Impaired Cardiorespiratory Fitness of Elite Athletes after Asymptomatic or Mild SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Study Design
2.2. Instruments and Measurements
2.2.1. Electrocardiographic Monitoring
2.2.2. Respiratory Function
2.2.3. Aerobic Capacity and Metabolic Response to Effort
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cardiovascular Function
3.2. Respiratory Function
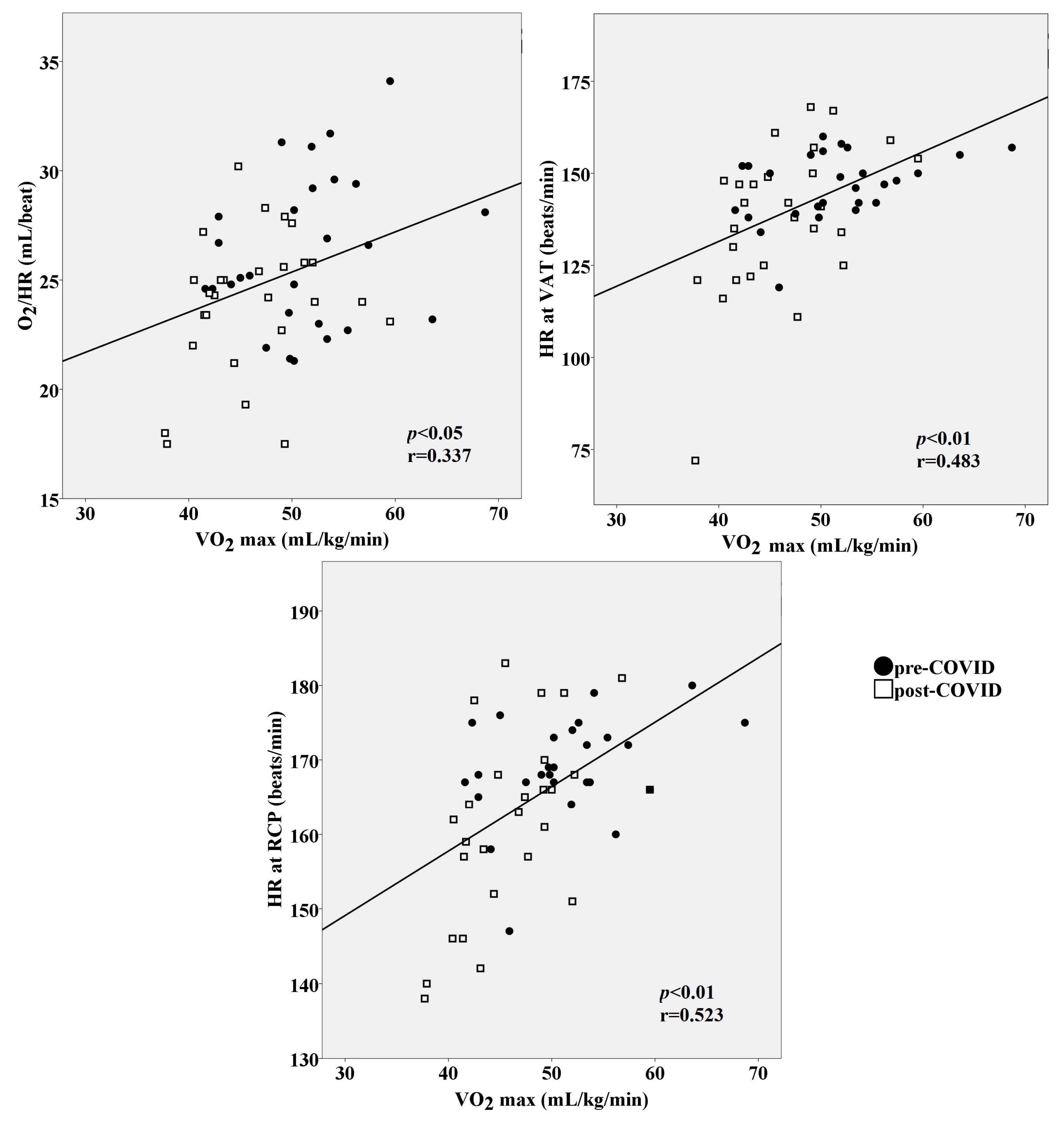
3.3. Aerobic Capacity and Metabolic Response to Effort
4. Discussion
5. Study Limitations and Practical Applications
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Esendağli, D.; Yilmaz, A.; Akçay, Ş.; Özlü, T. Post-COVID syndrome: Pulmonary complications. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 51, 3359–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaye, A.D.; Spence, A.L.; Mayerle, M.; Sardana, N.; Clay, C.M.; Eng, M.R.; Luedi, M.M.; Turpin, M.A.C.; Urman, R.D.; Cornett, E.M. Impact of COVID-19 infection on the cardiovascular system: An evidence-based analysis of risk factors and outcomes. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2021, 35, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, L.K.; Deadwiler, B.; Haratian, A.; Bolia, I.K.; Weber, A.E.; Petrigliano, F.A. Effects of COVID-19 on the Musculoskeletal System: Clinician’s Guide. Orthop. Res. Rev. 2021, 13, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kariyawasam, J.C.; Jayarajah, U.; Riza, R.; Abeysuriya, V.; Seneviratne, S.L. Gastrointestinal manifestations in COVID-19. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 115, 1362–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19). Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/coronavirus#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 29 April 2024).
