Asteroid Saponins: A Review of Their Bioactivity and Selective Cytotoxicity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Overview
2.2. Asteroid-Derived Saponin Haemolytic Activity
2.3. Asteroid-Derived Saponin Antimicrobial Activity and Applications
2.4. Asteroid-Derived Saponin Anticancer Agents
2.4.1. Saponin Susceptible Cancer Cells
2.4.2. Cell Line Dependent Cytotoxicity
2.4.3. Structure-Dependent Cytotoxicity
2.4.4. Synergistic Anticancer Applications
2.5. Multi-Assay Testing for Asteroid-Derived Saponins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Collection
4.2. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calabro, K.; Kalahroodi, E.L.; Rodrigues, D.; Diaz, C.; Cruz, M.; Cautain, B.; Laville, R.; Reyes, F.; Perez, T.; Soussi, B.; et al. Poecillastrosides, Steroidal Saponins from the Mediterranean Deep-Sea Sponge Poecillastra compressa (Bowerbank, 1866). Mar Drugs 2017, 15, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, G.; Kerem, Z.; Makkar, H.P.; Becker, K. The biological action of saponins in animal systems: A review. Br. J. Nutr. 2002, 88, 587–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, G.; Kerem, Z.; Makkar, H.P.S.; Becker, K. Reflections on ‘The biological action of saponins in animal systems: A review’. Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 127, 1034–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeyer, M.; De Winter, J.; Caulier, G.; Eeckhaut, I.; Flammang, P.; Gerbaux, P. Molecular diversity and body distribution of saponins in the sea star Asterias rubens by mass spectrometry. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 168, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Simone, F.; Dini, A.; Finamore, E.; Minale, L.; Pizza, C.; Riccio, R.; Zollo, F. Starfish saponins. Part 5. Structure of sepositoside A, a novel steroidal cyclic glycoside from the starfish Echinaster sepositus. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1. 1981, 0, 1855–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.-F.; Yi, Y.-H.; Li, L.; Sun, P.; Zhang, S.-Q.; Zhao, Y.-P. Bioactive Asterosaponins from the Starfish Culcita novaeguineae. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.-F.; Yi, Y.-H.; Li, L.; Sun, P.; Zhang, S.-Q.; Zhao, Y.-P. Three new asterosaponins from the starfish Culcita novaeguineae and their bioactivity. Planta Med. 2005, 71, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.F.; Yi, Y.H.; Li, L.; Sun, P.; Zhang, S.Q.; Zhao, Y.P. Asterosaponins from the starfish Culcita novaeguineae and their bioactivities. Fitoterapia 2006, 77, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaieb, I. Saponins as insecticides: A review. Tunis. J. Plant Prot. 2010, 5, 39–50. [Google Scholar]
- Adel, M.M.; Sehnal, F.; Jurzysta, M. Effects of alfalfa saponins on the moth Spodoptera littoralis. J. Chem. Ecol. 2000, 26, 1065–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.R.; Zhang, Y.; Jacob, M.R.; Khan, S.I.; Zhang, Y.J.; Li, X.C. Antifungal activity of C-27 steroidal saponins. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1710–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, E.; Stoya, G.; Volkner, A.; Richter, W.; Lemke, C.; Linss, W. Hemolysis of human erythrocytes with saponin affects the membrane structure. Acta Histochem. 2000, 102, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorent, J.H.; Quetin-Leclercq, J.; Mingeot-Leclercq, M.-P. The amphiphilic nature of saponins and their effects on artificial and biological membranes and potential consequences for red blood and cancer cells. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 8803–8822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eeckhaut, I.; Caulier, G.; Brasseur, L.; Flammang, P.; Gerbaux, P.; Parmentier, E. Effects of holothuroid ichtyotoxic saponins on the gills of free-living fishes and symbiotic pearlfishes. Biol. Bull. 2015, 228, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malyarenko, T.V.; Malyarenko, O.S.; Kicha, A.A.