The Impact of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter-2 Inhibition on Insulin Resistance and Inflammation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patients
2.2. Clinical, Anthropometric, and Laboratory Data
2.3. Insulin Resistance and Inflammation Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Findings and Their Interpretation
4.2. Strengths and Weaknesses
4.3. Relevance of the Findings: Implications for Clinicians and Policymakers
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Piovani, D.; Nikolopoulos, G.K.; Bonovas, S. Non-Communicable Diseases: The Invisible Epidemic. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magliano, D.J.; Boyko, E.J. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th ed.; IDF Diabetes Atlas: Brussels, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, J.C.N.; Lim, L.L.; Wareham, N.J.; Shaw, J.E.; Orchard, T.J.; Zhang, P.; Lau, E.S.H.; Eliasson, B.; Kong, A.P.S.; Ezzati, M.; et al. The Lancet Commission on diabetes: Using data to transform diabetes care and patient lives. Lancet 2021, 396, 2019–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 1. Improving Care and Promoting Health in Populations: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, S8–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, M.J.; Aroda, V.R.; Collins, B.S.; Gabbay, R.A.; Green, J.; Maruthur, N.M.; Rosas, S.E.; Del Prato, S.; Mathieu, C.; Mingrone, G.; et al. Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2022. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia 2022, 65, 1925–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratton, I.M.; Adler, A.I.; Neil, H.A.; Matthews, D.R.; Manley, S.E.; Cull, C.A.; Hadden, D.; Turner, R.C.; Holman, R.R. Association of glycaemia with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 35): Prospective observational study. BMJ 2000, 321, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2021 Diabetes Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of diabetes from 1990 to 2021, with projections of prevalence to 2050: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2023, 402, 203–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration; Sarwar, N.; Gao, P.; Seshasai, S.R.; Gobin, R.; Kaptoge, S.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Ingelsson, E.; Lawlor, D.A.; Selvin, E.; et al. Diabetes mellitus, fasting blood glucose concentration, and risk of vascular disease: A collaborative meta-analysis of 102 prospective studies. Lancet 2010, 375, 2215–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallon, V.; Verma, S. Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors on Kidney and Cardiovascular Function. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2021, 83, 503–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Stefansson, B.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Chertow, G.M.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.F.; Mann, J.F.E.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Lindberg, M.; Rossing, P.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, B.; Perkovic, V.; Matthews, D.R. Canagliflozin and Cardiovascular and Renal Events in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiviott, S.D.; Raz, I.; Bonaca, M.P.; Mosenzon, O.; Kato, E.T.; Cahn, A.; Silverman, M.G.; Zelniker, T.A.; Kuder, J.F.; Murphy, S.A.; et al. Dapagliflozin and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinman, B.; Lachin, J.M.; Inzucchi, S.E. Empagliflozin, Cardiovascular Outcomes, and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Reeves, W.B.; Awad, A.S. Pathophysiology of diabetic kidney disease: Impact of SGLT2 inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2021, 17, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaccari, A. Expanding the Use of SGLT2i in Diabetes Beyond Type 2. