The Impact of Therapeutic Plasma Exchange on Inflammatory Markers and Acute Phase Reactants in Patients with Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Search Protocol
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Supporting Literature for the Safety and Efficacy of TPE
4.2. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lorini, F.L.; Matteo, D.M.; Gritti, P.; Grazioli, L.; Benigni, A.; Zacchetti, L. Coagulopathy and COVID-19. Eur. Heart J. Suppl. 2020, 23, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manolescu, D.; Timar, B.; Bratosin, F.; Rosca, O.; Citu, C.; Oancea, C. Predictors for COVID-19 Complete Remission with HRCT Pattern Evolution: A Monocentric, Prospective Study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papava, I.; Dehelean, L.; Romosan, R.S.; Bondrescu, M.; Dimeny, C.Z.; Domuta, E.M.; Bratosin, F.; Bogdan, I.; Grigoras, M.L.; Tigmeanu, C.V.; et al. The Impact of Hyper-Acute Inflammatory Response on Stress Adaptation and Psychological Symptoms of COVID-19 Patients. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batah, S.S.; Fabro, A.T. Pulmonary pathology of ARDS in COVID-19: A pathological review for clinicians. Respir. Med. 2021, 176, 106239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broască, L.; Trușculescu, A.A.; Ancușa, V.M.; Ciocârlie, H.; Oancea, C.-I.; Stoicescu, E.-R.; Manolescu, D.L. A Novel Method for Lung Image Processing Using Complex Networks. Tomography 2022, 8, 1928–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zodpey, S.P.; Negandhi, H.; Kamal, V.K.; Bhatnagar, T.; Ganeshkumar, P.; Athavale, A. Determinants of severity among hospitalised COVID-19 patients: Hospital-based case-control study, India, 2020. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0261529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citu, C.; Burlea, B.; Gorun, F.; Motoc, A.; Gorun, O.M.; Malita, D.; Ratiu, A.; Margan, R.; Grigoras, M.L.; Bratosin, F.; et al. Predictive Value of Blood Coagulation Parameters in Poor Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients: A Retrospective Observational Study in Romania. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fericean, R.M.; Citu, C.; Manolescu, D.; Rosca, O.; Bratosin, F.; Tudorache, E.; Oancea, C. Characterization and Outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Overweight and Obese Patients: A Dynamic Comparison of COVID-19 Pandemic Waves. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, D.; Salah, E.H.; Taeimah, M.; Khatta, R.; Salem, R. The COVID-19 Cytokine Storm; What We Know So Far. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanase, A.; Manea, A.; Scurtu, A.D.; Bratu, L.M.; Chioran, D.; Dolghi, A.; Alexoi, I.; Abed, H.; Lazureanu, V.; Dehelean, C.A. The “Invisible Enemy” SARS-CoV-2: Viral Spread and Drug Treatment. Medicina 2022, 58, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirnea, L.; Bratosin, F.; Vidican, I.; Cerbu, B.; Turaiche, M.; Timircan, M.; Margan, M.-M.; Marincu, I. The Efficacy of Convalescent Plasma Use in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients. Medicina 2021, 57, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mungmungpuntipantip, R.; Wiwanitkit, V. Antithrombin, COVID-19, and Fresh Frozen Plasma Treatment. Turk. J. Haematol. 2021, 38, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, W.; Huang, S. Introduction to therapeutic plasma exchange. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2019, 58, 228–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmanabhan, A.; Connelly-Smith, L.; Aqui, N.; Balogun, R.A.; Klingel, R.; Meyer, E.; Pham, H.P.; Schneiderman, J.; Witt, V.; Wu, Y.; et al. Guidelines on the Use of Therapeutic Apheresis in Clinical Practice—Evidence-Based Approach from the Writing Committee of the American Society for Apheresis: The Eighth Special Issue. J. Clin. Apher. 2019, 34, 171–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gucyetmez, B.; Atalan, H.K.; Sertdemir, I.; Cakir, U.; Telci, L.; COVID-19 Study Group. Therapeutic plasma exchange in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in intensive care unit: A retrospective study. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerbu, B.; Grigoras, M.L.; Bratosin, F.; Bogdan, I.; Citu, C.; Bota, A.V.; Timircan, M.; Bratu, M.L.; Levai, M.C.; Marincu, I. Laboratory Profile of COVID-19 Patients with Hepatitis C-Related Liver Cirrhosis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: Explanation and elaboration. BMJ 2009, 339, b2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, L.; Tam, D.N.H.; Elshafay, A.; Dang, T.; Hirayama, K.; Huy, N.T. Quality assessment tools used in systematic reviews of in vitro studies: A systematic review. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2021, 21, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamis, F.; Al-Zakwani, I.; Al Hashmi, S.; Al Dowaiki, S.; Al Bahrani, M.; Pandak, N.; Khalili, H.; Memish, Z. Therapeutic plasma exchange in adults with severe COVID-19 infection. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 99, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, Y.; Kusaoi, M.; Hiki, M.; Murayama, G.; Abe, Y.; Nozawa, K.; Takahashi, K.; Yamaji, K.; Tamura, N.; Naito, T. Combination therapy with plasma exchange and glucocorticoid may be effective for severe COVID-19 infection: A retrospective observational study. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2021, 25, 33887110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemian, S.M.R.; Shafigh, N.; Afzal, G.; Jamaati, H.; Tabarsi, P.; Marjani, M.; Malekmohammad, M.; Mortazavi, S.M.; Khoundabi, B.; Mansouri, D. Plasmapheresis reduces cytokine and immune cell levels in COVID-19 patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Pulmonology 2021, 27, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamran, S.M.; Mirza, Z.-E.H.; Naseem, A.; Liaqat, J.; Fazal, I.; Alamgir, W.; Saeed, F.; Saleem, S.; Nisar, S.; Yousaf, M.A.; et al. Therapeutic plasma exchange for coronavirus disease-2019 triggered cytokine release syndrome; A retrospective propensity matched control study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0244853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faqihi, F.; Alharthy, A.; Alodat, M.; Kutsogiannis, D.J.; Brindley, P.G.; Karakitsos, D. Therapeutic plasma exchange in adult critically ill patients with life-treathening SARS-CoV-2 disease: A pilot study. J. Crit. Care 2020, 60, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, J.; Gratacos-Ginès, J.; Olivas, P.; Costa, M.; Nieto, S.; Mateo, D.; Sanchez, M.B.; Aguillar, F.; Bassegoda, O.; Ruiz, P.; et al. Plasma exchange: An effective rescue therapy in critically ILL patients with coronavirus disease 2019 infection. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48, e1350–e1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluck, W.L.; Callahan, S.P.; Brevetta, R.A.; Stenbit, A.E.; Smith, W.M.; Martin, J.C.; Blenda, A.V.; Arce, S.; Edenfield, W.J. Efficacy of therapeutic plasma exchange in the treatment of penn class 3 and 4 cytokine release syndrome complicating COVID-19. Respir. Med. 2020, 175, 106188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaid, I.; Essaad, O.; Al Aidouni, G.; Aabdi, M.; Berrichi, S.; Taouihar, S.; Marbouh, M.; Bkiyer, H.; Abda, N.; Housni, B. Therapeutic plasma exchange in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in intensive care unit: Cases series. Ann. Med. Surg. 2021, 71, 102920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faqihi, F.; Alharthy, A.; Abdulaziz, S.; Balhamar, A.; Alomari, A.; Al Aseri, Z.; Tamim, H.; Alqahtani, S.A.; Ktsogiannis, D.J.; Brindley, P.G.; et al. Therapeutic plasma exchange in patients with life- treathening COVID-19: A randomized control clinical trial. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2021, 57, 106334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassaniazad, M.; Vahedi, S.M.; Samimagham, R.H.; Gharibzadeh, A.; Beyranvand, S.; Abbasi, H.; Nikpoor, A.R. Improvement of clinical outcome, laboratory findings and inflammatory cytokines levels using plasmapheresis therapy in severe COVID-19 cases. Respir. Med. 2021, 189, 106669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, Z.; Khan, A.A.; Yousuf, H.; Khalid, K.; Abbasi, S.M.; Waheed, Y. Role of Therapeutic Plasmapheresis in SARS-CoV-2 Induced Cytokine Release Syndrome: A Retrospective Cohort Study on COVID-19 Patients. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2022, 15, 4907–4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cegolon, L.; Einollahi, B.; Panahi, Y.; Imanizadeh, S.; Rezapour, M.; Javanbakht, M.; Nikpouraghdam, M.; Abolghasemi, H.; Mastrangelo, G. On Therapeutic Plasma Exchange Against Severe COVID-19- Associated Pneumonia: An Observational Clinical Study. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 809823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diskin, C.J.; Maldonado, R.; Leon, J.; Dansby, L.M.; Carter, T.B.; Radcliff, L.; Diskin, C.D. How effective is rescue therapeutic plasma exchange in treatment of SARS-Coronavirus-2? Ther. Apher. Dial. 2023, 27, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabibi, S.; Tabibi, T.; Conic, R.R.; Banisaeed, N.; Streiff, M.B. Therapeutic Plasma Exchange: A potential Management Strategy for Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients. J. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 35, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balagholi, S.; Dabbaghi, R.; Eshghi, P.; Mousavi, S.A.; Heshmati, F.; Mohammadi, S. Potential of therapeutic plasmapheresis in treatment of COVID-19 patients: Immunopathogenesis and coagulopathy. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2020, 59, 102993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Tan, C.; Zhou, H.; Hu, Y.; Shen, G. Changes of serum IL-10, IL-1β, IL-6, MCP-1, TNF-α, IP-10 and IL-4 in COVID-19 patients. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 75, e14462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardi, A.; Meidaninikjeh, S.; Nikfarjam, S.; Majidi Zolbanin, N.; Jafari, R. Interleukin-1 in COVID-19 Infection: Immunopathogenesis and Possible Therapeutic Perspective. Viral Immunol. 2021, 34, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. Interleukin (IL-6) immunotherapy. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, T.; Snow, C.; Saleem, N.; Ambler, G.; Nastouli, E. Tocilizumab in COVID-19: A meta-analysis, trial sequential analysis, and meta-regression of randomized-controlled trials. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 641–652. [Google Scholar]