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Ivanchina, N.V. In Vitro Anticancer and Cancer-Preventive Activity of New Triterpene Glycosides from the Far Eastern Starfish Solaster pacificus. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeogun, A.; Alaka, O.; Taiwo, V.; Fagade, S. Some pathological effects of sub-lethal concentrations of the methanolic extracts of Raphia hookeri on Clarias gariepinus. Afr. J. Biomed. Res. 2012, 15, 105–115. [Google Scholar]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Avilov, S.A.; Andrijaschenko, P.V.; Popov, R.S.; Chingizova, E.A.; Kalinin, V.I.; Dmitrenok, P.S. Triterpene Glycosides from the Far Eastern Sea Cucumber Psolus chitonoides: Chemical Structures and Cytotoxicities of Chitonoidosides E(1), F, G, and H. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Avilov, S.A.; Andrijaschenko, P.V.; Popov, R.S.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Chingizova, E.A.; Kalinin, V.I. Unusual Structures and Cytotoxicities of Chitonoidosides A, A(1), B, C, D, and E, Six Triterpene Glycosides from the Far Eastern Sea Cucumber Psolus chitonoides. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-Z.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Han, H.; Fan, R.-P.; Hu, Y.; Zhong, L.; Kou, J.-P.; Yu, B.-Y. Advances in the antitumor activities and mechanisms of action of steroidal saponins. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2018, 16, 732–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA Development & Approval Process | Drugs. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/development-approval-process-drugs (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- EMA Human Regulatory: Overview. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory-overview (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- Farias, C.B.B.; Almeida, F.C.G.; Silva, I.A.; Souza, T.C.; Meira, H.M.; Soares da Silva, R.d.C.F.; Luna, J.M.; Santos, V.A.; Converti, A.; Banat, I.M.; et al. Production of green surfactants: Market prospects. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 51, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Tyagi, A.; Bhansali, P.; Pareek, S.; Singh, V.; Ilyas, A.; Mishra, R.; Poddar, N.K. Saponins: Extraction, bio-medicinal properties and way forward to anti-viral representatives. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 150, 112075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Lee, S.; Kang, S.-S.; Shin, H.-S. Selected commercial plants: A review of extraction and isolation of bioactive compounds and their pharmacological market value. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 82, 89–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Kaur, R.; Kumar, S.; Saini, R.K.; Sharma, S.; Pawde, S.V.; Kumar, V. Saponins: A concise review on food related aspects, applications and health implications. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 2, 100191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukiyoshi, T.; Masazumi, M.; Masaji, Y. Application of Saponin-Containing Plants in Foods and Cosmetics. In Alternative Medicine; Hiroshi, S., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; Chapter 5. [Google Scholar]
- Jolly, A.; Kim, H.; Moon, J.-Y.; Mohan, A.; Lee, Y.-C. Exploring the imminent trends of saponins in personal care product development: A review. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 205, 117489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malyarenko, T.V.; Kicha, A.A.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Malyarenko, O.S.; Kuzmich, A.S.; Stonik, V.A.; Ivanchina, N.V. New Triterpene Glycosides from the Far Eastern Starfish Solaster pacificus and Their Biological Activity. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzara, V.; Arizza, V.; Luparello, C.; Mauro, M.; Vazzana, M. Bright Spots in the Darkness of Cancer: A Review of Starfishes-Derived Compounds and Their Anti-Tumor Action. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.J.; Cummins, S.F.; Motti, C.A.; Wang, T. A mass spectrometry database for the identification of marine animal saponin-related metabolites. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 6893–6907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, N.N.Q.; Fukushima, E.O.; Muranaka, T. Structure and hemolytic activity relationships of triterpenoid saponins and sapogenins. J. Nat. Med. 2017, 71, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanchina, N.V.; Kicha, A.A.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Stonik, V.A.; Riguera, R.; Jiménez, C. Hemolytic Polar Steroidal Constituents of the Starfish Aphelasterias japonica. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanchina, N.V.; Kicha, A.A.; Malyarenko, T.V.; Ermolaeva, S.D.; Yurchenko, E.A.; Pislyagin, E.A.; Van Minh, C.; Dmitrenok, P.S. Granulatosides D, E and other polar steroid compounds from the starfish Choriaster granulatus. Their immunomodulatory activity and cytotoxicity. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 2623–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malyarenko, T.V.; Kharchenko, S.D.; Kicha, A.A.; Ivanchina, N.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Chingizova, E.A.; Pislyagin, E.A.; Evtushenko, E.V.; Antokhina, T.I.; Minh, C.V.; et al. Anthenosides L-U, Steroidal Glycosides with Unusual Structural Features from the Starfish Anthenea aspera. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 3047–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanchina, N.V.; Kicha, A.A.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Dmitrenok, A.S.; Chaikina, E.L.; Stonik, V.A.; Gavagnin, M.; Cimino, G. Polar steroidal compounds from the far eastern starfish Henricia leviuscula. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.H.; Li, F.M.; Hong, J.K.; Lee, C.O.; Cho, H.Y.; Im, K.S.; Jung, J.H. Four new saponins from the starfish. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 51, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngoan, B.T.; Hanh, T.T.; Vien, L.T.; Diep, C.N.; Thao, N.P.; Thao do, T.; Thanh, N.V.; Cuong, N.X.; Nam, N.H.; Thung, D.C.; et al. Asterosaponins and glycosylated polyhydroxysteroids from the starfish Culcita novaeguineae and their cytotoxic activities. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 17, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.H.; Li, F.; Alam, N.; Liu, Y.H.; Hong, J.K.; Lee, C.K.; Im, K.S.; Jung, J.H. New saponins from the starfish. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 1649–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malyarenko, T.V.; Kicha, A.A.; Ivanchina, N.V.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Ermakova, S.P.; Stonik, V.A. Cariniferosides A-F and other steroidal biglycosides from the starfish Asteropsis carinifera. Steroids 2011, 76, 1280–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kicha, A.A.; Malyarenko, T.V.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Popov, R.S.; Malyarenko, O.S.; Ermakova, S.P.; Ivanchina, N.V. Polar steroid compounds from the Arctic starfish Asterias microdiscus and their cytotoxic properties against normal and tumor cells in vitro. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 5765–5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanchina, N.V.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Kicha, A.A.; Malyarenko, T.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Ermakova, S.P.; Stonik, V.A. Two New Asterosaponins from the Far Eastern Starfish Lethasterias fusca. Nat. Prod. Prod. Commun. 2012, 7, 1934578X1200700711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, D.T.; Kicha, A.A.