Neuromuscular Ultrasound in Intensive Care Unit-Acquired Weakness: Current State and Future Directions
Abstract
1. Introduction
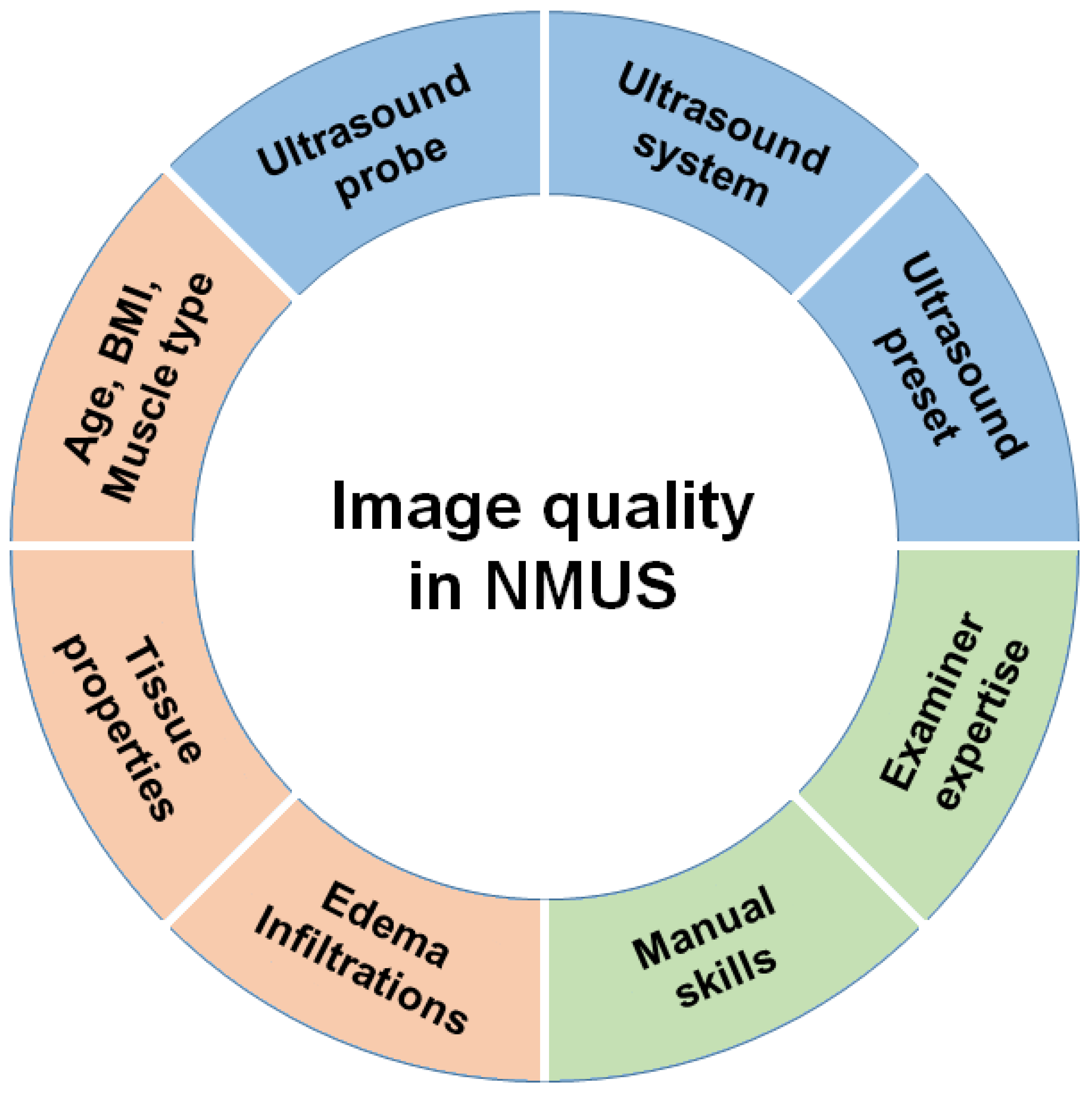
2. Basics of NMUS in the Intensive Care Setting
2.1. Basics for the Examination
2.2. Specialties in the Intensive Care Setting
3. Current State of NMUS in ICUAW
3.1. Skeletal Muscles
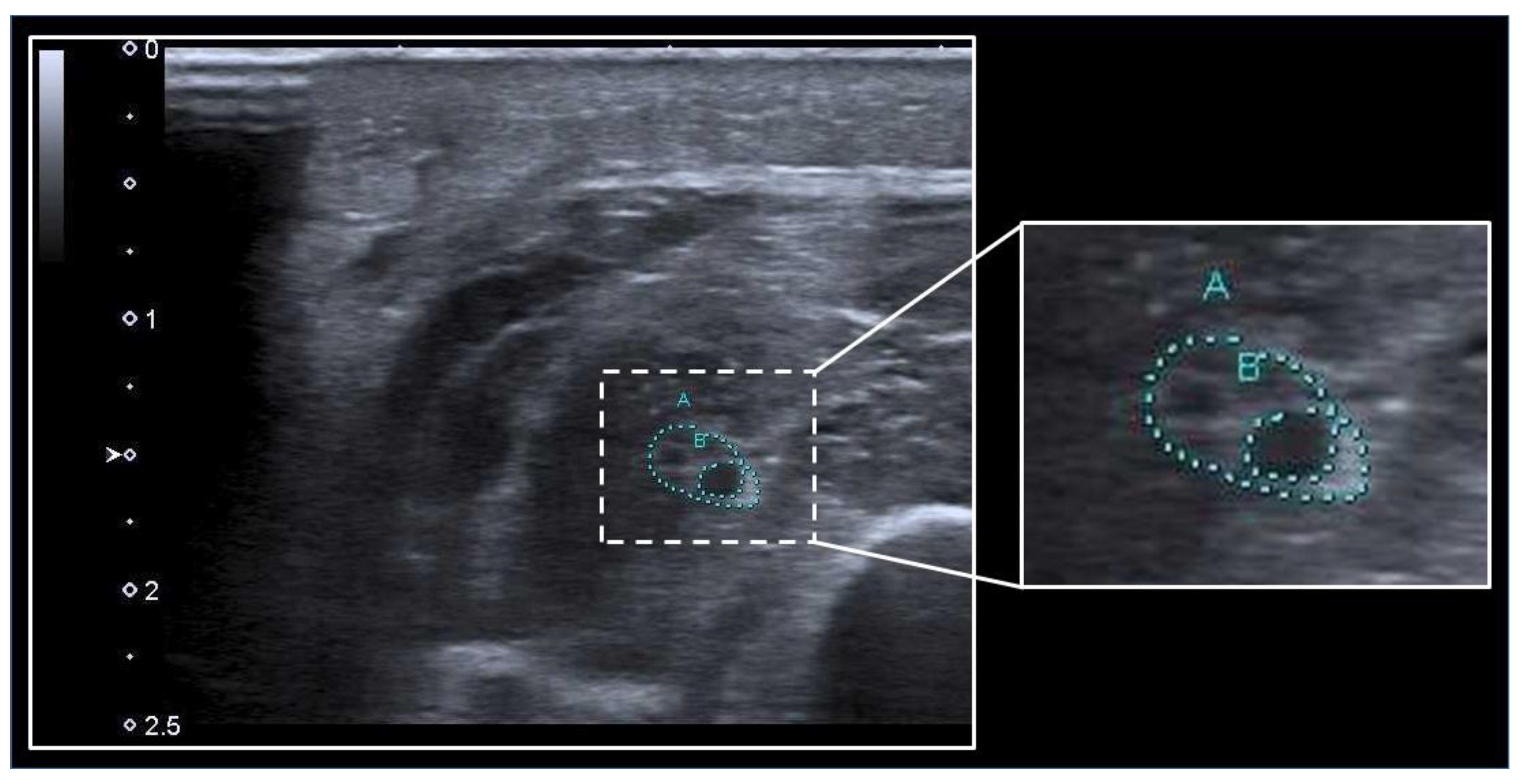
3.2. Peripheral Nerves
3.3. Diaphragm
3.4. Parameters of Muscle Quantity and Their Diagnostic Value for ICUAW
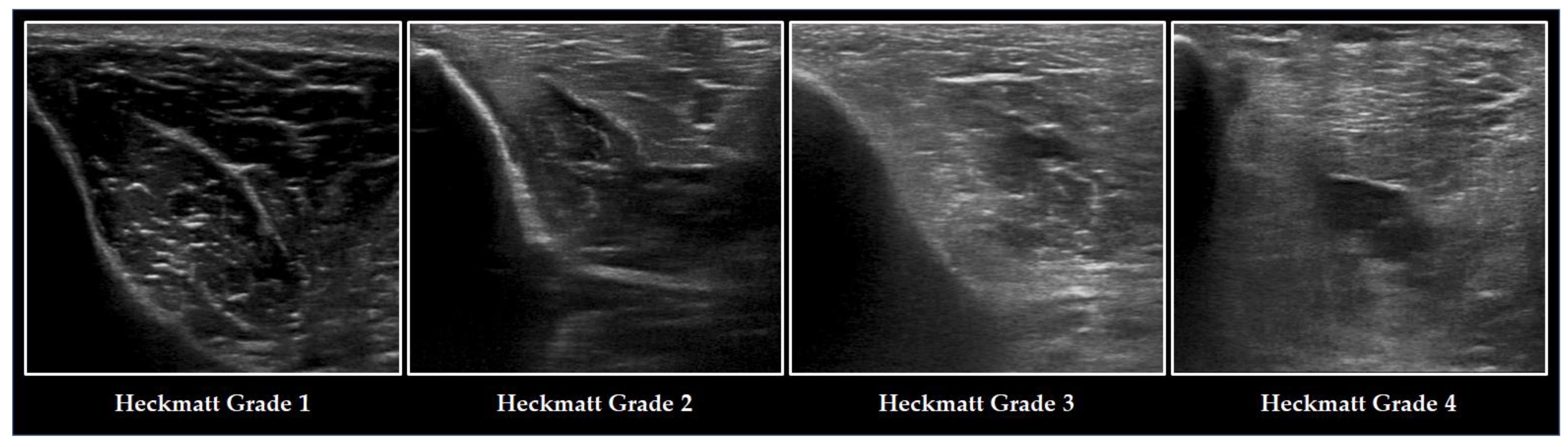
3.5. Parameters of Muscle Quality and Their Diagnostic Value for ICUAW
4. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hermans, G.; van den Berghe, G. Clinical review: Intensive care unit acquired weakness. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, R.D.; Marshall, S.A.; Cornblath, D.R.; Hoke, A.; Needham, D.M.; De Jonghe, B.; Ali, N.; Sharshar, T. A framework for diagnosing and classifying intensive care unit-acquired weakness. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 37, S299–S308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, O.; Reid, M.B.; Berghe, G.V.D.; Vanhorebeek, I.; Hermans, G.; Rich, M.M.; Larsson, L. The Sick and the Weak: Neuropathies/Myopathies in the Critically Ill. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 1025–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Aerde, N.; Meersseman, P.; Debaveye, Y.; Wilmer, A.; Gunst, J.; Casaer, M.P.; Bruyninckx, F.; Wouters, P.J.; Gosselink, R.; Berghe, G.V.D.; et al. Five-year impact of ICU-acquired neuromuscular complications: A prospective, observational study. Intensiv. Care Med. 2020, 46, 1184–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senger, D.; Erbguth, F. Critical-illness-Myopathie und -Polyneuropathie. Med. Klin. Intensive Notf. 2017, 112, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klawitter, F.; Oppitz, M.