Influence of Dulaglutide on Serum Biomarkers of Atherosclerotic Plaque Instability: An Interventional Analysis of Cytokine Profiles in Diabetic Subjects—A Pilot Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
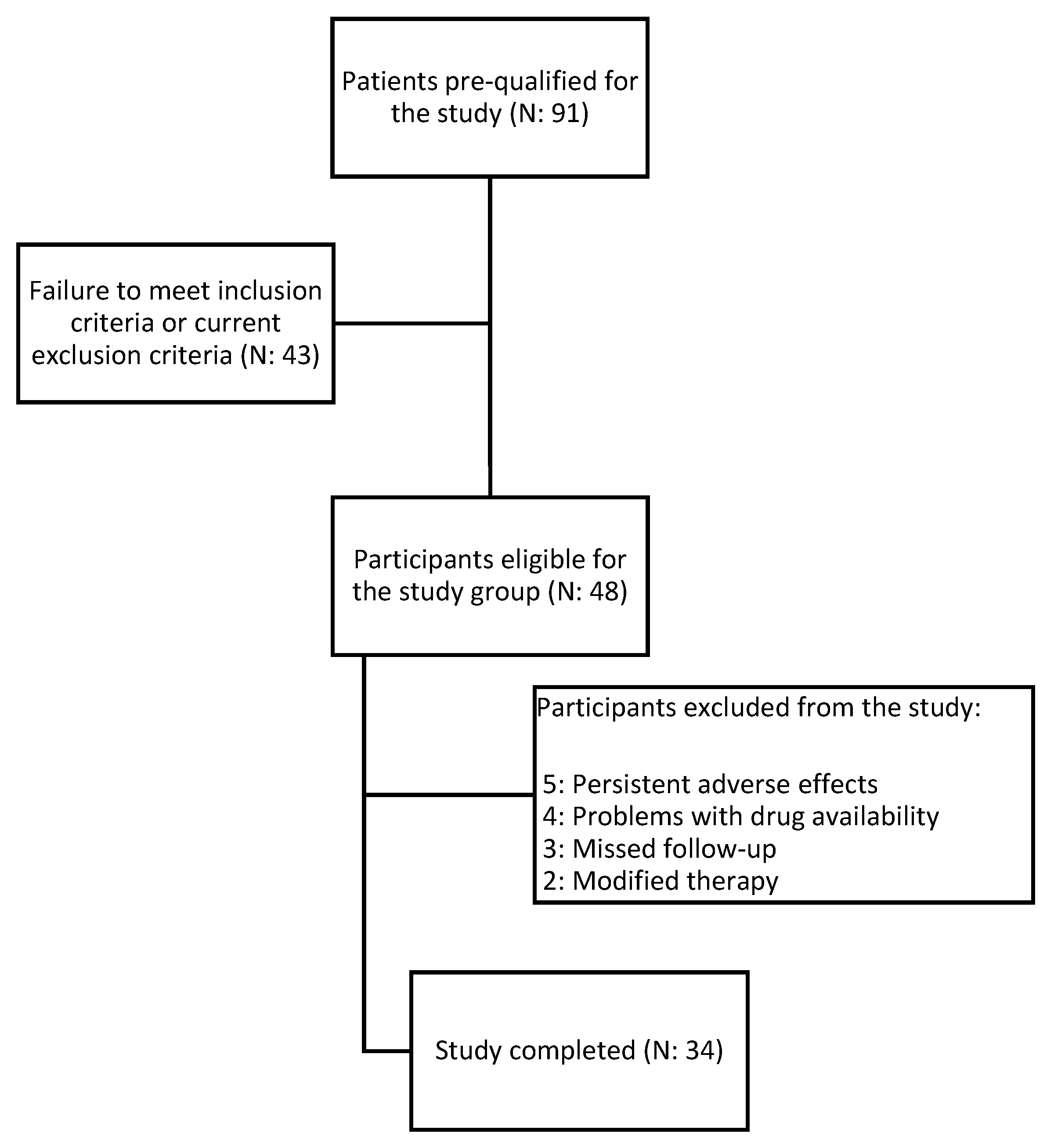
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Laboratory and Anthropometric Measurements
2.4. Arteriosclerotic Plaque Examination
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Group Characteristics
3.2. Biochemical Effect after Treatment
3.3. Effect of Treatment on Biochemical Markers of Atherosclerotic Plaque Vulnerability
3.4. Occurrence of Adverse Events
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2021 Diabetes Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of diabetes from 1990 to 2021, with projections of prevalence to 2050: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2023, 402, 203–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, N.; Sattar, N. Cardiovascular risk in diabetes mellitus: Epidemiology, assessment and prevention. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2023, 20, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frostegård, J. Immunity, atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. BMC Med. 2013, 11, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruhashi, T.; Higashi, Y. Pathophysiological Association between Diabetes Mellitus and Endothelial Dysfunction. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebari-Benslaiman, S.; Galicia-García, U.; Larrea-Sebal, A.; Olaetxea, J.R.; Alloza, I.; Vandenbroeck, K.; Benito-Vicente, A.; Martín, C. Pathophysiology of Atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutgens, E.; van Suylen, R.J.; Faber, B.C.; Gijbels, M.J.; Eurlings, P.M.; Bijnens, A.P.; Cleutjens, K.B.; Heeneman, S.; Daemen, M.J. Atherosclerotic plaque rupture: Local or systemic process? Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 2123–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Garlanda, C.; Bottazzi, B.; Peri, G.; Doni, A.; Martinez de la Torre, Y.; Latini, R. The long pentraxin PTX3 in vascular pathology. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2006, 45, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamarullah, W.; Nurcahyani; Multazam, R.B.; Josephine, C.M. Pentraxin 3 concentration is associated with poor outcomes in patients with coronary artery disease: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Acta Cardiol. 2022, 77, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Wang, Z.; Lei, W.; Shen, M.; Tang, J.; Xu, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H. Pentraxin 3: A promising therapeutic target for cardiovascular diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 93, 102163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tazaki, R.; Tanigawa, J.; Fujisaka, T.; Shibata, K.; Takeda, Y.; Ishihara, T.; Hoshiga, M.; Hanafusa, T.; Ishizaka, N. Plasma Pentraxin3 Level Is Associated with Plaque Vulnerability Assessed by Optical Coherence Tomography in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. Int. Heart J. 2016, 57, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, S.; Ikeda, S.; Yoshida, T.; Nakata, T.; Takeno, M.; Masuda, N.; Koide, Y.; Kawano, H.; Maemura, K. Elevated levels of systemic pentraxin 3 are associated with thin-cap fibroatheroma in coronary culprit lesions: Assessment by optical coherence tomography and intravascular ultrasound. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2013, 6, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christ-Crain, M. Vasopressin and Copeptin in health and disease. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2019, 20, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, D.; Cheng, J.; Qiu, L.; Cheng, X. Copeptin as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Cardiovascular Diseases. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 901990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhomoud, I.S.; Talasaz, A.; Mehta, A.; Kelly, M.S.; Sisson, E.M.; Bucheit, J.D.; Brown, R.; Dixon, D.L. Role of lipoprotein(a) in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: A review of current and emerging therapies. Pharmacotherapy 2023, 43, 1051–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehberger Likozar, A.; Zavrtanik, M.; Šebeštjen, M. Lipoprotein(a) in atherosclerosis: From pathophysiology to clinical relevance and treatment options. Ann. Med. 2020, 52, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kronenberg, F.; Mora, S.; Stroes, E.S.G.; Ference, B.A.; Arsenault, B.J.; Berglund, L.; Dweck, M.R.; Koschinsky, M.; Lambert, G.; Mach, F.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and aortic stenosis: A European Atherosclerosis Society consensus statement. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 4, 3925–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampsas, S.; Xenou, M.; Oikonomou, E.; Pantelidis, P.; Lysandrou, A.; Sarantos, S.; Goliopoulou, A.; Kalogeras, K.; Tsigkou, V.; Kalpis, A.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) in Atherosclerotc Diseases: From Pathophysiology to Diagnosis and Treatment. Molecules 2023, 28, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Kinoshita, D.; Nagata, T.; Asakura, K.; Katamine, M.; Katsura, A.; Hashimoto, T.; Minami, Y.; Ako, J. Lipoprotein (a) levels and vulnerable characteristics in nonculprit plaque in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Int. J. Cardiol. Heart Vasc. 2022, 43, 101120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muramatsu, Y.; Minami, Y.; Kato, A.; Katsura, A.; Sato, T.; Kakizaki, R.; Nemoto, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Fujiyoshi, K.; Meguro, K.; et al. Lipoprotein (a) level is associated with plaque vulnerability in patients with coronary artery disease: An optical coherence tomography study. Int. J. Cardiol. Heart Vasc. 2019, 24, 100382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jönsson, S.; Lundberg, A.K.; Jonasson, L. Overexpression of MMP-9 and its inhibitors in blood mononuclear cells after myocardial infarction—Is it associated with depressive symptomatology? PLoS ONE 2014, 25, e105572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, P.J.; Gomez, I.G.; Wille, P.T.; Raines, E.W. Macrophage expression of active MMP-9 induces acute plaque disruption in apoE-deficient mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, W.; Lavalle-Cobo, A.; Lobo, M.; Masson, G.; Molinero, G. Novel antidiabetic drugs and risk of cardiovascular events in patients without baseline metformin use: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2021, 28, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marso, S.P.; Daniels, G.H.