Neurological Side Effects of TNF-α Inhibitors Revisited: A Review of Case Reports
Abstract
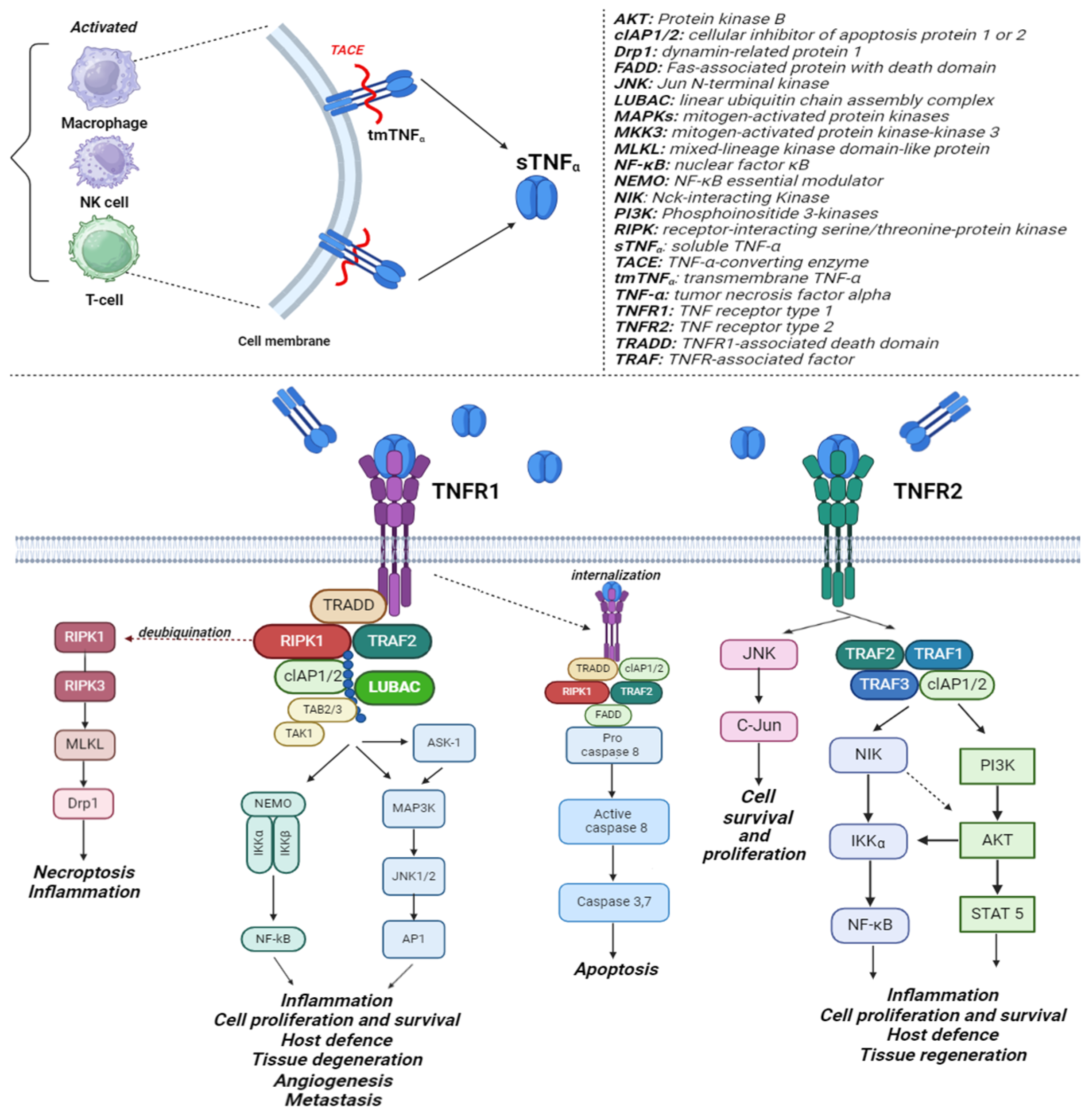
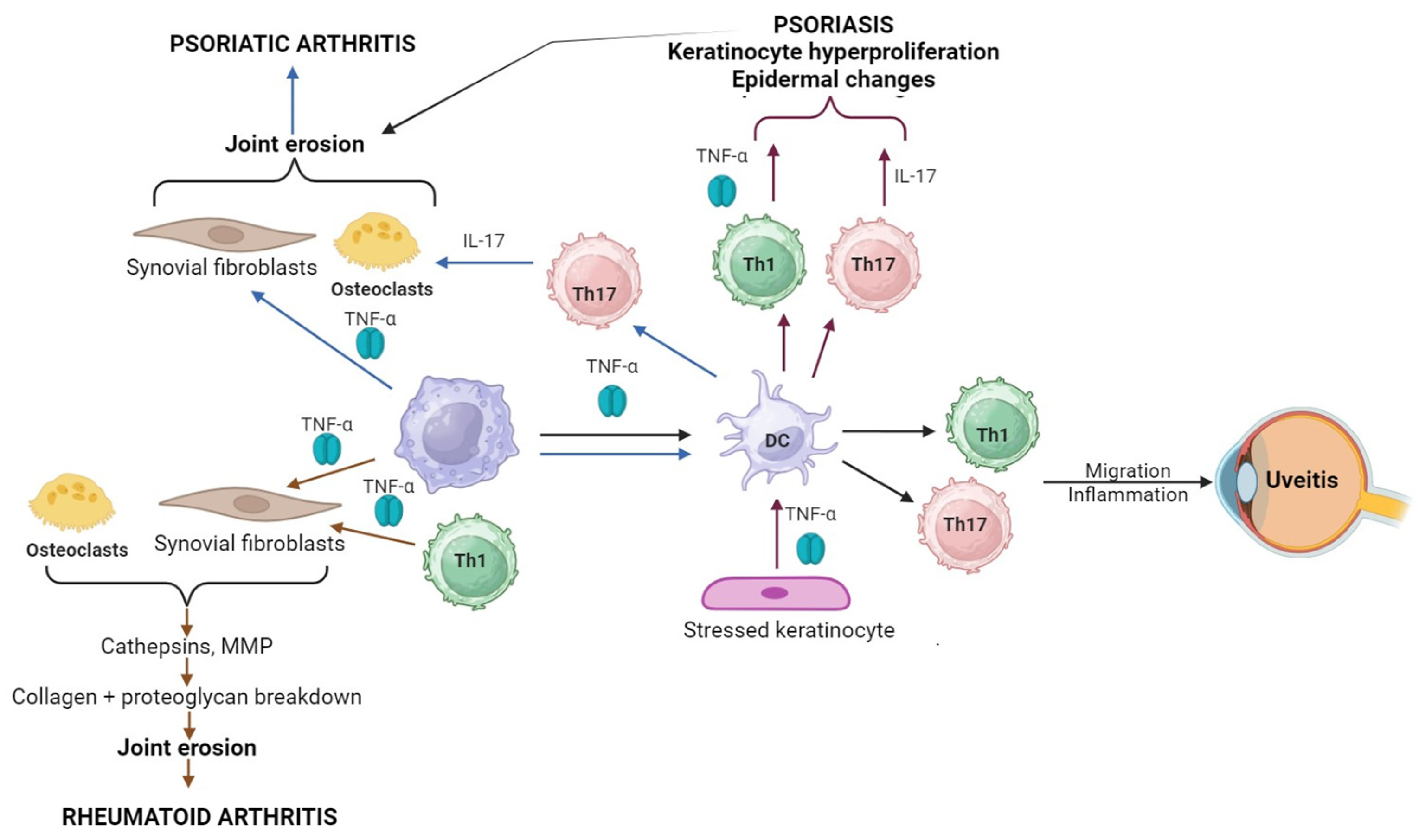
:1. Introduction
| Type | Mechanism of Action | Date of Approval (FDA) | Approved Indications | Administration | Pharmacodynamics | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Etanercept | Dimeric soluble fusion protein—the extracellular ligand-binding portion of the human p75 TNFR (TNFR2) linked to the Fc portion of human IgG1 | Inhibits the binding of TNF-α and TNF-β to cell surface TNFRs → renders TNF biologically inactive. | 1998 | RA, JIA, PsA, PsO, AS, nr-axSpA | Subcutaneously weekly |
| [22,23,24,25,26] |
| Infliximab | Chimeric IG1κ monoclonal antibody (75% human and 25% mouse) | Selectively neutralizes the biological activity of TNFα by binding to the tmTNF-α + sTNF-α → inhibits the binding of TNFα to TNFR. No binding/inactivation of TNF-β | 1998 | AS, CD, JIA, PsO, PsA, RA, UC, nr-axSpA | Intravenously every 6–8 weeks |
| [27,28,29,30,31] |
| Adalimumab | Fully human IgG1 monoclonal antibody specific for human TNF-α | Binds specifically to TNF-α → blocks its interaction with the p55 and p75 cell surface TNFR (TNFR1 and TNFR2). In the presence of complement, lyses cells that express at the surface TNF. No binding/inactivation of TNF-β | 2002 | AS, CD, JIA, PsO, PsA, RA, UC, Uveitis, nr-axSpA | Subcutaneously every other week |
| [32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40] |
| Golimumab | Fully human IgG1 κ monoclonal antibody specific for human TNF-α | Selectively neutralizes the biological activity of TNFα by binding to the tmTNF-α + sTNF-α → inhibits the binding of TNFα to TNFR. No binding/inactivation of TNF-β. | 2009 | AS, PsA, RA, UC, nr-axSpA | Subcutaneously every month |
| [41,42,43,44] |
| Certolizumab pegol | Humanized antibody Fab’ fragment conjugated with two polyethylene glycol molecules, specific for human TNF-α | Selectively neutralizes the biological activity of TNFα by binding to the tmTNF-α + sTNF-α → inhibits the binding of TNFα to TNFR. No binding/inactivation of TNF-β. Does not contain a fragment-crystallizable (Fc) region = does not fix complement or cause antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in vitro. | 2008 | AS, CD, PsA, RA, nr-axSpA | Subcutaneously; remission induction weeks 0, 2 and 4, maintenance of remission every 4 weeks |
| [45,46,47] |
2. TNF-α Mechanism of Action
3. Research Methods
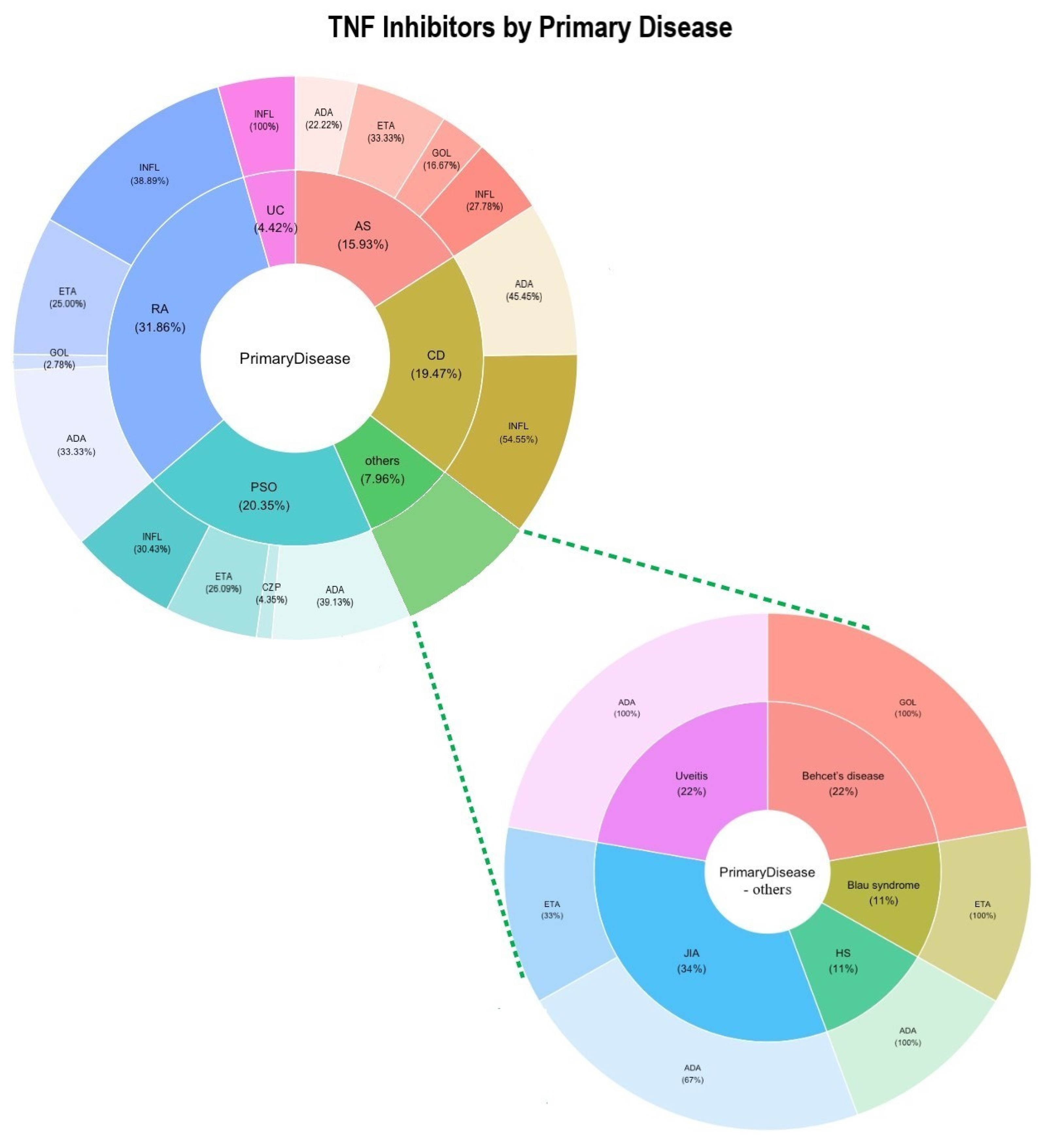
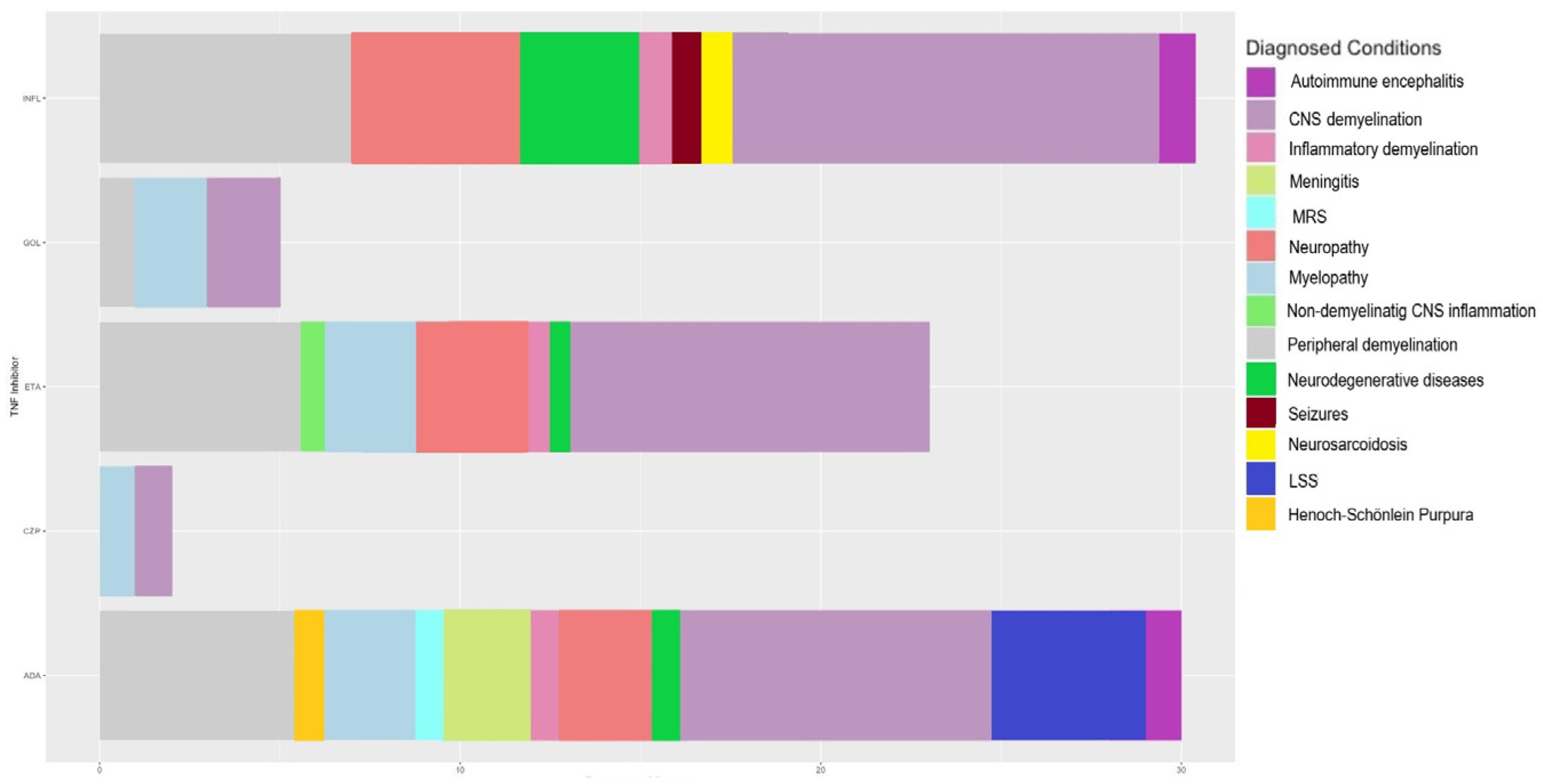
4. Results
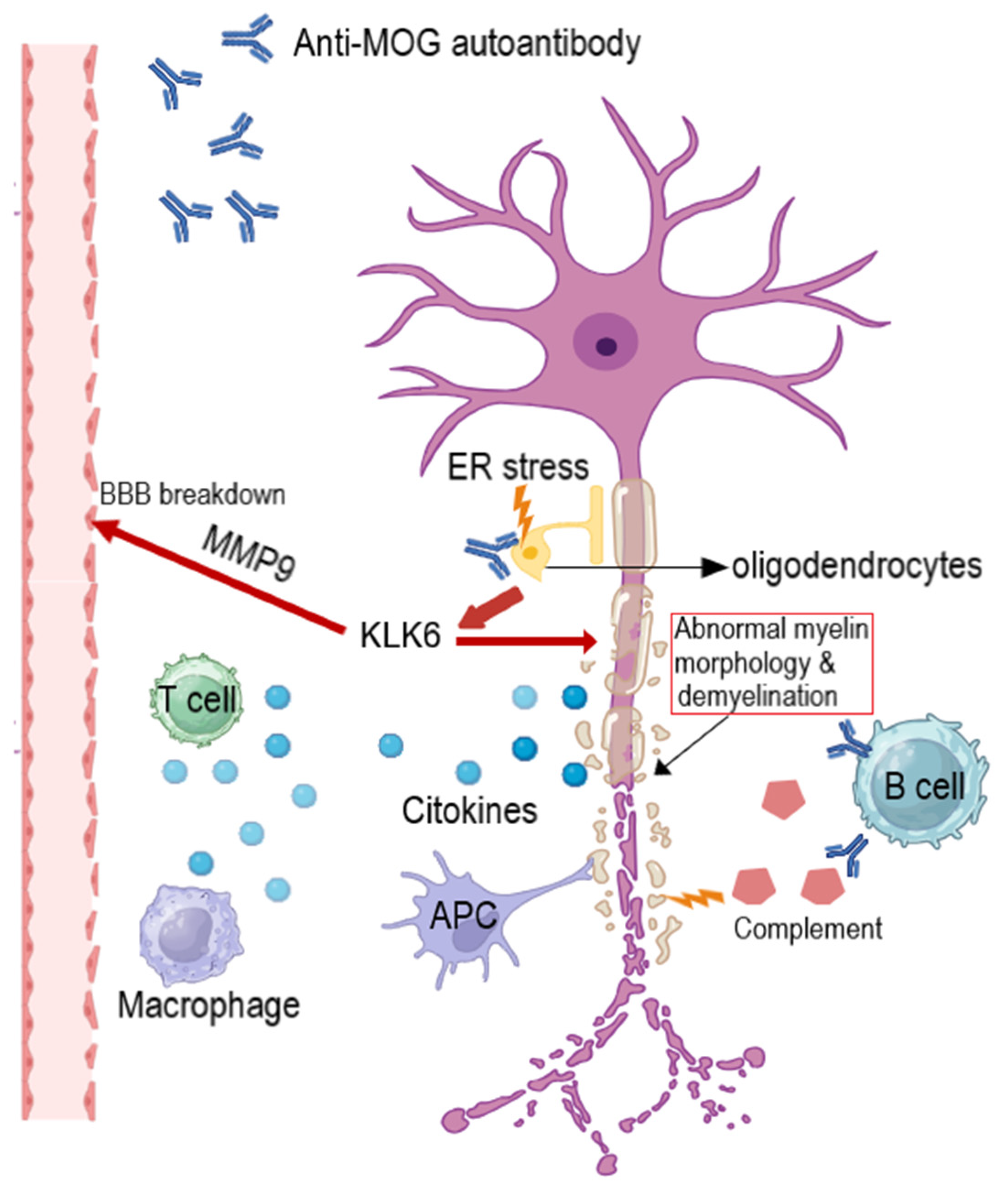
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coates, L.C.; Marzo-Ortega, H.; Bennett, A.N.; Emery, P. Anti-TNF therapy in ankylosing spondylitis: Insights for the clinician. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2010, 2, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagnini, C.; Cominelli, F. Tumor Necrosis Factor’s Pathway in Crohn’s Disease: Potential for Intervention. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horneff, G.; Minden, K.; Rolland, C.; Daly, A.C.H.; Borlenghi, C.; Ruperto, N. Efficacy and safety of TNF inhibitors in the treatment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: A systematic literature review. Pediatr. Rheumatol. 2023, 21, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yost, J.; Gudjonsson, J.E. The role of TNF inhibitors in psoriasis therapy: New implications for associated comorbidities. F1000 Med. Rep. 2009, 1, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantravadi, S.; Ogdie, A.; Kraft, W.K. Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors in psoriatic arthritis. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 10, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MA, X.; XU, S. TNF inhibitor therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Biomed. Rep. 2013, 1, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, N.; Lo, S.W.; Sikafi, R.; Barnes, T.; Segal, J.; Smith, P.J.; Limdi, J.K. A review of the therapeutic management of ulcerative colitis. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2022, 15, 175628482211381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, I.; Rodrigues, F.B.; Sousa, D.C.; Duarte, G.S.; Romão, V.C.; Marques-Neves, C.; Costa, J.; Fonseca, J.E. Anti-TNF Drugs for Chronic Uveitis in Adults—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Nascimento, I.J.; da Silva-Júnior, E.F. TNF-α Inhibitors from Natural Compounds: An Overview, CADD Approaches, and their Exploration for Anti-inflammatory Agents. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2022, 25, 2317–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, S.; Rama Chaitanya Sreedhara, S.; Banerjee, S.; Chatterjee, S. TNF α Signaling Beholds Thalidomide Saga: A Review of Mechanistic Role of TNF-α Signaling Under Thalidomide. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 1456–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotla, V.; Goel, S.; Nischal, S.; Heuck, C.; Vivek, K.; Das, B.; Verma, A. Mechanism of action of lenalidomide in hematological malignancies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2009, 2, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhengxiang, L.; Wang, B.; Liu, H.; Shi, L. TNF Inhibitor Pomalidomide Sensitizes Glioblastoma Cells to EGFR Inhibition. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2020, 50, 474–480. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.; Shreshtha, A.K.; Thakur, M.S.; Patra, S. Xanthine scaffold: Scope and potential in drug development. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brustolim, D.; Ribeiro-dos-Santos, R.; Kast, R.E.; Altschuler, E.L.; Soares, M.B.P. A new chapter opens in anti-inflammatory treatments:The antidepressant bupropion lowers production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2006, 6, 903–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansen, C.B.; Jimenez-Solem, E.; Haerskjold, A.; Sand, F.L.; Thomsen, S.F. The Use and Safety of TNF Inhibitors during Pregnancy in Women with Psoriasis: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Wadhwa, M. Therapeutic use of specific tumour necrosis factor inhibitors in inflammatory diseases including COVID-19. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 140, 111785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauline, O.; Robert, M.; Bernardeau, C.; Hlavaty, A.; Fusaroli, M.; Roustit, M.; Cracowski, J.-L.; Khouri, C. Assessment of Reported Adverse Events After Interchanging Between TNF-α Inhibitor Biosimilars in the WHO Pharmacovigilance Database. BioDrugs 2023, 37, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, X.; Zhou, J.; Meng, D.; Zhu, P. Risk of Adverse Events After Anti-TNF Treatment for Inflammatory Rheumatological Disease. A Meta-Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 746396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, M.; D’Amico, F.; Bonovas, S.; Danese, S.