Comparison of Inter-Method Agreement and Reliability for Automatic Brain Volumetry Using Three Different Clinically Available Software Packages
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Image Acquisition
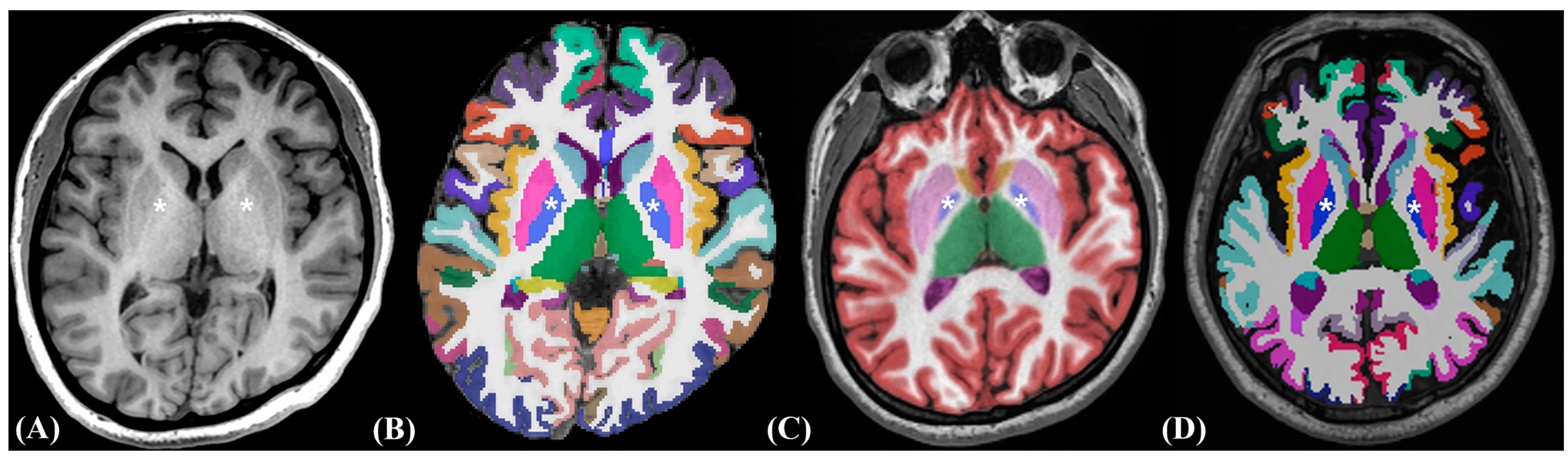
2.3. Image Post-Processing Volumetric Procedures
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of Total ICV
3.2. Comparison of the Measured Volumes of Segmented Brain Regions
3.3. Results of Subgroup Analyses by Presence or Absence of AD
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giorgio, A.; De Stefano, N. Clinical use of brain volumetry. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 37, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewer, J.B.; Magda, S.; Airriess, C.; Smith, M.E. Fully-Automated Quantification of Regional Brain Volumes for Improved Detection of Focal Atrophy in Alzheimer Disease. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 30, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Lee, S.A.; Jo, S.W.; Chang, S.-K.; Lim, Y.; Yoo, Y.S.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, S.H.; Sohn, C.-H. Agreement and Reliability between Clinically Available Software Programs in Measuring Volumes and Normative Percentiles of Segmented Brain Regions. Korean J. Radiol. 2022, 23, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, M.W.; Hannemann, N.P.; York, G.E.; Ritter, J.L.; Kini, J.A.; Lewis, J.D.; Sherman, P.M.; Velez, C.S.; Drennon, A.M.; Bolzenius, J.D.; et al. Comparing two processing pipelines to measure subcortical and cortical volumes in patients with and without mild traumatic brain injury. J. Neuroimaging 2017, 27, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochs, A.L.; Ross, D.E.; Zannoni, M.D.; Abildskov, T.J.; Bigler, E.D.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Comparison of automated brain volume measures obtained with NeuroQuant® and FreeSurfer. J. Neuroimaging 2015, 25, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yim, Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Oh, S.W.; Chung, M.S.; Park, J.E.; Moon, Y.; Jeon, H.J.; Moon, W.-J. Comparison of automated brain volume measures by NeuroQuant vs. Freesurfer in patients with mild cognitive impairment: Effect of slice thickness. Yonsei Med. J. 2021, 62, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, Y.J.; Baek, H.J.; Skare, S.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, J.; Yoon, S. Automated brain volumetry in patients with memory impairment: Comparison of conventional and ultrafast 3d t1-weighted MRI sequences using two software packages. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2022, 218, 1062–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, D.E.; Seabaugh, J.; Seabaugh, J.M.; Barcelona, J.; Seabaugh, D.; Wright, K.; Norwind, L.; King, Z.; Graham, T.J.; Baker, J.; et al. Updated review of the evidence supporting the medical and legal use of NeuroQuant® and NeuroGage® in patients with traumatic brain injury. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 715807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischl, B. FreeSurfer. Neuroimage 2012, 62, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherfey, J.S.; Soplata, A.E.; Ardid, S.; Roberts, E.A.; Stanley, D.A.; Pittman-Polletta, B.R.; Kopell, N.J. DynaSim: A MATLAB toolbox for neural modeling and simulation. Front. Neuroinform. 