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Kristensen, P.; Mann, J.F.; Nauck, M.A.; Nissen, S.E.; Pocock, S.; Poulter, N.R.; Ravn, L.S.; et al. Liraglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husain, M.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Donsmark, M.; Dungan, K.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Franco, D.R.; Jeppesen, O.K.; Lingvay, I.; Mosenzon, O.; Pedersen, S.D.; et al. Oral Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marso, S.P.; Bain, S.C.; Consoli, A.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Jódar, E.; Leiter, L.A.; Lingvay, I.; Rosenstock, J.; Seufert, J.; Warren, M.L.; et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerstein, H.C.; Colhoun, H.M.; Dagenais, G.R.; Diaz, R.; Lakshmanan, M.; Pais, P.; Probstfield, J.; Riesmeyer, J.S.; Riddle, M.C.; Rydén, L.; et al. Dulaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes (REWIND): A double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, N.; Husain, M.; Lehrke, M.; Verma, S.; Sattar, N. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists for the Reduction of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Circulation 2022, 146, 1882–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steen Carlsson, K.; Faurby, M.; Nilsson, K.; Wolden, M.L. Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease in Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective, Observational Study of Economic and Clinical Burden in Sweden. Diabetes Ther. 2023, 14, 1357–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hachuła, M.; Kosowski, M.; Ryl, S.; Basiak, M.; Okopień, B. Impact of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists on Biochemical Markers of the Initiation of Atherosclerotic Process. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, E.; Andreini, D.; Magnoni, M.; Masson, S.; Mushtaq, S.; Berti, S.; Canestrari, M.; Casolo, G.; Gabrielli, D.; Latini, R.; et al. Association of high-risk coronary atherosclerosis at CCTA with clinical and circulating biomarkers: Insight from CAPIRE study. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2021, 15, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagidullin, N.; Motloch, L.J.; Gareeva, D.; Hamitova, A.; Lakman, I.; Krioni, I.; Popov, D.; Zulkarneev, R.; Paar, V.; Kopp, K.; et al. Combining Novel Biomarkers for Risk Stratification of Two-Year Cardiovascular Mortality in Patients with ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, P.; Liu, C.; Sheng, Z.; Li, J.; Zhou, J.; Chen, R.; Chen, Y.; Song, L.; et al. Plasma Pentraxin-3 Combined with Plaque Characteristics Predict Cardiovascular Risk in ST-Segment Elevated Myocardial Infarction: An Optical Coherence Tomography Study. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 4409–4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejanović, V.V.; Stevuljević, J.K.; Vukašinović, A.; Miljković, M.; Kafedzic, S.; Zdravković, M.; Ilić, I.; Hinić, S.; Cerović, M.; Stefanović, M.; et al. Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Markers PTX3, CypA, and HB-EGF: How Are They Linked in Patients With STEMI? Angiology 2020, 71, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Tang, J.; Shi, C.; Zhang, T.; Li, J.; Guo, F.; Zhang, W. Pentraxin 3, TNF-α, and LDL-C Are Associated with Carotid Artery Stenosis in Patients with Ischemic Stroke. Front. Neurol. 