Abstract
In recent years, marine natural products have continued to serve as a pivotal resource for novel drug discovery. Globally, the number of studies focusing on Porifera has been on the rise, underscoring their considerable importance and research value. Marine sponges are prolific producers of a vast array of bioactive compounds, including terpenes, alkaloids, peptides, and numerous secondary metabolites. Over the past fifteen years, a substantial number of sponge-derived terpenes have been identified, exhibiting extensive structural diversity and notable biological activities. These terpenes have been isolated from marine sponges or their associated symbiotic microorganisms, with several demonstrating multifaceted biological activities, such as anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, cytotoxic, anticancer, and antioxidant properties. In this review, we summarize 997 novel terpene metabolites, detailing their structures, sources, and activities, from January 2009 to December 2024. The structural features and structure-activity relationship (SAR) of different types of terpenes are broadly analyzed and summarized. This systematic and comprehensive review will contribute to the summary of and speculation on the taxonomy, activity profiles, and SAR of terpenes and the development of sponge-derived terpenes as potential lead drugs.
1. Introduction
Marine sponges represent the most primitive form of multicellular animals, characterized by a specialized luminal tubular structure. After more than 500 million years of evolution, marine sponges have developed a unique chemical and physical defense mechanism to adapt to the high-pressure, high-salted, anoxic, and lucifugal environment []. Therefore, they produce a wide range of valuable secondary metabolites with multiple biological activities. Growing evidence indicates that sponges harbor a wealth of symbiotic or epiphytic microorganisms in their bodies, which are likely to be the true producers of bioactive secondary metabolites []. In some cases, these microbial associates comprise as much as 40% of the sponge volume and can contribute significantly to host metabolism []. These microorganisms not only serve as food for sponges but also play a crucial role in forming the defensive mechanisms of sponges []. The mutually beneficial symbiotic relationship between sponges and microorganisms exhibits rich chemical diversity, which is important for obtaining symbiotic natural products of significant biotechnological value [].
Indeed, sponges have great potential for discovering new drug candidates that can aid in the prevention and treatment of disease []. For example, Cytosar-U® (Ara-C), a secondary metabolite derived from the Caribbean sponge Cryptotheca crypta, was approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of leukemia in 1969, and it is still in use today for the treatment of acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) [,]. A large number of natural compounds are under preclinical investigation, and others are already on the market as drugs. Among the seven marine-derived drugs currently approved by the FDA, three are derived from sponges. In addition to Ara-C, which was mentioned earlier, there are vidarabine (Vira-A, Ara-A) and eribulin mesylate (Halaven®) []. However, none of them are terpenes. Nevertheless, some terpenoids derived from sponges have shown great potential for drug development in preclinical studies. Stellettin B is a marine triterpene isolated from the South China Sea sponge Jaspis stellifera. The research showed that stellettin B reduced the migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through reducing the activation of the MAPKs and FAK/PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathways []. It also ameliorated collagen-induced arthritis in mice and had anti-glioblastoma cancer and anti-non-small cell lung cancer activities [,,]. The chemical and biological investigation of marine sponges has consistently been one of the most active subfields within natural pharmaceutical discovery.
During the last fifteen years, it has been seen that sponge-associated terpenes have diverse chemical structures and a wide variety of biological activities (antimicrobial, antitumor, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, antimalarial, antitubercular, anti-aging, antifouling, and antiprotozoal) [,,]. Previous reviews have only generalized to a particular class of sponges, or a particular class of terpenes, such as nitrogen-containing or triterpenes, and have covered a short period of time [,,]; hence, the need for a comprehensive review that encompasses a substantial amount of data. This review collects all the related literature from January 2009 to December 2024 and completely describes the new sponge-associated terpenes from 249 articles. Figure 1 illustrates the percentage of different activities of new compounds discovered from January 2009 to December 2024. It is evident that cytotoxicity represents the biological activity with the most substantial proportion. Among the four primary terpenes contributing to this activity, sesterterpenes hold the largest share, followed by sesquiterpenes and diterpenes.
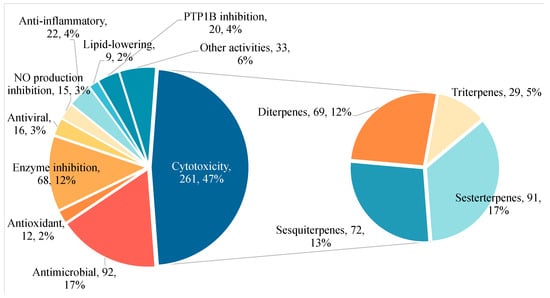
Figure 1.
Percentage distribution of new compounds with different bioactivities for 2009–2024.
A similar trend is observed for the total number of active compounds in each terpene category during 2009–2024 (Figure 2). However, there is no doubt that one compound can only be classified as active or inactive. While they are classified into specific type of activity, they may be reclassified as having multiple activities.
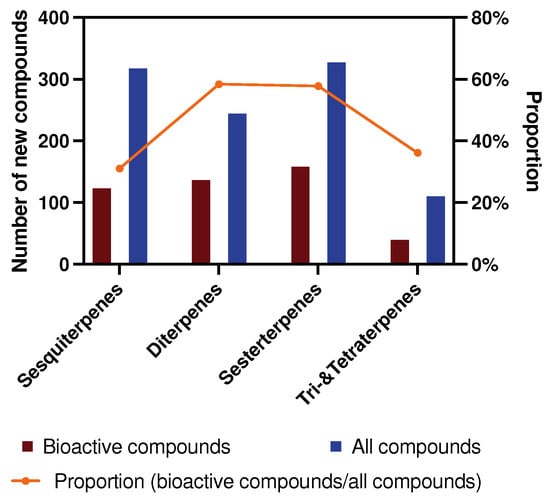
Figure 2.
The number and proportion of new bioactive compounds in different terpenes for 2009–2024.
Notably, with the increasing emphasis on, as well as the depth of research in, the field of marine sponges, the number of new sponge-derived compounds is on an overall downward trend. Similarly, the share of active compounds is also decreasing, especially reaching a low point in the years 2018–2020. However, in recent years, the number of new compounds has been on the rise with the advances in collection equipment and innovations in isolation methods, indicating that there is still a wealth of active compounds waiting to be discovered (Figure 3).
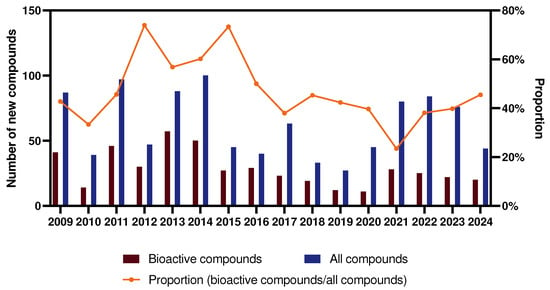
Figure 3.
Trends in the number and proportion of new bioactive compounds for 2009–2024.
2. Methodology
The data collection for this research was conducted using the major online databases Web of Science and PubMed, employing the following descriptors: marine sponge, new terpene and terpene, and new terpenoid and terpenoid. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) a publication date from 1 January 2009 to 31 December 2024; (2) written in English; (3) terpenes were first found in the article. Initially, 496 results were identified (325 from PubMed and 171 from Web of Science). The exclusion criteria included the following: (1) book chapters and patents; (2) duplicate studies; (3) studies that were not within the scope; (4) terpenes that were not new. As a result of this survey, the articles included in this systematic review comprise 249 publications and 997 compounds (Figure 4).
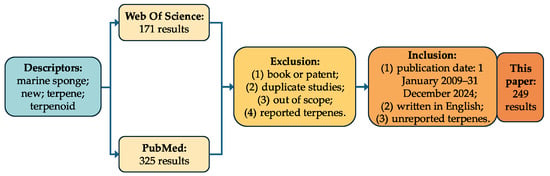
Figure 4.
The data collection flowchart of this research.
3. Different Class of Terpenoids
3.1. Sesquiterpenes
The drimane-type sesquiterpene is a saturated naphthalene alkane with 15 carbons. Compounds 1–7 were isolated from the marine fungus Aspergillus ustus derived from the marine sponge Suberites domuncula []. Compounds 4 and 5 showed cytotoxic activities against the L5178Y cell line with EC50 values of 5.3 and 0.6 μg/mL, respectively. Compound 8 was obtained from an EtOAc extract of the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus insuetus, which was isolated from the Mediterranean sponge Psammocinia sp. []. Compound 8 showed mild cytotoxicity towards MOLT-4 human leukemia cells. Two new drimane-type terpenes (9–10) were isolated from the marine sponge Hyrtios sp. collected from Papua New Guinea []. In 2015, eight 4,9-friedodrimane-type sesquiterpenoids (11–18) were acquired from the marine sponges Smenospongia aurea, Smenospongia cerebriformis, and Verongula rigida collected from Key Largo, Florida []. Compounds 12 and the mixture of 13 and 14 started to exert antiproliferative activities at a concentration of more than 20 μM. Compound 18 inhibited tumor growth against the SW480 and HCT116 cell lines with IC50 values of 3.24 and 2.95 μM, respectively. Further investigation revealed that 18 displayed more potent cytotoxic activity on a suppressed β-catenin response in the transcription of (CRP)-positive cancer cell. Compounds 19–24, which consisted of quinone (hydroquinone) and sesquiterpene moieties, were isolated from the marine sponge Dysidea sp. collected from the Federated States of Micronesia []. Notably, these compounds exhibited moderate to weak inhibition against Na+/K+-ATPase and cytotoxic activities towards the K562 and A549 cell lines. Three phenylspirodrimane-based meroterpenoids (25–27) with novel scaffolds were isolated from the sponge Niphates recondite-associated fungus Stachybotrys chartarum WGC-25C-6 []. Chartarolides A–C (25–27) exhibited remarkable cytotoxic activities against the HCT-116, HepG2, BGC-823, NCI-H1650, A2780, and MCF7 human tumor cell lines with IC50 values around 1.3 to 12.5 μM and showed strong inhibitory activities against the human tumor-related protein kinases of FGFR3, IGF1R, PDGFRb, and TrKB with IC50 values ranging from 2.6 to 20.3 μM.
Ebada and coworkers investigated a MeOH extract of the Indonesian marine sponge Dactylospongia elegans, afforded two undescribed drimane meroterpenoidal metabolites named dactylospongenones G and H (28–29) []. Yu and colleagues isolated ten sesquiterpenes (30–39) of different types from the sponge Pseudoceratina purpurea []. Pseudoceranoid D (33) showed weak cytotoxicity against the K562, H69AR, and MDAMB-231 cell lines with IC50 values of 3.01, 7.74, and 9.82 μM, respectively. Pseudoceranoid E (34) exhibited cytotoxicity against the H69AR cell line with an IC50 value of 2.85 μM. Daletos et al. had reported five new sesquiterpene aminoquinones (40–44) and two new sesquiterpene benzoxazoles (45–46) from the sponge Dactylospongia metachromia collected from Ambon, Indonesia []. Moreover, compounds 40–44 showed potent cytotoxicity against the mouse lymphoma cell line L5178Y with IC50 values ranging from 1.1 to 3.7 μM, and compounds 46 and 46 exhibited the strongest inhibitory activities against the ALK, FAK, IGF1-R, SRC, VEGF-R2, Aurora-B, and MET wt cell lines and NEK6 kinases (IC50 = 0.97–8.62 μM). Compounds 47–51 were isolated from the sponge Dactylospongia elegans collected in Palau and Malaysia []. The compounds 47 and 48 were found to activate HIF-1 and stimulate the expression of the HIF-1 target gene vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in both T47D and PC-3 cells. Compounds 52–54 were isolated and characterized from the Hyrtios sp. collected from the South China Sea []. Hyrtiolacton A (52) is the first example of a pyrone-containing 4,9-friedodrimane-type sesquiterpene. Nakijinol G (54) showed PTP1B inhibitory activity with IC50 values of 4.8 μM. Eleven new nitrogenous meroterpenoids (55–65) were isolated from the marine sponge Dysidea cinerea collected in the South China Sea []. Compounds 55–57 and 60 exhibited moderate inhibitory activities against PTP1B, ATP-citrate lyase, and SH2 domain-containing phosphatase-1 with IC50 values of 2.8–27 μM.