2018, 12, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpazza, C.; Ha, M.; Baecker, L.; Garcia-Dias, R.; Pinaya, W.; Vieira, S.; Mechelli, A. Translating research findings into clinical practice: A systematic and critical review of neuroimaging-based clinical tools for brain disorders. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Oh, S.W.; Chung, M.S.; Park, J.E.; Moon, Y.; Jeon, H.J.; Moon, W.-J. Clinically available software for automatic brain volumetry: Comparisons of volume measurements and validation of intermethod reliability. Korean J. Radiol. 2021, 22, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Park, J.-E.; Chung, M.-S.; Oh, S.-W.; Moon, W.-J. Expert opinions and recommendations for the clinical use of quantitative analysis software for MRI-based brain volumetry. J. Korean Radiol. Soc. 2021, 82, 1124–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, D.H.; Heo, H.; Song, S.; Shin, N.Y.; Nam, Y.; Yoo, S.W.; Kim, J.S.; Yoon, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Sung, Y.H.; et al. Automated assessment of the substantia nigra on susceptibility map-weighted imaging using deep convolutional neural networks for diagnosis of Idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2021, 85, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKhann, G.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Chertkow, H.; Hyman, B.T.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Kawas, C.H.; Klunk, W.E.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Manly, J.J.; Mayeux, R.; et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011, 7, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronald, C.P.; Glenn, E.S.; Stephen, C.W.; Robert, J.I.; Eric, G.T.; Emre, K. Mild cognitive impairment. Arch. Neurol. 1999, 56, 303. [Google Scholar]
- Renvall, V.; Witzel, T.; Wald, L.L.; Polimeni, J.R. Automatic cortical surface reconstruction of high-resolution T1 echo planar imaging data. Neuroimage 2016, 134, 338–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olejnik, S.; Algina, J. Measures of effect size for comparative studies: Applications, interpretations, and limitations. Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 2000, 25, 241–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Quantitative Methods in Psychology: A Power Primer. Psychol. Bull. 1992, 112, 155–159. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, D.E.; Ochs, A.L.; Tate, D.F.; Tokac, U.; Seabaugh, J.; Abildskov, T.J.; Bigler, E.D. High correlations between MRI brain volume measurements based on NeuroQuant® and FreeSurfer. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2018, 278, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klauschen, F.; Goldman, A.; Barra, V.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A.; Lundervold, A. Evaluation of Automated Brain MR Image Segmentation and Volumetry Methods; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.; Kim, H.; Moon, Y.; Moon, W.-J. Comparison of vendor-provided volumetry software and NeuroQuant using 3D T1-weighted images in subjects with cognitive impairment: How large is the inter-method discrepancy? Investig. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 24, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestor, S.M.; Gibson, E.; Gao, F.