Green Seaweed Caulerpa racemosa as a Novel Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Inhibitor in Overcoming Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Resistance: An Analysis Employing Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and In Vitro Research
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Compound Identification
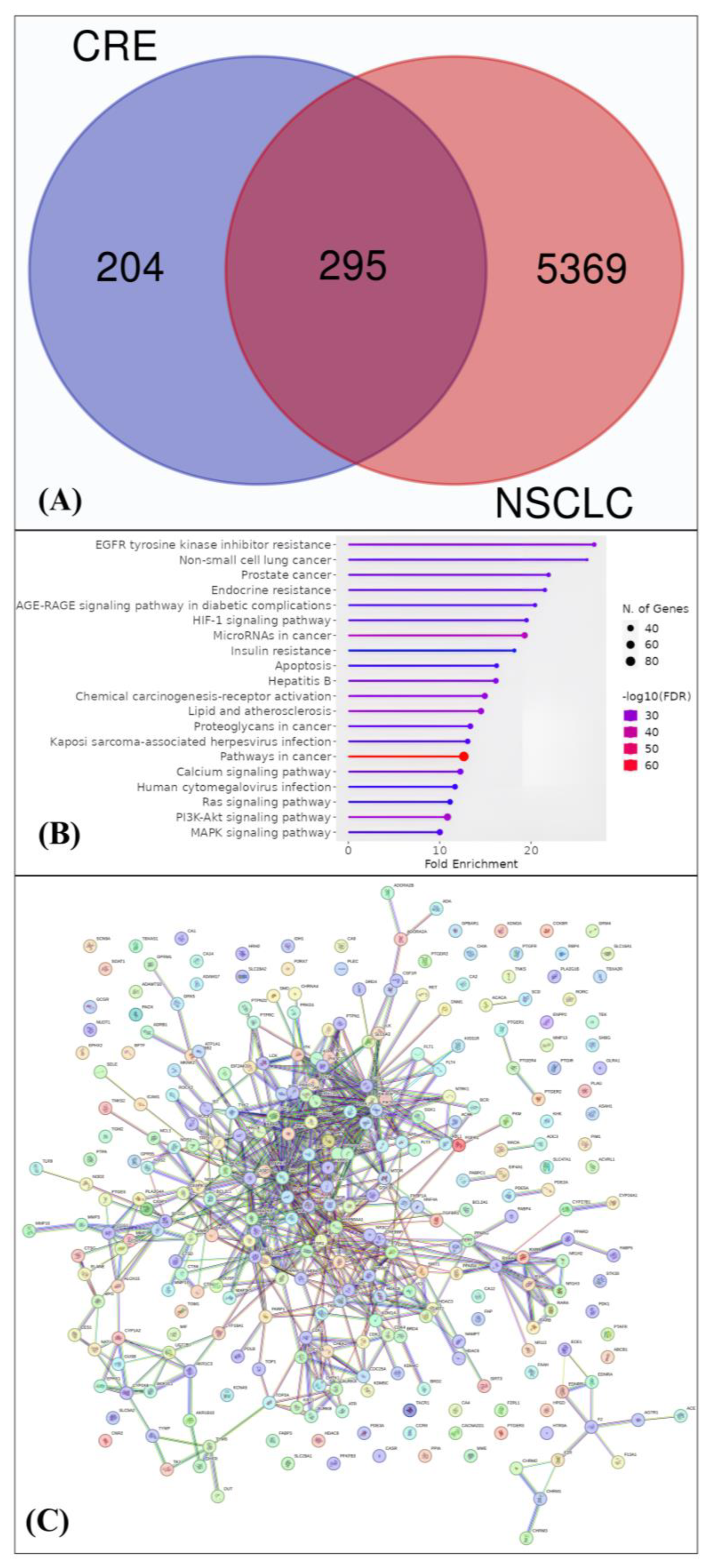
2.2. Pa Value, Toxicity Computation Analysis, Drug Likeness, and Analysis of Network Pharmacology
2.3. Docking Potency of Compounds in the CRE
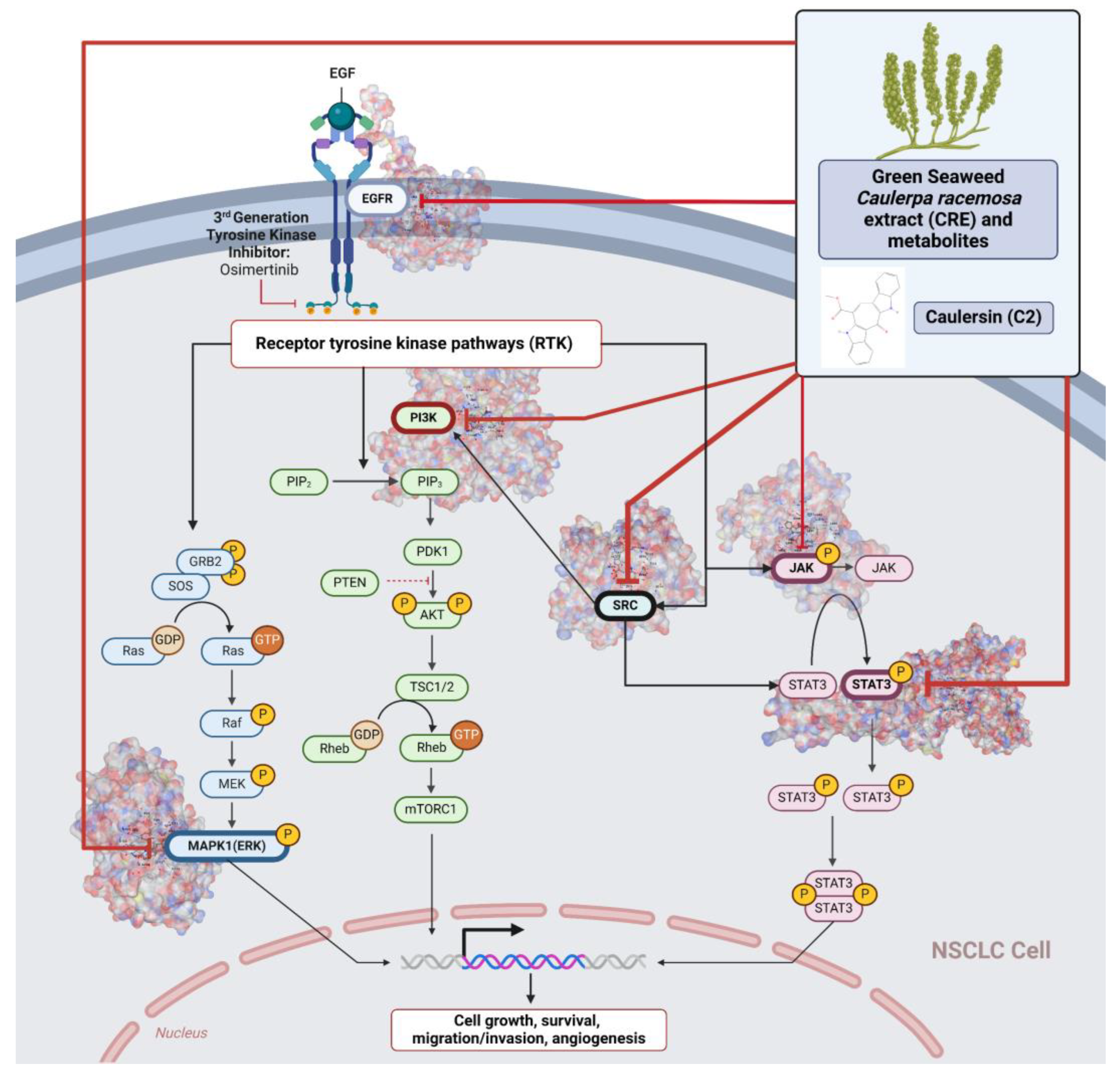
2.4. The Potential for Inhibiting NSCLC and the Safety of the CRE
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Caulerpa Racemosa Extract (CRE) Metabolites’ Compound Profiling
4.2. In Silico Study Assessment
4.2.1. Prediction of Bioactive Compound Activities, Toxicity Analysis, and Drug Likeness
4.2.2. Protein Target Identification and Analysis
4.2.3. Network Pharmacology Analysis
4.2.4. Molecular Docking Simulation
4.3. In Vitro Study on Cancer Cell Lines
4.3.1. Antiproliferative Activity and Cytotoxicity Test of CRE with MTT Assay
4.3.2. SRC, STAT3, PIK3CA, MAPK1, EGFR, and JAK1 Expression
4.4. Data Management and Analysis
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma’ruf, W.F.; Ibrahim, R.; Dewi, E.N.; Susanto, E.; Amalia, U. PROFIL RUMPUT LAUT Caulerpa racemosa DAN Gracilaria verrucosa SEBAGAI EDIBLE FOOD (Caulerpa racemosa and Gracilaria verrucosa Profile as Edible Foods). Saintek Perikan. Indones. J. Fish. Sci. Technol. 2013, 9, 68–74. [Google Scholar]
- Pangestuti, R.; Haq, M.; Rahmadi, P.; Chun, B.-S. Nutritional Value and Biofunctionalities of Two Edible Green Seaweeds (Ulva lactuca and Caulerpa racemosa) from Indonesia by Subcritical Water Hydrolysis. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permatasari, H.K.; Barbara Ulfa, E.N.; Adyana Daud, V.P.; Sulistomo, H.W.; Nurkolis, F. Caulerpa racemosa Extract Inhibits HeLa Cancer Cells Migration by Altering Expression of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Proteins. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 1052238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, S.M.; Neaz, S.; Alam, M.M.; Nur, J. Hypolipidemic Activity of Ethanolic Extract of Caulerpa recemosa. Birdem Med. J. 2019, 9, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, R.; Nurkolis, F.; Taslim, N.A.; Subali, D.; Surya, R.; Gunawan, W.B.; Alisaputra, D.; Mayulu, N.; Salindeho, N.; Kim, B. Carotenoids Composition of Green Algae Caulerpa racemosa and Their Antidiabetic, Anti-Obesity, Antioxidant, and Anti-Inflammatory Properties. Molecules 2023, 28, 3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganti, A.K.; Klein, A.B.; Cotarla, I.; Seal, B.; Chou, E. Update of Incidence, Prevalence, Survival, and Initial Treatment in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in the US. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 1824–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, C.L.; Zhang, A.L.; Bruno, D.S.; Almeida, F.A. NSCLC in the Era of Targeted and Immunotherapy: What Every Pulmonologist Must Know. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Bai, R.; Cui, J. Precision Targeted Therapy for EGFR Mutation-Positive NSCLC: Dilemmas and Coping Strategies. Thorac. Cancer 2023, 14, 1121–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, W. A Review of Research Progress on Mechanisms and Overcoming Strategies of Acquired Osimertinib Resistance. Anticancer Drugs 2022, 33, e76–e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Jiang, J.; Du, Y.; Liu, S.; Ge, X. Overexpression of Osimertinib-Resistant ABCG2 in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells; Research Square: Durham, NC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, T.; Xu, Q. Therapeutic Advances in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Focus on Clinical Development of Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy. MedComm 2020 2021, 2, 692–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, L.; Deng, C.; Liu, H.; Guo, Z.; Chang, Z.; Mo, J. Nuclear Protein 1 Promotes Unfolded Protein Response during Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Alleviates Apoptosis Induced by Cisplatin in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2021, 20, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanger, G.; Wonggo, D.; Taher, N.; Dotulong, V.; Setiawan, A.A.; Permatasari, H.K.; Maulana, S.; Nurkolis, F.; Tsopmo, A.; Kim, B. Green Seaweed Caulerpa racemosa—Chemical Constituents, Cytotoxicity in Breast Cancer Cells and Molecular Docking Simulation. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 12, 100621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Shao, H.; Zhang, C.; Hong, P.; Xiong, H. Separation of the Polysaccharides in Caulerpa racemosa and Their Chemical Composition and Antitumor Activity. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 110, 1435–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandlik, R.; Naik, S.; Tatiya, A. Evaluation of Physicochemical Properties of Seaweed, Caulerpa racemosa. Int. J. Res. Ayurveda Pharm. 2014, 5, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holleman, M.S.; van Tinteren, H.; Groen, H.J.; Al, M.J.; Uyl-de Groot, C.A. First-Line Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in EGFR Mutation-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Network Meta-Analysis. Onco. Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 1413–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namba, K.; Shien, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Torigoe, H.; Sato, H.; Yoshioka, T.; Takeda, T.; Kurihara, E.; Ogoshi, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; et al. Activation of AXL as a Preclinical Acquired Resistance Mechanism Against Osimertinib Treatment InEGFR-Mutant Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.