Spine Metastasis Is Associated with the Development of Brain Metastasis in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Identification of Brain or Bone Metastasis and Spine Involvement
2.3. Statistical Analysis
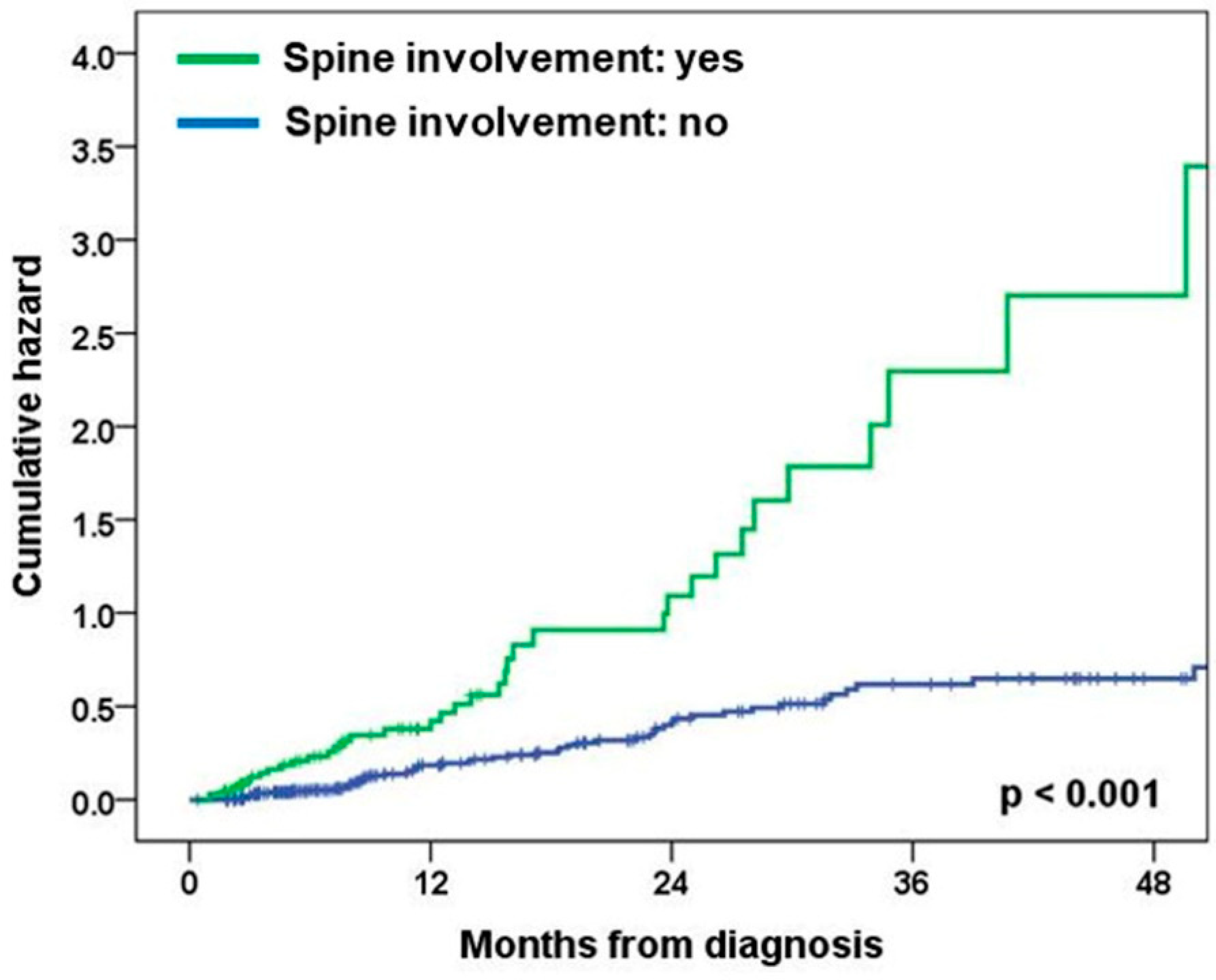
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics by BM at Diagnosis or Subsequent BM
3.2. Association of Spine Metastasis with BM at Diagnosis or Subsequent BM
3.3. Anatomic Proximity of BM Lesions to CSF Space in Patients with Spine Metastasis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; Sloan, A.E.; Davis, F.G.; Vigneau, F.D.; Lai, P.; Sawaya, R.E. Incidence proportions of brain metastases in patients diagnosed (1973 to 2001) in the Metropolitan Detroit Cancer Surveillance System. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 2865–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujoomdar, A.; Austin, J.H.; Malhotra, R.; Powell, C.A.; Pearson, G.D.; Shiau, M.C.; Raftopoulos, H. Clinical predictors of metastatic disease to the brain from non–small cell lung carcinoma: Primary tumor size, cell type, and lymph node metastases. Radiology 2007, 242, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, M.P.; Rodrigus, P.; Terhaard, C.; Rao, A.; Suh, J.; Roa, W.; Souhami, L.; Bezjak, A.; Leibenhaut, M.; Komaki, R. Survival and neurologic outcomes in a randomized trial of motexafin gadolinium and whole-brain radiation therapy in brain metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 2529–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popper, H.H. Progression and metastasis of lung cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2016, 35, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patchell, R.A. The management of brain metastases. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2003, 29, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhary, S.; Chamberlain, M. Leptomeningeal metastases: Current concepts and management guidelines. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2005, 3, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boire, A.; Zou, Y.; Shieh, J.; Macalinao, D.G.; Pentsova, E.; Massagué, J. Complement component 3 adapts the cerebrospinal fluid for leptomeningeal metastasis. Cell 2017, 168, 1101–1113.e1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, T.; Mason, J.; Chen, A.; Kuhn, P.; Woodward, W.A.; Tripathy, D.; Newton, P.K.; Ueno, N.T. Prediction of bone metastasis in inflammatory breast cancer using a markov chain model. Oncologist 2019, 24, 1322–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freret, M.E.; Wijetunga, N.A.; Shamseddine, A.A.; Higginson, D.S.; Schmitt, A.M.; Yamada, Y.; Lis, E.; Boire, A.; Yang, J.T.; Xu, A.J. Early Detection of Leptomeningeal Metastases Among Patients Undergoing Spinal Stereotactic Radiosurgery. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 8, 101154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubendorf, L.; Schöpfer, A.; Wagner, U.; Sauter, G.; Moch, H.; Willi, N.; Gasser, T.C.; Mihatsch, M.J. Metastatic patterns of prostate cancer: An autopsy study of 1,589 patients. Hum. Pathol. 2000, 31, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geldof, A.A. Models for cancer skeletal metastasis: A reappraisal of Batson’s plexus. Anticancer Res. 1997, 17, 1535–1539. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goldstraw, P.; Chansky, K.; Crowley, J.; Rami-Porta, R.; Asamura, H.; Eberhardt, W.E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Groome, P.; Mitchell, A.; Bolejack, V. The IASLC lung cancer staging project: Proposals for revision of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (eighth) edition of the TNM classification for lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.-S.; Ryu, H.J.; Lee, S.-N.; Memon, A.; Lee, S.-K.; Nam, H.-S.; Kim, H.-J.; Lee, K.-H.; Cho, J.-H.; Hwang, S.-S. Prognostic impact of minimal pleural effusion in non–small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Ouyang, T.; Krishnamoorthy, T.; Aregawi, D.G.; Zacharia, B.; Glantz, M.J. Role of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the pathogenesis and treatment of patients with brain metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, e14006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Lin, Z.; Hong, Y.; Fu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, T.; Zheng, Y.; Tian, J.; Liu, C.; Pu, W. Brain parenchymal and leptomeningeal metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 22372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, P.G.; Reiner, A.S.; Szenberg, O.R.; Clarke, J.L.; Panageas, K.S.; Perez, H.R.; Kris, M.G.; Chan, T.A.; DeAngelis, L.M.; Omuro, A.M. Leptomeningeal metastasis from non-small cell lung cancer: Survival and the impact of whole brain radiotherapy. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 382–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Yang, G.; He, H.; Yuan, T.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Shi, W.; Gao, P.; Dong, L.; Zhao, G. Leptomeningeal metastasis from solid tumors: Clinical features and its diagnostic implication. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, C.S.; Mustafa, M.A.; Richardson, G.E.; Alam, A.M.; Lee, K.S.; Hughes, D.M.; Escriu, C.; Zakaria, R. Genomic alterations and the incidence of brain metastases in advanced and metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023, 18, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Perez-Soler, R. Leptomeningeal metastases in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, e43–e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, P.; Yates, J.W.; Yang, Z.; Kim, D.-W.