Novel Immunohistochemical and Morphological Approaches in a Retrospective Study of Post-Mortem Myocarditis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Immunohistochemistry Analysis in Myocarditis
1.2. Myocarditis in Clinical Autopsies and Forensic Practice
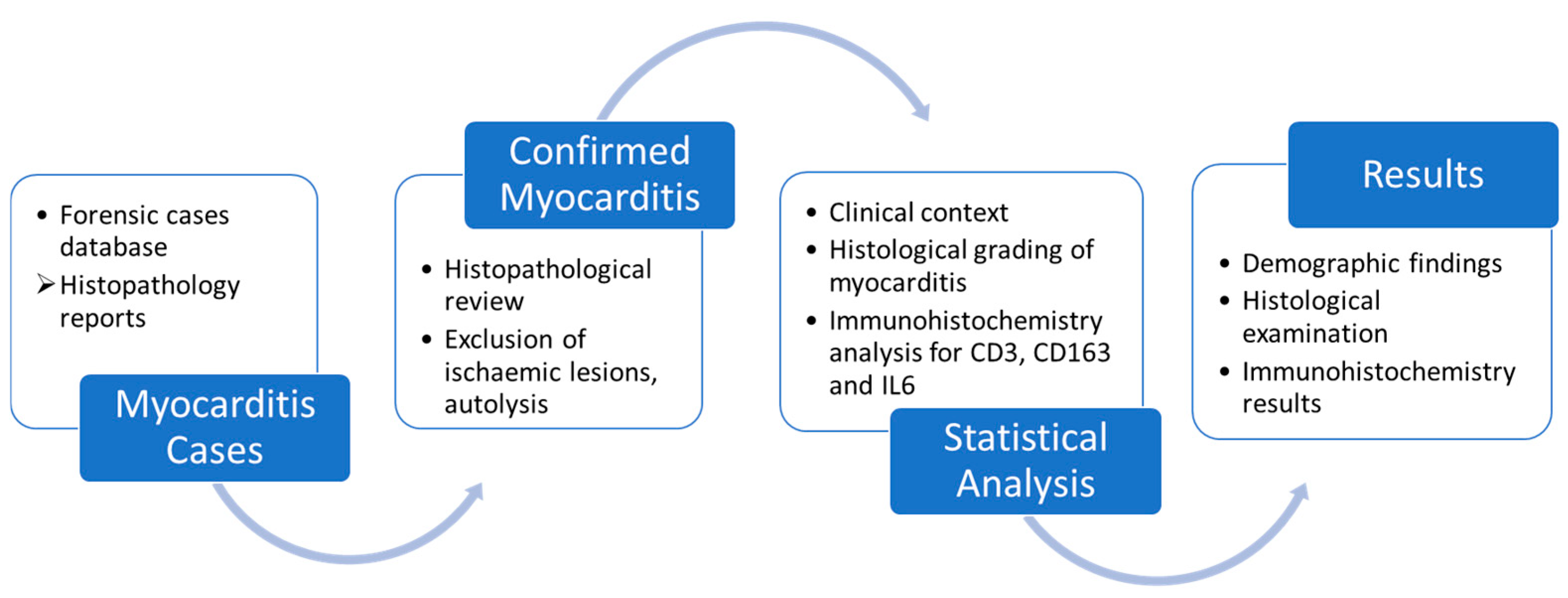
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Findings
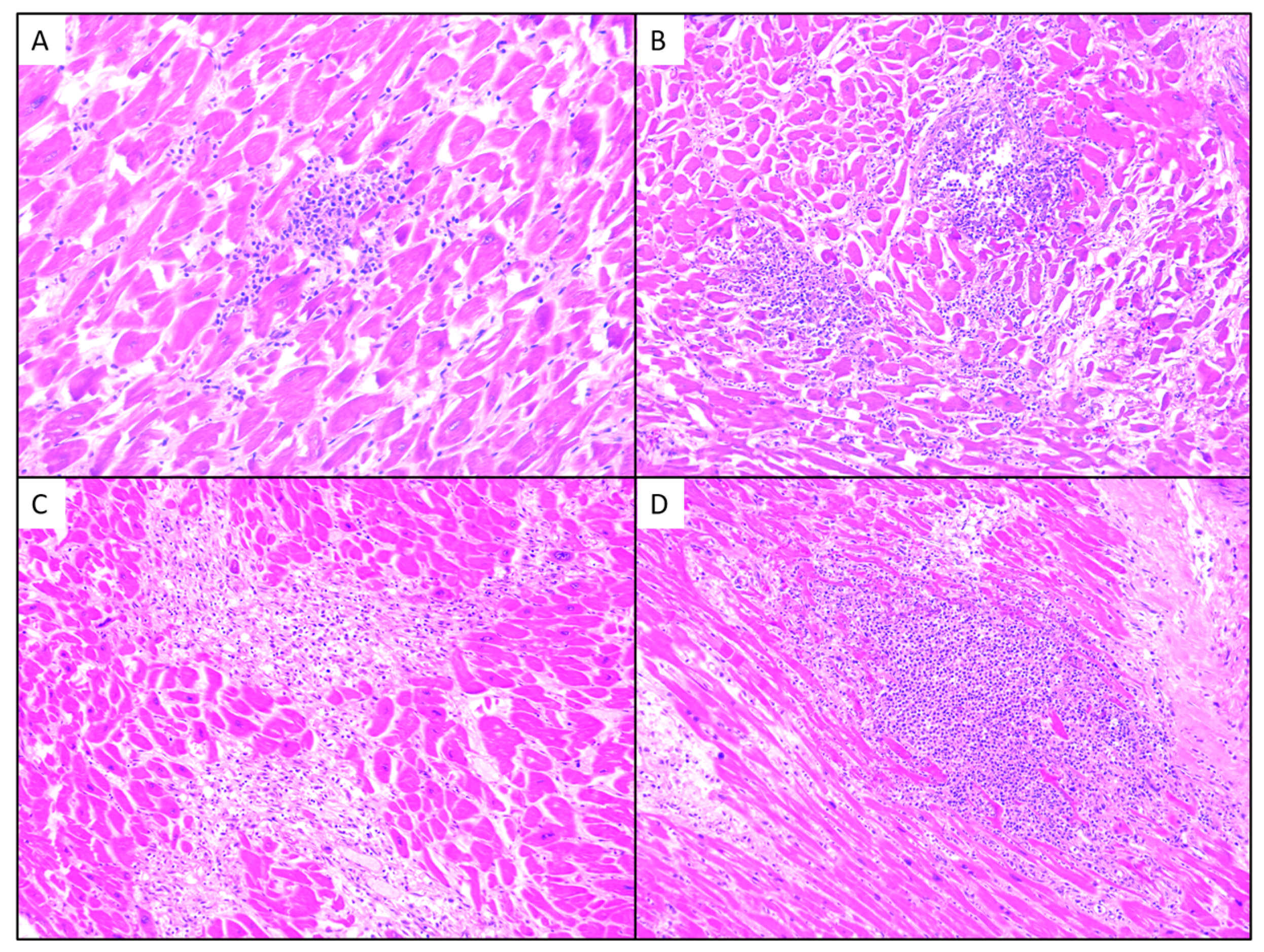
3.2. Histological Examination
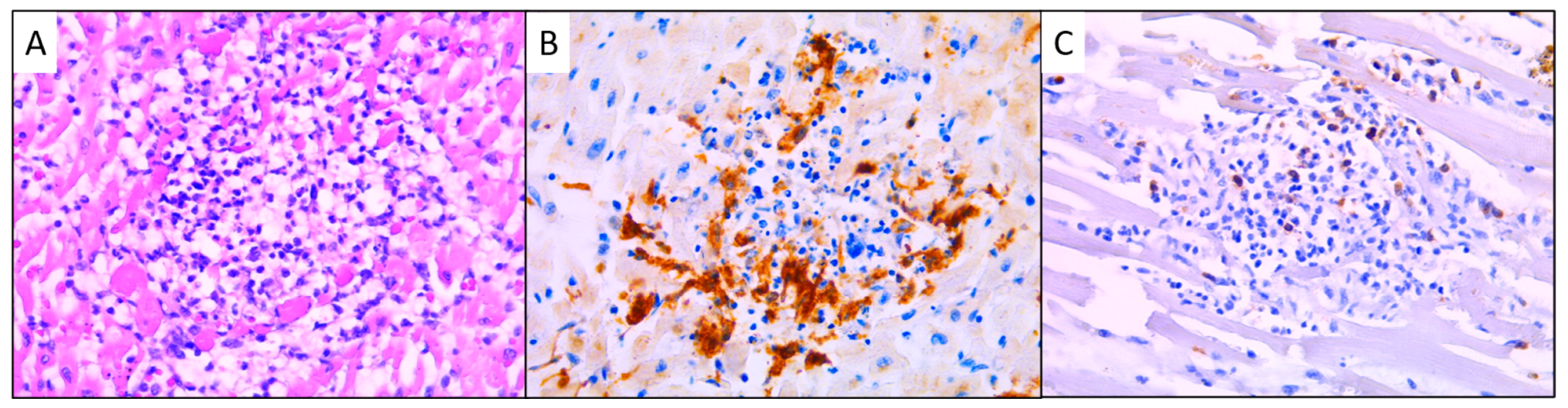
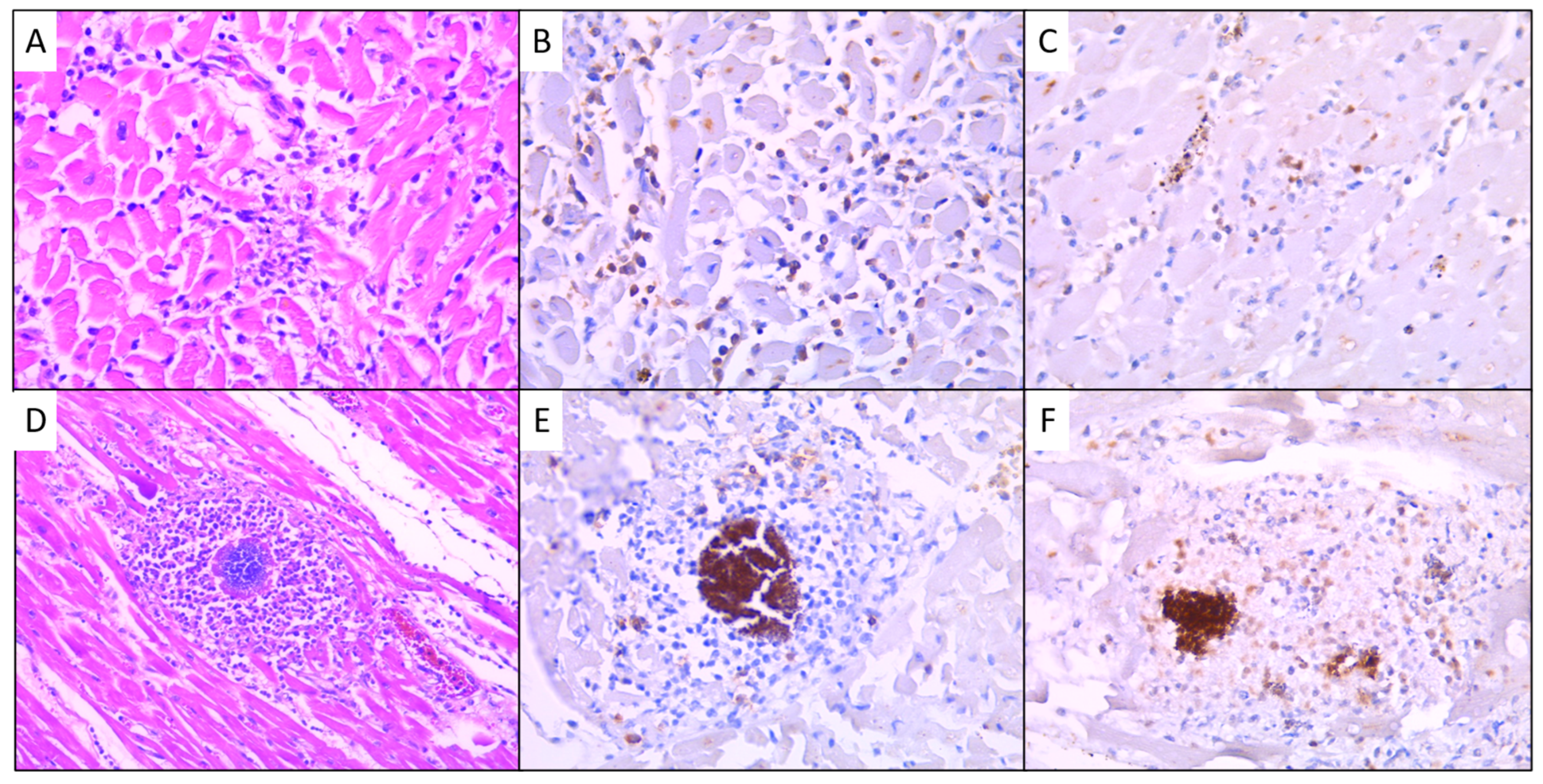
3.3. Immunohistochemical Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Caforio, A.L.; Calabrese, F.; Angelini, A.; Tona, F.; Vinci, A.; Bottaro, S.; Ramondo, A.; Carturan, E.; Iliceto, S.; Thiene, G.; et al. A prospective study of biopsy-proven myocarditis: Prognostic relevance of clinical and aetiopathogenetic features at diagnosis. Eur. Heart J. 2007, 28, 1326–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiene, G.; Bruneval, P.; Veinot, J.; Leone, O. Diagnostic use of the endomyocardial biopsy: A consensus statement. Virchows Arch. 2013, 463, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, L.T.; Baughman, K.L.; Feldman, A.M.; Frustaci, A.; Jessup, M.; Kuhl, U.; Levine, G.N.; Narula, J.; Starling, R.C.; Towbin, J.; et al. The Role of Endomyocardial Biopsy in the Management of Cardiovascular Disease. Circulation 2007, 116, 2216–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aretz, H.T. Myocarditis: The Dallas criteria. Hum. Pathol. 1987, 18, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caforio, A.L.P.; Pankuweit, S.; Arbustini, E.; Basso, C.; Gimeno-Blanes, J.; Felix, S.B.; Fu, M.; Heliö, T.; Heymans, S.; Jahns, R.; et al. Current state of knowledge on aetiology, diagnosis, management, and therapy of myocarditis: A position statement of the European Society of Cardiology Working Group on Myocardial and Pericardial Diseases. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 2636–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschöpe, C.; Ammirati, E.; Bozkurt, B.; Caforio, A.L.P.; Cooper, L.T.; Felix, S.B.; Hare, J.M.; Heidecker, B.; Heymans, S.; Hübner, N.; et al. Myocarditis and inflammatory cardiomyopathy: Current evidence and future directions. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2021, 18, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzmann, J.L.; Schlattmann, P.; Rigopoulos, A.G.; Noutsias, E.; Bigalke, B.; Pauschinger, M.; Tschope, C.; Sedding, D.; Schulze, P.C.; Noutsias, M. Meta-analysis on the immunohistological detection of inflammatory cardiomyopathy in endomyocardial biopsies. Heart Fail. Rev. 2020, 25, 277–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kühl, U.; Noutsias, M.; Schultheiss, H.-P. Immunohistochemical Analysis of Inflammatory Heart Disease. In The Role of Immune Mechanisms in Cardiovascular Disease; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; pp. 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herskowitz, A.; Ahmed-Ansari, A.; Neumann, D.A.; Beschorner, W.E.; Rose, N.R.; Soule, L.M.; Burek, C.L.; Sell, K.W.; Baughman, K.L. Induction of major histocompatibility complex antigens within the myocardium of patients with active myocarditis: A nonhistologic marker of myocarditis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1990, 15, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta-Ogo, K.; Sugano, Y.; Ogata, S.; Nakayama, T.; Komori, T.; Eguchi, K.; Dohi, K.; Yokokawa, T.; Kanamori, H.; Nishimura, S.; et al. Myocardial T-Lymphocytes as a Prognostic Risk-Stratifying Marker of Dilated Cardiomyopathy―Results of the Mul-ticenter Registry to Investigate Inflammatory Cell Infiltration in Dilated Cardiomyopathy in Tissues of Endomyocardial Biopsy (INDICATE Study). Circ. J. 2022, 86, 1092–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, M.H.M.; Hauck, F.; Dreyer, J.H.; Kempkes, B.; Niedobitek, G. Macrophage Polarisation: An Immunohistochemical Approach for Identifying M1 and M2 Macrophages. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rőszer, T. Understanding the Mysterious M2 Macrophage through Activation Markers and Effector Mechanisms. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 816460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabriek, B.O.; Dijkstra, C.D.; Berg, T.K.v.D. The macrophage scavenger receptor CD163. Immunobiology 2005, 210, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, S. Alternative activation of macrophages. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajpai, G.; Schneider, C.; Wong, N.; Bredemeyer, A.; Hulsmans, M.; Nahrendorf, M.; Epelman, S.; Kreisel, D.; Liu, Y.; Itoh, A.; et al. The human heart contains distinct macrophage subsets with divergent origins and functions. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1234–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, N.S.; Yarovinsky, T.O.; Pandya, P.; Ramgolam, V.S.; Moro, A.; Wu, Y.; Nicoli, S.; Hirschi, K.K.; Bender, J.R. Distinct hypoxia-induced translational profiles of embryonic and adult-derived macrophages. iScience 2023, 26, 107985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakkila, J.; Lotze, M.T.; Riga, C.; Jaffe, R. A Basis for Distinguishing Cultured Dendritic Cells and Macrophages in Cytospins and Fixed Sections. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 2005, 8, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, T.; Sugano, Y.; Yokokawa, T.; Nagai, T.; Matsuyama, T.; Ohta-Ogo, K.; Ikeda, Y.; Ishibashi-Ueda, H.; Nakatani, T.; Ohte, N.; et al. Clinical impact of the presence of macrophages in endomyocardial biopsies of patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017, 19, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, D.W. Plasma Siglec-5 and CD163 as Novel Biomarkers for Fulminant Myocarditis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abubakar, M.; Rasool, H.F.; Javed, I.; Raza, S.; Hashim, M.M.A.; Saleem, Z.; Abdullah, R.M.; Faraz, M.A.; Hassan, K.M.; Bhat, R.R.; et al. Comparative Roles of IL-1, IL-6, IL-10, IL-17, IL-18, 1L-22, IL-33, and IL-37 in Various Cardiovascular Diseases with Potential Insights for Targeted Immunotherapy. Cureus 2023, 15, e42494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Dhalla, N.S. The Role of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayat, M.; Mahmoudi, M.J.; Rose, N.R.; Rezaei, N. Proinflammatory cytokines in heart failure: Double-edged swords. Heart Fail. Rev. 2010, 15, 543–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose-John, S. IL-6 Trans-Signaling via the Soluble IL-6 Receptor: Importance for the Pro-Inflammatory Activities of IL-6. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P.; Rocha, V.Z. All roads lead to IL-6: A central hub of cardiometabolic signaling. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 259, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schieffer, B.; Selle, T.; Hilfiker, A.; Hilfiker-Kleiner, D.; Grote, K.; Tietge, U.J.; Trautwein, C.; Luchtefeld, M.; Schmittkamp, C.; Heeneman, S.; et al. Impact of Interleukin-6 on Plaque Development and Morphology in Experimental Atherosclerosis. Circulation 2004, 110, 