Natural Products from Actinomycetes Associated with Marine Organisms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
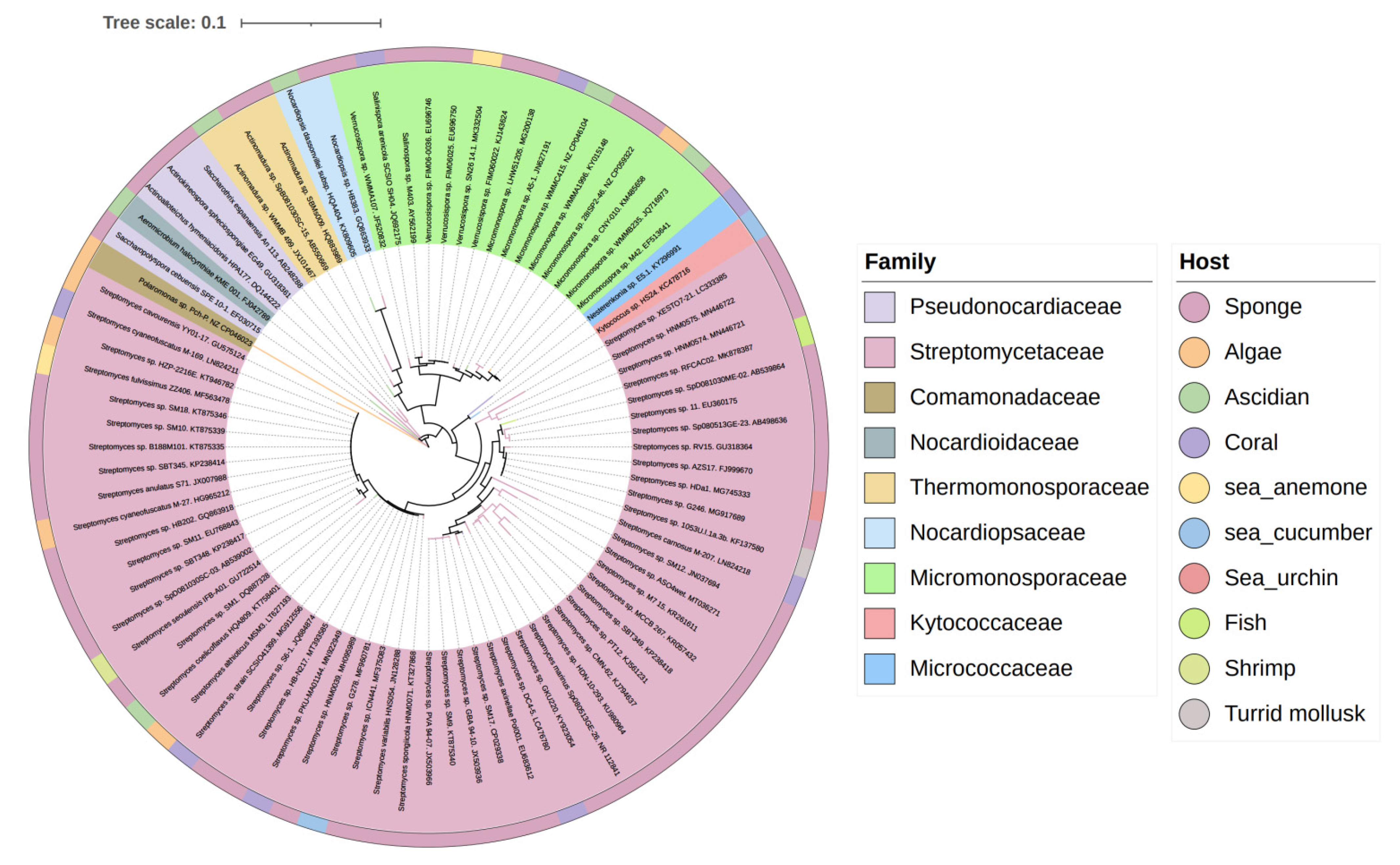
2. Biology of Actinomycetes Associated with Marine Animals, Marine Plants, Macroalgae, Cyanobacteria and Lichens
3. Chemical Structures and Biological Properties of the Actinomycetes Associated with Marine Animals, Marine Plants, Macroalgae, Cyanobacteria, and Lichens
3.1. Natural Products of the Actinomycetes Derived from Marine Animals
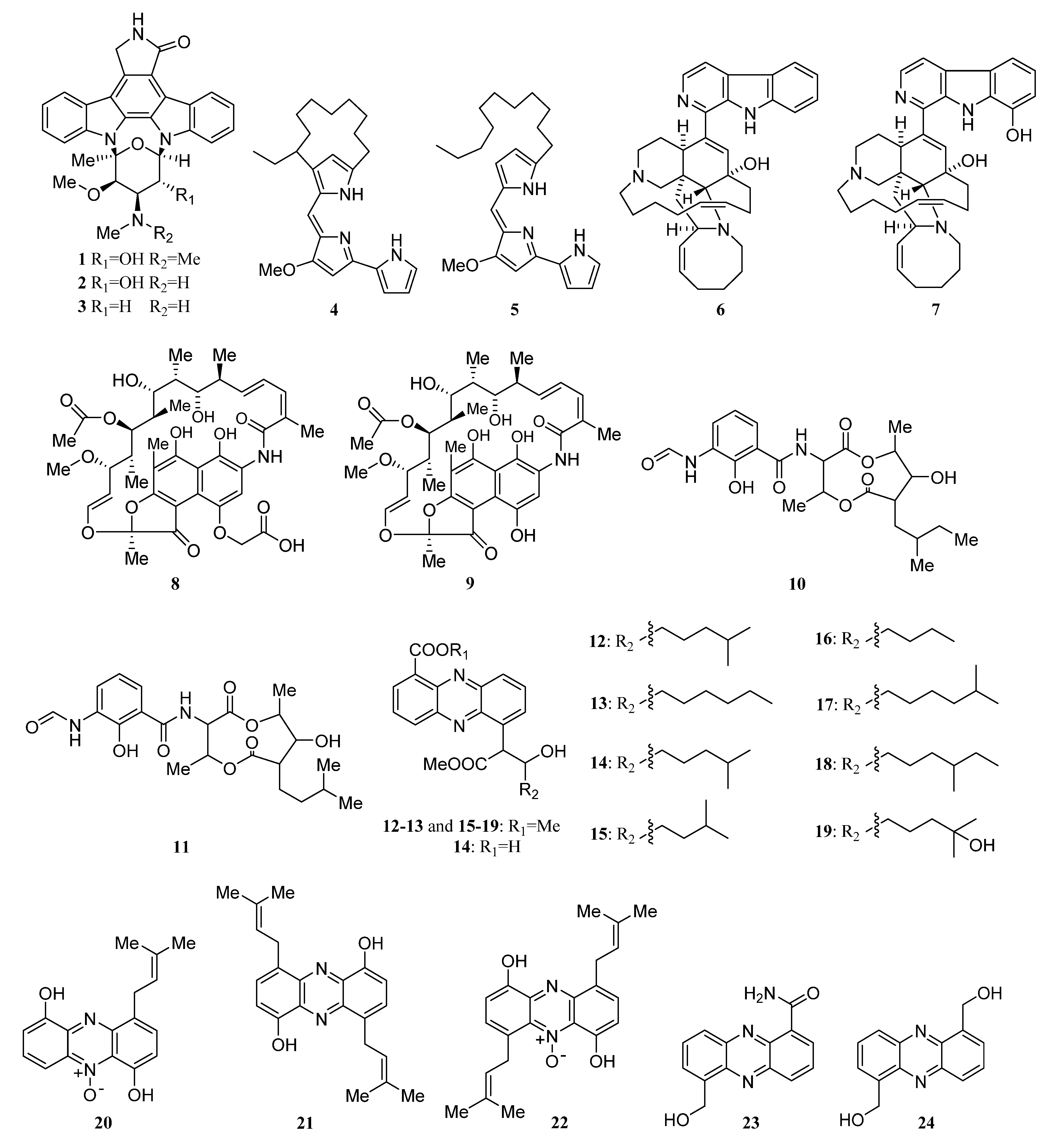
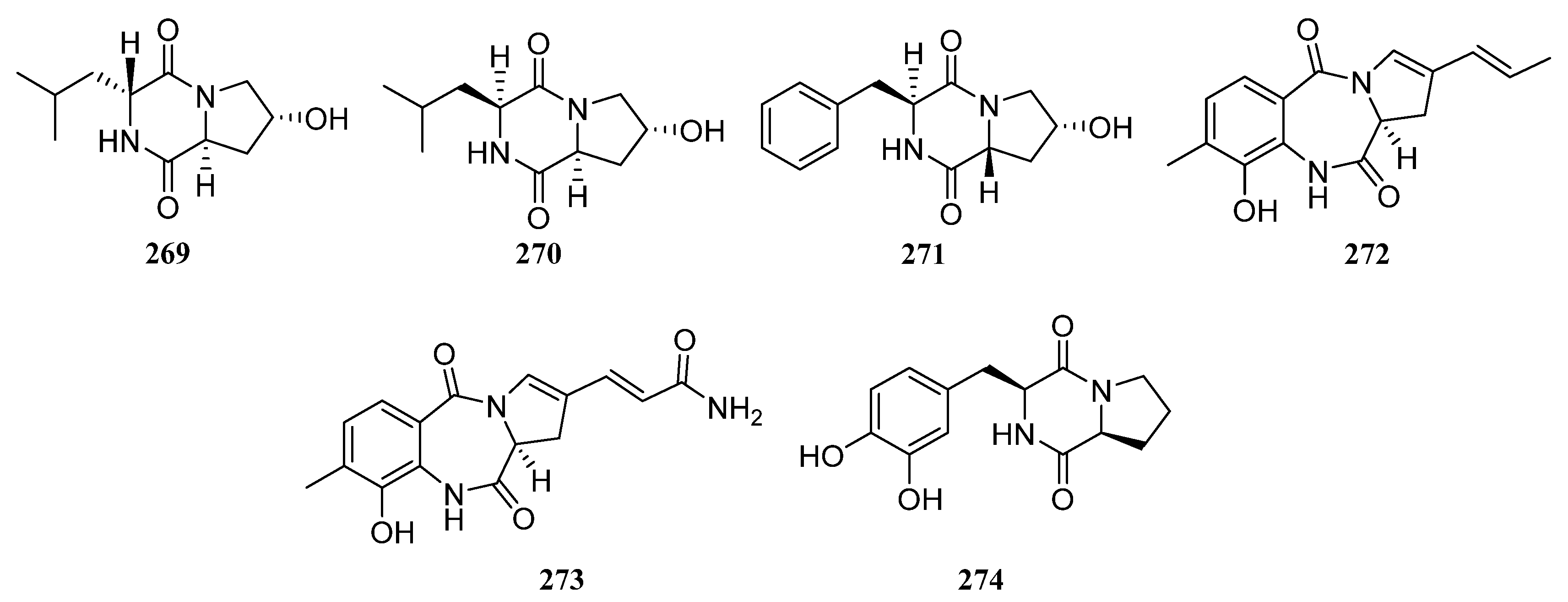
3.1.1. Alkaloids
Alkaloids Derived from the Sponge-Associated Actinomycetes
Alkaloids Derived from the Coral-Associated Actinomycetes
Alkaloids Derived from the Ascidian-Associated Actinomycetes
Alkaloids Derived from the Actinomycetes Associated with Other Marine Animals
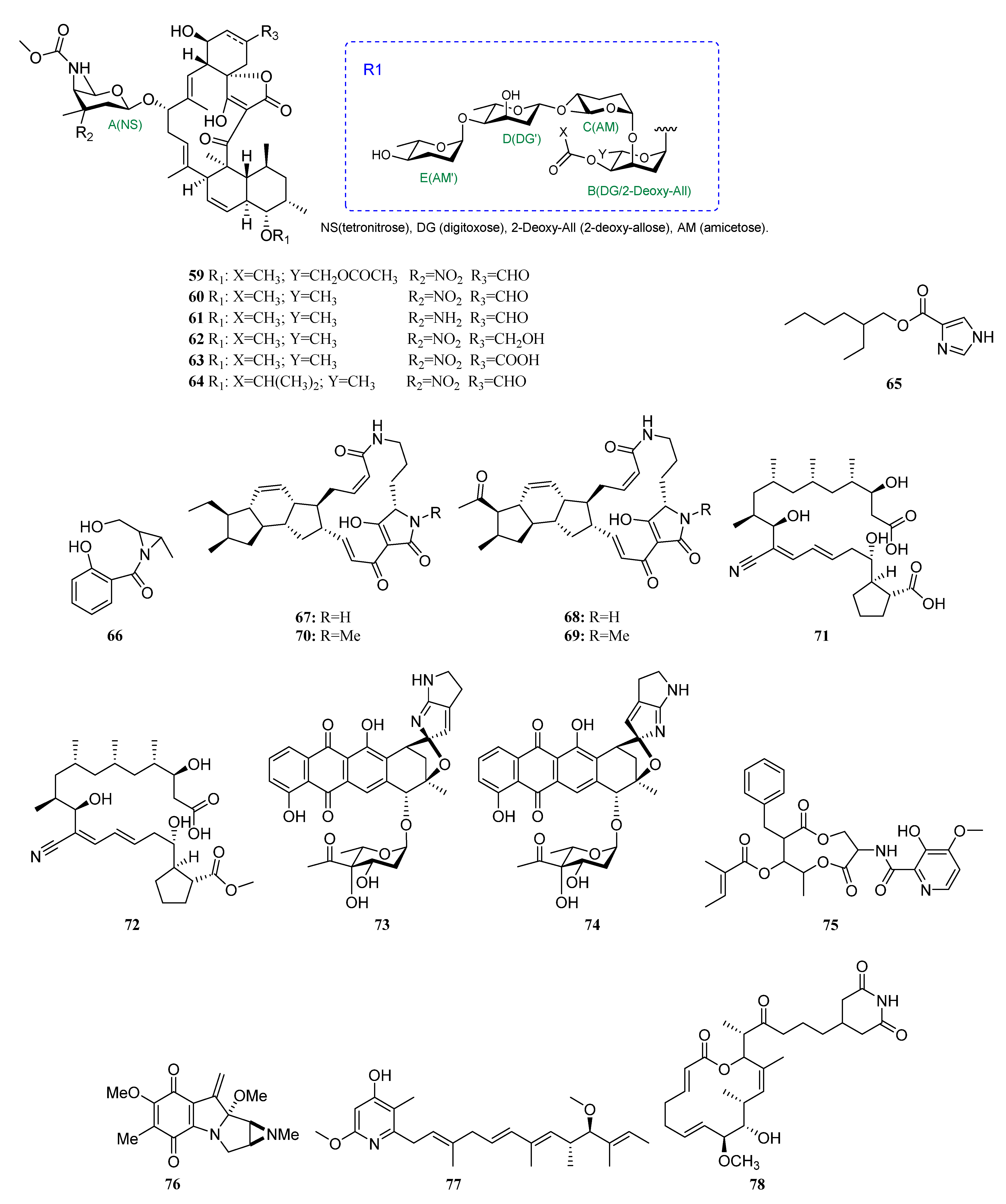
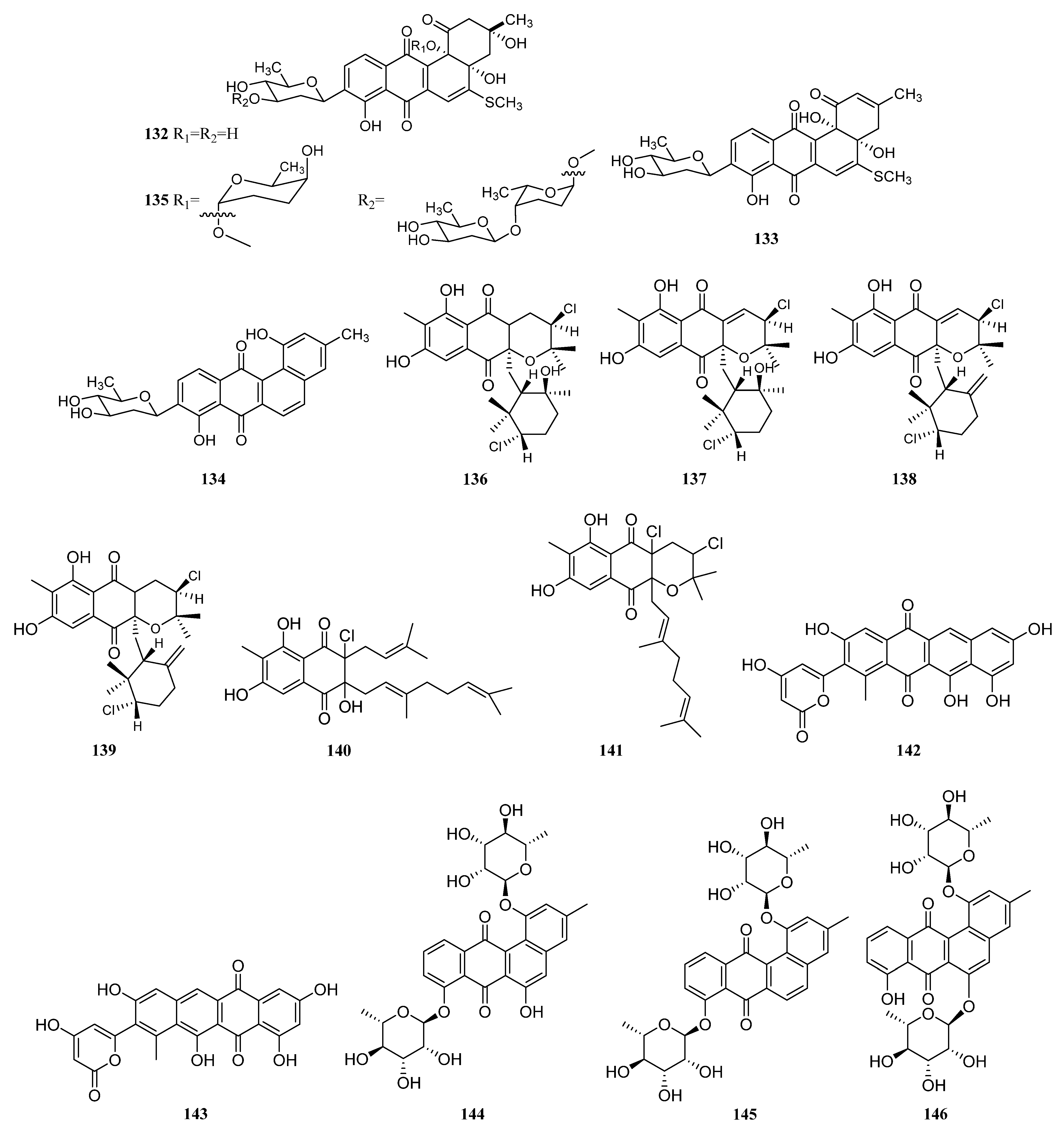
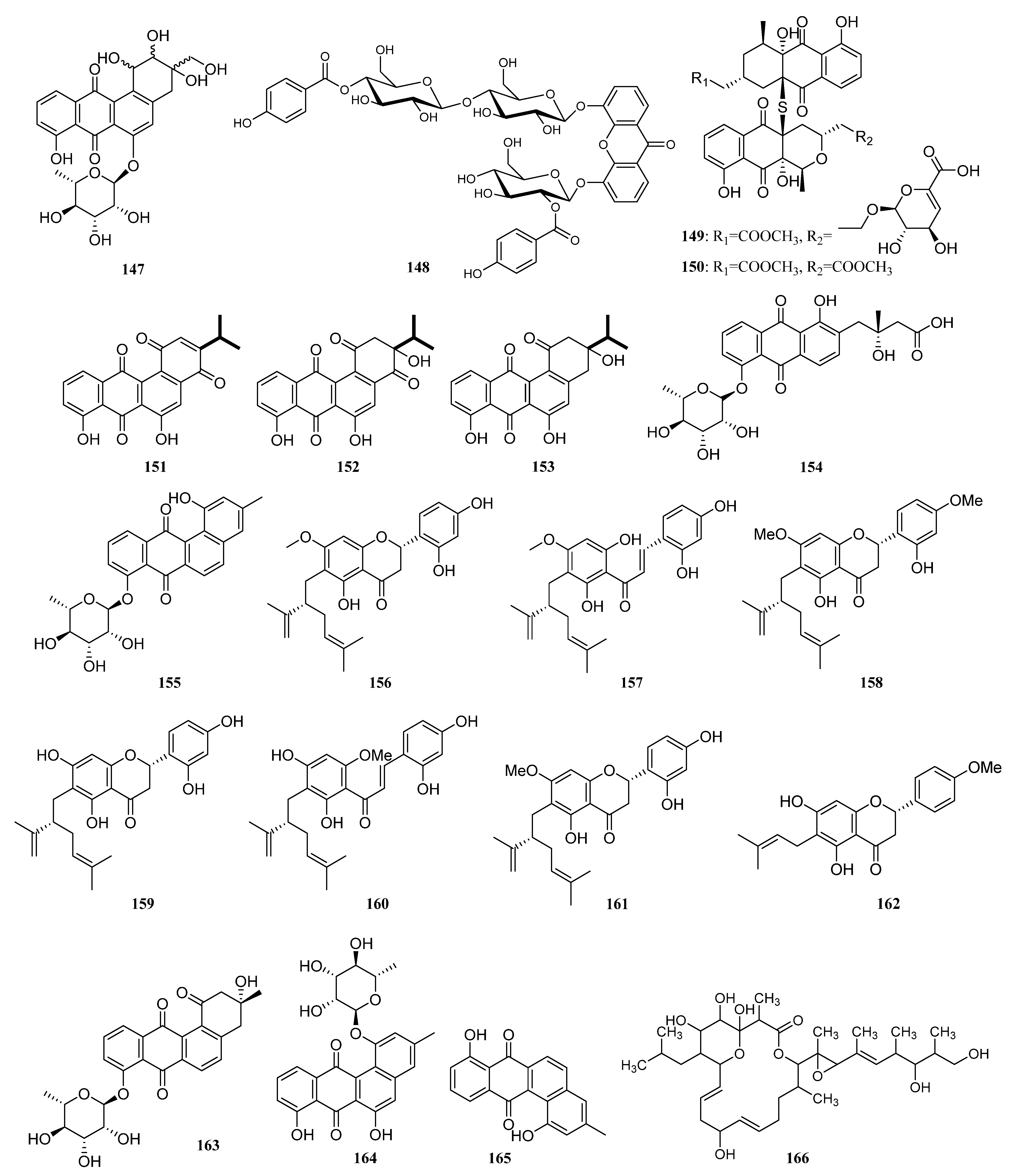
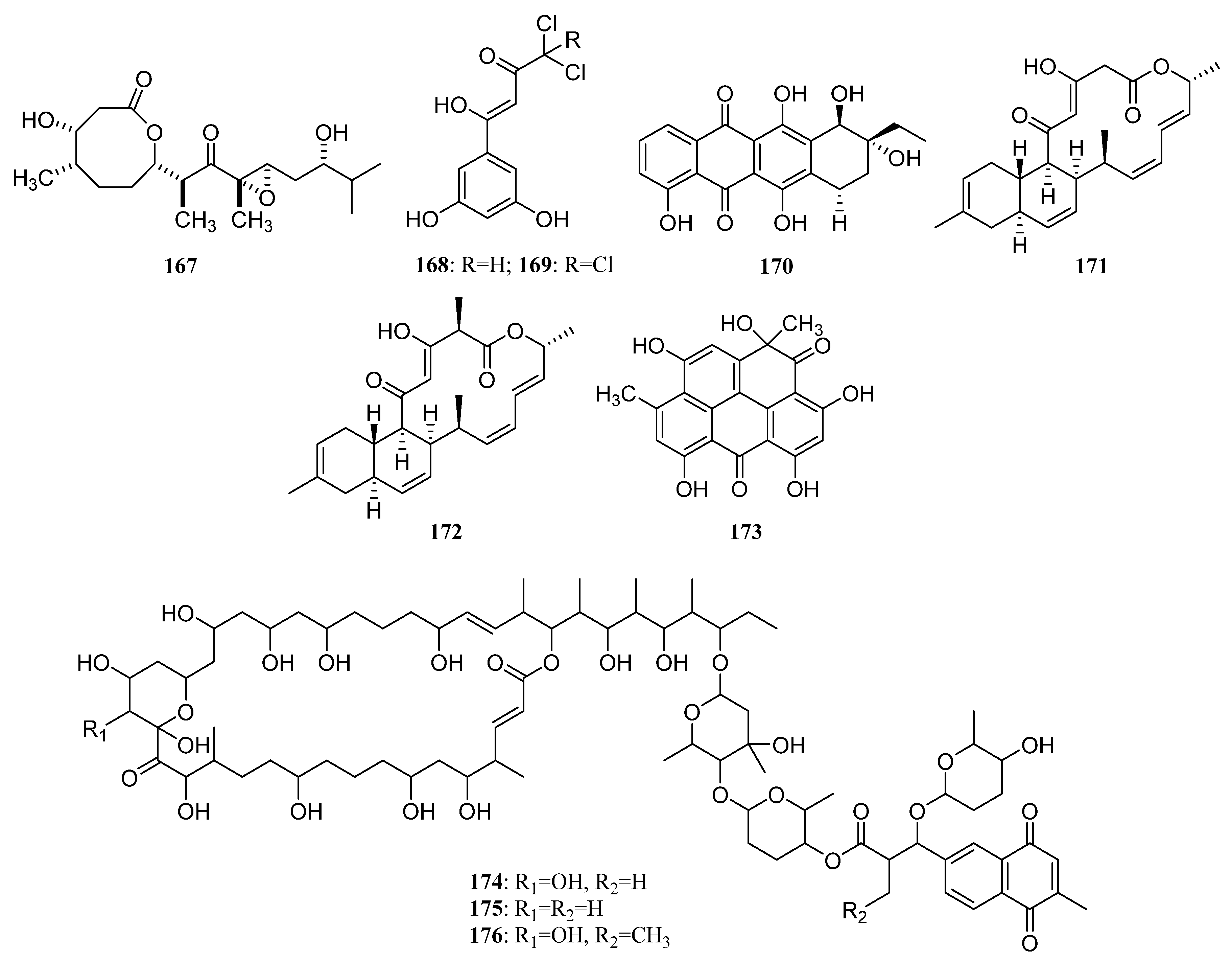
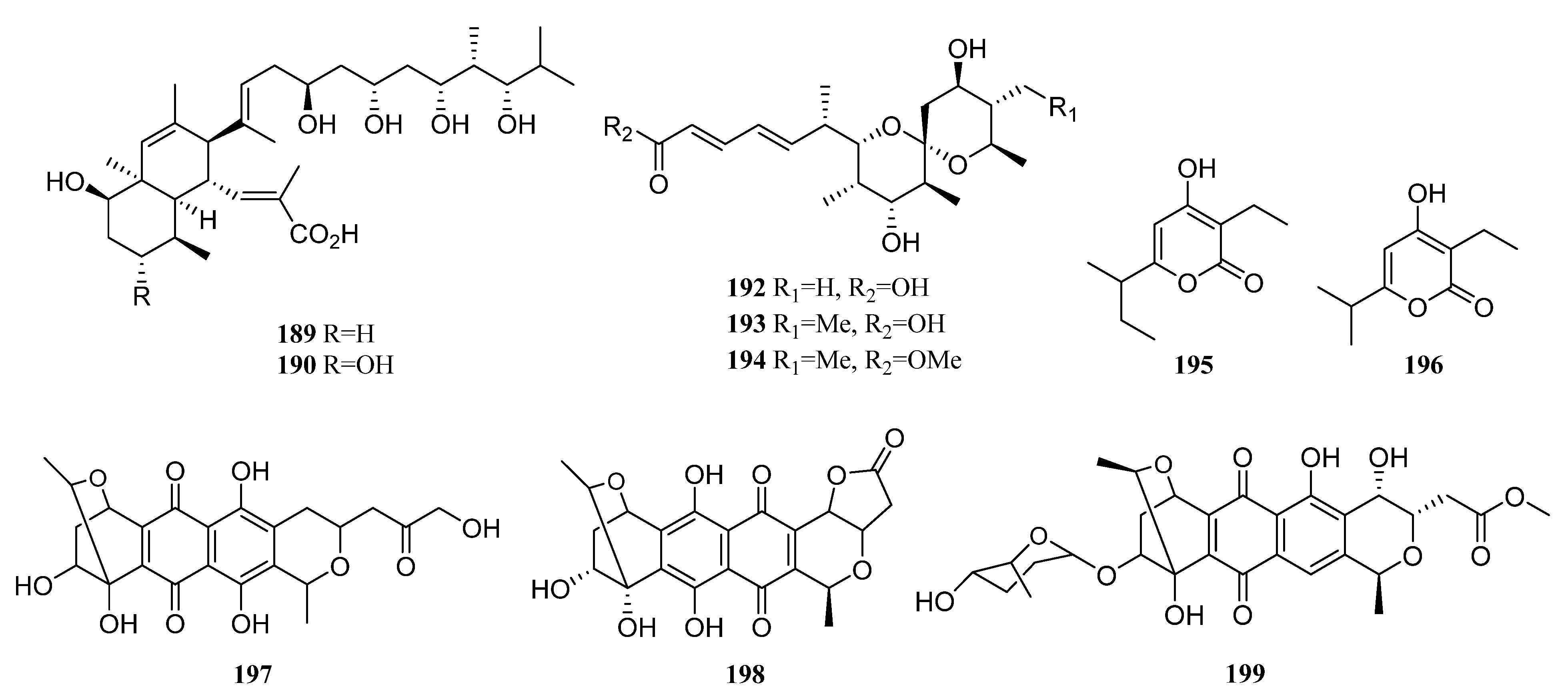
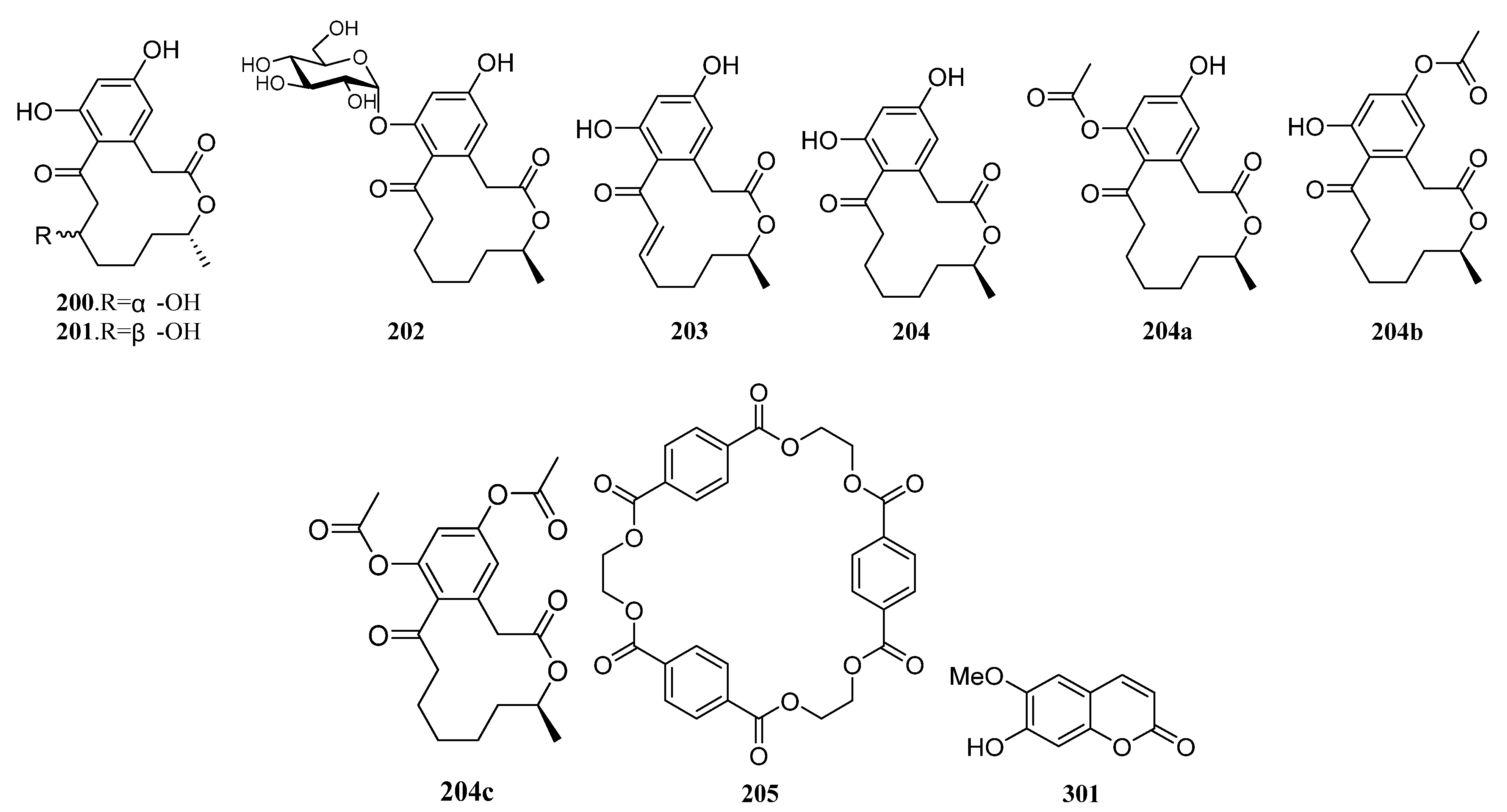
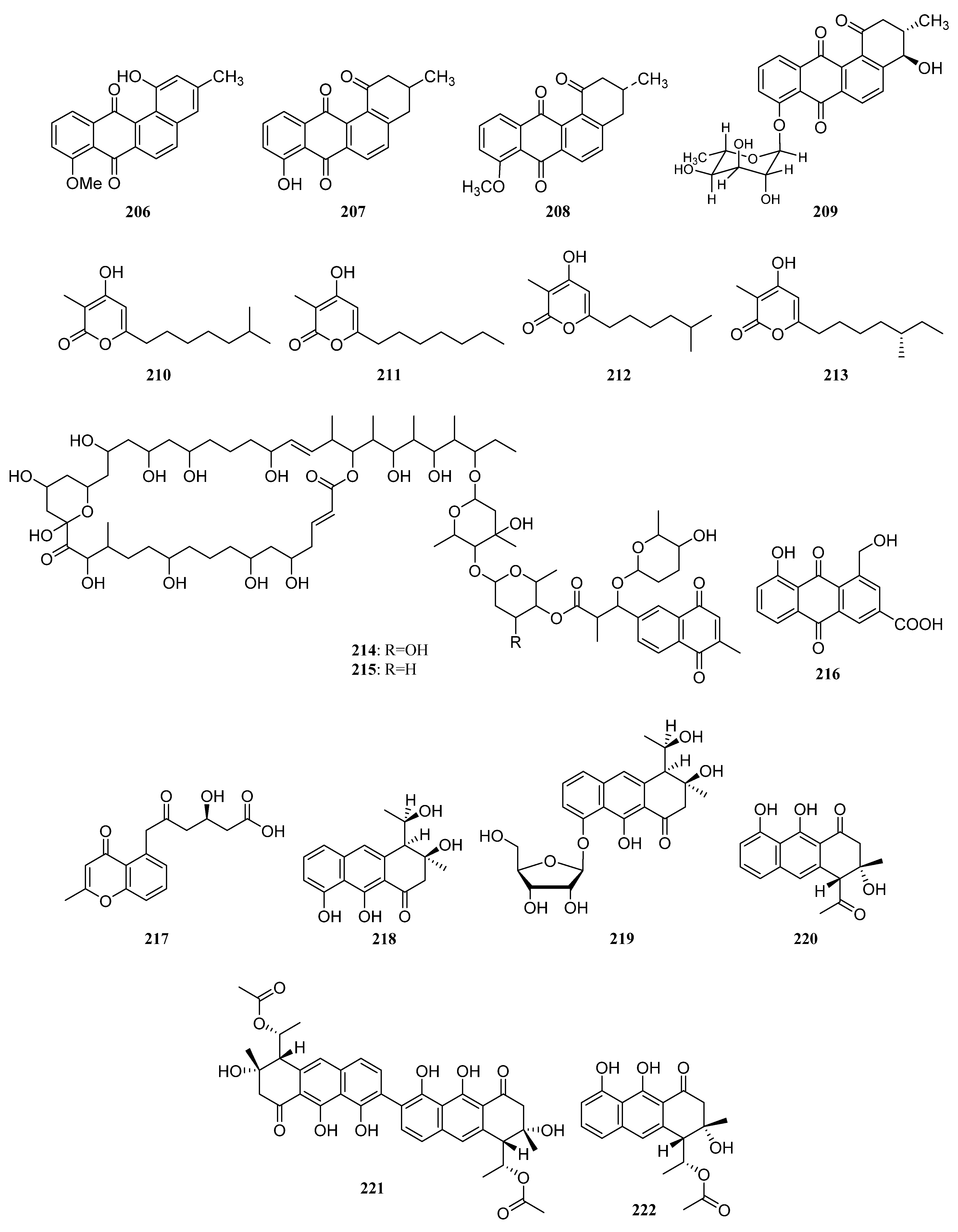
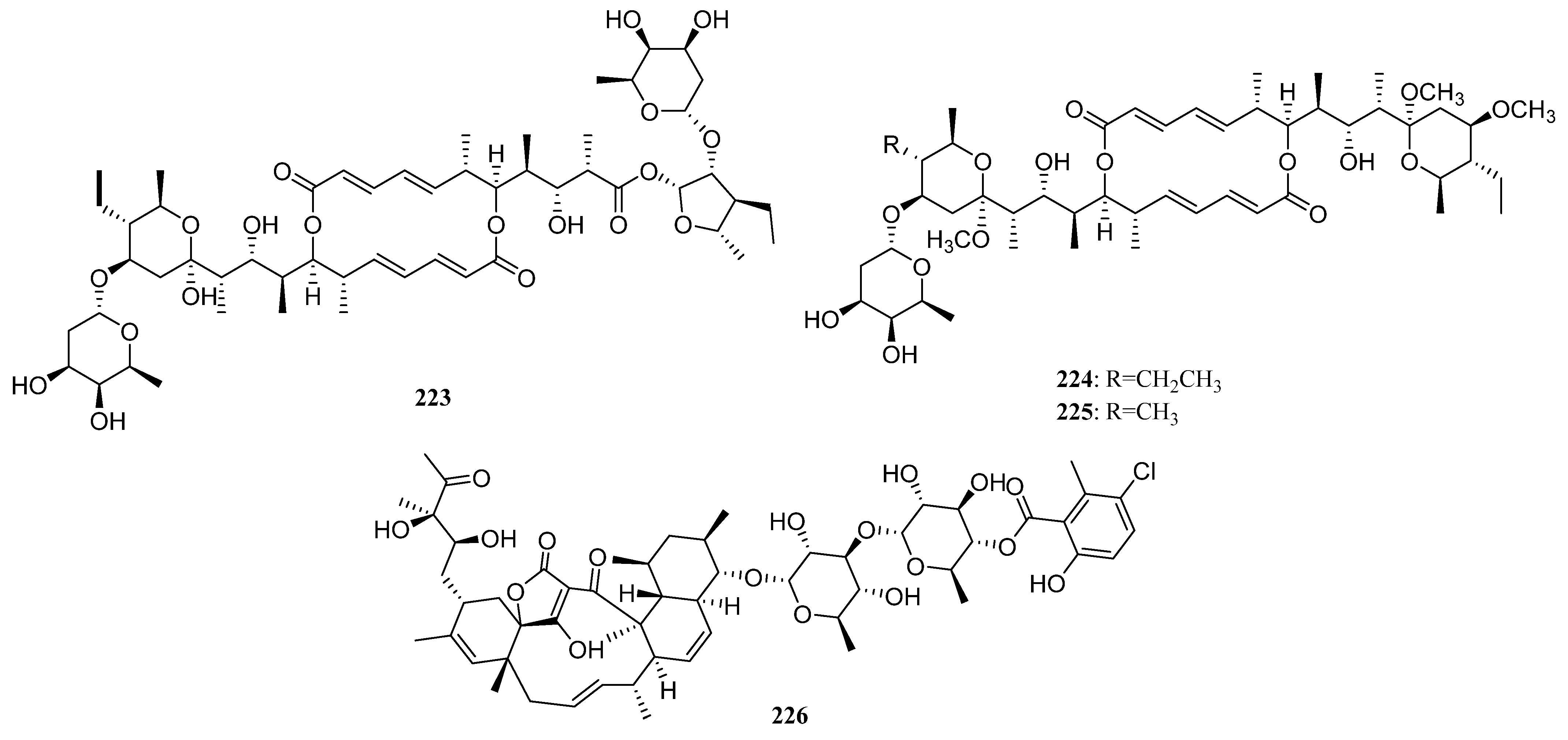
3.1.2. Polyketides
Polyketides Derived from the Sponge-Associated Actinomycetes
Polyketides Derived from the Coral-Associated Actinomycetes
Polyketides Derived from the Ascidian-Associated Actinomycetes
Polyketides Derived from the Sea Cucumber-Associated Actinomycetes
Polyketides Derived from the Actinomycetes Associated with Other Marine Invertebrates
Polyketides Derived from the Actinomycetes Associated with Marine Vertebrates
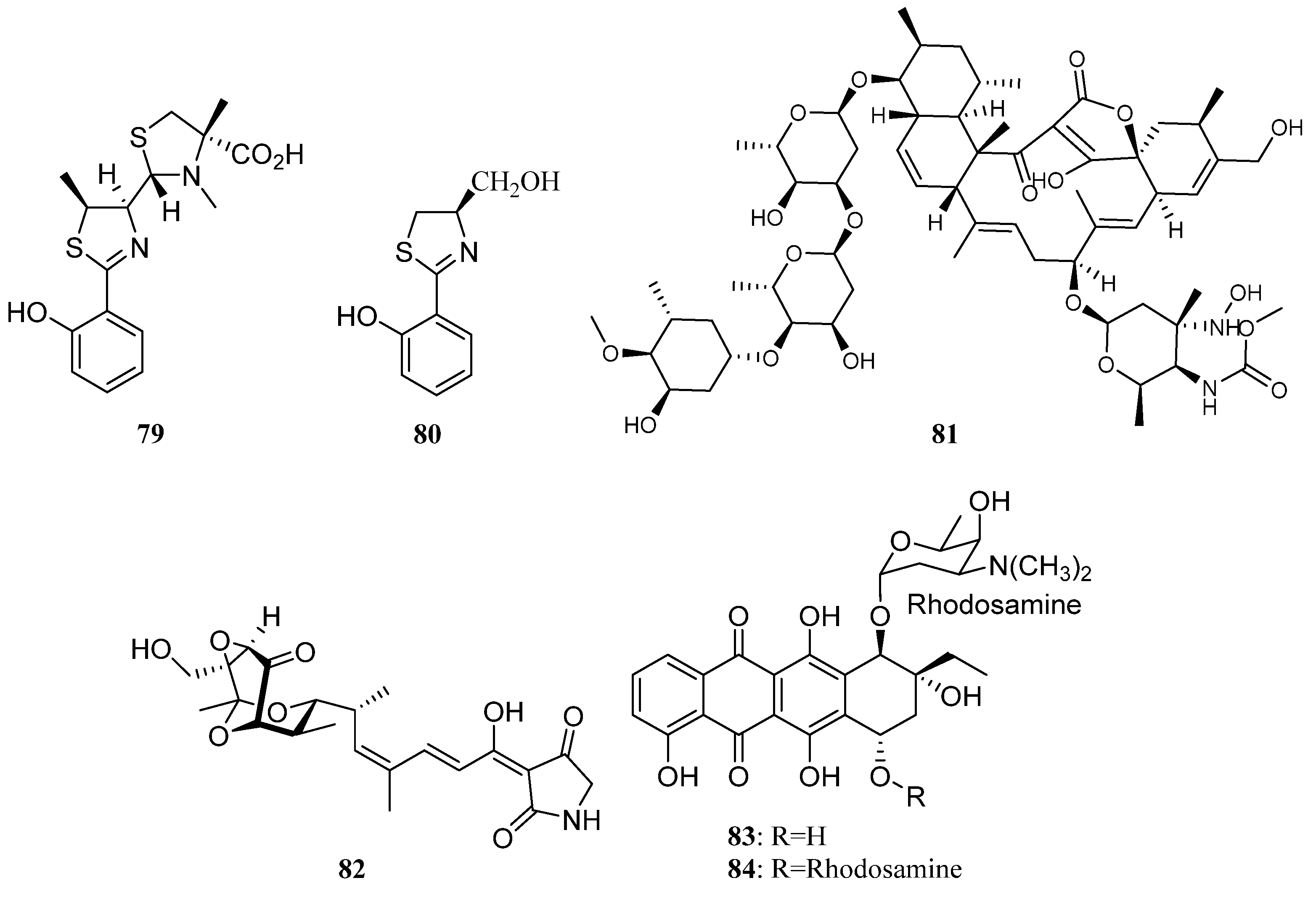
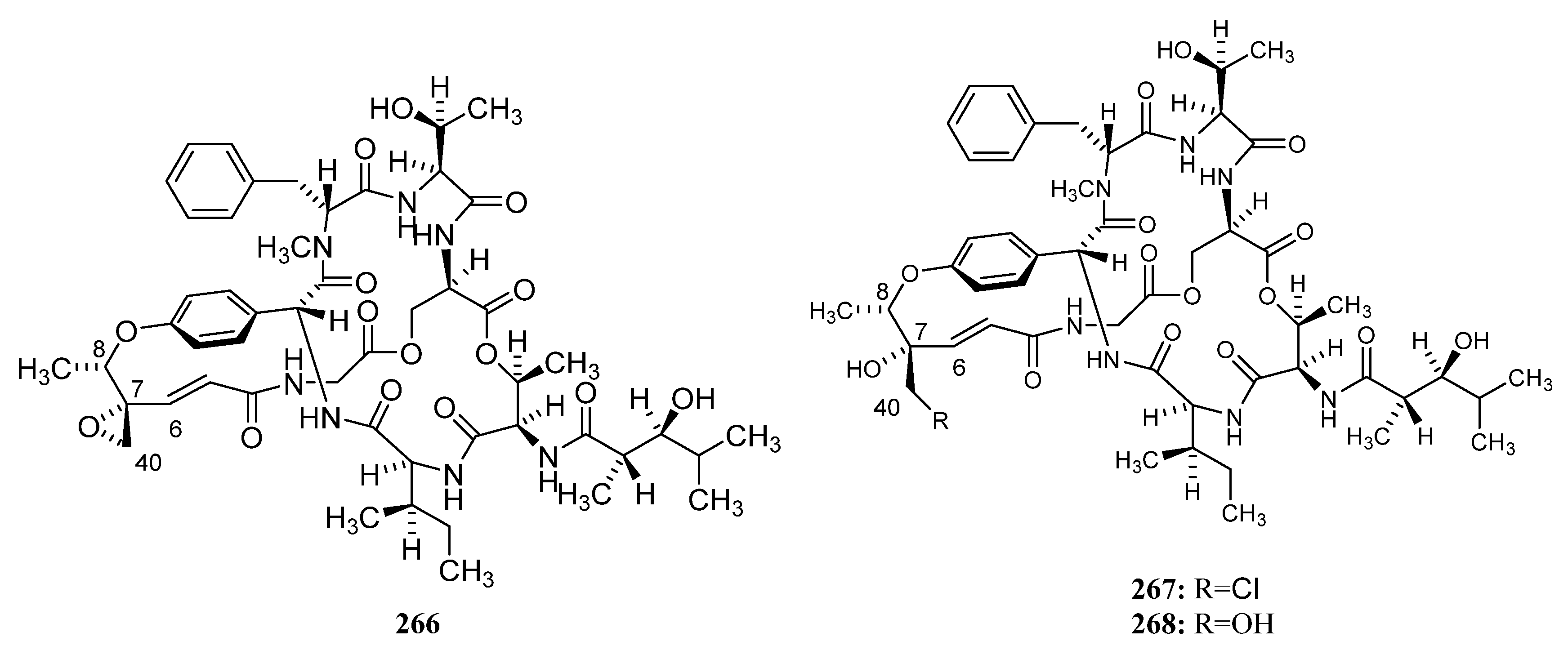
3.1.3. Peptides
Peptides Derived from the Sponge-Associated Actinomycetes
Peptides Derived from the Coral-Associated Actinomycetes
3.1.4. Peptides Derived from the Ascidian-Associated Actinomycetes
Peptides Derived from the Fish-Associated Actinomycetes
Peptides Derived from the Actinomycetes Associated with Other Marine Animals
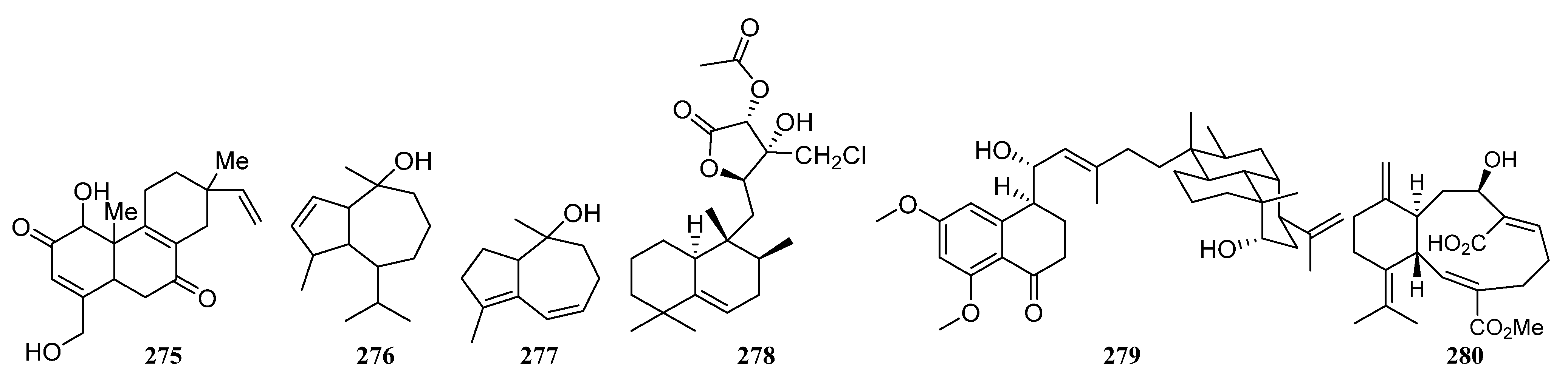
3.1.5. Terpenoids
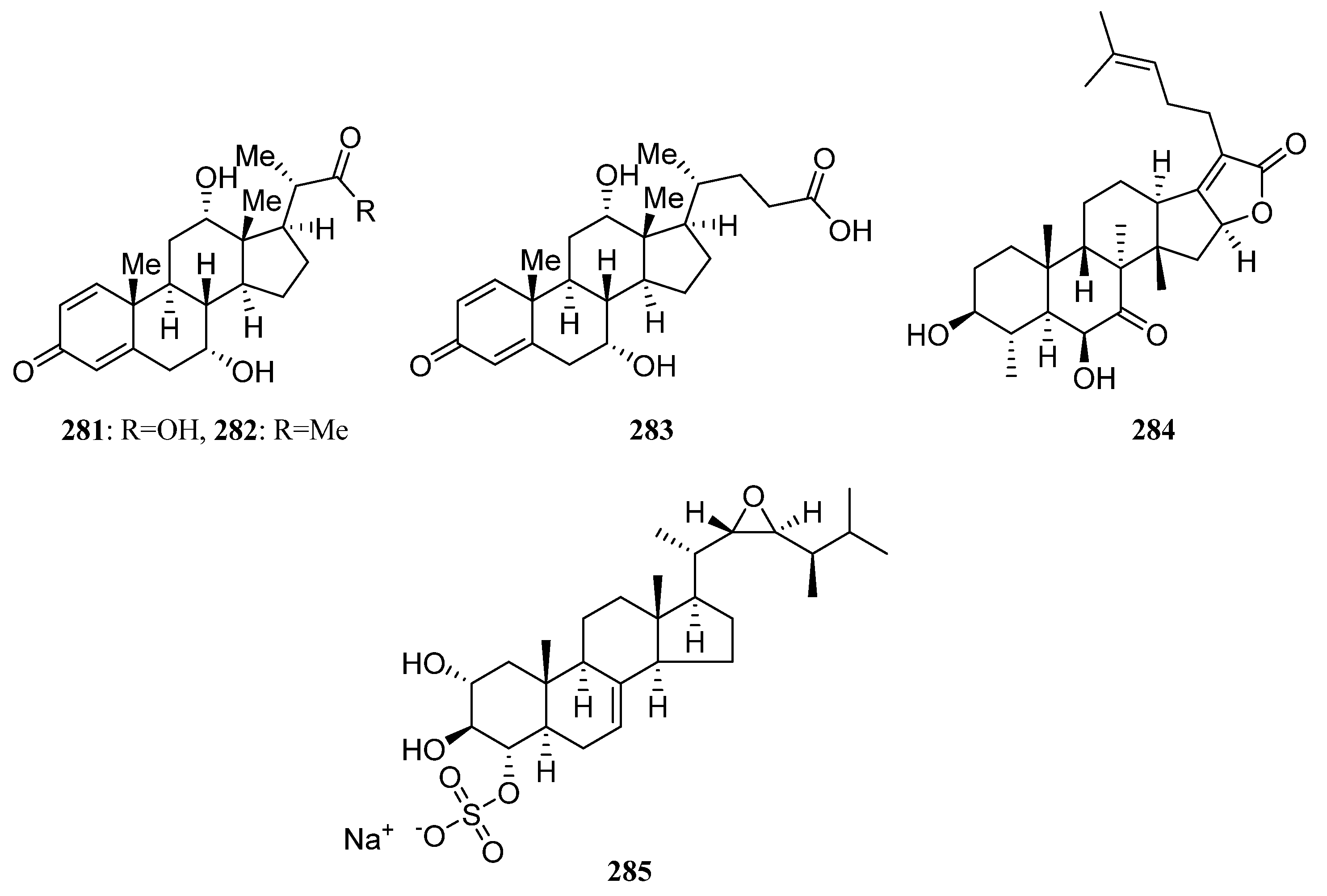
3.1.6. Steroids
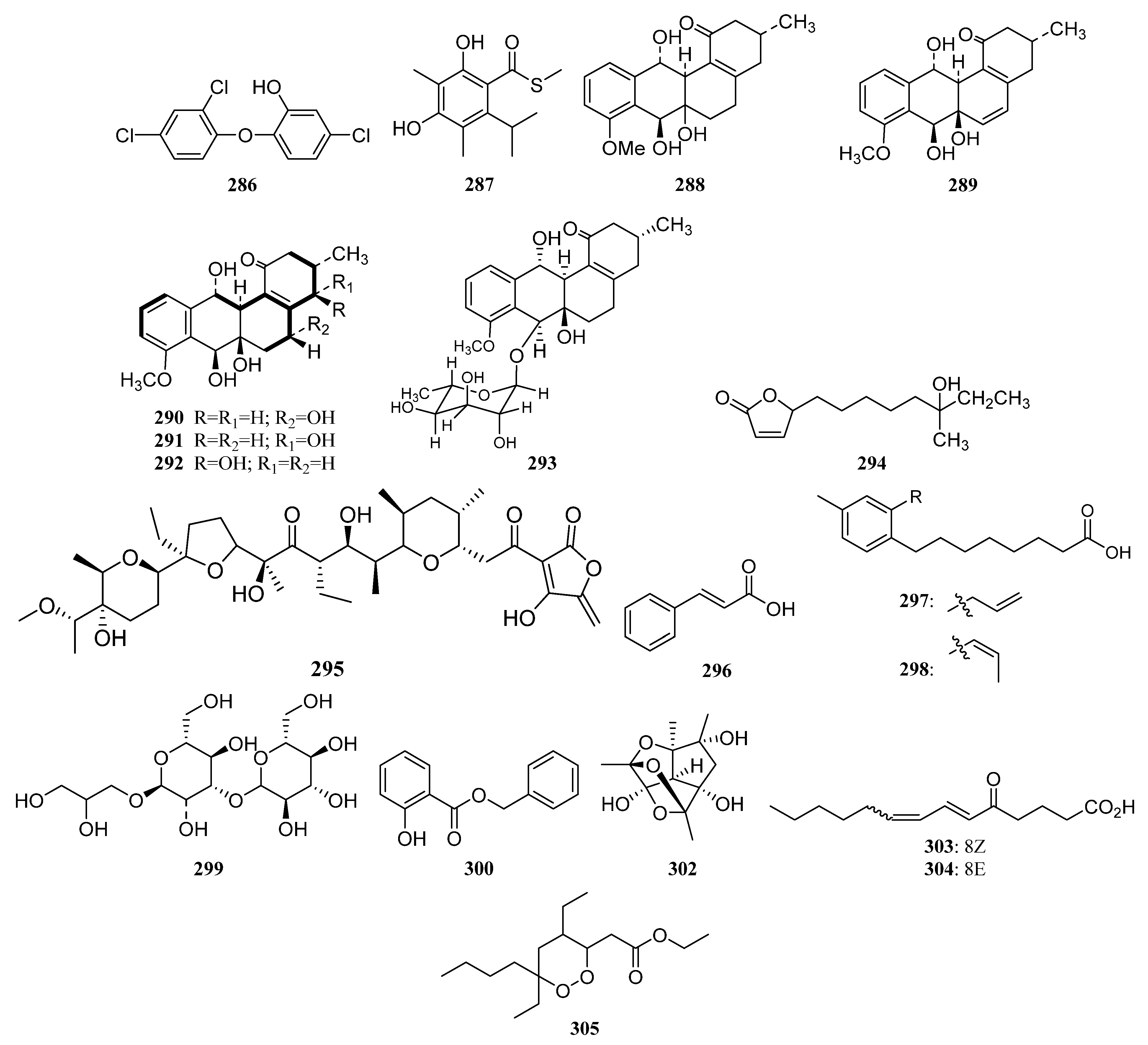
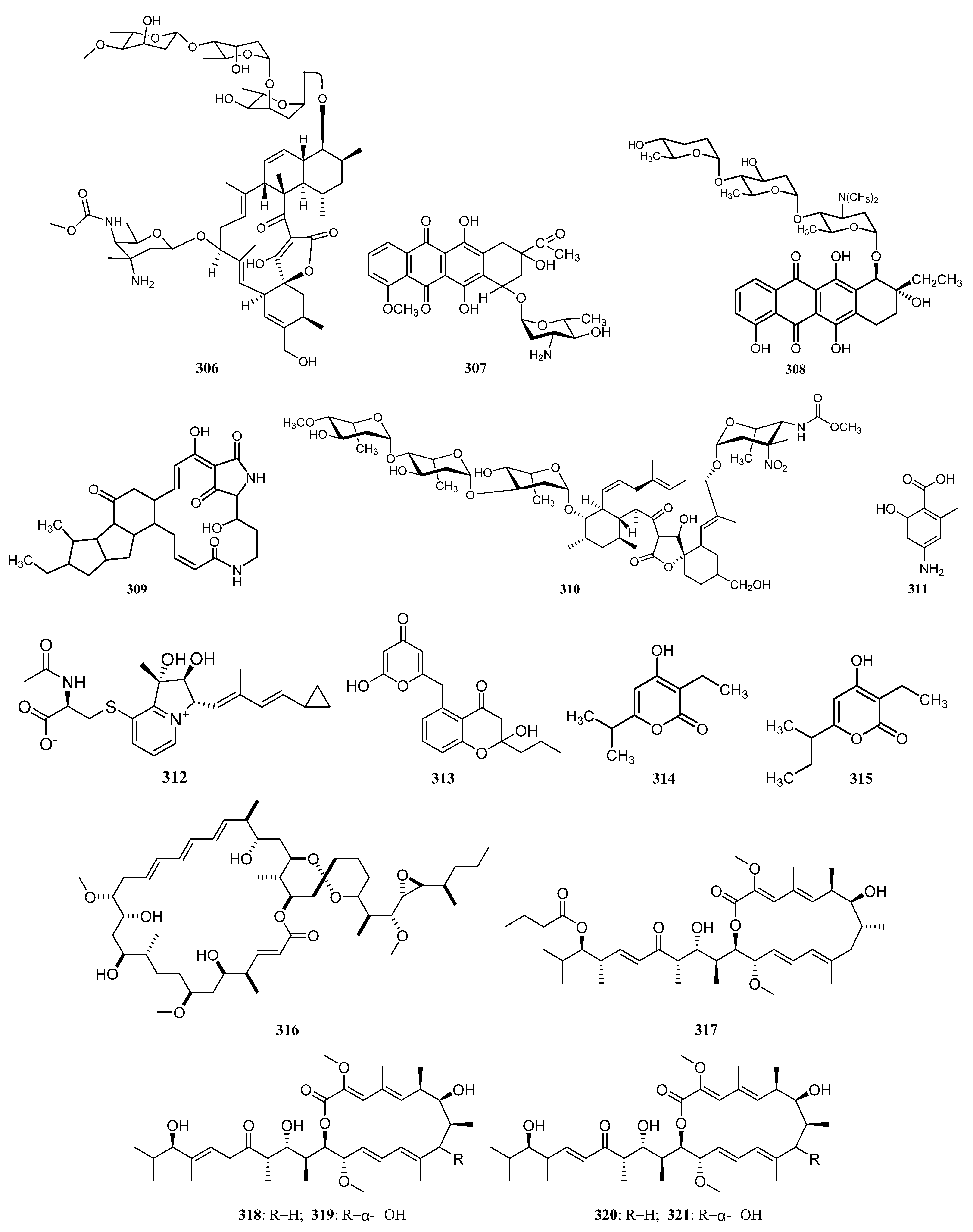
3.1.7. Other Structure Classes
3.2. Natural Products of the Actinomycetes Derived from Marine Plants, Macroalgae, Cyanobacteria, and Lichens
3.2.1. Alkaloids
Alkaloids Derived from the Brown Algae Associated Actinomycetes
Alkaloids Derived from the Green Algae Associated Actinomycetes
Alkaloids Derived from the Actinomycetes Associated with Lichens
3.2.2. Polyketides
Polyketides Derived from the Brown Algae Associated Actinomycetes
Polyketides Derived from the Green Algae ASSOCIATED Actinomycetes
Polyketides Derived from the Red Algae-Associated Actinomycetes
Polyketides Derived from the Cyanobacteria-Associated Actinomycetes
Polyketides Derived from the Actinomycetes Associated with Marine Plants
3.2.3. Peptides
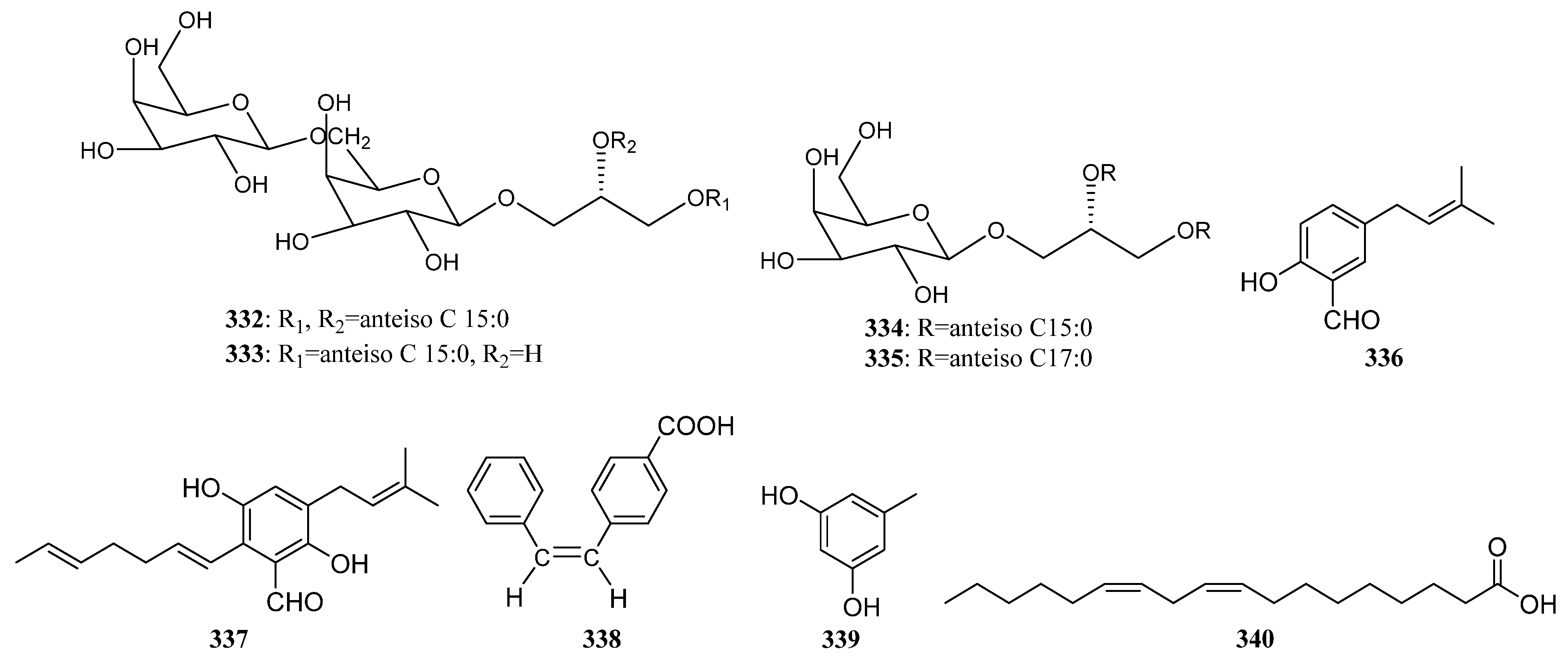
3.2.4. Other Structure Classes
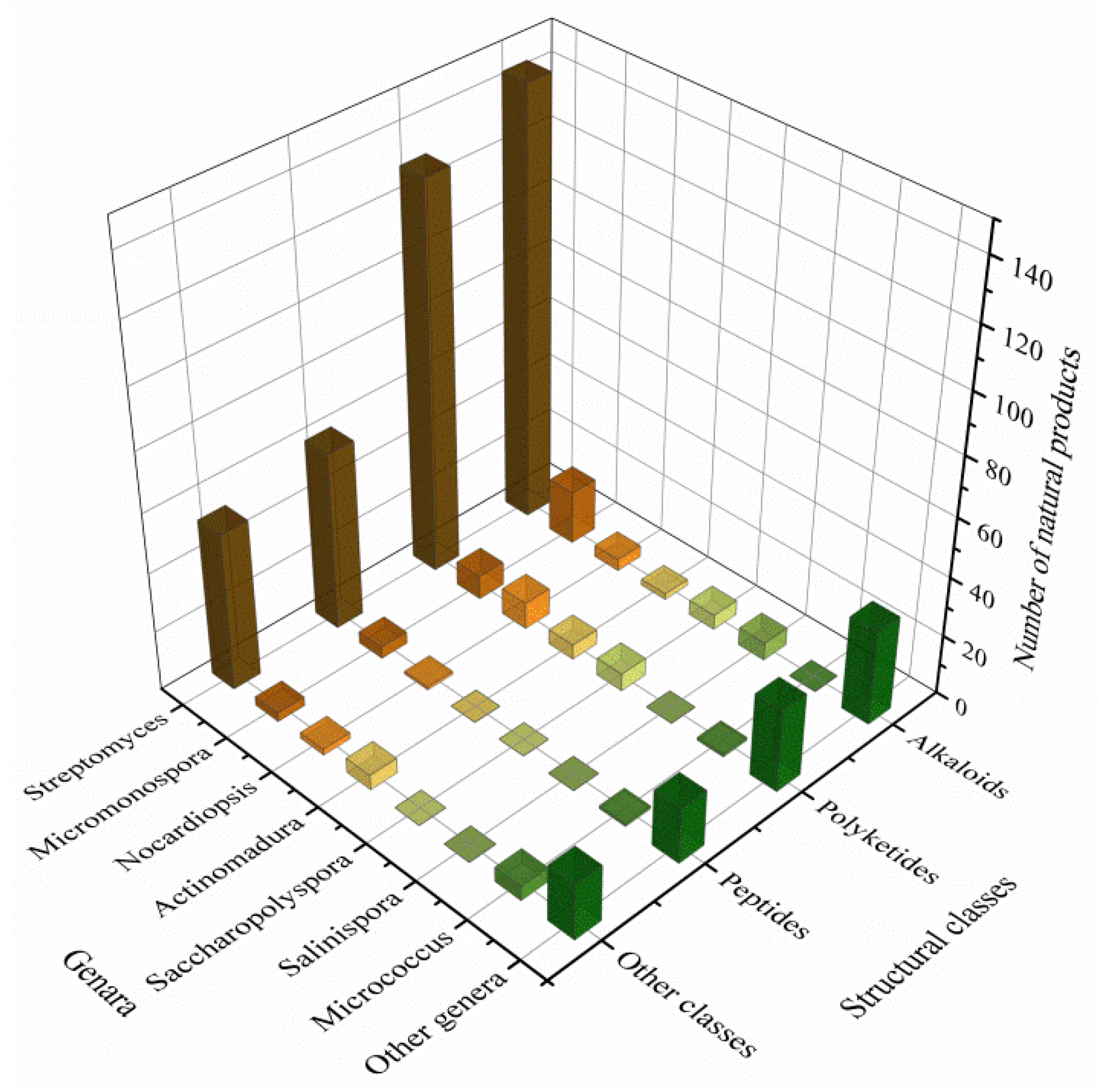
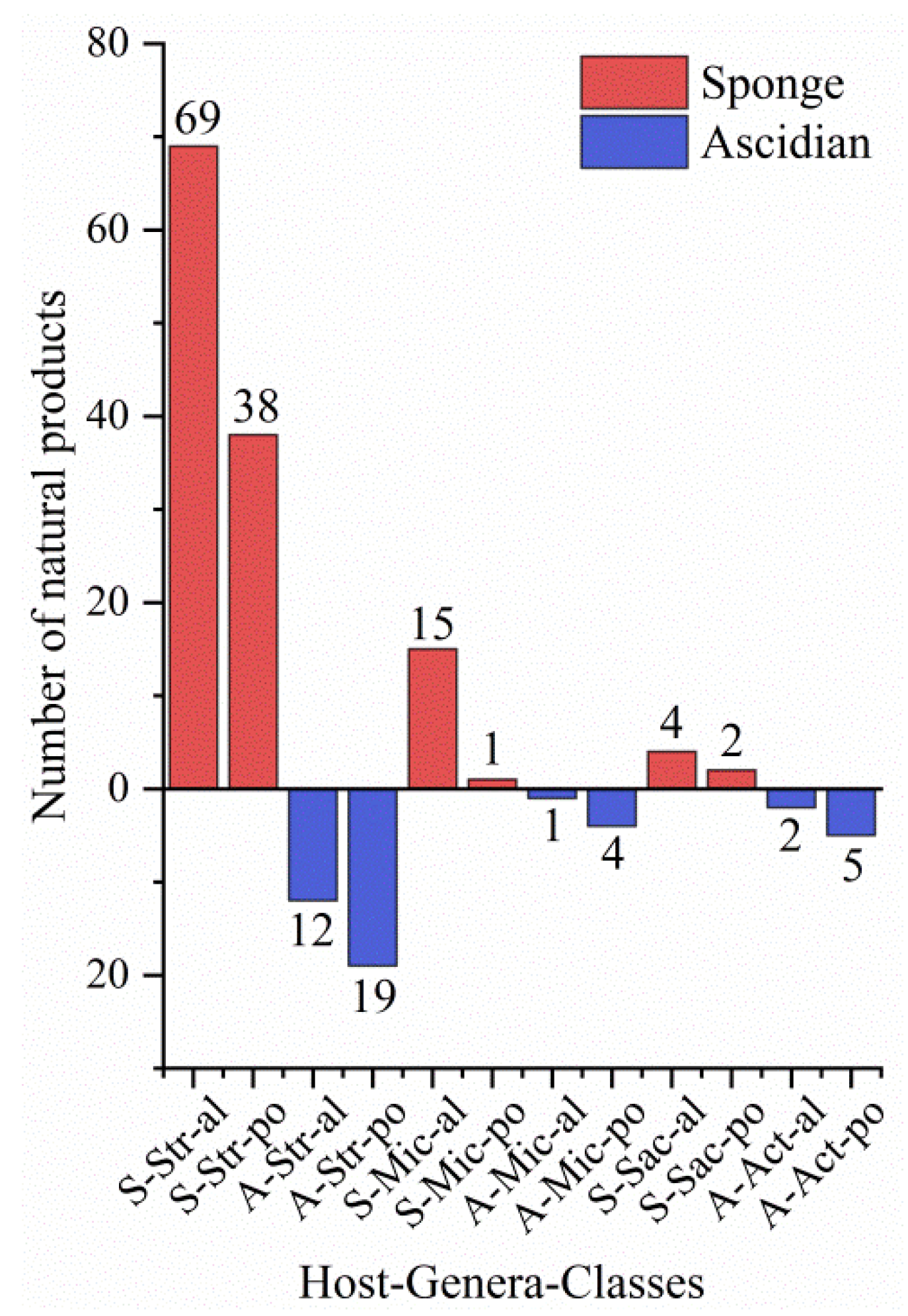
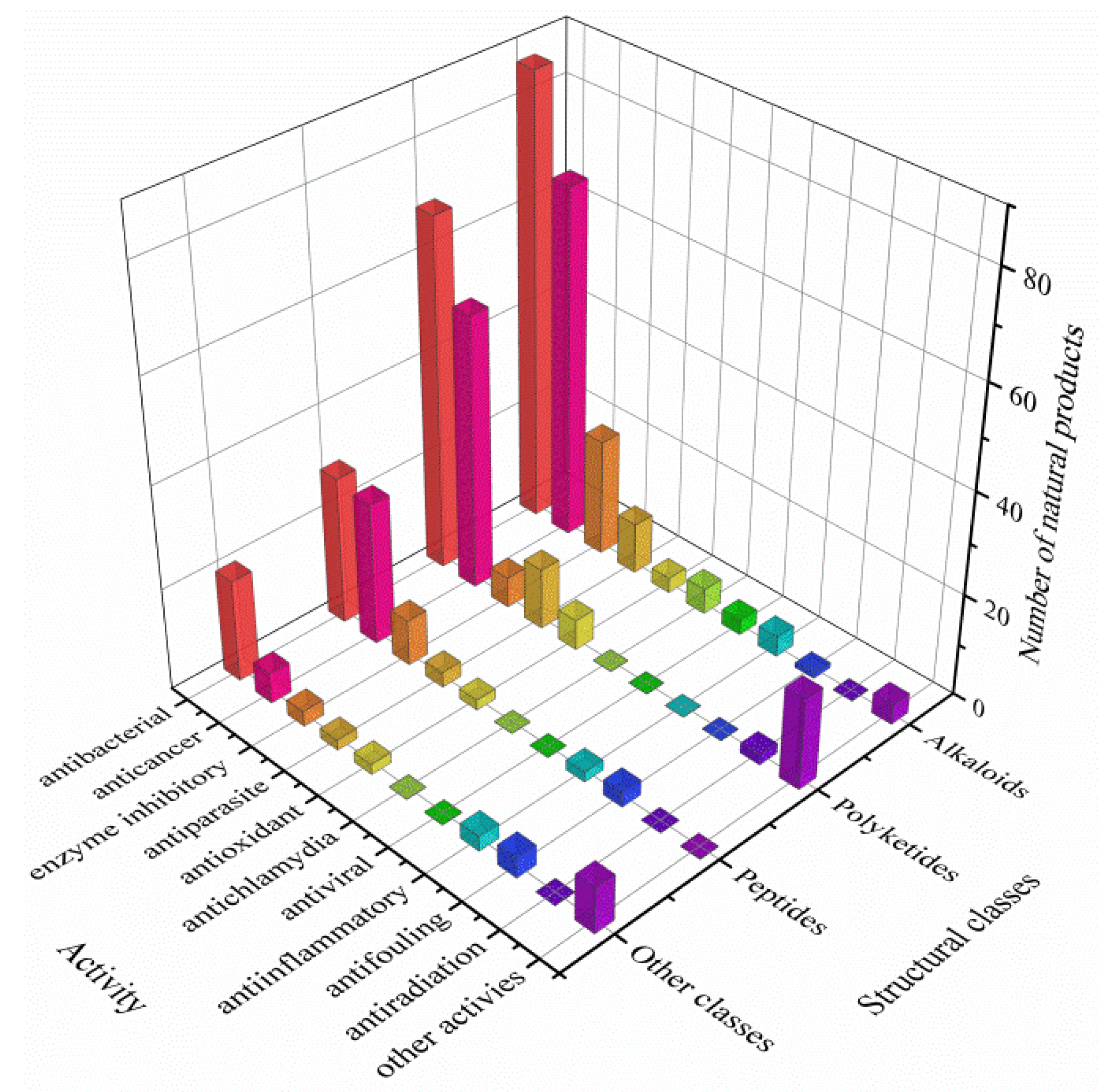
3.3. Data Analysis of the Secondary Metabolites from Actinomycetes Associated to Various Hosts
3.4. Clinical Information of the Secondary Metabolites
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jose, P.A.; Maharshi, A.; Jha, B. Actinobacteria in natural products research: Progress and prospects. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 246, 126708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, R.; Aalbersberg, W. Marine actinomycetes: An ongoing source of novel bioactive metabolites. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 167, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, J.; Stewart, A.; Song, B.; Hill, R.T.; Wright, J.L. Biodiversity of Actinomycetes Associated with Caribbean Sponges and Their Potential for Natural Product Discovery. Mar. Biotechnol. 2013, 15, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagannathan, S.; Manemann, E.; Rowe, S.; Callender, M.; Soto, W. Marine Actinomycetes, New Sources of Biotechnological Products. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zheng, Y.-Y.; Shao, C.-L.; Wang, C.-Y. Metabolites from marine invertebrates and their symbiotic microorganisms: Molecular diversity discovery, mining, and application. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2019, 1, 60–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jan, R.V. Biodiversity of Actinomycetes Associated with Caribbean Sponges of Puerto Rico, and Their Metabolic Profiles.; University of North Carolina Wilmington: Wilmington, NC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mary, T.R.J.; Kannan, R.R.; Iniyan, A.M.; Ramachandran, D.; Vincent, S.G.P. Cell wall distraction and biofilm inhibition of marine Streptomyces derived angucycline in methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 150, 104712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valliappan, K.; Sun, W.; Li, Z. Marine actinobacteria associated with marine organisms and their potentials in producing pharmaceutical natural products. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 7365–7377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Bayer, K.; Hentschel, U. Diversity, abundance and natural products of marine sponge-associated actinomycetes. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, L.M.C.; Blanco, J.A.D.L.F.; Baz, J.P.; Puentes, J.L.F.; Millán, F.R.; Vázquez, F.E.; Fernández-Chimeno, R.I.; Grávalos, D.G. 4’-N-Methyl-5’-hydroxystaurosporine and 5’-Hydroxystaurosporine, New Indolocarbazole Alkaloids from a Marine Micromonospora sp. Strain. J. Antibiot. 2000, 53, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, Z.; Pantazis, P.; Lange, T.S.; Wyche, J.H.; Hendrickson, E. The staurosporine analog, Ro-31-8220, induces apoptosis independently of its ability to inhibit protein kinase C. Cell Death Differ. 2000, 7, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schupp, P.; Steube, K.; Meyer, C.; Proksch, P.J.C.L. Anti-proliferative effects of new staurosporine derivatives isolated from a marine ascidian and its predatory flatworm. Cancer Lett. 2001, 174, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Cui, C.B.; Duan, L.; Gu, Q.Q.; Zhu, W.M. Potent in vitro anticancer activity of metacycloprodigiosin and undecylprodigiosin from a sponge-derived actinomycete Saccharopolyspora sp. Nov. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2005, 28, 1341–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.K.; Hewavitharana, A.K.; Shaw, N.; Fuerst, J.A. Discovery of a New Source of Rifamycin Antibiotics in Marine Sponge Actinobacteria by Phylogenetic Prediction. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 2118–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DiCioccio, R.A.; Srivastava, B.I. Structure-activity relationships and specificity of inhibition of DNA polymerases from normal and leukemia cells of man and from simian sarcoma virus by rifamycin derivatives. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1978, 61, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.M.; Xia, X.D.; Cui, Y.B.; Jiang, X.L.; Chao, M.; Cao, S.H. An update on progress in candidates and structure-activity relationships of the rifamycins. Chin. J. Antibiot. 2012, 37, 308–319. [Google Scholar]