The chemical structures of compounds 1–65 are depicted in Figure 5, while the remaining information, including names and marine sources, is presented in Table S1.
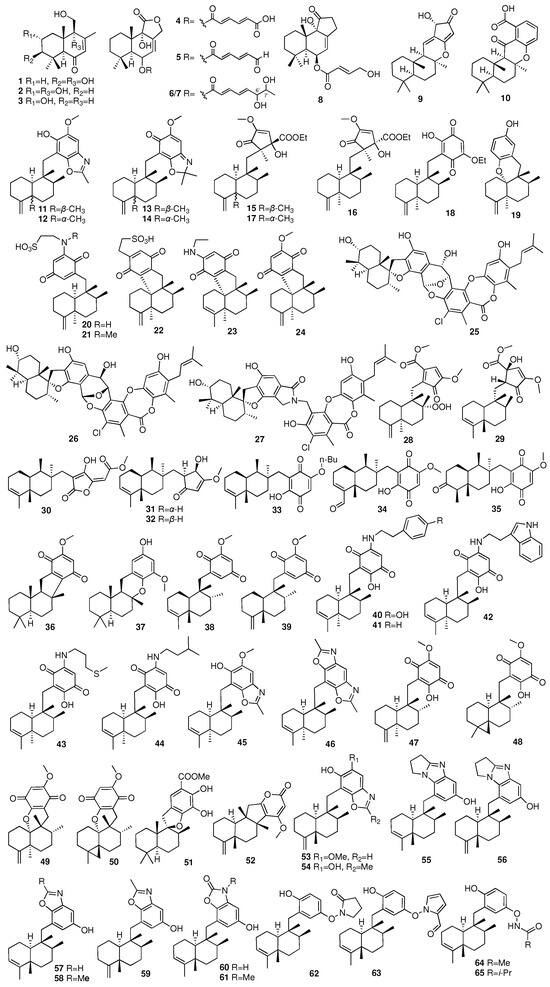
Figure 5.
Chemical structures of compounds 1–65.
Bisabolane-type sesquiterpenoids, a class of monocyclic sesquiterpenoids, are widely distributed in nature and have a variety of biological activities. Compounds 66–68 were isolated from the marine sponge Cacospongia mycofijiensis collected from Papua New Guinea []. Two of them (66 and 67) showed moderate inhibition against the parasite Trypanosoma brucei, which is responsible for sleeping sickness, with IC50 values of 6 and 16 μg/mL, respectively. Compound 69 had been isolated from the sponge Phycopsis sp. collected from the Mandapam coast in India []. Two new uncommon bisabolene-type sesquiterpenes (70–71) were isolated from the sponge Axinyssa sp. off the Lingshui Bay, Hainan Province, China []. Compounds 72–75 were isolated from the fungus Aspergillus sp., which was obtained from the sponge Xestospongia testudinaria collected from the South China Sea []. The antibacterial activity and in vitro cytotoxic activity tests revealed that 72–75 showed selective inhibitory activities on six pathogenic bacteria—S. albus, B. subtilis, B. cereus, S. lutea, E. coli, and M. tetragenus—and two marine bacterial strains, V. Parahaemolyticus and V. anguillarum. Moreover, 75 strongly inhibited larval settlement at a concentration of 25 μg/mL. Compounds 72–75 were also found to have weak-to-no inhibitory activity against the HL-60 and A-549 cell lines and acetylcholinesterase. The other three compounds, 76–78, were isolated from the same fungus and tested for the same activity []. The tests revealed that 76–78 showed selective inhibitory activities on all strains. In addition, 76 and 78 exhibited moderate cytotoxicity towards the HepG-2 human hepatoma cell line and Caski human cervical cell line.
An investigation of a Formosan sponge Axinyssa sp. collected from coral reefs off the coast of Pingtung in Taiwan, China, has led to the isolation of two nitrogenous bisabolene-type sesquiterpenes (79–80) []. Compound 79 exhibited moderate-to-weak cytotoxicity against the Molt4 and K562 cancer cell lines with IC50 values of 14.3 and 4.7 μg/mL, respectively. In 2016, a chemical investigation of the marine sponge Axinyssa variabilis yielded two new highly oxidized formamide bisabolene sesquiterpenes (81–82) []. A new rearranged nitrogenous bisabolene-type sesquiterpene, halichonic acid B (83), was obtained from the marine sponge Axinyssa sp. collected from the same place []. Wang and colleagues isolated six new bisabolane-type phenolic sesquiterpenoids, including plakordiols A-D (84–87), (7R, 10R)-hydroxycurcudiol (88), and (7R, 10S)-hydroxycurcudiol (89) from the marine sponge Plakortis simplex collected from the South China Sea []. Compound 88 inhibited bone morphogenic protein (BMP)-induced alkaline phosphatase activity in mutant BMP receptor-carrying C2C12 cells with IC50 values of 51 μM. The chemical structures of compounds 66–89 are depicted in Figure 6.
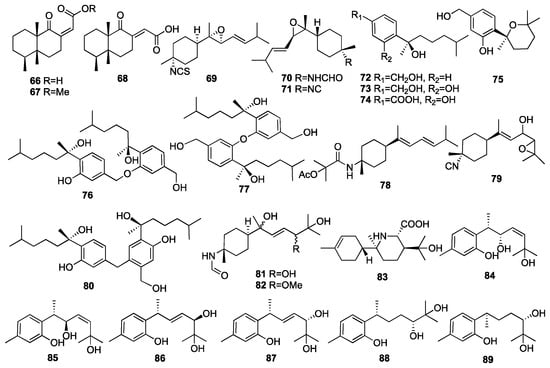
Figure 6.
Chemical structures of compounds 66–89.
Sesquiterpene quinone/quinols are characterized by a C15-sesquiterpenoid unit incorporating a C6-benzoquinone/quinol moiety []. In 2009, a new sesquiterpene aminoquinone named dysideamine (90) was obtained from the Indonesian marine sponge Dysidea sp. []. Compound 90 showed a neuroprotective effect against iodoacetic acid (IAA)-induced HT22 cell death at a concentration of 10 μM. Researchers from the Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica reported a new sesquiterpene quinone (91), which was isolated from the sponge Dysidea villos []. Compound 91 showed moderate PTP1B inhibitory activity and cytotoxicity with IC50 values of 39.50 and 19.45 μM, respectively. Takahashi et al. reported two new dimeric sesquiterpenoid quinones, nakijiquinones E-F (92–93), and nine sesquiterpenoid quinones, nakijiquinones J-R (94–102), from different sponges identified as Spongia sp., Sponge SS-1047, SS-265, and SS-1208 [,]. Compounds 103–106 were isolated from the South China Sea sponge Dysidea avara []. These compounds possessed the unprecedented “dysidavarane” carbon skeletons. Compound 103 showed growth inhibitory activity against the HeLa cell with an IC50 value of 39.9 μM, and dysidavarone D (106) showed cytotoxicity against four cell lines (HeLa, A549, MDA231, and QGY7703) with IC50 values of 28.8, 21.4, 11.6, and 28.1 μM, respectively. In addition, compounds 103 and 106 also exhibited inhibitory activities against PTP1B with IC50 values of 9.98 and 21.6 μM, respectively. Moreover, dysidavarone A (103) was totally synthesized in 2013 []. In 2012, three new sulfated meroterpenoids (107–109), including sesquiterpene and hydroquinone moieties, were isolated from the sponge Aka coralliphaga collected from southern Mexico []. All the compounds showed less potent radical-scavenging effects than Trolox. An indoesesquiterpene hydroquinone (110) and a bissesquiterpene hydroquinone (111) were isolated from the Thai sponge Smenospongia sp. []. Additionally, compounds 110 and 111 showed weak cytotoxicity against MOLT-3, HepG2, A549, HuCCA-1, HeLa, HL-60, and MDA-MB-231 with IC50 values ranging from 40.0 to 68.2 μM.
An investigation of the marine sponge Dysidea avara afforded a new sesquiterpene (-)-N-methylmelemeleone-A (112) []. Compound 112 showed very weak cytotoxic activity on human colon carcinoma cells, mouse lymphoma cells, and rat hepatoma cells. Compounds 113–115 were isolated with unprecedented carbon skeletons from the South China Sea sponge Dysidea avara []. Dysideanone B (114) showed cytotoxicity against the HeLa and HepG2 cell lines with IC50 values of 7.1 and 9.4 μM, respectively. Furthermore, compound 114 exhibited significant inhibitory effects on the nitric oxide production induced by lipopolysaccharide at 10 μM. Compounds 116–119 were isolated from the Caribbean sponge Aka coralliphagum collected off the coast of San Salvador in the Bahamas []. Compound 118 exhibited weak activity against the Gram-positive bacteria Staphylococcus aureus and Micrococcus luteus, and compound 119 showed cytotoxic activities against the L929 mouse fibroblasts, KB-31 epidermoid carcinoma, and breast cancer cell line MCF7. Three new sesquiterpene hydroquinones (120–122) were isolated from the marine sponge Dysidea sp. collected from Okinawa []. Compounds 120–122 had PTP1B inhibitory activities with IC50 values of 11, 9.5, and 6.5 μM, respectively. Two new sesquiterpene aminoquinones (123–124) were acquired from the sponge Spongia sp., which was collected in Vietnam []. Compounds 123 and 124 exhibited remarkable antibacterial activities against Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis with MIC values ranging from 6.25 to 12.5 μM. In contrast, they were inactive against Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli. The chemical structures of compounds 90–127 are depicted in Figure 7.
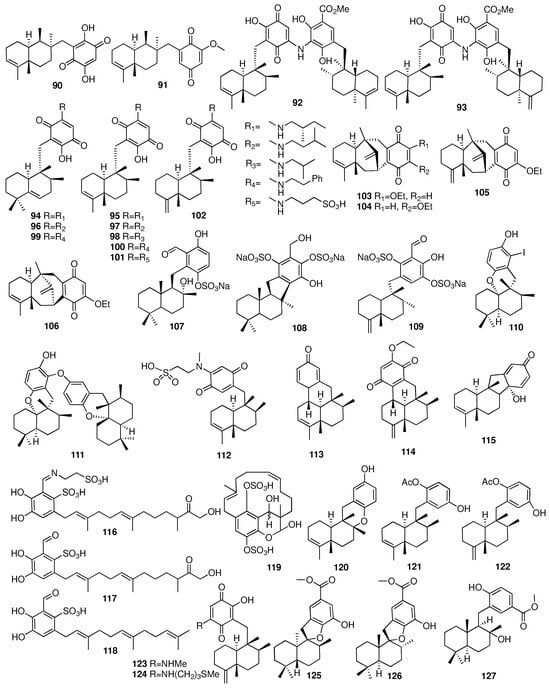
Figure 7.
Chemical structures of compounds 90–127.