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. TNF Inhibitors and Risk of Malignancy in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Systematic Review. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2021, 15, 840–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.-Y.; Yu, S.-J.; Chen, Y.-M.; Lai, K.-L.; Wu, Y.-D.; Liao, E.-C.; Hsieh, C.-L. Mechanisms of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Inhibitor-Induced Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 870724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosos, A.A.; Pelechas, E.; Kaltsonoudis, E.; Markatseli, T.E.; Voulgari, P.V. Biologic Therapies and Autoimmune Phenomena. Mediterr. J. Rheumatol. 2021, 32, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Enbrel® (Etanercept) Solution for Subcutaneous Use; U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 1998.
- Catrina, A.I.; Lampa, J.; Ernestam, S.; af Klint, E.; Bratt, J.; Klareskog, L.; Ulfgren, A.-K. Anti-tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha therapy (etanercept) down-regulates serum matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-3 and MMP-1 in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2002, 41, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimiuk, P.A.; Sierakowski, S.; Domyslawska, I.; Chwiecko, J. Effect of etanercept on serum levels of soluble cell adhesion molecules (sICAM-1, sVCAM-1, and sE-selectin) and vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2009, 38, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraoui, B.; Bykerk, V. Etanercept in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2007, 3, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios Rodriguez, V.; Poddubnyy, D. Etanercept for the treatment of non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 12, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Infliximab for Injection, for Intravenous Use; U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 1998.
- Elliott, M.J.; Maini, R.N.; Feldmann, M.; Kalden, J.R.; Antoni, C.; Smolen, J.S.; Leeb, B.; Breedveld, F.C.; Macfarlane, J.D.; Bijl, H. Randomised double-blind comparison of chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumour necrosis factor alpha (cA2) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 1994, 344, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.C.; Peters, A.M.; Paleolog, E.; Chapman, P.T.; Elliott, M.J.; McCloskey, R.; Feldmann, M.; Maini, R.N. Reduction of chemokine levels and leukocyte traffic to joints by tumor necrosis factor alpha blockade in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000, 43, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paleolog, E.M.; Hunt, M.; Elliott, M.J.; Feldmann, M.; Maini, R.N.; Woody, J.N. Deactivation of vascular endothelium by monoclonal anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha antibody in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1996, 39, 1082–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, E.; El-tantawi, G.; Matrawy, K.; Aldawoudy, A.; Naguib, A. Local infliximab injection of sacroiliac joints in non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: Impact on clinical and magnetic resonance imaging parameters of disease activity. Mod. Rheumatol. 2015, 25, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. HUMIRA® (Adalimumab) Injection, for Subcutaneous Use; U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2002.
