Hypoglycemic Drugs in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus and Heart Failure: A Narrative Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
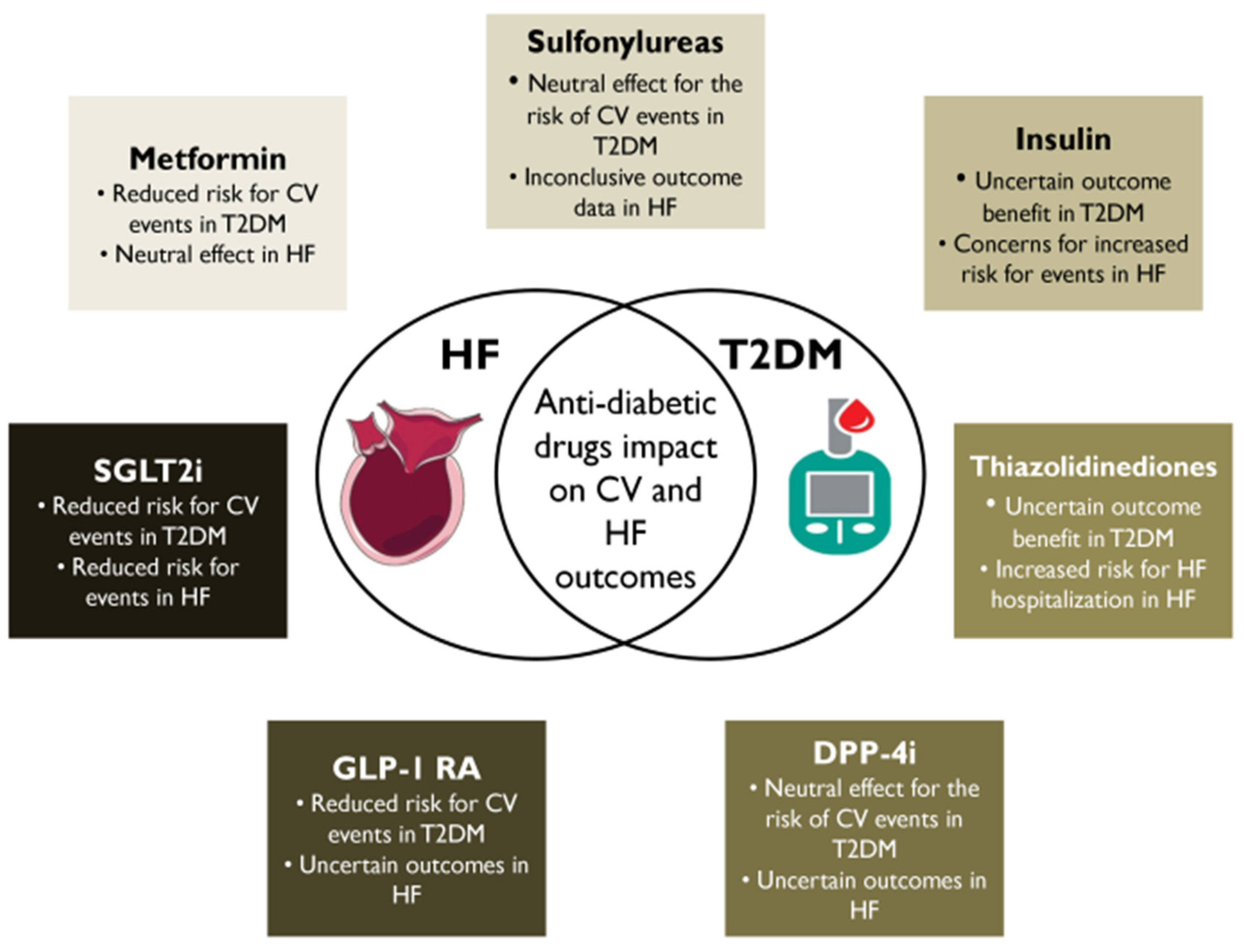
2. Metformin
2.1. Clinical Cardiac Impact
2.2. Clinical Decision-Making
3. SUs
3.1. Clinical Cardiac Impact
3.2. Clinical Decision-Making
4. Insulin
4.1. Clinical Cardiac Impact
4.2. Clinical Decision-Making
5. Thiazolidinediones (TZDs)
5.1. Clinical Cardiac Impact
5.2. Clinical Decision-Making
6. DPP-4 Inhibitors
6.1. Clinical Cardiac Impact
| Study | Year | Drug | N | Baseline HF (%) | Baseline CVD (%) | Median Follow-Up (Years) | HF Hospitalization Risk [HR (95%CI), p Value] | CV Death Risk [HR (95%CI), p Value] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAVOR-TIMI 53 [59] | 2013 | Saxagliptin | 16,492 | 12.8 | 78 | 2.1 | 1.27 (1.07–1.51) 0.007 | 1.03 (0.87–1.22) 0.72 |
| EXAMINE [63] | 2013 | Alogliptin | 5,380 | 28 | 100 | 1.5 | 1.07 (0.79–1.46) | 0.79 (0.60–1.04) 0.10 |
| TECOS [62] | 2015 | Sitagliptin | 14,671 | 18 | 100 | 3 | 1.00 (0.83–1.20) 0.98 | 1.03 (0.89–1.19) 0.71 |
| CARMELINA [33] | 2019 | Linagliptin | 6991 | 27 | 58 | 2.2 | 0.90 (0.74–1.08) 0.26 | 0.96 (0.81–1.14) 0.63 |
| CAROLINA * [34] | 2019 | Linagliptin | 6033 | 4.5 | 42 | 6.3 | 1.21 (0.92–1.59) | 1.00 (0.81–1.24) |
6.2. Clinical Decision-Making
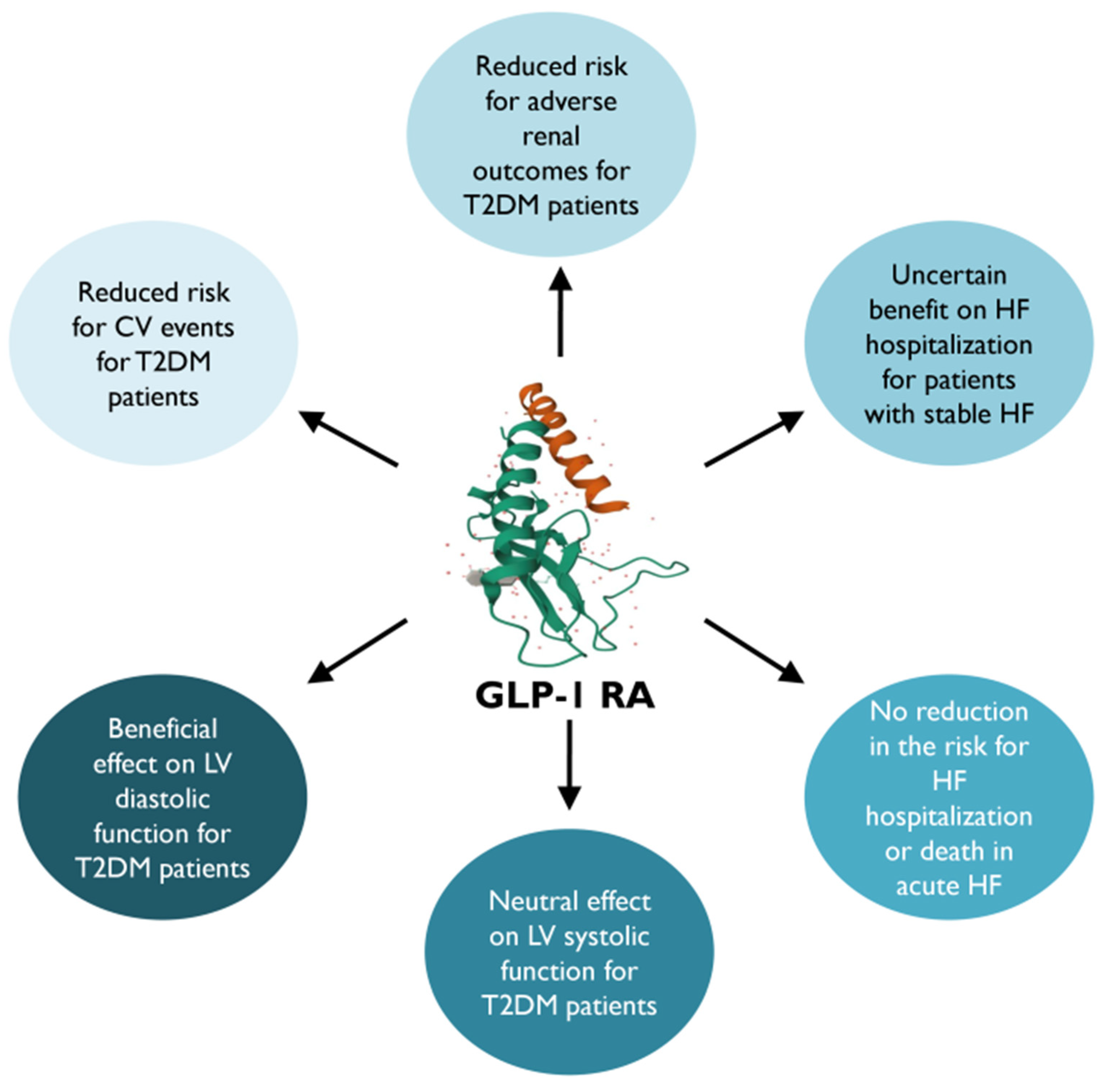
7. GLP-1 RAs
7.1. Clinical Cardiac Impact
7.2. Clinical Decision-Making
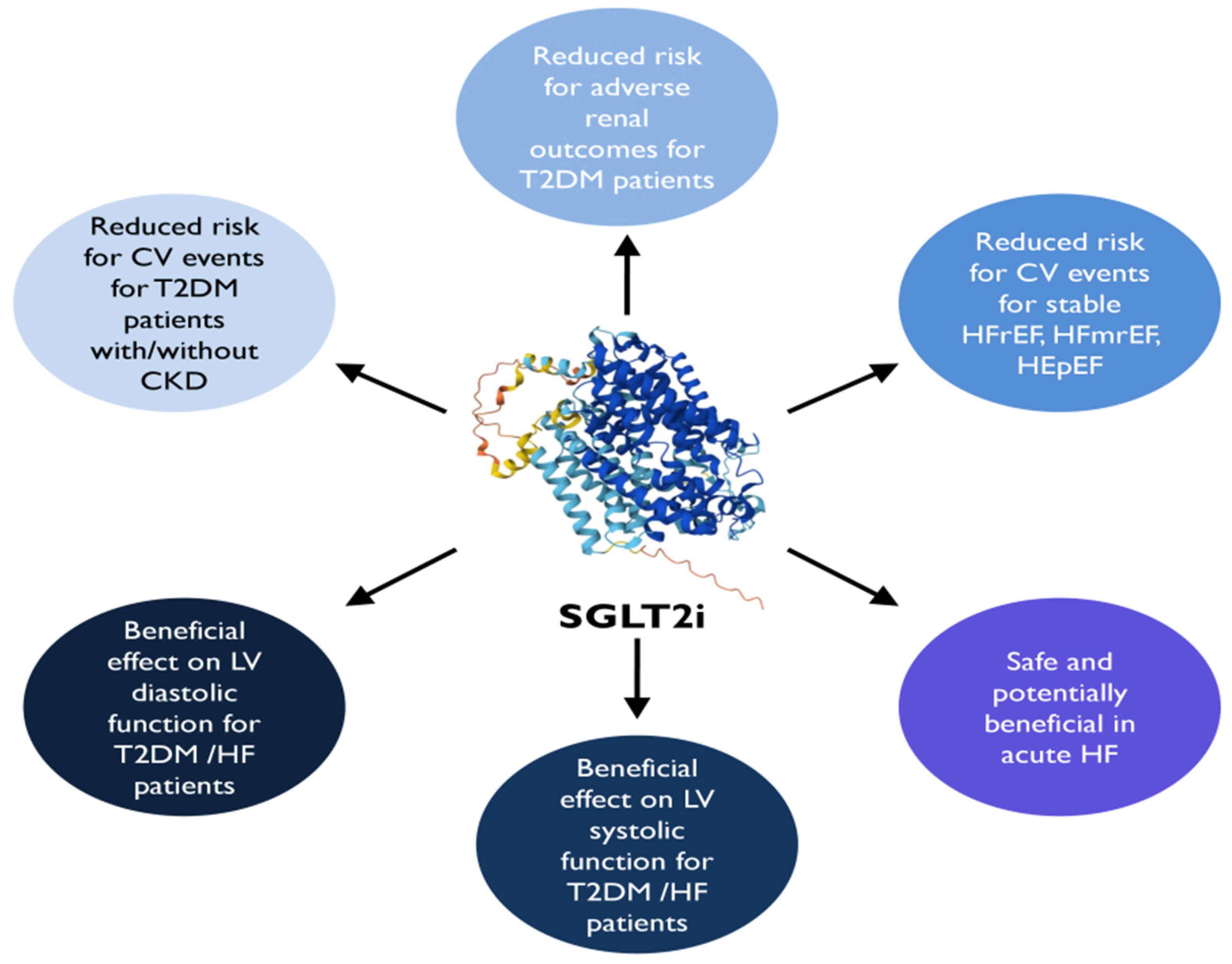
8. SGLT2i
8.1. Clinical Cardiac Impact
8.2. Major CVOTs
| Study | Year | Drug | N | Baseline HF (%) | Baseline CVD (%) | Median Follow-Up (Years) | HF Hospitalization Risk [HR (95%CI), p Value] | CV Death Risk [HR (95%CI), p Value] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMPA-REG [99] | 2015 | Empagliflozin | 7020 | 10 | 99 | 3.1 | 0.65 (0.50–0.85) 0.002 | 0.62 (0.49–0.77) <0.001 |
| CANVAS [100] | 2017 | Canagliflozin | 10,142 | 14.4 | 65.6 | 2.4 | 0.67 (0.52–0.87) | 0.87 (0.72–1.06) |
| DECLARE-TIMI 58 [101] | 2018 | Dapagliflozin | 17,160 | 10 | 41 | 4.2 | 0.73 (0.61−0.88) | 0.98 (0.82−1.17) |