Compounds 125–128 were isolated from the sponge Dysidea sp., which was collected from the South China Sea []. Compound 128 showed more potent antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, and Staphylococcus aureus than the other compounds. Eight new sesquiterpene quinones/hydroquinones (129–136) and one solvent-generated artifact (137) were isolated from the marine sponge Spongia pertusa Esper []. Compound 134 displayed CDK-2 affinity with a Kd value of 4.8 μM, and it was the first example of a marine sesquiterpene quinone with CDK-2 affinity. A new sesquiterpene quinone, neoisosmenospongine (138), was isolated though methods guided by bioassays. The marine sponge Dactylospongia metachromia was collected from Bajotalawaan in North Sulawesi []. In 2022, Chen and colleagues isolated four new sesquiterpene hydroquinones, xishaeleganins A–D (139–142), from the Xisha marine sponge Dactylospongia elegans []. Compound 140 showed significant antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus with a minimum inhibitory concentration value of 1.5 μg/mL. Dysideanones F-G (143–144) and dysiherbols D–E (145–146) were isolated from the marine sponge Dysidea avara collected from the South China Sea []. An anti-inflammatory evaluation showed that dysiherbols D–E exhibited moderate inhibitory activity on TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation in human HEK-293T cells with IC50 values of 10.2 and 8.6 μmol·L–1, respectively. Li and colleagues isolated six new sesquiterpene quinone/hydroquinone meroterpenoids, arenarialins A–F (147–152), from the marine sponge Dysidea arenaria collected from the South China Sea []. Arenarialins A–F showed inhibitory activities on the production of the inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-6 in LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophages with arenarialin D regulating the NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathway.
Takahashi et al. reported two novel merosesquiterpenoids (153–154) from different sponges identified as Spongiidae sp. []. Lastly, compounds 153 and 154 exhibited antimicrobial activities against Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, Micrococcus luteus, Aspergillus niger, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Candida albicans, and Cryptococcus neoformans. In 2010, a chemical investigation of the sponge Agelas nakamurai collected from Menjangan Island in Indonesia afforded two new diterpenes (155–156), containing the adenine-related moiety []. Compound 155 showed antibacterial activity against the planktonic form of S. epidermidis (MIC < 0.0877 μM) but did not inhibit biofilm formation. On the contrary, compound 156 showed biofilm formation inhibition but did not inhibit the growth of the planktonic bacteria. Utkina et al. isolated four new sesquiterpenoid arenarone derivatives (157–160) and a novel dimeric popolohuanone F (161) from the CHCl3 extract of the Australian marine sponge Dysidea sp. []. Compound 161 showed 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging activity with an IC50 value of 19 μM. Two new sesquiterpenoids (162–163) were obtained from a culture broth of the seawater-derived fungus Trichoderma sp. TPU1237 isolated from the marine sponge Dysidea sp. []. The IC50 values of compounds 162 and 163 against PTP1B were 53.1 and 65.1 μM, respectively. A few months later, they reported another merosesquiterpenoid (164) from another marine sponge Dysidea sp. []. Its absolute configuration was established by single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. Additionally, dysidinoid A (164) showed potent antibacterial activity against one strain of pathogenic bacteria, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), with an MIC90 value of 8.0 μg/mL. Four new tetracyclic meroterpenes (165–168) were isolated from an organic extract of the Dysidea sp. collected from the Xisha Islands []. The chemical structures of compounds 128–168 are depicted in Figure 8.
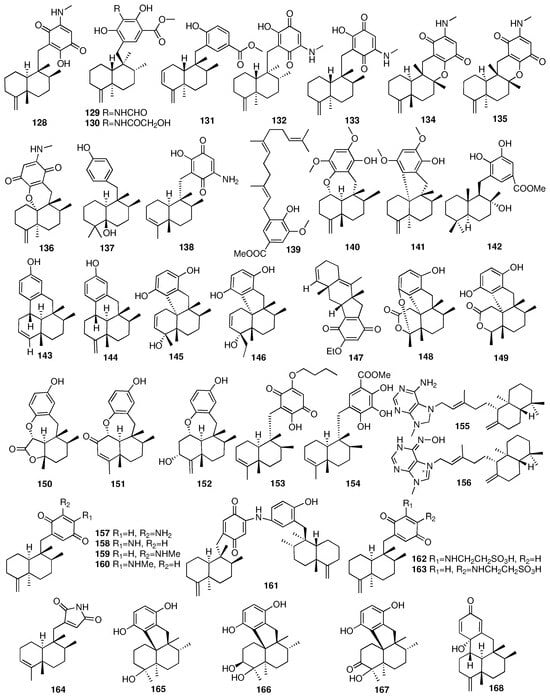
Figure 8.
Chemical structures of compounds 128–168.
Compound 169 was isolated by bioactivity-guided fractionation from a sponge-derived fungus Acremonium sp. obtained from the marine sponge Stelletta sp. J05B-1. The unique cyclic skeleton of compound 169 was unprecedented. Compounds 170–172 were isolated by bioactivity-guided fractionation from a sponge-derived fungus Acremonium sp. obtained from the marine sponge Stelletta sp. J05B-1 []. Three new nitrogen-containing terpenes (173–175) were isolated from the sponge Dysidea robusta collected in Brazil []. Compound 175 was the first furodysinin sesquiterpene derivative with a trans junction between the two six-membered rings of the 1,2,3,4,4a,7,8,8a-octahydro-1,1,6-trimethylnaphthalene moiety. Researchers from the Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica reported two new acetonyl-bearing sesquiterpenes (176–177) []. These metabolites were isolated from the sponge Dysidea fragilis collected from Hainan in China. Compounds 176 and 177 showed a weak inhibitory effect with inhibitory rates of 9.9% and 11.5% at a concentration of 20 μg/mL. In a study on the marine sponge Negombata corticata, four norterpene-related peroxides (178–181) were identified from its EtOH extract []. Compound 182 and its acetylated derivative (183), as well as two new sesquiterpene quinones (184–185), were isolated from the marine sponge Dactylospongia elegans, which was collected from Pugh Shoal, northeast of Truant Island []. All the compounds were found to have activities against human tumor cell lines (SF-268, H460, MCF-7, and HT-29) in the range of 1.8–46 μM. In the same year, they obtained three new merosesquiterpenoids (186–188) that were isolated from the marine sponge Thorecta reticulata collected off Hunter Island, Tasmania, Australia []. The cytotoxicity of compounds 186–188 was also assessed against a panel of human tumor cell lines (SF-268, H460, MCF-7, and HT-29) and a mammalian cell line (CHOK1). All the compounds were found to have 50% growth inhibition activities in the range of 2.1–130 μM, with compound 188 being the most active. Suto and coworkers isolated three new dimeric sesquiterpenoids (189–191) and one new eudesmane-type sesquiterpenoid (192) from the marine sponge Halichondria sp. collected from Unten Port in Okinawa []. Another six new metabolites of acremines A to R (193–198) were isolated from the fungus Acremonium persicinum cultured from the marine sponge Anomoianthella rubra []. Kiem and coworkers isolated seven new muurolane-type sesquiterpenes (199–205) from the marine sponge Dysidea cinerea [].
Researchers from the Tohoku Pharmaceutical University obtained three new unique sesquiterpenes (206–208) from the marine sponge Euryspongia sp. collected from Iriomote Island in Japan [], and the absolute configuration of 206 was determined after two years []. Compounds 209–213 were isolated from crude extracts of the marine sponge Ircinia sp. []. Two terpenoids (209, 212) showed PPARδ agonistic activities with EC50 values of 18 and 30 μg/mL, respectively. Wu et al. reported six new caryophyllene-based sesquiterpenoids (214–219) from the fungus Hansfordia sinuosae isolated from the South China Sea sponge Niphates sp. []. All the compounds showed weak cytotoxic activity against HCT-8, Bel7402, BGC823, A549, and A2780 with IC50 values of more than 10 μM. These compounds also showed weak inhibitory effects against the bacterial strains of Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus thuringensis, and Bacillus subtilis with MIC values of more than 125 μM. In addition, punctaporonin K (217) exhibited potent effects to reduce the triglycerides and total cholesterol at the intracellular level. Compounds 220–221 were isolated from a rice solid culture medium of the fungus Penicillium adametzioides AS-53 obtained from an undescribed sponge collected from Hainan Island in the South China Sea []. Compound 221 showed selective activity against the NCI-H446 cell line with an IC50 value of 5.0 μM. An investigation into the Hainan sponge Axinyssa variabilis yielded four new uncommon nitrogenous eudesmane-type sesquiterpenes (222–225) []. Compound 226 was isolated from the sponge Carteriospongia foliascens collected from the South China Sea []. The chemical structures of compounds 169–228 are depicted in Figure 9.
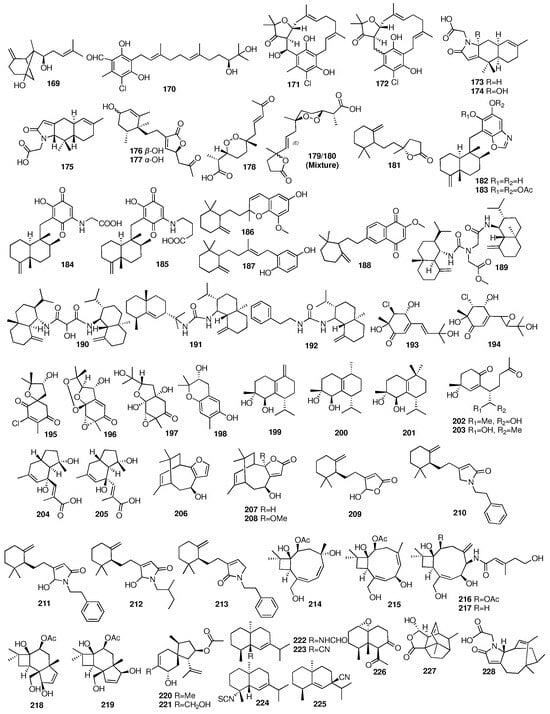
Figure 9.
Chemical structures of compounds 169–228.
Two new structurally unique bridged polycyclic sesquiterpenes (227–228) and two polycyclic sesquiterpenes (229–230) were obtained from the marine sponge Lamellodysidea herbacea, which was collected in Indonesia []. Eight new biosynthetically and chemically related sesquiterpenes (231–238) were isolated from the southern Australian marine sponge Dysidea sp. (CMB-01171) by the GNPS molecular networking approach []. Zhang and colleagues isolated ten undescribed eremophilanes, namely, copteremophilanes A-J (239–248), from a marine sponge Xestospongia testudinaria-associated fungus Penicillium copticola collected in Weizhou Island []. Ohte and colleagues isolated one new unique sesquiterpene lactone, bicyclolamellolactone A (249), from the Indonesian marine sponge Lamellodysidea sp. [] The Utkina et al. research group on a different marine sponge Dysidea sp. yielded a new unsymmetrical puupehenone-related dimer (250) []. In addition, diplopuupehenone (250) showed DPPH radical scavenging activity with an IC50 value of 8 μM. University of Hawaii researchers found a new potent antioxidant and antimicrobial meroterpenoid, puupehenol (251), from the deep-water Hawaiian sponge Dactylospongia sp. []. Compound 251 showed pronounced antioxidant properties and was relatively active towards the Gram-positive bacteria Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus cereus. Compound 252 was isolated from the mycelial extract of the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus aculeatus CRI323-04 obtained from the sponge Xestospongia testudinaria, and it possessed a novel [,] fenestrane ring system [].