2020, 10, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiraki, A.; Oyama, J.; Komoda, H.; Asaka, M.; Komatsu, A.; Sakuma, M.; Kodama, K.; Sakamoto, Y.; Kotooka, N.; Hirase, T.; et al. The glucagon-like peptide 1 analog liraglutide reduces TNF-α-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 2012, 221, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artunc-Ulkumen, B.; Pala, H.G.; Pala, E.E.; Yavasoglu, A.; Yigitturk, G.; Erbas, O. Exenatide improves ovarian and endometrial injury and preserves ovarian reserve in streptozocin induced diabetic rats. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2015, 1, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, D.; Toyoda, M.; Kimura, M.; Miyauchi, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Sato, H.; Tanaka, E.; Kuriyama, Y.; Miyatake, H.; Abe, M.; et al. Effects of liraglutide, a human glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue, on body weight, body fat area and body fat-related markers in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Intern. Med. 2013, 52, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Li, X.; Feng, Y.; Dong, G.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J. The Role of Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 in Atherosclerotic Plaque Instability. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 3872367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Lei, Y.; Inoue, A.; Piao, L.; Hu, L.; Jiang, H.; Sasaki, T.; Wu, H.; Xu, W.; Yu, C.; et al. Exenatide mitigated diet-induced vascular aging and atherosclerotic plaque growth in ApoE-deficient mice under chronic stress. Atherosclerosis 2017, 264, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolak, M.; Staszewska, T.; Juszczak, M.; Gałdyszyńska, M.; Bojanowska, E. Anti-inflammatory and pro-healing impacts of exendin-4 treatment in Zucker diabetic rats: Effects on skin wound fibroblasts. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 842, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, L.E.M.; Marinho, T.S.; Martins, F.F.; Aguila, M.B.; Mandarim-de-Lacerda, C.A. Treatment with semaglutide, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, improves extracllular matrix remodeling in the pancreatic islet of diet-induced obese mice. Life Sci. 2023, 319, 121502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.X.; Dong, N.X.; Zhou, C.X.; Wang, F.J.; Xing, N.; Ma, H.F.; Hou, L. Liraglutide Attenuates Restenosis After Vascular Injury in Rabbits with Diabetes Via the TGF-β/Smad3 Signaling Pathway. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2022, 28, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Katan, M.; Christ-Crain, M. The stress hormone copeptin: A new prognostic biomarker in acute illness. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2010, 140, w13101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schill, F.; Persson, M.; Engström, G.; Melander, O.; Enhörning, S. Copeptin as a marker of atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2021, 338, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leibnitz, S.; Christ-Crain, M.; Winzeler, B. Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on copeptin in healthy volunteers and patients with primary polydipsia. In Endocrine Abstracts; Bioscientifica: Bristol, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Heinla, K.; Vasar, E.; Reppo, I.; Sedman, T.; Volke, V. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists Induce Growth Hormone Secretion in Healthy Volunteers. Diabetes Ther. 2023, 14, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frøssing, S.; Nylander, M.; Kistorp, C.; Skouby, S.O.; Faber, J. Effect of liraglutide on atrial natriuretic peptide, adrenomedullin, and copeptin in PCOS. Endocr. Connect. 2018, 7, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winzeler, B.; Sailer, C.O.; Coynel, D.; Zanchi, D.; Vogt, D.R.; Urwyler, S.A.; Refardt, J.; Christ-Crain, M. A randomized controlled trial of the GLP-1 receptor agonist dulaglutide in primary polydipsia. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 1, e151800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niccoli, G.; Cin, D.; Scalone, G.; Panebianco, M.; Abbolito, S.; Cosentino, N.; Jacoangeli, F.; Refaat, H.; Gallo, G.; Salerno, G. Lipoprotein (a) is related to coronary atherosclerotic burden and a vulnerable plaque phenotype in angiographically obstructive coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis 2016, 246, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, E.M.; Ellis, K.L.; Barrett, P.H.R.; Watts, G.F.; Hung, J.; Beilby, J.P.; Thompson, P.L.; Stobie, P.; McQuillan, B.M. Lipoprotein(a) and apolipoprotein(a) isoform size: Associations with angiographic extent and severity of coronary artery disease, and carotid artery plaque. Atherosclerosis 2018, 275, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimikas, S. Lipoprotein(a): Novel target and emergence of novel therapies to lower cardiovascular disease risk. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2016, 23, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banach, M. Lipoprotein(a): The enemy that we still don’t know how to defeat. Eur. Heart J. Open. 2023, 3, oead080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechlioulis, A.; Markozannes, G.; Chionidi, I.; Liberopoulos, E.; Naka, K.K.; Ntzani, E.E.; Liatis, S.; Rizzo, M.; Rizos, E.C. The effect of SGLT2 inhibitors, GLP1 agonists, and their sequential combination on cardiometabolic parameters: A randomized, prospective, intervention study. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2023, 37, 108436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.; Toth, P.; Kulkarni, K.; Chiquette, E. Lipoprotein Effects of Exenatide in Diabetic Subjects with Elevated Pretreatment Levels of Serum Lipoprotein(a) Cholesterol. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2012, 6, 283–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariel, D.; Kim, S.H.; Abbasi, F.; Lamendola, C.A.; Liu, A.; Reaven, G.M. Effect of liraglutide administration and a calorie-restricted diet on lipoprotein profile in overweight/obese persons with prediabetes. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 24, 1317–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study Group | |
|---|---|
| Number of patients, n | 34 |
| Age, years | 61 |
| Women, n (%) | 19 (56%) |
| Men, n (%) | 15 (44%) |
| Body mass, kg | 102.6 |
| Height, cm | 168 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 36.29 |
| Overweight, n (%) | 8 (24%) |
| Obese, n (%) | 26 (76%) |
| WHO guidelines on physical activity, n (%) | 12 (35%) |