3493–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camps-Vilaro, A.; Camps-Vilaro, A.; Subirana, I.; Subirana, I.; Ramos, R.; Ramos, R.; Cainzos-Achirica, M.; Cainzos-Achirica, M.; Tizon-Marcos, H.; Tizon-Marcos, H.; et al. Five-Year Changes in Inflammatory, Metabolic, and Oxidative Biomarkers and 10-Year Cardiovascular Disease Incidence: The REGICOR Cohort Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markousis-Mavrogenis, G.; Tromp, J.; Ouwerkerk, W.; Devalaraja, M.; Anker, S.D.; Cleland, J.G.; Dickstein, K.; Filippatos, G.S.; van der Harst, P.; Lang, C.C.; et al. The clinical significance of interleukin-6 in heart failure: Results from the BIOSTAT-CHF study. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2019, 21, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broch, K.; Anstensrud, A.K.; Woxholt, S.; Sharma, K.; Tøllefsen, I.M.; Bendz, B.; Aakhus, S.; Ueland, T.; Amundsen, B.H.; Damås, J.K.; et al. Randomized Trial of Interleukin-6 Receptor Inhibition in Patients with Acute ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 1845–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savvatis, K.; Müller, I.; Fröhlich, M.; Pappritz, K.; Zietsch, C.; Hamdani, N.; Grote, K.; Schieffer, B.; Klingel, K.; Van Linthout, S.; et al. Interleukin-6 receptor inhibition modulates the immune reaction and restores titin phosphorylation in experimental myocarditis. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2014, 109, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amioka, N.; Nakamura, K.; Kimura, T.; Ohta-Ogo, K.; Tanaka, T.; Toji, T.; Akagi, S.; Nakagawa, K.; Toh, N.; Yoshida, M.; et al. Pathological and clinical effects of interleukin-6 on human myocarditis. J. Cardiol. 2021, 78, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, C.; Aguilera, B.; Banner, J.; Cohle, S.; d’Amati, G.; de Gouveia, R.H.; di Gioia, C.; Fabre, A.; Gallagher, P.J.; Leone, O.; et al. Guidelines for autopsy investigation of sudden cardiac death: 2017 update from the Association for European Cardiovascular Pathology. Virchows Arch. 2017, 471, 691–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- du Long, R.; Fronczek, J.; Niessen, H.W.M.; van der Wal, A.C.; de Boer, H.H. The histopathological spectrum of myocardial inflammation in relation to circumstance of death: A retrospective cohort study in clinical and forensic autopsies. Forensic Sci. Res. 2021, 7, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitulwatte, I.; Edirisinghe, P. Study on existence of inflammation in the myocardium in unequivocal acute traumatic deaths. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2020, 75, 102055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casali, M.B.; Lazzaro, A.; Gentile, G.; Blandino, A.; Ronchi, E.; Zoja, R. Forensic grading of myocarditis: An experimental contribution to the distinction between lethal myocarditis and incidental myocarditis. Forensic Sci. Int. 2012, 223, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, C.; Calabrese, F.; Angelini, A.; Carturan, E.; Thiene, G. Classification and histological, immunohistochemical, and molecular diagnosis of inflammatory myocardial disease. Heart Fail. Rev. 2013, 18, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishbein, G.A.; Leone, O.; Basso, C.; Fallon, J.T.; Klingel, K.; Tan, C. Commentary on why implementing and standardizing histologic diagnosis of myocarditis is crucial for the clinical setting and patient care. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2023, 64, 107515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitulwatte, I.D.; Kim, P.J.H.; Pollanen, M.S. Sudden death related myocarditis: A study of 56 cases. Forensic Sci. Med. Pathol. 2010, 6, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, K.M.; Mackey-Bojack, S.; Bennett, M.; Nwaudo, D.; Duncanson, E.; Maron, B.J. Sudden Unexpected Death Due to Myocarditis in Young People, Including Athletes. Am. J. Cardiol. 2021, 143, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, R.T.; Finocchiaro, G.; Westaby, J.; Chatrath, N.; Behr, E.R.; Papadakis, M.; Sharma, S.; Sheppard, M.N. Myocarditis and Sudden Cardiac Death in the Community: Clinical and Pathological Insights from a National Registry in the United Kingdom. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2023, 16, e012129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammirati, E.; Veronese, G.; Cipriani, M.; Moroni, F.; Garascia, A.; Brambatti, M.; Adler, E.D.; Frigerio, M. Acute and Fulminant Myocarditis: A Pragmatic Clinical Approach to Diagnosis and Treatment. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2018, 20, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordani, A.S.; Baritussio, A.; Vicenzetto, C.; Peloso-Cattini, M.G.; Pontara, E.; Bison, E.; Fraccaro, C.; Basso, C.; Iliceto, S.; Marcolongo, R.; et al. Fulminant Myocarditis: When One Size Does Not Fit All—A Critical Review of the Literature. Eur. Cardiol. Rev. 2023, 18, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brociek, E.; Tymińska, A.; Giordani, A.S.; Caforio, A.L.P.; Wojnicz, R.; Grabowski, M.; Ozierański, K. Myocarditis: Etiology, Pathogenesis, and Their Implications in Clinical Practice. Biology 2023, 12, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumeier, C.; Harms, D.; Aleshcheva, G.; Gross, U.; Escher, F.; Schultheiss, H.-P. Advancing Precision Medicine in Myocarditis: Current Status and Future Perspectives in Endomyocardial Biopsy-Based Diagnostics and Therapeutic Approaches. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falleti, J.; Orabona, P.; Municinò, M.; Castellaro, G.; Fusco, G.; Mansueto, G. An Update on Myocarditis in Forensic Pathology. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, O.; Veinot, J.P.; Angelini, A.; Baandrup, U.T.; Basso, C.; Berry, G.; Bruneval, P.; Burke, M.; Butany, J.; Calabrese, F.; et al. 2011 Consensus statement on endomyocardial biopsy from the Association for European Cardiovascular Pathology and the Society for Cardiovascular Pathology. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2012, 21, 245–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woudstra, L.; Biesbroek, P.S.; Emmens, R.W.; Heymans, S.; Juffermans, L.J.; van der Wal, A.C.; van Rossum, A.C.; Niessen, H.W.; Krijnen, P.A. CD45 is a more sensitive marker than CD3 to diagnose lymphocytic myocarditis in the endomyocardium. Hum. Pathol. 2017, 62, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dettmeyer, R.; Baasner, A.; Schlamann, M.; Padosch, S.A.; Haag, C.; Kandolf, R.; Madea, B. Role of Virus-Induced Myocardial Affections in Sudden Infant Death Syndrome: A Prospective Postmortem Study. Pediatr. Res. 2004, 55, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugita, J.; Fujiu, K.; Nakayama, Y.; Matsubara, T.; Matsuda, J.; Oshima, T.; Liu, Y.; Maru, Y.; Hasumi, E.; Kojima, T.; et al. Cardiac macrophages prevent sudden death during heart stress. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ptaszynska-Kopczynska, K.; Marcinkiewicz-Siemion, M.; Lisowska, A.; Waszkiewicz, E.; Witkowski, M.; Jasiewicz, M.; Miklasz, P.; Jakim, P.; Galar, B.; Musial, W.J.; et al. Alterations of soluble TWEAK and CD163 concentrations in patients with chronic heart failure. Cytokine 2016, 80, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimczak-Tomaniak, D.; Bouwens, E.; Schuurman, A.; Akkerhuis, K.M.; Constantinescu, A.; Brugts, J.; Westenbrink, B.D.; van Ramshorst, J.; Germans, T.; Pączek, L.; et al. Temporal patterns of macrophage- and neutrophil-related markers are associated with clinical outcome in heart failure patients. ESC Heart Fail. 2020, 7, 1190–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, C.; Burmester, G.R.; Strand, V.; Msihid, J.; Zilberstein, M.; Kimura, T.; van Hoogstraten, H.; Boklage, S.H.; Sadeh, J.; Graham, N.M.H.; et al. Sarilumab and adalimumab differential effects on bone remodelling and cardiovascular risk biomarkers, and predictions of treatment outcomes. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Grade | Histological Features of Fibrosis |
|---|---|
| 0 | Insignificant, residing only around the vessels, without extension towards the myocytes |
| 1: Adventitial | Mild/delicate fibrosis, featuring thin fibrous strands observed outside the perivascular tissue, yet without isolating or surrounding groups of myocytes |
| 2: Interstitial | Moderate fibrosis, wherein collagen bands are thickened and branched, occasionally leading to the isolation of myocyte groups/islets |
| 3: Remodelling | Marked fibrosis wherein interstitial connective tissue forms irregular, nodular areas, replacing specialized tissue |
| Grade | Histological Features of Inflammation |
|---|---|
| 0 | ≈14 inflammatory cells in a single focus |
| 1 | Mild/reduced myocardial inflammation occupies <10% of the examined section |
| 2 | Moderate inflammation occupies approximately 10–20% (grade 2) |
| 3 | Marked inflammation represents 20–30% of the examined section |
| 4 | Diffuse inflammation in aggressive/fulminant myocarditis occupying >1/3 of the examined section |
| Grade | Histological Features of Necrosis |
|---|---|
| 0 | No myocyte damage was confirmed in routine haematoxylin-eosin stain |
| 1 | Mild necrosis with individual cellular necrosis (1–3 cells), isolated and characterized solely by nuclear loss and increased cytoplasmic eosinophilia |
| 2 | Moderate necrosis with limited group of cells (4–20 cells), situated within the centre of the inflammatory focus |
| 3 | Marked/pronounced necrosis, featuring obliteration of cellular outlines within the inflammatory focus and the formation of necrotic islands |