| VERTIS-CV [103] | 2020 | Ertugliflozin | 8246 | 23.7 | 75.9 | 3 | 0.70 (0.54–0.90) | 0.92 (0.77–1.11) |
| DAPA-HF * [105] | 2019 | Dapagliflozin | 4744 | 100 | 56 | 1.5 | 0.7 (0.59–0.83) | 0.82 (0.69–0.98) |
| EMPEROR-reduced * [106] | 2020 | Empagliflozin | 3730 | 100 | 52 | 1.3 | 0.69 (0.59–0.81) | 0.92 (0.75–1.12) |
| SOLOIST-WHF [107] | 2020 | Sotagliflozin | 1222 | 100 | ΝA | 0.75 | 0.64 (0.49 to 0.83) <0.001 | 0.84 (0.58 to 1.22) 0.36 |
| EMPEROR-preserved * [108] | 2021 | Empagliflozin | 5988 | 100 | 35.5 | 2.2 | 0.71 (0.60–0.83) | 0.91 (0.76–1.09) |
| DELIVER [109] | 2022 | Dapagliflozin | 6263 | 100 | NA | 2.3 | 0.79 (0.69–0.91) | 0.88 (0.74–1.05) |
| CREDENCE [110] | 2019 | Canagliflozin | 4401 | 14.8 | 50.4 | 2.62 | 0.61 (0.47–0.8) <0.001 | 0.78 (0.61–1.00) 0.05 |
| SCORED [111] | 2020 | Sotagliflozin | 10,584 | 31 | 22 | 1.3 | 0.67 (0.55–0.82) <0.001 | 0.90 (0.73–1.12) 0.35 |
| DAPA-CKD * [112] | 2020 | Dapagliflozin | 4304 | 11 | 37.5 | 2.4 | 0.71 (0.55–0.92) ** | 0.81 (0.58–1.12) |
8.3. HF Outcome Trials
8.4. Cardiac Function Impact
9. SGLT2i and GLP-RA Combination
9.1. Established Knowledge
9.2. Future Directions
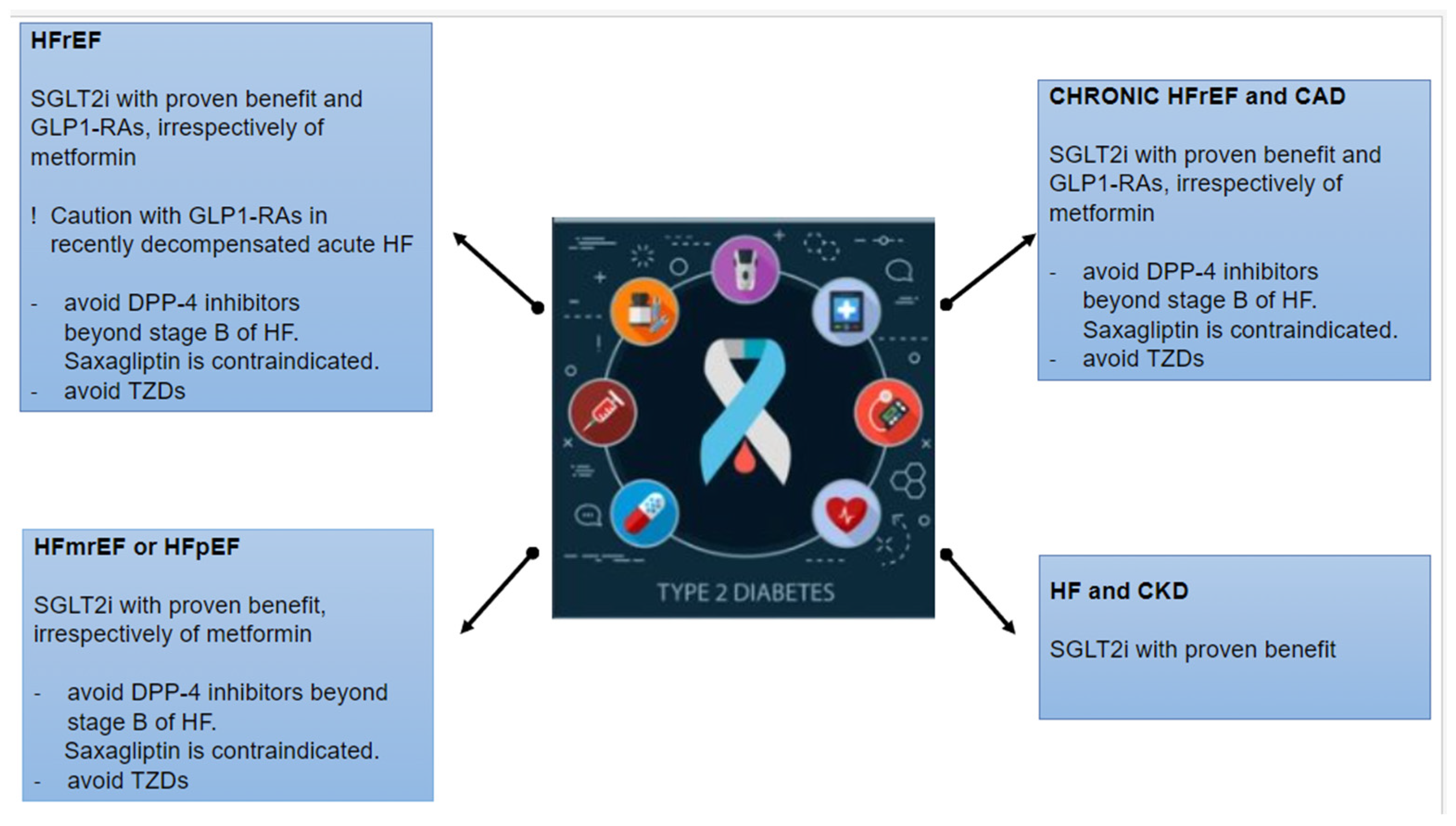
10. Indication of Antidiabetic Drugs in HF According to Guidelines
- Metformin remains the first-line treatment in combination with lifestyle interventions in patients with T2DM without cardio-renal comorbidities. In terms of CV and renal outcomes, novel antidiabetic agents (SGLT2is and GLP-1 RAs) have proven their beneficial effects on 3P-MACE, HF hospitalization, and mortality independent of metformin use. Hence, these drugs should be firstly considered in patients with established or a high risk of CVD, HF, and CKD, irrespectively of metformin use. In patients with T2DM and stable HF, metformin may be continued for glucose lowering if the eGFR remains > 30 mL/min/1.73 m2 but should be avoided in unstable or hospitalized individuals with HF.
- SUs have met controversial results concerning CV safety and the risk of HF hospitalization. Hence, in patients with T2DM and HF, SUs should only be considered in the case of poor glycemic control with alternative options and be used with caution.