- Perli, V.A.S.; Sordi, A.F.; Lemos, M.M.; Fernandes, J.S.A.; Capucho, V.B.N.; Silva, B.F.; Ramos, S.d.P.; Valdés-Badilla, P.; Mota, J.; Branco, B.H.M. Body composition and cardiorespiratory fitness of overweight COVID-19 survivors in different severity degrees: A cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, G.B. Physical activity and its relationship with COVID-19 cases and deaths: Analysis of U.S. counties. J. Sport Health Sci. 2021, 10, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goergen, J.; Bavishi, A.; Eimer, M.; Zielinski, A.R. COVID-19: The Risk to Athletes. Curr. Treat. Options Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 23, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Park, J.M.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, T.; Park, J.C. Impact of COVID-19 infection on sports performance of elite university athletes. J. Sport. Med. Phys. Fit. 2023, 63, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siopis, G. Elite athletes maintain peak performance after testing positive for SARS-CoV-2. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2022, 25, 195–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelliccia, A.; Sharma, S.; Gati, S.; Bäck, M.; Börjesson, M.; Caselli, S.; Collet, J.-P.; Corrado, D.; Drezner, J.A.; Halle, M.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines on sports cardiology and exercise in patients with cardiovascular disease. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 17–96, Erratum in Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 548–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.G.; Hull, J.H.; Rogers, J.; Pollock, N.; Dodd, M.; Haines, J.; Harris, S.; Loosemore, M.; Malhotra, A.; Pieles, G.; et al. Cardiorespiratory considerations for return-to-play in elite athletes after COVID-19 infection: A practical guide for sport and exercise medicine physicians. Br. J. Sport. Med. 2020, 54, 1157–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giusto, E.; Asplund, C.A. Persistent COVID and a Return to Sport. Curr. Sport. Med. Rep. 2022, 21, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faghy, M.A.; Ashton, R.E.M.; Parizher, G.; Smith, A.; Arena, R.; Gough, L.A.; Emery, M.S. COVID-19 and elite sport: Cardiovascular implications and return-to-play. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2023, 76, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Małek, Ł.A.; Marczak, M.; Miłosz-Wieczorek, B.; Konopka, M.; Braksator, W.; Drygas, W.; Krzywański, J. Cardiac involvement in consecutive elite athletes recovered from COVID-19: A magnetic resonance study. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2021, 53, 1723–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedeljkovic, I.P.; Giga, V.; Ostojic, M.; Djordjevic-Dikic, A.; Stojmenovic, T.; Nikolic, I.; Dikic, N.; Nedeljkovic-Arsenovic, O.; Maksimovic, R.; Dobric, M.; et al. Focal Myocarditis after Mild COVID-19 Infection in Athletes. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gluckman, T.J.; Bhave, N.M.; Allen, L.A.; Chung, E.H.; Spatz, E.S.; Ammirati, E.; Baggish, A.L.; Bozkurt, B.; Cornwell, W.K.; Harmon, K.G.; et al. 2022 ACC Expert Consensus Decision Pathway on Cardiovascular Sequelae of COVID-19 in Adults: Myocarditis and Other Myocardial Involvement, Post-Acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Return to Play: A Report of the American College of Cardiology Solution Set Oversight Committee. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, 1717–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaab, T.; Taube, C. Practical guide to cardiopulmonary exercise testing in adults. Respir. Res. 2022, 23, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gail, S.; Richard, F. Using Effect Size—Or Why the P Value Is Not Enough. J. Grad. Med. Educ. 2012, 4, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojmenovic, D.; Trunic, N.; Stojmenovic, T. A comparative study of aerobic capacity among elite basketball players according to five different positions in the team. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2022, 22, 2522–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petek, B.J.; Churchill, T.W.; Sawalla Guseh, J.; Loomer, G.; Gustus, S.K.; Lewis, G.D.; Weiner, R.B.; Baggish, A.L.; Wasfy, M.M. Utility of the oxygen pulse in the diagnosis of obstructive coronary artery disease in physically fit patients. Physiol. Rep. 2021, 9, e15105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazaheri, R.; Schmied, C.; Niederseer, D.; Guazzi, M. Cardiopulmonary Exercise Test Parameters in Athletic Population: A Review. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siopis, G. SARS-CoV-2 Does Not Affect Long-Term Performance of Top-level Elite Athletes. Curr. Sport. Med. Rep. 2021, 20, 569–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siopis, G. Athletic performance is not affected by SARS-CoV-2. Sci. Sport. 2022, 37, 329–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donina, Z.A. Causes of Hypoxemia in COVID-19. J. Evol. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 58, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, D.B.; Collins, S.É.; Stickland, M.K. Measurement and Interpretation of Exercise Ventilatory Efficiency. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, I.; Joseph, P.; Heerdt, P.M.; Cullinan, M.; Lutchmansingh, D.D.; Gulati, M.; Possick, J.D.; Systrom, D.M.; Waxman, A.B. Persistent Exertional Intolerance After COVID-19: Insights from Invasive Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing. Chest 2022, 161, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladlow, P.; O’Sullivan, O.; Bennett, A.N.; Barker-Davies, R.; Houston, A.; Chamley, R.; May, S.; Mills, D.; Dewson, D.; Rogers-Smith, K.; et al. The effect of medium-term recovery status after COVID-19 illness on cardiopulmonary exercise capacity in a physically active adult population. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 2022, 132, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herdy, A.H.; Ritt, L.E.; Stein, R.; Araújo, C.G.; Milani, M.; Meneghelo, R.S.; Ferraz, A.S.; Hossri, C.A.C.; de Almeida, A.E.M.; Fernandes-Silva, M.M.; et al. Cardiopulmonary Exercise Test: Background, Applicability and Interpretation. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2016, 107, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longobardi, I.; Prado, D.M.L.D.; Goessler, K.F.; Meletti, M.M.; de Oliveira Júnior, G.N.; de Andrade, D.C.O.; Gualano, B.; Roschel, H. Oxygen uptake kinetics and chronotropic responses to exercise are impaired in survivors of severe COVID-19. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2022, 323, H569–H576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Back, G.D.; Oliveira, M.R.; Camargo, P.F.; Goulart, C.L.; Oliveira, C.R.; Wende, K.W.; Junior, J.B.; Arbex, R.; Caruso, F.; Arena, R.; et al. Mild-to-moderate COVID-19 impact on the cardiorespiratory fitness in young and middle-aged populations. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2022, 55, e12118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisman, Y.; Buchvald, F.F.; Ring, A.M.; Wassilew, K.; Nielsen, K.G. Long-Term Lung Function and Exercise Capacity in Postinfectious chILD. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. Pulmonol. 2019, 32, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, M.J.; Lee, W.C.; Cho, H.Y.; Wu, M.F.; Hu, H.C.; Kao, K.C.; Chen, N.; Tsai, Y.; Huang, C. Recovery of pulmonary functions, exercise capacity, and quality of life after pulmonary rehabilitation in survivors of ARDS due to severe influenza A (H1N1) pneumonitis. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2018, 12, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarnieri, J.W.; Dybas, J.M.; Fazelinia, H.; Kim, M.S.; Frere, J.; Zhang, Y.; Albrecht, Y.S.; Murdock, D.G.; Angelin, A.; Singh, L.N.; et al. Targeted Down Regulation of Core Mitochondrial Genes During SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Preprint. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfarouk, K.O.; Alhoufie, S.T.S.; Hifny, A.; Schwartz, L.; Alqahtani, A.S.; Ahmed, S.B.M.; Alqahtani, A.M.; Alqahtani, S.S.; Muddathir, A.K.; Ali, H.; et al. Of mitochondrion and COVID-19. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2021, 36, 1258–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Pre-COVID-19 CPET Test | Post-COVID-19 CPET Test |
|---|---|---|
| HR max (bpm) | 181.74 ± 7.64 | 182.67 ± 7.92 |
| HR 1′ (bpm) | 157.81 ± 12.32 | 157.04 ± 11.61 |
| HR 2′ (bpm) | 129.33 ± 15.84 | 128.96 ± 15.12 |
| HR 3′ (bpm) | 114.96 ± 13.36 | 118.48 ± 12.61 |
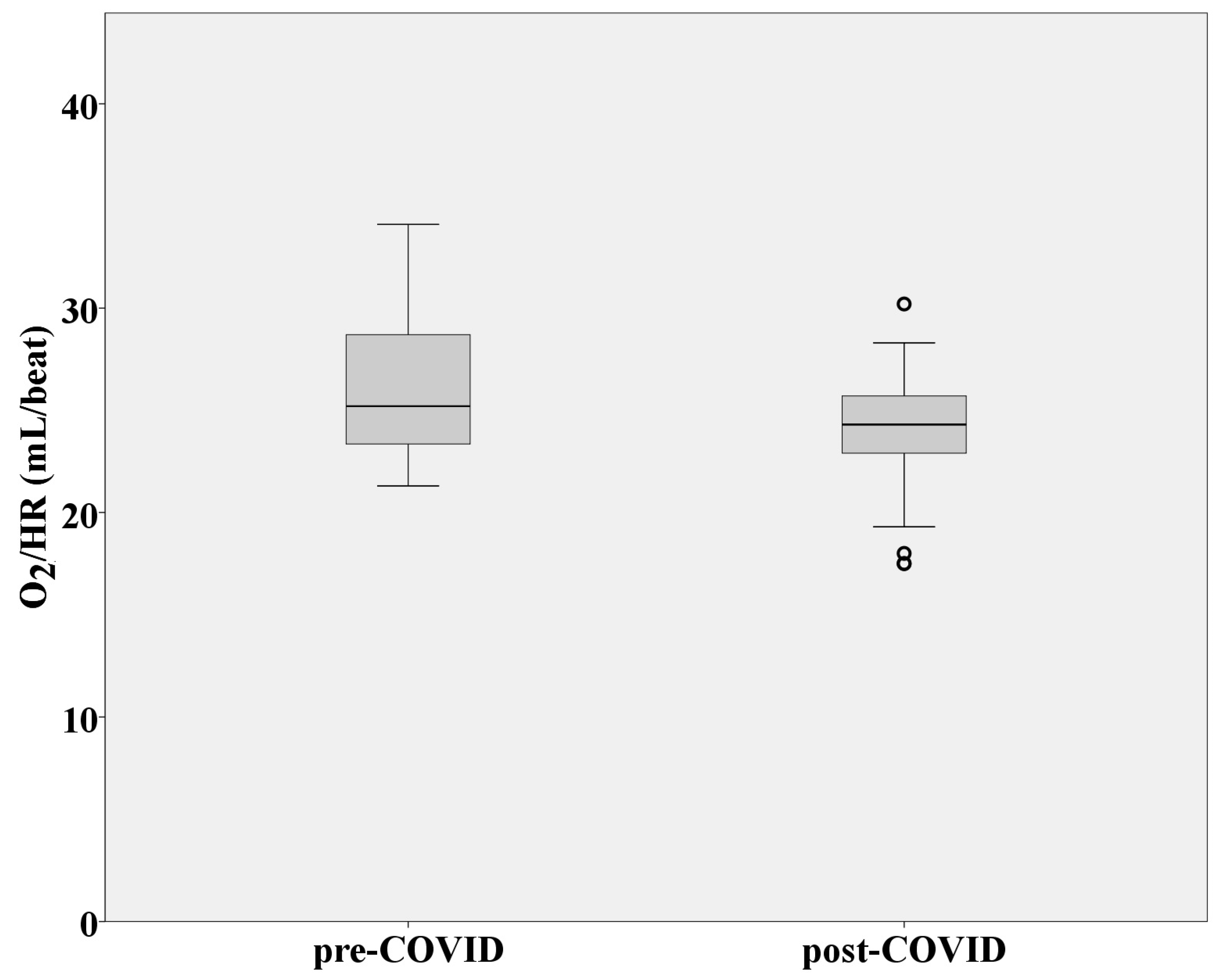
| VO2/HR (mL/beat) | 26.27 ± 3.48 | 23.99 ± 3.21 |
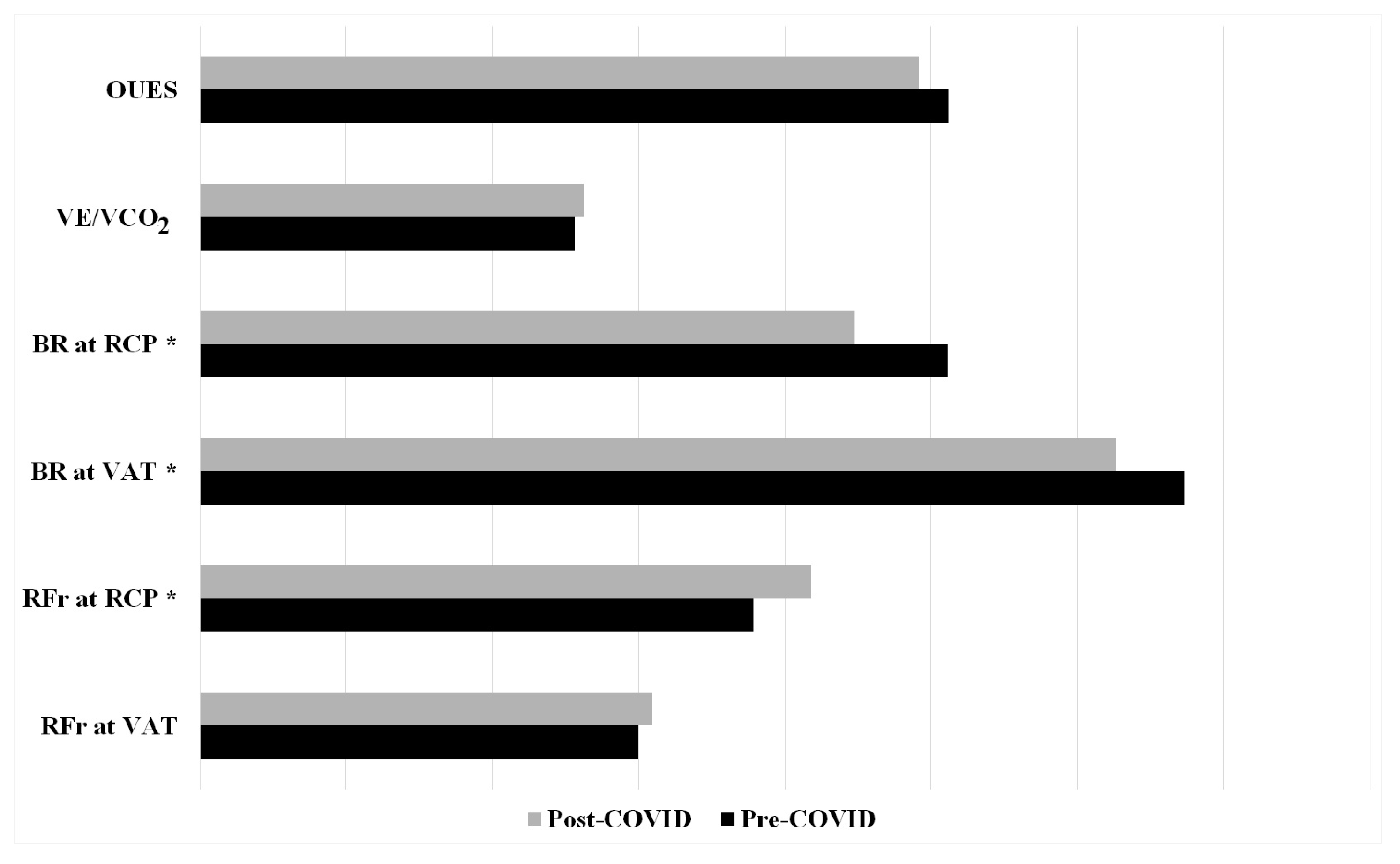
| RFr at VAT (brpm) | 29.99 ± 7.72 | 30.91 ± 7.33 |
| RFr at RCP (brpm) | 37.85 ± 7.39 | 41.81 ± 9.63 |
| BR at VAT (%) | 67.30 ± 5.70 | 62.65 ± 8.16 |
| BR at RCP (%) | 51.11 ± 9.62 | 44.79 ± 9.57 |
| VE/VCO2 slope | 25.65 ± 3.27 | 26.29 ± 2.65 |
| OUES | 5120.15 ± 847.20 | 4916.44 ± 788.50 |
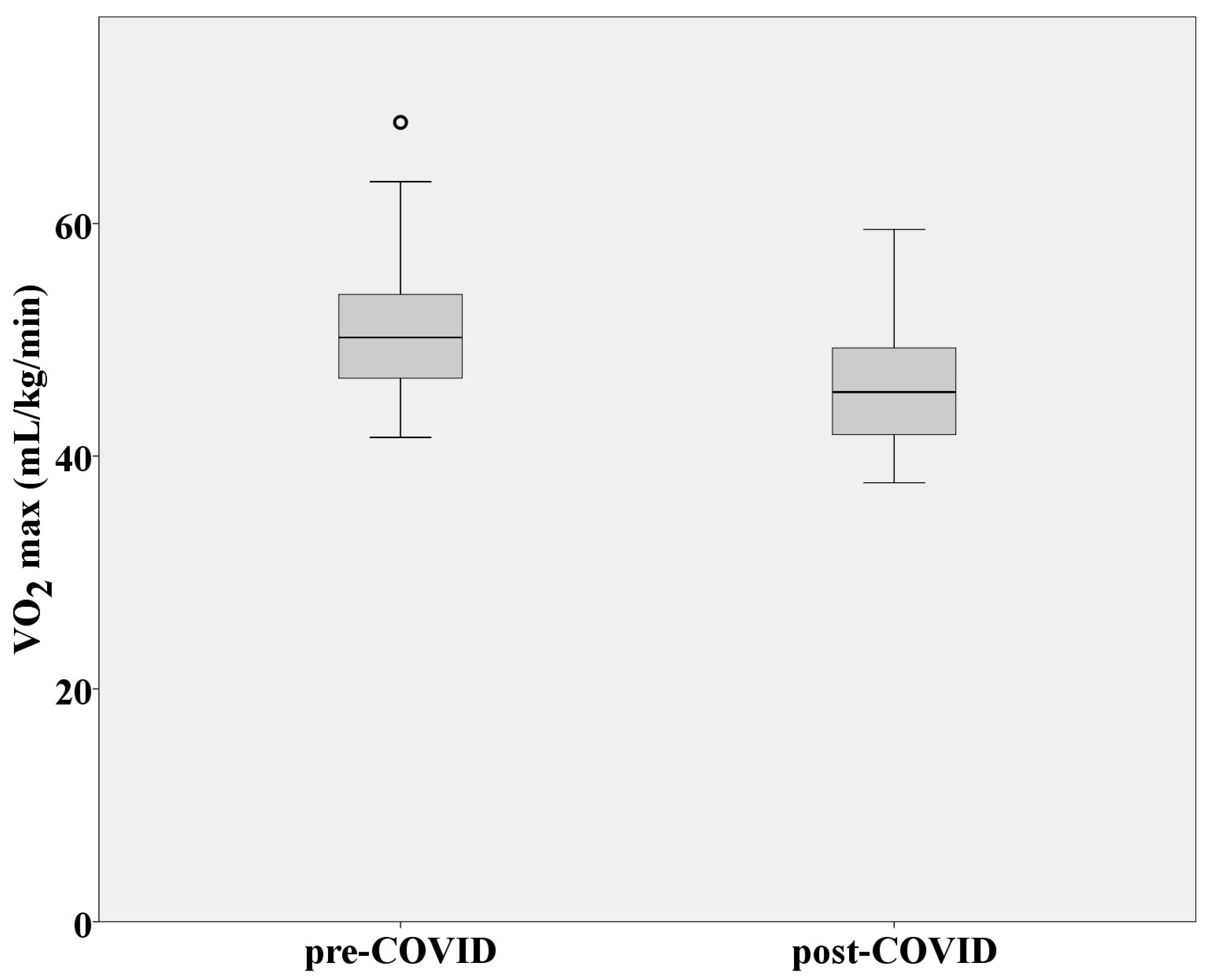
| VO2max (mL/kg/min) | 51.23 ± 6.47 | 46.2 ± 5.43 |
| Mean VO2 at speeds 8 and 9 km/h (mL/kg/min)—steady state | 26.24 ± 4.86 | 28.88 ± 5.14 |
| VO2 at VAT (mL/kg/min) | 34.33 ± 6.66 | 29.87 ± 5.88 |
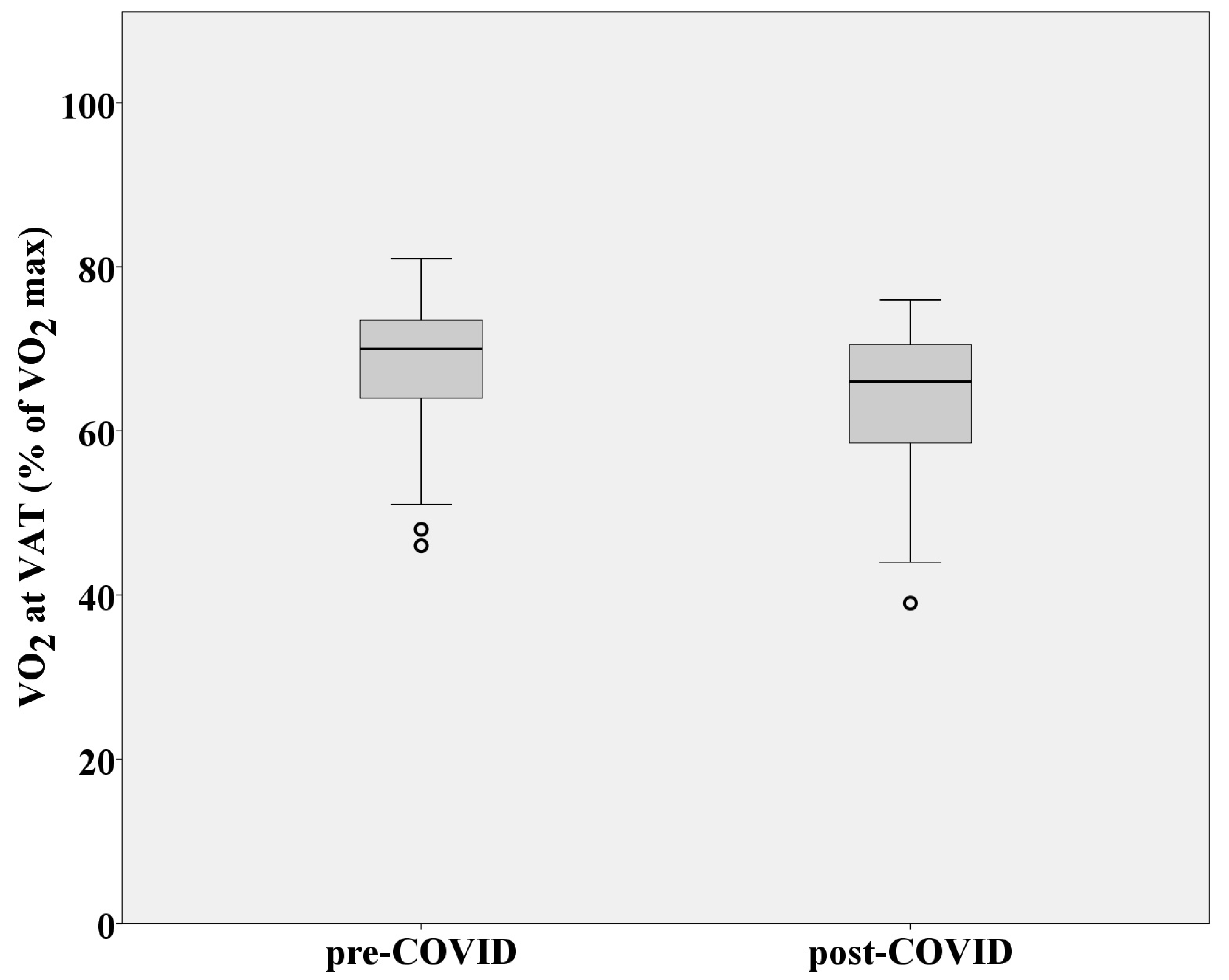