- Zdanowska, N.; Owczarczyk-Saczonek, A.; Czerwińska, J.; Nowakowski, J.J.; Kozera-Żywczyk, A.; Owczarek, W.; Zdanowski, W.; Placek, W. Methotrexate and Adalimumab Decrease the Serum Levels of Cardiovascular Disease Biomarkers (VCAM-1 and E-Selectin) in Plaque Psoriasis. Medicina 2020, 56, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, D.; Sumida, T. Adalimumab. Nihon Rinsho 2002, 60, 2384–2389. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, C.; Assche, G.V.; Colpaert, S.; Maerten, P.; Geboes, K.; Rutgeerts, P.; Ceuppens, J.L. Adalimumab induces apoptosis of human monocytes: A comparative study with infliximab and etanercept. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 21, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberoi, R.; Schuett, J.; Schuett, H.; Koch, A.-K.; Luchtefeld, M.; Grote, K.; Schieffer, B. Targeting Tumor Necrosis Factor-α with Adalimumab: Effects on Endothelial Activation and Monocyte Adhesion. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timis, T.-L.; Beni, L.; Florian, I.-A.; Orăsan, M.; Orăsan, R.I. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome and chronic inflammation in psoriasis before and after biologic therapy: A prospective study. Med. Pharm. Rep. 2023, 96, 368–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Carabali, W.; Boada-Robayo, L.; Chacón-Zambrano, D.; Criollo Porras, E.; Kerguelén Dumar, V.; De-la-Torre, A. Multiple Sclerosis in a Patient with Intermediate Uveitis and Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Treated with Adalimumab: A Case Report. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2023, 31, 1873–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnasser Alsukhni, R.; Jriekh, Z.; Aboras, Y. Adalimumab Induced or Provoked MS in Patient with Autoimmune Uveitis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Case Rep. Med. 2016, 2016, 1423131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burness, C.B.; Deeks, E.D. Adalimumab: In non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis. Drugs 2012, 72, 2385–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. SIMPONI (Gollmumab) Injection, Solution for Subcutaneous Use; U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2009.
- Kanbe, K.; Chiba, J.; Inoue, Y.; Taguchi, M.; Yabuki, A. Predictive factors related to the efficacy of golimumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Med. Insights. Arthritis Musculoskelet. Disord. 2015, 8, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, M.K.; Rahman, M.U.; Frederick, B.; Birbara, C.A.; de Vries, D.; Toedter, G.; Wu, X.; Chen, D.; Ranganath, V.K.; Westerman, M.E.; et al. Effects of subcutaneous and intravenous golimumab on inflammatory biomarkers in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Results of a phase 1, randomized, open-label trial. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 1214–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toussirot, E.; Vauchy, C.; Binda, D.; Michel, F. Golimumab in radiographic and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis: A review of clinical trials. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2016, 10, 2087–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. CIMZIA (Certolizumab Pegol) for Injection, for Subcutaneous Use; U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2008.
- Patel, V.K.; Ghosh, S. Certolizumab pegol in Crohn’s disease. Drugs Today 2008, 44, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, P.C.; Maksymowych, W.P.; Gensler, L.S.; Hall, S.; Rudwaleit, M.; Hoepken, B.; Bauer, L.; Kumke, T.; Kim, M.; de Peyrecave, N.; et al. Certolizumab Pegol Efficacy in Patients With Non-Radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis Stratified by Baseline MRI and C-Reactive Protein Status: An Analysis From the C-axSpAnd Study. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2022, 4, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedger, L.M.; McDermott, M.F. TNF and TNF-receptors: From mediators of cell death and inflammation to therapeutic giants—Past, present and future. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014, 25, 453–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpentier, I.; Coornaert, B.; Beyaert, R. Function and Regulation of Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Type 2. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 2205–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kist, M.; Kőműves, L.G.; Goncharov, T.; Dugger, D.L.; Yu, C.; Roose-Girma, M.; Newton, K.; Webster, J.D.; Vucic, D. Impaired RIPK1 ubiquitination sensitizes mice to TNF toxicity and inflammatory cell death. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 985–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, D.; Blaser, H.; Mak, T.W. Regulation of tumour necrosis factor signalling: Live or let die. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Gupta, S.C.; Kim, J.H. Historical perspectives on tumor necrosis factor and its superfamily: 25 years later, a golden journey. Blood 2012, 119, 651–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanden Berghe, T.; Linkermann, A.; Jouan-Lanhouet, S.; Walczak, H.; Vandenabeele, P. Regulated necrosis: The expanding network of non-apoptotic cell death pathways. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajant, H.; Siegmund, D. TNFR1 and TNFR2 in the Control of the Life and Death Balance of Macrophages. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Bai, L.; Chen, W.; Xu, S. The NF-kappaB activation pathways, emerging molecular targets for cancer prevention and therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2010, 14, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflug, K.M.; Sitcheran, R. Targeting NF-κB-Inducing Kinase (NIK) in Immunity, Inflammation, and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Bai, X.; Liang, T. Targeting TNFR2: A Novel Breakthrough in the Treatment of Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 862154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabal-Hierro, L.; Rodríguez, M.; Artime, N.; Iglesias, J.; Ugarte, L.; Prado, M.A.; Lazo, P.S. TRAF-mediated modulation of NF-kB AND JNK Activation by TNFR2. Cell. Signal. 2014, 26, 2658–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziadzio, M.; Reddy, V.; Rahman, S.; Mummery, C.; Keat, A. Is TNFα really a good therapeutic target in motoneuronal degeneration? A case of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in a patient with RA receiving infliximab. Rheumatology 2006, 45, 1445–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loustau, V.; Foltz, V.; Poulain, C.; Rozenberg, S.; Bruneteau, G. Diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in a patient treated with TNFα blockers for ankylosing spondylitis: Fortuitus association or new side effect of TNFα blockers? Jt. Bone Spine 2009, 76, 213–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padovan, M.; Caniatti, L.M.; Trotta, F.; Govoni, M. Concomitant rheumatoid arthritis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Report of two new cases and review of literature. Rheumatol. Int. 2011, 31, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández Alvarez, P.; Maldonado Pérez, B.; Castro Laria, L.; Argüelles-Arias, F. Autoimmune Encephalitis During Treatment With Adalimumab: A Case Report in Crohn’s Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2021, 27, e40–e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, M.-J.; Suh, Y.S.; Kim, H.-O.; Lee, S.-I.; Cheon, Y.-H. Bickerstaff brainstem encephalitis in a patient with ankylosing spondylitis on tumour necrosis factor-alpha inhibitor. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2018, 36, 343. [Google Scholar]
- Condamina, M.; Diaz, E.; Jamart, C.; Loget, J.; Durlach, A.; Salmon, J.-H.; Cadiot, G.; Viguier, M. Severe Attack of Henoch-Schönlein Purpura With Neurological Involvement During Adalimumab Treatment for Crohn’s Disease. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2020, 14, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faivre, A.; Franques, J.; De Paula, A.M.; Gutierrez, M.; Bret, S.; Aubert, S.; Attarian, S.; Pouget, J. Acute motor and sensory axonal neuropathy and concomitant encephalopathy during tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonist therapy. J. Neurol. Sci. 2010, 291, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.J.; Kwon, Y.N.; Lee, C.K.; Lee, J.S. Anti-NMDAR encephalitis in Crohn’s disease undergoing long-term infliximab treatment: A case report. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 957575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Bouldin, T.W.; Berger, R.G. A case of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in a patient treated with infliximab. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 3191–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oumerzouk, J.; Ahizoune, A.; Raggabi, A.; Mnaili, A.; Abida, N.; Benkirane, A.; Semlali, A.; Bourazza, A. Encéphalomyélite aiguë disséminée associée à une maladie de Crohn sous infliximab. Presse Med. 2017, 46, 975–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, M.; Curtis, J.R.; Baddley, J.W. A case report of progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy (PML) associated with adalimumab. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1429–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çimen Güneş, E.; Çolak, S.; Tekgöz, E.; Çınar, M.; Yılmaz, S. Golimumab-induced posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES): A case-based review. Clin. Rheumatol. 2023, 42, 3407–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Takahashi, H.; Wakasugi, H.; Sukawa, Y.; Saito, M.; Suzuki, C.; Naishiro, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Shinomura, Y.; Imai, K. Leukoencephalopathy during administration of etanercept for refractory rheumatoid arthritis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2007, 17, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldırım, R.; Cansu, D.Ü.; Arık, D.; Saylısoy, S.; Korkmaz, C. Aseptic meningitis in rheumatoid arthritis after anti-TNF administration: A case-based literature review. Rheumatol. Int. 2021, 41, 1845–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Luggen, M.; Herman, J.H.; Weiss, K.L.; Decourten-Myers, G.; Quinlan, J.G.; Khanna, D. Hypertrophic pachymeningitis in rheumatoid arthritis after adalimumab administration. J. Rheumatol. 2006, 33, 2344–2346. [Google Scholar]
