A Significant Association between Type 1 Diabetes and Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Meta-Analysis Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
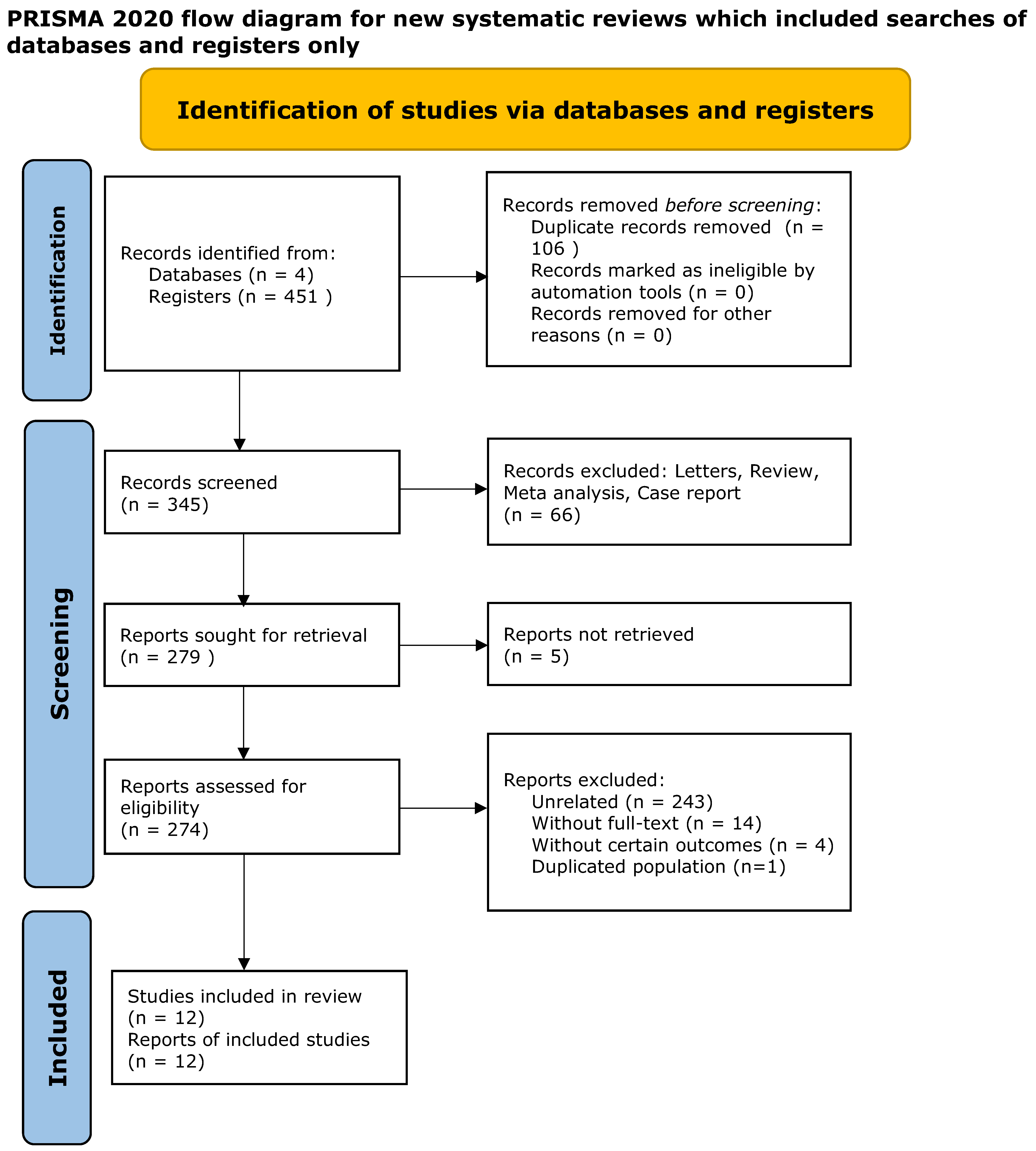
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics and Methodologies of the Included Studies
3.2. Meta-Analysis Results
3.3. Sensitivity Analysis Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buzzetti, R.; Zampetti, S.; Maddaloni, E. Adult-onset autoimmune diabetes: Current knowledge and implications for management. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Ferranti, S.D.; de Boer, I.H.; Fonseca, V.; Fox, C.S.; Golden, S.H.; Lavie, C.J.; Magge, S.N.; Marx, N.; McGuire, D.K.; Orchard, T.J.; et al. Type 1 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association and American Diabetes Association. Circulation 2014, 130, 1110–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, M.A.; Eisenbarth, G.S.; Michels, A.W. Type 1 diabetes. Lancet 2014, 383, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, R.H.; Xiao, S.D.; Megraud, F.; Leon-Barua, R.; Bazzoli, F.; van der Merwe, S.; Vaz Coelho, L.G.; Fock, M.; Fedail, S.; Cohen, H.; et al. Helicobacter pylori in developing countries. World Gastroenterology Organisation Global Guideline. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2011, 20, 299–304. [Google Scholar]
- Eusebi, L.H.; Zagari, R.M.; Bazzoli, F. Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter 2014, 19 (Suppl. 1), 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoder, G.; Muhammad, J.S.; Mahmoud, I.; Soliman, S.S.M.; Burucoa, C. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori and Its Associated Factors among Healthy Asymptomatic Residents in the United Arab Emirates. Pathogens 2019, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, F.; Rayner-Hartley, E.; Byrne, M.F. Extraintestinal manifestations of Helicobacter pylori: A concise review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 11950–11961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J.; Zavos, C.; Deretzi, G. The association between Helicobacter pylori infection and insulin resistance: A systematic review. Helicobacter 2011, 16, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.-W.; Fan, H.-C. Guillain–Barré syndrome associated with Helicobacter pylori infection in a male adolescent: A case report and literature review. Tungs Med. J. 2022, 16, 77–79. [Google Scholar]
- Vaira, D.; Gatta, L.; Ricci, C.; D’Anna, L.; Miglioli, M. Helicobacter pylori: Diseases, tests and treatment. Dig. Liver Dis. 2001, 33, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.C.; Wang, S.S.; Hsieh, Y.T.; Kuo, F.C.; Soon, M.S.; Wu, D.C. Helicobacter pylori infection associated with high HbA1c and type 2 diabetes. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 43, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.S.; Choi, Y.; Kim, N.; Lim, S.H.; Noh, G.; Kim, K.W.; Park, J.; Jo, H.; Yoon, H.; Shin, C.M.; et al. Long-term effect of the eradication of Helicobacter pylori on the hemoglobin A1c in type 2 diabetes or prediabetes patients. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2022, 37, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xing, Y.; Zhao, L.; Ma, H. The Association between Helicobacter pylori Infection and Glycated Hemoglobin A in Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis. J. Diabetes Res. 2019, 2019, 3705264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maluf, S.; Salgado, J.V.; Cysne, D.N.; Camelo, D.M.F.; Nascimento, J.R.; Maluf, B.V.T.; Silva, L.D.M.; Belfort, M.R.C.; Silva, L.A.; Guerra, R.N.M.; et al. Increased Glycated Hemoglobin Levels in Patients With Helicobacter pylori Infection Are Associated With the Grading of Chronic Gastritis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Luis, D.A.; de la Calle, H.; Roy, G.; de Argila, C.M.; Valdezate, S.; Canton, R.; Boixeda, D. Helicobacter pylori infection and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 1998, 39, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Song, L.; Hu, L.; Hu, M.; Lei, X.; Huang, Y.; Lv, Y. Helicobacter pylori infection is associated with diabetes among Chinese adults. J. Diabetes Investig. 2020, 11, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, N.S.; Nazli, R.; Zafar, H.; Fatima, S. Effects of lipid based Multiple Micronutrients Supplement on the birth outcome of underweight pre-eclamptic women: A randomized clinical trial. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 38, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gale, E.A. Type 1 diabetes in the young: The harvest of sorrow goes on. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 1435–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borenstein, M.; Higgins, J.P. Meta-analysis and subgroups. Prev. Sci. 2013, 14, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ Clin. Res. Ed. 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pocecco, M.; Buratti, E.; Tommasini, A.; Torre, G.; Not, T. High risk of Helicobacter pylori infection associated with cow’s milk antibodies in young diabetics. Acta Paediatr. 1997, 86, 700–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salardi, S.; Cacciari, E.; Menegatti, M.; Landi, F.; Mazzanti, L.; Stella, F.A.; Pirazzoli, P.; Vaira, D. Helicobacter pylori and type 1 diabetes mellitus in children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1999, 28, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, D.; Kendirci, M.; Kurtoglu, S.; Kula, M. Helicobacter pylori infection in children with insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 13, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candelli, M.; Rigante, D.; Marietti, G.; Nista, E.C.; Crea, F.; Bartolozzi, F.; Schiavino, A.; Pignataro, G.; Silveri, N.G.; Gasbarrini, G.; et al. Helicobacter pylori, gastrointestinal symptoms, and metabolic control in young type 1 diabetes mellitus patients. Pediatrics 2003, 111, 800–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, I.; Anaya, J.M.; Fraser, A.; Barzilai, O.; Ram, M.; Abad, V.; Arango, A.; García, J.; Shoenfeld, Y. Anti-infectious antibodies and autoimmune-associated autoantibodies in patients with type I diabetes mellitus and their close family members. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1173, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral, V.L.; Patrício, F.R.; Gabbay, M.A.; Dib, S.A.; Miszputen, S.J. Intraepithelial lymphocytes in duodenum from Brazilian adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Influence of Helicobacter pylori. Pediatr. Diabetes 2009, 10, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Eshmawy, M.M.; El-Hawary, A.K.; Abdel Gawad, S.S.; El-Baiomy, A.A. Helicobacter pylori infection might be responsible for the interconnection between type 1 diabetes and autoimmune thyroiditis. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2011, 3, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zekry, O.A.; Abd Elwahid, H.A. The association between Helicobacter pylori infection, type 1 diabetes mellitus, and autoimmune thyroiditis. J. Egypt. Public Health Assoc. 