Is There a Difference in the Distribution of Mechanoreceptors among the Three Sections of the Anterior Talofibular Ligament?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
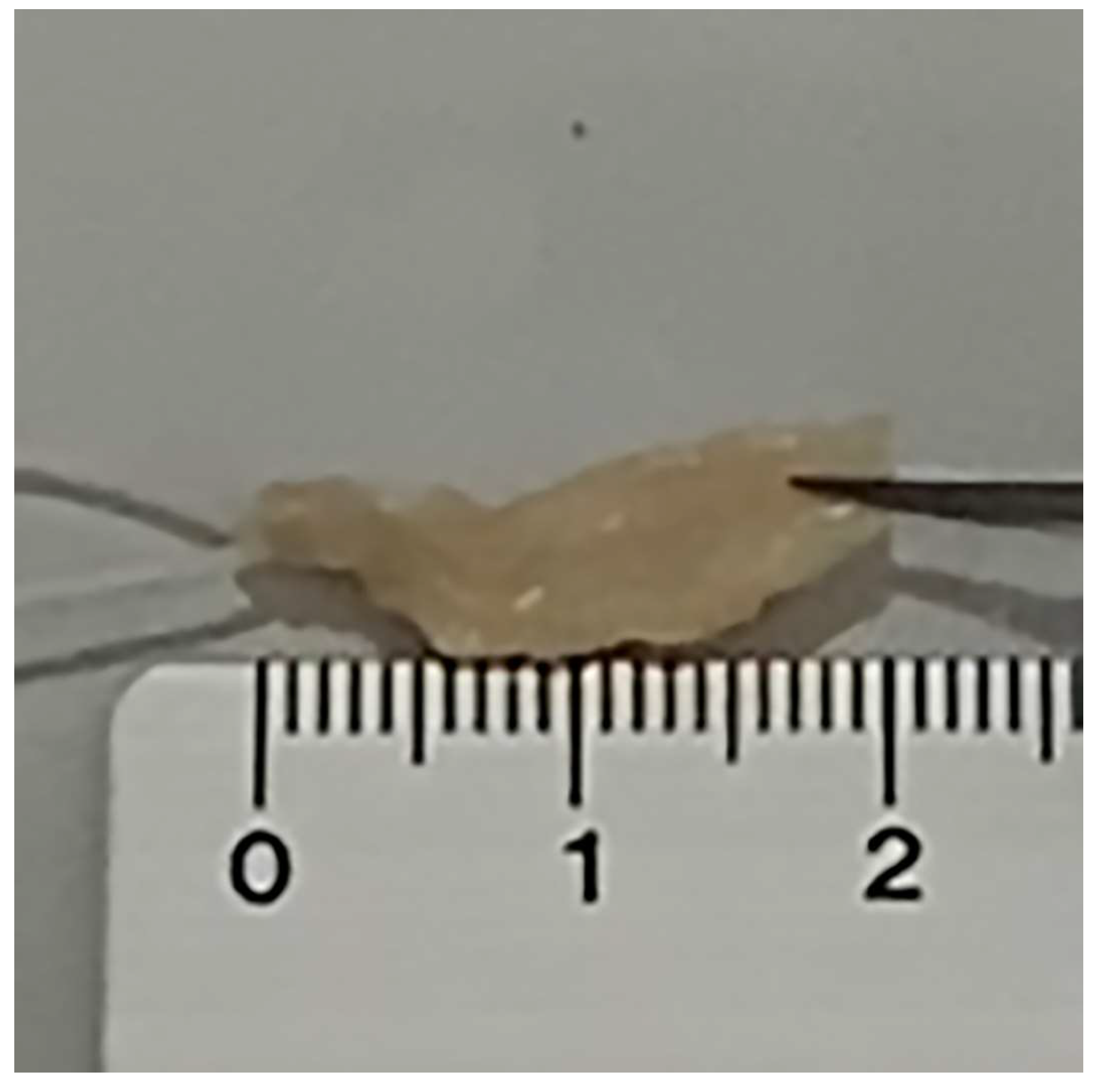
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
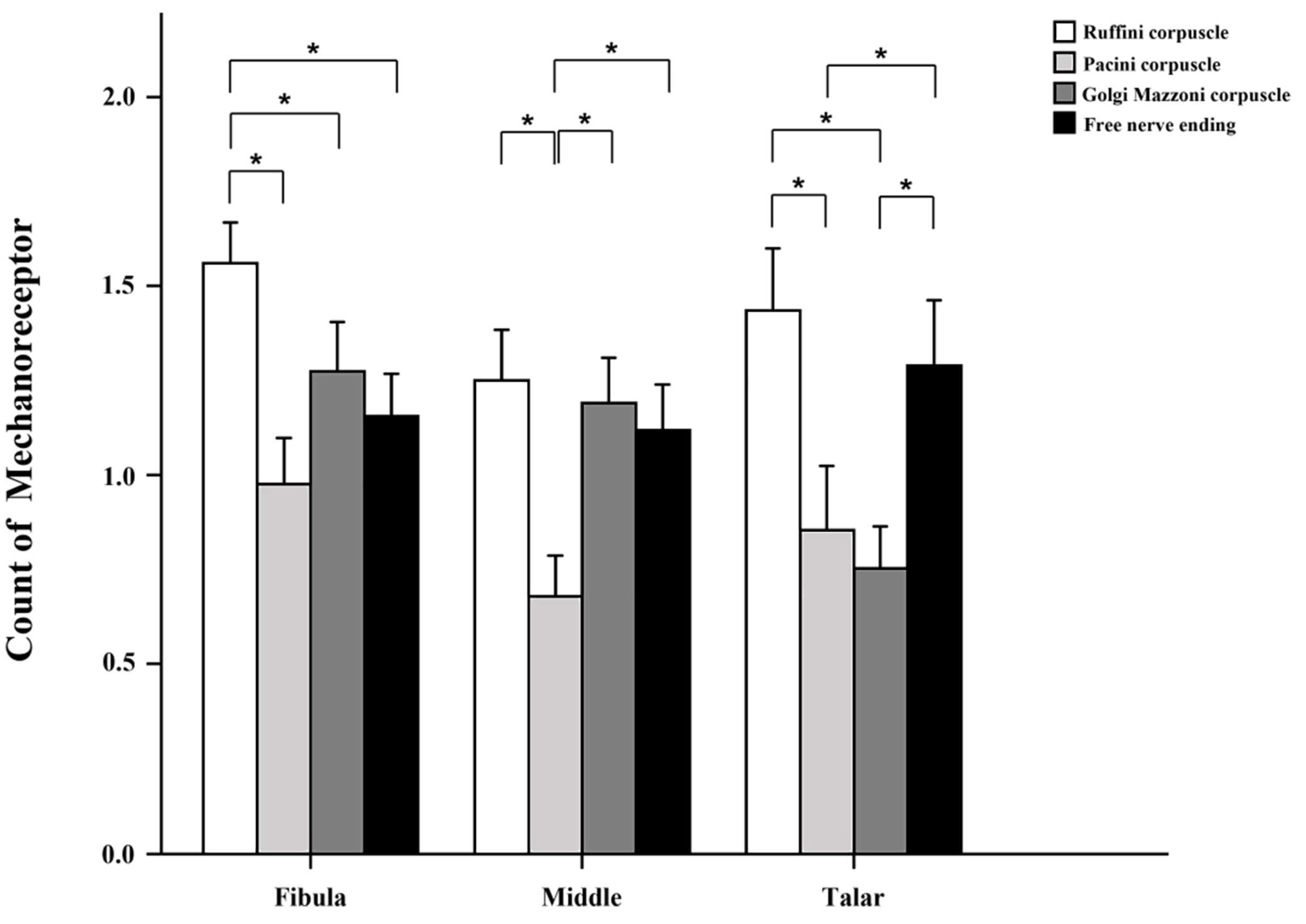
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Waterman, B.R.; Owens, B.D.; Davey, S.; Zacchilli, M.A.; Belmont, P.J., Jr. The epidemiology of ankle sprains in the United States. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2010, 92, 2279–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemler, E.; Thijs, K.M.; Badenbroek, I.; van de Port, I.G.; Hoes, A.W.; Backx, F.J. Long-term prognosis of acute lateral ankle ligamentous sprains: High incidence of recurrences and residual symptoms. Fam. Pract. 2016, 33, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rijn, R.M.; van Os, A.G.; Bernsen, R.M.; Luijsterburg, P.A.; Koes, B.W.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.M. What is the clinical course of acute ankle sprains? A systematic literature review. Am. J. Med. 2008, 121, 324–331.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, M.A.; Dean, M.R.; Hanham, I.W. The etiology and prevention of functional instability of the foot. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1965, 47, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delahunt, E.; Coughlan, G.F.; Caulfield, B.; Nightingale, E.J.; Lin, C.W.; Hiller, C.E. Inclusion criteria when investigating insufficiencies in chronic ankle instability. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2010, 42, 2106–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takebayashi, T.; Yamashita, T.; Sakamoto, N.; Yamada, Y.; Minaki, Y.; Ishii, S. Biomechanical characteristics of the lateral ligament of the ankle joint. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2002, 41, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Waddington, G.; Adams, R.; Anson, J.; Liu, Y. Assessing proprioception: A critical review of methods. J. Sport Health Sci. 2016, 5, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, M.R.; Cavalcante, M.L.; Leite, J.A.; Ferreira, F.V.; Castro, A.J.; Santana, M.G. Histomorphometric evaluation of mechanoreceptors and free nerve endings in human lateral ankle ligaments. Foot Ankle Int. 2008, 29, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kynsburg, A.; Pánics, G.; Halasi, T. Long-term neuromuscular training and ankle joint position sense. Acta Physiol. Hung. 2010, 97, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witchalls, J.B.; Waddington, G.; Adams, R.; Blanch, P. Chronic ankle instability affects learning rate during repeated proprioception testing. Phys. Ther. Sports 2014, 15, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillier, S.; Immink, M.; Thewlis, D. Assessing Proprioception: A Systematic Review of Possibilities. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2015, 29, 933–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, M.A. Instability of the foot after injuries to the lateral ligament of the ankle. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1965, 47, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rein, S.; Hagert, E.; Hanisch, U.; Lwowski, S.; Fieguth, A.; Zwipp, H. Immunohistochemical analysis of sensory nerve endings in ankle ligaments: A cadaver study. Cells Tissues Organs 2013, 197, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rein, S.; Manthey, S.; Zwipp, H.; Witt, A. Distribution of sensory nerve endings around the human sinus tarsi: A cadaver study. J. Anat. 2014, 224, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, E.D.; Rhyu, I.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, D.S.; Ahn, J.H.; Lee, Y.K. Can Bassett’s ligament be removed? Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2016, 24, 1236–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kim, Y.B.; Kim, T.G.; Lee, S.W.; Park, S.H.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, Y.J.; Koh, Y.G. Reliability and Validity of Magnetic Resonance Imaging for the Evaluation of the Anterior Talofibular Ligament in Patients Undergoing Ankle Arthroscopy. Arthroscopy 2015, 31, 1540–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimny, M.L.; St Onge, M.; Schutte, M. A modified gold chloride method for the demonstration of nerve endings in frozen sections. Stain. Technol. 