New 675 nm Laser Device: The Innovative and Effective Non-Ablative Resurfacing Technique
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
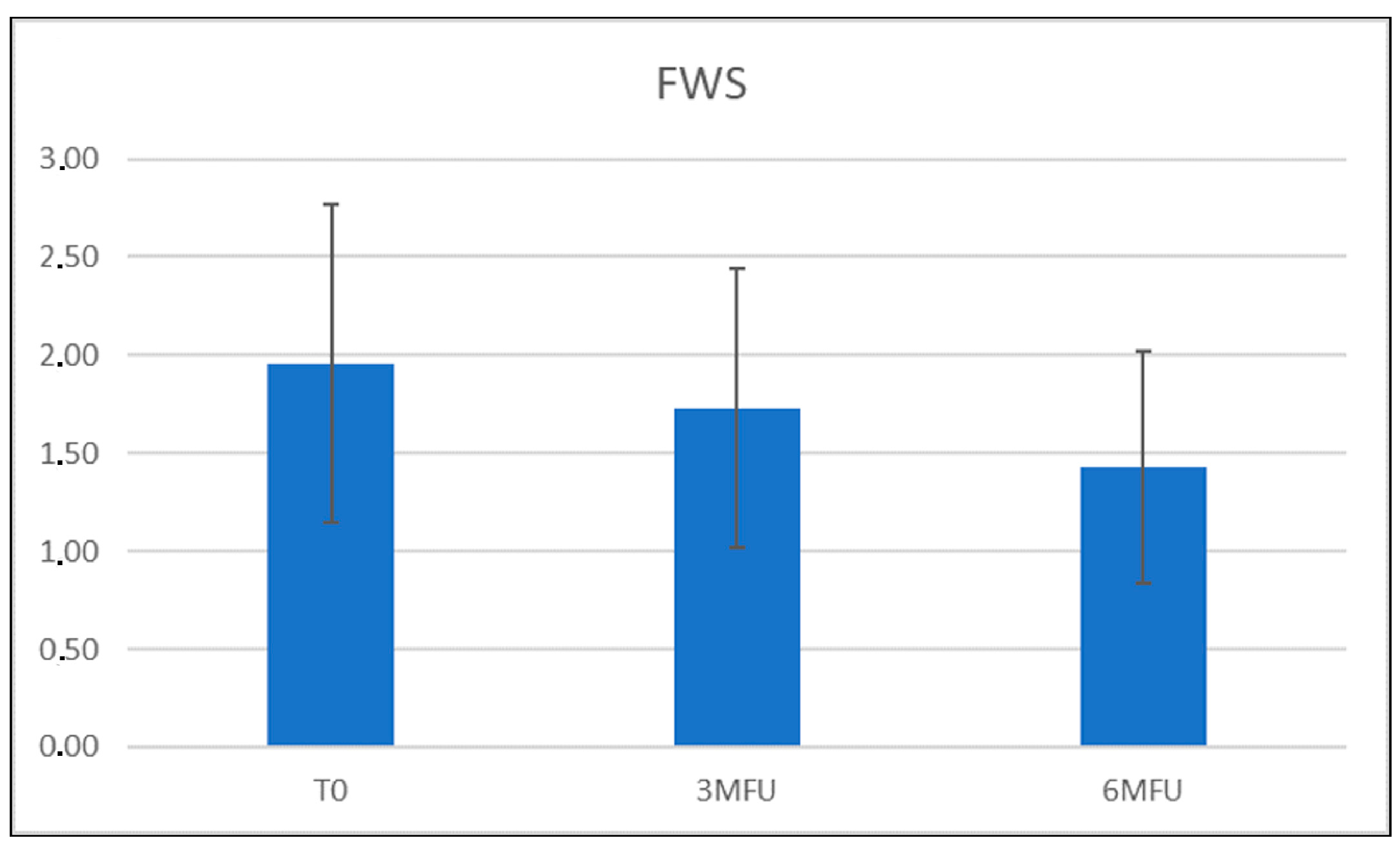
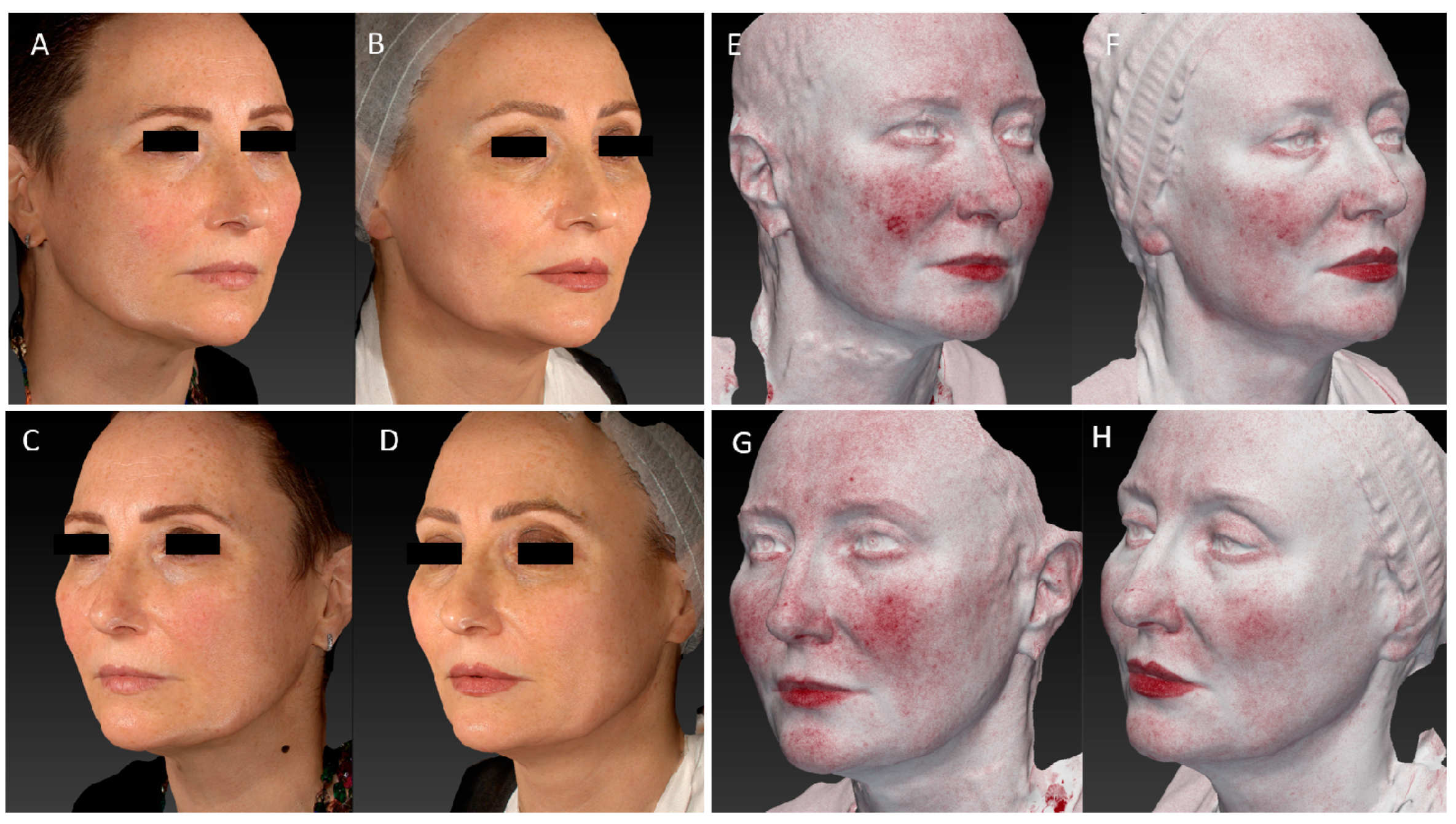
3.1. Wrinkles Evaluation
3.2. Pain Assessment
3.3. Adverse Events
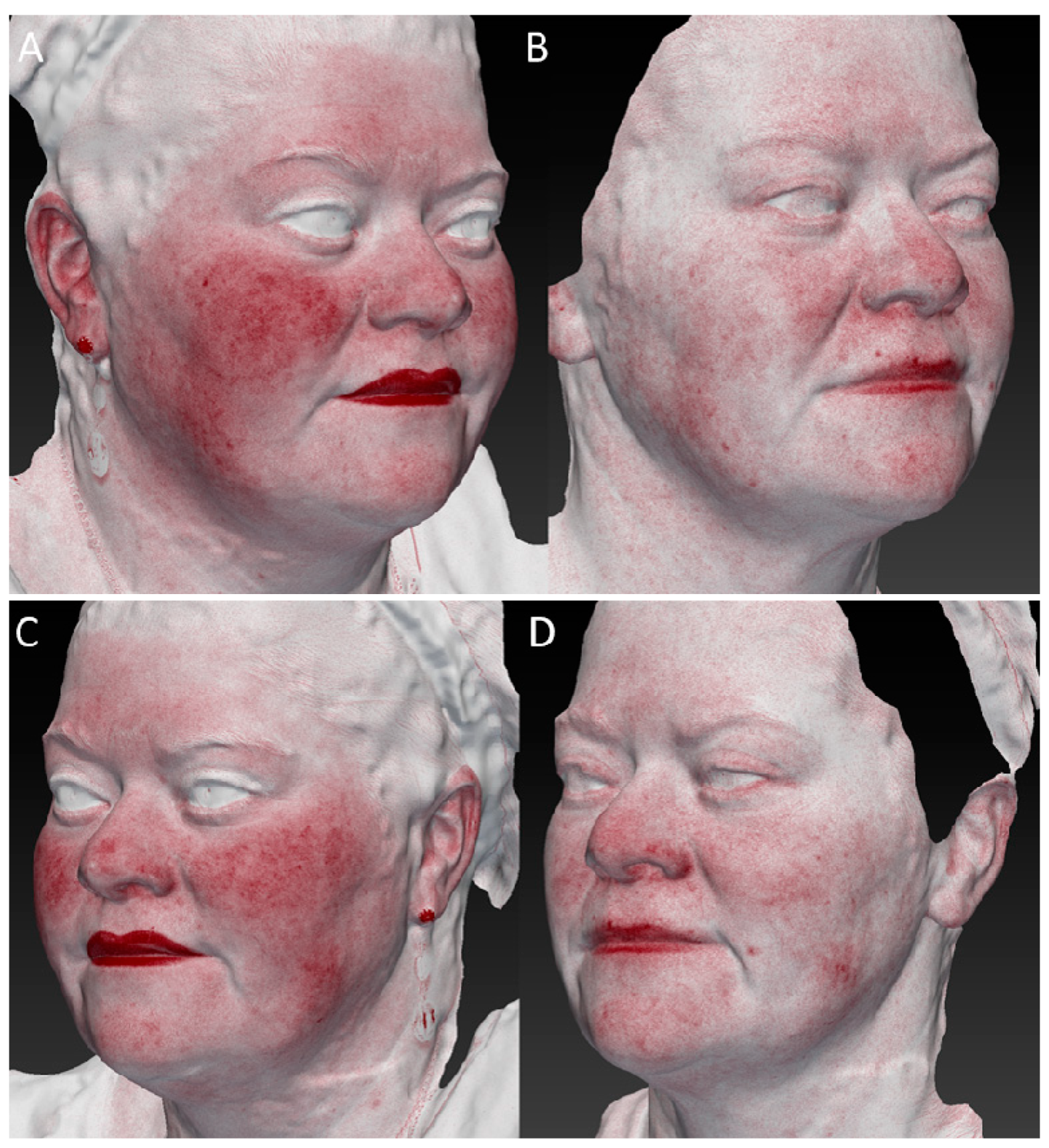
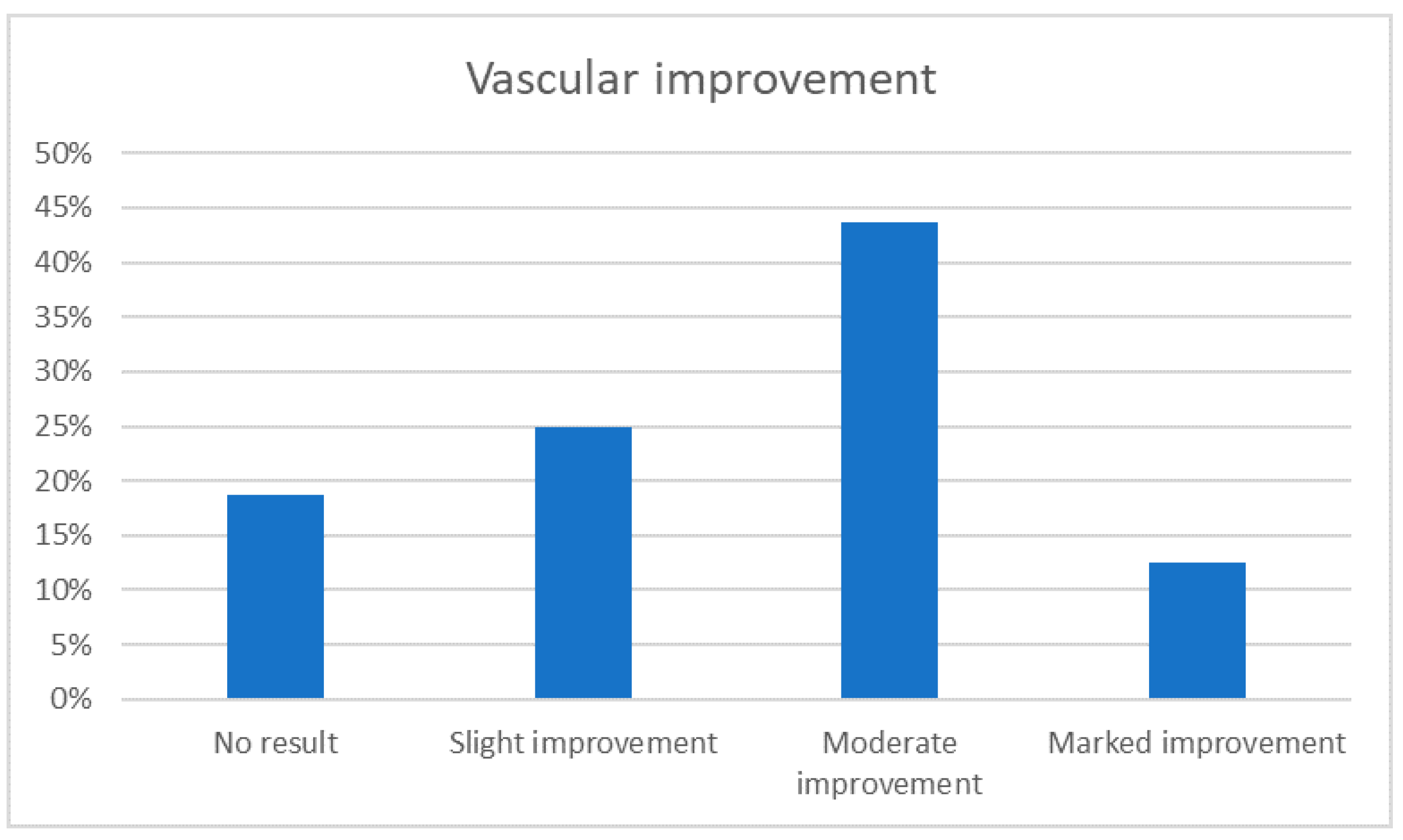
3.4. Vascular Improvement
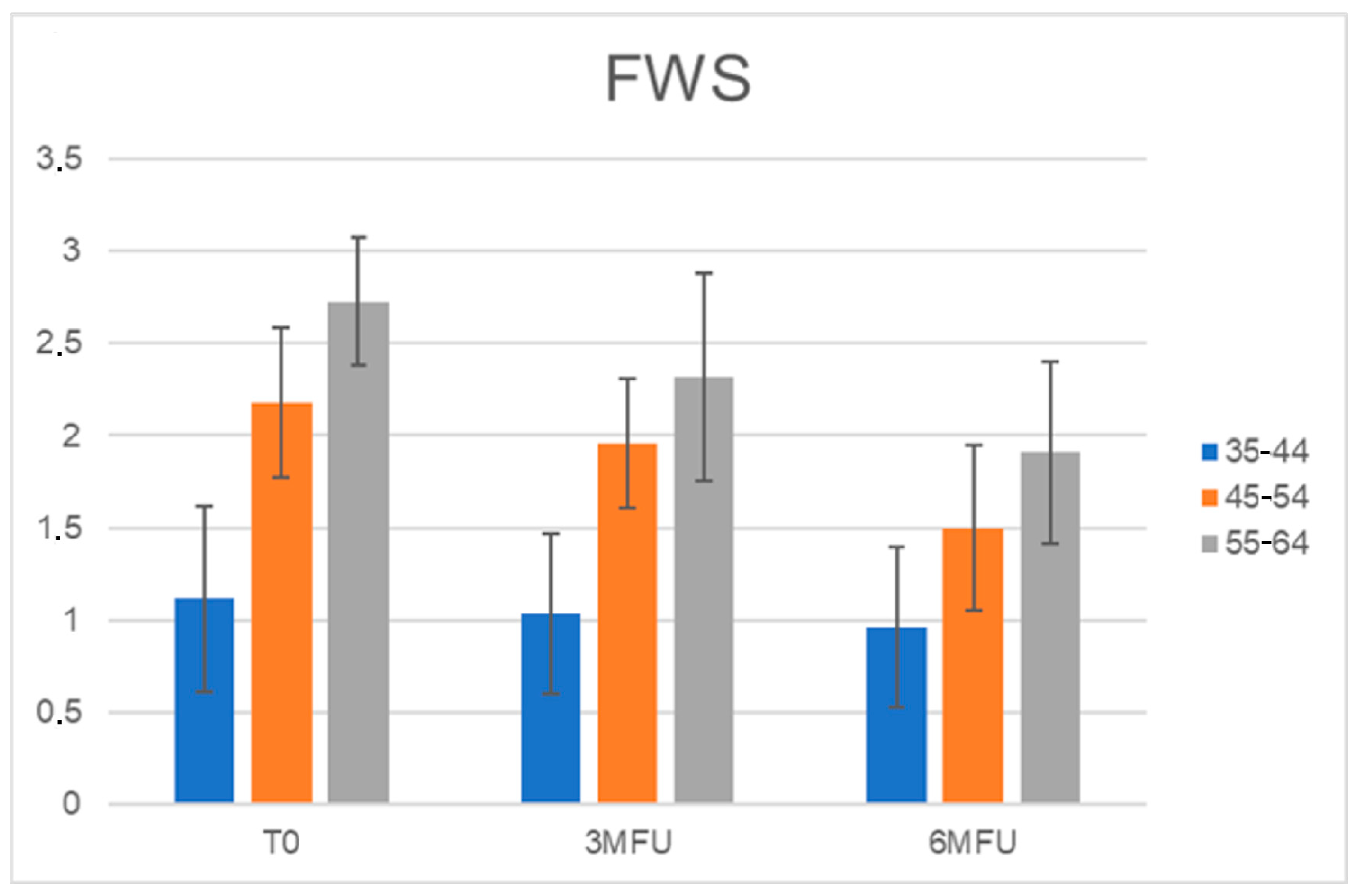
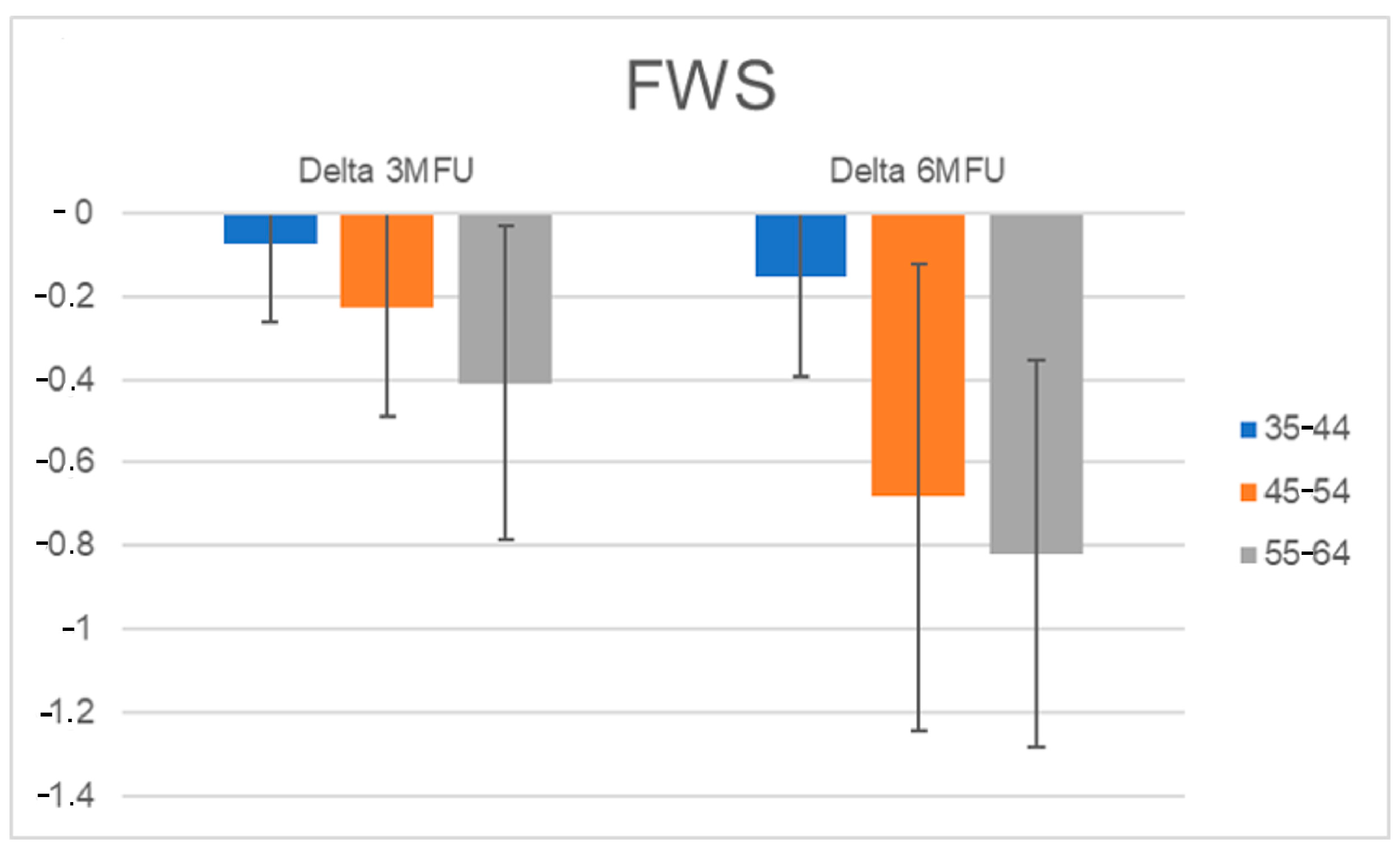
3.5. Wrinkles Assessment for Each Age Group
4. Discussion
Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pozner, J.N.; DiBernardo, B.E. Laser Resurfacing: Full Field and Fractional. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2016, 43, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanzi, E.L.; Lupton, J.R.; Alster, T.S. Lasers in dermatology: Four decades of progress. Rev. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2003, 49, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conforti, C.; Zalaudek, I.; Vezzoni, R.; Retrosi, C.; Fai, A.; Fadda, S.; Di Michele, E.; Dianzani, C. Chemical peeling for acne and melasma: Current knowledge and innovations. Ital. J. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 15, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannarozzo, G.; Silvestri, M.; Tamburi, F.; Sicilia, C.; Del Duca, E.; Scali, E.; Bennardo, L.; Nisticò, S.P. A new 675-nm laser device in the treatment of acne scars: An observational study. Lasers Med. Sci. 2021, 36, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisticò, S.P.; Tolone, M.; Zingoni, T.; Tamburi, F.; Scali, E.; Bennardo, L.; Cannarozzo, G. A New 675 nm Laser Device in the Treatment of Melasma: Results of a Prospective Observational Study. Photobiomodulation Photomed. Laser Surg. 2020, 38, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccolo, D.; Kostaki, D.; Crisman, G.; Conforti, C. Resurfacing with a new 675-nm laser device: A case series. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 1343–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannarozzo, G.; Fazia, G.; Bennardo, L.; Tamburi, F.; Amoruso, G.F.; Del Duca, E.; Nisticò, S. A New 675 nm Laser Device in the Treatment of Facial Aging: A Prospective Observational Study. Obs. Study Photobiomodulation Photomed. Laser Surg. 2021, 39, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannarozzo, G.; Bennardo, L.; Zingoni, T.; Pieri, L.; Del Duca, E.; Nisticò, S.P. Histological Skin Changes After Treatment with 675nm Laser. Photobiomodulation Photomed. Laser Surg. 2021, 39, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonan, P.; Verdelli, A.; Pieri, L.; Fusco, I.; Linpiyawan, R. Facial rejuvenation: A safe and effective treatment with a fractional non-ablative 675 nm laser in Asian population. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 4070–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonan, P.; Verdelli, A.; Pieri, L.; Fusco, I. Could 675-nm Laser Treatment Be Effective for Facial Melasma Even in Darker Phototype? Photobiomodulation Photomed. Laser Surg. 2021, 39, 634–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riita, R.; Mataleena, P.; Arja, J. Increased expression of collagen type and in human skin as a consequence of radiotherapy. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2002, 294, 178–184. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Rest, M.; Garrone, R. Collagen family of proteins. FASEB J. 1991, 5, 2814–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.; Yanhua, R.; Fang-gang, N.; Guo-an, Z. The content and ratio of type I and III collagen in skin differ with age and injury. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 2524–2529. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, L.; Jin, X.Q.; Xiang, D.L. Study on the collagen constitution of hyperplastic scars in different ages and its influencing factors. Chin. J. Burn. 2003, 19, 236–240. [Google Scholar]
- Rong, Y.-H.; Zhang, G.-A.; Wang, C.; Ning, F.-G. Quantification of type I and III collagen content in normal human skin in different age groups. Chin. J. Burn. 2008, 24, 51–53. [Google Scholar]
- Manturova, N.E.; Smirnova, G.O.; Stupin, V.A.; Silina, E.V. The ratio of collagen types I/III as a marker of skin aging and prognosis of aesthetic facial surgery results. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2018, 10, 2543–2546. [Google Scholar]
- Barolet, D.; Roberge, C.J.; Auger, F.A.; Boucher, A.; Germain, L. Regulation of skin collagen metabolism In vitro using a pulsed 660 nm LED light source: Clinical correlation with a single-blinded study. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 2751–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.; Dai, T.; Sharma, S.K.; Huang, Y.Y.; Carroll, J.D.; Hamblin, M.R. The nuts and bolts of low-level laser (light) therapy. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 40, 516–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, D.H.; Abrahamse, H. The role of laser fluence in cell viability, proliferation, and membrane integrity of wounded human skin fibroblasts following helium-neon laser irradiation. Lasers Surg. Med. 2006, 38, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zungu, I.L.; Hawkins Evans, D.; Abrahamse, H. Mitochondrial responses of normal and injured human skin fibroblasts follow-ing low level laser irradiation—An in vitro study. Photochem. Photobiol. 2009, 85, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Naim, J.O.; Lanzafame, R.J. Effects of photostimulation on wound healing in diabetic mice. Lasers Surg. Med. 1997, 20, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindl, A.; Pernerstorfer-Schön, H.; Kerschan, K.; Knobler, R. Diabetic