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, 50–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, D.M.; Ahmed, N.; Tariq, H.; Walgamage, M.; Walgamage, T.; Mohammed, A.; Chou, J.T.; Kaluzna-Oleksy, M.; Lesiak, M.; Straburzynska-Migaj, E. SGLT2 Inhibitors in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Heart Failure-A Concise Review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelinson, D.S.; Sosa, J.M.; Chilton, R.J. SGLT2 inhibitors: A narrative review of efficacy and safety. J. Osteopath. Med. 2021, 121, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saisho, Y. SGLT2 Inhibitors: The Star in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes? Diseases 2020, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallon, V. The mechanisms and therapeutic potential of SGLT2 inhibitors in diabetes mellitus. Annu. Rev. Med. 2015, 66, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.; Nguyen, T.V. Expanding the Role of SGLT2 Inhibitors Beyond Diabetes: A Case-Based Approach. Sr. Care Pharm. 2023, 38, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, E.M. SGLT2 Inhibitors: Physiology and Pharmacology. Kidney360 2021, 2, 2027–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriyama, S. A Potential Mechanism of Cardio-Renal Protection with Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Amelioration of Renal Congestion. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2019, 44, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelniker, T.A.; Braunwald, E. Mechanisms of Cardiorenal Effects of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udell, J.A.; Jones, W.S.; Petrie, M.C.; Harrington, J.; Anker, S.D.; Bhatt, D.L.; Hernandez, A.F.; Butler, J. Sodium Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibition for Acute Myocardial Infarction: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, 2058–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvatore, T.; Galiero, R.; Caturano, A.; Rinaldi, L.; Di Martino, A.; Albanese, G.; Di Salvo, J.; Epifani, R.; Marfella, R.; Docimo, G.; et al. An Overview of the Cardiorenal Protective Mechanisms of SGLT2 Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iordan, L.; Gaita, L.; Timar, R.; Avram, V.; Sturza, A.; Timar, B. The Renoprotective Mechanisms of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors (SGLT2i)-A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sofiani, M.E.; Ganji, S.S.; Kalyani, R.R. Body composition changes in diabetes and aging. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2019, 33, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.S.; Al-Gindan, Y.Y.; Govan, L.; Hankey, C.R.; Lean, M.E.J. Associations of BMI, waist circumference, body fat, and skeletal muscle with type 2 diabetes in adults. Acta Diabetol. 2019, 56, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preis, S.R.; Massaro, J.M.; Robins, S.J.; Hoffmann, U.; Vasan, R.S.; Irlbeck, T.; Meigs, J.B.; Sutherland, P.; D’Agostino, R.B., Sr.; O’Donnell, C.J.; et al. Abdominal subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue and insulin resistance in the Framingham heart study. Obesity 2010, 18, 2191–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrannini, G.; Hach, T.; Crowe, S.; Sanghvi, A.; Hall, K.D.; Ferrannini, E. Energy Balance After Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibition. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 1730–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratama, K.G.; Tandarto, K.; Hengky, A. Weight Loss Effect of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 (Sglt2) Inhibitors in Patients with Obesity without Diabetes: A Systematic Review. Acta Endocrinol. 