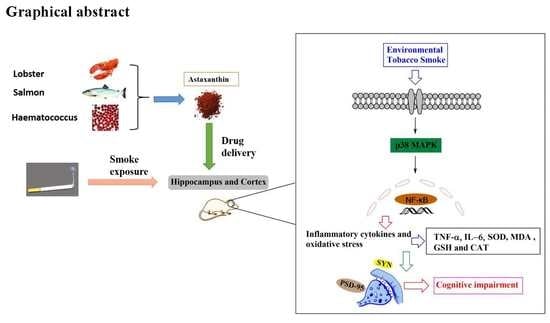
Astaxanthin Attenuates Environmental Tobacco Smoke-Induced Cognitive Deficits: A Critical Role of p38 MAPK
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of ATX Treatment on Exposure to ETS Induced Cognitive Decline
2.2. Effects of ATX Treatment on Exposure to ETS Induced Parameters of Oxidative Stress in the Mouse Brain
2.3. Effects of ATX Treatment on Exposure to ETS-Induced Inflammation in the Hippocampus and Prefrontal Cortex
2.4. Effects of ATX on the Expressions of NF-κB p65 in the Hippocampus and Prefrontal Cortex
2.5. Effects of ATX on the Expressions of p38 MAPK and p- p38MAPK in the Hippocampus and Prefrontal Cortex of ETS Mice
2.6. Effects of ATX on the Expression of SYN mRNA and PSD-95 mRNA in the Mouse Brain of ETS mice
2.7. Effects of ATX on the Expression of Synaptic Proteins in the Mouse Brain
2.8. Effects of ATX on the Structure and Morphology of the Hippocampal Neurons
2.9. Molecular Docking Studies
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Animals
4.3. Smoke Generation
4.4. Morris Water Maze (MWM)
4.5. Measurement of Oxidative Stress
4.5.1. Determination of Lipid Peroxidation
4.5.2. Determination of SOD Activity
4.5.3. Determination of CAT Activity
4.5.4. Determination of GSH
4.6. Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.7. Western Blotting
4.8. Reverse Transcriptase-PCR (RT-PCR)
4.9. Histological Analysis
4.10. Molecular Docking Studies
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anstey, K.J.; Sanden, C.V.; Salim, A.; O’Kearney, R. Smoking as a Risk Factor for Dementia and Cognitive Decline: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 166, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Hu, Z.; Orton, S.; Chen, R.L.; Wei, L. Association of passive smoking with cognitive impairment in nonsmoking older adults: a systematic literature review and a new study of Chinese cohort. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry Neurol. 2013, 3, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, B.J.; Cauley, M.; Burke, D.A.; Kiany, A.; Slotkin, T.A.; Levin, E.D. Cognitive and Behavioral Impairments Evoked by Low Level Exposure to Tobacco Smoke Components: Comparison with Nicotine Alone. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 151, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzpatrick, C.; Barnett, T.A.; Pagani, L.S. Parental bad habits breed bad behaviors in youth: exposure to gestational smoke and child impulsivity. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2014, 93, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renda, T.; Baraldo, S.; Pelaia, G.; Bazzan, E.; Turato, G.; Papi, A.; Maestrelli, P.; Maselli, R.; Vatrella, A.; Fabbri, L.M. Increased activation of p38 MAPK in COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 31, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, X.; Zhang, S.; Huang, R.; Wei, L.; Tan, S.; Liang, C.; Lv, S.; Chen, Y.; Liang, S.; Tian, Y.; et al. Protective effect of madecassoside against cognitive impairment induced by D-galactose in mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2014, 124, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Kang, J.; Ferguson, M.E.; Nagarajan, S.; Badger, T.M.; Wu, X. Blueberries reduce pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-α and IL-6 production in mouse macrophages by inhibiting NF-κB activation and the MAPK pathway. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 1587–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Ling, W.H.; Duan, R.D. Lycopene suppresses LPS-induced NO and IL-6 production by inhibiting the activation of ERK, p38MAPK, and NF-kappaB in macrophages. Inflamm. Res. 2010, 59, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaisar, M.A.; Sivandzade, F.; Bhalerao, A.; Cucullo, L. Conventional and electronic cigarettes dysregulate the expression of iron transporters and detoxifying enzymes at the brain vascular endothelium: In vivo evidence of a gender-specific cellular response to chronic cigarette smoke exposure. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 682, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, B.T.; José, F.O.; Roberto, D.P. Reactive Oxygen Species: Physiological and Physiopathological Effects on Synaptic Plasticity. J. Exp. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 23–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, P.T.; Huang, H.W.; Yang, C.M.; Yang, W.S.; Yang, C.H. Astaxanthin Inhibits Expression of Retinal Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Mediators in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.M.R.; Liang, Y.; Cheng, J.J.; Daroch, M. Astaxanthin-Producing Green MicroalgaHaematococcus pluvialis: From Single Cell to High Value Commercial Products. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 531–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.G.; Zhang, W.; Sun, J.X.; Bai, W.B. Research progress of the structure, function, extraction and analysis of astaxanthin. Sci. Tech. Food Ind. 2009, 30, 355–359. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Amin, M.M.; Reza, H.M.; Saadi, H.M.; Mahmud, W.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Alam, M.M.; Kabir, N.; Saifullah, A.R.M.; Tropa, S.T.; Quddus, A.H.M.R. Astaxanthin ameliorates aluminum chloride-induced spatial memory impairment and neuronal oxidative stress in mice. E. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 777, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dae-Hee, L.; Lee, Y.J.; Han, K.K. Neuroprotective Effects of Astaxanthin in Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation in SH-SY5Y Cells and Global Cerebral Ischemia in Rat. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2010, 47, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tingting, Y.; Yan, Z.; Xia, Z.; Xiaotong, L. Astaxanthin Inhibits Acetaldehyde-Induced Cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y Cells by Modulating Akt/CREB and p38MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathways. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Q.; Li, W.; Wang, C.X.; Xie, G.B.; Zhou, X.M.; Shi, J.X.; Zhou, M.L. Astaxanthin offers neuroprotection and reduces neuroinflammation in experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Surg. Res. 2014, 192, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.M.; Lu, J.; Zheng, Y.L.; Zhou, Z.; Shan, Q.; Ma, D.F. Purple sweet potato color repairs d-galactose-induced spatial learning and memory impairment by regulating the expression of synaptic proteins. Neurobiol. Learn. Memory 2008, 90, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, R.E.; Jagadapillai, R.; Jing, C.; Webb, C.; Stocke, K.; Greene, R.M.; Pisano, M.M. Developmental clgarette smoke exposure II: Hippocampus proteome and metabolome profiles in adult offspring. Reprod. Toxicol. 2016, 65, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanska, K.; Krol, A.; Merecz-Kot, D.; Ligocka, D.; Mikolajewska, K.; Mirabella, F.; Chiarotti, F.; Calamandrei, G.; Hanke, W. Environmental Tobacco Smoke Exposure during Pregnancy and Child Neurodevelopment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oswald, M.C.W.; Brooks, P.S.; Zwart, M.F.; Mukherjee, A.; West, R.J.H.; Giachello, C.N.G.; Morarach, K.; Baines, R.A.; Sweeney, S.T.; Landgraf, M. Reactive oxygen species regulate activity-dependent neuronal plasticity in Drosophila. eLife 2018, 7, e39393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Chen, X.; Xin, G.; Li, X. Chronic exposure to the ionic liquid [C8mim]Br induces inflammation in silver carp spleen: Involvement of oxidative stress-mediated p38MAPK/NF-kappaB signalling and microRNAs. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 84, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Z.; Yu, C.; Xuan, Z.; Chen, H.; Dong, J.; Lu, W.; Song, Z.; Wei, Z. Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide induces cognitive dysfunction, mediated by neuronal inflammation via activation of the TLR4 signaling pathway in C57BL/6 mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.N.; Min, A.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Shin, S.K.; Yu, H.N.; Sohn, E.J.; Ahn, C.W.; Jung, S.U.; Park, S.H.; Kim, M.R. Deer Bone Extract Prevents Against Scopolamine-Induced Memory Impairment in Mice. J. Med. Food 2015, 18, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, R.; Clifford, A.; Lang, L.; Anstey, K.J. Is exposure to secondhand smoke associated with cognitive parameters of children and adolescents?- a systematic literature review. Ann. Epidemiol. 