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Malyarenko, T.V.; Popov, R.S.; Malyarenko, O.S.; Ermakova, S.P.; Thuy, T.T.T.; Long, P.Q.; Ivanchina, N.V. Asterosaponins from the tropical starfish Acanthaster planci and their cytotoxic and anticancer activities in vitro. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vien, L.T.; Ngoan, B.T.; Hanh, T.T.; Vinh, L.B.; Thung, D.C.; Thao, D.T.; Thanh, N.V.; Cuong, N.X.; Nam, N.H.; Kiem, P.V.; et al. Steroid glycosides from the starfish Pentaceraster gracilis. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 19, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanchina, N.V.; Maliarenko, T.V.; Kicha, A.A.; Kalinovskii, A.I.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Ermakova, S.P. Two new asterosaponins from the antarctic starfish Diplasterias brucei. Structures and cytotoxic activities. Bioorg. Khim. 2011, 37, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kicha, A.A.; Dinh, T.H.; Ivanchina, N.V.; Malyarenko, T.V.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Popov, R.S.; Ermakova, S.P.; Tran, T.T.; Doan, L.P. Three new steroid biglycosides, plancisides A, B, and C, from the starfish Acanthaster planci. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2014, 9, 1269–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levina, E.V.; Kalinovskii, A.I.; Ermakova, S.P.; Dmitrenok, P.S. Steroidal compounds from the Pacific starfish Mithrodia clavigera and their toxic properties against human melanoma cells. Bioorg. Khim. 2012, 38, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Malyarenko, T.V.; Ivanchina, N.V.; Malyarenko, O.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Evtushenko, E.V.; Minh, C.V.; Kicha, A.A. Two New Steroidal Monoglycosides, Anthenosides A(1) and A(2), and Revision of the Structure of Known Anthenoside A with Unusual Monosaccharide Residue from the Starfish Anthenea aspera. Molecules 2018, 23, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malyarenko, T.V.; Kicha, A.A.; Ivanchina, N.V.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Popov, R.S.; Vishchuk, O.S.; Stonik, V.A. Asterosaponins from the Far Eastern starfish Leptasterias ochotensis and their anticancer activity. Steroids 2014, 87, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.H.; Hong, J.K.; Lee, C.O.; Im, K.S.; Choi, J.S.; Jung, J.H. Cytotoxic sterols and saponins from the starfish. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Jang, H.; Hong, J.; Lee, C.-O.; Bae, S.-J.; Shin, S.; Jung, J.H. New cytotoxic sulfated saponins from the starfish Certonardoa semiregularis. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2005, 28, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Jang, H.; Hong, J.; Lee, C.-O.; Im, K.S.; Bae, S.-J.; Jung, J.H. Additional Cytotoxic Sterols and Saponins from the Starfish Certonardoa semiregularis. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1654–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vien, L.T.; Hanh, T.T.H.; Hong, P.T.; Thanh, N.V.; Huong, T.T.; Cuong, N.X.; Nam, N.H.; Thung, D.C.; Kiem, P.V.; Minh, C.V. Polar steroid derivatives from the Vietnamese starfish Astropecten polyacanthus. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.X.; Kang, Y.F.; Han, H. Three New Cytotoxic Polyhydroxysteroidal Glycosides from Starfish Craspidaster hesperus. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.-F.; Cheng, G.; Wu, J.; Chen, X.-L.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Wen, A.-D.; Lin, H.-W. Cytotoxic asterosaponins capable of promoting polymerization of tubulin from the starfish Culcita novaeguineae. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Tang, H.-F.; Qiu, F.; Lin, H.-W.; Tian, X.-R.; Yao, M.-N. Polyhydroxysteroidal Glycosides from the Starfish Anthenea chinensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, N.; Tang, H.F.; Qiu, F.; Lin, H.W.; Tian, X.R.; Zhang, W. A new polyhydroxysteroidal glycoside from the starfish Anthenea chinensis. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2009, 20, 1231–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kicha, A.A.; Ivanchina, N.V.; Huong, T.T.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Fedorov, S.N.; Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Long, P.Q.; Stonik, V.A. Two new asterosaponins, archasterosides A and B, from the Vietnamese starfish Archaster typicus and their anticancer properties. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 3826–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, L.-W.; Wang, C.-Z.; Yuan, C.-S. American ginseng: Potential structure–function relationship in cancer chemoprevention. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhong, S.; Li, T.; Zhang, J. Saponins as modulators of nuclear receptors. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 60, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attoub, S.; Arafat, K.; Khalaf, T.; Sulaiman, S.; Iratni, R. Frondoside A Enhances the Anti-Cancer Effects of Oxaliplatin and 5-Fluorouracil on Colon Cancer Cells. Nutrients 2018, 10, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Lu, Z.; Ding, N.; Ren, S.; Li, Y. Synthesis of the Pentasaccharide Moiety of Thornasterside A. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 2013, 6158–6166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanchina, N.V.; Kicha, A.A.; Stonik, V.A. Steroid glycosides from marine organisms. Steroids 2011, 76, 425–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Xun, X.; Wang, J.; Bao, L.; Thimmappa, R.; Ding, J.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, T.; et al. Sea cucumber genome provides insights into saponin biosynthesis and aestivation regulation. Cell Discov. 2018, 4, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitu, S.A.; Bose, U.; Suwansa-Ard, S.; Turner, L.H.; Zhao, M.; Elizur, A.; Ogbourne, S.M.; Shaw, P.N.; Cummins, S.F. Evidence for a saponin biosynthesis pathway in the body wall of the commercially significant sea cucumber Holothuria scabra. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claereboudt, E.J.S.; Caulier, G.; Decroo, C.; Colson, E.; Gerbaux, P.; Claereboudt, M.R.; Schaller, H.; Flammang, P.; Deleu, M.; Eeckhaut, I. Triterpenoids in Echinoderms: Fundamental Differences in Diversity and Biosynthetic Pathways. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thimmappa, R.; Wang, S.; Zheng, M.; Misra, R.C.; Huang, A.C.; Saalbach, G.; Chang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Hinman, V.; Bao, Z.; et al. Biosynthesis of saponin defensive compounds in sea cucumbers. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2022, 18, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Saponin | Cell Line Tested | Study No. | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Halityloside D | 11 | 3 | [37,38,39] |
| Thornasteroside A | 10 | 3 | [8,40,41] |
| Maculatoside | 8 | 2 | [42,43] |
| Halityloside A | 8 | 2 | [37,39] |
| Halityloside B | 8 | 2 | [37,39] |
| Certonardoside A | 8 | 2 | [36,38] |
| Certonardoside C | 8 | 2 | [36,38] |
| Certonardoside H | 8 | 2 | [36,38] |
| Cell Line | Organism | Tested Saponins | Study No. | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RPMI-7951 | Homo sapiens | 48 | 10 | [15,28,39,41,42,44,45,46,47,48] |
| SK-MEL-2 | 44 | 8 | [15,36,37,43,49,50,51,52] | |
| A549 | 30 | 5 | [36,49,50,51,53] | |
| SK-OV-3 | 27 | 4 | [36,49,50,51] | |
| XF498 | 27 | 4 | [36,49,50,51] | |
| HCT15 | 27 | 4 | [36,49,50,51] | |
| T-47D | 25 | 6 | [39,41,44,45,47,48] | |
| BEL-7402 | 22 | 7 | [6,7,8,53,54,55,56] | |
| K-562 | 19 | 6 | [3,4,5,22,29,30] | |
| HCT-116 | 16 | 4 | [39,41,44,45] | |
| HT-29 | 14 | 3 | [28,40,42] | |
| JB6 Cl41 | Mus musculus | 16 | 3 | [15,40,57] |
| Saponin | Chemical Formula | Structure | Concentration (µM) | Cell Viability Method | Incubation Period (h) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pacificusoside F | C55H83NaO25S | 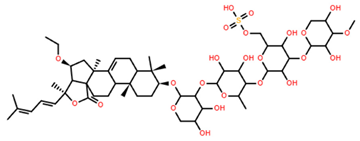 | 6.00 | MTS | 24 | [15] |