1985, 60, 305–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, M.A.; Wyke, B. The innervation of the knee joint. An anatomical and histological study in the cat. J. Anat. 1967, 101, 505–532. [Google Scholar]
- Cavalcante, M.L.; Rodrigues, C.J.; Mattar, R., Jr. Mechanoreceptors and nerve endings of the triangular fibrocartilage in the human wrist. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2004, 29, 432–435; discussion 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelson, J.D.; Hutchins, C. Mechanoreceptors in human ankle ligaments. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1995, 77, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Song, W.; Zheng, C.; Zhou, S.; Bai, S. Morphological study of mechanoreceptors in collateral ligaments of the ankle joint. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2015, 10, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiftan, G.S.; Ross, L.A.; Hahne, A.J. The effectiveness of proprioceptive training in preventing ankle sprains in sporting populations: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Sci. Med. Sports 2015, 18, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schutte, M.J.; Happel, L.T. Joint innervation in joint injury. Clin. Sports Med. 1990, 9, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, H.; Sjölander, P.; Sojka, P. Receptors in the knee joint ligaments and their role in the biomechanics of the joint. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 1991, 18, 341–368. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, M.A. Co-ordination exercises in the treatment of functional instability of the foot. Physiotherapy 1965, 51, 393–395. [Google Scholar]
- Gribble, P.A.; Bleakley, C.M.; Caulfield, B.M.; Docherty, C.L.; Fourchet, F.; Fong, D.T.; Hertel, J.; Hiller, C.E.; Kaminski, T.W.; McKeon, P.O.; et al. 2016 consensus statement of the International Ankle Consortium: Prevalence, impact and long-term consequences of lateral ankle sprains. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 50, 1493–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clanton, T.O.; Campbell, K.J.; Wilson, K.J.; Michalski, M.P.; Goldsmith, M.T.; Wijdicks, C.A.; LaPrade, R.F. Qualitative and Quantitative Anatomic Investigation of the Lateral Ankle Ligaments for Surgical Reconstruction Procedures. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2014, 96, e98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golanó, P.; Vega, J.; de Leeuw, P.A.; Malagelada, F.; Manzanares, M.C.; Götzens, V.; van Dijk, C.K. Anatomy of the ankle ligaments: A pictorial essay. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2016, 24, 944–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertel, J. Functional Anatomy, Pathomechanics, and Pathophysiology of Lateral Ankle Instability. J. Athl. Train. 2002, 37, 364–375. [Google Scholar]
- Bahr, R.; Bahr, I.A. Incidence of acute volleyball injuries: A prospective cohort study of injury mechanisms and risk factors. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 1997, 7, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertel, J.; Olmsted-Kramer, L.C. Deficits in time-to-boundary measures of postural control with chronic ankle instability. Gait Posture 2007, 25, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munn, J.; Sullivan, S.J.; Schneiders, A.G. Evidence of sensorimotor deficits in functional ankle instability: A systematic review with meta-analysis. J. Sci. Med. Sports 2010, 13, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, M.A. Treatment of ruptures of the lateral ligament of the ankle. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1965, 47, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeon, P.O.; Ingersoll, C.D.; Kerrigan, D.C.; Saliba, E.; Bennett, B.C.; Hertel, J. Balance training improves function and postural control in those with chronic ankle instability. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2008, 40, 1810–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauffin, H.; Tropp, H.; Odenrick, P. Effect of ankle disk training on postural control in patients with functional instability of the ankle joint. Int. J. Sports Med. 1988, 9, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.J.; Kim, Y.E.; Jun, H.J.; Lee, J.S.; Ji, S.H.; Ji, S.G.; Seo, T.