Production of Protein Hydrolysates from Cod Backbone Using Selected Enzymes: Evaluation of Antioxidative and Antimicrobial Activities of Hydrolysates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Protein Extraction Yield (PEY)
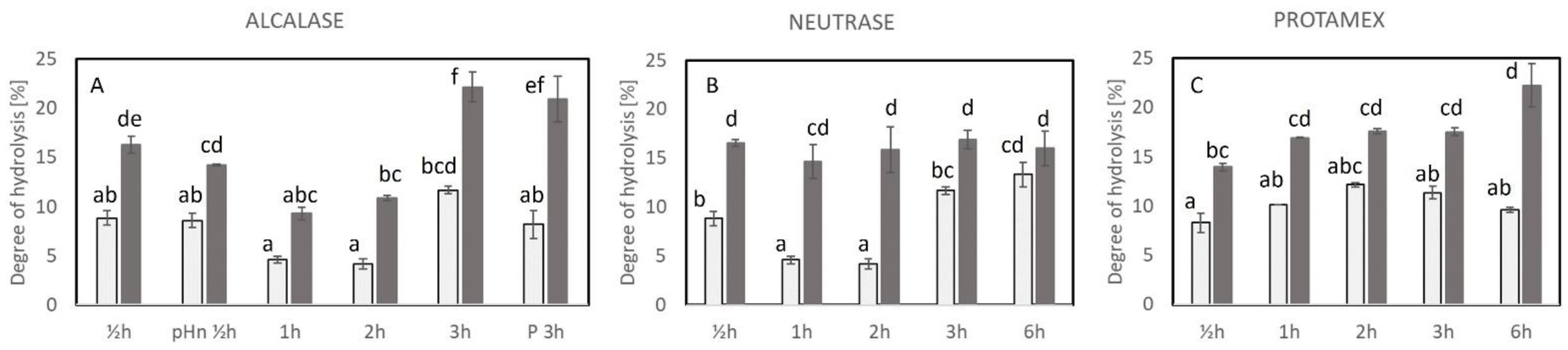
2.2. Degree of Hydrolysis (DH)
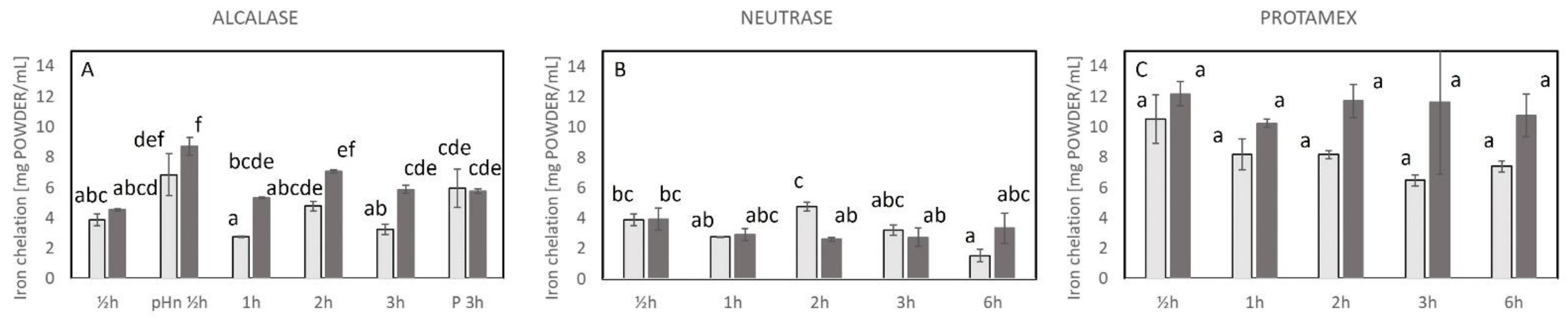
2.3. Antioxidative Properties of the Hydrolysates
2.3.1. Total and Free Amino Acids
2.3.2. Molecular Size (Selected Hydrolysates)
2.4. Antimicrobial Activity
3. Discussion
3.1. The Produced Fish Protein Hydrolysates: PEY and DH
3.2. Antioxidant Activities of the Fish Protein Hydrolysates
3.3. Lack of Antimicrobial Activity
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cod Fish
4.2. Sample Preparation
4.3. Hydrolysis
4.3.1. Procedure for the Enzyme Hydrolysis
4.3.2. Effect of Preheating or pH Adjustment Prior to Hydrolysis (Alcalase)
4.4. Protein Determination
4.5. Degree of Hydrolysis (DH) by the OPA Method
4.6. Protein Extraction Yield (PEY)
4.7. DPPH Radical Scavenging Capacity
4.8. Iron Chelation Capacity
4.9. Total and Free Amino Acid Content (Selected Hydrolysates)
4.10. Molecular Weight by SEC-MALS (Selected Hydrolysates)
4.11. Antimicrobial Assays
4.11.1. Culture Preparation
4.11.2. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Assay
4.11.3. Disk Diffusion Assay
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. Transition Towards an Ecosystem Approach to Fisheries in the Mediterranean Sea: Lessons Learned Through Selected Case Studies Climate Change Risks to Marine Ecosystems and Fisheries Projections to 2100 from the Fisheries and Marine Ecosystem Model Intercomparison Project; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Välimaa, A.L.; Mäkinen, S.; Mattila, P.; Marnila, P.; Pihlanto, A.; Mäki, M.; Hiidenhovi, J. Fish and Fish Side Streams Are Valuable Sources of High-Value Components. Food Qual. Saf. 2019, 3, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, N.R.A.; Yusof, H.M.; Sarbon, N.M. Functional and Bioactive Properties of Fish Protein Hydolysates and Peptides: A Comprehensive Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuine, R.; Rathnayake, A.U.; Byun, H.G. Biological Activity of Peptides Purified from Fish Skin Hydrolysates. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 22, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucak, I.; Afreen, M.; Montesano, D.; Carrillo, C.; Tomasevic, I.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Barba, F.J. Functional and Bioactive Properties of Peptides Derived from Marine Side Streams. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najafian, L.; Babji, A.S. A Review of Fish-Derived Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Peptides: Their Production, Assessment, and Applications. Peptides 2012, 33, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, D.; Lauritano, C.; Esposito, F.P.; Riccio, G.; Rizzo, C.; de Pascale, D. Fish Waste: From Problem to Valuable Resource. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.G.; Hwang, J.W.; Kang, H. Antioxidative and Anti-Atopic Dermatitis Effects of Peptides Derived from Hydrolyzed Sebastes Schlegelii tail By-Products. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Qiu, Y.T.; Wang, Y.M.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Novel Antioxidant Collagen Peptides of Siberian Sturgeon (Acipenser baerii) Cartilages: The Preparation, Characterization, and Cytoprotection of H2O2-Damaged Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVECs). Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, A.D.M.; Wu, H.; Hyldig, G.; Bøknæs, N.; Mejlholm, O.; Undeland, I.; Jacobsen, C. Oxidative Stability of Side-Streams from Cod Filleting—Effect of Antioxidant Dipping and Low-Temperature Storage. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, N.; Falch, E.; Slizyte, R.; Kumari, A.; Khushboo; Hjellnes, V.; Sharma, A.; Rajauria, G. Valorization of Fish Processing By-Products for Protein Hydrolysate Recovery: Opportunities, Challenges and Regulatory Issues. Food Chem. 2024, 459, 140244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasri, M. Protein Hydrolysates and Biopeptides: Production, Biological Activities, and Applications in Foods and Health Benefits. A Review. In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Volume 81, pp. 109–159. [Google Scholar]
- Yesiltas, B.; García-Moreno, P.J.; Gregersen, S.; Olsen, T.H.; Jones, N.C.; Hoffmann, S.V.; Marcatili, P.; Overgaard, M.T.; Hansen, E.B.; Jacobsen, C. Antioxidant Peptides Derived from Potato, Seaweed, Microbial and Spinach Proteins: Oxidative Stability of 5% Fish Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Food Chem. 2022, 385, 132699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bougatef, A.; Nedjar-Arroume, N.; Manni, L.; Ravallec, R.; Barkia, A.; Guillochon, D.; Nasri, M. Purification and Identification of Novel Antioxidant Peptides from Enzymatic Hydrolysates of Sardinelle (Sardinella aurita) by-Products Proteins. Food Chem. 2010, 118, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ma, X.; Che, S.; Wang, C.; Li, B. The Effect of Hydrolysis with Neutrase on Molecular Weight, Functional Properties, and Antioxidant Activities of Alaska Pollock Protein Isolate. J. Ocean Univ. China 2018, 17, 1423–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Li, T.; Yu, R.; Yan, C.; Ren, S.; Zhao, Y. Antioxidant Activities of Hydrolysates of Arca Subcrenata Prepared with Three Proteases. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennaas, N.; Hammami, R.; Beaulieu, L.; Fliss, I. Purification and Characterization of Four Antibacterial Peptides from Protamex Hydrolysate of Atlantic Mackerel (Scomber scombrus) by-Products. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 462, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Rocha, M.; Alemán, A.; Baccan, G.C.; López-Caballero, M.E.; Gómez-Guillén, C.; Montero, P.; Prentice, C. Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant, and Antimicrobial Effects of Underutilized Fish Protein Hydrolysate. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2018, 27, 592–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezeshk, S.; Ojagh, S.M.; Rezaei, M.; Shabanpour, B. Fractionation of Protein Hydrolysates of Fish Waste Using Membrane Ultrafiltration: Investigation of Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activities. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šližyte, R.; Mozuraityte, R.; Martínez-Alvarez, O.; Falch, E.; Fouchereau-Peron, M.; Rustad, T. Functional, Bioactive and Antioxidative Properties of Hydrolysates Obtained from Cod (Gadus morhua) Backbones. Process Biochem. 2009, 44, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Zhao, M.; Cui, C.; Zhao, H.; Yang, B. Effect of Degree of Hydrolysis on the Antioxidant Activity of Loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus) Protein Hydrolysates. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2009, 10, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sila, A.; Nedjar-Arroume, N.; Hedhili, K.; Chataigné, G.; Balti, R.; Nasri, M.; Dhulster, P.; Bougatef, A. Antibacterial Peptides from Barbel Muscle Protein Hydrolysates: Activity against Some Pathogenic Bacteria. LWT 2014, 55, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.H.; Luo, Q.B.; Pan, X.; Chi, C.F.; Sun, K.L.; Wang, B. Preparation, Identification, and Activity Evaluation of Ten Antioxidant Peptides from Protein Hydrolysate of Swim Bladders of Miiuy Croaker (Miichthys miiuy). J. Funct. Foods 2018, 47, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.F.; Wang, B.; Hu, F.Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhang, B.; Deng, S.G.; Wu, C.W. Purification and Identification of Three Novel Antioxidant Peptides from Protein Hydrolysate of Bluefin Leatherjacket (Navodon septentrionalis) Skin. Food Res. Int. 2015, 73, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.T.; Wang, Y.M.; Yang, X.R.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Gelatin and Antioxidant Peptides from Gelatin Hydrolysate of Skipjack Tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) Scales: Preparation, Identification and Activity Evaluation. Mar Drugs 2019, 17, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šližyte, R.; Daukšas, E.; Falch, E.; Storrø, I.; Rustad, T. Yield and Composition of Different Fractions Obtained after Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Cod (Gadus morhua) by-Products. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarpour, A.; Gregersen, S.; Marciel Gomes, R.; Marcatili, P.; Hegelund Olsen, T.; Jacobsen, C.; Overgaard, M.T.; Sørensen, A.-D.M. Biofunctionality of Enzymatically Derived Peptides from Codfish (Gadus morhua) Frame: Bulk In Vitro Properties, Quantitative Proteomics, and Bioinformatic Prediction. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarpour, A.; Gomes, R.M.; Gregersen, S.; Sloth, J.J.; Jacobsen, C.; Moltke Sørensen, A.D. Characterization of Cod (Gadus morhua) Frame Composition and Its Valorization by Enzymatic Hydrolysis. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2020, 89, 103469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Bao, H.N.D.; Dang, H.T.T.; Tómasson, T.; Arason, S.; Gudjónsdóttir, M. Protein Characteristics and Bioactivity of Fish Protein Hydrolysates from Tra Catfish (Pangasius hypophthalmus) Side Stream Isolates. Foods 2022, 11, 4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristinsson, H.G.; Rasco, B.A. Fish Protein Hydrolysates: Production, Biochemical, and Functional Properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2000, 40, 43–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjakul, S.; Morrissey, M.T. Protein Hydrolysates from Pacific Whiting Solid Wastes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 3423–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wald, M.; Schwarz, K.; Rehbein, H.; Bußmann, B.; Beermann, C. Detection of Antibacterial Activity of an Enzymatic Hydrolysate Generated by Processing Rainbow Trout By-Products with Trout Pepsin. Food Chem. 2016, 205, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, K.; Tokur, B. Optimization of Hydrolysis Conditions for the Production of Protein Hydrolysates from Fish Wastes Using Response Surface Methodology. Food Biosci. 2022, 45, 101312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ktari, N.; Fakhfakh, N.; Balti, R.; Ben Khaled, H.; Nasri, M.; Bougatef, A. Effect of Degree of Hydrolysis and Protease Type on the Antioxidant Activity of Protein Hydrolysates from Cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) By-Products. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2013, 22, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiansilakul, Y.; Benjakul, S.; Shahidi, F. Antioxidative Activity of Protein Hydrolysate from Round Scad Muscle Using Alcalase and Flavourzyme. J. Food Biochem. 2007, 31, 266–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klompong, V.; Benjakul, S.; Kantachote, D.; Shahidi, F. Antioxidative Activity and Functional Properties of Protein Hydrolysate of Yellow Stripe Trevally (Selaroides leptolepis) as Influenced by the Degree of Hydrolysis and Enzyme Type. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.C.; Chen, H.M.; Shiau, C.Y. Free Amino Acids and Peptides as Related to Antioxidant Properties in Protein Hydrolysates of Mackerel (Scomber austriasicus). Food Res. Int. 2003, 36, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-M.; Muramoto, K.; Yamauchi, F.; Fujimoto, K.; Nokihara, K. Antioxidative Properties of Histidine-Containing Peptides Designed from Peptide Fragments Found in the Digests of a Soybean Protein. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapakse, N.; Mendis, E.; Jung, W.K.; Je, J.Y.; Kim, S.K. Purification of a Radical Scavenging Peptide from Fermented Mussel Sauce and Its Antioxidant Properties. Food Res. Int. 2005, 38, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapakse, N.; Mendis, E.; Byun, H.G.; Kim, S.K. Purification and in Vitro Antioxidative Effects of Giant Squid Muscle Peptides on Free Radical-Mediated Oxidative Systems. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2005, 16, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørlie, M.; Hartmann, J.C.; Rasmussen, L.H.; Yesiltas, B.; Sørensen, A.D.M.; Gregersen Echers, S.; Jacobsen, C. Screening for Metal-Chelating Activity in Potato Protein Hydrolysates Using Surface Plasmon Resonance and Peptidomics. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabeena Farvin, K.H.; Andersen, L.L.; Otte, J.; Nielsen, H.H.; Jessen, F.; Jacobsen, C. Antioxidant Activity of Cod (Gadus morhua) Protein Hydrolysates: Fractionation and Characterisation of Peptide Fractions. Food Chem. 2016, 204, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Yu, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, J. Characterization of Structural and Functional Properties of Fish Protein Hydrolysates from Surimi Processing By-Products. Food Chem. 2014, 151, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melgosa, R.; Marques, M.; Paiva, A.; Bernardo, A.; Fernández, N.; Sá-Nogueira, I.; Simões, P. Subcritical Water Extraction and Hydrolysis of Cod (Gadus morhua) Frames to Produce Bioactive Protein Extracts. Foods 2021, 10, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushnie, T.P.T.; Cushnie, B.; Echeverría, J.; Fowsantear, W.; Thammawat, S.; Dodgson, J.L.A.; Law, S.; Clow, S.M. Bioprospecting for Antibacterial Drugs: A Multidisciplinary Perspective on Natural Product Source Material, Bioassay Selection and Avoidable Pitfalls. Pharm. Res. 2020, 37, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariotti, F.; Tomé, D.; Mirand, P.P. Converting Nitrogen into Protein—Beyond 6.25 and Jones’ Factors. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Guo, J.; Yuan, J. In Vitro Antioxidant Properties of Rutin. LWT 2008, 41, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabeena Farvin, K.H.; Baron, C.P.; Nielsen, N.S.; Jacobsen, C. Antioxidant Activity of Yoghurt Peptides: Part 1-In Vitro Assays and Evaluation in ω-3 Enriched Milk. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forghani, B.; Sørensen, A.D.M.; Sloth, J.J.; Undeland, I. Liquid Side Streams from Mussel and Herring Processing as Sources of Potential Income. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 8355–8365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Enzyme Applied 1 | Hydrolysis Condition | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (h) 2 | pH (Adjusted) | Temperature (°C) | Preheating | |
| Alcalase (A) | 0.5, 1, 2, 3 | 8.0 | 60 | - |
| Alcalase (A_pHn) | 0.5 | - | 60 | - |
| Alcalase (A_P) | 3 | 8.0 | 60 | 15 min, 90 °C |
| Neutrase (N) | 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 6 | 8.0 | 60 | - |
| Protamex (P) | 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 6 | 6.5 | 50 | - |
| Free Amino Acids [mg/g] 1 | Total Amino Acids [mg/g] 1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P_6hE | P_6hC | N_6hC | P_6hE | P_6hC | N_6hC | ||
| ARG | 16.5 ± 3.2 c | 6.3 ± 2.2 b | 1.4 ± 0.1 a | ARG | 56.6 ± 3.9 b | 49.0 ± 4.4 a | 51.6 ± 2.4 ab |
| SER | 3.6 ± 0.3 a | 3.9 ± 1.0 a | 3.1 ± 0.4 a | SER | 37.7 ± 2.5 b | 32.3 ± 2.3 a | 33.1 ± 2.9 ab |
| HYP | 6.2 ± 0.9 c | 2.5 ± 0.5 b | 1.0 ± 0.0 a | HYP | 33.2 ± 4.6 b | 26.8 ± 3.2 b | 17.6 ± 2.6 a |
| GLY | 4.2 ± 0.5 c | 3.0 ± 0.6 b | 1.4 ± 0.2 a | GLY | 108 ± 17 b | 101 ± 24 b | 64.7 ± 9.0 a |
| THR | 3.8 ± 0.6 c | 1.5 ± 0.3 b | 0.6 ± 0.0 a | THR | 19.6 ± 1.0 a | 18.0 ± 2.2 a | 23.6 ± 1.8 b |
| ALA | 16.4 ± 1.6 c | 9.7 ± 3.0 b | 4.1 ± 0.6 a | ALA | 68.9 ± 5.0 b | 61.5 ± 11 ab | 48.0 ± 4.6 a |
| PRO | 0.5 ± 0.1 ab | 0.7 ± 0.2 b | 0.3 ± 0.1 a | PRO | 57.9 ± 5.3 a | 55.3 ± 11 a | 41.9 ± 6.9 a |