Liang and colleagues in Jinan University isolated a pair of new valerenane sesquiterpene enantiomers (253–254) from the marine sponge Spongia sp. []. In 2018, researchers from the Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica had reported two rare new furano-trinorsesquiterpenoids (255–256), which were isolated from the n-BuOH portion of the Beihai sponge Spongia officinalis []. Further separation led to their corresponding enantiomers. All the new compounds were found to exhibit inhibitory activity against LasR and functioned as Pseudomonas aeruginosa QS inhibitors. Three new spiro-sesquiterpenoids, myrmekiones A–C (257–259), were isolated from the marine sponge Myrmekioderma sp. collected from the South China Sea []. Shen and coworkers conducted a detailed chemical investigation of the South China Sea nudibranch Hexabranchus sanguineus, as well as its possible prey the sponge Acanthella cavernosa, leading to the isolation of fifteen new nitrogenous sesquiterpenoids, namely, ximaocavernosins A–O, including seven cadinanes (260–266), seven spiroaxanes (267–273), and one aromadendrane (274) []. The same year, they isolated one new aromadendrane-type sesquiterpenoid (275) and three new cadinane-type sesquiterpenoids (276–278) from the Hainan sponge Acanthella cavernosa, namely, ximaocavernosin P, (+)-maninsigin D, (+)- and (−)-ximaocavernosin Q []. Four new nitrobenzoyl sesquiterpenoids, insulicolides D–G (279–282), were identified from Antarctican sponge-derived Aspergillus insulicola HDN151418. Further studies indicated that insulicolide D (279) could significantly suppress cell proliferation to induce apoptosis and blocked the migration and invasion of the pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cell lines with IC50 values of 2.3–22.9 μM [,]. The chemical structures of compounds 229–282 are depicted in Figure 10.
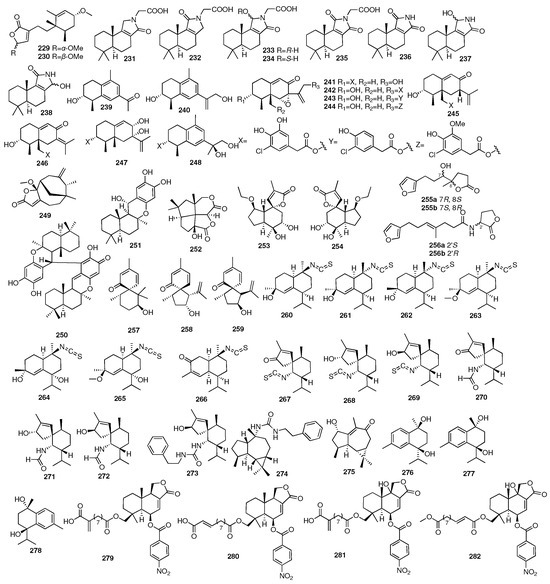
Figure 10.
Chemical structures of compounds 229–282.
Wen and colleagues isolated two new geosmin-type sesquiterpenoids and two new germacrane-type sesquiterpenoids under the guidance of MS/MS-based molecular networking, odoripenoids A–D (283–286) []. These compounds were obtained from the marine mesophotic zone sponge-associated Streptomyces sp. NBU3428. Compounds 283–284 showed anti-Candida albicans activity with MIC values of 16 and 32 μg/mL, respectively. Hao and colleagues isolated seven new sugar alcohol-conjugated acyclic sesquiterpenes, acremosides A–G (287–293), from a culture of the sponge-associated fungus Acremonium sp. []. IMB18-086 was cultivated with the heat-killed Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Acremosides A (287) and C–E (289–291) showed significant inhibitory activity against the hepatitis C virus (with EC50 values of 4.8–8.8 μM) with no cytotoxicity (CC50 of >200 μM). He and colleagues isolated one new marine fungus-derived sesquiterpenoid, Cpd-8 (294), that brought about TNF receptor superfamily-induced cell death []. Kiem and coworkers isolated an additional five new sesquiterpene derivatives (295–299) from another marine sponge Smenospongia cerebriformis in 2017 []. Compounds 295–299 showed moderate activity inhibiting LPS-stimulated NO production in BV2 cells with IC50 values ranging from 24.37 to 30.43 μM. Compounds 300–302 were isolated from the sponge Verongula cf. rigida collected in Thailand []. In particular, compound 300 was the first member of merosesquiterpenes with a polyketide side chain substituted on C-19. One new sesquiterpene, (+)-19-methylaminoavarone (303), was isolated from the Xisha Islands marine sponge Dysidea sp. It displayed various potent cytotoxic activities []. Fourteen undescribed nitrogenous merosesquiterpenoids, purpurols A–D (304–307) and puraminones A–J (308–317), were isolated from the sponge Pseudoceratina purpurea collected in the South China Sea []. In the bioassays, purpurols A and B showed weak anti-inflammation in zebrafish.
The chemical structures of compounds 283–317 are depicted in Figure 11, and the remaining information for compounds 66–317, including names and marine sources, is presented in Table S1.
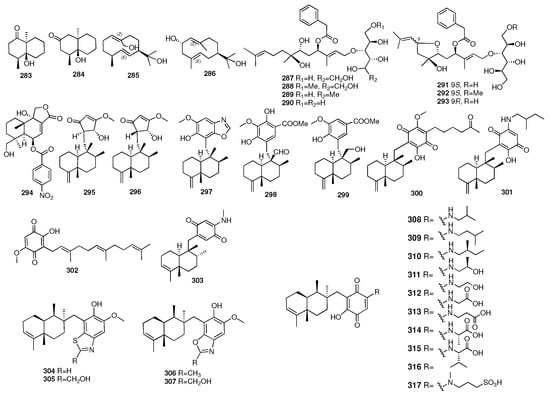
Figure 11.
Chemical structures of compounds 283–317.
3.2. Diterpenes
Diterpenes are a class of compounds consisting of four isoprene units with a wide range of activities. Compound 318 was isolated from the sponge Ciocalapata sp. []. It showed antimalarial activity with an IC50 value of 0.98 μg/mL. Chanthathamrongsiri et al. reported two new amphilectane-type diterpenes (319–320) from the sponge Stylissa cf. massa []. Compounds 319 and 320 had two different isonitrile-related functionalities. These two compounds showed antimalarial activity with IC50 values of 8.85 and 8.07 μM.
Spongian diterpenes are an important class of diterpenoid products. Compounds 321–322 were isolated from an unidentified sponge collected along the coast of Okinawa []. They exhibited significant cytotoxicty against NBT-T2 rat bladder epithelial cells with IC50 values of 5.6 and 12 μg/mL, respectively. In 2016, four additional new cytotoxic spongian diterpenes (323–326) were isolated from the acetone extract of Dysidea cf. Arenaria []. The cytotoxicity to NBT-T2 cells was examined, and they displayed IC50 values of 3.1, 1.9, 8.4, and 3.1 μM, respectively. Darwinolide (327) was isolated from the Antarctic dendroceratid sponge Dendrilla membranosa []. Darwinolide was cytotoxic against the biofilm phase of the methicillin-resistant S. aureus strain and J774 macrophage cell line with IC50 values of 33.2 and 73.4 μM. Moreover, it may provide a scaffold for the development of therapeutics for this difficult-to-treat infection. In 2017, an investigation of the sponge Darwinella cf. oxeata collected in Brazil afforded four new rearranged spongian diterpenoids (328–331) []. A chemical investigation of the Indonesian marine sponge Spongia ceylonensis had provided sixteen new spongian diterpene derivatives (332–347) [,,]. The inhibitory effects on the RANKL-induced osteoclasts in RAW264 macrophages revealed that ceylonin A (332) significantly inhibited the formation of multinuclear osteoclasts by 70% in a dose-dependent manner without cytotoxicity, followed by ceylonins E (336, 47%), F (337, 31%), and D (338, 28%).
In 2018, three new spongian diterpenes (348–350) were isolated from the acetone of the South China Sea sponge Spongia officinalis []. 3-nor-spongiolide A (348) had a rare 3-nor-spongian carbon skeleton, while 349 and 350 had γ-butenolide for ring D. A chemical investigation of the marine sponge Acanthodendrilla sp. collected in Pulau resulted in the isolation of two new spongian diterpene analogues (351–352) []. Bory and colleagues isolated three new diterpenes, Dendrillins B–D (353–355), from the Antarctic sponge Dendrilla antarctica, which was rich in defensive terpenoids with promising antimicrobial potential []. Compound 353 showed single-digit micromolar activity against the leishmaniasis parasite, and 354 had strong hits against MRSA biofilm cultures. Tai and colleagues isolated three new diterpenes, spongenolactones A–C (356–358), from a Red Sea sponge Spongia sp. They were the first 5,5,6,6,5-pentacyclic spongian diterpenes bearing a β-hydroxy group at C-1 []. All three compounds were found to exert inhibitory activity against superoxide anion generation in fMLF/CB-stimulated human neutrophils. Furthermore, 356 showed a higher activity against the growth of Staphylococcus aureus. Dyshlovoy and colleagues isolated a new diterpenen, spongionellol A (359), from the sponge Spongionella sp. []. It exhibited high activity and selectivity in human prostate cancer cells. Jin and colleagues isolated two new diterpenes (360–361) from the aquaculture sponge Spongia officinalis. Compound 360 showed cytotoxicity activity against the K562 cell line with an IC50 value of 7.3 μM []. Tai et al. isolated four new diterpenes, secodinorspongins A–D (362–365), from the Red Sea sponge Spongia sp. []. Compound 362 was found to exhibit inhibitory activity against the growth of S. aureus.
Sala and coworkers isolated two nitrogenous rearranged spongian nor-diterpenoids, dendrillic acids A (366) and B (367), from a marine sponge Dendrilla sp. There was mild antiprotozoal activity displayed by dendrillic acid B (367) against Giardia duodenalis []. Two new spongian furanoditerpenes (368–369) were isolated from a MeOH extract of the sponge Spongia tubulifera, collected in the Mexican Caribbean []. Compound 368 showed weak biological activity against the A549, A2058, HePG2, MCF-7, and MiaPaca-2 cell lines. Three new furanoditerpenoids (370–372) were isolated from the CH2Cl2 extract of the Spongia sp. collected from Fiji Islands []. One novel C21 terpenoidal metabolite (373) and two new C22 furanoterpenes (374–375) were isolated from the sponge Ircinia sp. collected from Orchid Island, Taiwan []. The pharmacological activitiy tests showed that compound 375 exhibited cytotoxicity against the K562, DLD-1, HepG2, and Hep3B cancer cell lines with IC50 values of 5.4, 0.03, 0.5, and 1.1 μM, respectively. Furthermore, compounds 374 and 375 were also found to exhibit significant cytotoxicity toward some cell lines. Thus, it is noteworthy to mention that the furan moiety in these compounds was critical for the cytotoxic activity of the C22 furanoterpenoids. Further investigation of the sponge Spongia officinalis has yielded a C21 furanterpene (376) [].
The chemical structures of compounds 318–376 are depicted in Figure 12, and the remaining information, including names and marine sources, is presented in Table S2.
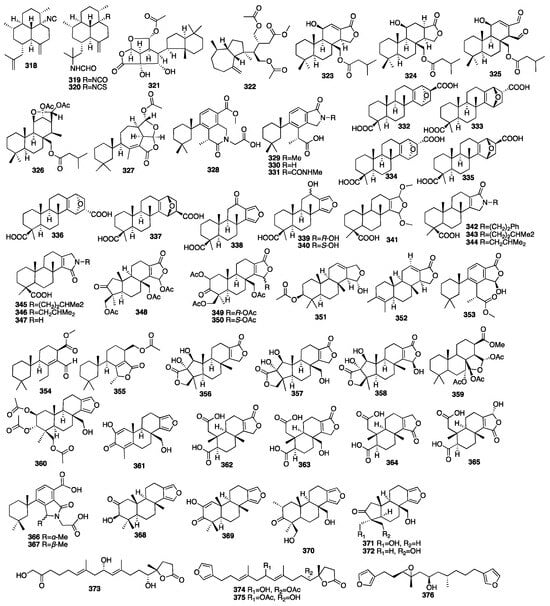
Figure 12.