-H.; Kim, Y.-O. Which Treatment is More Effective for Functional Ankle Instability: Strengthening or Combined Muscle Strengthening and Proprioceptive Exercises? J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2014, 26, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katonis, P.G.; Assimakopoulos, A.P.; Agapitos, M.V.; Exarchou, E.I. Mechanoreceptors in the posterior cruciate ligament. Histologic study on cadaver knees. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1991, 62, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutte, M.J.; Dabezies, E.J.; Zimny, M.L.; Happel, L.T. Neural anatomy of the human anterior cruciate ligament. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1987, 69, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
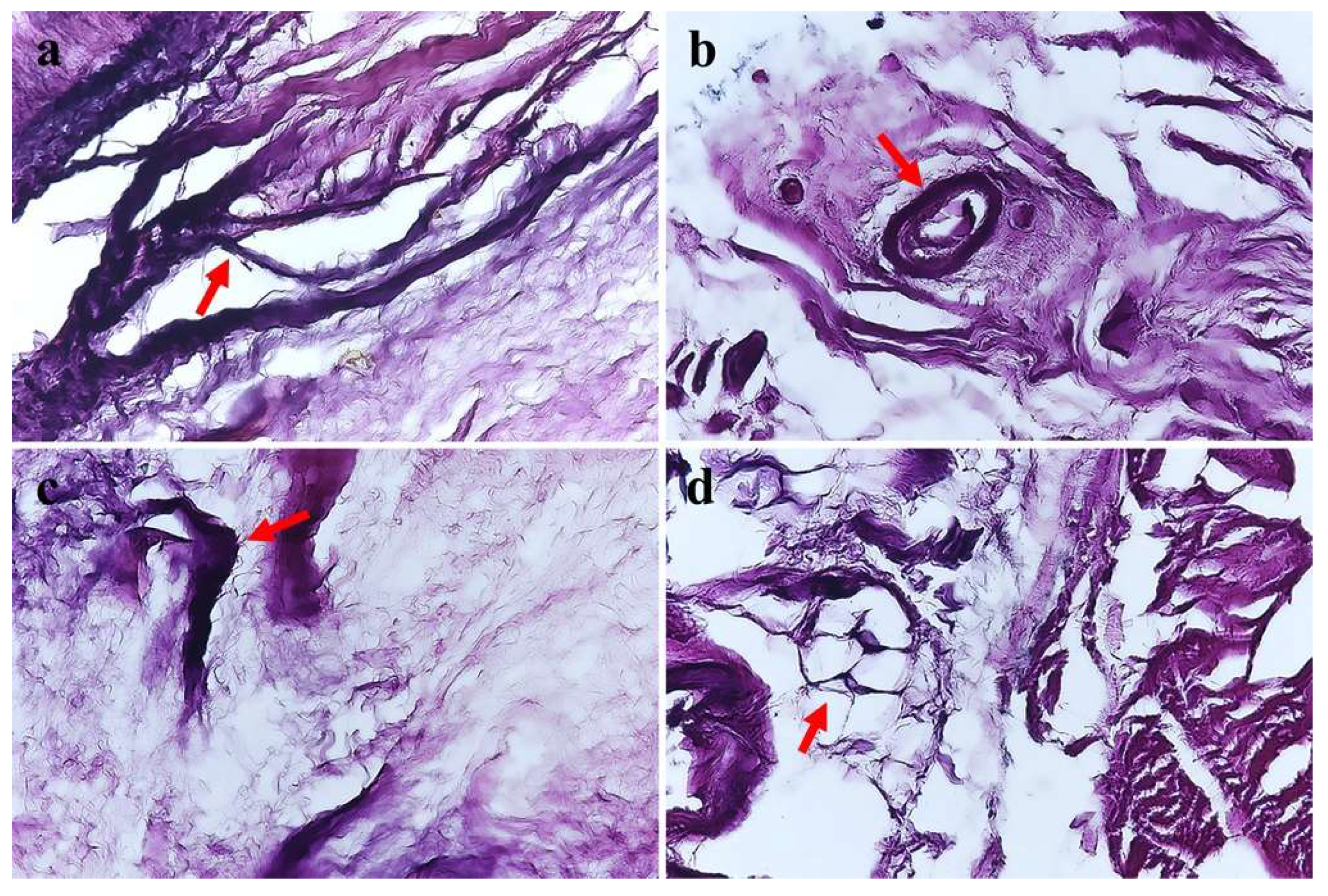

| Type | Name | Morphology | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Ruffini | Round shaped thinly myelinated globular corpuscles in clusters of 3 to 6 | Low threshold, slow adapting, static and dynamic |
| II | Pacini | Column or cone-shaped thickly myelinated corpuscles in clusters of 2 to 4 | Low threshold, rapidly adapting, dynamic |
| III | Golgi | Spindle-shaped thinly myelinated, and connected by thick nerve fibers | Low threshold, slow adapting, dynamic |
| IV | Free nerve ending | Non-myelinated, irregular | Transmit nociceptive sensation |
| Receptor | Section | Mean ± SD | p-Value Compared to M | p-Value Compared to T |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ruffini | F | 1.56 ± 1.0 | 0.006 | |
| M | 1.25 ± 1.23 | |||
| T | 1.44 ± 1.37 | |||
| Pacini | F | 0.98 ± 1.12 | ||
| M | 0.68 ± 0.98 | |||
| T | 0.86 ± 1.41 | |||
| Golgi | F | 1.27 ± 1.2 | 0.005 | |
| M | 1.2 ± 1.1 | 0.011 | ||
| T | 0.75 ± 0.91 | |||
| Free nerve ending | F | 1.16 ± 1.04 | ||
| M | 1.12 ± 1.10 | |||
| T | 1.29 ± 1.44 |
| Sections | Receptor | Mean ± SD | p Value Compared to V | p Value Compared to G | p Value Compared to F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fibular attachment | R | 1.56 ± 1.0 | 0.000 | 0.034 | 0.008 |