| Cucumarioside D | C61H94O27 |  | 6.10 | MTS | 24 | [15] |
| Pacificusoside D | C61H94O27 | 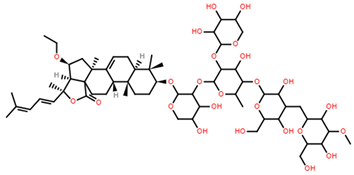 | 6.40 | MTS | 24 | [15] |
| Pacificusoside H | C55H83NaO26S | 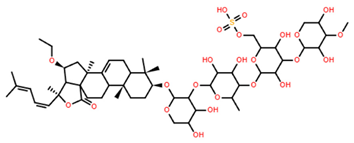 | 6.60 | MTS | 24 | [15] |
| Pacificusoside K | C48H73NaO23S |  | 7.40 | MTS | 24 | [15] |
| Pacificusoside G | C54H82O22 | 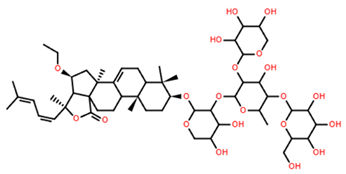 | 8.70 | MTS | 24 | [15] |
| Pacificusoside I | C54H84O26 | 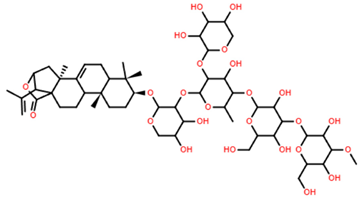 | 8.70 | MTS | 24 | [15] |
| Archasteroside B | C57H95NaO27S | 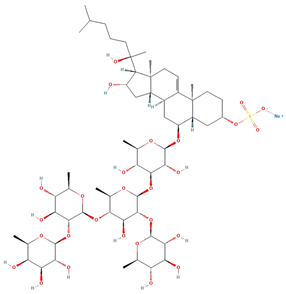 | 18.00 | MTS | 6 | [57] |
| Pacificusoside E | C54H82O22 | 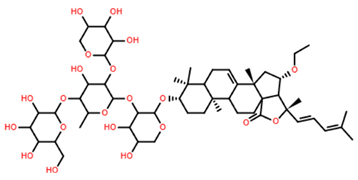 | 31.50 | MTS | 24 | [15] |
| Pacificusoside J | C47H72O20 |  | 32.80 | MTS | 24 | [15] |
| Thornasteroside A | C56H91NaO28S | 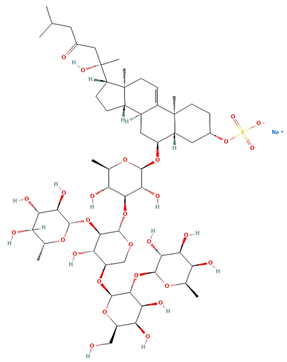 | 34.00 | MTS | 24 | [40] |
| Archasteroside A | C59H97NaO28S | 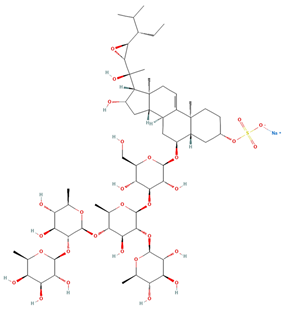 | 37.00 | MTS | 6 | [57] |
| Versicoside A | C62H101NaO33S | 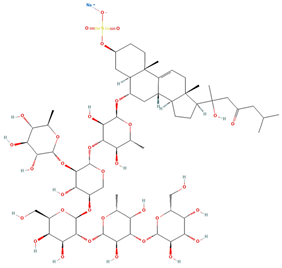 | 69.00 | MTS | 24 | [40] |
| Regularoside A | C58H95NaO28S | 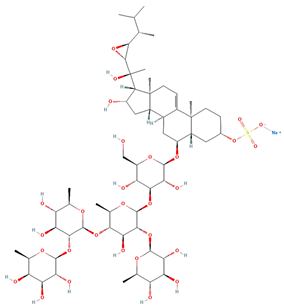 | >50 | MTS | 6 | [57] |
| Aphelasteroside A | C32H55NaO12S | 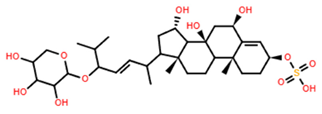 | >100 | MTS | 24 | [40] |
| Asterone Thornasteroside A | C50H79NaO27S | 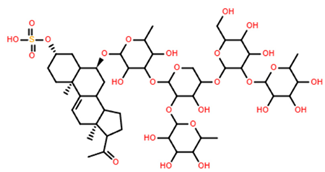 | >100 | MTS | 24 | [40] |
| Cell Line | Cell Type Description | Concentration (µM) | Cell Viability Method | Incubation Period (h) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BEL-7402 | human hepatoma | 7.39 * | SRB | 48 | [8] |
| K-562 | human leukaemia | 10.61 * | MTT | 48 | [8] |
| MDA-MB-231 | human breast | 28.00 | MTS | 24 | [40] |
| HT-29 | human colorectal carcinoma | 32.00 | MTS | 24 | [40] |
| JB6 CI41 | non-cancerous mouse epidermal | 34.00 | MTS | 24 | [40] |
| THP-1 | human monocytic leukaemia | 39.00 | MTS | 24 | [40] |
| Raji | human Burkitt’s lymphoma | 48.00 | MTS | 24 | [40] |
| RPMI-7951 | human melanoma | 50.00 | MTS | 24 | [41] |
| HCT-116 | human colorectal carcinoma | 82.00 | MTS | 24 | [41] |
| T-47D | human breast | 94.00 | MTS | 24 | [41] |
| Saponin | Structure | Cell Line | Measure | Concentration (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saponin 1 (C55H89NaO27S) |  | Erythrocyte | ED50 | 12.79 * |
| Pyricularia oryzae | MMDC | 6.39 * | ||
| K-562 (1) | IC50 | 2.85 * | ||
| BEL-7402 (2) | IC50 | 2.04 * | ||
| Saponin 2 (C49H77NaO26S) |  | Erythrocyte | ED50 | >34.75 * |
| Pyricularia oryzae | MMDC | 222.38 * | ||
| K-562 (1) | IC50 | >43.4 * | ||
| BEL-7402 (2) | IC50 | >43.4 * | ||
| Saponin 3 (C56H91NaO27S) | 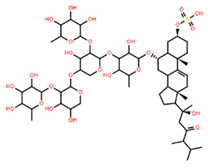 | Erythrocyte | ED50 | 24.50 * |
| Pyricularia oryzae | MMDC | 3.16 * | ||
| K-562 (1) | IC50 | 2.96 * | ||
| BEL-7402 (2) | IC50 | 1.49 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smith, S.J.; Wang, T.; Cummins, S.F. Asteroid Saponins: A Review of Their Bioactivity and Selective Cytotoxicity. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22120552
Smith SJ, Wang T, Cummins SF. Asteroid Saponins: A Review of Their Bioactivity and Selective Cytotoxicity. Marine Drugs. 2024; 22(12):552. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22120552
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmith, Stuart J., Tianfang Wang, and Scott F. Cummins. 2024. "Asteroid Saponins: A Review of Their Bioactivity and Selective Cytotoxicity" Marine Drugs 22, no. 12: 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22120552
APA StyleSmith, S. J., Wang, T., & Cummins, S. F. (2024). Asteroid Saponins: A Review of Their Bioactivity and Selective Cytotoxicity. Marine Drugs, 22(12), 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22120552






