A Nine-Gene Expression Signature Distinguished a Patient with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Who Underwent Prolonged Periodic Fasting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Patient #1
2.2.1. Diagnostic Assessment
2.2.2. Nutrition and Fasting Periods
2.2.3. Lymphocytosis
2.3. Patients #2, #3, #4, #5, and #6
2.4. Selection of B Cells
2.5. Total RNA Preparation
2.6. Gene Expression Profiling Experiments
2.7. Bioinformatic Analysis of GEP Data
3. Results
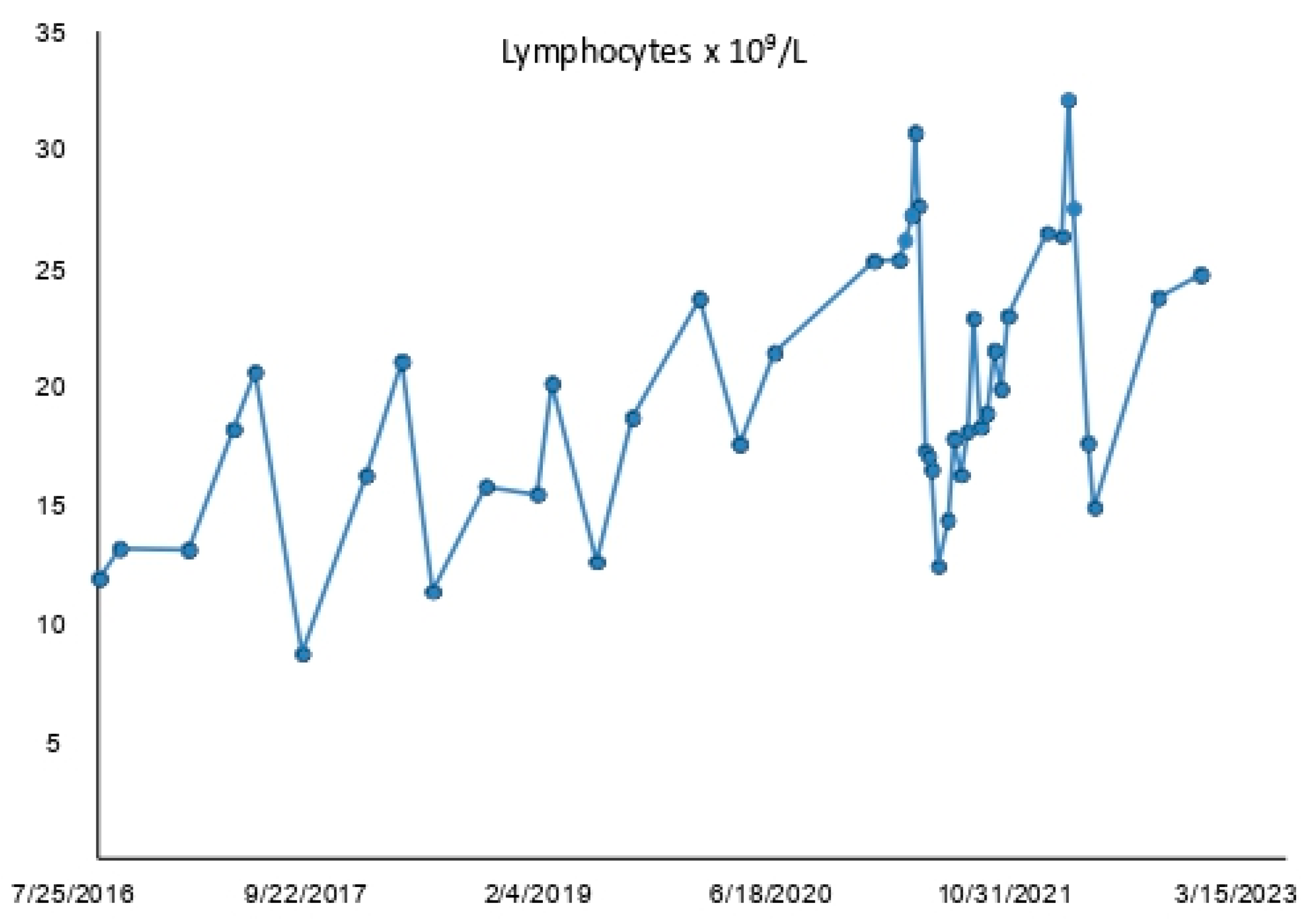
3.1. ALC and Lymphocytosis Trend of Patient #1
3.2. ALC and Lymphocytosis of Patients #2, #3, #4, #5, and #6
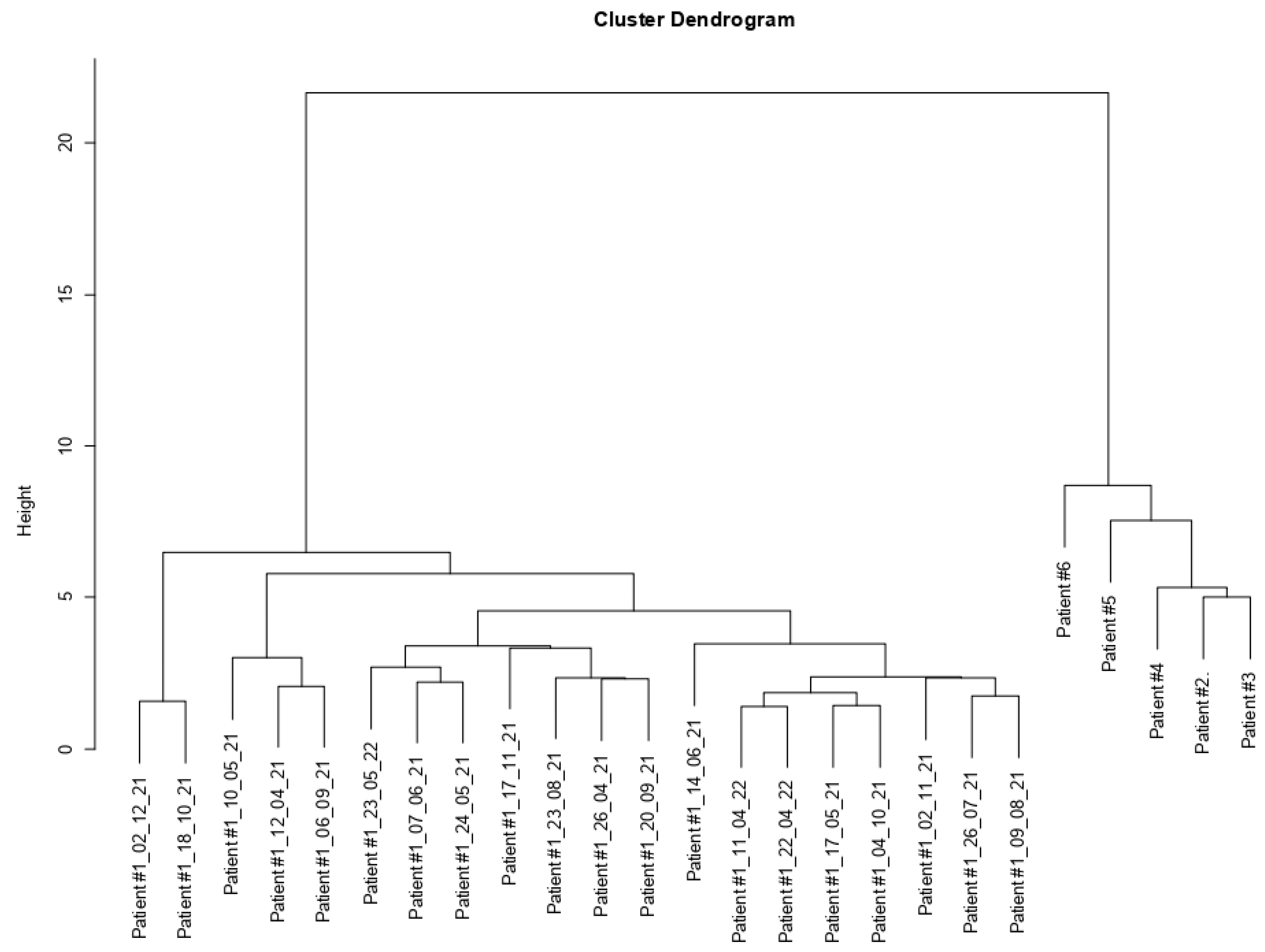
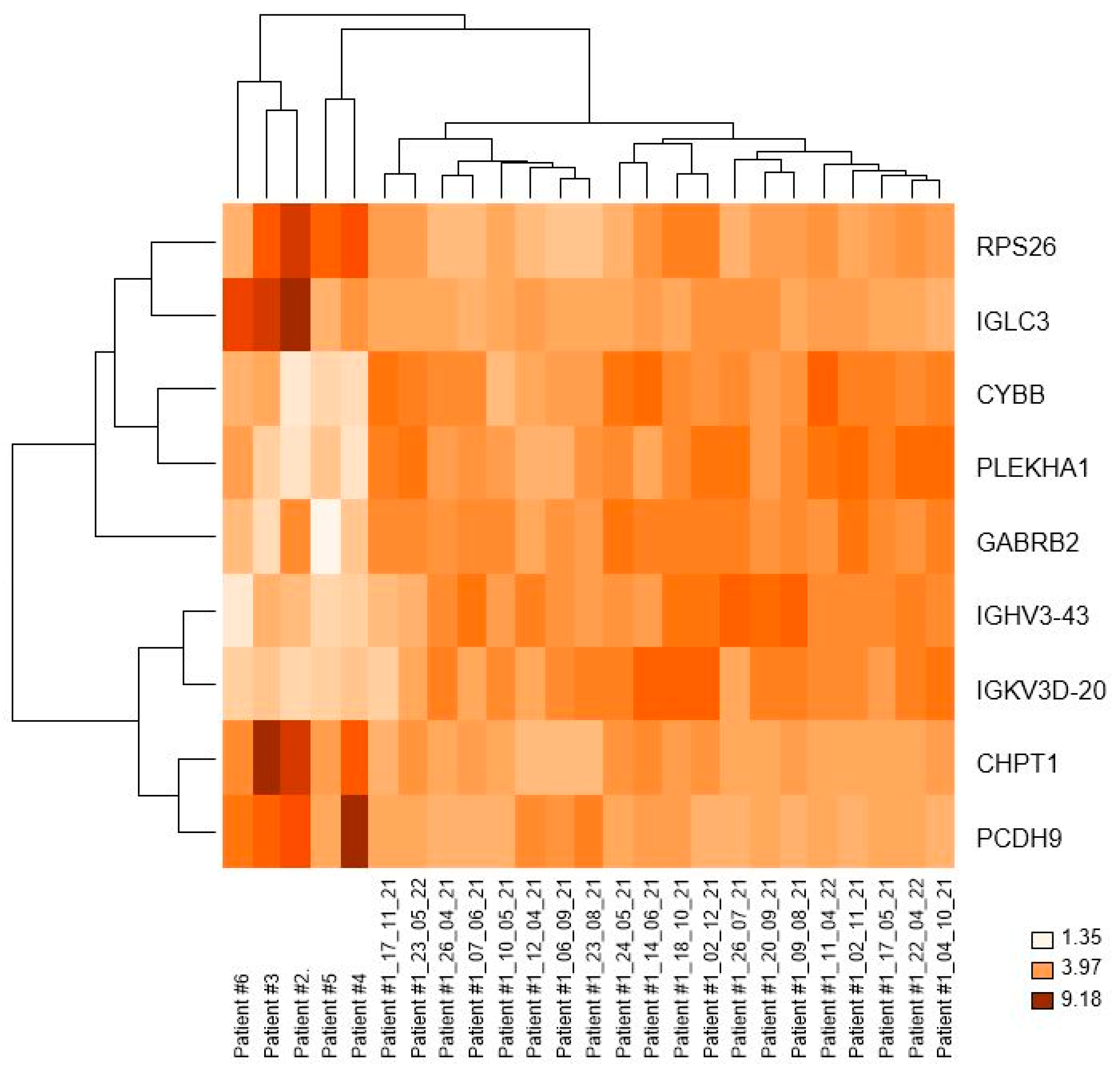
3.3. Cluster Dendrogram Patient #1 vs. Patients #2, #3, #4, #5, and #6
3.4. Nine Genes Were Differently Expressed in the CLL Patient Who Followed Prolonged Periodic Fasting vs. CLL Patients with a Varied Diet
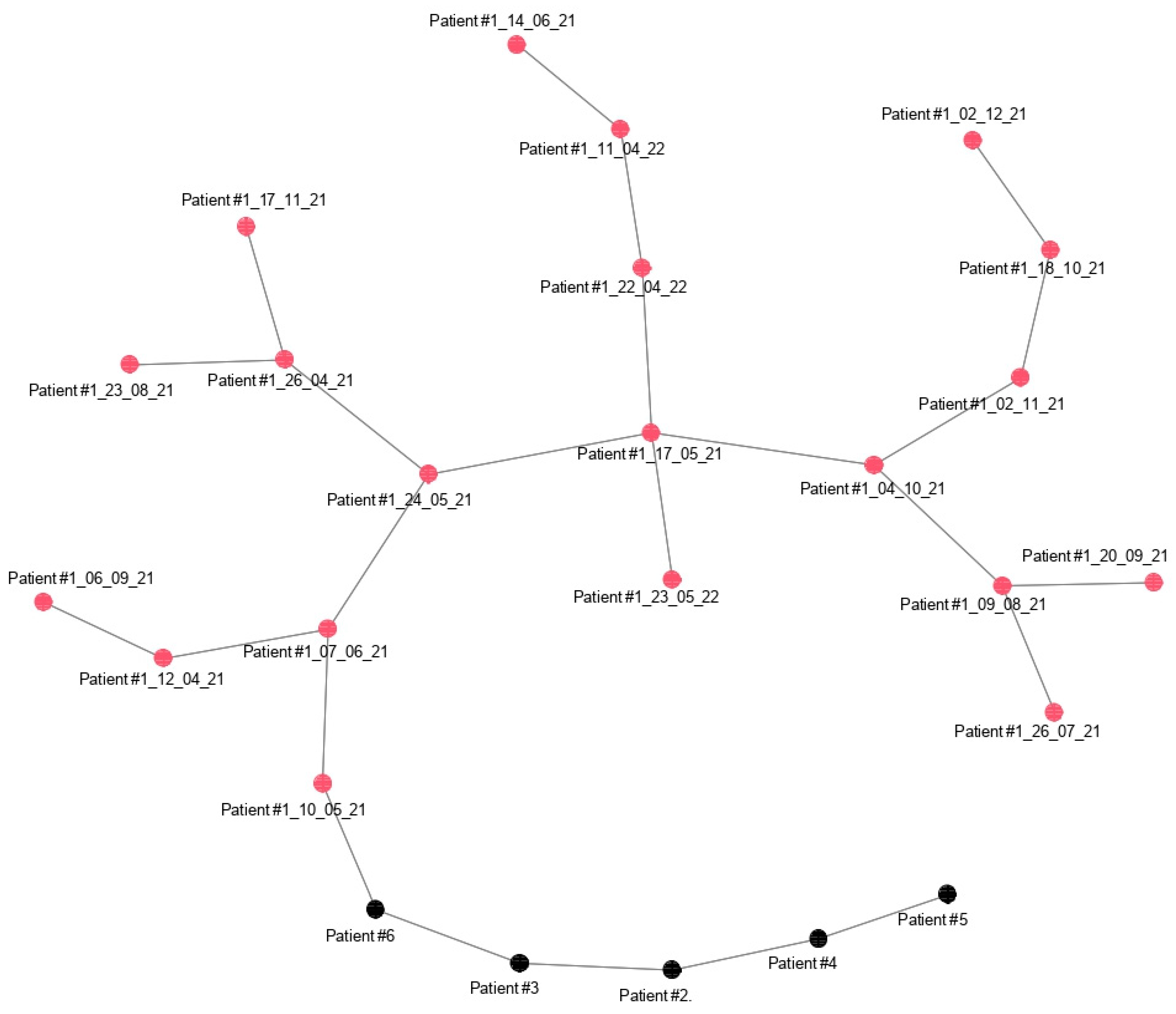
3.5. Minimun Spanning Tree (MST) of Patient #1 vs. Patients #2, #3, #4, #5, and #6
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hallek, M.; Al-Sawaf, O. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: 2022 update on diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 1679–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kipps, T.J.; Stevenson, F.K.; Wu, C.J.; Croce, C.M.; Packham, G.; Wierda, W.G.; O’Brien, S.; Gribben, J.; Rai, K. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 16096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montague, A.M.; Pathak, S. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia with Variant Genetics. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hallek, M.; Cheson, B.D.; Catovsky, D.; Caligaris-Cappio, F.; Dighiero, G.; Döhner, H.; Hillmen, P.; Keating, M.; Montserrat, E.; Chiorazzi, N.; et al. iwCLL guidelines for diagnosis, indications for treatment, response assessment, and supportive management of CLL. Blood 2018, 131, 2745–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroers, R.; Griesinger, F.; Trümper, L.; Haase, D.; Kulle, B.; Klein-Hitpass, L.; Sellmann, L.; Dührsen, U.; Dürig, J. Combined analysis of ZAP-70 and CD38 expression as a predictor of disease progression in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2005, 19, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, K.R.; Sawitsky, A.; Cronkite, E.P.; Chanana, A.D.; Levy, R.N.; Pasternack, B.S. Clinical staging of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1975, 46, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Binet, J.L.; Auquier, A.; Dighiero, G.; Chastang, C.; Piguet, H.; Goasguen, J.; Vaugier, G.; Potron, G.; Colona, P.; Oberling, F.; et al. A new prognostic classification of chronic lymphocytic leukemia derived from a multivariate survival analysis. Cancer 1981, 48, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, N.E.; Hampel, P.J.; Van Dyke, D.L.; Parikh, S.A. CLL update 2022: A continuing evolution in care. Blood Rev. 2022, 54, 100930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catherwood, M.A.; Gonzalez, D.; Donaldson, D.; Clifford, R.; Mills, K.; Thornton, P. Relevance of TP53 for CLL diagnostics. J. Clin. Pathol. 2019, 72, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiorazzi, N.; Chen, S.S.; Rai, K.R. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2021, 11, a035220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, L.; Thorvaldsdottir, B.; Sutton, L.A.; Karakatsoulis, G.; Meggendorfer, M.; Parker, H.; Nadeu, F.; Brieghel, C.; Laidou, S.; Moia, R.; et al. Different prognostic impact of recurrent gene mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia depending on IGHV gene somatic hypermutation status: A study by ERIC in HARMONY. Leukemia 2023, 37, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Kipps, T.J. The pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2014, 9, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrisqueta, P.; Medina, D.; Villacampa, G.; Lu, J.; Alcoceba, M.; Carabia, J.; Boix, J.; Tazón-Vega, B.; Iacoboni, G.; Bobillo, S.; et al. A gene expression assay based on chronic lymphocytic leukemia activation in the microenvironment to predict progression. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 5763–5773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trojani, A.; Di Camillo, B.; Tedeschi, A.; Lodola, M.; Montesano, S.; Ricci, F.; Vismara, E.; Greco, A.; Veronese, S.; Orlacchio, A.; et al. Gene expression profiling identifies ARSD as a new marker of disease progression and the sphingolipid metabolism as a potential novel metabolism in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Biomark. 