-C.; Goettel, N.; Berger, M.M.; Hodgson, C.; Weber-Carstens, S.; Schaller, S.J.; Ehler, J. A Global Survey on Diagnostic, Therapeutic and Preventive Strategies in Intensive Care Unit—Acquired Weakness. Medicina 2022, 58, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klawitter, F.; Schaller, S.J.; Söhle, M.; Reuter, D.A.; Ehler, J. Intensive Care Unit-Acquired Weakness. Die Anaesthesiol. 2022, 71, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, B.A.; Jones, G.D.; Curtis, A.A.; Murphy, P.B.; Douiri, A.; Hopkinson, N.S.; Polkey, M.I.; Moxham, J.; Hart, N. Clinical predictive value of manual muscle strength testing during critical illness: An observational cohort study. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patejdl, R.; Klawitter, F.; Walter, U.; Zanaty, K.; Schwandner, F.; Sellmann, T.; Porath, K.; Ehler, J. A novel ex vivo model for critical illness neuromyopathy using freshly resected human colon smooth muscle. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patejdl, R.; Walter, U.; Rosener, S.; Sauer, M.; Reuter, D.A.; Ehler, J. Muscular Ultrasound, Syndecan-1 and Procalcitonin Serum Levels to Assess Intensive Care Unit-Acquired Weakness. Can. J. Neurol. Sci./J. Can. Sci. Neurol. 2019, 46, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieske, L.; Verhamme, C.; Witteveen, E.; Bouwes, A.; Dettling-Ihnenfeldt, D.S.; Van Der Schaaf, M.; Schultz, M.J.; Van Schaik, I.N.; Horn, J. Feasibility and Diagnostic Accuracy of Early Electrophysiological Recordings for ICU-Acquired Weakness: An Observational Cohort Study. Neurocrit. Care 2014, 22, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puthucheary, Z.A.; Rawal, J.; McPhail, M.; Connolly, B.; Ratnayake, G.; Chan, P.; Hopkinson, N.S.; Padhke, R.; Dew, T.; Sidhu, P.S.; et al. Acute Skeletal Muscle Wasting in Critical Illness. JAMA 2013, 310, 1591–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhorebeek, I.; Latronico, N.; Berghe, G.V.D. ICU-acquired weakness. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 637–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, N.; Kobayashi, S.; Tanji, Y.; Hasegawa, A.; Tase, C.; Ugawa, Y. Widespread muscle involvement in critical illness myopathy revealed by MRI. Muscle Nerve 2011, 44, 842–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildiz, O.K.; Yildiz, B.; Avci, O.; Hasbek, M.; Kanat, S. Clinical, Neurophysiological and Neuroimaging Findings of Critical Illness Myopathy After COVID-19. Cureus 2021, 13, e13807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokkoku, K.; Erra, C.; Cuccagna, C.; Coraci, D.; Gatto, D.M.; Glorioso, D.; Padua, L. Intensive Care Unit-Acquired Weakness and Positioning-Related Peripheral Nerve Injuries in COVID-19: A Case Series of Three Patients and the Latest Literature Review. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, A.; Carlier, R.; Descatha, A. Critical illness myopathy and whole body MRI. Intensiv. Care Med. 2015, 42, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daste, C.; Mihoubi, F.; Roren, A.; Dumitrache, A.; Carlier, N.; Benghanem, S.; Ruttimann, A.; Mira, J.-P.; Pène, F.; Roche, N.; et al. Early shoulder-girdle MRI findings in severe COVID-19–related intensive care unit-acquired weakness: A prospective cohort study. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehmann, R.; Enax-Krumova, E.; Meyer-Frießem, C.H.; Schlaffke, L. Quantitative muscle MRI displays clinically relevant myostructural abnormalities in long-term ICU-survivors: A case–control study. BMC Med. Imaging 2023, 23, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labin, E.; Manousakis, G. Correlation of MRI with Muscle Biopsy Findings in Critical Illness Myopathy (P3.459). Neurology 2018, 90 (Suppl. S15). Available online: https://n.neurology.org/content/90/15_Supplement/P3.459 (accessed on 19 March 2023).