2013, 88, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chobot, A.; Bak-Drabik, K.; Skała-Zamorowska, E.; Krzywicka, A.; Kwiecień, J.; Polańska, J. Helicobacter pylori infection in type 1 diabetes children and adolescents using 13C urea breath test. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2014, 63, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, S.M.; Mubarak, S.M.; Omer, I.M.; Abdullah, M.A. Helicobacter pylori infection and the onset of type 1 diabetes mellitus in Sudanese children. Sudan. J. Paediatr. 2016, 16, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Bazmamoun, H.; Rafeey, M.; Nikpouri, M.; Ghergherehchi, R. Helicobacter Pylori Infection in Children with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Case-Control Study. J. Res. Health Sci. 2016, 16, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Esmaeili Dooki, M.R.; Alijanpour Aghamaleki, M.; Noushiravani, N.; Hosseini, S.R.; Moslemi, L.; Hajiahmadi, M.; Pournasrollah, M. Helicobacter pylori infection and type 1 diabetes mellitus in children. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2020, 19, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toporowska-Kowalska, E.; Wasowska-Królikowska, K.; Szadkowska, A.; Bodalski, J. Helicobacter pylori infection and its metabolic consequences in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Med. Wieku Rozw. 2007, 11, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.N.; Yu, W.L.; Zhu, H.T.; Ding, J.X.; Yu, C.H.; Li, Y.M. Is Helicobacter pylori infection associated with glycemic control in diabetics? World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 5407–5416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, J.; Lv, Z. Association of Helicobacter pylori infection with diabetes mellitus and diabetic nephropathy: A meta-analysis of 39 studies involving more than 20,000 participants. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 45, 930–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansori, K.; Moradi, Y.; Naderpour, S.; Rashti, R.; Moghaddam, A.B.; Saed, L.; Mohammadi, H. Helicobacter pylori infection as a risk factor for diabetes: A meta-analysis of case-control studies. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020, 20, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdichizzi, G.; Bottari, M.; Pallio, S.; Fera, M.; Carbone, M.; Barresi, G. Gastric infection by Helicobacter pylori and antral gastritis in hyperglycemic obese and in diabetic subjects. New Microbiol. 1996, 19, 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree, J. Role of cytokines in pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori-induced mucosal damage. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1998, 43, 46S–55S. [Google Scholar]
- Senturk, O.; Canturk, Z.; Cetinarslan, B.; Ercin, C.; Hulagu, S.; Canturk, N.Z. Prevalence and comparisons of five different diagnostic methods for Helicobacter pylori in diabetic patients. Endocr. Res. 2001, 27, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickup, J.C.; Day, C.; Bailey, C.J.; Samuel, A.; Chusney, G.D.; Garland, H.O.; Hamilton, K.; Balment, R.J. Plasma sialic acid in animal models of diabetes mellitus: Evidence for modulation of sialic acid concentrations by insulin deficiency. Life Sci. 1995, 57, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkonen, K.H.; Ringner, M.; Ljungh, A.; Wadström, T. High-affinity binding of laminin by Helicobacter pylori: Evidence for a lectin-like interaction. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 1993, 7, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, A.D.; Manson, J.E.; Rifai, N.; Buring, J.E.; Ridker, P.M. C-reactive protein, interleukin 6, and risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus. JAMA 2001, 286, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bener, A.; Micallef, R.; Afifi, M.; Derbala, M.; Al-Mulla, H.M.; Usmani, M.A. Association between type 2 diabetes mellitus and Helicobacter pylori infection. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 18, 225–229. [Google Scholar]