- Manson, J.J.; Naja, M.B.B.S.M.; Ledlie, A.; Goulden, M.B.B.S.B.; Khan, E.; Mehta, M.B.B.S.P. COVID-19-associated hyperinflammation and escalation of patient care: A retrospective longitudinal cohort study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2020, 2, e594–e602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafzadeh-Kian, S.; Campbell, M.R.; Jara Aguirre, J.C.; Walsh, J.; Kumanovics, A.; Jenkinson, G. Role of immune mediators in predicting hospitalization of SARS-CoV-2 positive patients. Cytokine 2022, 150, 155790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosquera-Sulbaran, J.A.; Pedreañez, A.; Carrero, Y.; Callejas, D. C-reactive protein as an effector molecule in COVID-19 pathogenesis. Rev. Med. Virol. 2021, 31, e2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentner, J.; Adams, T.; Knutson, V.; Zeien, S.; Abbas, H.; Moosavi, R. C-reactive protein levels associated with COVID-19 outcomes in the United States. J. Osteopath. Med. 2021, 121, 869–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, H.; Song, C.; Lu, R.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, F. Early Prediction of Disease Progression in Patients with Severe COVID-19 Using C-Reactive Protein to Albumin Ratio. Dis. Markers 2021, 2021, 6304189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.D.; Ding, M.; Dong, X.; Zhang, J.J.; Kursat, A.A.; Azkur, D. Risk factors for severe and critically ill COVID-19 patients: A review. Eur. Allergy 2021, 76, 428–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaquero-Roncero, L.; Sánchez-Barrado, E.; Escobar-Macias, D.; Arribas-Pérez, P.; González de Castro, R.; González-Porras, J. C-Reactive protein and SOFA scale: A simple score as early predictor of critical care requirement in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in Spain. Rev. Esp. Anestesiol. Reanim. 2021, 68, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nusshag, C.; Morath, C.; Speer, C.; Kaelble, F.; Zeier, M.; Boxberger, M.; Schulze-Schleithoff, E.; Fiedler, M.O.; Weigand, M.A.; Merle, U. Plasma Exchange in Patients with Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Single-Center Experience. Crit. Care Explor. 2021, 3, e0517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuluöztürk, M.; Deveci, F.; Turgut, T.; Öner, Ö. The Glasgow Prognostic Score and fibrinogen to albumin ratio as prognostic factors in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2021, 15, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarbock, A.; Küllmar, M.; Kindgen-Milles, D.; Wempe, C.; Gerss, J.; Brandenburger, T. Effect of Regional Citrate Anticoagulation vs Systemic Heparin Anticoagulation During Continuous Kidney Replacement Therapy on Dialysis Filter Life Span and Mortality Among Critically Ill Patients with Acute Kidney Injury a Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 324, 1629–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, J.; Noubouossie, D.F.; Gandotra, S.; Cao, L. Elevated Plasma Fibrinogen Is Associated with Excessive Inflammation and Disease Severity in COVID-19 Patients. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 73405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayit, A.T.; Elmali, M.; Deveci, A.; Gedikli, O. Relationship between acute phase reactants and prognosis in patients with or without COVID-19 pneumonia. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2021, 63, e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahat, R.K.; Panda, S.; Rathore, V.; Swain, S.; Yadav, L.; Sah, S.P. The dynamics of inflammatory markers in coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2021, 11, 100727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Samkari, H.; Karp Leaf, R.S.; Dzik, W.H.; Carlson, J.C.T.; Fogerty, A.E.; Waheed, A.; Goodarzi, K.; Bendapudi, P.K.; Bornikova, L.; Gupta, S.; et al. COVID-19 and coagulation: Bleeding and thrombotic manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Blood 2020, 136, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glick, J.H. Serum lactate dehydrogenase isoenzyme and total lactate dehydrogenase values in healt and disease, and clinical evaluation of these tests by means of discriminant analysis. Am. J. Clin. Pthol. 2016, 52, 320–328. [Google Scholar]