2022, 18, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.K.; Kim, Y.J.; Jung, C.H. Effect of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors on Weight Reduction in Overweight and Obese Populations without Diabetes: A Systematic Review and a Meta-Analysis. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2021, 30, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The, E.-K.C.G.; Herrington, W.G.; Staplin, N.; Wanner, C.; Green, J.B.; Hauske, S.J.; Emberson, J.R.; Preiss, D.; Judge, P.; Mayne, K.J.; et al. Empagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolinder, J.; Ljunggren, O.; Kullberg, J.; Johansson, L.; Wilding, J.; Langkilde, A.M.; Sugg, J.; Parikh, S. Effects of dapagliflozin on body weight, total fat mass, and regional adipose tissue distribution in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with inadequate glycemic control on metformin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 1020–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Yang, W.; Gao, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, S.; Han, X.; Ji, L. The Association Between the Dosage of SGLT2 Inhibitor and Weight Reduction in Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A Meta-Analysis. Obesity 2018, 26, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.J.; Eriksson, J.W. Emerging Role of SGLT-2 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Obesity. Drugs 2019, 79, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkovic, V.; Jardine, M.J.; Neal, B.; Bompoint, S.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Charytan, D.M.; Edwards, R.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; Bull, S.; et al. Canagliflozin and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes and Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekeres, Z.; Toth, K.; Szabados, E. The Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors on Lipid Metabolism. Metabolites 2021, 11, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccardi, F.; Webb, D.R.; Htike, Z.Z.; Youssef, D.; Khunti, K.; Davies, M.J. Efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2016, 18, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, Y.; Ogawa, W. SGLT2 inhibitors for genetic and acquired insulin resistance: Considerations for clinical use. J. Diabetes Investig. 2020, 11, 1431–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Sathyapalan, T.; Maleki, M.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Sahebkar, A. Molecular mechanisms by which SGLT2 inhibitors can induce insulin sensitivity in diabetic milieu: A mechanistic review. Life Sci. 2020, 240, 117090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Sato, E.; Mishima, E.; Miyazaki, M.; Tanaka, T. What’s New in the Molecular Mechanisms of Diabetic Kidney Disease: Recent Advances. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, A.; Hirose, T.; Sato, S.; Ito, H.; Takahashi, C.; Ishikawa, R.; Kamada, A.; Oba-Yabana, I.; Kimura, T.; Takahashi, K.; et al. Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor suppresses renal injury in rats with renal congestion. Hypertens. Res. 2024, 47, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Guo, X.; Yan, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, D.; Chen, G.; Zhang, W.; Tang, C.; et al. Dapagliflozin Attenuates Contrast-induced Acute Kidney Injury by Regulating the HIF-1alpha/HE4/NF-kappaB Pathway. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2022, 79, 904–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakour, N.; Karami, S.; Iranshahi, M.; Butler, A.E.; Sahebkar, A. Antifibrotic effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors: A comprehensive review. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2024, 18, 102934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, T.; Xian, J.