- Maramattom, B.V. Screening Power of Short Tau Inversion Recovery Muscle Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Critical Illness Myoneuropathy and Guillain–Barre Syndrome in the Intensive Care Unit. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 26, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robba, C.; Wong, A.; Poole, D.; Al Tayar, A.; Arntfield, R.T.; Chew, M.S.; Corradi, F.; Douflé, G.; Goffi, A.; Lamperti, M.; et al. Basic ultrasound head-to-toe skills for intensivists in the general and neuro intensive care unit population: Consensus and expert recommendations of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensiv. Care Med. 2021, 47, 1347–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.; Galarza, L.; Forni, L.; De Backer, D.; Slama, M.; Cholley, B.; McLean, A.; Vieillard-Baron, A.; Lichtenstein, D.; Volpicelli, G.; et al. Recommendations for core critical care ultrasound competencies as a part of specialist training in multidisciplinary intensive care: A framework proposed by the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM). Crit. Care 2020, 24, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Alfen, N.; Mah, J.K. Neuromuscular Ultrasound: A New Tool in Your Toolbox. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. J. Can. Sci. Neurol. 2018, 45, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijntjes, J.; van Alfen, N. Muscle ultrasound: Present state and future opportunities. Muscle Nerve. 2020, 63, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolo, F.; Valentina, D.G.; Silvia, C.; Tommaso, P.; Elena, C.; Martin, D.; John, J.M.; Davide, C. The possible predictive value of muscle ultrasound in the diagnosis of ICUAW in long-term critically ill patients. J. Crit. Care 2022, 71, 154104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelmenson, D.A.; Quan, D.; Moss, M. What is the diagnostic accuracy of single nerve conduction studies and muscle ultrasound to identify critical illness polyneuromyopathy: A prospective cohort study. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, A.; Teschner, U.; Porzelius, C.; Ludewig, K.; Zielske, J.; Witte, O.W.; Brunkhorst, F.M.; Axer, H. Muscle ultrasound for early assessment of critical illness neuromyopathy in severe sepsis. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klawitter, F.; Walter, U.; Patejdl, R.; Endler, J.; Reuter, D.A.; Ehler, J. Sonographic Evaluation of Muscle Echogenicity for the Detection of Intensive Care Unit-Acquired Weakness: A Pilot Single-Center Prospective Cohort Study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadda, V.; Kumar, R.; Khilnani, G.C.; Kalaivani, M.; Madan, K.; Tiwari, P.; Mittal, S.; Mohan, A.; Bhalla, A.S.; Guleria, R. Trends of loss of peripheral muscle thickness on ultrasonography and its relationship with outcomes among patients with sepsis. J. Intensive Care 2018, 6, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijntjes, J.; van der Hoeven, J.; Saris, C.G.J.; Doorduin, J.; van Alfen, N. Visual versus quantitative analysis of muscle ultrasound in neuromuscular disease. Muscle Nerve 2022, 66, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillen, S.; van Keimpema, M.; Nievelstein, R.A.; Verrips, A.; van Kruijsbergen-Raijmann, W.; Zwarts, M.J. Skeletal muscle ultrasonography: Visual versus quantitative evaluation. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2006, 32, 1315–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, F.O.; Cartwright, M.S. Neuromuscular Ultrasound; W.B. Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hommel, A.L.; Cartwright, M.S.; Walker, F.O. The use of ultrasound in neuromuscular diagnoses. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 2017, 7, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, J.M.; Dexter, W.W. Basics of Musculoskeletal Ultrasound, 2nd ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Gutierrez, H.; Martucci, M.; Poussaint, A.; Qi, K.; Sanchez, B.; Rutkove, S.B. Quantitative muscle ultrasound in upper extremity mononeuropathies. Muscle Nerve 2019, 60, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Seguel, F.; Pinto-Concha, J.J.; Ríos-Castro, F.; Silva-Gutiérrez, A.; Camus-Molina, A.; Mayer, K.P.; Parry, S.M. Evaluating a Muscle Ultrasound Education Program: Theoretical Knowledge, Hands-on Skills, Reliability, and Satisfaction of Critical Care Physiotherapists. Arch. Rehabil. Res. Clin. Transl. 