- Imamura, N.; Nishijima, M.; Adachi, K.; Sano, H. Novel antimycin antibiotics, urauchimycins A and B, produced by marine actinomycete. J. Antibiot. 1993, 46, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitova, M.I.; Lang, G.; Wiese, J.; Imhoff, J.F. Subinhibitory Concentrations of Antibiotics Induce Phenazine Production in a Marine Streptomyces sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 824–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunbamrung, N.; Dramae, A.; Srichomthong, K.; Supothina, S.; Pittayakhajonwut, P. Streptophenazines I–L from Streptomyces sp. BCC21835. Phytochem. Lett. 2014, 10, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel-Elardo, S.M.; Gulder, T.; Hentschel, U.; Bringmann, G. Cebulactams A1 and A2, new macrolactams isolated from Saccharopolyspora cebuensis, the first obligate marine strain of the genus Saccharopolyspora. Cheminform 2009, 49, 6889–6892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel-Elardo, S.M.; Kozytska, S.; Bugni, T.S.; Ireland, C.M.; Moll, H.; Hentschel, U. Anti-Parasitic Compounds from Streptomyces sp. Strains Isolated from Mediterranean Sponges. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motohashi, K.; Takagi, M.; Shin-Ya, K. Tetracenoquinocin and 5-iminoaranciamycin from a sponge-derived Streptomyces sp. Sp080513GE-26. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumikawa, M.; Khan, S.; Takagi, M.; Shin-Ya, K. Sponge-Derived Streptomyces Producing Isoprenoids via the Mevalonate Pathway. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Izumikawa, M.; Motohashi, K.; Mukai, A.; Takagi, M.; Shin-Ya, K. Distribution of the 3-hydroxyl-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene and isoprenoid production in marine-derived Actinobacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2010, 304, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, J.Y.; Khan, S.T.; Takagi, M.; Shin-ya, K. JBIR-58, a new salicylamide derivative, isolated from a marine sponge-derived Streptomyces sp. SpD081030ME-02. J. Antibiot. Tokyo 2010, 63, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-L.; Gao, Y.; Xue, D.-Q.; Liu, H.-L.; Peng, C.-S.; Zhang, F.-L.; Li, Z.-Y.; Guo, Y.-W. Streptomycindole, an Indole Alkaloid from a Marine Streptomyces sp. DA22 Associated with South China Sea Sponge Craniella australiensis. Helvetica Chim. Acta 2011, 94, 1838–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.-B.; Xi, T.; Li, J.; Wang, P.; Li, F.-C.; Lin, Y.-C.; Qin, S. Lobophorin C and D, New Kijanimicin Derivatives from a Marine Sponge-Associated Actinomycetal Strain AZS17. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Szesny, M.; Othman, E.M.; Schirmeister, T.; Grond, S.; Stopper, H.; Hentschel, U. Antioxidant and Anti-Protease Activities of Diazepinomicin from the Sponge-Associated Micromonospora Strain RV115. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2208–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, O.; Yagi, M.; Tanaka, M.; Kiyoto, S.; Okuhara, M.; Kohsaka, M. WS-9659 A and B, novel testosterone 5.ALPHA.-reductase inhibitors isolated from a Streptomyces. I. Taxonomy, fermentation, isolation, physico-chemical characteristics. J. Antibiot. 1989, 42, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosoya, T.; Hirokawa, T.; Takagi, M.; Shin-ya, K. Trichostatin analogues JBIR-109, JBIR-110, and JBIR-111 from the marine sponge-derived Streptomyces sp. RM72. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumikawa, M.; Kawahara, T.; Hwang, J.-H.; Takagi, M.; Shin-Ya, K. JBIR-107, a New Metabolite from the Marine-Sponge-Derived Actinomycete, Streptomyces tateyamensisNBRC 105047. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2013, 77, 663–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Sun, W.; Yu, Y.; Li, Z.; Deng, Z.; Lin, S. A new glutarimide derivative from marine sponge-derived Streptomyces anulatus S71. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 1602–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Prasad, P.; Subramani, R.; Aalbersberg, W. Production and purification of a bioactive substance against multi-drug resistant human pathogens from the marine-sponge-derived Salinispora sp. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 4, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vicente, J.; Stewart, A.K.; Van Wagoner, R.M.; Elliott, E.; Bourdelais, A.J.; Wright, J.L.C. Monacyclinones, New Angucyclinone Metabolites Isolated from Streptomyces sp. M7_15 Associated with the Puerto Rican Sponge Scopalina ruetzleri. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4682–4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reimer, A.; Blohm, A.; Quack, T.; Grevelding, C.G.; Kozjak-Pavlovic, V.; Rudel, T.; Hentschel, U.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Inhibitory activities of the marine streptomycete-derived compound SF2446A2 against Chlamydia trachomatis and Schistosoma mansoni. J. Antibiot. 2015, 68, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhen, X.; Gong, T.; Liu, F.; Zhang, P.-C.; Zhou, W.-Q.; Li, Y.; Zhu, P. A New Analogue of Echinomycin and a New Cyclic Dipeptide from a Marine-Derived Streptomyces sp. LS298. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6947–6961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Espinosa, A.; Socha, A.M.; Ryke, E.; Rowley, D.C. Antiamoebic properties of the actinomycete metabolites echinomycin A and tirandamycin A. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 111, 2473–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Vodanovic-Jankovic, S.; Ledeboer, N.; Huang, S.-X.; Rajski, S.R.; Kron, M.; Shen, B. Tirandamycins from Streptomyces sp. 17944 Inhibiting the Parasite Brugia malayi Asparagine tRNA Synthetase. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 2034–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamaoki, T.; Nomoto, H.; Takahashi, I.; Kato, Y.; Morimoto, M.; Tomita, F. Staurosporine, a potent inhibitor of phospholipidCa++dependent protein kinase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1986, 135, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Othman, E.M.; Fekete, A.; Krischke, M.; Stopper, H.; Edrada-Ebel, U.; Mueller, M.J.; Hentschel, U.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Strepoxazine A, a new cytotoxic phenoxazin from the marine sponge-derived bacterium Streptomyces sp. SBT345. Tetrahedron Lett. 2016, 57, 4196–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, C.; Othman, E.M.; Reimer, A.; Grüne, M.; Kozjak-Pavlovic, V.; Stopper, H.; Hentschel, U.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Ageloline A, new antioxidant and antichlamydial quinolone from the marine sponge-derived bacterium Streptomyces sp SBT345. Tetrahedron Lett. 2016, 57, 2786–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekurova, O.N.; Pérez-Victoria, I.; Martín, J.; Degnes, K.F.; Sletta, H.; Reyes, F.; Zotchev, S.B. New Deferoxamine Glycoconjugates Produced upon Overexpression of Pathway-Specific Regulatory Gene in the Marine Sponge-Derived Streptomyces albus PVA94-07. Molecules 2016, 21, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elsayed, Y.; Refaat, J.; Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Ahmed, S.; Fouad, M.A. Rhodozepinone, a new antitrypanosomal azepino-diindole alkaloid from the marine sponge-derived bacterium Rhodococcus sp. UA13. Med. Chem. Res. 2017, 26, 2751–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.L.; Chen, D.; Huang, L.; Ni, M.