The Influence of Sildenafil–Metformin Combination on Hyperalgesia and Biochemical Markers in Diabetic Neuropathy in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Experimental Animals
2.3. Induction of Diabetes Mellitus
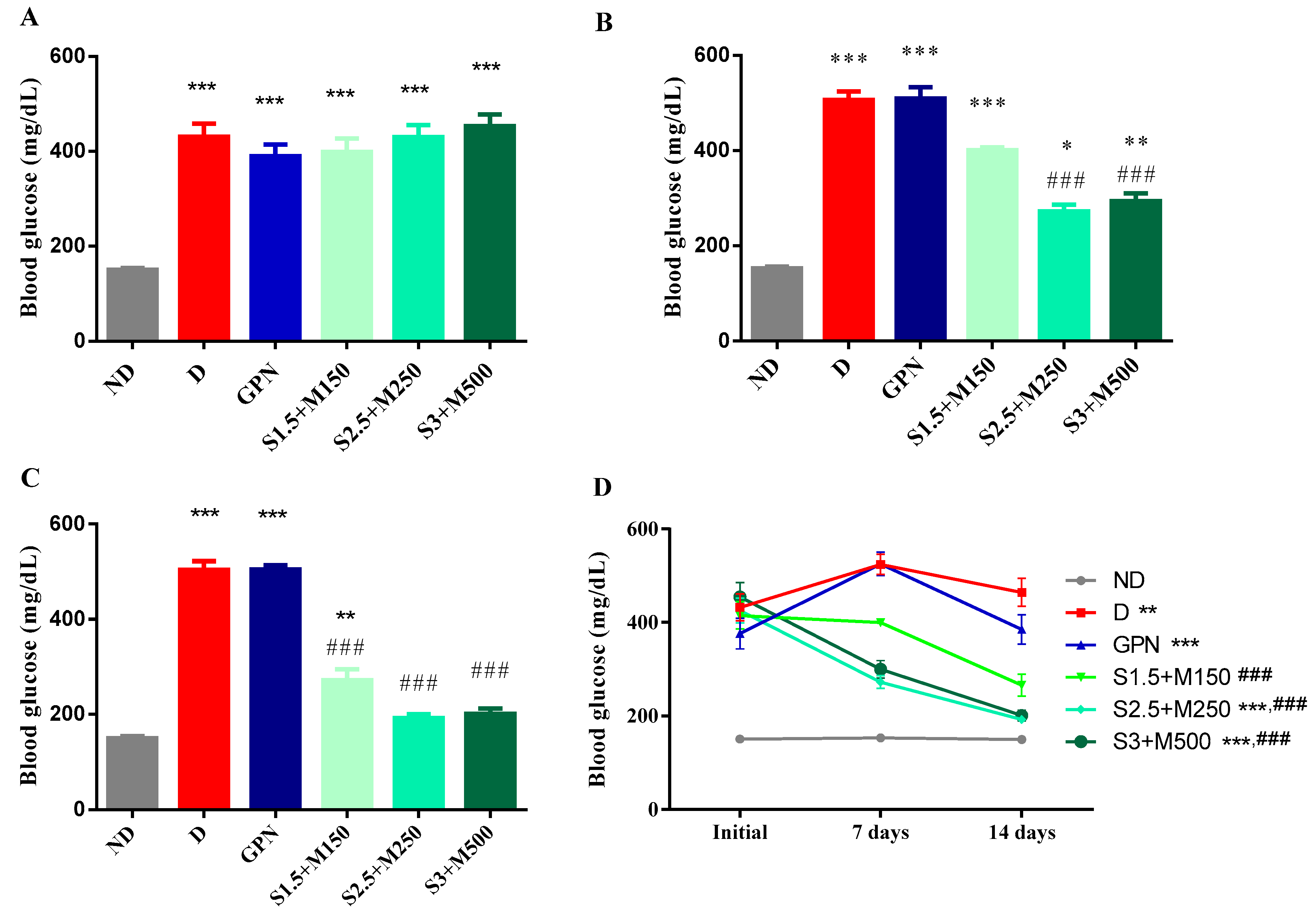
2.4. Blood Glucose Levels
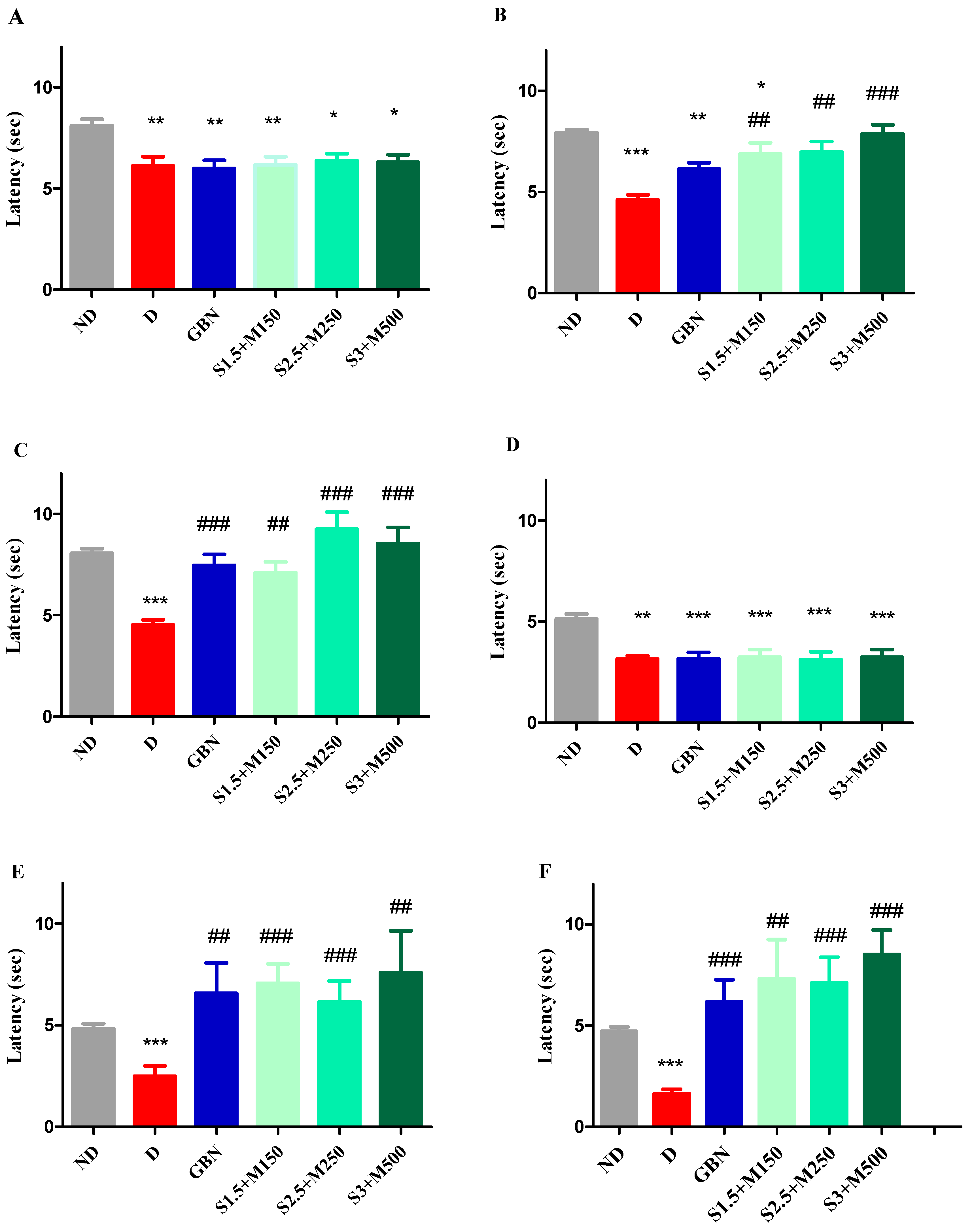
2.5. Tests for the Evaluation of the Antihyperalgesic Effect
2.5.1. Heat Hypersensitivity
2.5.2. Cold Allodynia
2.6. Biochemical Assay of Mouse Brain and Liver Homogenates
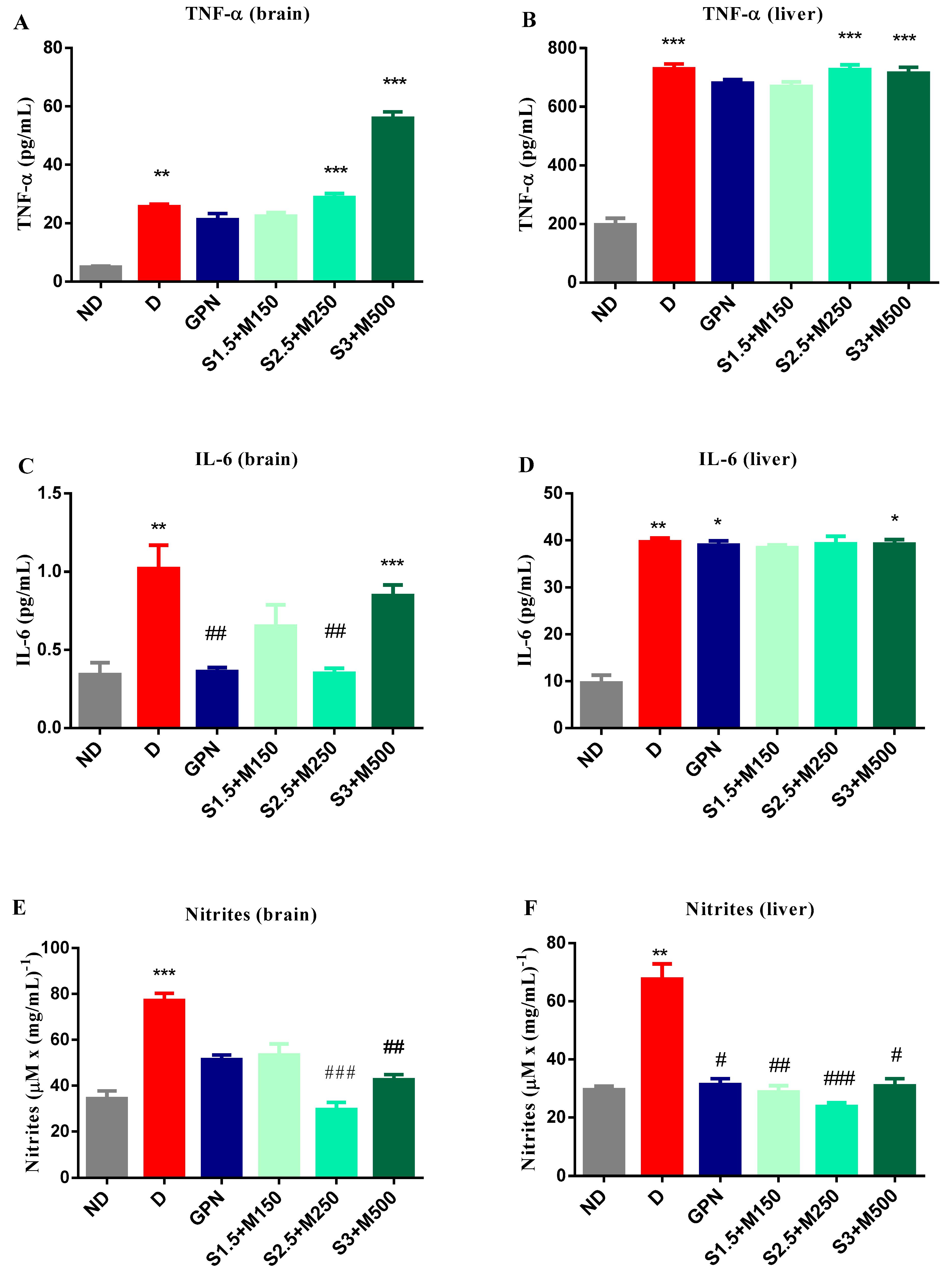
2.6.1. Assessment of TNF-α and Il-6
2.6.2. Griess Assessment of NOS Activity
2.6.3. Protein Content
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Blood Glucose Level
3.2. Evaluation of the Antihyperalgesic Effect
3.2.1. Heat Hypersensitivity
3.2.2. Cold Hypersensitivity
3.3. Biochemical Assay of Mouse Brain and Liver Homogenates
3.3.1. Assessment of TNF-α and Il-6
3.3.2. Griess Assessment of NOS Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramachandran, A.; Snehalatha, C.; Nanditha, A. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes. In Textbook of Diabetes; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2016; pp. 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IDF Diabetes Atlas. Available online: https://idf.org/e-library/epidemiology-research/diabetes-atlas.html (accessed on 6 September 2022).
- Feldman, E.L.; Callaghan, B.C.; Pop-Busui, R.; Zochodne, D.W.; Wright, D.E.; Bennett, D.L.; Bril, V.; Russell, J.W.; Viswanathan, V. Diabetic neuropathy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019, 5, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.J.; Boulton, A.J.M.; Macleod, A.F.; Williams, D.R.R.; Sonksen, P.H. A multicentre study of the prevalence of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in the United Kingdom hospital clinic population. Diabetologia 1993, 36, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, C.A.; Malik, R.A.; van Ross, E.R.E.; Kulkarni, J.; Boulton, A.J.M. Prevalence and Characteristics of Painful Diabetic Neuropathy in a Large Community-Based Diabetic Population in the U.K. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 2220–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Horak, H.; Tiryaki, E. Diabetic neuropathies. Muscle Nerve 2021, 63, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulton, A.J.M. Diabetic neuropathy and foot complications. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowling, F.L.; Rashid, S.T.; Boulton, A.J.M. Preventing and treating foot complications associated with diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfaye, S.; Chaturvedi, N.; Eaton, S.E.M.; Ward, J.D.; Manes, C.; Ionescu-Tirgoviste, C.; Witte, D.R.; Fuller, J.H. Vascular risk factors and diabetic neuropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfaye, S.; Vileikyte, L.; Rayman, G.; Sindrup, S.H.; Perkins, B.A.; Baconja, M.; Vinik, A.I.; Boulton, A.J.M. Painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: Consensus recommendations on diagnosis, assessment and management. Diabetes. Metab. Res. Rev. 2011, 27, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfaye, S.; Boulton, A.J.M.; Dickenson, A.H. Mechanisms and management of diabetic painful distal symmetrical polyneuropathy. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 2456–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, A.K.; Nones, C.F.; Reis, R.C.; Chichorro, J.G.; Cunha, J.M. Diabetic neuropathic pain: Physiopathology and treatment. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 432–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Dougherty, P.M. Dynamic effects of TNF-α on synaptic transmission in mice over time following sciatic nerve chronic constriction injury. J. Neurophysiol. 2013, 110, 1663–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Clemente, J.M.; Mauricio, D.; Richart, C.; Broch, M.; Caixas, A.; Megia, A.; Gimenez-Palop, O.; Simon, I.; Martinez-Riquelme, A.; Gimenez-Perez, G.; et al. Diabetic neuropathy is associated with activation of the TNF-alpha system in subjects with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Clin. Endocrinol. 