2021, 3, 100142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Santibanez, R.; Dietz, A.R.; Bucelli, R.C.; Zaidman, C.M. Nerve ultrasound reliability of upper limbs: Effects of examiner training. Muscle Nerve 2017, 57, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidman, C.M.; Wu, J.S.; Wilder, S.; Darras, B.T.; Rutkove, S.B. Minimal training is required to reliably perform quantitative ultrasound of muscle. Muscle Nerve 2014, 50, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, T.S.; de Queiroz, R.S.; Ramos, A.C.C.; Martinez, B.P.; Silva, C.M.D.S.E.; Gomes-Neto, M. Ultrasound Protocols to Assess Skeletal and Diaphragmatic Muscle in People Who Are Critically Ill: A Systematic Review. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2021, 47, 3041–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuest, K.E.; Lanz, H.; Schulz, J.; Ulm, B.; Bennett, V.A.; Grunow, J.J.; Weiss, B.; Blobner, M.; Schaller, S.J. Comparison of Different Ultrasound Methods to Assess Changes in Muscle Mass in Critically ill Patients. J. Intensive Care Med. 2022, 38, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagoort, I.; Hortobágyi, T.; Vuillerme, N.; Lamoth, C.J.C.; Murgia, A. Age- and muscle-specific reliability of muscle architecture measurements assessed by two-dimensional panoramic ultrasound. Biomed. Eng. Online 2022, 21, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, J.N.; Lanferdini, F.J.; Karam, J.Y.P.; Fontana, H.D.B. Examination of the confounding effect of subcutaneous fat on muscle echo intensity utilizing exogenous fat. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 46, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisse, A.L.; May, C.; Motte, J.; Pedreiturria, X.; Breuer, T.G.K.; Schneider-Gold, C.; Marcus, K.; Gold, R.; Yoon, M.-S.; Pitarokoili, K. New Approaches to Critical Illness Polyneuromyopathy: High-Resolution Neuromuscular Ultrasound Characteristics and Cytokine Profiling. Neurocrit. Care 2020, 35, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witteveen, E.; Sommers, J.; Wieske, L.; Doorduin, J.; van Alfen, N.; Schultz, M.J.; van Schaik, I.N.; Horn, J.; Verhamme, C. Diagnostic accuracy of quantitative neuromuscular ultrasound for the diagnosis of intensive care unit-acquired weakness: A cross-sectional observational study. Ann. Intensive Care 2017, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Bear, D.; Patel, B.; Puthucheary, Z. Clinical Application of Ultrasound in Intensive Care Unit-Acquired Weakness. Ultraschall der Med. Eur. J. Ultrasound 2020, 41, 244–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubé, B.-P.; Dres, M.; Mayaux, J.; Demiri, S.; Similowski, T.; Demoule, A. Ultrasound evaluation of diaphragm function in mechanically ventilated patients: Comparison to phrenic stimulation and prognostic implications. Thorax 2017, 72, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goligher, E.C.; Laghi, F.; Detsky, M.E.; Farias, P.; Murray, A.; Brace, D.; Brochard, L.J.; Bolz, S.S.; Rubenfeld, G.D.; Kavanagh, B.P.; et al. Measuring diaphragm thickness with ultrasound in mechanically ventilated patients: Feasibility, reproducibility and validity. Intensive Care Med. 2015, 41, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naoi, T.; Morita, M.; Koyama, K.; Katayama, S.; Tonai, K.; Sekine, T.; Hamada, K.; Nunomiya, S. Upper Arm Muscular Echogenicity Predicts Intensive Care Unit-acquired Weakness in Critically Ill Patients. Prog. Rehabil. Med. 2022, 7, 20220034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitiello, L.; Salerno, G.; De Bernardo, M.; D’Aniello, O.; Capasso, L.; Marotta, G.; Rosa, N. Ultrasound Detection of Intracranial Hypertension in Brain Injuries. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 870808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, L.; Loizides, A.; Gruber, H.; Skalla, E.; Haushammer, S.; Horlings, C.; Beer, R.; Helbok, R.; Löscher, W.N. Differentiation of Critical Illness Myopathy and Critical Illness Neuropathy Using Nerve Ultrasonography. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulinski, C.; Viard, M.; Vlazak, A.; Habig, K.; Juenemann, M.; Best, C.; Schirotzek, I.; Kaps, M.; Krämer, H.H. Neuromuscular sonography detects changes in muscle echotexture and nerve diameter in ICU patients within 24 h. J. Ultrasound 2021, 25, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdmann, A.; Motte, J.; Brünger, J.; Grüter, T.; Gold, R.; Pitarokoili, K.; Fisse, A.L. Nerve Echogenicity in Polyneuropathies of Various Etiologies—Results of a Retrospective Semi-Automatic Analysis of High-Resolution Ultrasound Images. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisse, A.L.; Pitarokoili, K.; Motte, J.; Gamber, D.; Kerasnoudis, A.; Gold, R.; Yoon, M.