-Q.; Kiss, A.; Black, S.E.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. A direct morphometric comparison of five labeling protocols for multi-atlas driven automatic segmentation of the hippocampus in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage 2013, 66, 50–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischl, B.; Salat, D.H.; Busa, E.; Albert, M.; Dieterich, M.; Haselgrove, C.; van der Kouwe, A.; Killiany, R.; Kennedy, D.; Klaveness, S.; et al. Whole brain segmentation: Automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron 2002, 33, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, T.; Nakai, Y.; Aoki, S.; Oba, H.; Toyoda, K.; Kitajima, K.; Furui, S. Contribution of metals to brain MR signal intensity: Review articles. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2016, 34, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Oh, S.W.; Chung, M.S.; Park, J.E.; Moon, Y. Evaluation of reproducibility of brain volumetry between commercial software, inbrain and established research purpose method, FreeSurfer. J. Clin. Neurol. 2021, 17, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R., Jr. Continuing Medical Education: Alzheimer Disease: New Concepts on Its Neurobiology and the Clinical Role Imaging Will Play. Radiology 2012, 263, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tae, W.S.; Kim, S.S.; Lee, K.U.; Nam, E.-C.; Kim, K.W. Validation of hippocampal volumes measured using a manual method and two automated methods (FreeSurfer and IBASPM) in chronic major depressive disorder. Neuroradiology 2008, 50, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morey, R.A.; Petty, C.M.; Xu, Y.; Hayes, J.P.; Wagner, H.R., II; Lewis, D.V.; LaBar, K.S.; Styner, M.; McCarthy, G. A comparison of automated segmentation and manual tracing for quantifying hippocampal and amygdala volumes. Neuroimage 2009, 45, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenette, J.P.; Stern, R.A.; Tripodis, Y.; Chua, A.S.; Schultz, V.; Sydnor, V.J.; Somes, N.; Karmacharya, S.; Lepage, C.; Wrobel, P.; et al. Automated versus manual segmentation of brain region volumes in former football players. Neuroimage Clin. 2018, 18, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Normal (n = 21) | MCI (n = 24) | AD (n = 33) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years a | 48.7 ± 18.1 (range: 21–78) | 75.7 ± 6.93 (range: 63–85) | 74.5 ± 7.81 (range: 58–89) |
| Sex | |||
| Female | 10 (47.6%) | 15 (62.5%) | 27 (81.8%) |
| Male | 11 (52.4%) | 9 (37.5%) | 6 (18.2%) |
| MMSE score a | 29.56 ± 1.42 | 27.83 ± 1.61 | 20.19 ± 4.36 |
| CDR a | 0.01 ± 0.07 | 0.52 ± 0.27 | 0.86 ± 0.41 |
| NQ | FS | HAD | p | NQ vs. FS | NQ vs. HAD | FS vs. HAD | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | ICC | d | p | ICC | d | p | ICC | d | |||||
| Total | 1427.37 ± 152.94 | 1414.41 ± 142.18 | 1381.46 ± 140.69 | <0.001 | 0.101 | 0.967 (0.948–0.979) | 0.088 | <0.001 | 0.926 (0.885–0.953) | 0.312 | <0.001 | 0.961 (0.939–0.975) | 0.233 |
| Non-AD | 1473.69 ± 158.79 | 1446.49 ± 144.85 | 1420.02 ± 139.01 | <0.001 | 0.007 | 0.965 (0.936–0.981) | 0.179 | 0.04 | 0.894 (0.808–0.942) | 0.360 | 0.040 | 0.937 (0.886–0.966) | 0.186 |