-Q.; Wen, Y.; Gupta, P.; Lei, Z.-N.; Cai, C.-Y.; Liang, G.; Yang, D.-H.; Chen, Z.-S.; Xie, Y.-A. Y6, an Epigallocatechin Gallate Derivative, Reverses ABCG2-Mediated Mitoxantrone Resistance. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dent, P. Met in Lung Cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2014, 15, 653–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertino, E.M.; Gentzler, R.D.; Clifford, S.; Kolesar, J.; Muzikansky, A.; Haura, E.B.; Piotrowska, Z.; Camidge, D.R.; Stinchcombe, T.E.; Hann, C.L.; et al. Phase IB Study of Osimertinib in Combination with Navitoclax in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC Following Resistance to Initial EGFR Therapy (ETCTN 9903). Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 27, 1604–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Dong, H.; Chen, W.; Wang, B.; Ji, D.; Zhang, W.; Shi, X.; Feng, X. Case Report: Heterogeneity of Resistance Mechanisms in Different Lesions Co-Mediate Acquired Resistance to First-Line Icotinib in EGFR Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 906364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Yang, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. Combination TS-1 Plus EGFR-tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs) for the Treatment of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer After Progression on First-line or Further EGFR-TKIs: A Phase II, Single-arm Trial. Thorac. Cancer 2018, 9, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, P.; Jablons, D.M.; Yang, C.; Li, Y. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Pathway, Yes-Associated Protein (YAP) and the Regulation of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sequist, L.V.; Waltman, B.A.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Digumarthy, S.; Turke, A.B.; Fidias, P.; Bergethon, K.; Shaw, A.T.; Gettinger, S.; Cosper, A.K.; et al. Genotypic and Histological Evolution of Lung Cancers Acquiring Resistance to EGFR Inhibitors. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 75ra26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaoka, T.; Ohba, M.; Ohmori, T. Molecular-Targeted Therapies for Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and Its Resistance Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, P.N.; Klempner, S.J. Profile of Rociletinib and Its Potential in the Treatment of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2016, 7, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tricker, E.M.; Xu, C.; Uddin, S.; Capelletti, M.; Ercan, D.; Ogino, A.; Pratilas, C.A.; Rosen, N.; Gray, N.S.; Wong, K.