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, H.; Bao, X. Antichlamydial Dimeric Indole Derivatives from Marine Actinomycete Rubrobacter radiotolerans. Planta Med. 2017, 83, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Othman, E.M.; Stopper, H.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Hentschel, U.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Isolation of Petrocidin A, a New Cytotoxic Cyclic Dipeptide from the Marine Sponge-Derived Bacterium Streptomyces sp. SBT348. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Che, Q.; Liang, Q.; Han, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, T.; Li, D. Anthranosides A-C, Anthranilate Derivatives from a Sponge-Derived Streptomyces sp. CMN-62. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 5466–5469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hawary, S.S.; Sayed, A.; Mohammed, R.; Khanfar, M.; Rateb, M.E.; Mohammed, T.A.; Hajjar, D.; Hassan, H.; Gulder, T.A.M.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. New Pim-1 Kinase Inhibitor From the Co-culture of Two Sponge-Associated Actinomycetes. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, T.; Zhen, X.; Li, X.-L.; Chen, J.-J.; Chen, T.-J.; Yang, J.-L.; Zhu, P. Tetrocarcin Q, a New Spirotetronate with a Unique Glycosyl Group from a Marine-Derived Actinomycete Micromonospora carbonacea LS276. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Kong, F.; Zhou, S.; Huang, D.; Zheng, J.; Zhu, W. Streptomyces tirandamycinicus sp. nov., a Novel Marine Sponge-Derived Actinobacterium With Antibacterial Potential Against Streptococcus agalactiae. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.-H.; Lian, Y.-Y.; Fang, D.-S.; Chen, L.; Jia, J.; Zhang, W.-L.; Lin, R.; Xie, Y.; Bi, H.-K.; Jiang, H. Identification and antimicrobial properties of a new alkaloid produced by marine-derived Verrucosispora sp. FIM06-0036. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-H.; Zhang, W.-L.; Chen, L.; Lin, R.; Xie, Y.; Fang, D.-S.; Lian, Y.-Y.; Jiang, H. Isolation, purification and identification of two new alkaloids metabolites from marine-derived Verrucosispora sp. FIM06025. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 33, 2897–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfike, A.; Attia, E.Z.; Desoukey, S.Y.; Hajjar, D.; Makki, A.A.; Schupp, P.J.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. New bioactive metabolites from the elicited marine sponge-derived bacterium Actinokineospora spheciospongiae sp. nov. AMB Express 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaneesha, M.; Hasin, O.; Sivakumar, K.C.; Ravinesh, R.; Naman, C.B.; Carmeli, S.; Sajeevan, T.P. DNA Binding and Molecular Dynamic Studies of Polycyclic Tetramate Macrolactams (PTM) with Potential Anticancer Activity Isolated from a Sponge-Associated Streptomyces zhaozhouensis subsp. mycale subsp. nov. Mar. Biotechnol. 2019, 21, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Li, Y.; Banakar, S.P.; Liu, L.; Shao, C.; Li, Z.; Wang, C. New Metabolites From the Co-culture of Marine-Derived Actinomycete Streptomyces rochei MB037 and Fungus Rhinocladiella similis 35. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, D.D.; Trinh, T.T.V.; Mai, H.D.T.; Vu, V.N.; Le, H.M.; Thi, Q.V.; Nguyen, M.A.; Duong, T.T.; Tran, D.T.; Chau, V.M.; et al. Antimicrobial lavandulylated flavonoids from a sponge-derived Streptomyces sp. G248 in east vietnam sea. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, D.D.; Do, T.Q.; Doan Thi Mai, H.; Vu Thi, Q.; Nguyen, M.A.; Le Thi, H.M.; Tran, D.T.; Chau, V.M.; Cong Thung, D.; Pham, V.C. Antimicrobial lavandulylated flavonoids from a sponge-derived actinomycete. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Back, C.; Stennett, H.; Williams, S.; Wang, L.; Gomez, J.O.; Abdulle, O.; Duffy, T.; Neal, C.; Mantell, J.; Jepson, M.; et al. A New Micromonospora Strain with Antibiotic Activity Isolated from the Microbiome of a Mid-Atlantic Deep-Sea Sponge. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhalifah, D.H.M. Sponge-associated sp. RM66 metabolome induction with N-acetylglucosamine: Antibacterial, antifungal and anti-trypanosomal activities. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 4691–4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhadrami, H.; Thissera, B.; Hassan, M.; Behery, F.; Ngwa, C.; Hassan, H.; Pradel, G.; Abdelmohsen, U.; Rateb, M. Bio-Guided Isolation of Antimalarial Metabolites from the Coculture of Two Red Sea Sponge-Derived Actinokineospora and Rhodococcus spp. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Fandong, K.; Yuanfei, W. Antibiotic Metabolites from the Coral-Associated Actinomycete Streptomyces sp. OUCMDZ-1703. Chin. J. Chem. 2013, 31, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Braña, A.F.; Sarmiento-Vizcaíno, A.; Osset, M.; Pérez-Victoria, I.; Martín, J.; de Pedro, N.; de la Cruz, M.; Díaz, C.; Vicente, F.; Reyes, F.; et al. Lobophorin K, a New Natural Product with Cytotoxic Activity Produced by Streptomyces sp. M-207 Associated with the Deep-Sea Coral Lophelia pertusa. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cong, Z.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, P.; Liao, S.; Yang, B.; Zhou, X.; Huang, D.; Wang, J. Cytotoxic anthracycline and antibacterial tirandamycin analogues from a marine-derived Streptomyces sp. SCSIO 41399. J. Antibiot. 2019, 72, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Z.; Chen, S.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Khan, I.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, C. A new uridine derivative and a new indole derivative from the coral-associated actinomycete Pseudonocardia sp. SCSIO 11457. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hu, J.-S.; Xu, J.-L.; Shao, C.-L.; Wang, G.-Y. Biological and Chemical Diversity of Ascidian-Associated Microorganisms. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Janso, J.E.; Haltli, B.; Eustaquio, A.; Kulowski, K.; Waldman, A.J.; Zha, L.; Nakamura, H.; Bernan, V.S.; He, H.; Carter, G.T.; et al. Discovery of the lomaiviticin biosynthetic gene cluster in Salinispora pacifica. Tetrahedron 2014, 70, 4156–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, H.; Ding, W.D.; Bernan, V.S.; Richardson, A.D.; Ireland, C.M.; Greenstein, M.; Ellestad, G.A.; Carter, G.T. Lomaiviticins A and B, potent antitumor antibiotics from Micromonospora lomaivitiensis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 5362–5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charan, R.D.; Schlingmann, G.; Janso, J.; Bernan, V.; Feng, X.; Carter, G.T. Diazepinomicin, a New Antimicrobial Alkaloid from a Marine Micromonospora sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1431–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, Y.; Shirasaki, S.; Shiba, S.; Kawasaki, T.; Matsuo, Y.; Adachi, K.; Shizuri, Y. Piericidins C7 and C8, New Cytotoxic Antibiotics Produced by a Marine Streptomyces sp. ChemInform 2007, 38, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asolkar, R.N.; Kirkland, T.N.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Arenimycin, an antibiotic effective against rifampin- and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from the marine actinomycete Salinispora arenicola. J. Antibiot. Tokyo 2010, 63, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.H.; Yang, H.O.; Sohn, Y.C.; Kwon, H.C. Aeromicrobium halocynthiae sp. nov., a taurocholic acid-producing bacterium isolated from the marine ascidian Halocynthia roretzi. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 2793–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyche, T.P.; Piotrowski, J.S.; Hou, Y.; Braun, D.; Deshpande, R.; Mcilwain, S.; Ong, I.M.; Myers, C.L.; Guzei, I.A.; Westler, W.M. Forazoline A: Marine-derived polyketide with antifungal in vivo efficacy. Angewandte Chemie 2014, 126, 11767–11770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.A.; Badr, J.M.; Harakeh, S.M. Bioactive 2(1H)-Pyrazinones and Diketopiperazine Alkaloids from a Tunicate-Derived Actinomycete Streptomyces sp. Molecules 2016, 21, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, C.; Takada, T.; Yamada, T.; Minoura, K.; Uchida, K.; Matsumura, E.; Numata, A. Halichomycin, a new class of potent cytotoxic macrolide produced by an actinomycete from a marine fish. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994, 35, 5013–5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.M.S.; Insua, M.M.; Baz, J.P.; Puentes, J.L.F.; Hernández, L.M.C. New Cytotoxic Indolic Metabolites from a MarineStreptomyces. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 863–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xie, L.; Xia, G.; Zhang, J.; Nie, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, R. A new tetrodotoxin-producing actinomycete, Nocardiopsis dassonvillei, isolated from the ovaries of puffer fish Fugu rubripes. Toxicon 2005, 45, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahyudin, N.A. Actinomycetes and Fungi Associated with Marine Invertebrates: A Potential Source of Bioactive Compounds. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Canterbury Biological Sciences, Canterbury, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Takagi, M.; Motohashi, K.; Izumikawa, M.; Khan, S.T.; Hwang, J.H.; Shin-Ya, K. JBIR-66, a new metabolite isolated from tunicate-derived Saccharopolyspora sp. SS081219JE-28. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2010, 74, 2355–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Z.; Koch, M.; Pond, C.D.; Mabeza, G.; Seronay, R.A.; Concepcion, G.P.; Barrows, L.R.; Olivera, B.M.; Schmidt, E.W. Structure and activity of lobophorins from a turrid mollusk-associated Streptomyces sp. J. Antibiot. 2013, 67, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawahara, T.; Itoh, M.; Izumikawa, M.; Kozone, I.; Sakata, N.; Tsuchida, T.; Shin-Ya, K. New hydroxamate metabolite, MBJ-0003, from Micromonospora sp. 29867. J. Antibiot. 2013, 67, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambavane, V.; Tokdar, P.; Parab, R.; Sreekumar, E.S.; Mahajan, G.; Mishra, P.D.; D’Souza, L.; Ranadive, P. Caerulomycin A—An Antifungal Compound Isolated from Marine Actinomycetes. Adv. Microbiol. 2014, 04, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnani, N.; Chevrette, M.G.; Adibhatla, S.N.; Zhang, F.; Yu, Q.; Braun, D.R.; Nelson, J.; Simpkins, S.W.; McDonald, B.R.; Myers, C.L.; et al. Coculture of Marine Invertebrate-Associated Bacteria and Interdisciplinary Technologies Enable Biosynthesis and Discovery of a New Antibiotic, Keyicin. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 3093–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.T.; Tran, V.H.; Vu, V.N.; Mai, H.D.T.; Le, T.H.M.; Vu, T.Q.; Nguyen, H.H.; Chau, V.M.; Pham, V.C. Antimicrobial metabolites from a marine-derived Actinomycete Streptomyces sp. G278. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 3223–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chai, W.; Song, T.; Ma, M.; Lian, X.-Y.; Zhang, Z. Anti-glioma Natural Products Downregulating Tumor Glycolytic Enzymes from Marine Actinomycete Streptomyces sp. ZZ406. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, K.B.; Wang, W.; Bi, S.F.; Mei, Y.N.; Deng, X.Z.; Jiao, R.H.; Tan, R.X.; Ge, H.M. Discovery, Biosynthesis, and Heterologous Production of Streptoseomycin, an Anti-Microaerophilic Bacteria Macrodilactone. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 2967–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.-K.; Wang, R.; Chen, S.-Q.; Chen, F.-X.; Liu, T.-M.; Yang, M.-Q. Anthocidins A⁻D, New 5-Hydroxyanthranilic Acid Related Metabolites from the Sea Urchin-Associated Actinobacterium, Streptomyces sp. HDa1. Molecules 2018, 23, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Z.-K.; Wang, R.; Liu, T.-M.; Chen, F.-X.; Yang, M.-Q. A new flavonoid derivative and a new 5-hydroxyanthranilic acid derivative from the sea urchin-derived Streptomyces sp. HDa1. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 21, 992–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wu, Q.; Xie, Q.; Ling, C.; Zhang, H.; Sun, C.; Ju, J. New Borrelidins from Onchidium sp. Associated Streptomyces olivaceus SCSIO LO13. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17, e1900560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, J.; Liu, C.L.; Xiang, L.; Ma, S.Y.; Li, W.; Jiao, R.H.; Tan, R.X.; Ge, H.M. New borrelidin derivatives from an endophytic Streptomyces sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2018, 59, 4517–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, B.; Gregory, M.A.; Moss, S.J.; Carletti, I.; Sheridan, R.M.; Kaja, A.; Ward, M.; Olano, C.; Mendez, C.; Salas, J.A.; et al. Separation of anti-angiogenic and cytotoxic activities of borrelidin by modification at the C17 side chain. Bioorg.Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 5814–5817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañedo, L.M.; Puentes, J.L.F.; Baz, J.P.; Huang, X.-H.; Rinehart, K.L. IB-96212, a Novel Cytotoxic Macrolide Produced by a Marine Micromonospora. II. Physico-chemical Properties and Structure Determination. J. Antibiot. 2000, 53, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perez, M.; Schleissner, C.; Rodriguez, P.; Zuniga, P.; Benedit, G.; Sanchez-Sancho, F.; de la Calle, F. PM070747, a new cytotoxic angucyclinone from the marine-derived Saccharopolyspora taberi PEM-06-F23-019B. J. Antibiot. Tokyo 2009, 62, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneemann, I.; Ohlendorf, B.; Zinecker, H.; Nagel, K.; Wiese, J.; Imhoff, J.F. Nocapyrones A-D, gamma-pyrones from a Nocardiopsis strain isolated from the marine sponge Halichondria panicea. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1444–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pimentel-Elardo, S.M.; Buback, V.; Gulder, T.A.; Bugni, T.S.; Reppart, J.; Bringmann, G.; Ireland, C.M.; Schirmeister, T.; Hentschel, U. New Tetromycin Derivatives with Anti-Trypanosomal and Protease Inhibitory Activities. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1682–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lu, Y.; Cao, S. Antimicrobial compounds from marine actinomycetes. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2020, 43, 677–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supong, K.; Thawai, C.; Suwanborirux, K.; Choowong, W.; Supothina, S.; Pittayakhajonwut, P. Antimalarial and antitubercular C-glycosylated benz[α]anthraquinones from the marine-derived Streptomyces sp. BCC45596. Phytochem. Lett. 2012, 5, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria-Mercado, I.E.; Prieto-Davo, A.; Jensen, A.P.R.; Fenical, W. Antibiotic Terpenoid Chloro-Dihydroquinones from a New Marine Actinomycete. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauermeister, A.; Pereira, F.; Grilo, I.; Godinho, C.C.; Paulino, M.; Almeida, V.; Gobbo-Neto, L.; Prieto-Davó, A.; Sobral, R.G.; Lopes, N.P.; et al. Intra-clade metabolomic profiling of MAR4 Streptomyces from the Macaronesia Atlantic region reveals a source of anti-biofilm metabolites. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 1099–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shomura, T.; Gomi, S.; Ito, M.; Yoshida, J.; Tanaka, E.; Amano, S.; Watabe, H.-O.; Ohuchi, S.; Itoh, J.; Sezaki, M.; et al. Studies on new antibiotics SF2415. I. Taxonomy, fermentation, isolation, physico-chemical properties and biological activities. J. Antibiot. 1987, 40, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.C.; Hwang, E.; Kim, T.; Ham, J.; Kim, S.Y.; Kwon, H.C. Nocatriones A and B, Photoprotective Tetracenediones from a Marine-Derived Nocardiopsis sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 2326–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Cheng, C.; Viegelmann, C.; Zhang, T.; Grkovic, T.; Ahmed, S.; Quinn, R.J.; Hentschel, U.; Edrada-Ebel, R. Dereplication Strategies for Targeted Isolation of New Antitrypanosomal Actinosporins A and B from a Marine Sponge Associated-Actinokineospora sp. EG49. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1220–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grkovic, T.; Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Othman, E.M.; Stopper, H.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Hentschel, U.; Quinn, R.J. Two new antioxidant actinosporin analogues from the calcium alginate beads culture of sponge-associated Actinokineospora sp. strain EG49. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 5089–5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltamany, E.E.; Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Ibrahim, A.K.; Hassanean, H.A.; Hentschel, U.; Ahmed, S.A. New antibacterial xanthone from the marine sponge-derived Micrococcus sp. EG45. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 4939–4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Q.; Tan, H.; Han, X.; Zhang, X.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, T.; Li, D. Naquihexcin A, a S-Bridged Pyranonaphthoquinone Dimer Bearing an Unsaturated Hexuronic Acid Moiety from a Sponge-Derived Streptomyces sp. HDN-10-293. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 3358–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Nepal, K.K.; Chen, J.; Harmody, D.; Zhu, H.; McCarthy, P.J.; Wright, A.E.; Wang, G. Nocardiopsistins A-C: New angucyclines with anti-MRSA activity isolated from a marine sponge-derived Nocardiopsis sp. HB-J378. Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 2018, 3, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapiolas, D.M.; Roman, M.; Fenical, W.; Stout, T.J.; Clardy, J. Octalactins A and B: Cytotoxic eight-membered-ring lactones from a marine bacterium, Streptomyces sp. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 4682–4683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Peng, C.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z. Functional Gene-Guided Discovery of Type II Polyketides from Culturable Actinomycetes Associated with Soft Coral Scleronephthya sp. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez, V.; Martín, J.; Sarmiento-Vizcaíno, A.; De La Cruz, M.; García, L.A.; Blanco, G.; Reyes, F. Anthracimycin B, a Potent Antibiotic against Gram-Positive Bacteria Isolated from Cultures of the Deep-Sea Actinomycete Streptomyces cyaneofuscatus M-169. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramalingam, V.; Mahamuni, D.; Rajaram, R. In vitro and in silico approaches of antibiofilm activity of 1-hydroxy-1-norresistomycin against human clinical pathogens. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 132, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, T.; Harunari, E.; Oku, N.; Igarashi, Y. Iseolides A–C, antifungal macrolides from a coral-derived actinomycete. J. Antibiot. 2020, 73, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, T.A.; Dmitrenok, A.S.; Sobolevskaya, M.P.; Shevchenko, L.S.; Mikhailov, V.V. Ubiquinone Q9 from a marine isolate of an actinobacterium Nocardia sp. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2002, 51, 1951–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Piel, J. A Gene Cluster from a Marine Streptomyces Encoding the Biosynthesis of the Aromatic Spiroketal Polyketide Griseorhodin A. Chem. Biol. 2002, 9, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Socha, A.M.; Garcia, D.; Sheffer, R.; Rowley, D.C. Antibiotic Bisanthraquinones Produced by a Streptomycete Isolated from a Cyanobacterium Associated with Ecteinascidia turbinata. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1070–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, T.D.S.; Jimenez, P.C.; Ferreira, E.G.; Silveira, E.R.; Filho, R.B.; Pessoa, O.D.L.; Costa-Lotufo, L.V. Anthracyclinones from Micromonospora sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyche, T.P.; Standiford, M.; Hou, Y.; Braun, D.; Johnson, D.A.; Johnson, J.A.; Bugni, T.S. Activation of the Nuclear Factor E2-Related Factor 2 Pathway by Novel Natural Products Halomadurones A–D and a Synthetic Analogue. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 5089–5099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wyche, T.P.; Alvarenga, R.F.R.; Piotrowski, J.S.; Duster, M.N.; Warrack, S.R.; Cornilescu, G.; De Wolfe, T.J.; Hou, Y.; Braun, D.R.; Ellis, G.A.; et al. Chemical Genomics, Structure Elucidation, and in Vivo Studies of the Marine-Derived Anticlostridial Ecteinamycin. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 2287–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nong, X.-H.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Xu, X.-Y.; Wang, J.; Qi, S.-H. Nahuoic Acids B–E, Polyhydroxy Polyketides from the Marine-Derived Streptomyces sp. SCSGAA 0027. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 79, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, X.-H.; Wei, X.-Y.; Qi, S.-H. Pteridic acids C–G spirocyclic polyketides from the marine-derived Streptomyces sp. SCSGAA 0027. J. Antibiot. 2017, 70, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, A.A.; Gromek, S.M.; Balunas, M.J. Upregulation and Identification of Antibiotic Activity of a Marine-Derived Streptomyces sp. via Co-Cultures with Human Pathogens. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, X.; Anjum, K.; Song, T.; Wang, W.; Yu, S.; Huang, H.; Lian, X.-Y.; Zhang, Z. A new curvularin glycoside and its cytotoxic and antibacterial analogues from marine actinomycete Pseudonocardia sp. HS7. HS7. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 30, 1156–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinovskaya, N.I.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Romanenko, L.A.; Pushilin, M.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Kuznetsova, T.A. New Angucyclinones from the Marine Mollusk Associated Actinomycete Saccharothrix espanaensis An 113. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2008, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalinovskaya, N.I.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Romanenko, L.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Kuznetsova, T.A. New Angucyclines and Antimicrobial Diketopiperazines from the Marine Mollusk-Derived Actinomycete Saccharothrix espanaensis An 113. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2010, 5, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shin, H.J.; Lee, H.-S.; Lee, J.S.; Shin, J.; Lee, M.A.; Lee, H.