Chemical structures of compounds 318–376.
Peter T. Northcote and colleagues isolated eleven new hamigeran-style diterpenes (377–387) from the New Zealand marine sponge Hamigera tarangaensis []. Most of these compounds have a unique tricyclic skeleton and moderate levels of cytotoxicity. Later, further investigation of the dictyoceratid marine sponge Hamigera tarangaensis yielded seven new members of the hamigeran family of diterpenoids (388–394) []. Most of the new hamigerans exhibited micromolar activity towards the HL-60 promyelocytic leukaemic cell line, and hamigeran G (378) also selectively displayed antifungal activity in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Compounds 395–403 were isolated from the marine sponge Hamigera tarangaensis collected from Cavalli Island, New Zealand []. Hamigeran M (395) exhibited the strongest degree of potency at a concentration of 6.9 μM, and the other compounds showed cytotoxicity against the HL-60 cell line with IC50 values ranging from 14.1 to 33.3 μM. Wojnar and coworkers investigated the extracts of the sponge Darwinella oxeata, and they obtained nine new nitrogenous spongian diterpenes (404–412) []. A spectroscopy-guided analysis of a Tongan dictyoceratid marine sponge afforded four new diterpenes (413–416) [].
Two new nitrogenous prenylbisabolanes (417–418) were isolated from the hexane and acetone extracts of the marine Lithistid sponge Theonella swinhoei, which was obtained from the coral reef of Iriomote Island in Japan []. Compounds 419–421 were isolated from an EtOAc extract of the marine sponge Spongia officinalis collected from the South China Sea []. In addition, all the compounds exhibited moderate inhibition against LPS-induced NO production in RAW264.7 macrophages with IC50 values of 12-32 μM. Another chemical study on the marine sponge Fascaplysinopsis reticulata has led to the isolation of a new dolabellane-type diterpenoid (422) []. Luo et al. isolated another new dolabellane diterpene, 6,10,18-triacetoxy-2E,7E-dolabelladiene (423), from the South China Sea sponge Luffariella variabilis []. It demonstrated cytotoxicity towards MCF-7 with an IC50 value of 79.2 μM. Wang and colleagues purified seven new kalihinane diterpenoids, kalihioxepanes A-G (424–430), from the sponge A. cavernosa collected in the South China Sea. Kalihioxepane A (424) displayed strong cytotoxicity against H69 and K562 tumor cells, while kalihioxepane B (425) showed moderate cytotoxicity against K562 cells []. Wang and colleagues isolated eight unreported α-acyloxy amides substituted kalihinane diterpenes, named kalihiacyloxyamides A–H (431–438), from the South China Sea sponge Acanthella cavernosa []. Compounds 433 and 435 exhibited cytotoxicity against the K562 cell line with IC50 values of 6.4 and 6.3 μM, respectively. The IC50 values of compounds 435 and 438 against the MDA-MB-231 cell line were 7.3 and 7.9 μM, respectively. The chemical structures of compounds 377–438 are depicted in Figure 13.
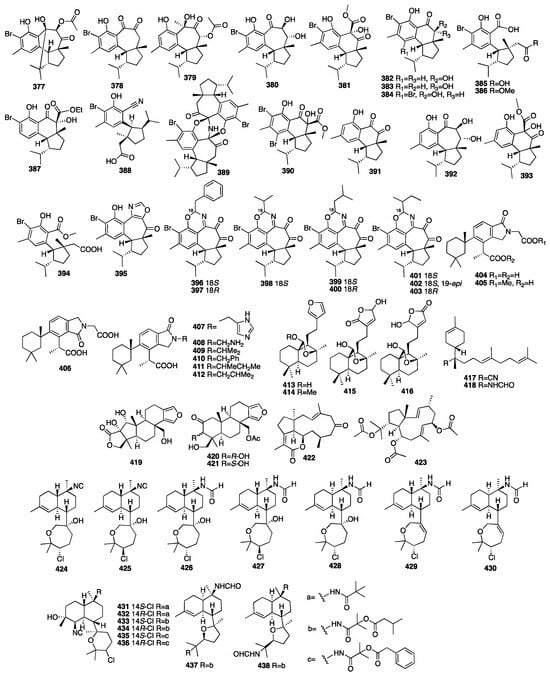
Figure 13.
Chemical structures of compounds 377–438.
Thirteen new structurally related meroterpenoids, including three tricyclics (439, 446–447), six bicyclics (440–445), and four monocyclics (448–451), were isolated from the fungus Alternaria sp. JJY-32 obtained from the sponge Callyspongia sp. collected off the coast of Hainan Island in China []. The NF-κB inhibitory activity of all the compounds showed a weak-to-moderate effect in the RAW264.7 cell line with IC50 values ranging from 39 to more than 100 μM. Sixteen new phenylspirodrimane-style sesterterpenes (452–467) were isolated from the endophytic fungus Stachybotrys chartarum collected from the marine sponge Niphates recondite []. The isoindolone-drimane dimer chartarlactam L (462) was determined as a new skeleton. The bioassay results revealed that seven new compounds (455–457, 462–463, and 465–466) exhibited potent lipid-lowering effects in HepG2 cells in a dose of 10 μM. Additionally, four compounds (456–457, 462, and 467) showed significant inhibition of the intracellular triglyceride (TG) levels in the same cell model, whereas five compounds (455–457, 464, and 466) dramatically reduced total cholesterol (TC).
In 2009, five new diterpene formamides (468–472) were reported from the tropical marine sponge Cymbastela hooperi []. In an in vitro antiplasmodial experiment, compound 468 was found to have moderate activity (IC50 = 0.5 μg/mL) and compound 469 had weak activity (IC50 = 14.8 μg/mL), but 470–472 were inactive. Moreover, compound 468 was the rarely natural product that contained both formamide and isonitrile functionalities within the same molecule. Compounds 473–476 were isolated from the marine sponge Spongionella sp. []. All the compounds showed cytotoxic activity against K562 human chronic myelogenous leukemia cells, with IC50 values ranging from 4.5 to 15 μM. Meanwhile, they showed slightly toxicity toward the normal PBMC cells, with IC50 values ranging from 6.5 to 30 μM. Moreover, all the compounds were proved to be active at a concentration of 100 μM, with gracillin L (475) being the most potent (with an inhibition rate = 75%) towards the protein tyrosine kinase EGF-R, and, similarly, as active as the positive control, genistein, which showed an 80% inhibition. Four new spongian-class diterpenes (477–480) were isolated from the sponge Dysidea cf. arenaria collected in Okinawa []. All the compounds showed cytotoxicity against NBT-T2 rat bladder epithelial cells with IC50 values of 10, 1.9, >10, and >10 μg/mL. Four novel 9-N-methyladeninium diterpenoids (481–484) were isolated from the marine sponge Agelas sp. collected in Papua New Guinea []. These compounds represented higher unsaturated 9-N-methyladeninium bicyclic diterpenoid derivatives. All the isolated compounds were evaluated for inhibitory activity against Trypanosoma brucei, as well as for cytotoxicity against Jurkat cells. Compounds 482 and 483 displayed significant inhibitory action against T. brucei with IC50 values of 3.6 and 3.0 μg/mL. Moreover, compounds 481–483 showed cytotoxicity against Jurkat cells with IC50 values of 8.4, 3.3, and 25.0 μg/mL. The chemical structures of compounds 439–484 are depicted in Figure 14.
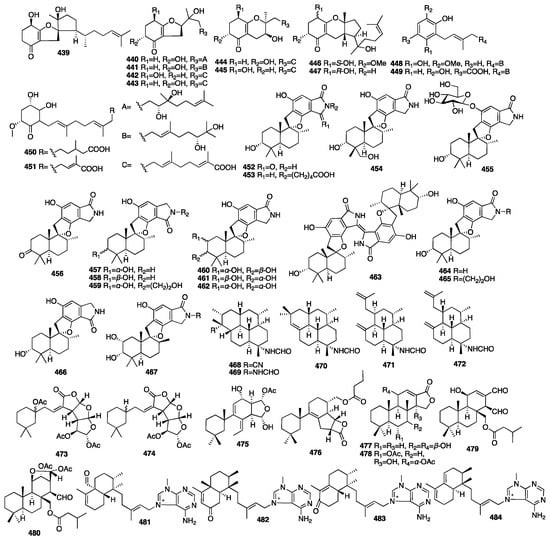
Figure 14.
Chemical structures of compounds 439–484.
In 2010, a study on the marine sponge Negombata corticata, a norterpene-related peroxide (485) was also identified from its EtOH extract []. Three new unusual C21 terpenoids (486–488) were isolated from a MeOH extract of the marine sponge Clathria compressa collected from Panama City in Florida []. Clathric acid (486) showed an MIC value of 32 μg/mL against Staphylococcus aureus (ATTC 6538P) and 64 μg/mL against both methicillin-resistant (ATTC 33591) and vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA). One new oxygenated terpenoid (489) was isolated from the marine sponge Coscinoderma matthewsi collected from the Inner Gneerings Reef, Southeast Queensland, and another two (490–491) were isolated from another sponge Dysidea sp. collected from the same place []. A chemical investigation of a MeOH extract of the South China Sea sponge Cacospongia sp. yielded two terpenoids belonging to two different skeleton types, including the unusual C17 γ-lactone norditerpenoids (492) and the rare C21 pyridine meroterpenoid (493) []. In 2013, an investigation of the marine sponge Agelas axifera led to the isolation of three new pyrimidine diterpenes (494–496) []. All the compounds were found to be moderate inhibitors to cancer cell growth, such as the P388, BXPC-3, MCF-7, SF-268, NCI-H460, KML20L2, and DU-145 cell lines. In addition, axistatins 1–3 (494–496) had identical antimicrobial profiles, inhibiting Gram-positive bacteria, the exquisitely sensitive Gram-negative pathogen Neisseria gonorrheae, and the opportunistic fungus Cryptococcus neoformans.
Four new cytotoxic diterpenoid pseudodimers (497–500) were isolated from the marine sponge Phorbas gukhulensis collected off the coast of Gagu-do, Korea []. All the compounds exhibited significant cytotoxicity against the K562 and A549 cell lines with IC50 values ranging from 0.04 to 0.55 μM. Compound 501 was isolated from the Indonesian sponge Haliclona sp. []. It showed moderate cytotoxicity against NBT-T2 cells with an IC50 value of 4.8 μg/mL and also had antioxidant activity against DPPH with an IC50 value of 3.2 μg/mL. Two new IDO inhibitory meroterpenoids (502–503) were isolated from the sponge Xestospongia vansoesti collected in the Philippines []. Compounds 504–505 were isolated from the fungus Arthrinium sp. obtained from the inner tissues of a sponge Sarcotragus muscarum collected off the coast of southern Turkey []. Compound 506 was isolated from two unidentified species belonging to the genus Spongia. In an antibacterial assay, it showed a certain degree of inhibitory effect against E. coli []. It inhibited sea urchin embryo development at a concentration of 20 μg/mL and above, as well as DNA biosynthesis at a dose of 10 μg/mL. A bioassay-guided fractionation of a MeOH extract of the fungus Arthrinium sp., isolated from the Mediterranean sponge Geodia cydonium, afforded five new diterpenoids (507–511) []. Myrocin D (511) inhibited VEGF-A-dependent endothelial cell sprouting with an IC50 value of 2.6 μM, whereas the other compounds were inactive. Compounds 512–513 were isolated from the fungal strain Dichotomomyces cejpii obtained from the Callyspongia sp. cf. C. flammea []. Indole derivative 512 was found to be a CB2 antagonist, while compound 513 was identified as the first selective GPR18 antagonist. Compounds 514–516 were isolated from an Indonesian sponge of the genus Spongia []. Compound 516 was unusual, as the D-ring was a pyridyl ring system rather than the standard δ-lactone. Compound 831 modestly inhibited aromatase with an IC50 value of 34 μM and induced quinone reductase 1 activity with a CD of 11.2 μM, but the remaining isolates were inactive.