- Manco, M.; Putignani, L.; Bottazzo, G.F. Gut microbiota, lipopolysaccharides, and innate immunity in the pathogenesis of obesity and cardiovascular risk. Endocr. Rev. 2010, 31, 817–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, S.; Ma, Y.; Jin, C.; Lv, J.; Tong, M.; Wang, B.; Li, L.; Ning, Y. Association between Helicobacter pylori Infection and Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study in China. J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 2020, 7201379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, M.; Lin, Y.; Kikuchi, S. Helicobacter pylori Infection in Children and Adolescents. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1149, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Author | Year | Nation | Study Design | Sample Size | Gender (Male/Female) | Age | Control Group | Measurement of Association Odds Ratio (95% C.I.) | Type of Diabetes (Mean of HbA1c) (Duration) | H. pylori Test Method | Control Var. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M Pocecco, et al. [23] | 1997 | Italy | Case-Control Study | 379 (Control: 310; Case: 69) | 213/166 | 16 | Admitted for minor extra-abdominal surgery with no history of abdominal pain | 6.08 (2.94, 12.58) | DM (-) (-) | ELISA | Age, sex, education and economic status |
| S Salardi, et al. [24] | 1999 | Italy | Case-Control Study | 339 (Control: 236; Case: 103) | N/A | 12 | Patients attending the hospital for minor endocrine disorders | 1.79 ( 0.93, 3.44) | T1DM (-) (4.96 ± 3.22 years) | RIBASIA | Age |
| Arslan D., et al. [25] | 2000 | Turkey | Case-Control Study | 130 (Control: 42; Case: 88) | N/A | 12 | Healthy children | 2.80 (1.29 to 6.10) | T1DM (11.08 ± 3.17) (3.85 Years) | ELISA | - |
| Marcello Candelli, et al. [26] | 2003 | Italy | Case-Control Study | 268 (Control: 147; Case: 121) | 145/123 | 14.96 | Healthy participants | 0.98 (0.58, 1.66) | T1DM (8.2 ± 1.4 ) (79.7 ± 55.5 months) | C-UBT | Age, sex, and social class |
| Krause I, et al. [27] | 2009 | Colombia | Case-Control Study | 197 (Control: 140; Case: 57) | N/A | 16 | Healthy subjects | 3.35 (1.72, 6.53) | T1DM (-) (8.8 ± 8.7 years) | ELISA | - |
| Cabral VL, et al. [28] | 2009 | Brazil | Case-Control Study | 45 (Control: 30; Case: 15) | N/A | 17.6 | Adolescents with the histological findings of gastric and duodenal biopsies with normal mucosal architecture | 0.38 (0.10, 1.39) | T1DM (-) (8 ± 3.6 years) | Rapid Urease Test | - |
| El-Eshmawy M.M., et al. [29] | 2011 | Egypt | Case-Control Study | 242 (Control: 80; Case: 162) | 108/134 | 19.49 | Healthy subjects | 3.58 (2.01, 6.39) | T1DM (8.2 ± 1.75) (7.29 ± 7.9 years) | ELISA | Age, sex and socioeconomic status |
| Zekry O.A., et al. [30] | 2013 | Egypt | Case-Control Study | 120 (Control: 60; Case: 60) | N/A | 12.53 | Healthy children who were selected from among relatives | 2.4 (1.25,4.58) | T1DM (-) (-) | ELISA | Age, sex and socioeconomic |
| Agata Chobot, et al. [31] | 2014 | Poland | Case-Control Study | 447 (Control: 298; Case: 149) | 201/246 | 13.4 | Healthy children and adolescents | 0.65 (0.36, 1.18) | T1DM (7.69 ± 1.63 ) (4.6 ± 3.5 years) | C-UBT | Age and sex |
| Samah M Osman, et al. [32] | 2016 | Sudan | Case-Control Study | 180 (Control: 90; Case: 90) | 96/84 | 1-18 | Healthy children | 0.95 (0.51, 1.76) | T1DM (-) (duration < 6 month) | ELISA | Age and sex |