- Insulin should be considered in patients with DM and acute decompensated HF.
- TZDs: Pioglitazone could be considered as second-line therapy in patients at very high risk or with established CVD, if the glycemic target is not achieved or novel agents are contraindicated. However, TZDs (pioglitazone and rosiglitazone) are generally contraindicated in patients with T2DM at risk or with established HF due to the increase in HF incidence.
- DPP-4 inhibitors (sitagliptin and linagliptin) showed a neutral effect on the risk of HF hospitalization or 3P-MACE and may be considered for DM management in patients with HF. Only saxagliptin was related to an increased risk of HF hospitalization, and it is not recommended in patients with T2DM at risk or with manifest HF. However, the AHA/ACCF/HFSA consensus recommends avoiding DPP-4 inhibitors over stage-B HF.
- GLP-1 RAs are highly recommended in patients with T2DM, with or without established CVD and irrespectively of other hypoglycemic therapies or glycose-lowering targets. Specifically, a GLP-1 RA with proven benefits could be used in patients with very high risk for CVD (>55 years, hypertension, smoking, dyslipidemia, obesity, or albuminuria) and should be used in patients with established CVD, to reduce 3P-MACE. GLP-1 RAs (lixisenatide, liraglutide, exenatide, semaglutide, and dulaglutide) had a neutral effect on HF hospitalization and could be considered as an alternative treatment of DM in patients with HF. However, it would be preferable to avoid GLP-1 RAs in HFrEF and recently decompensated acute HF.
- SGLT2is are recommended in patients with T2DM with or without established CVD, HF, or CKD (eGFR > 20 mL/min per 1.73 m²), to reduce 3P-MACE and improve kidney outcomes, irrespectively of other antidiabetic drugs or glucose-lowering goals. Specifically, dapagliflozin, empagliflozin, and sotagliflozin are strongly recommended in patients with T2DM and CVD or HF, irrespectively of LVEF, to reduce HF hospitalization and CV death.