| Smokers, n (%) | |
| Active | 6 (17%) |
| Past | 9 (26%) |
| Alcohol abuse, % | 0 |
| Comorbidity, n (%) | |
| Hypertension | 28 (82%) |
| Ischemic heart disease | 10 (29%) |
| Chronic kidney diseases | 8 (24%) |
| Thyroid diseases | 6 (18%) |
| Heart failure | 4 (11%) |
| Study Group before Treatment | Study Group after Treatment | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | p Value | |||
| BMI kg/m2 | 36.29 | 6.9 | 34.4 | 7 | <0.001 | ||
| HbA1C % | 8.8 * | 1.3 | 7.77 | 1.04 | <0.001 | ||
| GFR mL/min/1.73 m2 | 68.09 | 12.4 | 70.09 | 18.28 | 0.44 | ||
| Weight kg | 102.61 | 22.4 | 97.37 | 22.8 | <0.001 | ||
| WHR | 0.98 | 0.065 | 0.97 | 0.06 | 0.42 | ||
| SBP mmHg | 135.53 | 13.05 | 129.5 | 9.57 | <0.01 | ||
| Creatinine mg/dL | 1.09 | 0.15 | 1.07 | 0.18 | 0.6 | ||
| ASP U/I | 33.21 | 14.3 | 29.47 | 10.3 | 0.14 | ||
| Median | Q1 | Q3 | Median | Q1 | Q3 | p Value | |
| DBP mmHg | 84.5 | 78.25 | 90 | 79 | 72 | 81.75 | <0.01 |
| TC mg/dL | 165.55 | 150.7 | 207.1 | 172.75 | 148.1 | 221.62 | 0.48 |
| LDL mg/dL | 86 | 69 | 105.75 | 88.5 | 64 | 119.25 | 0.86 |
| HDL mg/dL | 48.45 | 44.4 | 53.37 | 51.5 | 46.73 | 63.76 | 0.056 |
| non-HDL mg/dL | 113.7 | 98 | 155.75 | 118.75 | 95.95 | 159.74 | 0.79 |
| TG mg/dL | 169.45 | 109.23 | 204.55 | 152.55 | 117 | 193.5 | 0.87 |
| Glucose mg/dL | 161.9 | 143.1 | 197.38 | 134.4 | 117.9 | 170.78 | <0.01 |
| ALT (U/I) | 27 | 21 | 49.5 | 30 | 26 | 43.75 | 0.96 |
| GGTP U/I | 39.5 | 30 | 53.75 | 38.5 | 28.25 | 53 | 0.90 |
| FIB-4 | 1.5 | 1.18 | 1.98 | 1.38 | 1.15 | 1.67 | <0.01 |
| Study Group before Treatment | Study Group after Treatment | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | p Value | |||
| Copeptin pg/mL | 190.44 | 66.67 | 172.83 | 52.35 | p > 0.05 | ||
| Median | Q1 | Q3 | Median | Q1 | Q3 | ||
| Lp(a) mg/dL | 12.67 | 6.83 | 41.72 | 11.95 | 7.32 | 23.21 | p < 0.05 |
| PTX3 pg/mL | 1288 | 1174.5 | 1381.5 | 1023.5 | 1008 | 1173 | p < 0.001 |
| MMP-9 pg/mL | 294.15 | 256.48 | 312.7 | 277.35 | 245.28 | 303.63 | p < 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hachuła, M.; Kosowski, M.; Basiak, M.; Okopień, B. Influence of Dulaglutide on Serum Biomarkers of Atherosclerotic Plaque Instability: An Interventional Analysis of Cytokine Profiles in Diabetic Subjects—A Pilot Study. Medicina 2024, 60, 908. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60060908
Hachuła M, Kosowski M, Basiak M, Okopień B. Influence of Dulaglutide on Serum Biomarkers of Atherosclerotic Plaque Instability: An Interventional Analysis of Cytokine Profiles in Diabetic Subjects—A Pilot Study. Medicina. 2024; 60(6):908. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60060908
Chicago/Turabian StyleHachuła, Marcin, Michał Kosowski, Marcin Basiak, and Bogusław Okopień. 2024. "Influence of Dulaglutide on Serum Biomarkers of Atherosclerotic Plaque Instability: An Interventional Analysis of Cytokine Profiles in Diabetic Subjects—A Pilot Study" Medicina 60, no. 6: 908. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60060908
APA StyleHachuła, M., Kosowski, M., Basiak, M., & Okopień, B. (2024). Influence of Dulaglutide on Serum Biomarkers of Atherosclerotic Plaque Instability: An Interventional Analysis of Cytokine Profiles in Diabetic Subjects—A Pilot Study. Medicina, 60(6), 908. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60060908