| Hassan Bazmamoun, et al. [33] | 2016 | Iran | Case-Control Study | 160 (Control: 80; Case: 80) | 63/97 | 9.37 | Non-Diabetic children from the same clinic | 2.25 (1.20 to 4.24) | T1DM (-) (2.14 ± 0.43) | EIA Test | Age, sex and socioeconomic status |
| Esmaeili Dooki MR, et al. [34] | 2020 | Iran | Case-Control Study | 168 (Control: 105 ; Case: 63) | 81/87 | 10.44 | Children without Diabetes Mellitus | 1.18 (0.58, 2.42) | T1DM (-) (at least 6 months) | Stool Test | Age and gender |
| Author | Year | Nation | Study Design | Sample Size | Gender (Male/Female) | Diabetic-Age (Year) | Diabetic-HbA1c (%) | Diabetic-Duration (Year) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HP+ | HP− | HP+ | HP− | HP+ | HP− | ||||||
| M Pocecco, et al. [23] | 1997 | Italy | Case-Control Study | 69 | 42/27 | 16 | 11 | 7.6 | 7.1 | 3 | 2 |
| S Salardi, et al. [24] | 1999 | Italy | Case-Control Study | 103 | N/A | 13.2 ± 3.4 | 11.2 ± 3.4 | N/A | N/A | 6 ± 3.4 | 4.3 ± 3.2 |
| Arslan D., et al. [25] | 2000 | Turkey | Case-Control Study | 88 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Marcello Candelli, et al. [26] | 2003 | Italy | Case-Control Study | 121 | 65/56 | 16 ± 5.6 | 14.3 ± 5.5 | 8.05 ± 4.52 | 7.9 ± 10 | 8.05 ± 4.52 | 5.35 ± 4.09 |
| Krause I, et al. [27] | 2009 | Colombia | Case-Control Study | 57 | 24/33 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Cabral VL, et al. [28] | 2009 | Brazil | Case-Control Study | 15 | 6/9 | 18 | 17 | N/A | N/A | 7 | 10 |
| El-Eshmawy M.M., et al. [29] | 2011 | Egypt | Case-Control Study | 162 | 72/90 | 20.1 ± 4.6 | 19.8 ± 4.34 | 8.3 ± 1.58 | 6.8 ± 2.3 | 8.9 ± 8.6 | 4.22 ± 2.35 |
| Zekry O.A., et al. [30] | 2013 | Egypt | Case-Control Study | 60 | N/A | 12.0 ± 2.4 | 12.89 ±2.29 | 7.75 ± 1.67 | 5.72 ±1.2 | 9.25 ± 2.73 | 6.11 ± 1.78 |
| Agata Chobot, et al. [31] | 2014 | Poland | Case-Control Study | 149 | 67/82 | 13.3 ± 3.3 | 13.9 ±3.6 | 7.82 ± 1.42 | 7.60 ± 1.66 | 5.3 ± 3.9 | 4.4 ± 3.4 |
| Samah M Osman, et al. [32] | 2016 | Sudan | Case-Control Study | 90 | 50/40 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Hassan Bazmamoun, et al. [33] | 2016 | Iran | Case-Control Study | 80 | 32/48 | 7.7 ± 0.86 | 7.58 ± 0.65 | 8 ± 0.65 | 7.9 ± 0.40 | 2.72 ± 0.55 | 1.26 ± 0.13 |
| Esmaeili Dooki MR, et al. [34] | 2020 | Iran | Case-Control Study | 63 | 34/29 | 8.84 ± 2.03 | 7.45± 2.9 | 8.08 ± 1.51 | 7.9 ± 0.40 | 2.74 ± 1.62 | 3.16 ± 2.57 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chua, W.-K.; Hong, Y.-K.; Hu, S.-W.; Fan, H.-C.; Ting, W.-H. A Significant Association between Type 1 Diabetes and Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Meta-Analysis Study. Medicina 2024, 60, 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60010119
Chua W-K, Hong Y-K, Hu S-W, Fan H-C, Ting W-H. A Significant Association between Type 1 Diabetes and Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Meta-Analysis Study. Medicina. 2024; 60(1):119. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60010119
Chicago/Turabian StyleChua, Wei-Kian, Yi-Kai Hong, Shu-Wei Hu, Hueng-Chuen Fan, and Wei-Hsin Ting. 2024. "A Significant Association between Type 1 Diabetes and Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Meta-Analysis Study" Medicina 60, no. 1: 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60010119
APA StyleChua, W.-K., Hong, Y.-K., Hu, S.-W., Fan, H.-C., & Ting, W.-H. (2024). A Significant Association between Type 1 Diabetes and Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Meta-Analysis Study. Medicina, 60(1), 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60010119