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bozkurt, B.; Coats, A.J.S.; Tsutsui, H.; Abdelhamid, C.M.; Adamopoulos, S.; Albert, N.; Anker, S.D.; Atherton, J.; Böhm, M.; Butler, J.; et al. Universal Definition and Classification of Heart Failure: A Report of the Heart Failure Society of America, Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology, Japanese Heart Failure Society and Writing Committee of the Universal Definition of Heart Failure: Endorsed by the Canadian Heart Failure Society, Heart Failure Association of India, Cardiac Society of Australia and New Zealand, and Chinese Heart Failure Association. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2021, 23, 352–380. [Google Scholar]
- Petersmann, A.; Nauck, M.; Müller-Wieland, D.; Kerner, W.; Müller, U.A.; Landgraf, R.; Freckmann, G.; Heinemann, L. Definition, Classification and Diagnostics of Diabetes Mellitus. Lab. Med. 2018, 42, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savarese, G.; Becher, P.M.; Lund, L.H.; Seferovic, P.; Rosano, G.M.C.; Coats, A.J.S. Global Burden of Heart Failure: A Comprehensive and Updated Review of Epidemiology. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 118, 3272–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Wu, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhu, D.; Chen, F.; Chen, J.; Ji, X.; Hou, K. The Global, Regional and National Burden of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in the Past, Present and Future: A Systematic Analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1192629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Ley, S.H.; Hu, F.B. Global Aetiology and Epidemiology of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, A.; Prosperi, S.; Severino, P.; Myftari, V.; Labbro Francia, A.; Cestiè, C.; Pierucci, N.; Marek-Iannucci, S.; Mariani, M.V.; Germanò, R.; et al. Current Approaches to Worsening Heart Failure: Pathophysiological and Molecular Insights. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.J.; Aroda, V.R.; Collins, B.S.; Gabbay, R.A.; Green, J.; Maruthur, N.M.; Rosas, S.E.; Del Prato, S.; Mathieu, C.; Mingrone, G.; et al. Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, 2022. A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 2753–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijnen, M.; Duschek, E.J.J.; Boom, H.; van Vliet, M. The Effects of Antidiabetic Agents on Heart Failure. Neth. Heart J. Mon. J. Neth. Soc. Cardiol. Neth. Heart Found. 2022, 30, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giugliano, D.; Longo, M.; Signoriello, S.; Maiorino, M.I.; Solerte, B.; Chiodini, P.; Esposito, K. The Effect of DPP-4 Inhibitors, GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and SGLT-2 Inhibitors on Cardiorenal Outcomes: A Network Meta-Analysis of 23 CVOTs. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2023 Focused Update of the 2021 ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure; ESC: Sophia Antipolis, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Cintra, R.M.; Nogueira, A.C.; Bonilha, I.; Luchiari, B.M.; Coelho-Filho, O.R.; Coelho, O.R.; Schwartzmann, P.; Muscellie, E.; Nadruz, W.; Carvalho, L.S.F.; et al. Glucose-Lowering Drugs and Hospitalization for Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Additive-Effects Network Meta-Analysis with More Than 500 000 Patient-Years. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 3060–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.L.; Roddick, A.J.; Aghar-Jaffar, R.; Shun-Shin, M.J.; Francis, D.; Oliver, N.; Meeran, K. Association Between Use of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors, Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Agonists, and Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors with All-Cause Mortality in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA 2018, 319, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlay, S.M.; Givertz, M.M.; Aguilar, D.; Allen, L.A.; Chan, M.; Desai, A.S.; Deswal, A.; Dickson, V.V.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Lekavich, C.L.; et al. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Heart Failure: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association and the Heart Failure Society of America: This Statement Does Not Represent an Update of the 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA Heart Failure Guideline Update. Circulation 2019, 140, e294–e324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halabi, A.; Sen, J.; Huynh, Q.; Marwick, T.H. Metformin Treatment in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Regression Analysis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Effect of intensive blood-glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34). Lancet 1998, 352, 854–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, S.; Ramachandra, C.J.A.; Ja, K.M.M.; Yap, J.; Shim, W.; Wei, L.; Hausenloy, D.J. Mechanisms Underlying Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: From Pathophysiology to Novel Therapeutic Targets. Cond. Med. 2020, 3, 82. [Google Scholar]
- Kuan, W.; Beavers, C.J.; Guglin, M.E. Still Sour about Lactic Acidosis Years Later: Role of Metformin in Heart Failure. Heart Fail. Rev. 2018, 23, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurich, D.T.; Majumdar, S.R.; Mcalister, F.A.; Tsuyuki, R.T. Improved Clinical Outcomes Associated with Metformin in Patients with Diabetes and Heart Failure. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 2345–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, C.; Søgaard, P.; Hoffmann, S.; Hansen, P.R.; Vaag, A.; Major-Pedersen, A.; Hansen, T.F.; Bech, J.; Køber, L.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; et al. Metformin Is Associated with Improved Left Ventricular Diastolic Function Measured by Tissue Doppler Imaging in Patients with Diabetes. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 163, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, M.; Al-Talabany, S.; McKinnie, A.; Mordi, I.R.; Singh, J.S.S.; Gandy, S.J.; Baig, F.; Hussain, M.S.; Bhalraam, U.; Khan, F.; et al. A Randomized Controlled Trial of Metformin on Left Ventricular Hypertrophy in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease without Diabetes: The MET-REMODEL Trial. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 3409–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, M.J.; Diamantidis, C.J.; McDuffie, J.R.; Cameron, C.B.; Stanifer, J.W.; Mock, C.K.; Wang, X.; Tang, S.; Nagi, A.; Kosinski, A.S.; et al. Clinical Outcomes of Metformin Use in Populations with Chronic Kidney Disease, Congestive Heart Failure, or Chronic Liver Disease: A Systematic Review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2017, 166, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krentz, A.J.; Bailey, C.J. Oral Antidiabetic Agents: Current Role in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Drugs 2005, 65, 385–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, A.; Shetty, S.; Cai, B.; D’Souza, A.O. Hypoglycemia Incidence Rates and Associated Health Care Costs in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treated with Second-Line Linagliptin or Sulfonylurea after Metformin Monotherapy. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2016, 22, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sola, D.; Rossi, L.; Schianca, G.P.C.; Maffioli, P.; Bigliocca, M.; Mella, R.; Corlianò, F.; Fra, G.P.; Bartoli, E.; Derosa, G.; et al. State of the Art Paper Sulfonylureas and Their Use in Clinical Practice. Arch. Med. Sci. 2015, 4, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeller, M.; Danchin, N.; Simon, D.; Vahanian, A.; Lorgis, L.; Cottin, Y.; Berland, J.; Gueret, P.; Wyart, P.; Deturck, R.; et al. Impact of Type of Preadmission Sulfonylureas on Mortality and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Diabetic Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 4993–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douros, A.; Yin, H.; Yu, O.H.Y.; Filion, K.B.; Azoulay, L.; Suissa, S. Pharmacologic Differences of Sulfonylureas and the Risk of Adverse Cardiovascular and Hypoglycemic Events. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 1506–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, S.H.; Lee, J.; Choi, S.; Vandermeer, B.; Abdelmoneim, A.S.; Featherstone, T.R. Mortality Risk among Sulfonylureas: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.-M.; Lin, M.-S.; Tsai, C.-H.; Huang, C.-L.; Chang, N.-C. Effects of Sulfonylureas on Left Ventricular Mass in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2007, 292, H608–H613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ADVANCE Collaborative Group. Intensive Blood Glucose Control and Vascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2560–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAlister, F.A.; Eurich, D.T.; Majumdar, S.R.; Johnson, J.A. The Risk of Heart Failure in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Treated with Oral Agent Monotherapy. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2008, 10, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roumie, C.L.; Min, J.Y.; D’Agostino McGowan, L.; Presley, C.; Grijalva, C.G.; Hackstadt, A.J.; Hung, A.M.; Greevy, R.A.; Elasy, T.; Griffin, M.R.; et al. Comparative Safety of Sulfonylurea and Metformin Monotherapy on the Risk of Heart Failure: A Cohort Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e005379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaccaro, O.; Masulli, M.; Nicolucci, A.; Bonora, E.; Del Prato, S.; Maggioni, A.P.; Rivellese, A.A.; Squatrito, S.; Giorda, C.B.; Sesti, G.; et al. Effects on the Incidence of Cardiovascular Events of the Addition of Pioglitazone versus Sulfonylureas in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Inadequately Controlled with Metformin (TOSCA.IT): A Randomised, Multicentre Trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstock, J.; Perkovic, V.; Johansen, O.E.; Cooper, M.E.; Kahn, S.E.; Marx, N.; Alexander, J.H.; Pencina, M.; Toto, R.D.; Wanner, C. Effect of Linagliptin vs Placebo on Major Cardiovascular Events in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes and High Cardiovascular and Renal Risk: The CARMELINA Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2019, 321, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstock, J.; Kahn, S.E.; Johansen, O.E.; Zinman, B.; Espeland, M.A.; Woerle, H.J.; Pfarr, E.; Keller, A.; Mattheus, M.; Baanstra, D.; et al. Effect of Linagliptin vs Glimepiride on Major Adverse Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: The CAROLINA Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2019, 322, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, C.; Olesen, J.B.; Hansen, P.R.; Weeke, P.; Norgaard, M.L.; Jørgensen, C.H.; Lange, T.; Abildstrøm, S.Z.; Schramm, T.K.; Vaag, A.; et al. Metformin Treatment Is Associated with a Low Risk of Mortality in Diabetic Patients with Heart Failure: A Retrospective Nationwide Cohort Study. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 2546–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliadis, F.; Kadoglou, N.; Didangelos, T. Insulin and the Heart. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2011, 93, S86–S91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The ORIGIN Trial Investigators. Basal Insulin and Cardiovascular and Other Outcomes in Dysglycemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pocock, S.J.; Wang, D.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Yusuf, S.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Swedberg, K.B.; Östergren, J.; Michelson, E.L.; Pieper, K.S.; Granger, C.B.; et al. Predictors of Mortality and Morbidity in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure. Eur. Heart J. 2006, 27, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, S.S.; Levy, D.; Vasan, R.S.; Wang, T.J. The Framingham Heart Study and the Epidemiology of Cardiovascular Disease: A Historical Perspective. Lancet 2014, 383, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, L.B.; Mi, X.; Mentz, R.J.; Green, J.B.; Anstrom, K.J.; Hernandez, A.F.; Curtis, L.H. Management of Newly Treated Diabetes in Medicare Beneficiaries with and without Heart Failure. Clin. Cardiol. 2017, 40, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murcia, A.M.; Hennekens, C.H.; Lamas, G.A.; Jiménez-Navarro, M.; Rouleau, J.L.; Flaker, G.C.; Goldman, S.; Skali, H.; Braunwald, E.; Pfeffer, M.A.; et al. Impact of Diabetes on Mortality in Patients with Myocardial Infarction and Left Ventricular Dysfunction. Arch. Intern. Med. 2004, 164, 2273–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2019 ESC Guidelines on Diabetes, Pre-Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Diseases Developed in Collaboration with the EASD: The Task Force for Diabetes, Pre-Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Rev. Esp. Cardiol. Engl. Ed. 2020, 73, 404.
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Inzucchi, S.; Abdul-Ghani, M.; Nissen, S.E. Pioglitazone: The Forgotten, Cost-Effective Cardioprotective Drug for Type 2 Diabetes. Diab. Vasc. Dis. Res. 2019, 16, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yki-Järvinen, H. Thiazolidinediones. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1106–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissen, S.E.; Wolski, K. Effect of Rosiglitazone on the Risk of Myocardial Infarction and Death from Cardiovascular Causes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 2457–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieffer, C.M.; Robertson, A.S. Impact of FDA-Required Cardiovascular Outcome Trials on Type 2 Diabetes Clinical Study Initiation From 2008 to 2017. Ther. Innov. Regul. Sci. 2019, 54, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Home, P.D.; Pocock, S.J.; Beck-Nielsen, H.; Curtis, P.S.; Gomis, R.; Hanefeld, M.; Jones, N.P.; Komajda, M.; McMurray, J.J. Rosiglitazone Evaluated for Cardiovascular Outcomes in Oral Agent Combination Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes (RECORD): A Multicentre, Randomised, Open-Label Trial. Lancet 2009, 373, 2125–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dormandy, J.A.; Charbonnel, B.; Eckland, D.J.A.; Erdmann, E.; Massi-Benedetti, M.; Moules, I.K.; Skene, A.M.; Tan, M.H.; Lefèbvre, P.J.; Murray, G.D.; et al. Secondary Prevention of Macrovascular Events in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in the PROactive Study (PROspective pioglitAzone Clinical Trial In macroVascular Events): A Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet 2005, 366, 1279–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdmann, E.; Charbonnel, B.; Wilcox, R.G.; Skene, A.M.; Massi-Benedetti, M.; Yates, J.; Tan, M.; Spanheimer, R.; Standl, E.; Dormandy, J.A.; et al. Pioglitazone Use and Heart Failure in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Preexisting Cardiovascular Disease. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 2773–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lago, R.M.; Singh, P.P.; Nesto, R.W. Congestive Heart Failure and Cardiovascular Death in Patients with Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes given Thiazolidinediones: A Meta-Analysis of Randomised Clinical Trials. Lancet 2007, 370, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naka, K.K.; Pappas, K.; Papathanassiou, K.; Papamichael, N.D.; Kazakos, N.; Kanioglou, C.; Makriyiannis, D.; Katsouras, C.S.; Liveris, K.; Tsatsoulis, A.; et al. Lack of Effects of Pioglitazone on Cardiac Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Evidence of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction: A Tissue Doppler Imaging Study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2010, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, T.D.; Miller, A.B.; Elkayam, U.; Bhattacharya, M.; Perez, A. Pioglitazone and Heart Failure: Results from a Controlled Study in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Systolic Dysfunction. J. Card. Fail. 2008, 14, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, A.D.; Park, C.; March, K.; Coady, E.; Khir, A.; Chaturvedi, N.; Thom, S.A.M. A Randomized Placebo Controlled Double Blind Crossover Study of Pioglitazone on Left Ventricular Diastolic Function in Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 167, 1329–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, G.D.; Solis-Herrera, C.; Molina-Wilkins, M.; Martinez, S.; Merovci, A.; Cersosimo, E.; Chilton, R.J.; Iozzo, P.; Gastaldelli, A.; Abdul-Ghani, M.; et al. Pioglitazone Improves Left Ventricular Diastolic Function in Subjects with Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 1530–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attaran, F.; Emami, S.; Sohrabi, M.; Malek, M.; Ajdarkosh, H.; Khoonsari, M.; Ismail-Beigi, F.; Khamseh, M.E. Effect of Empagliflozin and Pioglitazone on Left Ventricular Function in Patients with Type Two Diabetes and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease without Established Cardiovascular Disease: A Randomized Single-Blind Clinical Trial. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023, 23, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Tian, R.; Zhang, X.-J.; Cai, J.; She, Z.-G.; Li, H. Effects of Treatment of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease on Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 9, 1120085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, J.E.; Drucker, D.J. Pharmacology, Physiology, and Mechanisms of Incretin Hormone Action. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 819–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inzucchi, S.E.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Buse, J.B.; Diamant, M.; Ferrannini, E.; Nauck, M.; Peters, A.L.; Tsapas, A.; Wender, R.; Matthews, D.R.; et al. Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes: A Patient-Centered Approach. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 1364–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scirica, B.M.; Bhatt, D.L.; Braunwald, E.; Steg, P.G.; Davidson, J.; Hirshberg, B.; Ohman, P.; Frederich, R.; Wiviott, S.D.; Hoffman, E.B.; et al. Saxagliptin and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3599–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, P.; Ong, J.P.; Garg, V.; Altaha, M.; Bello, O.; Singal, S.R.; Verma, S.; Yan, A.T.; Connelly, K.A. The Effects of Saxagliptin on Cardiac Structure and Function Using Cardiac MRI (SCARF). Acta Diabetol. 2021, 58, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, J.B.; Bethel, M.A.; Armstrong, P.W.; Buse, J.B.; Engel, S.S.; Garg, J.; Josse, R.; Kaufman, K.D.; Koglin, J.; Korn, S.; et al. Effect of Sitagliptin on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, W.B.; Cannon, C.P.; Heller, S.R.; Nissen, S.E.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Bakris, G.L.; Perez, A.T.; Fleck, P.R.; Mehta, C.R.; Kupfer, S.; et al. Alogliptin after Acute Coronary Syndrome in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patoulias, D.I.; Boulmpou, A.; Teperikidis, E.; Katsimardou, A.; Siskos, F.; Doumas, M.; Papadopoulos, C.E.; Vassilikos, V. Cardiovascular Efficacy and Safety of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors: A Meta-Analysis of Cardiovascular Outcome Trials. World J. Cardiol. 2021, 13, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enzan, N.; Matsushima, S.; Kaku, H.; Tohyama, T.; Nagata, T.; Ide, T.; Tsutsui, H. Beneficial Effects of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors on Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction and Diabetes. JACC Asia 2023, 3, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Tanaka, A.; Kusunose, K.; Amano, R.; Matsuhisa, M.; Daida, H.; Ito, M.; Tsutsui, H.; Nanasato, M.; Kamiya, H.; et al. Effect of Sitagliptin on the Echocardiographic Parameters of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Subgroup Analysis of the PROLOGUE Study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2017, 16, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, L.M.; Kydd, A.C.; Read, P.A.; Ring, L.S.; Bond, S.J.; Hoole, S.P.; Dutka, D.P. Chronic Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibition with Sitagliptin Is Associated with Sustained Protection against Ischemic Left Ventricular Dysfunction in a Pilot Study of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Coronary Artery Disease. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 7, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cioffi, G.; Giorda, C.B.; Lucci, D.; Nada, E.; Ognibeni, F.; Mancusi, C.; Latini, R.; Maggioni, A.P. Effects of Linagliptin on Left Ventricular DYsfunction in Patients with Type 2 DiAbetes and Concentric Left Ventricular Geometry: Results of the DYDA 2 Trial. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2021, 28, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurray, J.J.V.; Ponikowski, P.; Bolli, G.B.; Lukashevich, V.; Kozlovski, P.; Kothny, W.; Lewsey, J.D.; Krum, H. Effects of Vildagliptin on Ventricular Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Heart Failure: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. JACC Heart Fail. 2018, 6, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thoma, R.; Löffler, B.; Stihle, M.; Huber, W.; Ruf, A.; Hennig, M. Structural Basis of Proline-Specific Exopeptidase Activity as Observed in Human Dipeptidyl Pepti-Dase-IV. Structure 2003, 11, 947–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.K.; Hackett, T.A.; Galli, A.; Flynn, C.R. GLP-1: Molecular Mechanisms and Outcomes of a Complex Signaling System. Neurochem. Int. 2019, 128, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Kapoor, N. Contemporary Classification of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists (GLP1RAs). Diabetes Ther. 2021, 12, 2133–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeffer, M.A.; Claggett, B.; Diaz, R.; Dickstein, K.; Gerstein, H.C.; Køber, L.V.; Lawson, F.C.; Ping, L.; Wei, X.; Lewis, E.F. Lixisenatide in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Acute Coronary Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2247–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, S.L.; Rørth, R.; Jhund, P.S.; Docherty, K.F.; Sattar, N.; Preiss, D.; Køber, L.; Petrie, M.C.; McMurray, J.J.V. Cardiovascular, Mortality, and Kidney Outcomes with GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cardiovascular Outcome Trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves, J.S.; Vasques-Nóvoa, F.; Borges-Canha, M.; Leite, A.R.; Sharma, A.; Carvalho, D.; Packer, M.; Zannad, F.; Leite-Moreira, A.; Ferreira, J.P.; et al. Risk of Adverse Events with Liraglutide in Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Post Hoc Analysis of the FIGHT Trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brønden, A.; Christensen, M.B.; Glintborg, D.; Snorgaard, O.; Kofoed-Enevoldsen, A.; Madsen, G.K.; Toft, K.; Kristensen, J.K.; Højlund, K.; Hansen, T.K.; et al. Effects of DPP-4 Inhibitors, GLP-1 Receptor Agonists, SGLT-2 Inhibitors and Sulphonylureas on Mortality, Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes: A Network Meta-analyses-driven Approach. Diabet. Med. 2023, 40, e15157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husain, M.; Consoli, A.; De Remigis, A.; Pettersson Meyer, A.S.; Rasmussen, S.; Bain, S. Semaglutide Reduces Cardiovascular Events Regardless of Metformin Use: A Post Hoc Subgroup Analysis of SUSTAIN 6 and PIONEER 6. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsapas, A.; Karagiannis, T.; Avgerinos, I.; Liakos, A.; Bekiari, E. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists for Cardiovascular Outcomes with and without Metformin. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cardiovascular Outcomes Trials. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 177, 108921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marso, S.P.; Baeres, F.M.M.; Bain, S.C.; Goldman, B.; Husain, M.; Nauck, M.A.; Poulter, N.R.; Pratley, R.E.; Thomsen, A.B.; Buse, J.B.; et al. Effects of Liraglutide on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Diabetes with or without Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 1128–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marso, S.P.; Bain, S.C.; Consoli, A.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Jódar, E.; Leiter, L.A.; Lingvay, I.; Rosenstock, J.; Seufert, J.; Warren, M.L.; et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerstein, H.C.; Colhoun, H.M.; Dagenais, G.R.; Diaz, R.; Lakshmanan, M.; Pais, P.; Probstfield, J.; Riesmeyer, J.S.; Riddle, M.C.; Rydén, L.; et al. Dulaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes (REWIND): A Double-Blind, Randomised Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstein, H.C.; Sattar, N.; Rosenstock, J.; Ramasundarahettige, C.; Pratley, R.; Lopes, R.D.; Lam, C.S.P.; Khurmi, N.S.; Heenan, L.; Del Prato, S.; et al. Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes with Efpeglenatide in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 896–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holman, R.R.; Bethel, M.A.; Mentz, R.J.; Thompson, V.P.; Lokhnygina, Y.; Buse, J.B.; Chan, J.C.; Choi, J.; Gustavson, S.M.; Iqbal, N.; et al. Effects of Once-Weekly Exenatide on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1228–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, A.F.; Green, J.B.; Janmohamed, S.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Granger, C.B.; Jones, N.P.; Leiter, L.A.; Rosenberg, A.E.; Sigmon, K.N.; Somerville, M.C.; et al. Albiglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease (Harmony Outcomes): A Double-Blind, Randomised Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet 2018, 392, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husain, M.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Donsmark, M.; Dungan, K.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Franco, D.R.; Jeppesen, O.K.; Lingvay, I.; Mosenzon, O.; Pedersen, S.D.; et al. Oral Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athithan, L.; Gulsin, G.S.; McCann, G.P.; Levelt, E. Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: Pathophysiology, Theories and Evidence to Date. World J. Diabetes 2019, 10, 490–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, J.P.; Sharma, A.; Vasques-Nóvoa, F.; Angélico-Gonçalves, A.; Leite, A.R.; Borges-Canha, M.; Carvalho, D.; Packer, M.; Zannad, F.; Leite-Moreira, A.; et al. Albiglutide in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Post-hoc Analysis from Harmony Outcomes. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2022, 24, 1792–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, N.; Lee, M.M.Y.; Kristensen, S.L.; Branch, K.R.H.; Del Prato, S.; Khurmi, N.S.; Lam, C.S.P.; Lopes, R.D.