- Akça, Ü.K.; Sökmen, O.; Bölek, E.Ç.; Demir, S.; Kılıç, L.; Çevik, I.Ü.; Bilginer, Y. A case report of intracranial hypertension and aseptic meningitis: Anti-tumor necrosis factor associated or juvenile idiopathic arthritis related. Turk. J. Pediatr. 2021, 63, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreras, P.; Mealy, M.A.; Pardo, C.A. TNF-alpha inhibitor associated myelopathies: A neurological complication in patients with rheumatologic disorders. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 373, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caracseghi, F.; Izquierdo-Blasco, J.; Sanchez-Montanez, A.; Melendo-Perez, S.; Roig-Quilis, M.; Modesto, C. Etanercept-Induced Myelopathy in a Pediatric Case of Blau Syndrome. Case Rep. Rheumatol. 2011, 2011, 134106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudsi, M.; Shahada, Z.; Haidar, G.; Safiah, M.H.; Khalayli, N. Golimumab therapy-induced isolated myelitis in a Behcet’s disease patient: A case report. Ann. Med. Surg. 2023, 85, 951–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kon, T.; Hasui, K.; Suzuki, C.; Nishijima, H.; Tomiyama, M. Isolated myelitis in a patient with Behcet’s disease during golimumab therapy. J. Neuroimmunol. 2021, 354, 577533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadikolias, K.; Kouklakis, G.; Heliopoulos, I.; Argyropoulou, P.; Papanas, N.; Tzilonidou, M.; Prassopoulos, P.; Piperidou, H. Acute paraplegia after the initiation of anti-tumour necrosis factor-α therapy for Crohn’s disease. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 19, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Azzi, E.; Salmon, A.; Osmont, M.-N.; Perdriger, A. Reversible anti-TNFα treatment induced dementia: A case report. Jt. Bone Spine 2021, 88, 105044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellesi, M.; Logullo, F.; Bella, P.; Provinciali, L. CNS demyelination during anti–tumor necrosis factor alpha therapy. J. Neurol. 2006, 253, 668–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthelot, C.N.; George, S.J.; Hsu, S. Distal lower extremity paresthesia and foot drop developing during adalimumab therapy. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2005, 53, S260–S262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boggs, J.M.E.; Barnes, L. Demyelination during anti-tumour necrosis factor therapy for psoriasis. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 43, 577–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamon, M.A.; Nicolas, G.; Deviere, F.; Letournel, F.; Dubas, F. Demyelinating neuropathy during anti-TNF alpha treatment with a review of the literature. Rev. Neurol. 2007, 163, 1232–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hare, N.C.; Hunt, D.P.J.; Venugopal, K.; Ho, G.-T.; Beez, T.; Lees, C.W.; Gibson, R.; Weller, B.; Satsangi, J. Multiple sclerosis in the context of TNF blockade and inflammatory bowel disease. QJM 2014, 107, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onasanya, J.; Beach, R.A. A case report about adalimumab-induced radiologically isolated syndrome: A significant side effect of tumour necrosis factor inhibitors. SAGE Open Med. Case Rep. 2021, 9, 2050313X2110030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sršen, S. How to Treat Patients after Serious Adverse Effects Caused by TNF Inhibitors? Acta Clin. Croat. 2020, 59, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barešić, M.; Reihl Crnogaj, M.; Zadro, I.; Anić, B. Demyelinating disease (multiple sclerosis) in a patient with psoriatic arthritis treated with adalimumab: A case-based review. Rheumatol. Int. 2021, 41, 2233–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercieca, C.; Vella, N.; Borg, A.A. Demyelination during anti-TNFα therapy for ankylosing spondylitis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2012, 22, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Li, R.; Chang, Y.; She, H.; Kermode, A.G.; Qiu, W. Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-associated disorders coexisting with ankylosing spondylitis: Potential association between demyelination and tumor necrosis factor inhibitors. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2021, 51, 102889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cereda, C.; Zecca, C.; Mazzucchelli, L.; Valci, L.; Staedler, C.; Bassetti, C.; Gobbi, C. Tumefactive demyelinating lesions during etanercept treatment requiring decompressive hemicraniectomy. Mult. Scler. J. 2013, 19, 820–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cay, H.F.; Gungor, H.A.; Sezer, I.; Kacar, C.; Balci, N. Adverse effect of TNF-alpha blocker? Demyelination in an ankylosing spondylitis patient: A case report. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2006, 31, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicotte, N.L.; Voskuhl, R.R. Onset of multiple sclerosis associated with anti-TNF therapy. Neurology 2001, 57, 1885–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelmann, A.; Patejdl, R.; Wagner, S.; Benecke, R.; Zettl, U.K. Cerebral MRI lesions and anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha therapy. J. Neurol. 2008, 255, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanos, A.H.; Kosmidou, M.; Giannopoulos, S. Vertebral artery hypoplasia in posterior circulation cerebral ischemia. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2013, 115, 1194–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetkin, M.F.; Kendirci, M.; İsmailoğullari, S.; Gültekin, M.; Baydemir, R.; Sarilar, A.Ç.; Köse, E.G.; Akcakoyunlu, M.; Erbay, Ü.Z.; Erol, K.; et al. A case of fulminant demyelinating disease associated with golimumab treatment. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2020, 195, 105887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Jimeno, T.; Carvajal, A.; Mata, C.; Aurrecoechea, E. Demyelinating disease in a patient with psoriatic arthritis and family history of multiple sclerosis treated with infliximab. J. Rheumatol. 2006, 33, 1457–1458. [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen, L.; Lambertsen, K.; Nguyen, N.; Byg, K.-E.; Nielsen, H. The Role of Non-Selective TNF Inhibitors in Demyelinating Events. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubcenco, E.; Ottaway, C.A.; Chen, D.L.; Baker, J.P. Neurological symptoms suggestive of demyelination in Crohn’s disease after infliximab therapy. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 18, 565–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, H.J.; Flak, B. Demyelination-like syndrome in Crohn’s disease after infliximab therapy. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 19, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadia, M.; Herbort, C.P. Infliximab-induced Demyelination Causes Visual Disturbance Mistaken for Recurrence of HLA-B27-related Uveitis. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2010, 18, 482–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanno, M.; Nakamura, I.; Kobayashi, S.; Kurihara, K.; Ito, K. New-onset demyelination induced by infliximab therapy in two rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin. Rheumatol. 2006, 25, 929–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.W.J.; Weinshenker, B.G.; Sandborn, W.J. Demyelination during anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapy with infliximab for Crohn’s disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2004, 10, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, Y.; Otsuka, A.; Egawa, G.; Inoue, Y.; Kuzuya, A.; Takahashi, R.; Miyachi, Y.; Kabashima, K. Multiple neurological abnormalities, including pontine hemorrhage, multiple sclerosis and aseptic meningitis, during anti-TNF-α therapy in psoriatic arthritis. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2015, 25, 487–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, T.; Nakamura, I.; Miura, A.; Momoyama, G.; Ito, K. New-onset multiple sclerosis associated with adalimumab treatment in rheumatoid arthritis: A case report and literature review. Clin. Rheumatol. 2013, 32, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uygunoğlu, U.; Uluduz, D.; Taşçılar, K.; Saip, S. Multiple sclerosis during adalimumab treatment in a case with ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatol. Int. 2014, 34, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir Subías, A.; García-López, S.; Sebastián Torres, B.; Ollero Domenche, L.; García Gámez, A.; Gomollón, F. Esclerosis múltiple como efecto adverso de los agentes antifactor de necrosis tumoral alfa: Una complicación infrecuente pero relevante de infliximab en la enfermedad de Crohn. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 36, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.R.; Korman, N.J. Psoriasis and Co-Morbidities: Approach to Treatment with Biologics. Psoriasis Forum 2006, 12, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theibich, A.; Dreyer, L.; Magyari, M.; Locht, H. Demyelinizing neurological disease after treatment with tumor necrosis factor alpha-inhibiting agents in a rheumatological outpatient clinic: Description of six cases. Clin. Rheumatol. 2014, 33, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, M.; Balato, N.; Ayala, F.; Cirillo, T.; Balato, A. Multiple sclerosis following anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha therapy for psoriasis: First case in Italy? Ital. J. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 153, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, L.G.M.; Sasso, L.S.; Nelli, C.J.; Bernardes Filho, F.; de Abreu, M.A.M.M. Optic neuritis due to immunobiologics: First Brazilian case report. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2013, 88, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aungsumart, S.; Apiwattanakul, M. Concurrent anterior and posterior visual pathway impairment in a patient treated with infliximab. J. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 367, 22–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, B.H.; Crowe, J.L. Oculomotor Nerve Demyelination Secondary to Certolizumab Pegol. JCR J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 24, 234–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, W.; Takada, K.; Miyasaka, N.; Kohsaka, H. Myelitis and optic neuritis induced by a long course of etanercept in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. BMJ Case Rep. 2014, 2014, bcr2014205779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drury, J.; Hickman, S.J. Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia Associated with Anti-TNFα Medication. Strabismus 2015, 23, 30–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faillace, C.; de Almeida, J.R.M.; de Carvalho, J.F. Optic neuritis after infliximab therapy. Rheumatol. Int. 2013, 33, 1101–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durel, C.-A.; Feurer, E.; Pialat, J.-B.; Berthoux, E.; Chapurlat, R.D.; Confavreux, C.B. Etanercept may induce neurosarcoidosis in a patient treated for rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Neurol. 2013, 13, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrios, I.; Jun-O’Connell, A.; Ghiran, S.; Ionete, C. A case of neurosarcoidosis secondary to treatment of etanercept and review of the literature. BMJ Case Rep. 2015, 2015, bcr2014208188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarand, J.; Zochodne, D.W.; Martin, L.O.; Voll, C. Neurological complications of infliximab. J. Rheumatol. 2006, 33, 1018–1020. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alexopoulou, A.; Koskinas, J.; Soultati, A.; Katsaounis, P.; Kilidireas, K.; Papageorgiou, C.; Antoniou, C.; Katsambas, A.; Archimandritis, A. Acute bilateral phrenic neuropathy following treatment with adalimumab. Clin. Rheumatol. 2009, 28, 1337–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshekhlee, A.; Basiri, K.; Miles, J.D.; Ahmad, S.A.; Katirji, B. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy associated with tumor necrosis factor-α antagonists. Muscle Nerve 2010, 41, 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; Powell, R.; Llewelyn, G.; Anstey, A. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy complicating anti TNF therapy for chronic plaque psoriasis. Case Rep. 2011, 2011, bcr0820114674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGinty, R.N.; McNamara, B.; Moore, H. DADS neuropathy associated with anti-TNF-α therapy. BMJ Case Rep. 2015, 2015, bcr2015211781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Frutos-Lezaun, M.; Bidaguren, A.; de la Riva, P.; Meneses, C.F.; Olascoaga, J. Bilateral Retrobulbar Optic Neuropathy Associated With Golimumab. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2017, 40, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, M.; Asano, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Shida, R.; Takahashi, T.; Yoshizaki, A.; Mitsui, A.; Shibata, S.; Araki, M.; Watanabe, R.; et al. The development of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy during adalimumab treatment in a patient with psoriasis vulgaris. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2016, 26, 404–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naruse, H.; Nagashima, Y.; Maekawa, R.; Etoh, T.; Hida, A.; Shimizu, J.; Kaida, K.; Shiio, Y. Successful treatment of infliximab-associated immune-mediated sensory polyradiculopathy with intravenous immunoglobulin. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 20, 1618–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birnbaum, J.; Bingham, C.O. Non-length-dependent and length-dependent small-fiber neuropathies associated with tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-inhibitor therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Expanding the spectrum of neurological disease associated with TNF-inhibitors. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2014, 43, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowan, C.R.; Tubridy, N.; Cullen, G. Multifocal Motor Neuropathy Associated with Infliximab. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2015, 9, 1174–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genç, H.M.; Kutlubay, B.; Sürmeli, R.; Sözen, H.G.; Sözeri, B. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating neuropathy after etanercept therapy in the course of juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Turk. J. Pediatr. 2023, 65, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.L.; Rajabally, Y.A. Steroid-induced inflammatory neuropathy in a patient on tumor necrosis factor-α antagonist therapy. J. Clin. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2010, 12, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, A.; Chan, H.; Macdonell, R.A.L.; Shuey, N.; Khong, J.J. Bilateral facial nerve palsies secondary to chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy following adalimumab treatment. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2018, 164, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wu, L. Infliximab-induced seizures in a patient with Crohn’s disease: A case report. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021, 21, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigo, F.; Bongiovanni, L.G.; Cerini, R.; Manganotti, P.; Storti, M.; Fiaschi, A. Infliximab-related seizures: A first case study. Epileptic Disord. 2011, 13, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soubrier, M.; Haïk, S.; Hauw, J.-J.; Corvol, J.C.; Lyon-Caen, O.; Dougados, M. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in a patient treated by etanercept for rheumatoid arthritis (RA): Just a coincidence? Jt. Bone Spine 2010, 77, 174–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, K.F.; Martins, G.A.; Galvão, K.R.F.; Kurizky, P.S. Lewis-Sumner syndrome associated with infliximab therapy for psoriasis. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2017, 92, 156–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirillo, G.; Todisco, V.; Tedeschi, G. Lewis–Sumner syndrome associated with infliximab therapy in ulcerative colitis. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 37, 1005–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nancey, S.; Bouhour, F.; Boschetti, G.; Magnier, C.; Gonneau, P.-M.; Souquet, J.-C.; Kaiserlian, D.; Flourie, B. Lewis and Sumner syndrome following infliximab treatment in Crohn’s disease: A report of 2 cases. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2010, 16, 1450–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurmann, P.T.; Van Linthoudt, D.; So, A.K.-L. Miller–Fisher syndrome in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis treated with adalimumab. Clin. Rheumatol. 2009, 28, 93–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnarajan, G.; Thompson, A.; Dodridge, C.; Parry, A.; Elston, J. Novel Variant of Miller Fisher Syndrome Occurring With Tumor Necrosis Factor α Antagonist Therapy. JAMA Neurol. 2015, 72, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudio, A.; Corrado, A.; Santoro, N.; Maruotti, N.; Cantatore, F.P. Melkersson-Rosenthal Syndrome in a Patient with Psoriatic Arthritis Receiving Etanercept. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2013, 26, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cançado, G.G.L.; Vilela, E.G. Guillain–Barré syndrome during adalimumab therapy for Crohn’s disease: Coincidence or consequence? Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Natividade, N.B.; Felix, P.A.O.; Lerer, C. Guillain-Barré syndrome in a patient on adalimumab for the treatment of psoriasis. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2017, 92, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Lario, B.; Prieto-Tejedo, R.; Colazo-Burlato, M.; Macarrón-Vicente, J. Severe Guillain–Barré syndrome in a patient receiving anti-TNF therapy. Consequence or coincidence. A case-based review. Clin. Rheumatol. 2013, 32, 1407–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patwala, K.; Crump, N.; De Cruz, P. Guillain-Barré syndrome in association with antitumour necrosis factor therapy: A case of mistaken identity. BMJ Case Rep. 2017, 2017, bcr-2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchra, A.; Benbouazza, K.; Hajjaj-Hassouni, N. Guillain–Barre in a patient with ankylosing spondylitis secondary to ulcerative colitis on infliximab therapy. Clin. Rheumatol. 2009, 28, 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesarini, M.; Angelucci, E.; Foglietta, T.; Vernia, P. Guillain–Barrè syndrome after treatment with human anti-tumor necrosis factorα (adalimumab) in a Crohn’s disease patient: Case report and literature review. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2011, 5, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-H.; Park, J.-S.; Park, D. Successful IVIG treatment without discontinuation of TNF-α blocker in Guillain-Barre syndrome induced by adalimumab in patient with Crohn’s disease. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 39, 595–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psarelis, S.; Hajineocli, A.P.D.; Hadjicosta, E.; Elliott, H.S.A.; Johnson, P. Is secukinumab a safe alternative treatment for ankylosing spondylitis with Guillain Barré syndrome after anti-TNF-α treatment? Case report and literature review. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 36, 1197–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacy, D.; Johnson, R.; Pendleton, J. Demyelinating Disease Associated with Use of Etanercept in Patients with Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies. J. Rheumatol. 2008, 35, 1469–1471. [Google Scholar]