| MET | 6.9 ± 0.7 c | 1.5 ± 0.3 b | 0.4 ± 0.0 a | MET | 16.6 ± 2.9 a | 15.2 ± 3.2 a | 17.1 ± 1.7 a |
| ASP | 3.5 ± 0.9 c | 1.8 ± 1.0 b | 0.3 ± 0.0 a | ASP | 49.6 ± 1.4 a | 49.6 ± 8.4 a | 58.8 ± 7.3 a |
| VAL | 8.9 ± 1.4 b | 1.6 ± 0.6 a | 0.4 ± 0.2 a | VAL | 24.2 ± 1.2 a | 24.8 ± 5.6 a | 29.7 ± 3.5 a |
| HIS | 4.4 ± 0.7 b | 0.5 ± 0.1 a | 0.1 ± 0.0 a | HIS | 11.8 ± 1.5 a | 13.2 ± 3.3 a | 15.1 ± 2.3 a |
| LYS | 4.6 ± 1.1 b | 0.6 ± 0.3 a | 0.3 ± 0.1 a | LYS | 47.0 ± 2.7 a | 43.3 ± 5.8 a | 63.5 ± 9.7 b |
| GLU | 4.3 ± 0.6 b | 3.3 ± 2.0 b | 0.9 ± 0.0 a | GLU | 82.6 ± 4.5 a | 70.3 ± 11 a | 84.0 ± 10 a |
| TRP | 1.2 ± 0.2 b | 0.2 ± 0.0 a | 0.1 ± 0.0 a | TRP | 0.2 ± 0.1 a | 0.2 ± 0.3 a | 0.2 ± 0.2 a |
| LEU | 6.9 ± 1.3 c | 3.0 ± 0.5 b | 0.5 ± 0.2 a | LEU | 36.5 ± 5.4 a | 31.3 ± 6.2 a | 37.8 ± 2.8 a |
| PHE | 8.0 ± 0.7 b | 1.2 ± 0.1 a | 0.4 ± 0.0 a | PHE | 16.7 ± 3.4 a | 18.3 ± 4.1 a | 19.3 ± 2.0 a |
| ILE | 8.0 ± 1.0 c | 3.5 ± 0.6 b | 0.7 ± 0.3 a | ILE | 19.9 ± 2.8 a | 19.4 ± 3.9 a | 25.0 ± 4.0 a |
| C-C | 0.1 ± 0.0 | C-C | 1.8 ± 0.1 a | 2.4 ± 0.3 b | 4.4 ± 0.3 c | ||
| TYR | 4.2 ± 0.5 c | 1.1 ± 0.2 b | 0.5 ± 0.0 a | TYR | 6.1 ± 0.6 a | 9.2 ± 1.3 b | 14.0 ± 1.9 c |
| SUM | 112 ± 15 c | 45.8 ± 13 b | 16.4 ± 1.2 a | SUM | 695 ± 57 a | 641 ± 103 a | 649 ± 70 a |
| Sample 1 | Mw (kDa) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| >200 | 200–100 | 100–10 | 10–1 | 1 | ||
| No Enzymes, Control (C) | A_½ hC (N_½ hC) | 49.1 | 50.9 | |||
| A_pHn_½ hC | 45.0 | 55.0 | ||||
| P_½ hC | 26.5 | 73.5 | ||||
| A_P_3hC | 41.8 | 58.2 | ||||
| N_6hC | 47.6 | 28.0 | 24.4 | |||
| Enzyme Added (E) | N_6hE | 1.8 | 29.1 | 53.2 | 15.9 | |
| P_6hE | 15.4 | 84.6 | ||||
| A_P_3hE | 0.3 | 1.5 | 3.2 | 95.0 | ||
| A_3hE | 0.3 | 0.6 | 2.1 | 97.0 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marinou, D.; Jacobsen, C.; Odelli, D.; Sarigiannidou, K.; Sørensen, A.-D.M. Production of Protein Hydrolysates from Cod Backbone Using Selected Enzymes: Evaluation of Antioxidative and Antimicrobial Activities of Hydrolysates. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23030125
Marinou D, Jacobsen C, Odelli D, Sarigiannidou K, Sørensen A-DM. Production of Protein Hydrolysates from Cod Backbone Using Selected Enzymes: Evaluation of Antioxidative and Antimicrobial Activities of Hydrolysates. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(3):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23030125
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarinou, Dimitra, Charlotte Jacobsen, Davide Odelli, Krystalia Sarigiannidou, and Ann-Dorit Moltke Sørensen. 2025. "Production of Protein Hydrolysates from Cod Backbone Using Selected Enzymes: Evaluation of Antioxidative and Antimicrobial Activities of Hydrolysates" Marine Drugs 23, no. 3: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23030125
APA StyleMarinou, D., Jacobsen, C., Odelli, D., Sarigiannidou, K., & Sørensen, A.-D. M. (2025). Production of Protein Hydrolysates from Cod Backbone Using Selected Enzymes: Evaluation of Antioxidative and Antimicrobial Activities of Hydrolysates. Marine Drugs, 23(3), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23030125