-S. Nerve echogenicity and intranerve CSA variability in high-resolution nerve ultrasound (HRUS) in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP). J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogarty, M.J.; Mantilla, C.B.; Sieck, G.C. Breathing: Motor Control of Diaphragm Muscle. Physiology 2018, 33, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supinski, G.S.; Morris, P.E.; Dhar, S.; Callahan, L.A. Diaphragm Dysfunction in Critical Illness. Chest 2018, 153, 1040–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklar, M.C.; Dres, M.; Fan, E.; Rubenfeld, G.D.; Scales, D.C.; Herridge, M.; Rittayamai, N.; Harhay, M.O.; Reid, W.D.; Tomlinson, G.; et al. Association of Low Baseline Diaphragm Muscle Mass With Prolonged Mechanical Ventilation and Mortality Among Critically Ill Adults. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e1921520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coiffard, B.; Riegler, S.; Sklar, M.C.; Dres, M.; Vorona, S.; Reid, W.D.; Brochard, L.J.; Ferguson, N.D.; Goligher, E.C. Diaphragm echodensity in mechanically ventilated patients: A description of technique and outcomes. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soilemezi, E.; Savvidou, S.; Sotiriou, P.; Smyrniotis, D.; Tsagourias, M.; Matamis, D. Tissue Doppler Imaging of the Diaphragm in Healthy Subjects and Critically Ill Patients. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 202, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoni, M.; Piva, S.; Beretta, A.; Bongiovanni, F.; Contarino, R.; Artigas, R.M.; Ceresoli, L.; Marchesi, M.; Falappi, M.; Belleri, M.; et al. Occurrence and Effects on Weaning From Mechanical Ventilation of Intensive Care Unit Acquired and Diaphragm Weakness: A Pilot Study. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 930262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dres, M.; Dubé, B.-P.; Mayaux, J.; Delemazure, J.; Reuter, D.; Brochard, L.; Similowski, T.; Demoule, A. Coexistence and Impact of Limb Muscle and Diaphragm Weakness at Time of Liberation from Mechanical Ventilation in Medical Intensive Care Unit Patients. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thille, A.W.; Boissier, F.; Muller, M.; Levrat, A.; Bourdin, G.; Rosselli, S.; Frat, J.-P.; Coudroy, R.; Vivier, E. Role of ICU-acquired weakness on extubation outcome among patients at high risk of reintubation. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dres, M.; Jung, B.; Molinari, N.; Manna, F.; Dubé, B.-P.; Chanques, G.; Similowski, T.; Jaber, S.; Demoule, A. Respective contribution of intensive care unit-acquired limb muscle and severe diaphragm weakness on weaning outcome and mortality: A post hoc analysis of two cohorts. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, B.; Moury, P.H.; Mahul, M.; de Jong, A.; Galia, F.; Prades, A.; Albaladejo, P.; Chanques, G.; Molinari, N.; Jaber, S. Diaphragmatic dysfunction in patients with ICU-acquired weakness and its impact on extubation failure. Intensiv. Care Med. 2015, 42, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivier, E.; Roche-Campo, F.; Brochard, L.; Dessap, A.M. Determinants of diaphragm thickening fraction during mechanical ventilation: An ancillary study of a randomised trial. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1700783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazzini, B.; Märkl, T.; Costas, C.; Blobner, M.; Schaller, S.J.; Prowle, J.; Puthucheary, Z.; Wackerhage, H. The rate and assessment of muscle wasting during critical illness: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Ruijven, I.M.; Stapel, S.N.; Molinger, J.; Weijs, P.J. Monitoring muscle mass using ultrasound: A key role in critical care. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2021, 27, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatino, A.; Regolisti, G.; di Mario, F.; Ciuni, A.; Palumbo, A.; Peyronel, F.; Maggiore, U.; Fiaccadori, E. Validation by CT scan of quadriceps muscle thickness measurement by ultrasound in acute kidney injury. J. Nephrol. 2019, 33, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardo, E.; El Behi, H.; Boizeau, P.; Verdonk, F.; Alberti, C.; Lescot, T. Reliability of ultrasound measurements of quadriceps muscle thickness in critically ill patients. BMC Anesthesiol. 2018, 18, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillquist, M.; Kutsogiannis, D.J.; Wischmeyer, P.E.; Kummerlen, C.; Leung, R.; Stollery, D.; Karvellas, C.; Preiser, J.-C.; Bird, N.; Kozar, R.; et al. Bedside Ultrasound Is a Practical and Reliable Measurement Tool for Assessing Quadriceps Muscle Layer Thickness. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2014, 38, 886–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, M.S.; Demar, S.; Griffin, L.P.; Balakrishnan, N.; Harris, J.M.; Walker, F. Validity and reliability of nerve and muscle ultrasound. Muscle Nerve 2013, 47, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, M.T.; Mourtzakis, M.; Day, A.; Leung, R.; Watharkar, S.; Kozar, R.; Earthman, C.; Kuchnia, A.; Dhaliwal, R.; Moisey, L.; et al. Validation of Bedside Ultrasound of Muscle Layer Thickness of the Quadriceps in the Critically Ill Patient (VALIDUM Study). J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2016, 41, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wu, J.; Gu, Q.; Gu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ge, X.; Sun, X.; Lian, J.; Zeng, Q. Changes in muscle ultrasound for the diagnosis of intensive care unit acquired weakness in critically ill patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, K.P.; Bastin, M.L.T.; Montgomery-Yates, A.A.; Pastva, A.M.; Dupont-Versteegden, E.E.; Parry, S.M.; Morris, P.E. Acute skeletal muscle wasting and dysfunction predict physical disability at hospital discharge in patients with critical illness. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annetta, M.G.; Pittiruti, M.; Silvestri, D.; Grieco, D.L.; Maccaglia, A.; La Torre, M.F.; Magarelli, N.; Mercurio, G.; Caricato, A.; Antonelli, M. Ultrasound assessment of rectus femoris and anterior tibialis muscles in young trauma patients. Ann. Intensive Care 2017, 7, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parry, S.M.; El-Ansary, D.; Cartwright, M.S.; Sarwal, A.; Berney, S.; Koopman, R.; Annoni, R.; Puthucheary, Z.; Gordon, I.R.; Morris, P.E.; et al. Ultrasonography in the intensive care setting can be used to detect changes in the quality and quantity of muscle and is related to muscle strength and function. J. Crit. Care 2015, 30, 1151.e9–1151.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimopoulos, S.; Raidou, V.; Elaiopoulos, D.; Chatzivasiloglou, F.; Markantonaki, D.; Lyberopoulou, E.; Vasileiadis, I.; Marathias, K.; Nanas, S.; Karabinis, A. Sonographic muscle mass assessment in patients after cardiac surgery. World J. Cardiol. 2020, 12, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, G.; Zhang, J.; Mou, Z.; Luo, J.; Xie, Y. Acute reduction of erector spinae muscle cross-sectional area is associated with ICU-AW and worse prognosis in patients with mechanical ventilation in the ICU. Medicine 2021, 100, e27806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schefold, J.C.; Bierbrauer, J.; Weber-Carstens, S. Intensive care unit-acquired weakness (ICUAW) and muscle wasting in critically ill patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2010, 1, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formenti, P.; Umbrello, M.; Coppola, S.; Froio, S.; Chiumello, D. Clinical review: Peripheral muscular ultrasound in the ICU. Ann. Intensive Care 2019, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caresio, C.; Molinari, F.; Emanuel, G.; Minetto, M.A. Muscle echo intensity: Reliability and conditioning factors. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2014, 35, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckmatt, J.; Leeman, S.; Dubowitz, V. Ultrasound imaging in the diagnosis of muscle disease. J. Pediatr. 1982, 101, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Lei, B.; Liu, L.; Li, S.X.; Ni, D.; Wang, T. Deep Learning in Medical Ultrasound Analysis: A Review. Engineering 2019, 5, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosny, A.; Parmar, C.; Quackenbush, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Artificial intelligence in radiology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, Y.; Yang, J.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, S. Artificial intelligence in musculoskeletal ultrasound imaging. Ultrasonography 2021, 40, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katakis, S.; Barotsis, N.; Kakotaritis, A.; Tsiganos, P.; Economou, G.; Panagiotopoulos, E.; Panayiotakis, G. Muscle Cross-Sectional Area Segmentation in Transverse Ultrasound Images Using Vision Transformers. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katakis, S.; Barotsis, N.; Kakotaritis, A.; Economou, G.; Panagiotopoulos, E.; Panayiotakis, G. Automatic Extraction of Muscle Parameters with Attention UNet in Ultrasonography. Sensors 2022, 22, 5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritsche, P.; Wirth, P.; Franchi, M.V.; Faude, O. ACSAuto-semi-automatic assessment of human vastus lateralis and rectus femoris cross-sectional area in ultrasound images. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caresio, C.; Salvi, M.; Molinari, F.; Meiburger, K.M.; Minetto, M.A. Fully Automated Muscle Ultrasound Analysis (MUSA): Robust and Accurate Muscle Thickness Measurement. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2016, 43, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xie, C.; Chen, Z.; Li, Q. Automatic Tracking of Muscle Cross-Sectional Area Using Convolutional Neural Networks with Ultrasound. J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 38, 2901–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzola, F.; van Alfen, N.; Salvi, M.; De Santi, B.; Doorduin, J.; Meiburger, K.M. Automatic segmentation of ultrasound images of gastrocnemius medialis with different echogenicity levels using convolutional neural networks. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2020, 2020, 2113–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlina, P.; Billings, S.; Joshi, N.; Albayda, J. Automated diagnosis of myositis from muscle ultrasound: Exploring the use of machine learning and deep learning methods. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uçar, E. Classification of myositis from muscle ultrasound images using deep learning. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 71, 103277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, A.-H.; Chen, J.-R.; Liu, S.-H.; Lu, C.-H.; Lin, C.-W.; Shieh, J.-Y.; Weng, W.-C.; Tsui, P.-H. Deep Learning of Ultrasound Imaging for Evaluating Ambulatory Function of Individuals with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Author | Year of Publication | Study Design | Patients (n) | Study Cohort | Assessed Muscles | Study Endpoints |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Naoi et al. [49] | 2022 | retrospective, single-center | 34 | non-surgical | BB, BRA, TA, EDL | Relations between ME, MRC-SS, MMT and FIM |
| Klawitter et al. [29] | 2022 | prospective single-center | 51, 38 with image analysis | perioperative | BB, BR, QF, TA | Differences in ME between ICUAW and non-ICUAW patients; correlation of ME with MRC-SS, mRS, Barthel Index |
| Paolo et al. [26] | 2022 | prospective single-center | 50 | medical, surgical | RF, IC | Changes in RF-CSA, PA, diaphragm and intercostal muscle thickness |
| Patejdl et al. [10] | 2019 | prospective single-center | 18 | perioperative | BB, BR, QF, TA | Changes in ME; serum biomarker; correlation with mRS |
| Kelmenson et al. [27] | 2018 | prospective single-center | 95 | medical, cardiac, (neuro)surgical | upper arm and upper thigh muscles | Diagnostic accuracy of single nerve conduction studies and NMUS |
| Hadda et al. [30] | 2018 | prospective single-center | 70 | non-surgical | BB, CB, QF | Changes in muscle thickness up to 90 days; LOS in hospital, mechanical ventilation time, survival rate |
| Witteveen et al. [45] | 2017 | prospective single-center | 71 | medical, surgical | BB, TA, RF, FCR | Muscle thickness; muscle echo intensity; median nerve CSA |
| Grimm et al. [28] | 2013 | prospective single-center | 28 | neurological | BB, FE, QF, TA | ME; number of muscle fasciculations |
| Author | Year of Publication | Study Design | Patients (n) | Study Cohort | Assessed Nerves | Study Endpoints |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gruber et al. [51] | 2022 | prospective, single-center | 16 | neurological | median, ulnar, fibular | nerve CSA; ultrasound pattern sum score |
| Bulinski et al. [52] | 2022 | prospective, single-center | 17 | neurological, neurosurgical | peroneal, tibial, sural | nerve CSA |
| Erdmann et al. [53] | 2022 | retrospective, single-center | 66 | mixed neurological | median, ulnar, radial, fibular, tibial | nerve echogenicity |
| Fisse et al. [44] | 2021 | prospective, single-center | 35 | medical, neurological | median, ulnar, radial, tibial, sural, vagal | nerve CSA; ME; cytokine analysis |
| Witteveen et al. [45] | 2017 | prospective, single-center | 71 | medical, surgical | median, peroneal | muscle thickness; ME; nerve CSA; nerve thickness; intraneural vascularization |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klawitter, F.; Walter, U.; Axer, H.; Patejdl, R.; Ehler, J. Neuromuscular Ultrasound in Intensive Care Unit-Acquired Weakness: Current State and Future Directions. Medicina 2023, 59, 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59050844
Klawitter F, Walter U, Axer H, Patejdl R, Ehler J. Neuromuscular Ultrasound in Intensive Care Unit-Acquired Weakness: Current State and Future Directions. Medicina. 2023; 59(5):844. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59050844
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlawitter, Felix, Uwe Walter, Hubertus Axer, Robert Patejdl, and Johannes Ehler. 2023. "Neuromuscular Ultrasound in Intensive Care Unit-Acquired Weakness: Current State and Future Directions" Medicina 59, no. 5: 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59050844
APA StyleKlawitter, F., Walter, U., Axer, H., Patejdl, R., & Ehler, J. (2023). Neuromuscular Ultrasound in Intensive Care Unit-Acquired Weakness: Current State and Future Directions. Medicina, 59(5), 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59050844







