Daily Physical Training Improved Coronal Imbalance of Adult Degenerative Scoliosis: A Case Report
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Case Report
2.1. Patinet Information
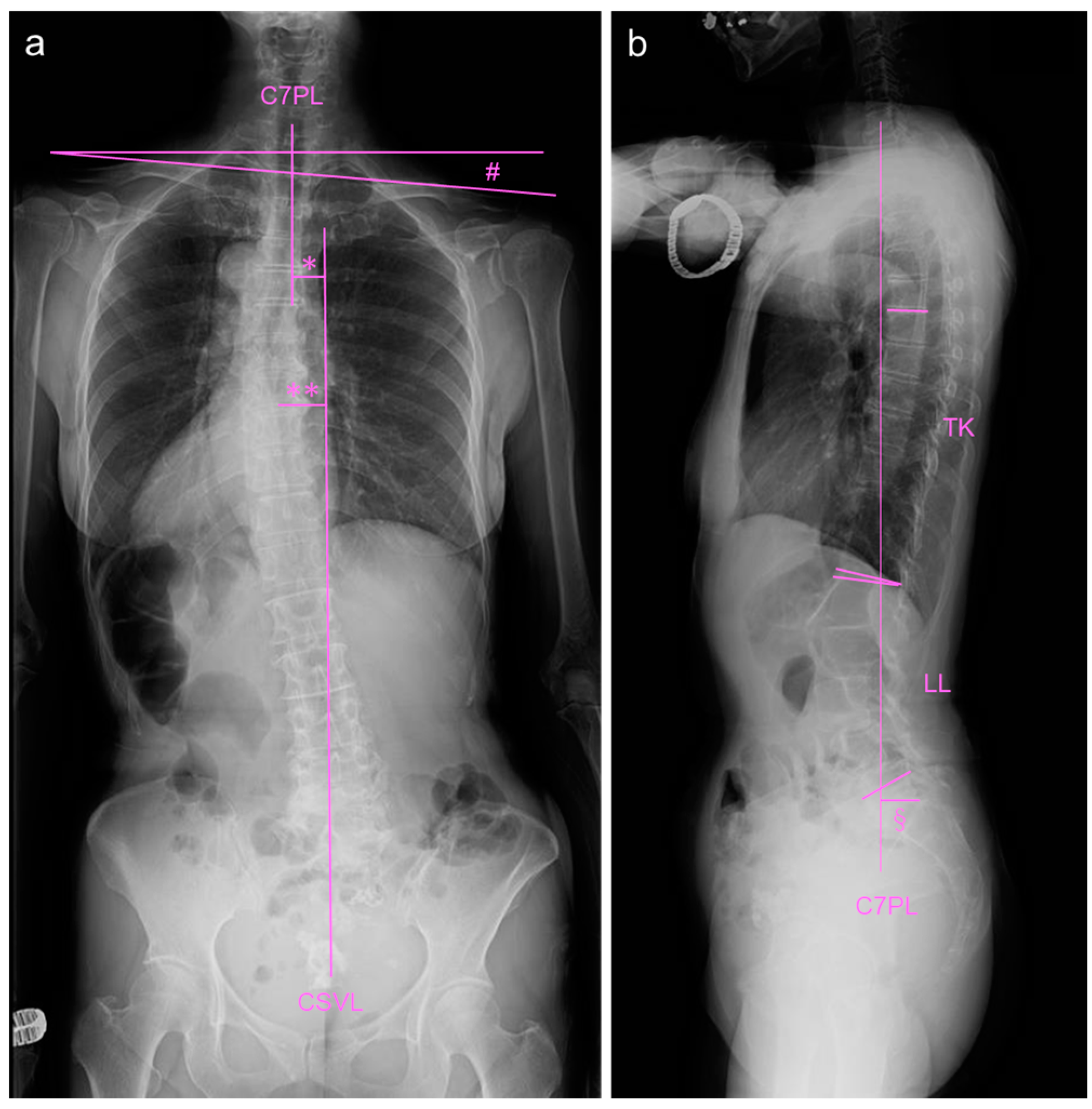
2.2. Image Examinations at First Visit
2.3. Daily Physical Training
2.4. Image Examinations after Six Months of Daily Physical Exercise
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Graham, R.B.; Sugrue, P.A.; Koski, T.R. Adult degenerative scoliosis. Clin. Spine Surg. 2016, 29, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diebo, B.G.; Shah, N.V.; Boachie-Adjei, O.; Zhu, F.; A Rothenfluh, D.; Paulino, C.B.; Schwab, F.J.; Lafage, V. Adult spinal deformity. Lancet 2019, 394, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gür, G.; Ayhan, C.; Yakut, Y. The effectiveness of core stabilization exercise in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A randomized controlled trial. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2017, 41, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hlaing, S.S.; Puntumetakul, R.; Khine, E.E.; Boucaut, R. Effects of core stabilization exercise and strengthening exercise on proprioception, balance, muscle thickness and pain related outcomes in patients with subacute nonspecific low back pain: A randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negrini, A.; Negrini, M.G.; Donzelli, S.; Romano, M.; Zaina, F.; Negrini, S. Scoliosis-specific exercises can reduce the progression of severe curves in adult idiopathic scoliosis: A long-term cohort study. Scoliosis 2015, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Negrini, A.; Parzini, S.; Negrini, M.G.; Romano, M.; Atanasio, S.; Zaina, F.; Negrini, S. Adult scoliosis can be reduced through specific seas exercises: A case report. Scoliosis 2008, 3, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ozyemisci Taskiran, O. Rehabilitation in adult spinal deformity. Turk. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2020, 66, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, M.; Negrini, A.; Parzini, S.; Tavernaro, M.; Zaina, F.; Donzelli, S.; Negrini, S. Seas (scientific exercises approach to scoliosis): A modern and effective evidence based approach to physiotherapic specific scoliosis exercises. Scoliosis 2015, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schizas, C.; Theumann, N.; Burn, A.; Tansey, R.; Wardlaw, D.; Smith, F.W.; Kulik, G. Qualitative grading of severity of lumbar spinal stenosis based on the morphology of the dural sac on magnetic resonance images. Spine 2010, 35, 1919–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwab, F.; Ungar, B.; Blondel, B.; Buchowski, J.; Coe, J.; Deinlein, D.; DeWald, C.; Mehdian, H.; Shaffrey, C.; Tribus, C.; et al. Scoliosis research society-schwab adult spinal deformity classification: A validation study. Spine 2012, 37, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, E.; Altaf, F.; Oh, L.J.; Gray, R.J. Adult degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Orthopedics 2017, 40, e930–e939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marty-Poumarat, C.; Scattin, L.; Marpeau, M.; de Loubresse, C.G.; Aegerter, P. Natural history of progressive