2011, 11, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilous, N.; Abramenko, I.; Chumak, A.; Dyagil, I.; Martina, Z. Analysis of LPL gene expression in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Exp. Oncol. 2019, 41, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Sathiaseelan, V.; Moore, A.; Tan, S.; Chilamakuri, C.S.R.; Roamio Franklin, V.N.; Shahsavari, A.; Jakwerth, C.A.; Hake, S.B.; Warren, A.J.; et al. ZAP-70 constitutively regulates gene expression and protein synthesis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2021, 137, 3629–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döhner, H.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Benner, A.; Leupolt, E.; Kröber, A.; Bullinger, L.; Döhner, K.; Bentz, M.; Lichter, P. Genomic aberrations and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 1910–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mauro, S.; Scamporrino, A.; Petta, S.; Urbano, F.; Filippello, A.; Ragusa, M.; Di Martino, M.T.; Scionti, F.; Grimaudo, S.; Pipitone, R.M.; et al. Serum coding and non-coding RNAs as biomarkers of NAFLD and fibrosis severity. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 1742–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gelder, R.N.; von Zastrow, M.E.; Yool, A.; Dement, W.C.; Barchas, J.D.; Eberwine, J.H. Amplified RNA synthesized from limited quantities of heterogeneous cDNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irizarry, R.A.; Bolstad, B.M.; Collin, F.; Cope, L.M.; Hobbs, B.; Speed, T.P. Summaries of Affymetrix GeneChip probe level data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tusher, V.G.; Tibshirani, R.; Chu, G. Significance analysis of microarrays applied to the ionizing radiation response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 5116–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storey, J.D.; Tibshirani, R. Statistical significance for genomewide studies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9440–9445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Peng, J.; Ma, S.; Ding, Y.; Huang, T.; Zhao, S.; Gao, L.; Liang, X.; Li, C.; Ma, C. Ribosomal protein S26 serves as a checkpoint of T-cell survival and homeostasis in a p53-dependent manner. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 1844–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.Y.; Yu, Y.; Xie, M.; Yang, M.H.; Zhu, S.; Yang, L.C.; Kang, R.; Tang, D.L.; Zhao, L.L.; Cao, L.Z. Digital gene expression profiling analysis of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 4321–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, M.; Liu, X.; Yang, W.; Song, H.; Zhao, X.; Ai, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, H. Identification of a Lipid Metabolism-Associated Gene Signature Predicting Survival in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 9503–9513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesko, J.; Triebl, A.; Stacher-Priehse, E.; Fink-Neuböck, N.; Lindenmann, J.; Smolle-Jüttner, F.M.; Köfeler, H.C.; Hrzenjak, A.; Olschewski, H.; Leithner, K. Phospholipid dynamics in ex vivo lung cancer and normal lung explants. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, S.; Buckstein, R.; Spaner, D.E. A link between hypercholesterolemia and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2016, 57, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCaw, L.; Shi, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, Y.J.; Spaner, D.E. Low Density Lipoproteins Amplify Cytokine-signaling in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Cells. eBioMedicine 2017, 15, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Wei, G.H.; Liu, D.; Wang, L.; Hou, Y.; Zhu, S.; Peng, L.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Su, H.; et al. Whole-genome and Transcriptome Sequencing of Prostate Cancer Identify New Genetic Alterations Driving Disease Progression. Eur. Urol. 2018, 73, 322–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Zhang, Z. Screening of potentially crucial genes and regulatory factors involved in epithelial ovarian cancer using microarray analysis. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yu, G.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, Z. Downregulation of PCDH9 predicts prognosis for patients with glioma. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2012, 19, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, Q.; Li, S.; Li, S.; Zhao, Z.; Gao, H.; Wang, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, Y.; et al. Dual inhibition of PCDH9 expression by miR-215-5p up-regulation in gliomas. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 10287–10297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Xiang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, G. Loss of PCDH9 is associated with the differentiation of tumor cells and metastasis and predicts poor survival in gastric cancer. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2015, 32, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, M.; Smith, S.M.; Lee, A.G.; Chae, H.D.; Spiteri, E.; Erdmann, J.; Galperin, I.; Jones, L.M.; Donato, M.; Abidi, P.; et al. Comparison of the Transcriptomic Signatures in Pediatric and Adult CML. Cancers 2021, 13, 6263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumeister, J.; Maié, T.; Chatain, N.; Gan, L.; Weinbergerova, B.; de Toledo, M.A.S.; Eschweiler, J.; Maurer, A.; Mayer, J.; Kubesova, B.; et al. Early and late stage MPN patients show distinct gene expression profiles in CD34+ cells. Ann. Hematol. 2021, 100, 2943–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Liu, B.Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.G.; Cao, G.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, S.L. Identification of differentially expressed genes in salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma cells associated with metastasis. Arch. Med. Sci. 2016, 12, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knott, E.L.; Leidenheimer, N.J. A Targeted Bioinformatics Assessment of Adrenocortical Carcinoma Reveals Prognostic Implications of GABA System Gene Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Jin, W.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, E.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, O.; Zhang, X. GABRB2 plays an important role in the lymph node metastasis of papillary thyroid cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 492, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Gong, Y.Z.; Shao, M.N.; Ruan, G.T.; Xie, H.L.; Liao, X.W.; Wang, X.K.; Han, Q.F.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, L.C.; et al. Distinct diagnostic and prognostic values of γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor family genes in patients with colon adenocarcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Zhao, H.; Sun, B.; Han, X.; Zhou, D.; Cui, Z.; Ma, X.