2005, 63, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uceyler, N.; Rogausch, J.P.; Toyka, K.V.; Sommer, C. Differential expression of cytokines in painful and painless neuropathies. Neurology 2007, 69, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, C.E.; Brunskill, N.J. Cellular and physiological effects of C-peptide. Clin. Sci. 2009, 116, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phaniendra, A.; Jestadi, D.B.; Periyasamy, L. Free Radicals: Properties, Sources, Targets, and Their Implication in Various Diseases. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 30, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, D.; Zochodne, D.W. NO Pain: Potential Roles of Nitric Oxide in Neuropathic Pain. Pain Pract. 2004, 4, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pușcașu, C.; Zanfirescu, A.; Negreș, S. Recent Progress in Gels for Neuropathic Pain. Gels 2023, 9, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, R.; Smith, D.; Franklin, G.; Gronseth, G.; Pignone, M.; David, W.S.; Armon, C.; Perkins, B.A.; Bril, V.; Rae-Grant, A.; et al. Oral and Topical Treatment of Painful Diabetic Polyneuropathy: Practice Guideline Update Summary. Neurology 2022, 98, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attal, N.; Cruccu, G.; Baron, R.; Haanpää, M.; Hansson, P.; Jensen, T.S.; Nurmikko, T. EFNS guidelines on the pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain: 2010 revision. Eur. J. Neurol. 2010, 17, 1113-e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chopp, M.; Szalad, A.; Jia, L.; Lu, X.; Lu, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.G. Sildenafil ameliorates long term peripheral neuropathy in type II diabetic mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, T.J.; Das, V.; Dussor, G. Adenosine Monophosphate-activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) Activators for the Prevention, Treatment and Potential Reversal of Pathological Pain. Curr. Drug Targets 2016, 17, 908–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, F.M.; Cheetham, S.; Vickers, S.; Chapman, V. Characterisation of Pain Responses in the High Fat Diet/Streptozotocin Model of Diabetes and the Analgesic Effects of Antidiabetic Treatments. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deftu, A.-F.; Chu Sin Chung, P.; Laedermann, C.J.; Gillet, L.; Pertin, M.; Kirschmann, G.; Decosterd, I. The Antidiabetic Drug Metformin Regulates Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Na V 1.7 via the Ubiquitin-Ligase NEDD4-2. Eneuro 2022, 9, ENEURO.0409-21.2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pușcașu, C.; Mihai, P.; Zbârcea, C.E.; Zanfirescu, A.; Chiriță, C.; Viorica Ghiță, C.I.; Negreş, S. Investigation of antihyperalgesic effects of different doses of sildenafil and metformin in alloxan-induced diabetic neuropathy in mice. Farmacia 2023, 71, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devita, V.T.; Young, R.C.; Canellos, G.P. Combination versus single agent chemotherapy: A review of the basis for selection of drug treatment of cancer. Cancer 1975, 35, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesney, M.A.; Morin, M.; Sherr, L. Adherence to HIV combination therapy. Soc. Sci. Med. 2000, 50, 1599–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jukema, J.W.; van der Hoorn, J.W. Amlodipine and atorvastatin in atherosclerosis: A review of the potential of combination therapy. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2004, 5, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecikoza, U.; Tomić, M.; Nastić, K.; Micov, A.; Stepanović-Petrović, R. Synergism between metformin and analgesics/vitamin B12 in a model of painful diabetic neuropathy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisold, W.; Cavaletti, G.; Windebank, A.J. Peripheral neuropathies from chemotherapeutics and targeted agents: Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Neuro. Oncol. 2012, 14, iv45–iv54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New, R.A.T. Screening Methods in Pharmacology. Yale J. Biol. Med. 1965, 38, 309. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2591164 (accessed on 9 May 2023).