| V | 0.98 ± 1.12 | ||||
| G | 1.27 ± 1.2 | ||||
| F | 1.16 ± 1.04 | ||||
| Mid-ligament | R | 1.25 ± 1.23 | 0.000 | ||
| V | 0.68 ± 0.98 | 0.001 | 0.002 | ||
| G | 1.2 ± 1.1 | ||||
| F | 1.12 ± 1.10 | ||||
| Talar attachment | R | 1.44 ± 1.37 | 0.001 | 0.002 | |
| V | 0.86 ± 1.41 | 0.022 | |||
| G | 0.75 ± 0.91 | 0.041 | |||
| F | 1.29 ± 1.44 |
| Intraobserver Reliability | Interobserver Reliability | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICC | 95% ± CI | ICC | 95% ± CI | |
| Ruffini | 0.873 | 0.823–0.913 | 0.876 | 0.819–0.917 |
| Vater–Pacini | 0.898 | 0.858–0.930 | 0.888 | 0.838–0.925 |
| Golgi–Mazzoni | 0.863 | 0.810–0.906 | 0.825 | 0.783–0.911 |
| Free nerve ending | 0.903 | 0.866–0.934 | 0.846 | 0.776–0.897 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, Y.; Park, W.; Lee, H.; Choi, Y.; Kim, S.; Yeo, E.; Lee, H.; Jung, K.; Lee, B.; Lee, M.; et al. Is There a Difference in the Distribution of Mechanoreceptors among the Three Sections of the Anterior Talofibular Ligament? Medicina 2023, 59, 1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59091510
Lee Y, Park W, Lee H, Choi Y, Kim S, Yeo E, Lee H, Jung K, Lee B, Lee M, et al. Is There a Difference in the Distribution of Mechanoreceptors among the Three Sections of the Anterior Talofibular Ligament? Medicina. 2023; 59(9):1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59091510
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Youngkoo, Wonseok Park, Hyerim Lee, Youngsuk Choi, Sunghwan Kim, Euidong Yeo, Hongseop Lee, Kijin Jung, Byungryul Lee, Myoungjin Lee, and et al. 2023. "Is There a Difference in the Distribution of Mechanoreceptors among the Three Sections of the Anterior Talofibular Ligament?" Medicina 59, no. 9: 1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59091510
APA StyleLee, Y., Park, W., Lee, H., Choi, Y., Kim, S., Yeo, E., Lee, H., Jung, K., Lee, B., Lee, M., & Kim, W. (2023). Is There a Difference in the Distribution of Mechanoreceptors among the Three Sections of the Anterior Talofibular Ligament? Medicina, 59(9), 1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59091510