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Cantarini, M.; Pickup, K.; Jordan, A.; Hickey, M.; Grist, M. Preclinical comparison of osimertinib with other EGFR-TKIs in EGFR-mutant NSCLC brain metastases models, and early evidence of clinical brain metastases activity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 5130–5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainor, J.F.; Sherman, C.A.; Willoughby, K.; Logan, J.; Kennedy, E.; Brastianos, P.K.; Chi, A.S.; Shaw, A.T. Alectinib salvages CNS relapses in ALK-positive lung cancer patients previously treated with crizotinib and ceritinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gainor, J.F.; Chi, A.S.; Logan, J.; Hu, R.; Oh, K.S.; Brastianos, P.K.; Shih, H.A.; Shaw, A.T. Alectinib dose escalation reinduces central nervous system responses in patients with anaplastic lymphoma kinase–positive non–small cell lung cancer relapsing on standard dose alectinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Kane, G.M.; Leighl, N.B. Are immune checkpoint blockade monoclonal antibodies active against CNS metastases from NSCLC?—Current evidence and future perspectives. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, T.W.; Richardson, P.F.; Bailey, S.; Brooun, A.; Burke, B.J.; Collins, M.R.; Cui, J.J.; Deal, J.G.; Deng, Y.-L.; Dinh, D. Discovery of (10 R)-7-Amino-12-fluoro-2, 10, 16-trimethyl-15-oxo-10, 15, 16, 17-tetrahydro-2H-8, 4-(metheno) pyrazolo [4, 3-h][2, 5, 11]-benzoxadiazacyclotetradecine-3-carbonitrile (PF-06463922), a macrocyclic inhibitor of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) and c-ros oncogene 1 (ROS1) with preclinical brain exposure and broad-spectrum potency against ALK-resistant mutations. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 4720–4744. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, S.; Bexelius, C.; Munk, V.; Leighl, N. The impact of brain metastasis on quality of life, resource utilization and survival in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2016, 45, 139–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, K.; Buchanan, I.; Martirosian, V.; Neman, J. Clinical perspectives in brain metastasis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2019, 10, a037051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Hu, L.; Bok, S.; Yallowitz, A.R.; Cung, M.; McCormick, J.; Zheng, L.J.; Debnath, S.; Niu, Y.; Tan, A.Y. A vertebral skeletal stem cell lineage driving metastasis. Nature 2023, 621, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Brain Metastasis | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes (n = 238) | No (n = 664) | p Value | |
| Age, median | 0.108 | ||
| >69 | 106 (44.5) | 336 (50.6) | |
| ≤69 | 132 (55.5) | 328 (49.4) | |
| Gender | 0.015 | ||
| Male | 137 (57.6) | 441 (66.4) | |
| Female | 101 (42.4) | 223 (33.6) | |
| Smoking history | <0.001 | ||
| Ever | 138 (58.2) | 465 (71.1) | |
| Never | 99 (41.8) | 189 (28.9) | |
| ECOG performance status | 0.057 | ||
| 0–1 | 132 (56.2) | 416 (63.2) | |
| ≥2 | 103 (43.8) | 242 (36.8) | |
| Histology | 0.003 | ||
| SQC | 34 (14.3) | 154 (23.2) | |
| ADC | 188 (79.0) | 447 (67.3) | |
| Others | 16 (6.7) | 63 (9.5) | |
| EGFR mutation | 0.013 | ||
| Negative | 147 (61.8) | 468 (70.5) | |