-K.; et al. Combined EGFR/MEK Inhibition Prevents the Emergence of Resistance in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 960–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, T.N.M.; Kim, M.-K.; Vo, V.T.A.; Choi, J.-W.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, H.-W.; Cha, S.-K.; Park, K.-S.; Jeong, Y. Inhibition of Oncogenic Src Induces FABP4-Mediated Lipolysis via PPARγ Activation Exerting Cancer Growth Suppression. EBioMedicine 2019, 41, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.-L.; Chen, C.-M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, C.-Z.; Lin, L.-Z. Glucose-Regulated Protein 78 Signaling Regulates Hypoxia-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in A549 Cells. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Xu, L.-F.; Zhang, J.; Kong, S.-Y.; Wu, M.; Lao, Y.-Z.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, L.; Xu, H. SRC and MEK Co-Inhibition Synergistically Enhances the Anti-Tumor Effect in Both Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) and Erlotinib-Resistant NSCLC. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, T.-R.; Park, H.-J.; Park, M.N.; Kim, B.; Park, S.-H. The Root Bark of Morus Alba L. Suppressed the Migration of Human Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells through Inhibition of Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition Mediated by STAT3 and Src. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, G.; Rao, S.; Gurbani, D.; Henning, N.J.; Jiang, J.; Che, J.; Yang, A.; Ficarro, S.B.; Marto, J.A.; Aguirre, A.J.; et al. Structure-Based Design of a Potent and Selective Covalent Inhibitor for SRC Kinase That Targets a P-Loop Cysteine. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 1624–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, T.; Ozasa, H.; Aoki, W.; Aburaya, S.; Funazo, T.; Furugaki, K.; Yoshimura, Y.; Ajimizu, H.; Okutani, R.; Yasuda, Y.; et al. Alectinib Resistance in ALK-Rearranged Lung Cancer by Dual Salvage Signaling in a Clinically Paired Resistance Model. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murillo, M.M.; Rana, S.; Spencer-Dene, B.; Nye, E.; Stamp, G.; Downward, J. Disruption of the Interaction of RAS with PI 3-Kinase Induces Regression of EGFR-Mutant-Driven Lung Cancer. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 3545–3553.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Wang, X.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Laster, K.V.; Liu, K.; Dong, Z.; Kim, D.J. Anwulignan Is a Novel JAK1 Inhibitor That Suppresses Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Growth. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 2645–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurkolis, F.; Permatasari, H.K. LC-HRMS DATA of Caulerpa racemosa. 2022. Available online: https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/LC-HRMS_DATA_OF_Caulerpa_racemosa/20518485/1 (accessed on 4 June 2024).
