Delta and Theta Band Power Alterations During Face and Face Pareidolia Perception in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: An Electroencephalographic Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. EEG Recording
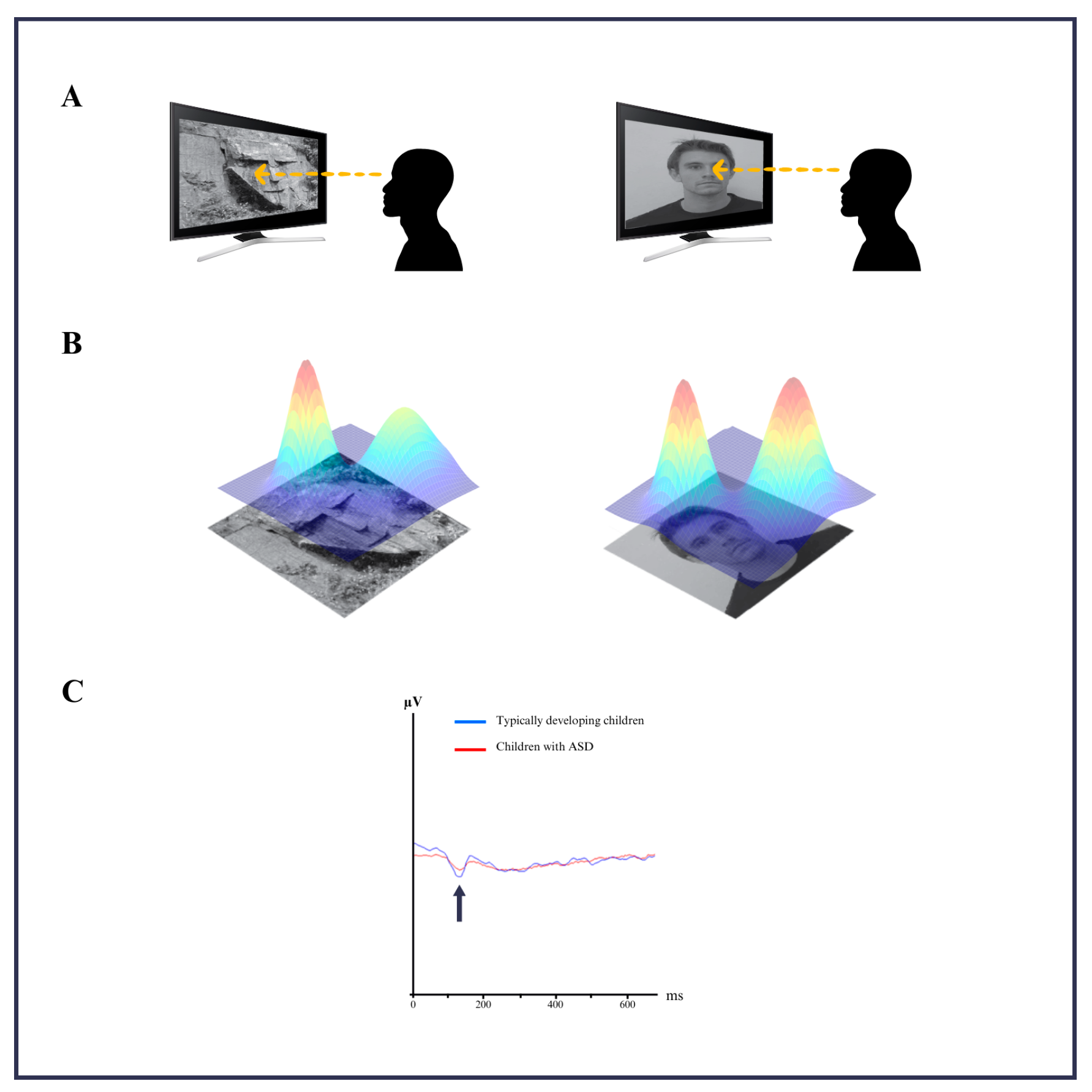
2.3. Stimuli and Experimental Design
2.4. EEG Data Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
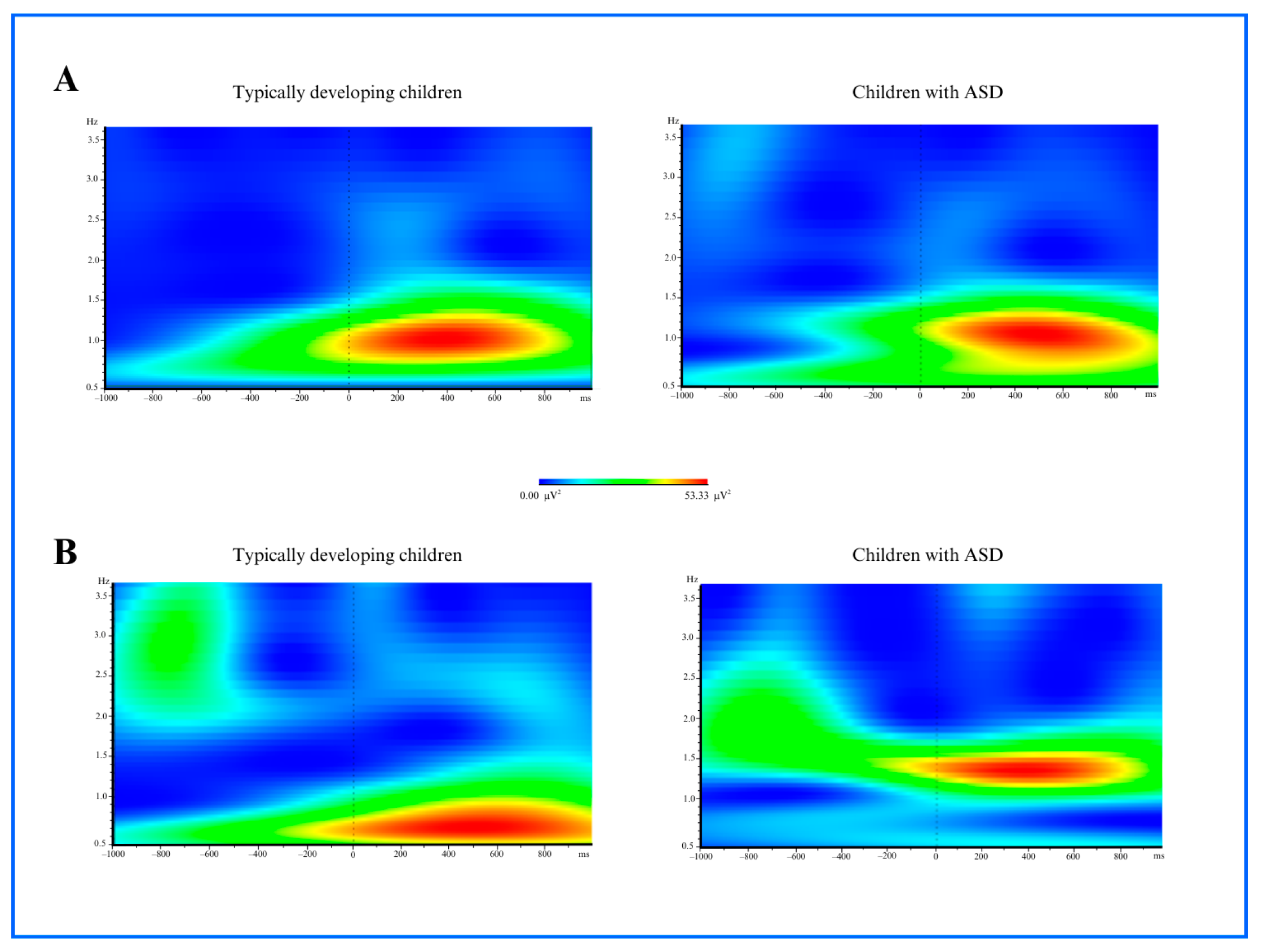
3.1. Time and Frequency Analysis Results
3.1.1. Delta Power
3.1.2. Theta Power
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASD | Autism Spectrum Disorder |
| EEG | Electroencephalography |
| ERP | Event-related potential |
| FFA | Fusiform Face Area |
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Webber, J.; Scheuermann, B. Educating Students with Autism: A Quick Start Manual, 1st ed.; Pro ed: Austin, TX, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ülke Kürkçüoğlu, B. 0-6 Yaş Arası Çocukların Temel Gelişimsel Özellikleri: Bilişsel Gelişim ve Dil Gelişimi. In Erken Çocukluk Eğitimi, 5th ed.; Diken, İ.H., Ed.; Pegem Akademi: Ankara, Türkiye, 2018; pp. 135–168. [Google Scholar]
- Jagadapillai, R. Atypical Autism: Causes, Diagnosis and Support. Medicina 2024, 60, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abalı, O. Otizm: Tanı, Tedavi ve Eğitimde Güncel Bilgiler; Ediba Yayıncılık: İstanbul, Turkey, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, B.T.; Doyle, E. Autism Spectrum Disorders: From A to Z: Assessment, Diagnosis… & More! Future Horizons Inc.: Arlington, TX, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Darıca, N.; Gümüşçü, S.; Pişkin, Ü. Otizm ve Otistik Çocukların Özellikleri, 5th ed.; Özgür Yayınları: İstanbul, Türkiye, 2011; pp. 33–58, 62–68. [Google Scholar]
- Alp, H. Otistik Çocuklarda Görülen Davranış Problemlerinin Düzeltilmesiyle Hareket Eğitimi ve Fiziksel Aktivitelerin Ilişkisi. Ph.D. Thesis, Celal Bayar University, Manisa, Turkey, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kizir, M. Ayrık Denemelerle Öğretimin Çevrimiçi Sunulan Aile Eğitim Programıyla Kazanımının İncelenmesi. Ph.D. Thesis, Abant İzzet Baysal University, Bursa, Turkey, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- De Boer, S.R. Successful Inclusion for Students with Autism: Creating a Complete, Effective ASD Inclusion Programme; Jossey-Bass: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Özlü-Fazlıoğlu, Y.; Baran, G. Duyusal Entegrasyon Programının Duyusal ve Davranış Problemleri Üzerine Etkisi; Ankara Üniversitesi Basımevi: Ankara, Türkiye, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Payne, V.G.; Isaacs, L.D. Human Motor Development: A Lifespan Approach, 9th ed.; Holcomb Hathaway: Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Burak, Y. Otizmli Çocukların Eğitsel Yerleştirilmesi, Kaynaştırılması ve Bütünleştirilmesinde Öğretmenlerle İlgili Değişkenlerin İncelenmesi. Master’s Thesis, Trakya Üniversitesi, Sosyal Bilimler Enstitüsü, Edirne, Turkey, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Uljarevic, M.; Hamilton, A. Recognition of Emotions in Autism: A Formal Meta-Analysis. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2013, 43, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diken, İ.H. Özel Eğitime Gereksinimi Olan Öğrenciler ve Özel Eğitim, 12th ed.; Pegem Akademi Yayıncılık: Ankara, Türkiye, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kırcaali-İftar, G. Otizm spektruma genel bakışlı. In Otizm Spektrum Bozukluğu Olan Çocuklar ve Eğitimleri Içinde, 3rd ed.; Tekin-İftar, E., Ed.; Vize Yayıncılık: Ankara, Türkiye, 2014; pp. 17–44. [Google Scholar]
- Bilmez, H. Öğretimi Ortak Dikkate Tepki Verme Becerisinin Otizm Spektrum Bozukluğu Olan Çocuklara. Master’s Thesis, Sosyal Bilimler Enstitüsü, Anadolu Üniversitesi, Eskişehir, Turkey, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yapa, M.; Kırcaali, İ.G. Otistik Özellik Gösteren Çocuklara İletişim Becerilerinin Kazandırılması; Yapa Yayın: İstanbul, Türkiye, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sökmen, N. Otizm, Eğitimde Yansımalar; Arel Eğitim Kurumları: İstanbul, Türkiye, 2010; pp. 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Özbey, Ç. Otizm ve Otistik Çocukların Eğitimi; İnkılap Kitabevi: İstanbul, Türkiye, 2005; pp. 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, G.; Osterling, J. Early Recognition of Children with Autism: A Study of First Birthday Home Video Tapes. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 1994, 24, 305–317. [Google Scholar]
- Volkmar, F.R.; Chawarska, K.; Klin, A. Autism Spectrum Disorders in Infants and Toddlers: An Introduction. In Autism Spectrum Disorders in Infants and Toddlers: Diagnosis, Assessment, and Treatment; Chawarska, K., Klin, A., Volkmar, F.R., Eds.; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Senju, A.; Tojo, Y.; Dairoku, H.; Hasegawa, T. Reflexive orienting in response to eye gaze and an arrow in children with and without autism. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2004, 45, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrmann, M.; Avidan, G.; Leonard, G.L.; Kimchi, R.; Luna, B.; Humphreys, K.; Minshew, N. Configural Processing in Autism and Its Relationship to Face Processing. Neuropsychologia 2007, 44, 110–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Haan, M. Neurocognitive Mechanisms for the Development of Face Processing. In Handbook of Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience; Nelson, C.A., Luciana, M., Eds.; MIT Press: London, UK, 2008; pp. 509–520. [Google Scholar]