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, L. A predictive analysis approach for paediatric and adult high-grade glioma: miRNAs and network insight. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belotti, Y.; Tolomeo, S.; Yu, R.; Lim, W.T.; Lim, C.T. Prognostic Neurotransmitter Receptors Genes Are Associated with Immune Response, Inflammation and Cancer Hallmarks in Brain Tumors. Cancers 2022, 14, 2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, A.M.; Kreisberg, J.F.; Ideker, T. Analysis of Matched Tumor and Normal Profiles Reveals Common Transcriptional and Epigenetic Signals Shared across Cancer Types. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, R. The Effect of Fasting on Human Metabolism and Psychological Health. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 5653739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, S.; Sapkota, N.; Han, Z. Effect of fasting on cancer: A narrative review of scientific evidence. Cancer Sci. 2022, 113, 3291–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Patient | Age at Diagnosis (y) | Time from Diagnosis to B Cell Selection (y) | Sex | Binet Stage | Rai Stage | IGVH Gene | TP53 Mutation Status | FISH * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | 50 | 5 | M | A | 0 | MT | UM | del(13q) |
| #2 | 64 | 2 | M | C | IV | UM | UM | negative |
| #3 | 64 | 3 | M | C | IV | UM | UM | trisomy 12; del(11q) |
| #4 | 70 | 3 | M | B | II | UM | UM | trisomy 12 |
| #5 | 51 | 12 | M | B | II | MT | UM | negative |
| #6 | 70 | 12 | F | B | II | MT | UM | monosomy 13q14 |
| Patient | Time-Points | Date | Lymphocyte Count × 109/L |
|---|---|---|---|
| #2 | 1 | June 2019 * | 8.00 |
| #2 | 2 | December 2019 | 19.0 |
| #2 | 3 | May 2020 | 39.34 |
| #3 | 1 | February 2018 * | 10.50 |
| #3 | 2 | October 2018 | 12.36 |
| #3 | 3 | April 2019 | 11.91 |
| #3 | 4 | October 2021 | 106.68 |
| #4 | 1 | November 2018 * | 14.05 |
| #4 | 2 | December 2018 | 25.31 |
| #4 | 3 | June 2019 | 97.70 |
| #4 | 4 | August 2021 | 234.94 |
| #4 | 5 | October 2021 | 279.44 |
| #5 | 1 | May 2009 * | 9.6 |
| #5 | 2 | August 2009 | 11.4 |
| #5 | 3 | November 2009 | 12.6 |
| #5 | 4 | June 2010 | 13.58 |
| #5 | 5 | February 2011 | 15.1 |
| #5 | 6 | October 2011 | 16.6 |
| #5 | 7 | May 2012 | 19.92 |
| #5 | 8 | January 2013 | 23.37 |
| #5 | 9 | May 2013 | 21 |