-S.; Lee, Y.-J.; Yun, J.; Kang, J.S. Violapyrones H and I, New Cytotoxic Compounds Isolated from Streptomyces sp. Associated with the Marine Starfish Acanthaster planci. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3283–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pérez, M.; Schleissner, C.; Fernandez, R.; Rodriguez, P.; Reyes, F.; Zuniga, P.; De La Calle, F.; Cuevas, C. PM100117 and PM100118, new antitumor macrolides produced by a marine Streptomyces caniferus GUA-06-05-006A. J. Antibiot. 2015, 69, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Ding, W.; Sun, C.; Ji, X.; Ling, C.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Ju, J. Julichrome Monomers from Marine Gastropod Mollusk-Associated Streptomyces and Stereochemical Revision of Julichromes Q 3 5 and Q 3 3. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17, e2000057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Minoura, K.; Numata, A. Halichoblelide, a Potent Cytotoxic Macrolide from a Streptomyces Species Separated from a Marine Fish. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 1721–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Kikuchi, T.; Tanaka, R.; Numata, A. Halichoblelides B and C, potent cytotoxic macrolides from a Streptomyces species separated from a marine fish. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 2842–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, J.L.; Sanchez, L.M.; Koo, B.-M.; Doherty, J.S.; Rajendram, M.; Huang, K.C.; Gross, C.A.; Linington, R.G. Marine Mammal Microbiota Yields Novel Antibiotic with Potent Activity Against Clostridium difficile. ACS Infect. Dis. 2018, 4, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Yu, L.; Peng, C.; Li, Z.; Guo, Y. Diketopiperazines from two strains of South China Sea sponge-associated microorganisms. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2010, 38, 931–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumikawa, M.; Khan, S.; Komaki, H.; Takagi, M.; Shin-Ya, K. JBIR-31, a new teleocidin analog, produced by salt-requiring Streptomyces sp. NBRC 105896 isolated from a marine sponge. J. Antibiot. 2009, 63, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Motohashi, K.; Takagi, M.; Shin-Ya, K. Tetrapeptides possessing a unique skeleton, JBIR-34 and JBIR-35, isolated from a sponge-derived actinomycete, Streptomyces sp. Sp080513GE-23. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 226–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motohashi, K.; Inaba, K.; Fuse, S.; Doi, T.; Izumikawa, M.; Khan, S.T.; Takagi, M.; Takahashi, T.; Shin-ya, K. JBIR-56 and JBIR-57, 2(1H)-pyrazinones from a marine sponge-derived Streptomyces sp. SpD081030SC-03. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1630–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyche, T.P.; Hou, Y.; Braun, D.; Cohen, H.C.; Xiong, M.P.; Bugni, T.S. First Natural Analogs of the Cytotoxic Thiodepsipeptide Thiocoraline A from a Marine Verrucosispora sp. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 6542–6547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Zhang, G.; Philippe, A.; Schmitz, W.; Pimentel-Elardo, S.M.; Hertlein-Amslinger, B.; Hentschel, U.; Bringmann, G. Cyclodysidins A–D, cyclic lipopeptides from the marine sponge-derived Streptomyces strain RV15. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-S.; Shin, H.J.; Jang, K.H.; Kim, T.S.; Oh, K.-B.; Shin, J. Cyclic Peptides of the Nocardamine Class from a Marine-Derived Bacterium of the Genus Streptomyces. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 623–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, D.; Wahidullah, S.; Meena, R. Attenuation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence by marine invertebrate-derived Streptomyces sp. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 56, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomo, S.; González, I.; De La Cruz, M.; Martínez, I.G.; Tormo, J.R.; Anderson, M.; Hill, R.; Vicente, F.; Reyes, F.; Genilloud, O. Sponge-Derived Kocuria and Micrococcus spp. as Sources of the New Thiazolyl Peptide Antibiotic Kocurin. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1071–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, J.; Sousa, T.D.S.; Crespo, G.; Palomo, S.; González, I.; Tormo, J.R.; De La Cruz, M.; Anderson, M.; Hill, R.T.; Vicente, F.; et al. Kocurin, the True Structure of PM181104, an Anti-Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Thiazolyl Peptide from the Marine-Derived Bacterium Kocuria palustris. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kitani, S.; Ueguchi, T.; Igarashi, Y.; Leetanasaksakul, K.; Thamchaipenet, A.; Nihira, T. Rakicidin F, a new antibacterial cyclic depsipeptide from a marine sponge-derived Streptomyces sp. J. Antibiot. 2017, 71, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasaka, N.; Kaweewan, I.; Ohnishi-Kameyama, M.; Kodani, S. Isolation of a new antibacterial peptide actinokineosin from Actinokineospora spheciospongiae based on genome mining. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 64, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.H.; Yuan, W.; Li, Z.Y.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Sun, J.B.; Gui, Y.H.; Wang, J.; Ye, B.P.; Lin, H.W. Anti-MRSA actinomycins D1-D4 from the marine sponge-associated Streptomyces sp. LHW52447—ScienceDirect. Tetrahedron 2018, 74, 5914–5919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitzer, J.; Streibel, M.; Langer, H.-J.; Grond, S. First Y-type actinomycins from Streptomyces with divergent structure-activity relationships for antibacterial and cytotoxic properties. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meienhofer, J.; Atherton, E. Structure—Activity Relationships in the Actinomycins. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1973, 16, 203–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.A.; Badr, J.M.; Harakeh, S.M.; Genta-Jouve, G. Bioactive Diketopiperazines and Nucleoside Derivatives from a Sponge-Derived Streptomyces Species. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kiran, G.S.; Sajayan, A.; Priyadharshini, G.; Balakrishnan, A.; Prathiviraj, R.; Sabu, A.; Selvin, J. A novel anti-infective molecule nesfactin identified from sponge associated bacteria Nesterenkonia sp. MSA31 against multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 157, 104923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boger, D.L.; Ichikawa, S. Total Syntheses of Thiocoraline and BE-22179: Establishment of Relative and Absolute Stereochemistry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 2956–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Gui, M.; Li, H.; Yu, C.; Li, H.; Zeng, Z.; Sun, P. Secondary Metabolites from Marine Micromonospora: Chemistry and Bioactivities. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17, 2000024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyche, T.P.; Hou, Y.; Vazquez-Rivera, E.; Braun, D.; Bugni, T.S. Peptidolipins B–F, Antibacterial Lipopeptides from an Ascidian-Derived Nocardia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ou, Y.-X.; Huang, J.-F.; Li, X.-M.; Kang, Q.-J.; Pan, Y.-T. Three new 2,5-diketopiperazines from the fish intestinal Streptomyces sp. MNU FJ-36. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 30, 1771–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trischman, J.A.; Tapiolas, D.M.; Jensen, P.R.; Dwight, R.; Fenical, W.; Mckee, T.C.; Ireland, C.M.; Stout, T.J.; Clardy, J. Salinamides A and B: Anti-inflammatory depsipeptides from a marine streptomycete. Cheminform 1994, 25, 757–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, B.S.; Trischman, J.A.; Seng, D.; Kho, D.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Salinamides, Antiinflammatory Depsipeptides from a Marine Streptomycete. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 1145–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.M.; Degen, D.; Jang, K.H.; Ebright, R.H.; Fenical, W. Salinamide F, new depsipeptide antibiotic and inhibitor of bacterial RNA polymerase from a marine-derived Streptomyces sp. J. Antibiot. 2014, 68, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lombó, F.; Velasco, A.; Castro, A.; Calle, F.; Braña, A.F.; Sánchez-Puelles, J.M.; Méndez, C.; Salas, J.A. Deciphering the Biosynthesis Pathway of the Antitumor Thiocoraline from a Marine Actinomycete and Its Expression in Two Streptomyces Species. ChemBioChem 2006, 7, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, R.; Xu, H.; Cui, J.; Ge, H.; Tan, R. Neuraminidase Inhibitors from marine-derived actinomycete Streptomyces seoulensis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 114, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, M.; Motohashi, K.; Khan, S.T.; Hashimoto, J.; Shin-Ya, K. JBIR-65, a new diterpene, isolated from a sponge-derived Actinomadura sp. SpB081030SC-15. J. Antibiot. Tokyo 2010, 63, 401–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, L.; Chen, G.; Zhang, S.; You, T.; Liu, F. In Vitro Antioxidant and Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitory Activities of the Sesquiterpenes of a Symbiotic Actinomycete Streptomyces sp. from South China Sea. Asian J. Chem. 2013, 25, 6865–6869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Adnani, N.; Braun, D.R.; Ellis, G.A.; Barns, K.J.; Parker-Nance, S.; Guzei, I.A.; Bugni, T.S. Micromonohalimanes A and B: Antibacterial Halimane-Type Diterpenoids from a Marine Micromonospora Species. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 2968–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marchbank, D.H.; Ptycia-Lamky, V.C.; Decken, A.; Haltli, B.A.; Kerr, R.G. Guanahanolide A, a Meroterpenoid with a Sesterterpene Skeleton from Coral-Derived Streptomyces sp. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 6399–6403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.-F.; Chen, M.-J.; Liang, D.-E.; Shi, L.-M.; Ying, Y.-M.; Shan, W.-G.; Li, G.-Q.; Zhan, Z.-J. Streptomyces albogriseolus SY67903 Produces Eunicellin Diterpenoids Structurally Similar to Terpenes of the Gorgonian Muricella sibogae, the Bacterial Source. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1641–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, L.; Kaufmann, K.; Garcia, R.; Schwär, G.; Huch, V.; Müller, R. Bendigoles D–F, bioactive sterols from the marine sponge-derived Actinomadura sp. SBMs009. Bioorg Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 6570–6575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bultel-Poncé, V.; Debitus, C.; Bergé, J.; Cerceau, C.; Guyot, M. Metabolites from the sponge-associated bacterium Micrococcus luteus. J. Mar. Biotechnol. 1998, 6, 233. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Li, Q.-L.; Ji, N.-Y.; Liu, B.; Zhang, W.; Cao, X.-P. Deoxyuridines from the Marine Sponge Associated Actinomycete Streptomyces microflavus. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, G.; Wyche, T.P.; Fry, C.G.; Braun, D.R.; Bugni, T.S. Solwaric Acids A and B, Antibacterial Aromatic Acids from a Marine Solwaraspora sp. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wicke, C.; Hüners, M.; Wray, V.; Nimtz, M.; Bilitewski, U.; Lang, S. Production and Structure Elucidation of Glycoglycerolipids from a Marine Sponge-Associated Microbacterium Species. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamed, A.; Abdel-Razek, A.; Frese, M.; Wibberg, D.; El-Haddad, A.F.; Ibrahim, T.M.A.; Kalinowski, J.; Sewald, N.; Shaaban, M. New oxaphenalene derivative from marine-derived Streptomyces griseorubens sp. ASMR4. Z. Für. Nat. B 2017, 72, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.-L.; Chen, R.; Yang, S.; Xia, J.-M.; Zhang, G.-Y.; Chen, C.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.-W. Nesteretal A, A Novel Class of Cage-Like Polyketide from Marine-Derived Actinomycete Nesterenkonia halobia. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 8174–8177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.R.; Harunari, E.; Oku, N.; Matsuura, N.; Trianto, A.; Igarashi, Y. Two antibacterial and PPARalpha/gamma-agonistic unsaturated keto fatty acids from a coral-associated actinomycete of the genus Micrococcus. Beilstein. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.D.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Lobophorins A and B, new antiinflammatory macrolides produced by a tropical marine bacterium. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1999, 9, 2003–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brana, A.F.; Fiedler, H.P.; Nava, H.; Gonzalez, V.; Sarmiento-Vizcaino, A.; Molina, A.; Acuna, J.L.; Garcia, L.A.; Blanco, G. Two Streptomyces species producing antibiotic, antitumor, and anti-inflammatory compounds are widespread among intertidal macroalgae and deep-sea coral reef invertebrates from the central Cantabrian Sea. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 69, 512–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliwa, E.M.; Abdel-Razek, A.S.; Frese, M.; Halawa, A.H.; El-Agrody, A.M.; Bedair, A.H.; Sewald, N.; Shaaban, M. New naturally occurring phenolic derivatives from marine Nocardiopsis sp. AS23C: Structural elucidation and in silico computational studies. Vietnam. J. Chem. 2019, 57, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Chai, W.; Lian, X.-Y.; Zhang, Z. A unique indolizinium alkaloid streptopertusacin A and bioactive bafilomycins from marine-derived Streptomyces sp. HZP-2216E. Phytochemistry 2017, 144, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X.; Liang, Y.; Anjum, K.; Chen, L.; Lian, X.-Y. Bioactive Bafilomycins and a New N-Arylpyrazinone Derivative from Marine-derived Streptomyces sp. HZP-2216E. Planta Med. 2017, 83, 1405–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Shu, C.; Li, Q.; Lian, X.-Y.; Zhang, Z. Novel cyclohexene and benzamide derivatives from marine-associated Streptomyces sp. ZZ502. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 2151–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.-S.; Tian, L.; Chen, G.; Li, Z.-Q.; Xu, W.-F.; Pei, Y.-H. Two new compounds from the metabolites of a marine-derived actinomycete Streptomyces cavourensis YY01-17. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 15, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djinni, I.; Defant, A.; Kecha, M.; Mancini, I. Antibacterial Polyketides from the Marine Alga-Derived Endophitic Streptomyces sundarbansensis: A Study on Hydroxypyrone Tautomerism. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.C.; Machado, H.; Jang, K.H.; Trzoss, L.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Integration of Genomic Data with NMR Analysis Enables Assignment of the Full Stereostructure of Neaumycin B, a Potent Inhibitor of Glioblastoma from a Marine-Derived Micromonospora. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 10775–10784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Braña, A.F.; Sarmiento-Vizcaíno, A.; Pérez-Victoria, I.; Martín, J.; Otero, L.; Palacios-Gutiérrez, J.