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Pratley, R.E.; et al. Cardiovascular, Mortality, and Kidney Outcomes with GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalzo, R.L.; Moreau, K.L.; Ozemek, C.; Herlache, L.; McMillin, S.; Gilligan, S.; Huebschmann, A.G.; Bauer, T.A.; Dorosz, J.; Reusch, J.E.B.; et al. Exenatide Improves Diastolic Function and Attenuates Arterial Stiffness but Does Not Alter Exercise Capacity in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2017, 31, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akyay, O.Z.; Sahin, T.; Cakmak, Y.; Tarkun, I.; Selek, A.; Canturk, Z.; Cetinarslan, B.; Karakaya, D. Comparison of the Effects of Exenatide and Insulin Glargine on Right and Left Ventricular Myocardial Deformation as Shown by 2D-Speckle-Tracking Echocardiograms. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2022, 25, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizino, M.B.; Jazet, I.M.; Westenberg, J.J.M.; van Eyk, H.J.; Paiman, E.H.M.; Smit, J.W.A.; Lamb, H.J. Effect of Liraglutide on Cardiac Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 18, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ida, S.; Kaneko, R.; Imataka, K.; Okubo, K.; Shirakura, Y.; Azuma, K.; Fujiwara, R.; Takahashi, H.; Murata, K. Effects of Oral Antidiabetic Drugs and Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists on Left Ventricular Diastolic Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Heart Fail. Rev. 2021, 26, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huixing, L.; Di, F.; Daoquan, P. Effect of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists on Prognosis of Heart Failure and Cardiac Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Clin. Ther. 2023, 45, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margulies, K.B.; Hernandez, A.F.; Redfield, M.M.; Givertz, M.M.; Oliveira, G.H.; Cole, R.; Mann, D.L.; Whellan, D.J.; Kiernan, M.S.; Felker, G.M.; et al. Effects of Liraglutide on Clinical Stability Among Patients with Advanced Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2016, 316, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorsal, A.; Kistorp, C.; Holmager, P.; Tougaard, R.S.; Nielsen, R.; Hänselmann, A.; Nilsson, B.; Møller, J.E.; Hjort, J.; Rasmussen, J.; et al. Effect of Liraglutide, a Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Analogue, on Left Ventricular Function in Stable Chronic Heart Failure Patients with and without Diabetes (LIVE)-a Multicentre, Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017, 19, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.S.; Fonarow, G.C.; McGuire, D.K.; Hernandez, A.F.; Vaduganathan, M.; Rosenstock, J.; Handelsman, Y.; Verma, S.; Anker, S.D.; McMurray, J.J.V.; et al. Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists and Heart Failure: The Need for Further Evidence Generation and Practice Guidelines Optimization. Circulation 2020, 142, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Underwood, C.R.; Garibay, P.; Knudsen, L.B.; Hastrup, S.; Peters, G.H.; Rudolph, R.; Reedtz-Runge, S.C. Structure of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 in Complex with the Extracellular Domain of the Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca-Correa, J.I.; Correa-Rotter, R. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors Mechanisms of Action: A Review. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 777861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinman, B.; Wanner, C.; Lachin, J.M.; Fitchett, D.; Bluhmki, E.; Hantel, S.; Mattheus, M.; Devins, T.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J.; et al. Empagliflozin, Cardiovascular Outcomes, and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, B.; Perkovic, V.; Mahaffey, K.W.; De Zeeuw, D.; Fulcher, G.; Erondu, N.; Shaw, W.; Law, G.; Desai, M.; Matthews, D.R.; et al. Canagliflozin and Cardiovascular and Renal Events in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 644–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiviott, S.D.; Raz, I.; Bonaca, M.P.; Mosenzon, O.; Kato, E.T.; Cahn, A.; Silverman, M.G.; Zelniker, T.A.; Kuder, J.F.; Murphy, S.A.; et al. Dapagliflozin and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilding, J.P.H.; Evans, M.; Fernando, K.; Gorriz, J.L.; Cebrian, A.; Diggle, J.; Hicks, D.; James, J.; Newland-Jones, P.; Ali, A.; et al. The Place and Value of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors in the Evolving Treatment Paradigm for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Narrative Review. Diabetes Ther. 2022, 13, 847–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, C.P.; Pratley, R.; Dagogo-Jack, S.; Mancuso, J.; Huyck, S.; Masiukiewicz, U.; Charbonnel, B.; Frederich, R.; Gallo, S.; Cosentino, F.; et al. Cardiovascular Outcomes with Ertugliflozin in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1425–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavender, M.A.; Norhammar, A.; Birkeland, K.I.; Jørgensen, M.E.; Wilding, J.P.; Khunti, K.; Fu, A.Z.; Bodegård, J.; Blak, B.T.; Wittbrodt, E.; et al. SGLT-2 Inhibitors and Cardiovascular Risk. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 2497–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurray, J.J.V.; Solomon, S.D.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Køber, L.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Martinez, F.A.; Ponikowski, P.; Sabatine, M.S.; Anand, I.S.; Bělohlávek, J.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1995–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, M.; Anker, S.D.; Butler, J.; Filippatos, G.; Pocock, S.J.; Carson, P.; Januzzi, J.; Verma, S.; Tsutsui, H.; Brueckmann, M.; et al. Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes with Empagliflozin in Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1413–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, D.L.; Szarek, M.; Steg, P.G.; Cannon, C.P.; Leiter, L.A.; McGuire, D.K.; Lewis, J.B.; Riddle, M.C.; Voors, A.A.; Metra, M.; et al. Sotagliflozin in Patients with Diabetes and Recent Worsening Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anker, S.D.; Butler, J.; Filippatos, G.; Ferreira, J.P.; Bocchi, E.; Böhm, M.; Brunner-La Rocca, H.-P.; Choi, D.-J.; Chopra, V.; Chuquiure-Valenzuela, E.; et al. Empagliflozin in Heart Failure with a Preserved Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, S.D.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Claggett, B.; de Boer, R.A.; DeMets, D.; Hernandez, A.F.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Lam, C.S.P.; Martinez, F.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Heart Failure with Mildly Reduced or Preserved Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkovic, V.; Jardine, M.J.; Neal, B.; Bompoint, S.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Charytan, D.M.; Edwards, R.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; Bull, S.; et al. Canagliflozin and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes and Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, D.L.; Szarek, M.; Pitt, B.; Cannon, C.P.; Leiter, L.A.; McGuire, D.K.; Lewis, J.B.; Riddle, M.C.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Kosiborod, M.N.; et al. Sotagliflozin in Patients with Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Stefánsson, B.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Chertow, G.M.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.-F.; Mann, J.F.E.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Lindberg, M.; Rossing, P.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damman, K.; Beusekamp, J.C.; Boorsma, E.M.; Swart, H.P.; Smilde, T.D.J.; Elvan, A.; Van Eck, J.W.M.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Voors, A.A. Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled, Multicentre Pilot Study on the Effects of Empagliflozin on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Acute Decompensated Heart Failure (EMPA-RESPONSE-AHF). Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biegus, J.; Voors, A.A.; Collins, S.P.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Teerlink, J.R.; Angermann, C.E.; Tromp, J.; Ferreira, J.P.; Nassif, M.E.; Psotka, M.A.; et al. Impact of Empagliflozin on Decongestion in Acute Heart Failure: The EMPULSE Trial. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahinya, M.; Khan, Z. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitor Therapy for the Primary and Secondary Prevention of Heart Failure in Patients with and without Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e37388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kommu, S. The Role of SGLT2 Inhibitors on Heart Failure Outcomes in Nondiabetic Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2024, 83, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, A.K.; Dhingra, N.K.; Hibino, M.; Gupta, V.; Verma, S. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors in Heart Failure with Reduced or Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Meta-Analysis. ESC Heart Fail. 2022, 9, 942–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Y.; Madhavan, M.V.; Stone, G.W.; Francis, D.P.; Makkar, R.; Bhatt, D.L.; Howard, J.P. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors in Patients with Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials. Eur. Heart J. Qual. Care Clin. Outcomes 2022, 8, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, M.; Pal, R.; Nair, K.; Mukhopadhyay, S. SGLT2 Inhibitors and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Heart Failure with Mildly Reduced and Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Indian Heart J. 2023, 75, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.-I. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors from Natural Products: Discovery of Next-Generation Antihyperglycemic Agents. Molecules 2016, 21, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.M.Y.; Brooksbank, K.J.M.; Wetherall, K.; Mangion, K.; Roditi, G.; Campbell, R.T.; Berry, C.; Chong, V.; Coyle, L.; Docherty, K.F.; et al. Effect of Empagliflozin on Left Ventricular Volumes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes, or Prediabetes, and Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction (SUGAR-DM-HF). Circulation 2021, 143, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prochaska, J.H.; Jünger, C.; Schulz, A.; Arnold, N.; Müller, F.; Heidorn, M.W.; Baumkötter, R.; Zahn, D.; Koeck, T.; Tröbs, S.-O.; et al. Effects of Empagliflozin on Left Ventricular Diastolic Function in Addition to Usual Care in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus-Results from the Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled EmDia Trial. Clin. Res. Cardiol. Off. J. Ger. Card. Soc. 2023, 112, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.J.M.; Gandy, S.; McCrimmon, R.; Houston, J.G.; Struthers, A.D.; Lang, C.C. A Randomized Controlled Trial of Dapagliflozin on Left Ventricular Hypertrophy in People with Type Two Diabetes: The DAPA-LVH Trial. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 3421–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.S.S.; Mordi, I.R.; Vickneson, K.; Fathi, A.; Donnan, P.T.; Mohan, M.; Choy, A.M.J.; Gandy, S.; George, J.; Khan, F.; et al. Dapagliflozin Versus Placebo on Left Ventricular Remodeling in Patients with Diabetes and Heart Failure: The REFORM Trial. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1356–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, C.F.; Teo, Y.H.; Teo, Y.N.; Syn, N.L.; See, R.M.; Leong, S.; Yip, A.S.Y.; Ong, Z.X.; Lee, C.-H.; Chan, M.Y.-Y.; et al. Effects of Sodium/Glucose Cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors on Cardiac Imaging Parameters: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 30, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carluccio, E.; Biagioli, P.; Reboldi, G.; Mengoni, A.; Lauciello, R.; Zuchi, C.; D’Addario, S.; Bardelli, G.; Ambrosio, G. Left Ventricular Remodeling Response to SGLT2 Inhibitors in Heart Failure: An Updated Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Studies. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Singh, R. Metabolic and Cardiovascular Benefits with Combination Therapy of SGLT-2 Inhibitors and GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Type 2 Diabetes. World J. Cardiol. 2022, 14, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clegg, L.E.; Penland, R.C.; Bachina, S.; Boulton, D.W.; Thuresson, M.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Gustavson, S.; Sjöström, C.D.; Ruggles, J.A.; Hernandez, A.F.; et al. Effects of Exenatide and Open-Label SGLT2 Inhibitor Treatment, given in Parallel or Sequentially, on Mortality and Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes: Insights from the EXSCEL Trial. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019, 18, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, D.R.; Essa, H.; Austin, P.; Preston, F.; Kargbo, I.; Ibarburu, G.H.; Ghuman, R.; Cuthbertson, D.J.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Alam, U.; et al. All-cause Mortality and Cardiovascular Outcomes with sodium-glucose Co-transporter 2 Inhibitors, Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and with Combination Therapy in People with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 2897–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikonomidis, I.; Pavlidis, G.; Thymis, J.; Birba, D.; Kalogeris, A.; Kousathana, F.; Kountouri, A.; Balampanis, K.; Parissis, J.; Andreadou, I.; et al. Effects of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists, Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors, and Their Combination on Endothelial Glycocalyx, Arterial Function, and Myocardial Work Index in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus after 12-Month Treatment. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e015716. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, A.K.; Carr, M.J.; Kontopantelis, E.; Leelarathna, L.; Thabit, H.; Emsley, R.; Buchan, I.; Mamas, M.A.; van Staa, T.P.; Sattar, N.; et al. Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular and Heart Failure Events with SGLT2 Inhibitors, GLP-1 Receptor Agonists, and Their Combination in Type 2. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belli, M.; Barone, L.; Bellia, A.; Sergi, D.; Lecis, D.; Prandi, F.R.; Milite, M.; Galluccio, C.; Muscoli, S.; Romeo, F.; et al. Treatment of HFpEF beyond the SGLT2-Is: Does the Addition of GLP-1 RA Improve Cardiometabolic Risk and Outcomes in Diabetic Patients? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gourdy, P.; Darmon, P.; Dievart, F.; Halimi, J.-M.; Guerci, B. Combining Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists (GLP-1RAs) and Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors (SGLT2is) in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM). Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidenreich, P.A.; Bozkurt, B.; Aguilar, D.; Allen, L.A.; Byun, J.J.; Colvin, M.M.; Deswal, A.; Drazner, M.H.; Dunlay, S.M.; Evers, L.R.; et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2022, 79, e263–e421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Study | Year | Drug | N | Baseline HF (%) | Baseline CVD (%) | Median Follow-up (Years) | HF Hospitalization Risk [HR (95%CI), p Value] | CV Death Risk [HR (95%CI), p Value] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ELIXA [73] | 2015 | Lixisenatide | 6068 | 22 | 100 | 2.1 | 0.96 (0.75–1.23) | 0.98 (0.78 −1.22) |
| LEADER [79] | 2016 | Liraglutide | 9340 | 17.8 | 81 | 3.8 | 0.87 (0.73–1.05) | 0.78 (0.66–0.93) |
| SUSTAIN-6 [80] | 2016 | Semaglutide | 3297 | 23.6 | 83 | 2.1 | 1.11 (0.77–1.61) | 0.98 (0.65–1.48) |
| REWIND [81] | 2019 | Dulaglutide | 9901 | 8.6 | 31.5 | 5.4 | 0.93 (0.77-1.12) | 0.91(0.78-1.06) |
| AMPLITUDE-O [82] | 2021 | Efpeglenatide | 4076 | 18.1 | 89.6 | 1.81 | 0.61 (0.38–0.98) | 0.72 (0.50–1.03) |
| EXSCEL [83] | 2017 | Exenatide | 14,752 | 16 | 73.1 | 3.2 | 0.94 (0.78−1.13) | 0.88 (0.76−1.02) |
| HARMONY [84] | 2018 | Albiglutide | 9463 | 20 | 100 | 1.6 | 0.71 (0.53–0.94) | 0.93 (0.73–1.19) |
| PIONEER-6 [85] | 2019 | Semaglutide | 3183 | NA | 85 | 1.3 | 0.86 (0.48–1.55) | 0.49 (0.27–0.92) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nikolaidou, A.; Ventoulis, I.; Karakoulidis, G.; Anastasiou, V.; Daios, S.; Papadopoulos, S.-F.; Didagelos, M.; Parissis, J.; Karamitsos, T.; Kotsa, K.; et al. Hypoglycemic Drugs in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus and Heart Failure: A Narrative Review. Medicina 2024, 60, 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60060912
Nikolaidou A, Ventoulis I, Karakoulidis G, Anastasiou V, Daios S, Papadopoulos S-F, Didagelos M, Parissis J, Karamitsos T, Kotsa K, et al. Hypoglycemic Drugs in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus and Heart Failure: A Narrative Review. Medicina. 2024; 60(6):912. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60060912
Chicago/Turabian StyleNikolaidou, Anastasia, Ioannis Ventoulis, Georgios Karakoulidis, Vasileios Anastasiou, Stylianos Daios, Spyridon-Filippos Papadopoulos, Matthaios Didagelos, John Parissis, Theodoros Karamitsos, Kalliopi Kotsa, and et al. 2024. "Hypoglycemic Drugs in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus and Heart Failure: A Narrative Review" Medicina 60, no. 6: 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60060912
APA StyleNikolaidou, A., Ventoulis, I., Karakoulidis, G., Anastasiou, V., Daios, S., Papadopoulos, S.-F., Didagelos, M., Parissis, J., Karamitsos, T., Kotsa, K., Ziakas, A., & Kamperidis, V. (2024). Hypoglycemic Drugs in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus and Heart Failure: A Narrative Review. Medicina, 60(6), 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60060912