| 4 | Extensive, confluent, infarct-like necrosis within an inflammatory setting |
| Age | Sex | Circumstances of Death |
|---|---|---|
| 75 | F | Traumatic injuries; hospitalization 2 days |
| 43 | M | Drug abuse; HIV-C3 stage; chronic HVC |
| 43 | M | Tuberculosis under treatment; bronchopneumonia |
| 25 | M | Fatal traffic incident |
| 30 | M | Drug abuse; severe craniocerebral traumatism |
| 73 | M | Liver cirrhosis; ethanol intoxication |
| 24 | F | Severe burns 45%; hospitalization 14 days |
| 64 | M | Sudden death |
| 46 | M | Sudden death |
| 52 | M | Type 2 diabetes mellitus; hypertension; ethanol withdrawal |
| 51 | M | AIDS-HIV infection; cerebral toxoplasmosis |
| 71 | M | Sudden death |
| 18 | M | Ischaemic stroke |
| 80 | F | Bilateral pneumonia |
| 83 | F | Drug abuse; bronchopneumonia |
| 18 | F | Endocarditis—mitral valve |
| 31 | F | Sudden death |
| 45 | M | Liver cirrhosis |
| 71 | M | SARS-CoV-2 infection |
| 63 | M | Colon adenocarcinoma stage IV |
| 76 | M | Sudden death |
| 46 | M | Sudden death |
| 48 | M | Drug abuse; bronchopneumonia |
| 61 | M | Endocarditis with prosthesis—aortic valve |
| 66 | M | Fatal traffic incident |
| 53 | M | Leptospirosis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neagu, O.; Chirică, V.; Luca, L.; Bosa, M.; Tița, A.; Ceaușu, M.C. Novel Immunohistochemical and Morphological Approaches in a Retrospective Study of Post-Mortem Myocarditis. Medicina 2024, 60, 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60081312
Neagu O, Chirică V, Luca L, Bosa M, Tița A, Ceaușu MC. Novel Immunohistochemical and Morphological Approaches in a Retrospective Study of Post-Mortem Myocarditis. Medicina. 2024; 60(8):1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60081312
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeagu, Oana, Violeta Chirică, Lăcrămioara Luca, Maria Bosa, Alina Tița, and Mihail Constantin Ceaușu. 2024. "Novel Immunohistochemical and Morphological Approaches in a Retrospective Study of Post-Mortem Myocarditis" Medicina 60, no. 8: 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60081312
APA StyleNeagu, O., Chirică, V., Luca, L., Bosa, M., Tița, A., & Ceaușu, M. C. (2024). Novel Immunohistochemical and Morphological Approaches in a Retrospective Study of Post-Mortem Myocarditis. Medicina, 60(8), 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60081312