| #5 | 10 | December 2013 | 26.7 |
| #5 | 11 | May 2014 | 24.6 |
| #5 | 12 | June 2015 | 35.2 |
| #5 | 13 | November 2015 | 51.10 |
| #5 | 14 | December 2016 | 52.3 |
| #5 | 15 | June 2017 | 62.0 |
| #5 | 16 | June 2021 | 141.6 |
| #6 | 1 | May 2009 * | 12.0 |
| #6 | 2 | August 2011 | 11.38 |
| #6 | 3 | January 2012 | 12.7 |
| #6 | 4 | June 2012 | 12.0 |
| #6 | 5 | January 2013 | 10.89 |
| #6 | 6 | June 2013 | 14.78 |
| #6 | 7 | December 2013 | 19.2 |
| #6 | 8 | June 2014 | 19.29 |
| #6 | 9 | December 2014 | 21.85 |
| #6 | 10 | June 2015 | 20.92 |
| #6 | 11 | December 2016 | 34.36 |
| #6 | 12 | January 2018 | 54.8 |
| #6 | 13 | June 2018 | 71.2 |
| #6 | 14 | February 2019 | 67.0 |
| #6 | 15 | September 2019 | 38.9 |
| #6 | 16 | April 2021 | 43.4 |
| #6 | 17 | October 2021 | 112.46 |
| Time-Points | Date | Nutrition and Fasting | Lymphocyte Count × 109/L |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 12 April 2021 | nutrition | 25.32 |
| 2 | 26 April 2021 | fasting | 26.12 |
| 3 | 10 May 2021 | fasting | 27.21 |
| 4 | 17 May 2021 | nutrition | 30.71 |
| 5 | 24 May 2021 | nutrition | 27.59 |
| 6 | 7 June 2021 | nutrition | 17.24 |
| 7 | 14 June 2021 | nutrition | 17.01 |
| 8 | 21 June 2021 | nutrition | 16.44 |
| 9 | 5 July 2021 | nutrition | 12.35 |
| 10 | 28 March 2022 | nutrition | 26.3 |
| 11 | 11 April 2022 | fasting | 32.07 |
| 12 | 22 April 2022 | fasting | 27.47 |
| 13 | 23 May 2022 | nutrition | 17.55 |
| 14 | 6 June 2022 | nutrition | 14.82 |
| Gene Symbol | Gene Name | log-Mean Group 2 | log-Mean Group 1 | FC 1st Group vs. 2nd Group | p Value | q Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IGLC3 | immunoglobulin lambda constant 3 (Kern-Oz+ marker) | 6.92 | 4.18 | −6.67 | 0.0000136 | 0.04493 |
| RPS26 | ribosomal protein S26 | 6.71 | 4.83 | −3.67 | 0.0000235 | 0.04926 |
| CHPT1 | choline phosphotransferase 1 | 3.72 | 2.29 | −2.69 | 0.0000149 | 0.04396 |
| PCDH9 | protocadherin 9 | 2.88 | 1.73 | −2.20 | 0.0000177 | 0.04219 |
| IGHV3-43 | immunoglobulin heavy variable 3-43 | 2.19 | 3.46 | 2.41 | 0.0000142 | 0.04362 |
| IGKV3D-20 | immunoglobulin kappa variable 3D-20 | 1.66 | 3.10 | 2.71 | 0.0000192 | 0.04460 |
| PLEKHA1 | pleckstrin homology domain containing, family A (phosphoinositide binding specific) member 1 | 2.72 | 4.36 | 3.13 | 0.0000173 | 0.04360 |