In 2015, a new meroditerpene (517) was isolated from the EtOH extract of the Okinawan marine sponge Strongylophora strongilata []. Other researchers from Kumamoto University reported two new additional strongylophorine derivatives (518–519) isolated from the EtOH extract of another marine sponge Petrosia corticata as proteasome inhibitors []. An p53–Hdm2 interaction inhibitor, niphateolide A (520), was isolated from the Indonesian marine sponge Niphates olemda []. Compound 517 had PTP1B inhibitory activity with an IC50 value of 8.7 μM. Compounds 518 and 519 exhibited potent inhibitory activity against the proteasome with IC50 values of 6.6 and 9.3 μM. Then, a new sulfate meroterpenoid named stachybotrin G (521) was discovered from the fungus Stachybotrys chartarum (MXH-X73) obtained from the marine sponge Xestospongia testudinaria []. In 2018, three new acetylated terpenoids (522–524) were isolated from a MeOH extract of the sponge Rhabdastrella providentiae collected by scuba divers in Vietnam []. Compounds 522–524 exhibited potential NO inhibitors with IC50 values of 20.4, 17.5, and 46.8 μM, respectively. The chemical structures of compounds 485–524 are depicted in Figure 15.
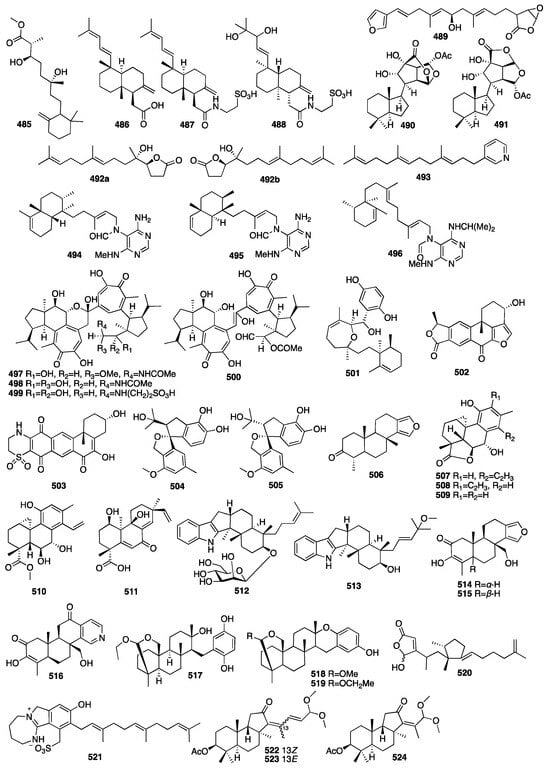
Figure 15.
Chemical structures of compounds 485–524.
A dimeric C21 meroterpenoid (525) was isolated from the marine sponge Dysidea arenaria []. Dysiarenone (525) showed inhibitory activity against COX-2 expression and the production of prostaglandin E2 with an IC50 value of 6.4 μM in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. A year later, two novel C19 terpenoids (526–527) with an unprecedented carbon skeleton were isolated from an EtOAc extract of the Stelletta sp. collected from Vietnamese waters []. Compounds 528–530 were isolated from the marine sponge Dysidea septosa []. Septosone A (528) featured an unprecedented “septosane” carbon skeleton. Moreover, compound 528 showed in vivo anti-inflammatory activity in CuSO4-induced transgenic fluorescent zebrafish likely through the inactivation of the NF-κB signaling pathway. Choi and colleagues isolated one diterpene alkaloid named (–)-agelamide D (531) from the marine sponge Agelas sp., which could be a natural radiosensitizer in hepatocellular carcinoma models [].
Kolesnikova and colleagues isolated four new isomalabaricane-derived nor-terpenoids, stellettins S–V (532–535), from a Vietnamese collection of a Stelletta sp. sponge []. Among them, compound 532 contained an acetylenic fragment, unprecedented in the isomalabaricane family and extremely rare in other marine sponge terpenoids. Jiang and colleagues isolated three new N-methyladenine-containing diterpenoids (536–538) from the coralline demosponge Astrosclera willeyana collected in Tonga []. Four new indole diterpenoids, ascandinines A–D (539–542), were isolated from an Antarctic sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus candidus HDN15-152 []. Among them, ascandinine C (541) displayed anti-influenza virus A (H1N1) activity with an IC50 value of 26 μM, while ascandinine D (542) showed cytotoxicity against HL-60 cells with an IC50 value of 7.8 mM. A chemical investigation of a Red Sea Spongia sp. led to the isolation of 17-dehydroxysponalactone (543), which was found to significantly reduce superoxide anion generation and elastase release at a concentration of 10 μM []. Zou and coworkers isolated two new meroterpenoids, guignardones Y–Z (544–545), from the fungus Penicillium sp. NBUF154, which was obtained from a 60m deep Crella sponge []. A biological evaluation showed that compound 544 exerted a potent inhibitory effect towards human EV71. Pech-Puch and coworkers isolated three new diterpene alkaloids (546–548) from the sponge Agelas citrina, collected on the coasts of the Yucatán Peninsula []. An evaluation of the antimicrobial activity against the Gram-positive pathogens showed that all of them were active, with (+)-10-epiagelasine B (547) being the most active compound with an MIC value in the range of 1–8 μg/mL. Cho and colleagues isolated three norditerpene cyclic peroxides (549–551) from the marine sponge Diacarnus spinipoculum []. Prieto et al. isolated one previously unreported 9,11-dihydrogracillinone A (552) from the sponge Dendrilla antarctica. The results obtained from experiments clearly indicated a potent antifouling activity for compound 552 []. Shen and colleagues isolated six new diterpenoids (553–558) from the sponge Chelonaplysilla sp. []. An unprecedented monocyclic diterpenoid featuring a 2,7-ring-opened halimane-type skeleton, echinohalimane B (559), and a new subersin-type diterpenoid, oculatolide B (560), were isolated from the sponge Sarcotragus sp. []. Wang and colleagues isolated a novel rearranged pimarane diterpenoid, pestanoid A (561), from the Chalinidae sp. sponge-derived fungus Pestalotiopsis sp. NBUF145 []. Compound 561 inhibited bone marrow monocyte osteoclastogenesis in vitro with IC50 values of 4.2 ± 0.2 μM.
The chemical structures of compounds 525–561 are depicted in Figure 16, and the remaining information for compounds 377–561, including names and marine sources, is presented in Table S2.
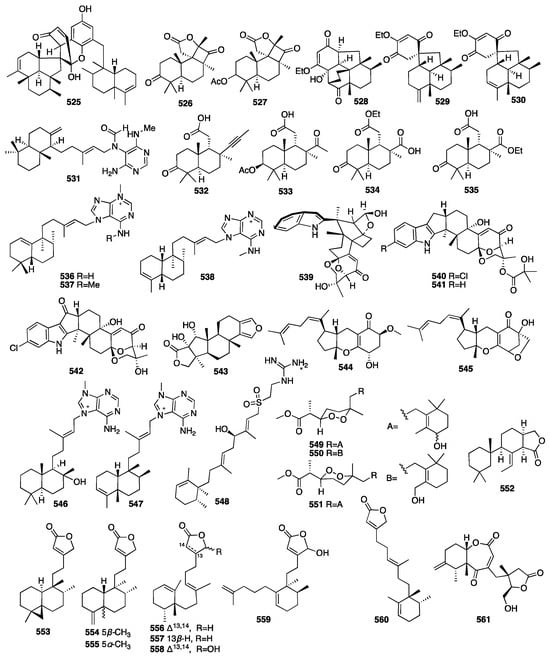
Figure 16.
Chemical structures of compounds 525–561.
3.3. Sesterterpenes
Sesterterpenes are rare in terrestrial plants and are mainly found in sponges and their associated microorganisms, such as coscinolactams A and B (562–563), two novel nitrogen-containing cheilanthane sesterterpenoids, isolated from the marine sponge Coscinoderma mathewsi []. In addition, these two compounds showed moderate anti-inflammatory activity, measured as their capability to inhibit PGE2 and NO production. Sesterterpenes have three main structural types: manoalide-type, hyrtiosane-type, and scalarane-type. Of these, the scalarane-type is the most common []. A bioassay-guided separation led to the isolation of three new scalarane sesterterpenes (564–566) from the acetone extract of the South China Sea sponge Phyllospongia foliascens []. Moreover, compound 565 showed cytotoxic activity against the P388 leukemia cell line with an IC50 value of 6.5 μg/mL. One year later, the same authors reported an additional new scalarane sesterterpene (567) from the same sponge []. A chemical investigation of an EtOAc-soluble fraction of the methanolic extract of the Thai sponge Hyrtios gumminae led to the isolation of four new sesterterpenes (568–571) []. Compounds 572–575 were isolated from the Indonesian marine sponge Carteriospongia foliascens, which was harvested near Makassar, Indonesia []. Compound 572 had moderate inhibition of RCE-Protease with an IC50 value of 38 μg/mL. Furthermore, the cytotoxic effect of 572 against four cell lines (PC-3, LoVo, CACO-2, and MDA-468) was more active than 573 with IC50 values of less than 10.0 μg/mL. In a parallel study on the marine sponge Carteriospongia foliascens, 15 novel sesterterpenes (576–590) were identified from its organic extract []. In addition, compound 579 showed remarkable antifouling activity against barnacle Balanus amphitrite and lethal activity against A. salina with EC50 values less than 2.5 μg/mL, LD50 values between 4.0 and 10.0 μg/mL. Compounds 591–595 were isolated from the sponge Hyatella sp., collected off the coast of Soheuksan-do in Korea []. These compounds exhibited moderate cytotoxicity and antibacterial activity and weak inhibitory activity against isocitrate lyase.
Three novel scalarane sesterterpenes (596–598) were isolated from a Korean marine sponge Psammocinia sp. Furthermore, they exhibited cytotoxicity against the intractable human cancer cell lines A498, ACHN, MIA-paca, and PANC-1, with IC50 values ranging from 0.4 to 48 μM []. In 2014, five new scalarane derivatives (599–603) were isolated from the organic extract of two Thorectidae sponge samples, Hyrtios sp. and Petrosaspongia sp., collected from the Fiji Islands []. Furthermore, these molecules were tested by AlphaScreen at several concentrations from 50 pM to 50 μM to deeply explore their inhibition profile. The results showed activities for compounds 600 and 601 with IC50 values of 0.6 μM and 0.4 nM. Compound 600 was also the most potent compound in reducing the binding of TDP-43 to its cognate DNA. Compounds 604–605 were isolated from a MeOH extract of the South China marine sponge Hyrtios erectus []. In 2015, a biology-guided fractionation of the Cl2H2 fraction of the marine sponge Phyllospongia lamellose collected from Shaab Saad, 13 km north of Hurghada, along the Red Sea, yielded five new scalarane-type sesterterpenes (606–610) []. All the compounds had different inhibitory activities against three cancer cell lines (MCF-7, HCT-116, and HePG-2) at the highest concentration of 10 μg/mL when compared to doxorubicin. Compound 610 showed the strongest inhibitory activity against Gram-positive strains. Peng and colleagues isolated six new 24-homoscalaranes, lendenfeldaranes E-J (611–616), from the marine sponge Lendenfeldia sp. []. Compounds 611–613 were proven to be the first anti-neutrophilic scalaranes.