- Prasad, S.N. Muralidhara Protective effects of geraniol (a monoterpene) in a diabetic neuropathy rat model: Attenuation of behavioral impairments and biochemical perturbations. J. Neurosci. Res. 2014, 92, 1205–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, S.; Gaur, S.; Mishra, R.; Singh, R.K.; Bajpai, S. Astaxanthin reduces oxidative stress and alleviates diabetic neuropathy in STZ-induced diabetic mice. Int. J. Diabetes Dev. Ctries. 2022, 43, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Veterinary Medical Association. AMVA Guidelines for the Euthanasia of Animals: 2020 Edition; American Veterinary Medical Association: Schaumburg, IL, USA, 2020; ISBN 9781882691098. Available online: https://www.avma.org/sites/default/files/2020-02/Guidelines-on-Euthanasia-2020.pdf (accessed on 14 May 2023).
- Gradinaru, D.; Margina, D.; Borsa, C.; Ionescu, C.; Ilie, M.; Costache, M.; Dinischiotu, A.; Prada, G.I. Adiponectin: Possible link between metabolic stress and oxidative stress in the elderly. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 29, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, K.M.; Espey, M.G.; Wink, D.A. A rapid, simple spectrophotometric method for simultaneous detection of nitrate and nitrite. Nitric Oxide 2001, 5, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihai, D.P.; Ungurianu, A.; Ciotu, C.I.; Fischer, M.J.M.; Olaru, O.T.; Nitulescu, G.M.; Andrei, C.; Zbarcea, C.E.; Zanfirescu, A.; Seremet, O.C.; et al. Effects of venlafaxine, risperidone and febuxostat on cuprizone-induced demyelination, behavioral deficits and oxidative stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem Mir, M.; Maqbool Darzi, M.; Musadiq Khan, H.; Ahmad Kamil, S.; Hassan Sofi, A.; Ahmad Wani, S. Pathomorphological effects of Alloxan induced acute hypoglycaemia in rabbits. Alexandria J. Med. 2013, 49, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrigal, J. The Increase in TNF-α Levels Is Implicated in NF-κB Activation and Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Expression in Brain Cortex after Immobilization Stress. Neuropsychopharmacology 2002, 26, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munhoz, C.; Madrigal, J.L.M.; Garcia-Bueno, B.; Pradillo, J.M.; Moro, M.A.; Lizasoain, I.; Lorenzo, P.; Scavone, C.; Leza, J.C. TNF-alpha accounts for short-term persistence of oxidative status in rat brain after two weeks of repeated stress. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 20, 1125–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivenza, R.; Moro, M.A.; Lizasoain, I.; Lorenzo, P.; Fernández, A.P.; Rodrigo, J.; Boscá, L.; Leza, J.C. Chronic Stress Induces the Expression of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase in Rat Brain Cortex. J. Neurochem. 2001, 74, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouidrat, Y.; Pizzol, D.; Cosco, T.; Thompson, T.; Carnaghi, M.; Bertoldo, A.; Solmi, M.; Stubbs, B.; Veronese, N. High prevalence of erectile dysfunction in diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 145 studies. Diabet. Med. 2017, 34, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar-Jiménez, F. Eficacia y seguridad del sildenafilo en varones con diabetes mellitus tipo 2 y disfunción eréctil. Med. Clin. 2002, 119, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, P.; Trivedi, N. A meta-analysis on efficacy and tolerability of sildenafil for erectile dysfunction in patients with diabetes mellitus. Indian J. Sex. Transm. Dis. AIDS 2018, 39, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buse, J.B.; Wexler, D.J.; Tsapas, A.; Rossing, P.; Mingrone, G.; Mathieu, C.; D’Alessio, D.A.; Davies, M.J. 2019 Update to: Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, 2018. A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ighodaro, O.M.; Adeosun, A.M.; Akinloye, O.A. Alloxan-induced diabetes, a common model for evaluating the glycemic-control potential of therapeutic compounds and plants extracts in experimental studies. Medicina 2017, 53, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.T.; Lei, C.L.; Bi, C.C.; Chen, Z.L.; Zhang, L. Effect of alloxan time administerDrug on establishing diabetic rabbit model. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 3, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenzen, S. The mechanisms of alloxan- and streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radenković, M.; Stojanović, M.; Prostran, M. Experimental diabetes induced by alloxan and streptozotocin: The current state of the art. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2016, 78, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.-N.; Yang, X.-S.; Hua, Z.; Xie, W. Serum levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in diabetic patients with peripheral neuropathic pain and the correlation among them. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2009, 89, 469–471. [Google Scholar]