| CYBB | cytochrome b-245, beta polypeptide | 3.77 | 5.48 | 3.27 | 0.0000131 | 0.04505 |
| GABRB2 | gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, beta 2 | 4.06 | 6.55 | 5.63 | 0.0000125 | 0.04876 |
| Gene Symbol | KEGG Pathway |
|---|---|
| RPS26 | hsa03010 Ribosome |
| CHPT1 | hsa00440 Phosphonate and phosphinate metabolism hsa00564 Glycerophospholipid metabolism hsa00565 Ether lipid metabolism hsa01100 Metabolic pathways hsa05231 Choline metabolism in cancer |
| CYBB | hsa04066 HIF-1 signaling pathway hsa04145 Phagosome hsa04216 Ferroptosis hsa04217 Necroptosis hsa04621 NOD-like receptor signaling pathway hsa04670 Leukocyte transendothelial migration |
| GABRB2 | hsa04080 Neuroactive ligand–receptor interaction hsa04726 Serotonergic synapse hsa04727 GABAergic synapse |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bossi, L.E.; Palumbo, C.; Trojani, A.; Melluso, A.; Di Camillo, B.; Beghini, A.; Sarnataro, L.M.; Cairoli, R. A Nine-Gene Expression Signature Distinguished a Patient with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Who Underwent Prolonged Periodic Fasting. Medicina 2023, 59, 1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59081405
Bossi LE, Palumbo C, Trojani A, Melluso A, Di Camillo B, Beghini A, Sarnataro LM, Cairoli R. A Nine-Gene Expression Signature Distinguished a Patient with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Who Underwent Prolonged Periodic Fasting. Medicina. 2023; 59(8):1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59081405
Chicago/Turabian StyleBossi, Luca Emanuele, Cassandra Palumbo, Alessandra Trojani, Agostina Melluso, Barbara Di Camillo, Alessandro Beghini, Luca Maria Sarnataro, and Roberto Cairoli. 2023. "A Nine-Gene Expression Signature Distinguished a Patient with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Who Underwent Prolonged Periodic Fasting" Medicina 59, no. 8: 1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59081405
APA StyleBossi, L. E., Palumbo, C., Trojani, A., Melluso, A., Di Camillo, B., Beghini, A., Sarnataro, L. M., & Cairoli, R. (2023). A Nine-Gene Expression Signature Distinguished a Patient with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Who Underwent Prolonged Periodic Fasting. Medicina, 59(8), 1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59081405