2013, 23, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amoskroohs, R.M.; Williams, M.T.; Braun, A.A.; Graham, D.L.; Webb, C.L.; Birtles, T.S.; Greene, R.M.; Vorhees, C.V.; Pisano, M.M. Neurobehavioral phenotype of C57BL/6J mice prenatally and neonatally exposed to cigarette smoke. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2013, 35, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Swomley, A.M.; Butterfield, D.A. Oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment: evidence from human data provided by redox proteomics. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 1669–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Pulliam, D.A.; Liu, Y.; Hamilton, R.T.; Jernigan, A.L.; Bhattacharya, A.; Sloane, L.B.; Qi, W.; Chaudhuri, A.; Buffenstein, R. Reduced mitochondrial ROS, enhanced antioxidant defense, and distinct age-related changes in oxidative damage in muscles of long-lived Peromyscus leucopus. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 304, R343–R355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.B.; Choe, E.S.; Kim, K.S.; Shim, S.M. The effect of tobacco smoke exposure on generation of reactive oxygen species and cellular membrane damage using a co-culture model system of blood-brain barrier with astrocytes. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2017, 33, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrożewicz, E.; Augustyniak, A.; Gęgotek, A.; Bielawska, K.; Skrzydlewska, E. Black-currant protection against oxidative stress formation. J.Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2013, 76, 1293–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, A.; Ng, C.; O’Callaghan, M.; Jensen, G.; Wong, H. In vitro and ex-vivo cellular antioxidant protection and cognitive enhancing effects of an extract of Polygonum minus Huds (Lineminus™) demonstrated in a Barnes Maze animal model for memory and learning. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Wang, X.; Xiang, Q.; Meng, X.; Peng, Y.; Du, N.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Q.; Wang, C.; Liu, X. Astaxanthin alleviates brain aging in rats by attenuating oxidative stress and increasing BDNF levels. Food Funct. 2013, 5, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arab, H.H.; Salama, S.A.; Maghrabi, I.A. Camel Milk Ameliorates 5-Fluorouracil-Induced Renal Injury in Rats: Targeting MAPKs, NF-κB and PI3K/Akt/eNOS Pathways. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 46, 1628–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, A.Q.; Khan, R.; Qamar, W.; Lateef, A.; Rehman, M.U.; Tahir, M.; Ali, F.; Hamiza, O.O.; Hasan, S.K.; Sultana, S. Geraniol attenuates 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA)-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in mouse skin: Possible role of p38 MAP Kinase and NF-κB. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2013, 94, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, W.S.; Kuzmicic, J.; Burrill, J.S.; Donoghue, M.A.; Foncea, R.; Jensen, M.D.; Lavandero, S.; Arriaga, E.A.; Bernlohr, D.A. Proinflammatory cytokines differentially regulate adipocyte mitochondrial metabolism, oxidative stress, and dynamics. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 306, E1033–E1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Wang, K.; Kolattukudy, P.E. Cerium oxide nanoparticles inhibit oxidative stress and nuclear factor-κB activation in H9c2 cardiomyocytes exposed to cigarette smoke extract. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 338, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Shi, C.; Chen, L.; Ma, P.; Li, K.; Jin, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, A. Effects of andrographolide on postoperative cognitive dysfunction and the association with NF-κB/MAPK pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 7367–7373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunakaran, S.; Ravindranath, V. Activation of p38 MAPK in the substantia nigra leads to nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB in MPTP-treated mice: implication in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2010, 109, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, H.; Fukuda, M.S.; Hayashi, T.A.; Noguchi, J. Structural dynamics of dendritic spines in memory and cognition. Trends Neurosci. 