- Corbin, J.D.; Francis, S.H. Cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase-5: Target of sildenafil. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 13729–13732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, E.; Wolter, S.; Dittmar, F.; Fernández, G.; Seifert, R. Differentiation between first and second messenger effects of cGMP. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2015, 16, A84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chopp, M.; Szalad, A.; Liu, Z.; Bolz, M.; Ãlvarez, F.M.; Lu, M.; Zhang, L.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, R.L.; et al. Phosphodiesterase-5 is a therapeutic target for peripheral neuropathy in diabetic mice. Neuroscience 2011, 193, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandera, B.C.; Pham, T.; Hill-Pryor, C.; Bah-Sow, M.; Franco, N.; Prasad, B.M.; Pizarro, J. Role of Growth Factors in Improved Skin Flap Viability Caused by Phosphodiesterase-5 Inhibitor. Am. Surg. 2010, 76, 614–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Chopp, M.; Zhang, Z. PDE5 inhibitors promote recovery of peripheral neuropathy in diabetic mice. Neural Regen. Res. 2017, 12, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Wei, Y.; Huang, M.; Wang, P.; Jia, S. Is metformin a possible treatment for diabetic neuropathy? J. Diabetes 2022, 14, 658–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melemedjian, O.K.; Asiedu, M.N.; Tillu, D.V.; Sanoja, R.; Yan, J.; Lark, A.; Khoutorsky, A.; Johnson, J.; Peebles, K.A.; Lepow, T.; et al. Targeting adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in preclinical models reveals a potential mechanism for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Mol. Pain 2011, 7, 1744–8069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Cao, J.; He, Q.; Xiong, L.; Chang, E.; Radovick, S.; Wondisford, F.E.; He, L. Metformin Activates AMP-activated Protein Kinase by Promoting Formation of the αβγ Heterotrimeric Complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Myers, R.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shen, X.; Fenyk-Melody, J.; Wu, M.; Ventre, J.; Doebber, T.; Fujii, N.; et al. Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Montalvo, A.; Mercken, E.M.; Mitchell, S.J.; Palacios, H.H.; Mote, P.L.; Scheibye-Knudsen, M.; Gomes, A.P.; Ward, T.M.; Minor, R.K.; Blouin, M.J.; et al. Metformin improves healthspan and lifespan in mice. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirooie, S.; Esmaeili, J.; Sureda, A.; Esmaeili, N.; Mirzaee Saffari, P.; Yousefi-Manesh, H.; Dehpour, A.R. Evaluation of the effects of metformin administration on morphine tolerance in mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 716, 134638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, M.M.; Lima, V.; Girão, V.C.C.; Teixeira, R.C.; Graça, J.R.V. Antinociceptive activity of sildenafil and adrenergic agents in the writhing test in mice. Pharmacol. Rep. 2008, 60, 339–344. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18622058 (accessed on 23 May 2023).
- Jain, N.K.; Patil, C.S.; Singh, A.; Kulkarni, S.K. Sildenafil, a Phosphodiesterase-5 Inhibitor, Enhances the Antinociceptive Effect of Morphine. Pharmacology 2003, 67, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, C.S.; Jain, N.K.; Singh, A.; Kulkarni, S.K. Modulatory Effect of Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors on Sildenafil-Induced Antinociception. Pharmacology 2003, 69, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, V.; Kroin, J.S.; Moric, M.; McCarthy, R.J.; Buvanendran, A. Antihyperalgesia effect of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activators in a mouse model of postoperative pain. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2019, 44, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusto, P.S.A.; Braga, A.V.; Rodrigues, F.F.; Morais, M.I.; Dutra, M.M.G.B.; Batista, C.R.A.; Melo, I.S.F.; Costa, S.O.A.M.; Goulart, F.A.; Coelho, M.M.; et al. Metformin antinociceptive effect in models of nociceptive and neuropathic pain is partially mediated by activation of opioidergic mechanisms. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 858, 172497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Back, S.K.; Won, S.Y.; Hong, S.K.; Na, H.S. Gabapentin relieves mechanical, warm and cold allodynia in a rat model of peripheral neuropathy. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 368, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zbârcea, C.E. Gabapentin, alone and associated with tramadol reduces peripheral paclitaxel-induced neuropathy in rats. Farmacia 2011, 59, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Walczak, J.S.; Pichette, V.; Leblond, F.; Desbiens, K.; Beaulieu, P. Behavioral, pharmacological and molecular characterization of the saphenous nerve partial ligation: A new model of neuropathic pain. Neuroscience 2005, 132, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, W.; Boroujerdi, A.; Bennett, G.J.; Luo, Z.D. Chemotherapy-evoked painful peripheral neuropathy: Analgesic effects of gabapentin and effects on expression of the alpha-2-delta type-1 calcium channel subunit. Neuroscience 2007, 144, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wodarski, R.; Clark, A.K.; Grist, J.; Marchand, F.; Malcangio, M. Gabapentin reverses microglial activation in the spinal cord of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Eur. J. Pain 2009, 13, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reda, H.M.; Zaitone, S.A.; Moustafa, Y.M. Effect