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, X.; Lu, H.; Lin, Y. SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin attenuates cardiac fibrosis and inflammation by reverting the HIF-2alpha signaling pathway in arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, J.M.; Heo, J.H.; Kim, D.J.; Park, S.H.; Sung, M.; Kim, J.; Oh, J.; Yang, D.H.; et al. Empagliflozin attenuates diabetic tubulopathy by improving mitochondrial fragmentation and autophagy. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2019, 317, F767–F780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Grotta, R.; de Candia, P.; Olivieri, F.; Matacchione, G.; Giuliani, A.; Rippo, M.R.; Tagliabue, E.; Mancino, M.; Rispoli, F.; Ferroni, S.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of SGLT-2 inhibitors via uric acid and insulin. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekkers, C.C.J.; Petrykiv, S.; Laverman, G.D.; Cherney, D.Z.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Heerspink, H.J.L. Effects of the SGLT-2 inhibitor dapagliflozin on glomerular and tubular injury markers. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 1988–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Kosiborod, M.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Cherney, D.Z.I. Renoprotective effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors. Kidney Int. 2018, 94, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchapakesan, U.; Pegg, K.; Gross, S.; Komala, M.G.; Mudaliar, H.; Forbes, J.; Pollock, C.; Mather, A. Effects of SGLT2 inhibition in human kidney proximal tubular cells--renoprotection in diabetic nephropathy? PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, M.; Takei, M.; Shiraishi, Y.; Suzuki, Y. Increased Hematocrit During Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor Therapy Indicates Recovery of Tubulointerstitial Function in Diabetic Kidneys. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2016, 8, 844–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theofilis, P.; Sagris, M.; Oikonomou, E.; Antonopoulos, A.S.; Siasos, G.; Tsioufis, K.; Tousoulis, D. The impact of SGLT2 inhibitors on inflammation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies in rodents. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 111, 109080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Liu, J.; Zhong, L.; Li, S.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Xiao, X. The effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on biomarkers of inflammation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1045235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; Initiative, S. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Prev. Med. 2007, 45, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEvoy, J.W.; McCarthy, C.P.; Bruno, R.M.; Brouwers, S.; Canavan, M.D.; Ceconi, C.; Christodorescu, R.M.; Daskalopoulou, S.S.; Ferro, C.J.; Gerdts, E.; et al. 2024 ESC Guidelines for the management of elevated blood pressure and hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 3912–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inker, L.A.; Eneanya, N.D.; Coresh, J.; Tighiouart, H.; Wang, D.; Sang, Y.; Crews, D.C.; Doria, A.; Estrella, M.M.; Froissart, M.; et al. New Creatinine- and Cystatin C-Based Equations to Estimate GFR without Race. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1737–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.R.; Soltani, S.; Meybodi, Z.H.; Marques-Vidal, P.; Firouzabadi, D.D.; Eshraghi, R.; Restrepo, D.; Ghoshouni, H.; Sarebanhassanabadi, M. Which surrogate insulin resistance indices best predict coronary artery disease? A machine learning approach. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, Q.; Ma, X.; Cheng, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X. Prognostic Value of Estimated Glucose Disposal Rate in Patients with Non-ST-Segment Elevation Acute Coronary Syndromes Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 24, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penno, G.; Solini, A.; Orsi, E.; Bonora, E.; Fondelli, C.; Trevisan, R.; Vedovato, M.; Cavalot, F.; Zerbini, G.; Lamacchia, O.; et al. Insulin resistance, diabetic kidney disease, and all-cause mortality in individuals with type 2 diabetes: A prospective cohort study. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, E.J.; Osman, J.L.; Cohen, H.W.; Rajpathak, S.N.; Lewis, O.; Crandall, J.P. Use of the estimated glucose disposal rate as a measure of insulin resistance in an urban multiethnic population with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 2280–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Lu, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, X. Insulin resistance assessed by estimated glucose disposal rate and risk of incident cardiovascular diseases among individuals without diabetes: Findings from a nationwide, population based, prospective cohort study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durmus, E.; Kivrak, T.; Gerin, F.; Sunbul, M.; Sari, I.; Erdogan, O. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio are Predictors of Heart Failure. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2015, 105, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Han, W.; Li, Y.; Jiang, M.; Ren, X.; Yang, P.; Jia, Y.; Sun, L.; Wang, R.; Shi, M.; et al. Changes in the estimated glucose disposal rate and incident cardiovascular disease: Two large prospective cohorts in Europe and Asia. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, T.; Fukui, T.; Nakanishi, N.; Yamamoto, S.; Tomoyasu, M.; Osamura, A.; Ohara, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Ito, Y.; Hirano, T. Dapagliflozin decreases small dense low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol and increases high-density lipoprotein 2-cholesterol in patients with type 2 diabetes: Comparison with sitagliptin. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2017, 16, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneto, H.; Obata, A.; Kimura, T.; Shimoda, M.; Kinoshita, T.; Matsuoka, T.A.; Kaku, K. Unexpected Pleiotropic Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors: Pearls and Pitfalls of This Novel Antidiabetic Class. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obata, A.; Kubota, N.; Kubota, T.; Iwamoto, M.; Sato, H.; Sakurai, Y.; Takamoto, I.; Katsuyama, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Fukazawa, M.; et al. Tofogliflozin Improves Insulin Resistance in Skeletal Muscle and Accelerates Lipolysis in Adipose Tissue in Male Mice. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 1029–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokono, M.; Takasu, T.; Hayashizaki, Y.; Mitsuoka, K.; Kihara, R.; Muramatsu, Y.; Miyoshi, S.; Tahara, A.; Kurosaki, E.; Li, Q.; et al. SGLT2 selective inhibitor ipragliflozin reduces body fat mass by increasing fatty acid oxidation in high-fat diet-induced obese rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 727, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Rodriguez, A.M.; Gonzalez-Ortiz, M.; Martinez-Abundis, E. Effect of Dapagliflozin on Insulin Secretion and Insulin Sensitivity in Patients with Prediabetes. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2020, 128, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaetis, G.S. Empagliflozin therapy and insulin resistance-associated disorders: Effects and promises beyond a diabetic state. Arch. Med. Sci. Atheroscler. Dis. 2021, 6, e57–e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohari, S.; Reshadmanesh, T.; Khodabandehloo, H.; Karbalaee-Hasani, A.; Ahangar, H.; Arsang-Jang, S.; Ismail-Beigi, F.; Dadashi, M.; Ghanbari, S.; Taheri, H.; et al. The effect of EMPAgliflozin on markers of inflammation in patients with concomitant type 2 diabetes mellitus and Coronary ARtery Disease: The EMPA-CARD randomized controlled trial. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2022, 14, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scisciola, L.; Cataldo, V.; Taktaz, F.; Fontanella, R.A.; Pesapane, A.; Ghosh, P.; Franzese, M.; Puocci, A.; De Angelis, A.; Sportiello, L.; et al. Anti-inflammatory role of SGLT2 inhibitors as part of their anti-atherosclerotic activity: Data from basic science and clinical trials. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 1008922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.D.; Naumova, A.V.; Isquith, D.; Sapp, J.; Huynh, K.A.; Tucker, I.; Balu, N.; Voronyuk, A.; Chu, B.; Ordovas, K.; et al. Dapagliflozin reduces systemic inflammation in patients with type 2 diabetes without known heart failure. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashayekhi, M.; Safa, B.I.; Gonzalez, M.S.C.; Kim, S.F.; Echouffo-Tcheugui, J.B. Systemic and organ-specific anti-inflammatory effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 35, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonora, B.M.; Avogaro, A.; Fadini, G.P. Extraglycemic Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors: A Review of the Evidence. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmas, C.E.; Silverio, D.; Tsomidou, C.; Salcedo, M.D.; Montan, P.D.; Guzman, E. The Impact of Insulin Resistance and Chronic Kidney Disease on Inflammation and Cardiovascular Disease. Clin. Med. Insights Endocrinol. Diabetes 2018, 11, 1179551418792257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrauben, S.J.; Jepson, C.; Hsu, J.Y.; Wilson, F.P.; Zhang, X.; Lash, J.P.; Robinson, B.M.; Townsend, R.R.; Chen, J.; Fogelfeld, L.; et al. Insulin resistance and chronic kidney disease progression, cardiovascular events, and death: Findings from the chronic renal insufficiency cohort study. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, K.R.; Brosius, F.C., 3rd; Cavender, M.A.; Fioretto, P.; Fowler, K.J.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Manley, T.; McGuire, D.K.; Molitch, M.E.; Mottl, A.K.; et al. SGLT2 Inhibition for CKD and Cardiovascular Disease in Type 2 Diabetes: Report of a Scientific Workshop Sponsored by the National Kidney Foundation. Diabetes 2021, 70, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.; Singhal, A.; Goyal, P. TG/HDL Ratio: A marker for insulin resistance and atherosclerosis in prediabetics or not? J. Family Med. Prim. Care 2021, 10, 3700–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baneu, P.; Vacarescu, C.; Dragan, S.R.; Cirin, L.; Lazar-Hocher, A.I.; Cozgarea, A.; Faur-Grigori, A.A.; Crisan, S.; Gaita, D.; Luca, C.T.; et al. The Triglyceride/HDL Ratio as a Surrogate Biomarker for Insulin Resistance. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciarambino, T.; Crispino, P.; Guarisco, G.; Giordano, M. Gender Differences in Insulin Resistance: New Knowledge and Perspectives. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 7845–7861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geer, E.B.; Shen, W. Gender differences in insulin resistance, body composition, and energy balance. Gend. Med. 2009, 6 (Suppl. S1), 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirtikar, U.; Kajale, N.; Patwardhan, V.; Khadilkar, V.; Khadilkar, A.V. Cardiometabolic Risk in Pre- and Post-Menopausal Women with Special Reference to Insulin Resistance: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Midlife Health 2020, 11, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arner, P.; Viguerie, N.; Massier, L.; Ryden, M.; Astrup, A.; Blaak, E.; Langin, D.; Andersson, D.P. Sex differences in adipose insulin resistance are linked to obesity, lipolysis and insulin receptor substrate 1. Int. J. Obes. 2024, 48, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenhill, C. Obesity: Sex differences in insulin resistance. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Liu, D.; Li, M.; He, J.; Fu, Y. Association between systemic immune-inflammation index and insulin resistance and mortality. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Luca, C.; Olefsky, J.M. Inflammation and insulin resistance. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, H. Correlation between insulin resistance and the rate of neutrophils-lymphocytes, monocytes-lymphocytes, platelets-lymphocytes in type 2 diabetic patients. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2024, 24, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, K.; Donmez, A.; Keser, G. Inflammation-induced thrombosis: Mechanisms, disease associations and management. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 1478–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonmez, O.; Sonmez, M. Role of platelets in immune system and inflammation. Porto Biomed. J. 2017, 2, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, K.Y.; Granger, D.N. Platelets: A critical link between inflammation and microvascular dysfunction. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.S.; Khan, M.S.; Butler, J. The Interplay Between Diabetes, Cardiovascular Disease, and Kidney Disease. In Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes; ADA Clinical Compendia Series; American Diabetes Association: Arlington, VA, USA, 2021; pp. 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Stark, K.; Massberg, S. Interplay between inflammation and thrombosis in cardiovascular pathology. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2021, 18, 666–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Schouwenburg, I.M.; Mahmoodi, B.K.; Veeger, N.J.; Bakker, S.J.; Kluin-Nelemans, H.C.; Meijer, K.; Gansevoort, R.T. Insulin resistance and risk of venous thromboembolism: Results of a population-based cohort study. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 1012–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasleen, B.; Vishal, G.K.; Sameera, M.; Fahad, M.; Brendan, O.; Deion, S.; Pemminati, S. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors: Benefits Versus Risk. Cureus 2023, 15, e33939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopaschuk, G.D.; Verma, S. Mechanisms of Cardiovascular Benefits of Sodium Glucose Co-Transporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors: A State-of-the-Art Review. JACC Basic. Transl. Sci. 2020, 5, 632–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Entire Group (n = 246) | Men (n = 134) | Women (n = 112) | p (Men vs. Women) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) a | 63.6 ± 8.3 | 62.6 ± 8.2 | 64.8 ± 8.3 | 0.043 |
| Diabetes duration (years) b | 8 [5; 14] | 8 (119.5) | 9 (128.3) | 0.329 |
| Weight (kg) b | 91 [80; 102] | 100 (160.7) | 80 (79) | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) b | 31.5 [31; 32.5] | 32.0 (139.2) | 31.0 (104.7) | <0.001 |
| Waist circumference (cm) a | 94.0 ± 13.6 | 100.8 ± 10.7 | 85.9 ± 12.3 | <0.001 |
| SBP (mmHg) b | 140.0 [134–143] | 139.5 (120.8) | 140.0 (126.7) | 0.514 |
| DBP (mmHg) b | 75 [70–85] | 75 (119.9) | 75 (127.7) | 0.387 |
| FPG (mg/dL) b | 179 [162; 193] | 180 (129) | 178 (116.9) | 0.183 |
| HbA1c (%) b | 8.4 [8.2; 8.6] | 8.4 (124.4) | 8.4 (122.4) | 0.829 |
| LDLc (mg/dL) b | 81.0 [76; 89] | 79.5 (114.6) | 84.0 (134.1) | 0.032 |
| Tg (mg/dL) a | 168.4 ± 32 | 170.9 ± 31.5 | 165.4 ± 32.5 | 0.179 |
| HDLc (mg/dL) b | 47 [43; 53] | 46 (119.4) | 47 (128.4) | 0.323 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) b | 79.0 [70; 90] | 78.5 (118.4) | 80.5 (129.5) | 0.224 |