2010, 33, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauniaux, E.; Burton, G. Morphological and biological effects of maternal exposure to tobacco smoke on the feto-placental unit. Early Hum. Dev. 2007, 83, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, Z.; Kang, L.; Geng, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Cui, H. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) influences spatial cognition and modulates hippocampal structural synaptic plasticity in aging mice. Exp. Gerontol. 2014, 58, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaques, J.A.; Doleski, P.H.; Castilhos, L.G.; Da, R.M.; Souza, V.C.; Carvalho, F.B.; Marisco, P.; Thorstenberg, M.L.; Rezer, J.F.; Ruchel, J.B. Free and nanoencapsulated curcumin prevents cigarette smoke-induced cognitive impairment and redox imbalance. Neurobiol. Learn. Memory 2013, 100, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Sun, L.; Gou, L.; Ling, X.; Feng, Y.; Wang, L.; Yin, X.; Liu, Y. Protective effect of l-theanine on chronic restraint stress-induced cognitive impairments in mice. Brain Res. 2013, 1503, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Fu, X.; Lan, N.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Li, C.; Shang, Y.; Huang, T.; Zhang, L. Luteolin protects against high fat diet-induced cognitive deficits in obesity mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 267, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Lan, N.; Ren, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, S.; Huang, X.; Yu, Y. Orientin improves depression-like behavior and BDNF in chronic stressed mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 1130–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, X.; Gou, L.; Fu, X.; Li, S.; Lan, N.; Yin, X. Protective effect of l -citrulline against ethanol-induced gastric ulcer in rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 34, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aebi, H. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1984, 105, 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Yu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zou, F.; Zhang, X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Huang, X.F.; Zhu, Y. Protective effect of the orientin on noise-induced cognitive impairments in mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 296, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Fang, T.; Yang, X.; Luo, X.; Guo, A.; Newell, K.A.; Huang, X.F.; Yu, Y. Galantamine improves cognition, hippocampal inflammation, and synaptic plasticity impairments induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, X.; Gou, L.; Sun, L.; Ling, X.; Yin, X. Luteolin attenuates diabetes-associated cognitive decline in rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2013, 94, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Target mRNA Sequences | Primer Sequence | Annealing Tm (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | 5′ ATGGTCACGCACGATTTCCC 3′ 5′ GAGACCTTCAACACCCCAGC 3′ | 59 |
| SYN | 5′-TCTTCCTGCAGAACAAGTACC-3′ 5′-CCTTGCATGTGTTCCCTGTCTG-3′ | 200 |
| PSD-95 | 5′- CCCAGACATCACAACCTCAT -3′ 5′- ACACCATTGACCGACAGGAT -3′ | 324 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Guo, A.-L.; Pang, Y.-P.; Cheng, X.-J.; Xu, T.; Li, X.-R.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Liu, Y. Astaxanthin Attenuates Environmental Tobacco Smoke-Induced Cognitive Deficits: A Critical Role of p38 MAPK. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17010024
Yang X, Guo A-L, Pang Y-P, Cheng X-J, Xu T, Li X-R, Liu J, Zhang Y-Y, Liu Y. Astaxanthin Attenuates Environmental Tobacco Smoke-Induced Cognitive Deficits: A Critical Role of p38 MAPK. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(1):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17010024
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xia, An-Lei Guo, Yi-Peng Pang, Xiao-Jing Cheng, Ting Xu, Xin-Rui Li, Jiao Liu, Yu-Yun Zhang, and Yi Liu. 2019. "Astaxanthin Attenuates Environmental Tobacco Smoke-Induced Cognitive Deficits: A Critical Role of p38 MAPK" Marine Drugs 17, no. 1: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17010024
APA StyleYang, X., Guo, A.-L., Pang, Y.-P., Cheng, X.-J., Xu, T., Li, X.-R., Liu, J., Zhang, Y.-Y., & Liu, Y. (2019). Astaxanthin Attenuates Environmental Tobacco Smoke-Induced Cognitive Deficits: A Critical Role of p38 MAPK. Marine Drugs, 17(1), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17010024