| VO2 at VAT (% of VO2max) | 67.78 ± 9.38 | 63.95 ± 9.49 |
| HR at VAT (bpm) | 146.55 ± 9.12 | 137.67 ± 20.32 |
| HR at RCP (bpm) | 168.93 ± 6.83 | 161.67 ± 12.56 |
| HR at RER = 1 (bpm) | 164.41 ± 10.71 | 152.30 ± 19.31 |
| RER max | 1.14 ± 0.046 | 1.17 ± 0.051 |
| Variables | ẞ Coefficient | Error | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| VO2/HR | 0.160 | 0.308 | 0.346 |
| VE/VCO2 slope | −0.063 | 0.297 | 0.646 |
| OUES | 0.117 | 0.001 | 0.499 |
| HR at VAT | 0.077 | 0.086 | 0.723 |
| HR at RCP | 0.412 | 0.124 | 0.051 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stojmenović, T.; Marković, S. Impaired Cardiorespiratory Fitness of Elite Athletes after Asymptomatic or Mild SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Medicina 2024, 60, 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60050786
Stojmenović T, Marković S. Impaired Cardiorespiratory Fitness of Elite Athletes after Asymptomatic or Mild SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Medicina. 2024; 60(5):786. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60050786
Chicago/Turabian StyleStojmenović, Tamara, and Srdjan Marković. 2024. "Impaired Cardiorespiratory Fitness of Elite Athletes after Asymptomatic or Mild SARS-CoV-2 Infection" Medicina 60, no. 5: 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60050786
APA StyleStojmenović, T., & Marković, S. (2024). Impaired Cardiorespiratory Fitness of Elite Athletes after Asymptomatic or Mild SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Medicina, 60(5), 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60050786