| AD | 1364.21 ± 120.35 | 1370.66 ± 127.97 | 1328.89 ± 126.94 | <0.001 | 1.000 | 0.971 (0.941–0.986) | 0.052 | <0.001 | 0.960 (0.919–0.980) | 0.286 | <0.001 | 0.992 (0.983–0.996) | 0.286 |
| Lt. Hemisphere | Rt. Hemisphere | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NQ | FS | HAD | NQ vs. FS * | NQ vs. HAD * | FS vs. HAD * | NQ | FS | HAD | NQ vs. FS * | NQ vs. HAD * | FS vs. HAD * | |
| Cortical GM | ||||||||||||
| Total | 230.15 ± 35.40 | 214.27 ± 24.32 | 188.19 ± 29.46 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 230.44 ± 35.13 | 213.13 ± 24.80 | 188.23 ± 28.59 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Non-AD | 245.44 ± 35.96 | 223.66 ± 24.34 | 202.75 ± 28.21 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 245.15 ± 36.00 | 223.38 ± 24.30 | 203.06 ± 26.61 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| AD | 209.30 ± 21.44 | 201.48 ± 17.77 | 168.32 ± 16.99 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 210.37 ± 21.62 | 199.15 ± 17.86 | 168.00 ± 16.18 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Cerebral WM | ||||||||||||
| Total | 210.82 ± 25.73 | 193.82 ± 25.73 | 203.10 ± 27.13 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 214.86 ± 25.70 | 192.46 ± 25.70 | 205.20 ± 28.14 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Non-AD | 216.22 ± 27.22 | 199.22 ± 27.22 | 210.94 ± 27.26 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 220.34 ± 27.61 | 197.94 ± 27.61 | 213.26 ± 28.53 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| AD | 203.47 ± 21.84 | 186.46 ± 21.84 | 192.42 ± 23.35 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 207.39 ± 21.03 | 184.99 ± 21.03 | 194.21 ± 23.88 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Hippocampus | ||||||||||||
| Total | 3.37 ± 0.80 | 3.60 ± 0.59 | 3.93 ± 0.44 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 3.52 ± 0.91 | 3.81 ± 0.65 | 4.08 ± 0.45 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Non-AD | 3.73 ± 0.80 | 3.83 ± 0.60 | 4.07 ± 0.38 | 0.378 | 0.005 | 0.002 | 3.93 ± 0.86 | 4.05 ± 0.57 | 4.15 ± 0.40 | |||
| AD | 2.87 ± 0.49 | 3.28 ± 0.41 | 3.75 ± 0.45 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 2.97 ± 0.66 | 3.47 ± 0.61 | 3.99 ± 0.50 | <0.001 | 0.021 | 0.259 |
| Amygdala | ||||||||||||
| Total | 1.48 ± 0.35 | 1.34 ± 0.29 | 1.51 ± 0.39 | <0.001 | 0.634 | <0.001 | 1.42 ± 0.30 | 1.52 ± 0.25 | 1.67 ± 0.34 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Non-AD | 1.58 ± 0.39 | 1.44 ± 0.26 | 1.59 ± 0.43 | <0.001 | 1.000 | <0.001 | 1.53 ± 0.33 | 1.63± 0.21 | 1.83 ± 0.29 | 0.024 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| AD | 1.34 ± 0.24 | 1.19 ± 0.27 | 1.40 ± 0.31 | <.001 | 0.136 | <0.001 | 1.26 ± 0.17 | 1.38 ± 0.21 | 1.46 ± 0.28 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Caudate | ||||||||||||
| Total | 3.17 ± 0.73 | 3.27 ± 0.51 | 3.41 ± 0.48 | 0.129 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 3.30 ± 0.71 | 3.23 ± 0.44 | 3.51 ± 0.49 | 0.910 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Non-AD | 2.99 ± 0.72 | 3.18 ± 0.52 | 3.26 ± 0.43 | 0.018 | 0.003 | 0.322 | 3.18 ± 0.71 | 3.19 ± 0.40 | 3.40 ± 0.46 | 1.000 | 0.008 | <0.001 |
| AD | 3.42 ± 0.68 | 3.39 ± 0.49 | 3.62 ± 0.48 | 1.000 | 0.019 | <0.001 | 3.46 ± 0.69 | 3.29 ± 0.48 | 3.66 ± 0.50 | 0.221 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Putamen | ||||||||||||