- Hoeboer, S.H.; Straaten, H.O.; Van, M.; Groeneveld, J.B.J. Albumin rather than C-reactive Protein may be valuable in predicting and monitoring the severity and course of acute respiratory distress syndrome in critically ill patients with or at risk for the syndrome after new onset fever. BMC Pulm. Med. 2015, 15, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bousquet, G.; Falgarone, G.; Deutsch, D.; Derolez, S.; Lopez-Sublet, M.; Goudot, F.X.; Amari, K.; Uzunhan, Y.; Bouchaud, O.; Pamoukdjian, F. ADL-dependency, D-Dimers, LDH and absence of anticoagulation are independently associated with one-month mortality in older inpatients with COVID-19. Aging 2020, 12, 11306–11313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poggiali, E.; Zaino, D.; Immovilli, P.; Rovero, L.; Losi, G.; Dacrema, A.; Nuccetelli, M.; Vadacca, G.B.; Guidetti, D.; Vercelli, A.; et al. Lactate dehydrogenase and C-reactive Protein as predictors of respiratory failure in COVID-19 patients. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2020, 509, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, B.M.; Aggarwal, G.; Wong, J.; Benoit, S.; Vikse, J.; Plebani, M.; Lippi, G. Lactate dehydrogenase levels predict coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) severity and mortality: A pooled analysis. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 38, 1722–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masumoto, A.; Kitai, T.; Matsumoto, S.; Kuroda, S.; Kohsaka, S.; Tachikawa, R.; Seo, R.; Doi, A.; Tomji, K.; Yonetsu, T.; et al. Impact of serum lactate dehydrogenase on the short-term prognosis of COVID-19 with pre-existing cardiovascular diseases. J. Cardiol. 2022, 79, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachim, I.Y.; Hachim, M.Y.; Hannawi, H.; Naeem, K.; Salah, A.; Hannawi, S. The inflammatory biomarkers profile of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and its association with patient’s outcome: A single centered study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Ren, H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J. Association between clinical characteristics and CT findings in patients with coronavirus disease-2019. Medicine 2021, 100, e27435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, M.N.; Sarwar, S.; Tarique, S.; Ahmed, M.; Tahir, H. Mortality in Patients of COVID-19 Infection: Biochemical Markers and its Cut-off Values for Predicting Outcome. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2022, 32, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Mahroum, N.; Alghory, A.; Kiyak, Z.; Alwani, A.; Seida, R.; Alrais, M. Ferritin -from iron, through inflammation and autoimmunity, to COVID-19. J. Autoimmun. 2022, 126, 102778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, K.; Kaur, H.; Sarma, P.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Sharma, D.J.; Prajapat, M. Serum ferritin as a predictive biomarker in COVID-19. A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression analysis. J. Crit. Care 2022, 67, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carubbi, F.; Salvati, L.; Alunno, A.; Maggi, F.; Borghi, E.; Mariani, R. Ferritin is associated with the severity of lung involvement but not with worse prognosis in patients with COVID-19: Data from two Italian COVID-19 units. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan Shah, S.S.T.; Naeem, I.; Wahid, B. Analyzing Correlation of Clinical Severity of COVID-19 with Other Biochemical Parameters: A Retrospective Study from Pakistan. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2021, 255, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| First Author, Country | Type of Study | Number of Patients | Number of TPE Treatment | Replacement Fluid | TPE Safety | Special Observations/Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F. Kharmis, Oman [19] | Case–control series | 11 TPE 20 Control group | 5 | FFP, citrate dextrose solution | Hypotension (1 patient) | Reduced inflammatory markers and SOFA scores. TPE should be utilized earlier in critically ill patients within 7–14 days of illness onset. |
| Y. Matsushita, Japan [20] | Retrospective study | 5 | 3–7 | FFP | Not reported | Positive evolution in 40% of patients. Decrease in CRP and improvement in PaO2/FiO2 ratio in all cases. |
| S. M. Hashemian, Iran [21] | Single group case series study | 15 | 3 | 5% human albumin solution and 0.9% saline. FFP from with positive detection anti-SARS COV-2 IgG and IgM (4 patients). | Not reported | Improvement in oxygenation status. Reduced inflammatory mediators p < 0.001. Improvement in hepatic functions. TPE offers safety and efficacy in removing inflammatory cytokine and acute phase proteins. |
| S. M. Kamran, Pakistan [22] | Retrospective observational study | 45 TPE 45 control group | 1–5 | FFP and normal saline 2:1 | Femoral artery puncture (1 patient) Thrombophlebitis of the femoral vein (1 patient) | Decreased duration of hospitalization. Reduced inflammatory markers. Better results of TPE when used closer (within 12 days) to onset of symptoms. |
| F. Faqihi, Saudi Arabia [23] | Prospective study | 10 | 5–7 | FFP or human albumin 5% | None | Significantly reduced inflammatory markers and improved PaO2/FiO2 ratios and SOFA scores. |
| J. Fernandez, Spain [24] | Single center case series study | 4 | 2–6 | Human albumin 5% | None | Reduced inflammatory markers. Effective rescue therapy in critically ill patients. Improved survival in very severe COVID-19 therapy. Decreased in severity scores. |
| W. L. Gluck, USA [25] | Single center case series study | 10 | 4–5 | FFP or human albumin 5% | None | Reduction in inflammatory markers. Improved oxygenation parameters. 4/4 of patients were liberated from supplemental oxygen. 2/6 patients were extubated within 14 days. |
| I. Zaid, Marocco [26] | Retrospective case series study | 7 | 3–5 | FFP | None | Significant reduction in inflammatory markers. TPE should be used earlier in critically ill patients. |
| F. Faqihi, Saudi Arabia [27] | Randomized controlled clinical trial study | 43 TPE 44 control group | 1–5 | FFP or human albumin 5% | None | Decrease in inflammatory markers. Increased lymphocytes and ADAMTS-13 activity. Duration of hospitalization in ICU was reduced in the TPE group. Faster clinical recovery decreased the SOFA score for TPE patients. |
| M. Hassaniazad, Iran [28] | Retrospective clinical study | 22 TPE 22 control group | 3 | Human albumin 5%, normal saline, FFP | None | TPE can effectively improve clinical symptoms and reduce inflammatory markers. |