- Morís, G. Inflammatory bowel disease: An increased risk factor for neurologic complications. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, A.J.; Spain, R.I.; Kruer, M.C.; Bourdette, D. Inflammatory neurological disease in patients treated with tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitors. Mult. Scler. J. 2011, 17, 1472–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunchok, A.; Aksamit, A.J.; Davis, J.M.; Kantarci, O.H.; Keegan, B.M.; Pittock, S.J.; Weinshenker, B.G.; McKeon, A. Association Between Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitor Exposure and Inflammatory Central Nervous System Events. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, N.; Woltjer, R.; Hamilton, B.; Neuwelt, E.A.; Rosenbaum, J.T. A 67-Year-Old Woman Receiving Tumor Necrosis Factor α Inhibitor Therapy Presenting With Neurologic Dysfunction. Arthritis Care Res. 2013, 65, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Bijl, A.E.; Emmer, B.J.; Breedveld, F.C.; Middelkoop, H.A.M.; Jurgens, C.K.; van Buchem, M.A.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; van der Grond, J. Advanced magnetic resonance imaging of the brain in patients treated with TNF-alpha blocking agents. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2007, 25, 301–304. [Google Scholar]
- Baumer, F.M.; Ouahed, J.; Verhave, M.; Rivkin, M.J. Fatal Central Nervous System Disease Following First Infliximab Infusion in a Child With Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Pediatr. Neurol. 2016, 57, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bando, Y. Mechanism of demyelination and remyelination in multiple sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Neuroimmunol. 2020, 11, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoridou, A.; Settas, L. Demyelination in rheumatic diseases. Postgrad. Med. J. 2008, 84, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atzeni, F.; Talotta, R.; Masala, I.F.; Gerardi, M.C.; Casale, R.; Sarzi-Puttini, P. Central nervous system involvement in rheumatoid arthritis patients and the potential implications of using biological agents. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 32, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atmaca, M.M.; Altiokka Uzun, G.; Shugaiv, E.; Kurtuncu, M.; Eraksoy, M. Association of Demyelinating and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Case Series and Overview of the Literature. Noro Psikiyatr. Ars. 2015, 52, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowowiejska, J.; Baran, A.; Flisiak, I. Psoriasis and neurodegenerative diseases—A review. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 917751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofat, N.; Malik, O.; Higgens, C.S. Neurological involvement in patients with rheumatic disease. QJM Int. J. Med. 2006, 99, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedr, E.M.; Rashad, S.M.; Hamed, S.A.; El-Zharaa, F.; Abdalla, A.K.H. Neurological complications of ankylosing spondylitis: Neurophysiological assessment. Rheumatol. Int. 2009, 29, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Lee, A.-H.; Shin, H.-Y.; Song, H.-R.; Park, J.-H.; Kang, T.-B.; Lee, S.-R.; Yang, S.-H. The Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-α) in Autoimmune Disease and Current TNF-α Inhibitors in Therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, M.; Busmail, A.; Penumetcha, S.S.; Ahluwalia, S.; Irfan, R.; Khan, S.A.; Rohit Reddy, S.; Vasquez Lopez, M.E.; Mohammed, L. Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Blockade and Multiple Sclerosis: Exploring New Avenues. Cureus 2021, 13, e18847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortí-Casañ, N.; Boerema, A.S.; Köpke, K.; Ebskamp, A.; Keijser, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, T.; Dolga, A.M.; Broersen, K.; Fischer, R.; et al. The TNFR1 antagonist Atrosimab reduces neuronal loss, glial activation and memory deficits in an acute mouse model of neurodegeneration. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, R.; Kontermann, R.E.; Pfizenmaier, K. Selective Targeting of TNF Receptors as a Novel Therapeutic Approach. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaltsonoudis, E.; Voulgari, P.V.; Konitsiotis, S.; Drosos, A.A. Demyelination and other neurological adverse events after anti-TNF therapy. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, C.; Geng, Z.; Li, S.; Yu, F. Etanercept for Ankylosing Spondylitis With Coexisting Demyelinating Myelitis. Am. J. Ther. 2019, 26, e629–e631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisternas, M.; Gutiérrez, M.; Jacobelli, S. Successful rechallenge with anti–tumor necrosis factor α for psoriatic arthritis after development of demyelinating nervous system disease during initial treatment: Comment on the article by Mohan et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 3107–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Primary Disease | TNF-α Inhibitor | Age/Sex | Family History of Neurological Diseases | Neurological Symptoms/Diagnosed Conditions | Therapeutic Measures | Outcome | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | RA | INFL | Not reported/M | Not reported | ALS | Discontinuation Riluzole | Progressive ALS | [59] |
| 2. | AS | INFL | 55/M | Not reported | ALS | Discontinuation Riluzole, alphatocopherol | Progressive ALS; death by respiratory insufficiency | [60] |
| 3. | RA | INFL | 65/F | Not reported | ALS | Discontinuation Riluzole not tolerated | Progressive ALS; death by respiratory insufficiency | [61] |
| 4. | CD | ADA | 53/F | Not reported | Demyelinating lesions/autoimmune encephalitis | Discontinuation Intravenous steroids, immunoglobulin | Resolution | [62] |
| 5. | AS | ADA | 30/F | Not reported | Demyelinating lesions/autoimmune encephalitis (Bickerstaff brainstem encephalitis) | Discontinuation Methylprednisolone, intravenous gamma globulin (IVIg), rituximab | Partial resolution | [63] |
| 6. | CD | ADA | 20/F | Not reported | Peripheral neuropathy/Henoch–Schönlein purpura with neurological involvement | Discontinuation ADA replaced with ustekinumab/methylprednisolone | Resolution | [64] |
| 7. | CD | INFL | 64/F | Neurofibromatosis | Acute neuropathy, encephalopathy | Discontinuation Polyvalent immunoglobulin | Partial resolution | [65] |
| 8. | CD | INFL | 27/F | Not reported | Non-demyelinating inflammatory CNS events/anti-NMDAR encephalitis | INFL replaced with ustekinumab Rituximab | Resolution | [66] |
| 9. | RA | INFL | 72/M | Not reported | Demyelinating progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy | Discontinuation | Persistent neurologic and cognitive deficits | [67] |
| 10. | CD | INFL | 45/F | Not reported | Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis | Discontinuation Methylprednisolone | Resolution | [68] |
| 11. | RA | ADA | 66/F | Not reported | Demyelinating progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy | Discontinuation | Worsening neurological symptoms | [67] |
| 12. | RA | ADA | 66/M | Not reported | Demyelinating leukoencephalopathy | Discontinuation Methylprednisolone Meloxicam | Partial resolution | [69] |
| 13. | AS | GOL | 45/F | Not reported | Demyelinating posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome | Discontinuation, anti-convulsant therapy (levetiracetam) | Resolution | [70] |
| 14. | RA | ETA | 74/F | Not reported | Demyelinating progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy | Discontinuation Supportive therapy | Slight improvement | [71] |
| 15. | RA | ETA | 47/F | Not reported | Leptomeningitis | Discontinuation Methylprednisolone, azathioprine, levetiracetam, valproic acid. | Significant resolution | [72] |
| 16. | RA | ADA | 77/M | Not reported | Hypertrophic pachymeningitis | Discontinuation, Prednisone | Resolution | [73] |
| 17. | JIA | ADA | 18/F | Not reported | Aseptic meningitis | Discontinuation Methylprednisolone | Resolution | [74] |
| 18. | RA | ADA | 52/F | Not reported | Acute myelopathy/paraplegia | Discontinuation Methylprednisolone (oral/i.v) | Partial resolution | [75] |
| 19. | CD | ADA | 52/F | Chronic myelitis | Partial resolution | |||
| 20. | RA | ADA | 42/M | Chronic myelitis | No response | |||
| 21. | RA Lupus | CZP | 54/F | Chronic myelitis | Partial resolution | |||
| 22. | Blau syndrome | ETA | 13/M | Not reported | Transverse myelitis | Discontinuation Methylprednisolone, prednisone | Resolution | [76] |
| 23. | Behcet’s disease | GOL | 34/M | Not reported | Demyelinating lesions | Discontinuation Steroid therapy | Resolution | [77] |
| 24. | Behcet’s disease | GOL | 51/F | Not reported | Multifocal myelitis | Discontinuation Steroid therapy | Resolution | [78] |
| 25. | CD | INFL | 40/M | Not reported | Extensive longitudinal myelopathy | Discontinuation Methylprednisolone, followed by oral prednisolone | Slight improvement | [79] |
| 26. | AS | ADA ETA | 50/M | Not reported | Rapidly progressive dementia | Discontinuation | Resolution | [80] |
| 27. | RA | ADA | 40/F | None | CNS demyelination | Discontinuation Methylprednisolone | Resolution | [81] |
| 28. | PSO | ADA | 36/F | None | CNS demyelination | Discontinuation | Resolution | [82] |
| 29. | PSO | ADA | 37/F | None | CNS demyelination | Discontinuation Intravenous immunoglobulin, oral corticosteroids | Resolution | [83] |
| 30. | RA | ADA | 39/F | Not reported | Chronic demyelinating neuropathy | Discontinuation | Resolution | [84] |
| 31. | CD | ADA | 34/F | None | Inflammatory demyelination | Discontinuation Steroid therapy | Slight improvement | [85] |
| 32. | HS | ADA | 29/M | Not reported | Demyelinating radiologically isolated syndrome | Discontinuation | Resolution | [86] |
| 33. | JIA | ADA | 14/M | Not reported | CNS active inflammatory process (no demyelination lesions) | Discontinuation High-dose corticosteroids | Partial resolution | [87] |
| 34. | PSO | ADA | 51/F | None | MS | Discontinuation high-dose corticosteroids | Partial resolution | [88] |
| 35. | AS | ETA | 34/M | None | CNS demyelination | Discontinuation | Slight improvement | [89] |