-J.; Fernández, J.; Mohamedi, Y.; Fontanil, T.; Salmón, M.; et al. Desertomycin G, a New Antibiotic with Activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Human Breast Tumor Cell Lines Produced by Streptomyces althioticus MSM3, Isolated from the Cantabrian Sea Intertidal Macroalgae Ulva sp. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rab, E.; Kekos, D.; Roussis, V.; Ioannou, E. α-Pyrone Polyketides from Streptomyces ambofaciens BI0048, an Endophytic Actinobacterial Strain Isolated from the Red Alga Laurencia glandulifera. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.-F.; Tian, L.; Fu, H.-W.; Hua, H.-M.; Pei, Y.-H. One new anthraquinone from marine Streptomyces sp. FX-58. Nat. Prod. Res. 2006, 20, 1207–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.Y.; Kang, J.Y.; Hong, Y.K.; Baek, H.H.; Shin, H.W.; Kim, M.S. Isolation and Structural Determination of the Antifouling Diketopiperazines from Marine-Derived Streptomyces praecox 291-11. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2012, 76, 1116–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, J.Y. Glycoglycerolipids Isolated from Marine Derived Streptomyces coelescens PK206-15. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2012, 76, 1746–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, Y.C.; Kim, M.S. Antibacterial benzaldehydes produced by seaweed-derived Streptomyces atrovirens PK288-21. Fish. Sci. 2012, 78, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar]
- Uzair, B.; Menaa, F.; Khan, B.A.; Mohammad, F.V.; Ahmad, V.U.; Djeribi, R.; Menaa, B. Isolation, purification, structural elucidation and antimicrobial activities of kocumarin, a novel antibiotic isolated from actinobacterium Kocuria marina CMG S2 associated with the brown seaweed Pelvetia canaliculata. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 206, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



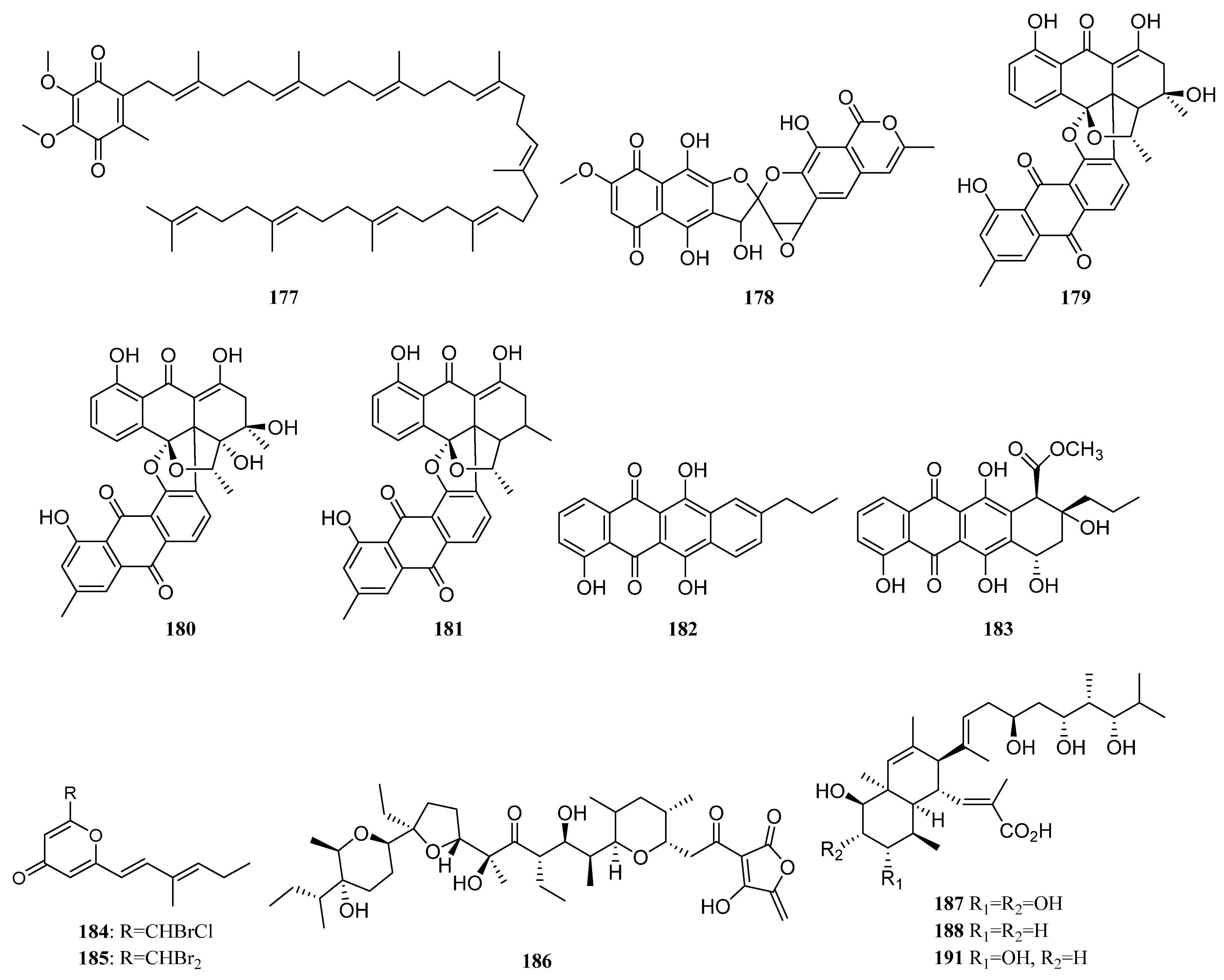


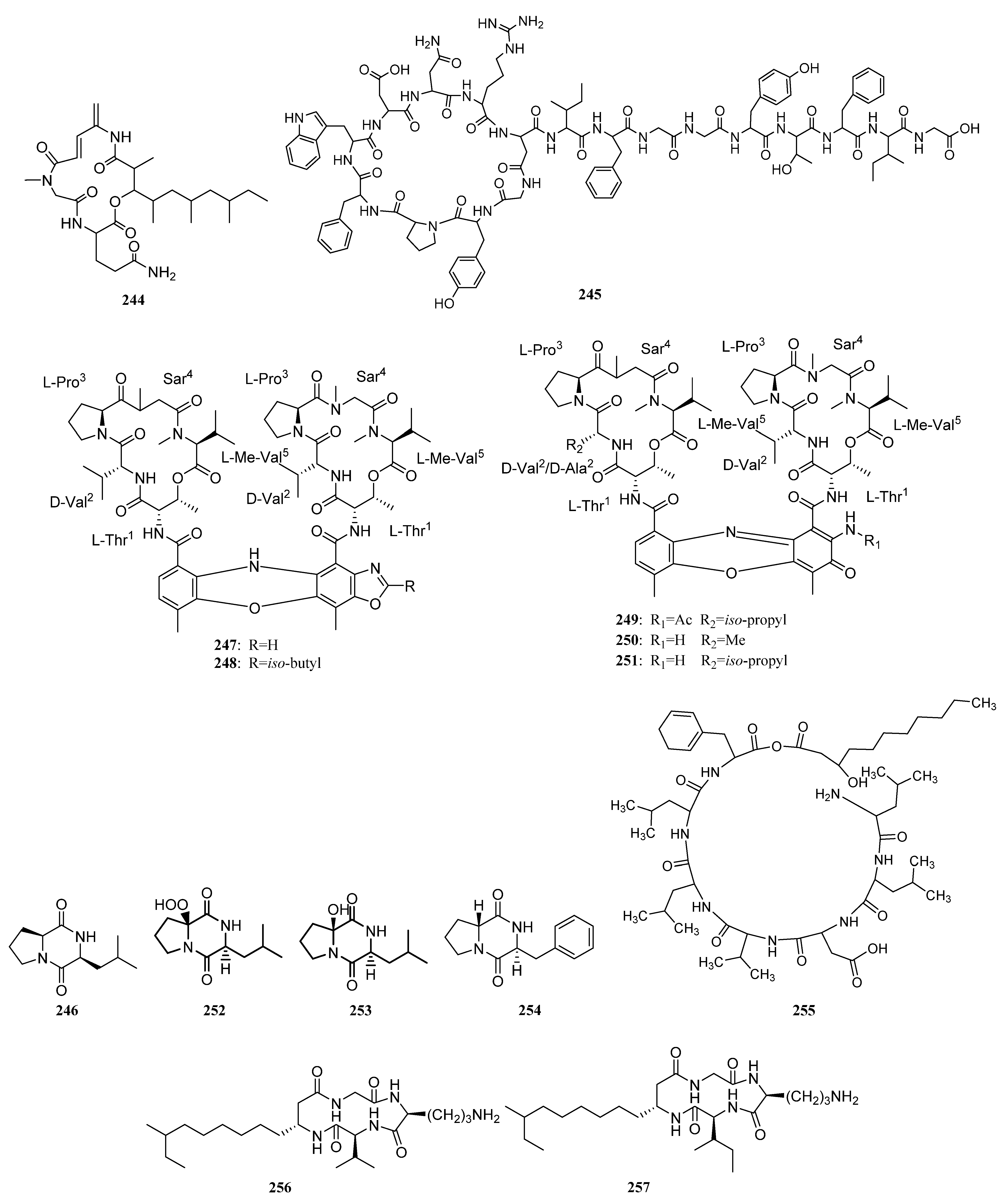
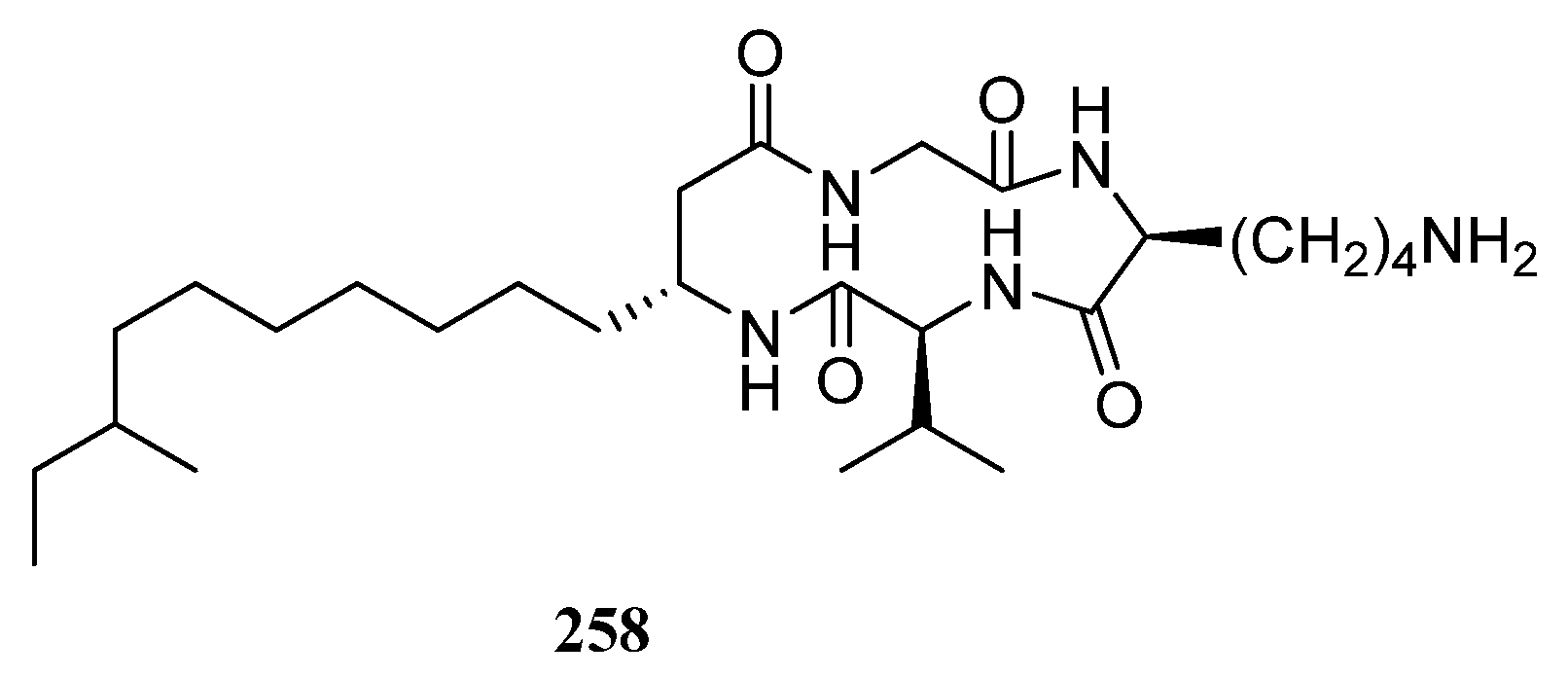
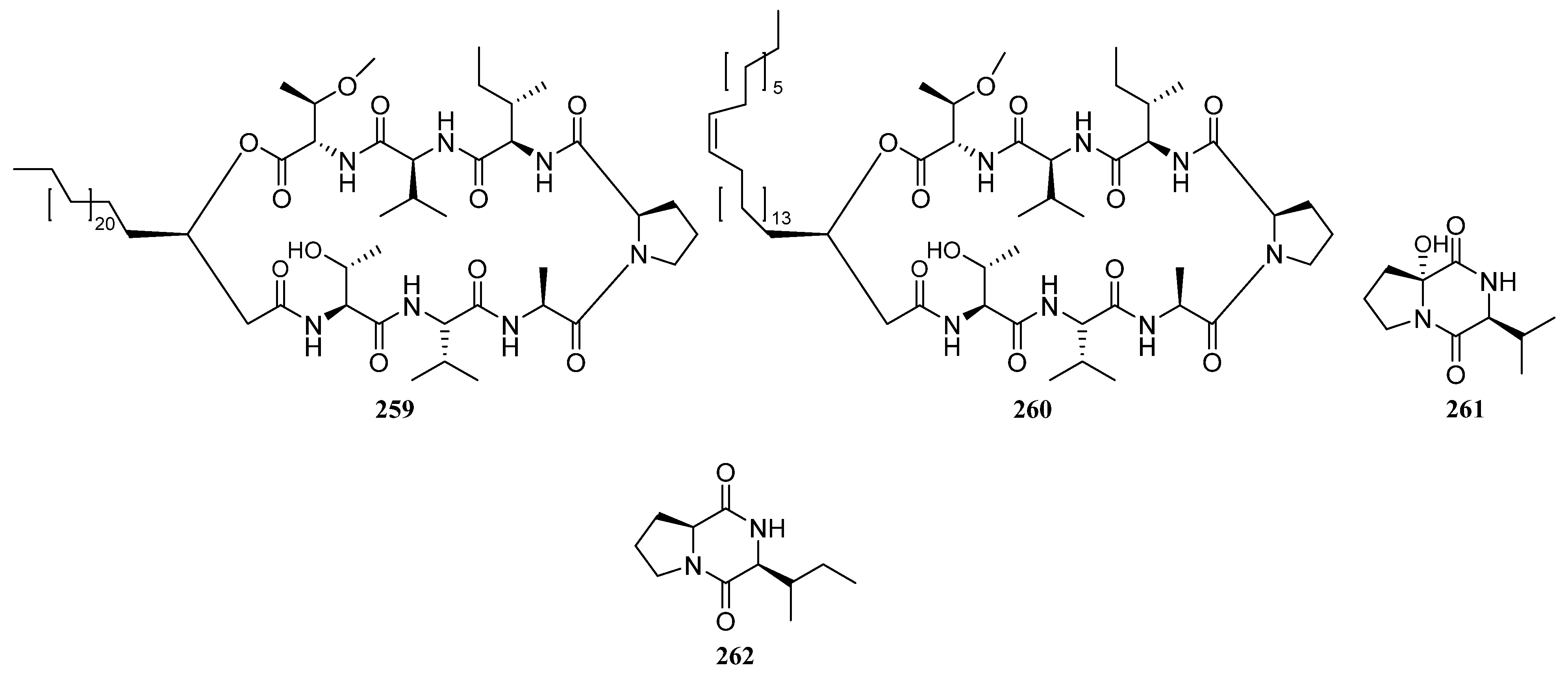
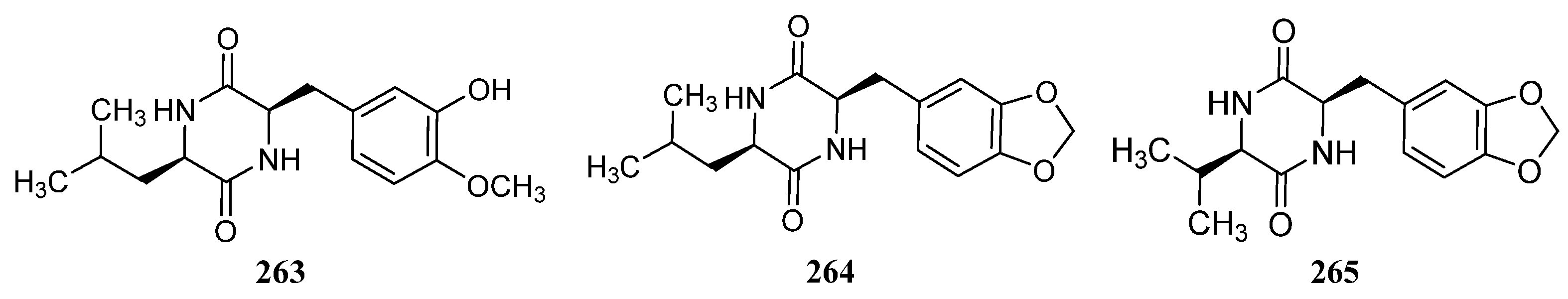



| Compounds | Study Title | Conditions | Related Compounds for Interventions | Phase | NCT Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rifamycin SV (9) | Rifamycin SV-MMX® 400 mg b.i.d. vs. Rifamycin SV-MMX® 600 mg t.i.d. vs. Placebo in Acute Uncomplicated Diverticulitis | Uncomplicated Diverticulitis | Rifamycin SV-MMX® | Phase 2 | NCT01847664 |
| Rifamycin SV-MMX® 600 mg Tablets Administered Three or Two Times Daily to Patients With IBS-D | Diarrhea-predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome | Rifamycin SV | Phase 2 | NCT03099785 | |
| Study to Evaluate Safety and Efficacy of Rifamycin SV Multi-Matrix System (MMX) for the Treatment of Traveler’s Diarrhea (TD) | Traveler’s Diarrhea | Rifamycin SV MMX | Phase 3 | NCT01142089 | |
| Rifamycin SV-MMX® Tablets Versus Ciprofloxacin Capsules in Acute Traveller’s Diarrhoea | Traveler’s Diarrhea | Rifamycin SV-MMX® | Phase 3 | NCT01208922 | |
| Diazepinomicin (28) | A Phase I Study of ECO-4601 in Patients With Advanced Cancer | Tumors Glioma Colorectal Cancer | ECO-4601 | Phase 1 | NCT00338026 |
| Efficacy Study of TLN-4601 in Patients With Recurring Glioblastoma Multiforme | Glioblastoma Multiforme | TLN-4601 | Phase 2 | NCT00730262 | |
| Staurosporine (3) | A Phase I Trial of Continuous Infusion UCN-01 in Patients With Refractory Neoplasms | Breast Cancer Lymphoma Neoplasm Prostatic Neoplasm | 7-hydroxystaurosporine (UCN-01) | Phase 1 | NCT00001444 |
| PK and Safety of Midostaurin in Subjects With Impaired Hepatic Function and Subjects With Normal Hepatic Function | Hepatic Impairment | Midostaurin | Phase 1 | NCT01429337 | |
| Phase I Combination of Midostaurin, Bortezomib, and Chemo in Relapsed/Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia | Acute Myeloid Leukemia AML With Multilineage Dysplasia Following Myelodysplastic Syndrome | Midostaurin | Phase 1 | NCT01174888 | |
| Azacitidine With or Without Nivolumab or Midostaurin, or Decitabine and Cytarabine Alone in Treating Older Patients With Newly Diagnosed Acute Myeloid Leukemia or High-Risk Myelodysplastic Syndrome | Acute Myeloid Leukemia Myelodysplastic Syndrome Myelodysplastic Syndrome With Excess Blasts-2 | Midostaurin | Phase 2 Phase 3 | NCT03092674 | |
| Tetrodotoxin (105) | Tetrodotoxin Open-label Efficacy and Safety Continuation Study | Pain Cancer | Tetrodotoxin | Phase 3 | NCT00726011 |
| Safety & Efficacy Study of Subcutaneous Tetrodotoxin for Moderate to Severe Inadequately Controlled Cancer-related Pain | Pain Cancer | Tetrodotoxin | Phase 3 | NCT00725114 | |
| Daunomycin (307) | Pilot Study Efficacy and Tolerance Fish Oil Emulsion Daunorubicin and Cytarabine Treatment of AML Younger Patients | Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) | Daunorubicin | Phase 2 | NCT01999413 |
| A Randomized Study of Gemtuzumab Ozogamicin (GO) With Daunorubicine and Cytarabine in Untreated Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Aged of 50–70 Years Old | Acute Myeloid Leukemia | Daunorubicin | Phase 3 | NCT00927498 | |
| Linoleic acid (340) | Proof of Principle Trial to Determine if Nutritional Supplement Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA) Can Modulate the Lipogenic Pathway in Breast Cancer Tissue | Breast Cancer | Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA) | Early Phase 1 | NCT00908791 |
| Conjugated Linoleic Acid / Leucine Versus Metformin on Visceral Fat in Metabolic Syndrome | Metabolic Syndrome | Conjugated linoleic acid/Leucine | Phase 2 | NCT02629627 | |
| Conjugated Linoleic Acid and Atherosclerosis | Atherosclerosis | Cis9, trans11 conjugated linoleic acid | Phase 3 | NCT00706745 | |
| Actinomycin D (251) | Dactinomycin in Treating Patients With Persistent or Recurrent Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia | Gestational Trophoblastic Tumor | Dactinomycin | Phase 2 | NCT00003688 |
| Addition of Ipilimumab (MDX-010) To Isolated Limb Infusion (ILI) With Standard Melphalan and Dactinomycin In The Treatment of Advanced Unresectable Melanoma of The Extremity | Melanoma | Dactinomycin | Phase 2 | NCT01323517 | |
| Methotrexate Compared With Dactinomycin in Treating Patients With Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia | Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia | Dactinomycin | Phase 3 | NCT00003702 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Xu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Han, B. Natural Products from Actinomycetes Associated with Marine Organisms. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19110629
Chen J, Xu L, Zhou Y, Han B. Natural Products from Actinomycetes Associated with Marine Organisms. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(11):629. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19110629
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jianing, Lin Xu, Yanrong Zhou, and Bingnan Han. 2021. "Natural Products from Actinomycetes Associated with Marine Organisms" Marine Drugs 19, no. 11: 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19110629
APA StyleChen, J., Xu, L., Zhou, Y., & Han, B. (2021). Natural Products from Actinomycetes Associated with Marine Organisms. Marine Drugs, 19(11), 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19110629