neuropathic foot ulcer: Successful treatment by low-intensity laser therapy. Dermatology 1999, 198, 314–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozza, D.H.; De Oliveira, M.G.; Weissmann, R.; Ramalho, L.M.P.; Singh, N.; Uppoor, A.; Naik, D.; Amaroli, A. Polarized light (400–2000 nm) and non-ablative laser (685 nm): A description of the wound healing process using immunohistochemical analysis. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2005, 23, 485–492. [Google Scholar]
- Bolton, P.; Young, S.; Dyson, M. The direct effect of 860 nm light on cell proliferation and on succinic dehydrogenase activity of human fibroblasts in vitro. Laser Ther. 1995, 7, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loevschall, H.; Arenholt-Bindslev, D. Effect of low level diode laser irradiation of human oral mucosa fibroblasts in vitro. Lasers Surg. Med. 1994, 14, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Naim, J.O.; Lanzafame, R.J. The effect of laser irradiation on the release of bFGF from 3T3 fibroblasts. Photochem. Photobiol. 1994, 59, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourreau-Schneider, N.; Ahmed, A.; Soudry, M.; Jacquemier, J.; Kopp, F.; Franquin, J.C.; Martin, P.M. Helium-neon laser treatment transforms fibroblasts into myofibroblasts. Am. J. Pathol. 1990, 137, 171–178. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, P.; Ridgway, T.D.; Higbee, R.G.; Howard, E.W.; Lucroy, M.D. Effect of wavelength on low-intensity laser irradia-tion-stimulated cell proliferation in vitro. Lasers Surg. Med. 2005, 36, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholkmann, F.; Kleiser, S.; Metz, A.J.; Zimmermann, R.; Mata Pavia, J.; Wolf, U.; Wolf, M. A review on continuous wave functional near-infrared spectroscopy and imaging instrumentation and methodology. Neuroimage 2014, 15, 6–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magni, G.; Pieri, L.; Fusco, I.; Madeddu, F.; Zingoni, T.; Rossi, F. Laser emission at 675 nm: In vitro study evidence of a promising role in skin rejuvenation. Regen. Ther. 2023, 22, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogant, S.R. Prejuvenation: Definition of the Term and Evolution of the Concept. Dermatol. Surg. 2021, 47, 871–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piccolo, D.; Crisman, G.; Dianzani, C.; Zalaudek, I.; Fusco, I.; Conforti, C. New 675 nm Laser Device: The Innovative and Effective Non-Ablative Resurfacing Technique. Medicina 2023, 59, 1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59071245
Piccolo D, Crisman G, Dianzani C, Zalaudek I, Fusco I, Conforti C. New 675 nm Laser Device: The Innovative and Effective Non-Ablative Resurfacing Technique. Medicina. 2023; 59(7):1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59071245
Chicago/Turabian StylePiccolo, Domenico, Giuliana Crisman, Caterina Dianzani, Iris Zalaudek, Irene Fusco, and Claudio Conforti. 2023. "New 675 nm Laser Device: The Innovative and Effective Non-Ablative Resurfacing Technique" Medicina 59, no. 7: 1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59071245
APA StylePiccolo, D., Crisman, G., Dianzani, C., Zalaudek, I., Fusco, I., & Conforti, C. (2023). New 675 nm Laser Device: The Innovative and Effective Non-Ablative Resurfacing Technique. Medicina, 59(7), 1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59071245