The chemical structures of compounds 562–616 are depicted in Figure 17, and the remaining information, including names and marine sources, is presented in Table S3.
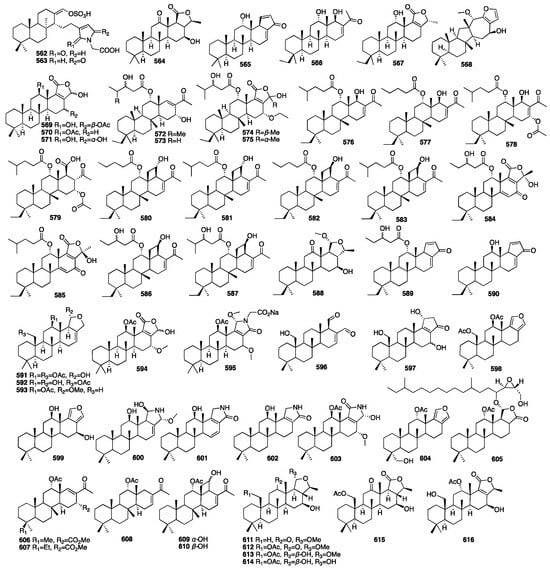
Figure 17.
Chemical structures of compounds 562–616.
In 2021, Shin and colleagues identified 15 new scalarane-type sesterterpenoids (617–631) from the marine sponge Dysidea sp., which was collected from the Province of Bohol in the Philippines []. The biological properties of all the compounds were evaluated using the MDA-MB-231 cancer cell line. Compound 623, which bears a pentenone E-ring, exhibited significant cytotoxicity with a GI50 value of 4.21 μM. Dysiscalarones A–E (632–636) were isolated from the marine sponge Dysidea granulosa collected from the South China Sea []. Dysiscalarones A–B (633–634) showed NO production inhibitory activity with respective IC50 values of 16.4 and 18.5 μM. Peng and colleagues isolated seven new homoscalaranes (637–643) from the marine sponge Lendenfeldia sp. collected in Taiwan []. Among them, compounds 637–639 exhibited potential anti-inflammatory activity. Chakraborty and Francis isolated hyrtioscalaranes A and B (644–645) from the Demosponge Hyrtios erectus []. They both exhibited significant anti-inflammatory activity and antioxidant activity. Tran and colleagues isolated eight new scalarane sesterterpenoids (646–653) from the sponge Hyrtios erectus []. All of them were found to show weak growth inhibitory activity against HeLa and MCF-7 cells, with a minimal IC50 value of 20.0 μM. Yu and colleagues isolated eight new scalarane sesterterpenes, phyllofenones F-M (654–661), from the marine sponge Phyllospongia foliascens collected from the South China Sea []. Among them, compounds 657 and 659 displayed weak inhibitory activity against S. aureus and E. coli, with MIC values of 16 and 8 μg/mL, respectively. Compounds 654–661 exhibited cytotoxic activity against the HeLa, HCT-116, H460, and SW1990 cancer cell lines, with IC50 values ranging from 3.4 to 19.8 μM. Yu and colleagues isolated five new scalarane derivatives featuring an unprecedented 6/6/6/5 tetracyclic dinorscalarane scaffold, phyllospongianes A-E (662–666), from the marine sponge Phyllospongia foliascens []. Compounds 662, 663, and 664 exhibited antibacterial activity against V. vulnificus, V. parahemolyticus, E. coli, S. aureus, E. faecalis, B. subtilis, and P. aeruginosa with MIC values ranging from 1 to 8 μg/mL. Furthermore, compound 661 exhibited significant cytotoxic activity on the MDA-MB-231, HepG2, C4-2-ENZ, MCF-7, H460, and HT-29 cancer cell lines with IC50 values in a range between 0.7 and 13.2 μM. Compound 667 and one new scalarane sesterterpenoid (668) were isolated from the sponge Hippospongia sp. collected from coral reefs in Taiwan []. In 2020, nine new C27 bishomoscalarane sesterterpenes (669–677) and five new C26 20,24-bishomo-25-norscalarane sesterterpenes (678–682) were isolated from a MeOH extract of the sponge Dysidea granulosa collected from the Xisha Islands of the South China Sea []. Compound 672 exhibited moderate antiproliferative activity against the HCT116, A-649, BEL-7402, and Jurkat cell lines with GI50 values of 6.4, 8.1, 11, and 13 μM, respectively. A new sesterterpene (683) was isolated from the acetone extract of the sponge Dysidea sp. in 2010 []. The chemical structures of compounds 617–683 are depicted in Figure 18.
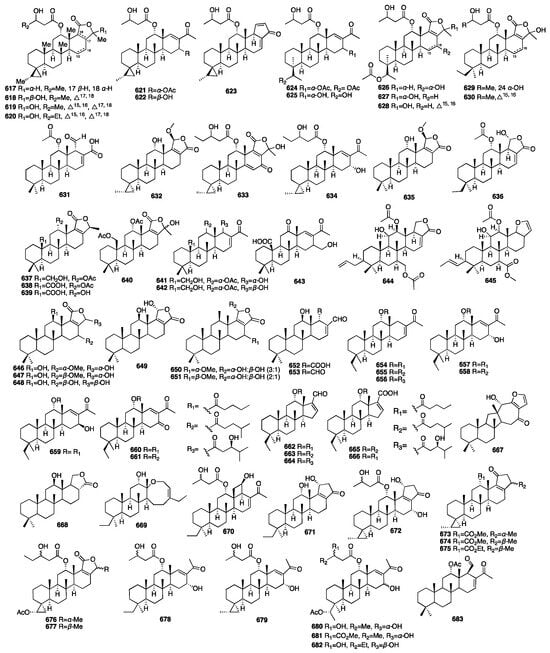
Figure 18.
Chemical structures of compounds 617–683.
Compounds 684–686 were obtained from the New Zealand marine sponge Semitaspongia bactriana with toxicity against the diatom Nitzschia closterium and bryozoan Bugula neritina []. Furthermore, all three compounds exhibited toxicity against B. neritina with EC50 values of 7.41, 1.22, and 1.59 μM, respectively. Studies on the organic extract of the marine sponge Hamigera sp. offered two new sesterterpenoids (687–688) []. Alotaketals A (687) and B (688) have an unprecedented alotane carbon skeleton, and they significantly activate the cAMP cell signaling pathway with EC50 values of 18 and 240 nM, respectively. One year later, ansellone A (689) was isolated from the sponge Phorbas sp. []. It was a new sesterterpenoid with the unprecedented “ansellane” carbon skeleton, and it also activated the cAMP signaling in HEK293 cells in the absence of hormone binding with an EC50 value of 14 μM. Later, four new sesterterpenoids (690–693) were isolated from specimens of the sponge Phorbas sp. collected in British Columbia []. Alotaketal C (693) activated cAMP signaling in HEK293 cells with an EC50 value of 6.5 μM. Compounds 694–696, with a spiroketal of the hydrobenzoyran moiety, were isolated from the Korean marine sponge Phorbas sp. []. Phorbaketal A (694) exhibited mild activity against human colorectal cancer HT-29 with an IC50 value of 12 μg/mL, hepatoma cancer HepG2 with an IC50 value of 11.2 μg/mL, and lung cancer A549 with an IC50 value of 11 μg/mL. Further investigation of the marine sponge of the genus Phorbas collected from Gageo Island, Korea, reported three additional sesterterpenoids named phorbaketals L–N (697–699) []. The cytotoxicity of compounds 697–699 was evaluated against three human cancer cell lines using the MTT assay. The results showed that compound 699 exhibited potent activity against the human pancreatic cancer cell line Panc-1 and the renal cancer cell lines A498 and ACHN with IC50 values of 11.4 μM, 18.7, and 24.4 μM, respectively. An additional nine new sesterterpenoids (700–708) were isolated from another Korean sponge Monanchora sp. []. The absolute configurations of these compounds were defined using the modified Mosher’s method and a CD spectroscopic data analysis. Compounds 704 and 705 showed weak cytotoxicity against the A498 human renal cancer cell line. Compound 708 showed moderate activity against all four human cancer cell lines, while the others were inactive. University of Auckland researchers achieved a total synthesis of 708 in 2015 []. Later, two new sesterterpenoids (709–710) were isolated from the Korean marine sponge Phorbas sp. []. The absolute stereochemistry of compound 709 was determined by the Mosher ester method and exhibited a positive effect on the calcium deposition activity in C3H10T1/2 cells. The same group at Seoul National University reported two unprecedented sesterterpenoids, phorone A (711) and isophorbasone A (712), which were isolated from Korean marine sponge Phorbas sp. []. The chemical structures of compounds 684–712 are depicted in Figure 19.
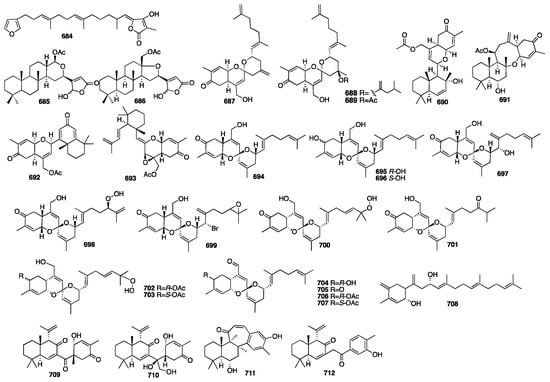
Figure 19.
Chemical structures of compounds 684–712.