| Z. Jamil, Saudi Arabia [29] | Retrospective cohort study | 81 TPE 81 control group | 5 | FFP, normal saline | None | Reduction of inflammatory markers. Improved PaO2/FiO2 ratio. Days of mechanical ventilation were reduced compared with the control group. Higher rate of survival in TPE group. |
| L. Cegolan, Iran [30] | A retrospective observational controlled study | 43 TPE 30 control group | 1–5 | 50% FFP + 50% human albumin 5% | None | Reduction of inflammatory markers. Mortality was lower in the TPE group due to the lower severity of patients with COVID-19. |
| CJ. Diskin, USA [31] | Prospective observational | 42 TPE 147 controls | 5 | FFP, convalescent plasma | 2 patients with “minor reactions” | Reduction of inflammatory markers. Higher rate of survival in TPE group. PaO2/FiO2 ratio in all cases. |
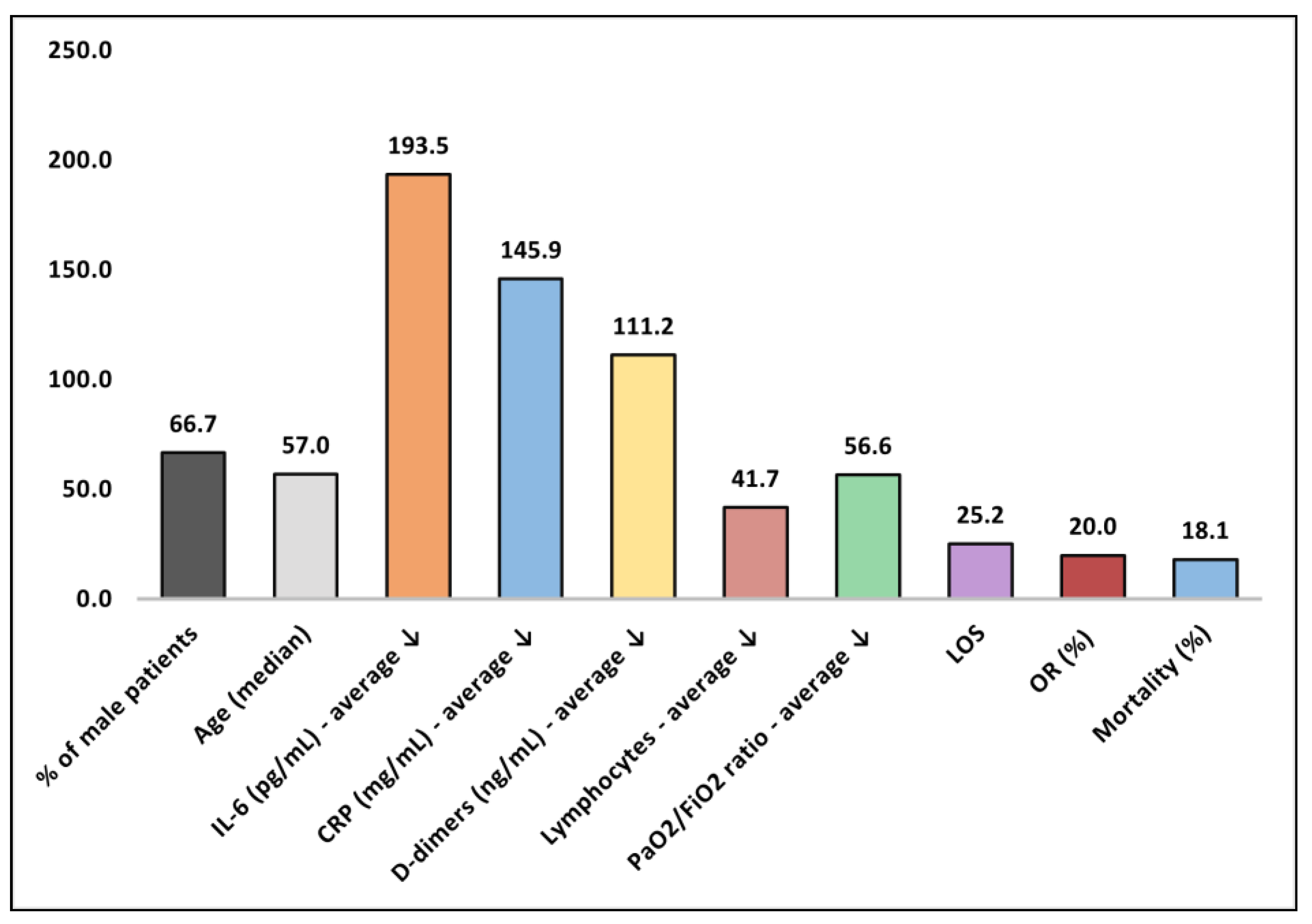
| No. | Quality Assessment | Male% | Age * | IL-6 (pg/mL) | CRP (mg/L) | D-dimer (ng/mL) | Ly (×109/L) | PaO2/ FiO2 | LOS | OR% | Mortality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 [19] | Acceptable | 100 | 50 | 334 | 336 | 23 | 60 | 15 | 19.0 | NR | 9.1% |
| 2 [20] | Low | 80.0 | 75 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 31.6 | NR | 60.0% |
| 3 [21] | Acceptable | 60.0 | 57 | 26 | 188 | NR | NR | 40 | 9.6 (ICU) | 17% | 40.0% |
| 4 [22] | Low | 92.0 | 60 | 17 | 250 | 150 | 54 | NR | 15.0 | NR | 17.9% |
| 5 [23] | Good | 70.0 | 51 | 128 | 58 | 65 | 55 | 23 | 15.0 (ICU) | NR | 10.0% |
| 6 [24] | Low | 100 | 57 | 20 | 66 | 81 | NR | 40 | 41.2 | NR | 0.0% |
| 7 [25] | Low | 30.0 | 52 | 26 | 123 | NR | NR | 43 | NR | NR | 0.0% |
| 8 [26] | Low | 57.1 | 57 | 574 | 133 | NR | 42 | 20 | 20.2 | NR | 0.0% |
| 9 [27] | Good | 82.8 | 48 | 423 | 201 | 40 | 50 | 165 | 19.0 (ICU) | 19% | 20.9% |
| 10 [28] | Acceptable | 50.0 | 61 | NR | 180 | N | 21 | 76 | NR | NR | 0.0% |
| 11 [29] | Good | 24.7 | 56 | NR | 24 | 308 | 10 | 69 | NR | 19% | 19.8% |
| 12 [30] | Acceptable | 50.0 | NR | NR | 146 | NR | NR | 22 | NR | 32% | 14% |
| 13 [31] | Good | 70.7% | 60 | NR | 46 | NR | NR | 110 | 24.1 | 13% | 43.9% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Porosnicu, T.M.; Sirbu, I.O.; Oancea, C.; Sandesc, D.; Bratosin, F.; Rosca, O.; Jipa, D.; Boeriu, E.; Bandi, S.S.S.; Pricop, M. The Impact of Therapeutic Plasma Exchange on Inflammatory Markers and Acute Phase Reactants in Patients with Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Medicina 2023, 59, 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59050867
Porosnicu TM, Sirbu IO, Oancea C, Sandesc D, Bratosin F, Rosca O, Jipa D, Boeriu E, Bandi SSS, Pricop M. The Impact of Therapeutic Plasma Exchange on Inflammatory Markers and Acute Phase Reactants in Patients with Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Medicina. 2023; 59(5):867. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59050867
Chicago/Turabian StylePorosnicu, Tamara Mirela, Ioan Ovidiu Sirbu, Cristian Oancea, Dorel Sandesc, Felix Bratosin, Ovidiu Rosca, Daniel Jipa, Estera Boeriu, Satya Sai Sri Bandi, and Marius Pricop. 2023. "The Impact of Therapeutic Plasma Exchange on Inflammatory Markers and Acute Phase Reactants in Patients with Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection" Medicina 59, no. 5: 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59050867
APA StylePorosnicu, T. M., Sirbu, I. O., Oancea, C., Sandesc, D., Bratosin, F., Rosca, O., Jipa, D., Boeriu, E., Bandi, S. S. S., & Pricop, M. (2023). The Impact of Therapeutic Plasma Exchange on Inflammatory Markers and Acute Phase Reactants in Patients with Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Medicina, 59(5), 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59050867