- Nurkolis, F.; Taslim, N.A.; Qhabibi, F.R.; Kang, S.; Moon, M.; Choi, J.; Choi, M.; Park, M.N.; Mayulu, N.; Kim, B. Ulvophyte Green Algae Caulerpa Lentillifera: Metabolites Profile and Antioxidant, Anticancer, Anti-Obesity, and In Vitro Cytotoxicity Properties. Molecules 2023, 28, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurkolis, F.; Taslim, N.A.; Subali, D.; Kurniawan, R.; Hardinsyah, H.; Gunawan, W.B.; Kusuma, R.J.; Yusuf, V.M.; Pramono, A.; Kang, S.; et al. Dietary Supplementation of Caulerpa racemosa Ameliorates Cardiometabolic Syndrome via Regulation of PRMT-1/DDAH/ADMA Pathway and Gut Microbiome in Mice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvez, M.; Ara, J.; Sultana, V.; Qasim, R.; Ahmad, V.U. Caulerpin. Acta Crystallogr. C 2000, 56, E96–E97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PubChem. Methyl 2-Oxo-10,21-diazapentacyclo[12.7.0.03,11.04,9.015,20]henicosa-1(14),3(11),4,6,8,12,15,17,19-Nonaene-12-Carboxylate. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/10593388 (accessed on 7 May 2024).
- PubChem. Caulerpenyne. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/5311436 (accessed on 7 May 2024).
- PubChem. Racemosin. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/155148 (accessed on 7 May 2024).
- PubChem. Hexadecanamide. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/69421 (accessed on 7 May 2024).
- PubChem. Oleamide. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/5283387 (accessed on 7 May 2024).
- PubChem. Eicosapentaenoic Acid. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/5282847 (accessed on 7 May 2024).
- PubChem. (1R,3S,5S,7R)-2,8-Dimethylidene-5-Prop-1-En-2-Ylcyclodecane-1,3,7-Triol. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/181557 (accessed on 7 May 2024).