| UACR (mg/g) b | 11.00 [6.7; 22] | 11.00 (123.7) | 11.20 (123.3) | 0.967 |
| Variable | Entire Group | Men | Women | p (Men vs. Women) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRP (mg/L) a | 4.37 ± 1.28 | 4.30 ± 1.3 | 4.40 ± 1.2 | 0.329 |
| NLR b | 0.72 [0.64; 0.74] | 0.72 (121.1) | 0.70 (126.3) | 0.563 |
| PLR b | 122 [115; 125] | 122 (122.4) | 122 (124.8) | 0.788 |
| Variable | Entire Group | Men | Women | p (Men vs. Women) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TG/HDLc a | 3.52 [2.94; 4.24] | 3.61 (131.1) | 3.45 (114.5) | 0.068 |
| TyG index b | 9.58 ± 0.23 | 9.63 ± 0.22 | 9.56 ± 0.23 | 0.020 |
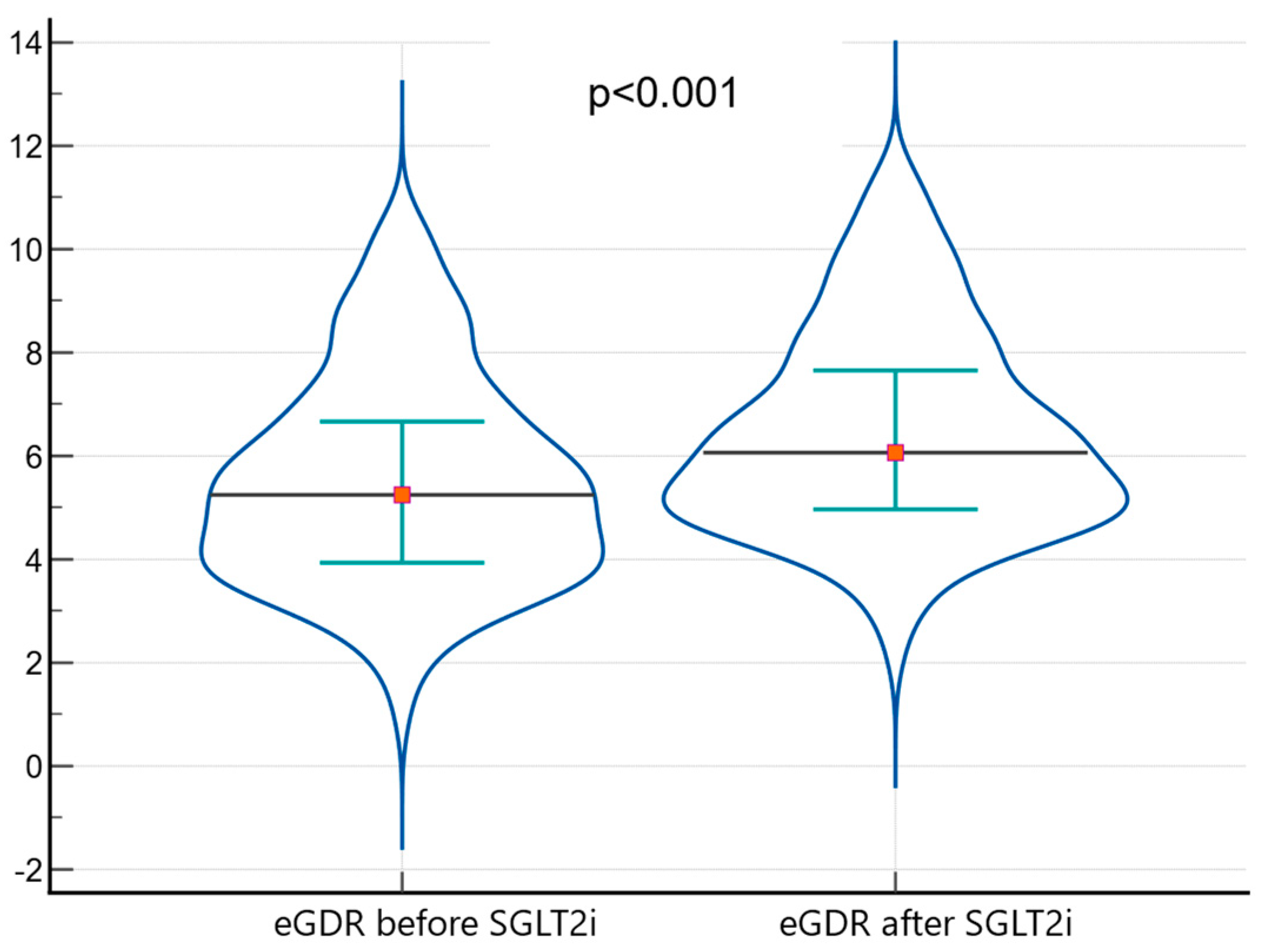
| eGDR (mg/kg/min) a | 5.24 [3.94; 7.17] | 4.30 (100.9) | 5.86 (150.5) | <0.001 |
| Before SGLT2i | After SGLT2i | Paired Difference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Difference (% Difference) | p-Value | |||
| Weight (kg) | 91 | 89 | −2 kg (2.22%) | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 31.5 | 30.0 | −1.5 kg/m2 (4.88%) | <0.001 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 140.0 | 135.0 | −5.0 mmHg (3.64%) | <0.001 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 75 | 70 | −5 mmHg (6.90%) | <0.001 |
| FPG (mg/dL) | 179 | 128 | −51 mg/dL (33.22%) | <0.001 |
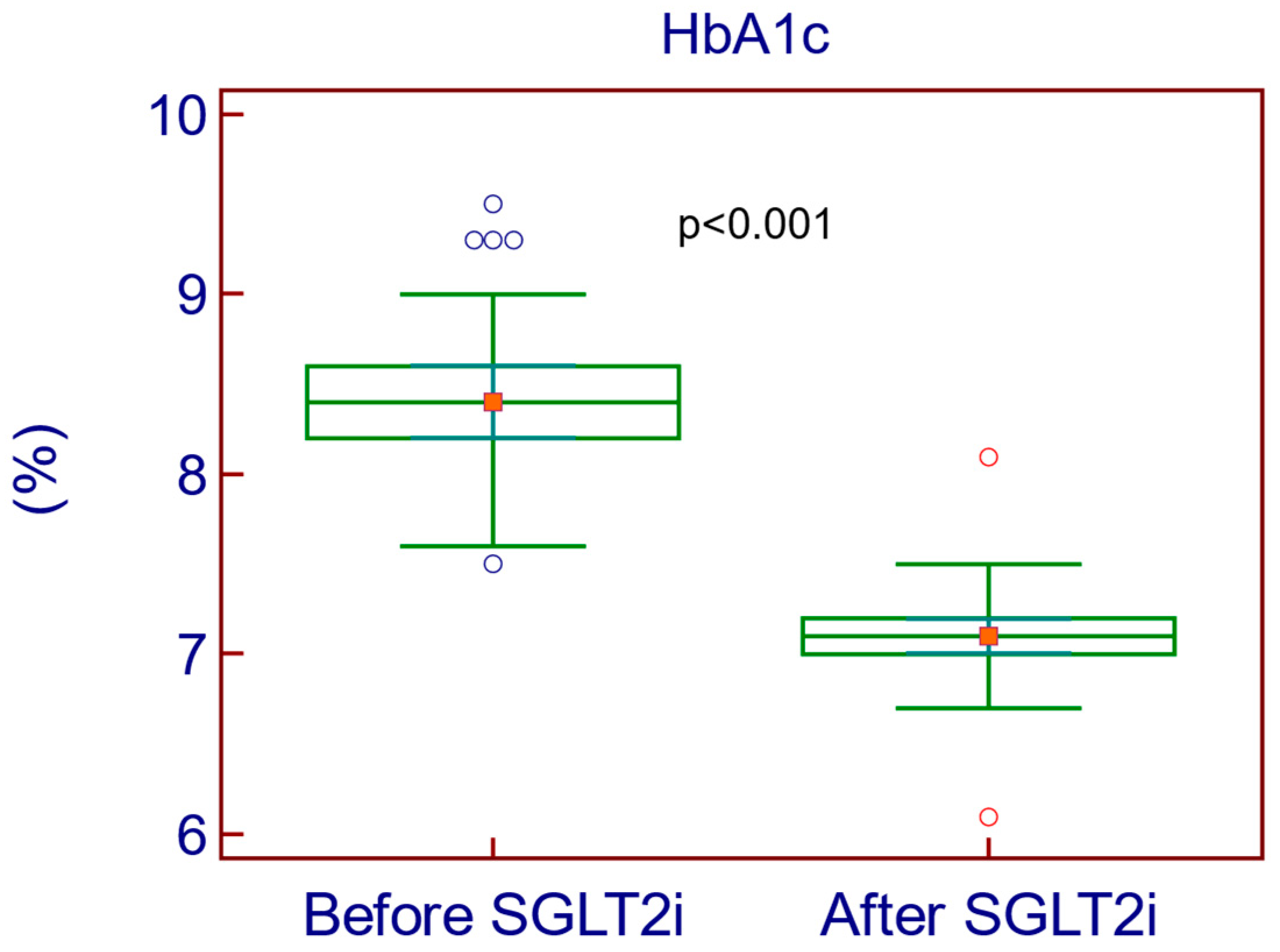
| HbA1c (%) | 8.4 | 7.1 | −1.3% (16.77%) | <0.001 |
| HDLc (mg/dL) | 47 | 49 | +2 mg/dL (4.17%) | <0.001 |
| eGFR (ml/min/1.73 m2) | 79.0 | 73.0 | −6.0 mL/min (7.89%) | <0.001 |
| UACR (mg/g) | 11.00 | 4.75 | −6.25 mg/g (79.37%) | <0.001 |
| NLR | 0.72 | 0.68 | −0.04 (5.71%) | <0.001 |
| PLR | 122 | 115 | −7 (5.91%) | <0.001 |
| TyG index | 9.58 | 9.23 | −0.35 (3.72%) | <0.001 |
| eGDR (mg/kg/min) | 5.24 | 6.07 | +0.83 (14.68%) | <0.001 |
| Before SGLT2i | After SGLT2i | Paired Difference | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 94.0 | 13.6 | 91.2 | 13 | −2.8 | 1.9 | −3.09 to −2.61 | <0.001 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 168.4 | 32 | 159.8 | 31.6 | −8.6 | 18.9 | −11.05 to −6.31 | <0.001 |
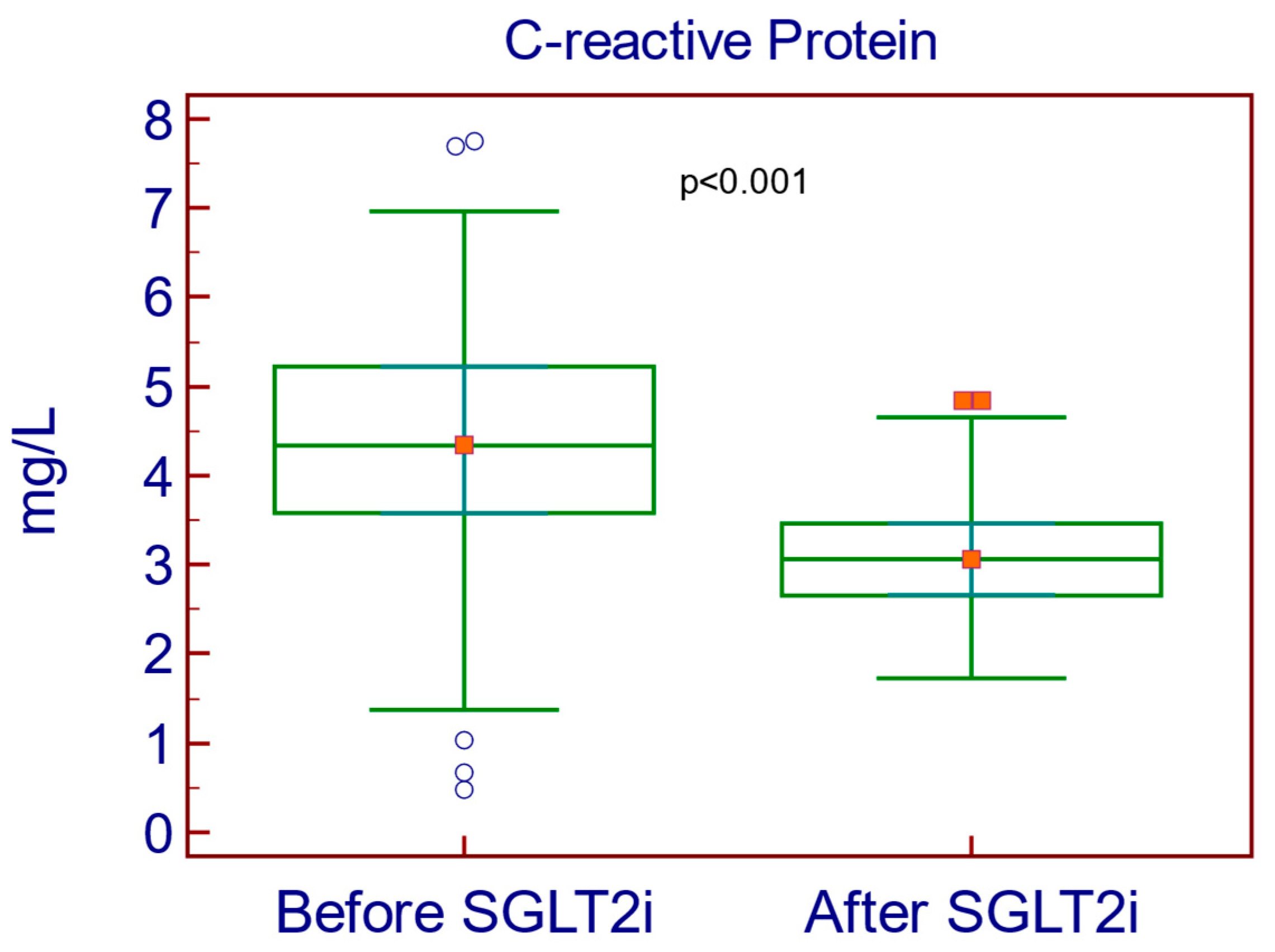
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) | 4.37 | 1.27 | 3.07 | 0.62 | −1.3 | 1.41 | −1.47 to −1.12 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iordan, L.; Lazar, S.; Timar, R.; Popescu, S.; Sorescu, T.; Albai, O.; Braha, A.; Timar, B.; Gaita, L. The Impact of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter-2 Inhibition on Insulin Resistance and Inflammation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Study. Medicina 2025, 61, 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61020209
Iordan L, Lazar S, Timar R, Popescu S, Sorescu T, Albai O, Braha A, Timar B, Gaita L. The Impact of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter-2 Inhibition on Insulin Resistance and Inflammation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Study. Medicina. 2025; 61(2):209. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61020209
Chicago/Turabian StyleIordan, Liana, Sandra Lazar, Romulus Timar, Simona Popescu, Teodora Sorescu, Oana Albai, Adina Braha, Bogdan Timar, and Laura Gaita. 2025. "The Impact of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter-2 Inhibition on Insulin Resistance and Inflammation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Study" Medicina 61, no. 2: 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61020209
APA StyleIordan, L., Lazar, S., Timar, R., Popescu, S., Sorescu, T., Albai, O., Braha, A., Timar, B., & Gaita, L. (2025). The Impact of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter-2 Inhibition on Insulin Resistance and Inflammation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Study. Medicina, 61(2), 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61020209