adult scoliosis. Spine 2007, 32, 1227–1234, discussion 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ploumis, A.; Transfledt, E.E.; Denis, F. Degenerative lumbar scoliosis associated with spinal stenosis. Spine J. 2007, 7, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritchett, J.W.; Bortel, D.T. Degenerative symptomatic lumbar scoliosis. Spine 1993, 18, 700–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teles, A.R.; Mattei, T.A.; Righesso, O.; Falavigna, A. Effectiveness of operative and nonoperative care for adult spinal deformity: Systematic review of the literature. Global Spine J. 2017, 7, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Everett, C.R.; Patel, R.K. A systematic literature review of nonsurgical treatment in adult scoliosis. Spine 2007, 32, S130–S134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Negrini, S.; Donzelli, S.; Aulisa, A.G.; Czaprowski, D.; Schreiber, S.; De Mauroy, J.C.; Diers, H.; Grivas, T.B.; Knott, P.; Kotwicki, T.; et al. 2016 sosort guidelines: Orthopaedic and rehabilitation treatment of idiopathic scoliosis during growth. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2018, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vleeming, A.; Schuenke, M.D.; Danneels, L.; Willard, F.H. The functional coupling of the deep abdominal and paraspinal muscles: The effects of simulated paraspinal muscle contraction on force transfer to the middle and posterior layer of the thoracolumbar fascia. J. Anat. 2014, 225, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagci, G.; Yakut, Y. Core stabilization exercises versus scoliosis-specific exercises in moderate idiopathic scoliosis treatment. Prosthetics Orthot. Int. 2019, 43, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraj, S.S.A.; Holewijn, R.M.; van Hooff, M.L.; de Kleuver, M.; Pellisé, F.; Haanstra, T.M. De novo degenerative lumbar scoliosis: A systematic review of prognostic factors for curve progression. Eur. Spine J. 2016, 25, 2347–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akeda, K.; Hasegawa, T.; Kawaguchi, K.; Yamada, J.; Takegami, N.; Fujiwara, T.; Sudo, A. Daily Physical Training Improved Coronal Imbalance of Adult Degenerative Scoliosis: A Case Report. Medicina 2023, 59, 1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59081443
Akeda K, Hasegawa T, Kawaguchi K, Yamada J, Takegami N, Fujiwara T, Sudo A. Daily Physical Training Improved Coronal Imbalance of Adult Degenerative Scoliosis: A Case Report. Medicina. 2023; 59(8):1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59081443
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkeda, Koji, Takahiro Hasegawa, Koki Kawaguchi, Junichi Yamada, Norihiko Takegami, Tatsuhiko Fujiwara, and Akihiro Sudo. 2023. "Daily Physical Training Improved Coronal Imbalance of Adult Degenerative Scoliosis: A Case Report" Medicina 59, no. 8: 1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59081443
APA StyleAkeda, K., Hasegawa, T., Kawaguchi, K., Yamada, J., Takegami, N., Fujiwara, T., & Sudo, A. (2023). Daily Physical Training Improved Coronal Imbalance of Adult Degenerative Scoliosis: A Case Report. Medicina, 59(8), 1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59081443