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissTargetPrediction: Updated Data and New Features for Efficient Prediction of Protein Targets of Small Molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W357–W364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.X.; Jung, D.; Yao, R. ShinyGO: A Graphical Gene-Set Enrichment Tool for Animals and Plants. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2628–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING Database in 2023: Protein-Protein Association Networks and Functional Enrichment Analyses for Any Sequenced Genome of Interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Gan, J.; Chen, S.; Xiao, Z.-X.; Cao, Y. CB-Dock2: Improved Protein-Ligand Blind Docking by Integrating Cavity Detection, Docking and Homologous Template Fitting. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W159–W164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace Hayes, A.; Loomis, T.A. Loomis’s Essentials of Toxicology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; ISBN 9780080535630. [Google Scholar]

| No | Observed Compounds | Molecular Formula | Observed MW (g/mol) | PubChem ID or Substance ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | Caulerpin | C24H18N2O4 | 398.4 | 5326018 |
| C2 | Caulersin | C21H14N2O3 | 342.3 | 10593388 |
| C3 | Caulerpenyne | C21H26O6 | 374.4 | 5311436 |
| C4 | Racemosin | C16H16O5 | 288.29 | 155148 |
| C5 | Hexadecanamide | C16H33NO | 255.44 | 69421 |
| C6 | Oleamide | C18H35NO | 281.5 | 5283387 |
| C7 | Eicosapentaenoic acid | C20H30O2 | 302.5 | 5282847 |
| C8 | Ageratriol | C15H24O3 | 252.35 | 181557 |
| No. | Pa Value * | Toxicity Computation Analysis ** | Drug Likeness *** | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kinase Inhibitor | Antineoplastic | Predicted LD50 (mg/kg) | Toxicity Class | Lipinski | Pfizer | GSK | |
| C1 | 0.727 | 0.711 | 1760 | 4 | Accepted | Accepted | Rejected |
| C2 | 0.815 | 0.711 | 3 | 5 | Accepted | Rejected | Rejected |
| C3 | 0.558 | 0.81 | 500 | 4 | Accepted | Accepted | Accepted |
| C4 | 0.434 | 0.796 | 1050 | 4 | Accepted | Rejected | Accepted |
| C5 | 0.769 | 0.393 | 1000 | 4 | Accepted | Rejected | Rejected |
| C6 | 0.838 | 0.414 | 750 | 4 | Accepted | Rejected | Rejected |
| C7 | 0.828 | 0.164 | 10,000 | 6 | Accepted | Rejected | Rejected |
| C8 | 0.554 | 0.945 | 5000 | 5 | Accepted | Accepted | Accepted |
| Name | Degree | Betweenness Centrality | Closeness Centrality | Overall Score | Pathway |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRC | 33 | 0.1839 | 0.4121 | 33.596 | EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Resistance, NSCLC, Cancer |
| STAT3 | 33 | 0.1448 | 0.4139 | 33.5586 | EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Resistance, HIF1 Signaling, NSCLC |
| PIK3CA | 29 | 0.0321 | 0.3569 | 29.389 | EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Resistance, HIF1 Signaling, NSCLC, Cancer, PIK3-AKT, RAS Signaling |
| MAPK1 | 26 | 0.1249 | 0.398 | 26.5229 | EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Resistance, HIF1 Signaling, MAPK, NSCLC, Cancer, PIK3-AKT, RAS Signaling |
| EGFR | 20 | 0.0426 | 0.3767 | 20.4192 | EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Resistance, HIF1 Signaling, NSCLC, Cancer, PIK3-AKT, RAS Signaling |
| JAK1 | 16 | 0.0039 | 0.3294 | 16.3333 | EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Resistance, NSCLC, Cancer, PIK3-AKT |
| ERBB2 | 14 | 0.0046 | 0.3569 | 14.3615 | NSCLC, Cancer |
| MTOR | 13 | 0.0502 | 0.3582 | 13.4084 | EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Resistance, HIF1 Signaling, Cancer, PIK3-AKT |
| BRAF | 10 | 0.0095 | 0.3278 | 10.3373 | EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Resistance, MAPK, NSCLC |
| ALK | 7 | 0.0002 | 0.2822 | 7.2824 | NSCLC, Cancer |