- Schultz, R.T.; Gauthier, I.; Klin, A.; Fulbright, R.K.; Anderson, A.W.; Volkmar, F.; Skudlarski, P.; Lacadie, C.; Cohen, D.J.; Gore, J.C. Abnormal Ventral Temporal Cortical Activity During Face Discrimination Among Individuals with Autism and Asperger Syndrome. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2000, 57, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waiter, G.D.; Williams, J.H.; Murray, A.D.; Gilchrist, A.; Perrett, D.I.; Whiten, A. A Voxel-Based Investigation of Brain Structure in Male Adolescents with Autistic Spectrum Disorder. Neuroimage 2004, 22, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, K.; Hamm, J.P.; Kirk, I.J. The Neurophysiological Correlates of Face Processing in Adults and Children with Asperger’s Syndrome. Brain Cogn. 2005, 59, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjikhani, N.; Kveraga, K.; Naik, P.; Ahlfors, S.P. Early (N170) Activation of Face-Specific Cortex by Face-Like Objects. Neuroreport 2009, 20, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranhão-Filho, P.; Vincent, M.B. Neuropareidolia: Diagnostic Clues Apropos of Visual Illusions. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2009, 67, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, J.D.; Catani, M. Disorders of Visual Perception. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psyc. 2010, 81, 1280–1287. [Google Scholar]
- Summerfield, C.; Egner, T.; Mangels, J.; Hirsch, J. Mistaking a House for a Face: Neural Correlates of Misperception in Healthy Humans. Cereb. Cortex 2006, 16, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akdeniz, G. Face-like pareidolia images are more difficult to detect than real faces in children with autism spectrum disorder. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2024, 33, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, C.; Stafford, M.; King, R.J. Brief Report: Seeing the Man in the Moon: Do Children with Autism Perceive Pareidolic Faces? A Pilot Study. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2016, 46, 3838–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmisano, A.; Chiarantoni, G.; Bossi, F.; Conti, A.; D’Elia, V.; Tagliente, S.; Nitsche, M.A.; Rivolta, D. Face Pareidolia Is Enhanced by 40 Hz Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation (tACS) of the Face Perception Network. Dent. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 29124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langdell, T. Face Perception: An Approach to the Study of Autism; Oxbridge Publishing: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Guillon, Q.; Rogé, B.; Rogé, B.; Afzali, M.H.; Baduel, S.; Kruck, J.; Hadjikhani, N. Intact Perception but Abnormal Orientation towards Face-like Objects in Young Children with ASD. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tautvydaitė, D.; Mares, I.; Rahman, M.S.; Burra, N.; Senju, A. Effect of perceived eye gaze on the N170 component—A systematic review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 143, 104913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, J.A.; Carey, A.; Asadi, F.; Wehrman, J.; Sowman, P.F.; Hourn, T.; Bedwin, J. Neural correlates of face perception modeled with a convolutional recurrent neural network. J. Neural Eng. 2023, 20, 026028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossi, F.; Ricciardelli, P.; Rivolta, D. Stimulus Inversion and Emotional Expressions Independently Affect Face and Body Perception: An ERP Study. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2024, 32, 2914–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowparast Rostami, H.; Hildebrandt, A.; Sommer, W. Sex-specific relationships between face memory and the N170 component in event-related potentials. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2020, 15, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetha, M.K.; Segalowitz, S.J.; Gatzke-Kopp, L.M. The reliability of visual ERP components in children across the first year of school. Dev. Psychobiol. 2021, 63, e22150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossi, F.; Bossi, F.; Premoli, I.; Pizzamiglio, S.; Balaban, S.; Ricciardelli, P.; Rivolta, D.; Rivolta, D. Theta- and Gamma-Band Activity Discriminates Face, Body and Object Perception. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Granados, M.D.; Mondragón-Ceballos, R.; Ayala-Guerrero, F.; Martínez-Mota, L.; Hernández-López, L.; Mayagoitia-Novales, L.; Ramírez-Salado, I. Perception of Masculinized or Feminized Men’s Faces and Its Relation to the Menstrual Cycle Phase of Women: Electrophysiological Evidence. Vis. Cogn. 2024, 31, 678–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigelt, S.; Koldewyn, K.; Kanwisher, N. Face Recognition Deficits in Autism Spectrum Disorders Are Both Domain-Specific and Process-Specific. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feuerriegel, D.; Churches, O.; Hofmann, J.; Keage, H.A. The N170 and Face Perception in Psychiatric and Neurological Disorders: A Systematic Review. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 1141–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churches, O.; Damiano, C.; Baron-Cohen, S.; Ring, H. Getting to know you: The acquisition of new face representations in autism spectrum conditions. Neuroreport 2012, 23, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z. Neural Correlates of Facial Recognition Deficits in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Comprehensive Review. Front. Psy. 2025, 15, 1464142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Siddiqui, H.S.; Rutherford, M.D. Face Perception and Social Cognitive Development in Early Autism: A Prospective Longitudinal Study from 3 Months to 7 Years of Age. Child Dev. 2024, 96, 104–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, R.J. What Does the Prefrontal Cortex Do in Affective Style? Psychol. Sci. 2004, 15, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibralic, S.; Kohlhoff, J.; Wallace, N.; McMahon, C.; Eapen, V. A systematic review of emotion regulation in children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 2019, 68, 101422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroop, R.; Bijlenga, D.; de Sonneville, L.; van der Meere, J.; Geurts, H.M. Atypical frontal EEG activity during cognitive control in children with autism spectrum disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2012, 42, 2187–2198. [Google Scholar]
