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannan, M.A.; Rahman, M.A.; Sohag, A.A.M.; Uddin, M.J.; Dash, R.; Sikder, M.H.; Rahman, M.S.; Timalsina, B.; Munni, Y.A.; Sarker, P.P.; et al. Black Cumin (Nigella sativa L.): A Comprehensive Review on Phytochemistry, Health Benefits, Molecular Pharmacology, and Safety. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Hasan, G.M.; Ansari, M.M.; Sharma, R.; Yadav, D.K.; Hassan, M.I. Therapeutic implications and clinical manifestations of thymoquinone. Phytochemistry 2022, 200, 113213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.Y.; Akter, Z.; Mei, Z.; Zheng, M.; Tania, M.; Khan, M.A. Thymoquinone in autoimmune diseases: Therapeutic potential and molecular mechanisms. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 134, 111157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Huang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Wu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Mingyao, E.; Qi, H.; et al. Therapeutic application of natural products: NAD(+) metabolism as potential target. Phytomedicine 2023, 114, 154768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erol, B.; Sari, U.; Amasyali, A.S.; Ozkanli, S.; Sogut, S.; Hanci, V.; Efiloglu, O.; Danacioglu, Y.O.; Engin, P.; Yencilek, F.; et al. Comparison of combined antioxidants and thymoquinone in the prevention of testis ischemia—Reperfusion injury. Andrology 2017, 5, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, R.R.; Rajpal, V.; Singh, P.; Saraf, S.A. Recent Findings on Thymoquinone and Its Applications as a Nanocarrier for the Treatment of Cancer and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasci, M.F.; Yaprak Sarac, E.; Gok Yurttas, A.; Atci, T.; Uslu, M.; Acar, A.; Gulec, M.A.; Alagoz, E. The effects of thymoquinone on steroid-induced femoral head osteonecrosis: An experimental study in rats. Jt. Dis. Relat. Surg. 2022, 33, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirui, P.K.; Cameron, J.; Benghuzzi, H.A.; Tucci, M.; Patel, R.; Adah, F.; Russell, G. Effects of sustained delivery of thymoqiunone on bone healing of male rats. Biomed. Sci. Instrum. 2004, 40, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Kalamegam, G.; Alfakeeh, S.M.; Bahmaid, A.O.; AlHuwait, E.A.; Gari, M.A.; Abbas, M.M.; Ahmed, F.; Abu-Elmagd, M.; Pushparaj, P.N. In vitro Evaluation of the Anti-inflammatory Effects of Thymoquinone in Osteoarthritis and in silico Analysis of Inter-Related Pathways in Age-Related Degenerative Diseases. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.Y.; He, T.; Li, X.L.; Xu, W.L.; Ge, Z.M. Urotensin-2 promotes collagen synthesis via ERK1/2-dependent and ERK1/2-independent TGF-beta1 in neonatal cardiac fibroblasts. Cell Biol. Int. 2011, 35, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Ding, W.; Song, N.; Dong, X.; Di, B.; Peng, F.; Tang, C. Urotensin II-induced collagen synthesis in cultured smooth muscle cells from rat aortic media and a possible involvement of transforming growth factor-beta1/Smad2/3 signaling pathway. Regul. Pept. 2013, 182, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogebakan, B.; Uruc, V.; Ozden, R.; Duman, I.G.; Yagiz, A.E.; Okuyan, H.M.; Aldemir, O.; Dogramaci, Y.; Kalaci, A. Urotensin II (U-II), a novel cyclic peptide, possibly associated with the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Peptides 2014, 54, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharstuhl, A.; Vitters, E.L.; van der Kraan, P.M.; van den Berg, W.B. Reduction of osteophyte formation and synovial thickening by adenoviral overexpression of transforming growth factor beta/bone morphogenetic protein inhibitors during experimental osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 3442–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaney Davidson, E.N.; Vitters, E.L.; van den Berg, W.B.; van der Kraan, P.M. TGF beta-induced cartilage repair is maintained but fibrosis is blocked in the presence of Smad7. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, N.; Kumagai, K.; Osaki, M.; Murata, M.; Tomita, M.; Hozumi, A.; Nozaki, Y.; Niwa, M. Pentosan reduces osteonecrosis of femoral head in SHRSP. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2010, 32, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, R.; Dahiya, S.; Dhingra, D.; Dilbaghi, N.; Kim, K.H.; Kumar, S. Improvement of antihyperglycemic activity of nano-thymoquinone in rat model of type-2 diabetes. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 295, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, Y.; Kumagai, K.; Miyata, N.; Niwa, M. Pravastatin reduces steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in SHRSP rats. Acta Orthop. 2012, 83, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, J.E. Early diagnosis and treatment of steroid induced avascular necrosis of bone. Br. Med. J. 1984, 288, 741–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Irisa, T.; Sugioka, Y.; Sueishi, K. Effects of pulse methylprednisolone on bone and marrow tissues: Corticosteroid-induced osteonecrosis in rabbits. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 40, 2055–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drescher, W.; Schneider, T.; Becker, C.; Hobolth, J.; Ruther, W.; Hansen, E.S.; Bunger, C. Selective reduction of bone blood flow by short-term treatment with high-dose methylprednisolone. An experimental study in pigs. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 2001, 83, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyanishi, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Irisa, T.; Yamashita, A.; Jingushi, S.; Noguchi, Y.; Iwamoto, Y. A high low-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio as a potential risk factor for corticosteroid-induced osteonecrosis in rabbits. Rheumatology 2001, 40, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, H.B.; Spillert, C.R. Effect of methylprednisolone on coagulation. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 1999, 91, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guan, X.Y.; Han, D. Role of hypercoagulability in steroid-induced femoral head necrosis in rabbits. J. Orthop. Sci. 2010, 15, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Zaane, B.; Nur, E.; Squizzato, A.; Gerdes, V.E.; Buller, H.R.; Dekkers, O.M.; Brandjes, D.P. Systematic review on the effect of glucocorticoid use on procoagulant, anti-coagulant and fibrinolytic factors. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2010, 8, 2483–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motomura, G.; Yamamoto, T.; Miyanishi, K.; Jingushi, S.; Iwamoto, Y. Combined effects of an anticoagulant and a lipid-lowering agent on the prevention of steroid-induced osteonecrosis in rabbits. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 3387–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, P.; Gao, H.; Pei, F.; Shen, B.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Z. Effects of an anticoagulant and a lipid-lowering agent on the prevention of steroid-induced osteonecrosis in rabbits. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2010, 91, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, B.; Li, P.; Lu, C.; Xu, Y.; Chen, W.; Lin, N. Pravastatin prevents steroid-induced osteonecrosis in rats by suppressing PPARgamma expression and activating Wnt signaling pathway. Exp. Biol. Med. 2014, 239, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichiseki, T.; Kaneuji, A.; Katsuda, S.; Ueda, Y.; Sugimori, T.; Matsumoto, T. DNA oxidation injury in bone early after steroid administration is involved in the pathogenesis of steroid-induced osteonecrosis. Rheumatology 2005, 44, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.L.; Tang, X.L. Effect of glucocorticoid-induced oxidative stress on the expression of Cbfa1. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 207, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Shi, Z.; Bi, W.; Liu, R.; Zhang, C.; Wang, K.; Dang, X. Beneficial effect of grape seed proanthocyanidin extract in rabbits with steroid-induced osteonecrosis via protecting against oxidative stress and apoptosis. J. Orthop. Sci. 2015, 20, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.B.; Li, K.H. Lipoic acid prevents steroid-induced osteonecrosis in rabbits. Rheumatol. Int. 2012, 32, 1679–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohandel, Z.; Farkhondeh, T.; Aschner, M.; Samarghandian, S. Anti-inflammatory effects of thymoquinone and its protective effects against several diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 138, 111492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulmez, M.I.; Okuyucu, S.; Dokuyucu, R.; Gokce, H. The effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester and thymoquinone on otitis media with effusion in rats. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 96, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirel, H.; Arli, C.; Ozgur, T.; Inci, M.; Dokuyucu, R. The Role of Topical Thymoquinone in the Treatment of Acute Otitis Externa; an Experimental Study in Rats. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2018, 14, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Fu, P.; Zhou, M.; Gu, Y.; Li, Y.; Qi, J. Role of urotensin II in advanced glycation end product-induced extracellular matrix synthesis in rat proximal tubular epithelial cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 1831–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrhan, F.; Hyckel, P.; Guentsch, A.; Nkenke, E.; Stockmann, P.; Schlegel, K.A.; Neukam, F.W.; Amann, K. Bisphosphonate-associated osteonecrosis of the jaw is linked to suppressed TGFbeta1-signaling and increased Galectin-3 expression: A histological study on biopsies. J. Transl. Med. 2011, 9, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Z. Roles of TGF-beta 1 signaling in the development of osteoarthritis. Histol. Histopathol. 2016, 31, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, K.J.; Blobe, G.C. Role of transforming growth factor-beta superfamily signaling pathways in human disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1782, 197–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Control (n = 10) | MPA (n = 10) | TMQ (n = 10) | MPA + TMQ (n = 10) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fatty degeneration | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 1.53 ± 0.1 | 0.30 ± 0.1 | 0.76 ± 0.2 b* |
| Osteonecrosis | 0.00 ± 0.01 | 3.50 ± 0.29 | 0.00 ± 0.01 | 2.13 ± 0.35 b* |
| 4-HNE | 0.97 ± 0.65 | 3.69 ± 0.22 a* | 1.29 ± 0.30 | 1.75 ± 0.28 b* |
| 8-OHdG | 0.95 ± 0.46 | 3.50 ± 0.34 a* | 1.37 ± 0.19 | 1.55 ± 0.41 b* |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yilmaz, M.; Dokuyucu, R. Effects of Thymoquinone on Urotensin-II and TGF-β1 Levels in Model of Osteonecrosis in Rats. Medicina 2023, 59, 1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59101781
Yilmaz M, Dokuyucu R. Effects of Thymoquinone on Urotensin-II and TGF-β1 Levels in Model of Osteonecrosis in Rats. Medicina. 2023; 59(10):1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59101781
Chicago/Turabian StyleYilmaz, Mehmet, and Recep Dokuyucu. 2023. "Effects of Thymoquinone on Urotensin-II and TGF-β1 Levels in Model of Osteonecrosis in Rats" Medicina 59, no. 10: 1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59101781
APA StyleYilmaz, M., & Dokuyucu, R. (2023). Effects of Thymoquinone on Urotensin-II and TGF-β1 Levels in Model of Osteonecrosis in Rats. Medicina, 59(10), 1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59101781