| 36. | AS | ETA | 26/F | Not reported | MOGAD | Discontinuation Methylprednisolone | Significant improvement | [90] |
| 37. | AS | ETA | 44/F | Not reported | Tumefactive CNS inflammatory demyelination | Discontinuation High-dose steroids | Significant improvement | [91] |
| 38. | AS | ETA | 36/M | MS (brother) | Acute transverse myelitis | Discontinuation Methylprednisolone | Resolution | [92] |
| 39. | Juvenile RA | ETA | 21/F | None | MS Optic neuritis | Discontinuation Methylprednisolone | Partial resolution | [93] |
| 40. | PSO | ETA | 55/M | None | MS | Discontinuation Methylprednisolone | No improvement | [94] |
| 41. | AS | ADA | 44/M | None | Demyelinating brain lesions | Discontinuation | Not reported | |
| 42. | RA | ETA | 26/F | Not reported | MS | Not reported | Not reported | [95] |
| 43. | AS | GOL | 41/M | None | Fulminant CNS demyelination | Discontinuation Steroid therapy Plasmapheresis | Resolution | [96] |
| 44. | PSO | INFL | 47/F | MS (sister) | MS | Discontinuation Steroid therapy | Partial resolution | [97] |
| 45. | PSO | INFL | 27/F | None | CNS demyelination | Discontinuation Steroid therapy Rituximab | Partial resolution | [98] |
| 46. | CD | INFL | 46/M | None | Inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropachronicth | Discontinuation Intravenous human immunoglobulin | Resolution | [99] |
| 47. | CD AS | INFL | 18/F | Not reported | CNS demyelination | Discontinuation | No improvement | [100] |
| 48. | AS Uveitis | INFL | 38/M | Not reported | Demyelinating brain lesions | Discontinuation | Resolution | [101] |
| 49. | RA | INFL | 56/M | Not reported | CNS demyelination | Discontinuation High-dose dexamethasone | Resolution | [102] |
| 50. | 66/F | Not reported | Discontinuation Oral prednisone | Significant improvement | ||||
| 51. | CD | INFL | 19/F | None | CNS demyelination | Discontinuation | Resolution | [103] |
| 52. | Uveitis JIA | ADA | 21/F | Not reported | MS | Discontinuation Cladribine | Resolution | [38] |
| 53. | PSO | ADA | 56/F | Not reported | MS aseptic meningitis | Discontinuation | Resolution | [104] |
| 54. | RA | ADA | 68/F | None | MS | Discontinuation | Resolution | [105] |
| 55. | Autoimmune Uveitis | ADA | 23/M | MS (family) | MS | Discontinuation Methylprednisolone, oral prednisolone | Resolution | [39] |
| 56. | AS | ADA | 36/M | None | MS | Discontinuation Methylprednisolone, oral prednisolone | Resolution | [106] |
| 57. | CD | INFL | 47/F | None | MS | Discontinuation | Resolution | [107] |
| 58. | UC | INFL | 35/F | MS (family) | MS | Discontinuation | Not reported | [108] |
| 59. | AS | INFL | 48/M | Not reported | MS | Discontinuation | Resolution | [109] |
| 60. | PSO | ADA | 41/M | CNS demyelination | Discontinuation | Resolution | ||
| 61. | PSO | ETA | 38/F | MS | Discontinuation Interferon beta-1a | Not reported | ||
| 62. | RA | ADA | 64/F | MS | Discontinuation | Not reported | ||
| 63. | AS | INFL | 34/F | Clinical isolated syndrome | Discontinuation | Resolution | ||
| 64. | PSO | INFL | 57/M | Peripheral demyelinating neuropathy | Discontinuation | Resolution | ||
| 65. | PSO | ETA | 48/M | Not reported | MS | Discontinuation | Resolution | [110] |
| 66. | PSO | INFL | 62/F | Not reported | Optic neuritis | Discontinuation Methylprednisolone | No improvement | [111] |
| 67. | PSO | INFL | 56/F | Not reported | CNS demyelination | Discontinuation Methylprednisolone | Significant improvement | [112] |
| 68. | PSO | CZP | 44/M | Not reported | Cranial nerve III demyelination | Discontinuation methylprednisolone | Resolution | [113] |
| 69. | RA | ETA | 64/F | Not reported | Myelitis optic neuritis | Discontinuation Methylprednisolone | Resolution | [114] |
| 70. | CD | ADA | 27/F | Not reported | Internuclear ophthalmoplegia | Discontinuation Steroid therapy | Resolution | [115] |
| 71. | RA | INFL | 53/F | Not reported | Optic neuritis | Discontinuation Steroid therapy | Resolution | [116] |
| 72. | RA | ETA | 40/F | Not reported | Neurosarcoidosis | Discontinuation Methylprednisolone, oral prednisolone | Partial resolution | [117] |
| 73. | RA Uveitis | ETA | 33/F | Not reported | Neurosarcoidosis | ETA replaced with INFL Steroid therapy | Significant improvement | [118] |
| 74. | RA | INFL | 50/F | None | Polineuropathy | Discontinuation Intravenous gammaglobulin | Slight improvement | [119] |
| 75. | 85/F | Mild sensory loss | Discontinuation Steroid therapy | Partial resolution | ||||
| 76. | 68/F | Not reported | Discontinuation | Slight improvement | ||||
| 77. | PSO | ADA | 65/F | Not reported | Acute bilateral symmetric phrenic neuropathy | Discontinuation Oxygen | Resolution | [120] |
| 78. | RA | ETA | 45/F | Not reported | Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy | Discontinuation Intravenous gammaglobulin | Partial resolution | [121] |
| 79. | INFL | 49/M | Not reported | |||||
| 80. | PSO | ADA | 53/F | GBS | Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy | Discontinuation Intravenous immunoglobulin | Resolution | [122] |
| 81. | RA | ADA | 52/M | Idiopathic Parkinson’s disease | DADS neuropathy | Discontinuation | Resolution | [123] |
| 82. | AS | GOL | 48/M | ALS (family) | Bilateral retrobulbar optic neuropathy | Discontinuation Methylprednisolone, oral prednisolone | No improvement | [124] |
| 83. | PSO | ADA | 42/M | Not reported | Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy | Discontinuation intravenous immunoglobulin | Resolution | [125] |
| 84. | PSO | INFL | 64/M | Not reported | Sensory polyradiculopathy | Discontinuation Intravenous immunoglobulin | Resolution | [126] |
| 85. | RA | INFL | 32/F | Not reported | Small-fiber neuropathies | Discontinuation | Partial resolution | [127] |
| 86. | 73/F | Not reported | Discontinuation Symptomatic treatment | Partial resolution | ||||
| 87. | 55/F | Not reported | Discontinuation | Significant improvement | ||||
| 88. | AS | INFL | 54/M | Not reported | MMNCB | Discontinuation | Significant improvement | [128] |
| 89. | UC | INFL | 30/M | None | Multifocal motor neuropathy | Discontinuation Intravenous immunoglobulin | Resolution | [128] |
| 90. | JIA | ETA | 12/F | Not reported | Chronic inflammatory demyelinating neuropathy | Discontinuation Intravenous immunoglobulins, steroids, plasma exchange | Limited response | [129] |
| 91. | RA | ADA | 44/F | Not reported | Inflammatory demyelinating neuropathy | Discontinuation Intravenous immunoglobulin | Partial resolution | [130] |
| 92. | CD | ADA | 37/M | Not reported | Chronic inflammatory demyelinating neuropathy | Discontinuation Intravenous immunoglobulins, steroids | Significant improvement | [131] |
| 93. | CD | INFL | 60/F | None | Seizures | Discontinuation | Resolution | [132] |
| 94. | CD | INFL | 74/M | Not reported | Seizures | Discontinuation | Resolution | [133] |
| 95. | RA | ETA | 74/F | Not reported | CJD | Discontinuation | Resolution | [134] |
| 96. | PSO | INFL | 40/M | Not reported | LSS | Discontinuation Intravenous immunoglobulin | Partial resolution | [135] |
| 97. | UC | INFL | 44/M | None | LSS | Discontinuation Intravenous immunoglobulin | Partial resolution | [136] |
| 98. | CD | INFL | 24/F | Not reported | LSS | Discontinuation Intravenous immunoglobulin | Resolution | [137] |
| 99. | 35/F | Not reported | ||||||
| 100. | RA | INFL | 77/F | Not reported | MFS | Discontinuation High-dose steroids, gabapentine | Slow improvement | [138] |
| 101. | UC | INFL | 43/F | Not reported | MFS | Discontinuation | Resolution | [139] |
| 102. | PSO | ETA | 42/F | Not reported | MFS | Discontinuation | Slow improvement | [140] |
| 103. | CD | ADA | 64/M | Not reported | GBS | Discontinuation | Resolution | [141] |
| 104. | PSO | ADA | 45/M | Not reported | GBS | Discontinuation | Partial resolution | [142] |
| 105. | RA | ADA | 50/F | Not reported | GBS | Discontinuation Prednisone, gabapentin | Partial resolution | [143] |
| 106. | CD | ADA | 37/M | Not reported | GBS | Discontinuation Intravenous immunoglobulin | Partial resolution | [144] |
| 107. | UC AS | INFL | 47/F | Not reported | GBS | Discontinuation intravenous immunoglobulin | Resolution | [145] |
| 108. | CD | ADA | 71/M | Not reported | GBS | Discontinuation Intravenous immunoglobulin, Methylprednisolone, plasmapheresis | Partial resolution | [146] |
| 109. | CD | ADA | 33/F | Not reported | GBS | Continuation of ADA treatment Intravenous immunoglobulin | Significant improvement | [147] |
| 110. | AS | ETA | 50/M | Not reported | GBS | Discontinuation Intravenous immunoglobulin, plasmapheresis | Resolution | [148] |
| 111. | PSO | ETA | 53/M | None | MS | Discontinuation Interferonβ Baclofen | Significant improvement | [149] |
| 112. | PSO | 42/M | None | MS | Discontinuation | Significant improvement | ||
| 113. | AS | 51/F | Not reported | Discontinuation | Mild improvement |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gogulescu, A.; Blidisel, A.; Soica, C.; Mioc, A.; Voicu, A.; Jojic, A.; Voicu, M.; Banciu, C. Neurological Side Effects of TNF-α Inhibitors Revisited: A Review of Case Reports. Medicina 2024, 60, 1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60091409
Gogulescu A, Blidisel A, Soica C, Mioc A, Voicu A, Jojic A, Voicu M, Banciu C. Neurological Side Effects of TNF-α Inhibitors Revisited: A Review of Case Reports. Medicina. 2024; 60(9):1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60091409
Chicago/Turabian StyleGogulescu, Armand, Alexandru Blidisel, Codruta Soica, Alexandra Mioc, Adrian Voicu, Alina Jojic, Mirela Voicu, and Christian Banciu. 2024. "Neurological Side Effects of TNF-α Inhibitors Revisited: A Review of Case Reports" Medicina 60, no. 9: 1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60091409
APA StyleGogulescu, A., Blidisel, A., Soica, C., Mioc, A., Voicu, A., Jojic, A., Voicu, M., & Banciu, C. (2024). Neurological Side Effects of TNF-α Inhibitors Revisited: A Review of Case Reports. Medicina, 60(9), 1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60091409