| Total | 5.62 ± 0.87 | 4.17 ± 0.72 | 4.00 ± 0.64 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 | 5.44 ± 0.91 | 4.21 ± 0.72 | 3.99 ± 0.67 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.0001 |
| Non-AD | 5.89 ± 0.89 | 4.41 ± 0.75 | 4.13 ± 0.66 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 4.47 ± 0.73 | 3.19 ± 0.40 | 4.14 ± 0.73 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.0001 |
| AD | 5.25 ± 0.69 | 3.83 ± 0.53 | 3.83 ± 0.59 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 1.000 | 5.01 ± 0.72 | 3.85 ± 0.53 | 3.78 ± 0.53 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.263 |
| Pallidum | ||||||||||||
| Total | 0.49 ± 0.16 | 1.92 ± 0.32 | 1.88 ± 0.32 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.512 | 0.46 ± 0.14 | 1.88 ± 0.30 | 1.85 ± 0.32 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 1.000 |
| Non-AD | 0.52 ± 0.18 | 1.87 ± 0.32 | 1.89 ± 0.32 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 1.000 | 0.50 ± 0.16 | 1.83 ± 0.24 | 1.90 ± 0.30 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.010 |
| AD | 0.45 ± 0.10 | 2.00 ± 0.30 | 1.87 ± 0.31 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.022 | 0.41 ± 0.89 | 1.94 ± 0.36 | 1.78 ± 0.33 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.068 |
| Thalamus | ||||||||||||
| Total | 7.44 ± 1.12 | 6.69 ± 0.94 | 6.38 ± 0.86 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 1.000 | 7.25 ± 1.01 | 6.13 ± 0.92 | 6.18 ± 0.85 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.159 |
| Non-AD | 7.81 ± 1.21 | 6.70 ± 1.04 | 6.68 ± 0.95 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 1.000 | 7.65 ± 1.09 | 6.50 ± 0.98 | 6.52 ± 0.90 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 1.000 |
| AD | 6.93 ± 0.72 | 5.97 ± 0.57 | 5.98 ± 0.50 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 1.000 | 6.71 ± 0.54 | 5.63 ± 0.54 | 5.72 ± 0.48 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 1.000 |
| Cerebellum | ||||||||||||
| Total | 60.91 ± 7.41 | 60.18 ± 6.88 | 56.02 ± 7.95 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 61.89 ± 7.67 | 60.57 ± 7.46 | 57.80 ± 7.77 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Non-AD | 63.78 ± 6.39 | 62.93 ± 5.91 | 59.42 ± 6.30 | 0.012 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 64.38 ± 6.97 | 63.20 ± 6.27 | 60.48 ± 6.48 | 0.004 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| AD | 56.99 ± 6.96 | 56.42 ± 6.38 | 51.39 ± 7.70 | 0.105 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 58.49 ± 7.35 | 56.98 ± 7.54 | 54.14 ± 7.98 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Lt. Hemisphere | Rt. Hemisphere | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NQ vs. FS | NQ vs. HAD | FS vs. HAD | NQ vs. FS | NQ vs. HAD | FS vs. HAD | |
| Cortical GM | ||||||
| Total | 0.945 (0.914–0.965) | 0.945 (0.914–0.965) | 0.945 (0.913–0.965) | 0.947 (0.916–0.966) | 0.944 (0.912–0.964) | 0.951 (0.923–0.969) |
| Non-AD | 0.939 (0.888–0.966) | 0.936 (0.884–0.965) | 0.954 (0.917–0.975) | 0.934 (0.880–0.964) | 0.932 (0.876–0.962) | 0.950 (0.910–0.973) |
| AD | 0.970 (0.939–0.985) | 0.876 (0.784–0.939) | 0.897 (0.791–0.949) | 0.990 (0.980–0.995) | 0.954 (0.909–0.977) | 0.974 (0.948–0.987) |
| Cerebral WM | ||||||