- Harmony, T. The functional significance of delta oscillations in human brain. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavanagh, J.F.; Frank, M.J. Frontal theta as a mechanism for learning from reward and punishment. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 978–982. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.; Li, X.; Xie, H.; Wu, J.; Geng, X.; Mao, W. EEG Connectivity Diversity Differences between Children with Autism and Typically Developing Children: A Comparative Study. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlhaas, P.J.; Singer, W. Neural synchrony in brain disorders: Relevance for cognitive dysfunctions and pathophysiology. Neuron 2010, 65, 600–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristic | TD Children | Children with ASD |
|---|---|---|
| Mean Age (SD) | 6.9 (2.0) | 7.1 (2.4) |
| Gender: Female/Male | 6/4 | 8/3 |
| Dominant Hand: R/L | 10/0 | 11/0 |
| Comorbid Illnesses | NA | NA |
| Claustrophobia | NA | NA |
| Disruptive Behavior (%) | 40.21 | 23.53 |
| Inattention (M) * | 6.05 | 2.83 |
| Performance IQ (M) | 96.42 | 99.21 |
| Verbal IQ (M) | 64.76 | 97.97 |
| Face Images | ||
| Mean Reaction Time (s) | 0.5371 | 0.5316 |
| Accuracy (%) | 68.12 | 53.33 |
| Face Pareidolia Images | ||
| Mean Reaction Time (s) | 0.6930 | 0.4670 |
| Accuracy (%) | 61.25 | 46.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akdeniz, G. Delta and Theta Band Power Alterations During Face and Face Pareidolia Perception in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: An Electroencephalographic Analysis. Medicina 2025, 61, 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040754
Akdeniz G. Delta and Theta Band Power Alterations During Face and Face Pareidolia Perception in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: An Electroencephalographic Analysis. Medicina. 2025; 61(4):754. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040754
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkdeniz, Gülsüm. 2025. "Delta and Theta Band Power Alterations During Face and Face Pareidolia Perception in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: An Electroencephalographic Analysis" Medicina 61, no. 4: 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040754
APA StyleAkdeniz, G. (2025). Delta and Theta Band Power Alterations During Face and Face Pareidolia Perception in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: An Electroencephalographic Analysis. Medicina, 61(4), 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040754