| Positive | 91 (38.2) | 196 (29.5) | |
| T category | 0.403 | ||
| Tx | 2 (0.8) | 16 (2.4) | |
| T1 | 9 (3.8) | 38 (5.7) | |
| T2 | 38 (16.0) | 113 (17.0) | |
| T3 | 53 (22.3) | 139 (20.9) | |
| T4 | 136 (57.1) | 358 (53.9) | |
| N category | 0.145 | ||
| N0 | 47 (19.7) | 180 (27.1) | |
| N1 | 21 (8.8) | 60 (9.0) | |
| N2 | 54 (22.7) | 137 (20.7) | |
| N3 | 116 (48.7) | 286 (43.1) | |
| M category | <0.001 | ||
| Others | 98 (41.2) | 411 (61.9) | |
| Bone | 140 (58.8) | 253 (38.1) | |
| Non-spine | 28 (20.0) | 85 (33.6) | |
| Spine | 112 (80.0) | 168 (66.4) | |
| Variables | Subsequent Brain Metastasis | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes (n = 82) | No (n = 202) | p Value | |
| Age, median | 0.034 | ||
| >69 | 25 (30.5) | 89 (44.1) | |
| ≤69 | 57 (69.5) | 113 (55.9) | |
| Gender | 0.003 | ||
| Male | 41 (50.0) | 139 (68.8) | |
| Female | 41 (50.0) | 63 (31.2) | |
| Smoking history | 0.008 | ||
| Ever | 46 (56.1) | 146 (72.3) | |
| Never | 36 (43.9) | 56 (27.7) | |
| ECOG performance status | 0.863 | ||
| 0–1 | 57 (71.2) | 146 (72.3) | |
| ≥2 | 23 (28.8) | 56 (27.7) | |
| Histology | 0.001 | ||
| SQC | 6 (7.3) | 49 (24.3) | |
| ADC | 72 (87.8) | 134 (66.3) | |
| Others | 4 (4.9) | 19 (9.4) | |
| EGFR mutation | <0.001 | ||
| Negative | 38 (46.3) | 147 (72.8) | |
| Positive | 44 (53.7) | 55 (27.2) | |
| T category | 0.879 | ||
| Tx | 3 (3.7) | 4 (2.0) | |
| T1 | 6 (7.3) | 14 (6.9) | |
| T2 | 13 (15.9) | 40 (19.8) | |
| T3 | 17 (20.7) | 41 (20.3) | |
| T4 | 43 (52.4) | 103 (51.0) | |
| N category | 0.109 | ||
| N0 | 21 (25.6) | 72 (35.6) | |
| N1 | 5 (6.1) | 23 (11.4) | |
| N2 | 17 (20.7) | 29 (14.4) | |
| N3 | 39 (47.6) | 78 (38.6) | |
| Bone metastasis | 0.001 | ||
| No | 42 (51.2) | 148 (73.3) | |
| Yes | 40 (48.8) | 54 (26.7) | |
| Non-spine | 14 (35.0) | 22 (40.7) | |
| Spine | 26 (65.0) | 32 (59.3) | |
| Variables | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p Value | OR (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Age, median | ||||
| >69 | reference | - | ||
| ≤69 | 1.28 (0.95–1.72) | 0.109 | ||
| Gender | ||||
| Male | reference | - | reference | - |
| Female | 1.46 (1.08–1.98) | 0.015 | 0.77 (0.44–1.36) | 0.371 |
| Smoking history | - | |||
| Ever | reference | reference | - | |
| Never | 1.77 (1.30–2.40) | <0.001 | 2.01 (1.12–3.60) | 0.020 |
| ECOG performance status | ||||
| 0–1 | reference | - | reference | - |
| ≥2 | 1.34 (0.99–1.82) | 0.057 | 1.26 (0.91–1.73) | 0.160 |
| Histology | ||||
| SQC | reference | - | reference | - |
| ADC | 1.91 (1.27–2.87) | 0.002 | 1.53 (0.97–2.42) | 0.067 |
| Others | 1.15 (0.59–2.23) | 0.679 | 1.11 (0.56–2.19) | 0.763 |
| EGFR mutation | ||||
| Negative | reference | - | reference | - |
| Positive | 1.48 (1.08–2.02) | 0.014 | 0.92 (0.63–1.33) | 0.643 |
| T category | ||||
| Tx–T1 | reference | - | reference | - |
| T2 | 1.65 (0.78–3.48) | 0.187 | 1.49 (0.69–3.24) | 0.310 |
| T3 | 1.87 (0.91–3.85) | 0.089 | 1.61 (0.75–3.42) | 0.219 |