| Total | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.983 (0.973–0.989) | 0.983 (0.973–0.989) | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.978 (0.965–0.986) | 0.978 (0.965–0.986) |
| Non-AD | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.990 (0.982–0.995) | 0.990 (0.982–0.995) | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.988 (0.978–0.993) | 0.988 (0.978–0.993) |
| AD | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.972 (0.944–0.986) | 0.972 (0.944–0.986) | 0.996 (0.992–0.998) | 0.988 (0.976–0.994) | 0.986 (0.972–0.993) |
| Hippocampus | ||||||
| Total | 0.918 (0.871–0.948) | 0.724 (0.567–0.824) | 0.842 (0.753–0.899) | 0.917 (0.869–0.947) | 0.621 (0.406–0.759) | 0.807 (0.698–0.877) |
| Non-AD | 0.904 (0.826–0.947) | 0.600 (0.271–0.780) | 0.780 (0.599–0.879) | 0.886 (0.793–0.938) | 0.523 (0.132–0.738) | 0.784 (0.607–0.881) |
| AD | 0.914 (0.826–0.958) | 0.895 (0.787–0.948) | 0.892 (0.782–0.947) | 0.947 (0.892–0.974) | 0.835 (0.665–0.918) | 0.863 (0.723–0.932) |
| Amygdala | ||||||
| Total | 0.916 (0.869–0.947) | 0.897 (0.838–0.934) | 0.924 (0.881–0.952) | 0.892 (0.830–0.931) | 0.898 (0.840–0.935) | 0.936 (0.900–0.959) |
| Non-AD | 0.897 (0.812–0.943) | 0.888 (0.795–0.938) | 0.890 (0.800–0.940) | 0.844 (0.715–0.914) | 0.870 (0.762–0.928) | 0.923 (0.860–0.958) |
| AD | 0.909 (0.815–0.955) | 0.887 (0.772–0.944) | 0.967 (0.933–0.984) | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.998 (0.996–0.999) | 0.999 (0.998–0.999) |
| Caudate | ||||||
| Total | 0.876 (0.805–0.821) | 0.843 (0.753–0.900) | 0.899 (0.842–0.936) | 0.631 (0.420–0.764) | 0.850 (0.764–0.904) | 0.787 (0.666–0.864) |
| Non-AD | 0.856 (0.783–0.921) | 0.780 (0.600–0.879) | 0.883 (0.787–0.936) | 0.780 (0.600–0.879) | 0.835 (0.700–0.909) | 0.870 (0.764–0.929) |
| AD | 0.903 (0.804–0.952) | 0.880 (0.757–0.941) | 0.915 (0.828–0.958) | 0.999 (0.998–1.000) | 0.997 (0.995–0.999) | 0.998 (0.997–0.999) |
| Putamen | ||||||
| Total | 0.824 (0.724–0.888) | 0.840 (0.749–0.898) | 0.912 (0.862–0.944) | 0.853 (0.770–0.906) | 0.796 (0.680–0.870) | 0.947 (0.916–0.966) |
| Non-AD | 0.810 (0.655–0.896) | 0.821 (0.675–0.902) | 0.973 (0.851–0.985) | 0.760 (0.563–0.868) | 0.977 (0.958–0.987) | 0.801 (0.639–0.891) |
| AD | 0.728 (0.449–0.866) | 0.869 (0.734–0.935) | 0.762 (0.518–0.882) | 1.000 (0.999–1.000) | 0.998 (0.997–0.999) | 0.999 (0.997–0.999) |
| Pallidum | ||||||
| Total | 0.117 (−0.385–0.437) | 0.558(0.307–0.718) | 0.778 (0.651–0.858) | 0.077 (−0.447–0.412) | 0.370 (0.012–0.598) | 0.710 (0.546–0.815) |
| Non-AD | 0.036 (−0.754–0.470) | 0.613 (0.296–0.788) | 0.792 (0.622–0.886) | 0.365 (−0.156–0.651) | 0.381 (−0.126–0.660) | 0.916 (0.847–0.954) |
| AD | 0.419 (−0.177–0.713) | 0.446 (−0.122–0.726) | 0.446 (−0.122–0.726) | −0.045 (−1.116–0.484) | 0.573 (0.136–0.789) | 0.232 (−0.554–0.621) |
| Thalamus | ||||||
| Total | 0.954 (0.923–0.971) | 0.925 (0.882–0.952) | 0.974 (0.960–0.984) | 0.908 (0.855–0.941) | 0.899 (0.842–0.936) | 0.982 (0.972–0.989) |
| Non-AD | 0.956 (0.920–0.976) | 0.938 (0.886–0.966) | 0.978 (0.960–0.988) | 0.899 (0.815–0.944) | 0.907 (0.832–0.949) | 0.984 (0.971–0.991) |
| AD | 0.907 (0.812–0.954) | 0.791 (0.577–0.897) | 0.928 (0.854–0.964) | 1.000 (0.999–1.000) | 0.998 (0.996–0.999) | 0.999 (0.997–0.999) |
| Cerebellum | ||||||
| Total | 0.985 (0.977–0.990) | 0.944 (0.912–0.964) | 0.941 (0.908–0.963) | 0.978 (0.965–0.986) | 0.953 (0.927–0.970) | 0.964 (0.943–0.977) |