| Compound and Controls as Ligands | SRC | STAT3 | PIK3CA | MAPK1 | EGFR | JAK1 | ERBB2 | MTOR | BRAF | ALK | Overall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Osimertinib | −8.8 | −7.4 | −10.8 | −8.3 | −8.1 | −8.9 | −9.4 | −9 | −8.7 | −8.6 | −88 |
| Mitoxantrone | −8.2 | −7.4 | −8.6 | −7.8 | −7.5 | −8.6 | −9.1 | −8.7 | −7.9 | −7.8 | −81.6 |
| C1 | −9.3 | −8.3 | −9.3 | −8.9 | −7.3 | −7.3 | −8.5 | −8.6 | −9.4 | −7.4 | −84.3 |
| C2 | −9.8 | −8.6 | −10 | −9.4 | −9.3 | −9.9 | −10.6 | −10.3 | −9.3 | −10 | −97.2 |
| C3 | −8.5 | −6.6 | −7.7 | −7 | −7 | −7.3 | −7.8 | −8.1 | −8.7 | −7.7 | −76.4 |
| C4 | −8.9 | −8.2 | −7.8 | −7.6 | −7.5 | −8.3 | −7.9 | −8.1 | −8.3 | −8.9 | −81.5 |
| C5 | −6.4 | −5.8 | −6.1 | −5.2 | −5.1 | −5.8 | −6.7 | −6 | −6.7 | −6.4 | −60.2 |
| C6 | −6.8 | −6.2 | −6 | −5.7 | −5.6 | −5.5 | −7.4 | −6 | −6.8 | −6.8 | −62.8 |
| C7 | −7.3 | −7.1 | −6.8 | −6.1 | −5.9 | −7.5 | −8.4 | −6.6 | −8 | −7.7 | −71.4 |
| C8 | −6.7 | −6.2 | −8.1 | −7.5 | −6.1 | −6.9 | −7.2 | −7.3 | −7.3 | −7.6 | −70.9 |
| Compound | Control | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Osimertinib | Mitoxantrone | |||
| Mean Difference | p-Value | Mean Difference | p-Value | |
| C1 | −0.37 | 0.753 | 0.27 | 0.905 |
| C2 | 0.92 | 0.036 * | 1.57 | <0.001 * |
| C4 | −0.65 | 0.237 | 0.01 | 1 |
| Proteins | C2 |
|---|---|
| SRC |  |
| STAT3 |  |
| PIK3CA |  |
| MAPK1 |  |
| EGFR | 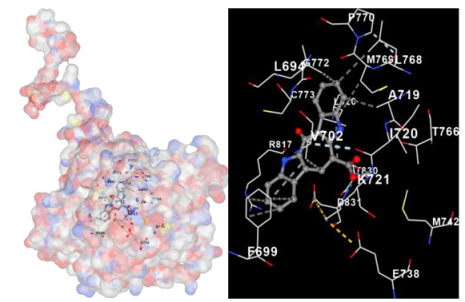 |
| JAK1 |  |
| Samples | NSCLC Cell Lines (PC-9) | Normal Cell Lines (HLF) |
|---|---|---|
| Osimertinib | 45.23 | 340.5 |
| Mitoxantrone | 98.4551 | 454.5505 |
| CRE | 289.301 | 1890.5470 |
| C1 | 102.4566 | 913.3324 |
| C2 | 56.8869 | 852.5669 |
| C4 | 183.6501 | 1090.5321 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lau, V.; Nurkolis, F.; Park, M.N.; Heriyanto, D.S.; Taslim, N.A.; Tallei, T.E.; Permatasari, H.K.; Tjandrawinata, R.R.; Moon, S.; Kim, B. Green Seaweed Caulerpa racemosa as a Novel Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Inhibitor in Overcoming Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Resistance: An Analysis Employing Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and In Vitro Research. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22060272
Lau V, Nurkolis F, Park MN, Heriyanto DS, Taslim NA, Tallei TE, Permatasari HK, Tjandrawinata RR, Moon S, Kim B. Green Seaweed Caulerpa racemosa as a Novel Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Inhibitor in Overcoming Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Resistance: An Analysis Employing Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and In Vitro Research. Marine Drugs. 2024; 22(6):272. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22060272
Chicago/Turabian StyleLau, Vincent, Fahrul Nurkolis, Moon Nyeo Park, Didik Setyo Heriyanto, Nurpudji Astuti Taslim, Trina Ekawati Tallei, Happy Kurnia Permatasari, Raymond R. Tjandrawinata, Seungjoon Moon, and Bonglee Kim. 2024. "Green Seaweed Caulerpa racemosa as a Novel Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Inhibitor in Overcoming Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Resistance: An Analysis Employing Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and In Vitro Research" Marine Drugs 22, no. 6: 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22060272
APA StyleLau, V., Nurkolis, F., Park, M. N., Heriyanto, D. S., Taslim, N. A., Tallei, T. E., Permatasari, H. K., Tjandrawinata, R. R., Moon, S., & Kim, B. (2024). Green Seaweed Caulerpa racemosa as a Novel Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Inhibitor in Overcoming Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Resistance: An Analysis Employing Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and In Vitro Research. Marine Drugs, 22(6), 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22060272