of levetiracetam versus gabapentin on peripheral neuropathy and sciatic degeneration in streptozotocin-diabetic mice: Influence on spinal microglia and astrocytes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 771, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moalem, G.; Tracey, D.J. Immune and inflammatory mechanisms in neuropathic pain. Brain Res. Rev. 2006, 51, 240–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, A.; Zacharowski, K.; Boehm, O.; Stevens, M.; Lipfert, P.; Von Giesen, H.J.; Wolf, A.; Freynhagen, R. Nitric oxide and pro-inflammatory cytokines correlate with pain intensity in chronic pain patients. Inflamm. Res. 2007, 56, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, C.; Schäfers, M. Mechanisms of neuropathic pain: The role of cytokines. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Mech. 2004, 1, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thacker, M.A.; Clark, A.K.; Marchand, F.; McMahon, S.B. Pathophysiology of peripheral neuropathic pain: Immune cells and molecules. Anesth. Analg. 2007, 105, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Empl, M.; Renaud, S.; Erne, B.; Fuhr, P.; Straube, A.; Schaeren-Wiemers, N.; Steck, A.J. TNF-alpha expression in painful and nonpainful neuropathies. Neurology 2001, 56, 1371–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, L.; Cahill, C.M. TNF-α and neuropathic pain—A review. J. Neuroinflammation 2010, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, J.; Yagihashi, S.; Toyota, T. The possible role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in diabetic polyneuropathy. Exp. Diabesity Res. 2003, 4, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfers, M.; Svensson, C.I.; Sommer, C.; Sorkin, L.S. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces mechanical allodynia after spinal nerve ligation by activation of p38 MAPK in primary sensory neurons. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 2517–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Gereau, R.W., IV. Acute p38-Mediated Modulation of Tetrodotoxin-Resistant Sodium Channels in Mouse Sensory Neurons by Tumor Necrosis Factor-α. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowenstein, C.J.; Dinerman, J.L.; Snyder, S.H. Nitric oxide: A physiologic messenger. Ann. Intern. Med. 1994, 120, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohan, D.E. Production of endothelin-1 by rat mesangial cells: Regulation by tumor necrosis factor. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1992, 119, 477–484. Available online: https://europepmc.org/article/med/1583403 (accessed on 18 May 2023). [PubMed]
- Coyne, D.W.; Nickols, M.; Bertrand, W.; Morrison, A.R. Regulation of mesangial cell cyclooxygenase synthesis by cytokines and glucocorticoids. Am. J. Physiol. 1992, 263, F97–F102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, J.F.; Mora-Fernández, C. The role of TNF-alpha in diabetic nephropathy: Pathogenic and therapeutic implications. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2006, 17, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afshari, K.; Dehdashtian, A.; Haddadi, N.S.; Haj-Mirzaian, A.; Iranmehr, A.; Ebrahimi, M.A.; Tavangar, S.M.; Faghir-Ghanesefat, H.; Mohammadi, F.; Rahimi, N.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of Metformin improve the neuropathic pain and locomotor activity in spinal cord injured rats: Introduction of an alternative therapy. Spinal Cord 2018, 56, 1032–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Sun, X.; Jiang, L.; Hu, L.; Kong, H.; Han, Y.; Qian, C.; Song, C.; Qian, Y.; Liu, W. Metformin reduces morphine tolerance by inhibiting microglial-mediated neuroinflammation. J. Neuroinflammation 2016, 13, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, B.; Shin, S.; Lee, A.; Lee, S.; Song, Y.; Ha, N.-J.; Cho, K.-H.; Kim, K. Metformin Down-regulates TNF-α Secretion via Suppression of Scavenger Receptors in Macrophages. Immune Netw. 2013, 13, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, M.; Soto, N.; Arredondo, M. Efecto de metformina sobre la expresión del factor de necrosis tumoral-α, los receptores Toll-like 2/4 y la PCR ultra sensible en sujetos obesos con diabetes tipo 2. Rev. Med. Chil. 2012, 140, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, L.; Lian, G.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Yao, X.; Yang, J.; Wu, C. Sildenafil attenuates LPS-induced pro-inflammatory responses through down-regulation of intracellular ROS-related MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways in N9 microglia. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Macedo, F.H.P.; Aires, R.D.; Fonseca, E.G.; Ferreira, R.C.M.; Machado, D.P.D.; Chen, L.; Zhang, F.-X.; Souza, I.A.; Lemos, V.S.; Romero, T.R.L.; et al. TNF-α mediated upregulation of NaV1.7 currents in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons is independent of CRMP2 SUMOylation. Mol. Brain 2019, 12, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, M.A.; Gibson, T.M.; Nangle, M.R.; Cameron, N.E. Effects of interleukin-6 treatment on neurovascular function, nerve perfusion and vascular endothelium in diabetic rats. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2010, 12, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doupis, J.; Lyons, T.E.; Wu, S.; Gnardellis, C.; Dinh, T.; Veves, A. Microvascular reactivity and inflammatory cytokines in painful and painless peripheral diabetic neuropathy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 2157–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, L.; Liu, X.; Zhu, X.; Ye, H.; Xiong, Q.; Li, Y.; et al. Proinflammatory cytokines predict the incidence of diabetic peripheral neuropathy over 5 years in Chinese type 2 diabetes patients: A prospective cohort study. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 31, 100649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magrinelli, F.; Briani, C.; Romano, M.; Ruggero, S.; Toffanin, E.; Triolo, G.; Peter, G.C.; Praitano, M.; Lauriola, M.F.; Zanette, G.; et al. The Association between Serum Cytokines and Damage to Large and Small Nerve Fibers in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aversa, A.; Vitale, C.; Volterrani, M.; Fabbri, A.; Spera, G.; Fini, M.; Rosano, G.M.C. Chronic administration of Sildenafil improves markers of endothelial function in men with Type 2 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2008, 25, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farghaly, H.S.M.; Mahmoud, A.M.; Abdel-Sater, K.A. Effect of dexmedetomidine and cold stress in a rat model of neuropathic pain: Role of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 776, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkul, A.; Ayhan, M.; Yenisey, C.; Akyol, A.; Guney, E.; Ergin, F.A. The role of oxidative stress and endothelial injury in diabetic neuropathy and neuropathic pain. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2010, 31, 261–264. Available online: https://europepmc.org/article/med/20424576 (accessed on 21 May 2023). [PubMed]
- Ramakrishna, V.; Jailkhani, R. Oxidative stress in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) patients. Acta Diabetol. 2008, 45, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, A.; Orhan, H.; Sayal, A.; Özata, M.; Şahin, G.; Isi̧mer, A. Oxidative stress and nitric oxide related parameters in type II diabetes mellitus: Effects of glycemic control. Clin. Biochem. 2001, 34, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togashi, H.; Sasaki, M.; Frohman, E.; Taira, E.; Ratan, R.R.; Dawson, T.M.; Dawson, V.L. Neuronal (type I) nitric oxide synthase regulates nuclear factor kappaB activity and immunologic (type II) nitric oxide synthase expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 2676–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doganay, S.; Evereklioglu, C.; Er, H.; Türköz, Y.; Sevinç, A.; Mehmet, N.; Savli, H. Comparison of serum NO, TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, sIL-2R, IL-6 and IL-8 levels with grades of retinopathy in patients with diabetes mellitus. Eye 2002, 16, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purwata, T.E. High TNF-alpha plasma levels and macrophages iNOS and TNF-alpha expression as risk factors for painful diabetic neuropathy. J. Pain Res. 2011, 4, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lós, D.B.; de Oliveira, W.H.; Duarte-Silva, E.; Sougey, W.W.D.; de Freitas, E.d.S.R.; de Oliveira, A.G.V.; Braga, C.F.; de França, M.E.R.; Araújo, S.M.d.R.; Rodrigues, G.B.; et al. Preventive role of metformin on peripheral neuropathy induced by diabetes. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 74, 105672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilron, I.; Max, M.B. Combination pharmacotherapy for neuropathic pain: Current evidence and future directions. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2005, 5, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negreş, S.; Chiriţă, C.; Moroşan, E.; Arsene, A.L. Experimental pharmacological model of diabetes induction with aloxan in rat. Farmacia 2013, 61, 313–323. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pușcașu, C.; Ungurianu, A.; Șeremet, O.C.; Andrei, C.; Mihai, D.P.; Negreș, S. The Influence of Sildenafil–Metformin Combination on Hyperalgesia and Biochemical Markers in Diabetic Neuropathy in Mice. Medicina 2023, 59, 1375. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59081375
Pușcașu C, Ungurianu A, Șeremet OC, Andrei C, Mihai DP, Negreș S. The Influence of Sildenafil–Metformin Combination on Hyperalgesia and Biochemical Markers in Diabetic Neuropathy in Mice. Medicina. 2023; 59(8):1375. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59081375
Chicago/Turabian StylePușcașu, Ciprian, Anca Ungurianu, Oana Cristina Șeremet, Corina Andrei, Dragoș Paul Mihai, and Simona Negreș. 2023. "The Influence of Sildenafil–Metformin Combination on Hyperalgesia and Biochemical Markers in Diabetic Neuropathy in Mice" Medicina 59, no. 8: 1375. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59081375
APA StylePușcașu, C., Ungurianu, A., Șeremet, O. C., Andrei, C., Mihai, D. P., & Negreș, S. (2023). The Influence of Sildenafil–Metformin Combination on Hyperalgesia and Biochemical Markers in Diabetic Neuropathy in Mice. Medicina, 59(8), 1375. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59081375