| Non-AD | 0.975 (0.955–0.986) | 0.909 (0.834–0.950) | 0.909 (0.834–0.950) | 0.969 (0.944–0.983) | 0.936 (0.883–0.965) | 0.934 (0.880–0.964) |
| AD | 0.988 (0.975–0.994) | 0.947 (0.892–0.974) | 0.942 (0.883–0.971) | 0.979 (0.957–0.990) | 0.954 (0.907–0.977) | 0.976 (0.952–0.988) |
| Lt. Hemisphere | Rt. Hemisphere | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NQ vs. FS | NQ vs. HAD | FS vs. HAD | NQ vs. FS | NQ vs. HAD | FS vs. HAD | |
| Cortical GM | ||||||
| Total | 0.52 | 1.29 | 0.97 | 0.57 | 1.32 | 0.93 |
| Non-AD | 0.71 | 1.32 | 0.79 | 0.71 | 1.33 | 0.80 |
| AD | 0.40 | 2.12 | 1.91 | 0.57 | 2.22 | 1.83 |
| Cerebral WM | ||||||
| Total | 0.66 | 0.29 | 0.35 | 0.87 | 0.36 | 0.47 |
| Non-AD | 0.62 | 0.19 | 0.43 | 0.81 | 0.25 | 0.54 |
| AD | 0.78 | 0.49 | 0.26 | 1.07 | 0.59 | 0.41 |
| Hippocampus | ||||||
| Total | 0.33 | 0.03 | 0.40 | 0.37 | 0.78 | 0.48 |
| Non-AD | 0.14 | 0.54 | 0.48 | 0.16 | 0.33 | 0.20 |
| AD | 0.90 | 1.87 | 1.09 | 0.79 | 1.74 | 0.93 |
| Amygdala | ||||||
| Total | 0.44 | 0.08 | 0.49 | 0.36 | 0.78 | 0.50 |
| Non-AD | 0.42 | 0.02 | 0.42 | 0.36 | 0.97 | 0.79 |
| AD | 0.59 | 0.21 | 0.72 | 0.63 | 0.86 | 0.32 |
| Caudate | ||||||
| Total | 0.16 | 0.39 | 0.28 | 0.12 | 0.34 | 0.60 |
| Non-AD | 0.30 | 0.17 | 0.46 | 0.02 | 0.37 | 0.49 |
| AD | 0.05 | 0.34 | 0.47 | 0.29 | 0.33 | 0.75 |
| Putamen | ||||||
| Total | 1.82 | 2.12 | 0.25 | 1.50 | 1.81 | 0.32 |
| Non-AD | 1.80 | 2.25 | 0.40 | 2.17 | 0.45 | 1.61 |
| AD | 2.31 | 2.21 | <0.01 | 1.83 | 1.95 | 0.13 |
| Pallidum | ||||||
| Total | 5.65 | 5.49 | 0.13 | 6.07 | 5.63 | 0.10 |
| Non-AD | 5.20 | 5.28 | 0.06 | 6.52 | 5.82 | 0.26 |
| AD | 6.93 | 6.17 | 0.43 | 2.25 | 2.01 | 0.46 |
| Thalamus | ||||||
| Total | 0.73 | 1.06 | 0.34 | 0.10 | 1.15 | 0.06 |
| Non-AD | 0.98 | 1.04 | 0.02 | 1.11 | 1.13 | 0.02 |
| AD | 1.48 | 1.53 | 0.02 | 2 | 1.94 | 0.18 |
| Cerebellum | ||||||
| Total | 0.10 | 0.64 | 0.56 | 0.17 | 0.53 | 0.36 |
| Non-AD | 0.14 | 0.69 | 0.57 | 0.18 | 0.58 | 0.43 |
| AD | 0.09 | 0.76 | 0.71 | 0.20 | 0.57 | 0.37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, K.H.; Heo, Y.J.; Baek, H.J.; Kim, J.-H.; Jang, J.Y. Comparison of Inter-Method Agreement and Reliability for Automatic Brain Volumetry Using Three Different Clinically Available Software Packages. Medicina 2024, 60, 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60050727
Choi KH, Heo YJ, Baek HJ, Kim J-H, Jang JY. Comparison of Inter-Method Agreement and Reliability for Automatic Brain Volumetry Using Three Different Clinically Available Software Packages. Medicina. 2024; 60(5):727. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60050727
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Kwang Ho, Young Jin Heo, Hye Jin Baek, Jun-Ho Kim, and Jeong Yoon Jang. 2024. "Comparison of Inter-Method Agreement and Reliability for Automatic Brain Volumetry Using Three Different Clinically Available Software Packages" Medicina 60, no. 5: 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60050727
APA StyleChoi, K. H., Heo, Y. J., Baek, H. J., Kim, J.-H., & Jang, J. Y. (2024). Comparison of Inter-Method Agreement and Reliability for Automatic Brain Volumetry Using Three Different Clinically Available Software Packages. Medicina, 60(5), 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60050727