| T4 | 1.87 (0.95–3.67) | 0.072 | 1.49 (0.74–3.04) | 0.268 |
| N category | ||||
| N0 | reference | - | reference | - |
| N1 | 1.34 (0.74–2.42) | 0.332 | 1.58 (0.85–2.94) | 0.150 |
| N2 | 1.51 (0.96–2.37) | 0.073 | 1.78 (1.10–2.86) | 0.019 |
| N3 | 1.55 (1.06–2.29) | 0.026 | 1.42 (0.93–2.15) | 0.105 |
| Bone metastasis | ||||
| Non-spine | reference | - | reference | - |
| Spine | 2.62 (1.93–3.57) | <0.001 | 2.42 (1.74–3.37) | <0.001 |
| Variables | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p Value | HR (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Age, median | ||||
| >69 | reference | - | ||
| ≤69 | 1.15 (0.72–1.84) | 0.566 | ||
| Gender | ||||
| Male | reference | - | ||
| Female | 1.30 (0.84–2.01) | 0.238 | ||
| Smoking history | ||||
| Ever | reference | - | ||
| Never | 1.19 (0.77–1.84) | 0.440 | ||
| ECOG performance status | ||||
| 0–1 | reference | - | ||
| ≥2 | 1.32 (0.81–2.16) | 0.260 | ||
| Histology | ||||
| SQC | reference | - | reference | - |
| ADC | 2.02 (0.88–4.67) | 0.099 | 2.07 (0.86–5.01) | 0.106 |
| Others | 2.29 (0.65–8.14) | 0.200 | 2.36 (0.64–8.72) | 0.197 |
| EGFR mutation | ||||
| Negative | reference | - | ||
| Positive | 1.34 (0.87–2.07) | 0.188 | ||
| T category | ||||
| Tx–T1 | reference | - | ||
| T2 | 0.67 (0.28–1.57) | 0.352 | ||
| T3 | 1.02 (0.45–2.29) | 0.966 | ||
| T4 | 0.92 (0.45–1.90) | 0.830 | ||
| N category | ||||
| N0 | reference | - | reference | - |
| N1 | 1.46 (0.55–3.89) | 0.451 | 1.83 (0.66–5.07) | 0.243 |
| N2 | 3.03 (1.58–5.78) | 0.001 | 2.99 (1.54–5.82) | 0.001 |
| N3 | 2.47 (1.45–4.21) | 0.001 | 2.32 (1.35–3.98) | 0.002 |
| Bone metastasis | ||||
| Non-spine | reference | - | reference | - |
| Spine | 2.46 (1.53–3.94) | <0.001 | 1.94 (1.19–3.18) | 0.008 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cha, H.-K.; Ryu, W.-K.; Lee, H.-Y.; Kim, H.-J.; Ryu, J.-S.; Lim, J.-H. Spine Metastasis Is Associated with the Development of Brain Metastasis in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Medicina 2024, 60, 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60010152
Cha H-K, Ryu W-K, Lee H-Y, Kim H-J, Ryu J-S, Lim J-H. Spine Metastasis Is Associated with the Development of Brain Metastasis in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Medicina. 2024; 60(1):152. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60010152
Chicago/Turabian StyleCha, Hyung-Keun, Woo-Kyung Ryu, Ha-Young Lee, Hyun-Jung Kim, Jeong-Seon Ryu, and Jun-Hyeok Lim. 2024. "Spine Metastasis Is Associated with the Development of Brain Metastasis in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients" Medicina 60, no. 1: 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60010152
APA StyleCha, H.-K., Ryu, W.-K., Lee, H.-Y., Kim, H.-J., Ryu, J.-S., & Lim, J.-H. (2024). Spine Metastasis Is Associated with the Development of Brain Metastasis in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Medicina, 60(1), 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60010152