The chemical investigation of a new collection of the sponge Ircinia formosana was carried out, which resulted in the isolation of seven new linear C22-furanosesterterpenoids (713–719) []. Among these compounds, compound 717 exhibited significant inhibition of the peripheral blood mononuclear cell proliferation induced by phytohemaglutinin. In 2011, further investigation of the sponge Spongia officinalis yielded a linear furanosesterterpene (720) []. A chemical investigation of the marine sponge Ircinia oros yielded two linear furanosesterterpenoids (721–722). They were the first examples of rare glycinyl lactam-type sesterterpenes []. In addition, these two compounds appeared to be moderately active against all protozoan parasite (P. falciparum, T. brucei rhodesiense, T. cruzi, and L. donovani) activities with IC50 values between 28 and 130 μM. Three new furanosesterterpene tetronic acids (723–725) were isolated from the Psammocinia sp., which was collected in North Sulawesi, Indonesia []. Sulawesins A and B (723–724) possessed unprecedented 5-(furan-3-yl)-4-hydroxycyclopent-2-enone moiety. Sulawesin C (725) was found to be the first dimer in this family. The inhibitory effects of compounds 723 and 724 towards USP7 had IC50 values of 2.9 and 4.6 μM, respectively. The absolute configuration of two new peroxiterpenes (726–727) was determined by the modified Mosher’s method []. These two compounds were isolated from the marine sponge Diacarnus bismarckensis. Compound 726 showed potential bioactivity against T. brucei with an IC50 value of 2 μg/mL. Two new cyclic peroxide norsesterterpene derivatives (728–729) were isolated and characterized from the acetone extract of the Red Sea sponge Diacarnus erythraeanus []. These two compounds displayed mean IC50 growth inhibitory activity against the Hs683, U373, A549, MCF-7, PC-3, LoVo, and B16F10 cell lines at concentrations of less than 10 μM. A chemical investigation of the sponge Diacarnus megaspinorhabdosa resulted in the isolation of one new norsesterpene cyclic peroxide, megaspinoxide A (730) []. Compound 730 showed strong activity against Bacillus cereus, Staphylococcus aureus, and Candida albicans at a concentration of 100 μg/disc. Eight new acyclic manoalide-related sesterterpenes (731–738) were isolated from the South China Sea sponge Hippospongia lachne []. The absolute configurations were determined by the modified Mosher’s method and CD data. Compound 731 exhibited cytotoxicity against the A549, HeLa, and HCT-116 cell lines with IC50 values of 0.05, 0.048, and 9.78 μM, respectively. Compound 731 also showed moderate PTP1B inhibitory activity with an IC50 value of 23.81 μM, and compound 732 also showed moderate cytotoxicity against the HCT-116 cell line and PTP1B inhibitory activity with IC50 values of 35.13 and 39.67 μM, respectively. In addition, compounds 732 and 735 showed weak anti-inflammatory activity, with IC50 values of 61.97 and 40.35 μM for PKCγ and PKCα, respectively. Compounds 739–746 were isolated from the sponge Coscinoderma sp., collected from Chuuk Island in Micronesia []. These compounds exhibited moderate cytotoxicity against the K562 cell line and inhibitory activity against isocitrate lyase and sortase A, as well as Na+/K+-ATPase. Compounds 747–748 were isolated from the fungus Aspergillus insuetus isolated from the Mediterranean sponge Petrosia ficiformis []. Compounds 747 and 748 were found to be inhibitors of the integrated chain (NADH oxidase activity) with IC50 values of 3.90 and 2.97 μM, respectively.
Robert J. Capon and colleagues from the University of Queensland found a new meroterpene sulfate fascioquinol A (749) together with two new meroterpenes, fascioquinol E (750) and fascioquinol F (751), from the Fasciospongia sp., which was collected from southern Australian deep waters []. These compounds displayed little or no inhibitory activity towards human cell lines. However, compound 749 displayed potential Gram-positive selective antibacterial activity towards S. aureus and B. subtilis. Compounds 752–756 were obtained from the fungus Aspergillus sp., which was isolated from the sponge Tethya aurantium collected in Italy []. These compounds were found to be similar with the known austalides A-L previously isolated from Aspergillus ustus. Later, an additional three new austalides (757–759) were isolated from a sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus aureolatus HDN14-107 []. Compound 759 exhibited weak activity against H1N1 with an IC50 value of 90 μM. Two new sesterterpenoids (760–761) were isolated from the marine sponge Cateriospongia flabellifera, which was collected in Vanuatu []. These two compounds had moderate growth inhibitory activity with IC50 values around 10–20 μM. In 2013, a report on the marine sponge Hyrtios communis yielded six novel sesterterpene analogues (762–767) []. Among these compounds, three of them (762–766) were the potent inhibitors of hypoxia (1% O2)-induced HIF-1 activation with IC50 values of 3.2, 3.5, and 6.2 μM, respectively.
The chemical structures of compounds 713–767 are depicted in Figure 20.
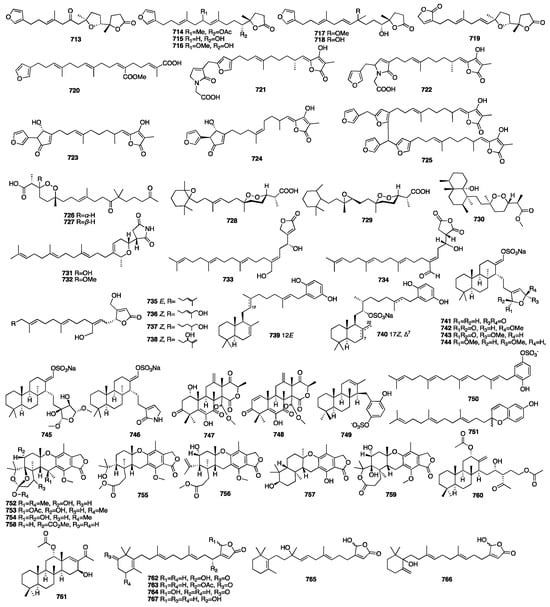
Figure 20.
Chemical structures of compounds 713–767.
Compounds 768–772 were isolated from the EtOH extract of the sponge Hippospongia lachne collected off Yongxing Island in the South China Sea []. Compounds 768 and 772 showed moderate PTP1B inhibitory activity with IC50 values of 5.2 and 8.7 μM, respectively. Compounds 770 and 771 exhibited weak PTP1B inhibitory activity with IC50 values of 33 and 14 μM, respectively. They also evaluated the cytotoxicity of these compounds against the A549, HeLa, and HCT-116 cancer cell lines, and only compound 768 exhibited weak activity against the HCT-116 cell line with an IC50 value of 11.6 μM. Woo and colleagues reported three tetracyclic sesterterpenes (773–775) from the Korean marine sponge Clathria gombawuiensis, which was collected from Chuuk Island, Micronesia []. All the compounds showed cytotoxicity against two cancer cell lines (K562 and A549) with IC50 values around 0.77–4.65 μM when compared with doxorubicin (IC50 = 0.79, 0.70 μM). Furthermore, compounds 773 and 775 showed moderate antibacterial activity, while their diastereomer 774 was virtually inactive. The same trend was also observed for the inhibition of the enzymes Na+/K+-ATPase and isocitrate lyase (ICL), which can be attributed to the 3-dimensional structure of spiroketal. Compound 776 was isolated from an EtOAc extract of the undescribed marine sponge-associated fungus Aspergillus similanensis KUFA 0013 []. It was evaluated for antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, Candida albicans ATCC 10231, and multidrug-resistant isolates from the environment. Chevalone E (776) showed synergism with the antibiotic oxacillin against MRSA. Two new unique sesterterpenes (777–778) with PTP1B inhibitory activity were isolated from the Indonesian marine sponge Hyattella sp. []. The inhibitory activity was 7.45 μM for compounds 777, and compound 778 showed a 42% inhibition at a concentration of 24.2 μM. Compounds 779–780 were isolated from the marine sponge Clathria gombawuiensis collected from Korean waters [].
In 2016, eight new sesterterpenoids (781–788) were isolated from a MeOH extract of the marine sponge Phorbas sp. collected in Howe Sound, British Columbia []. Compounds 781 and 787 were found to induce HIV proviral gene expression. In the next year, a pair of enantiomeric sesterterpenoids (789) were isolated from the EtOH extract of the marine sponge Hippospongia lachne collected from South China Sea []. Compounds 789a and 789b showed potent antifungal activity against three strains of hospital-acquired pathogenic fungi, Candida albicans SC5314, Candida glabrata 537, and Trichophyton rubrum, with MIC50 values between 0.125 and 0.25 μg/mL. A chemical investigation of the Mediterranean Homoscleromorpha sponge Oscarella balibaloi isolated and identified a new family of simple glucosylated sesterterpenes (790–793), named balibalosides []. In a study of the sponge Cacospongia sp., additional skeleton types, C25 manoalide-type sesterterpenoids (794–796), were isolated []. Oshimalides A (797) and B (798) were isolated from the Luffariella sp. marine sponge []. Luo and coworkers isolated eleven rare acyclic manoalide derivatives (799–810) from the sponge Luffariella variabilis collected in the South China Sea. Compounds 799–805 and 809 demonstrated cytotoxic activity against several human cancer cell lines with IC50 values ranging from 2 to 10 μM []. Yu and colleagues isolated five new γ-oxygenated butenolide sesterterpene derivatives, dactylospenes A–E (811–815). Compounds 811 and 813 exhibited moderate cytotoxicity against the DU145, SW1990, Huh7, and PANC-1 cancer cell lines with IC50 values in the range of 2.11–13.35 μM []. The chemical structures of compounds 768–815 are depicted in Figure 21.
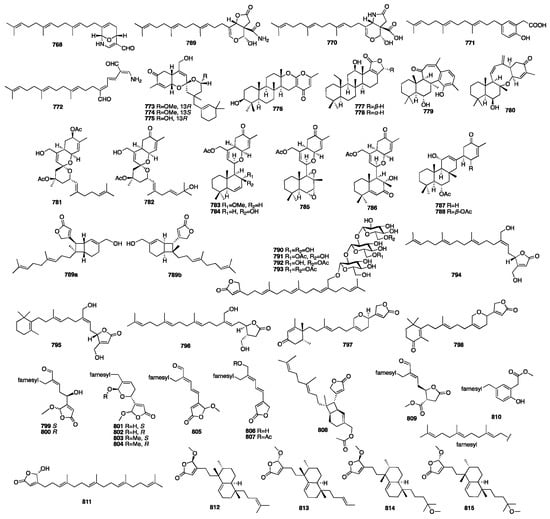
Figure 21.
Chemical structures of compounds 768–815.
Xu and colleagues, in research on the sponge Sarcotragus sp., found four new butenolide sesterterpenes featuring a rare methyl-transferred 6/6/6-tricyclic fused ring system with a butyrolactone moiety, Sarcotragusolides A–D (816–819); a γ-hydroxybutenolide sesterterpene derivative (820); and a new scalarane sesterterpene (821). Compounds 816a, 816b, and 817 presented modest cytotoxic activity against several human cancer cell lines []. Hang and colleagues isolated four new sesterterpenes, hippotulosas A–D (822–825), from the marine sponge Hippospongia fistulosa 1889 []. Bracegirdle and colleagues found several new suberitenone derivatives and terpenoids from the Antarctic sponge Suberites sp.: neosuberitenone (826), with a new carbon scaffold herein termed the ‘neosuberitane’ backbone; six suberitenone derivatives (827–832); an ansellane-type terpenoid (833); and a highly degraded sesterterpene (834). Suberitenone F (831) was found to be active against RSV in the biological activity test [].
Three new natural marine compounds, isosuberitenone B (835), 19-episuberitenone B (836), and isooxaspirosuberitenone (837), were isolated from the Antarctic sponge Phorbas areolatus []. Compounds 835–837 represented new chemical entities of suberitane sesterterpenoids. These compounds were found to exhibit moderate cytotoxic activity, whereas 835 and 836 displayed significant activity against the A549, HepG2, HT-29, and MCF-7 cell lines with IC50 values of less than 10 μM. Majer and coworkers isolated two new ircinianin-type sesterterpenoids, ircinianin lactone B (838) and ircinianin lactone C (839), from the marine sponge Ircinia wistarii. Ircinianin lactones B and C represented new ircinianin terpenoids with a modified oxidation pattern []. Compounds 840–842 were isolated from an organic extract of the marine sponge Fasciospongia sp. collected in Palau []. These compounds exhibited inhibitory activity against Streptomyces 85E in the hyphae formation inhibition assay. Only compound 842 demonstrated a moderate cytotoxic effect on MCF-7 (IC50 = 13.4 μM), LNCaP (IC50 = 21.8 μM), and LU-1 cells (IC50 = 5.0 μM), respectively. A study on the marine sponge Negombata corticata, a norterpene-related peroxide (843), was identified from its EtOH extract []. Compounds 844–846 were obtained from the EtOAc extract of the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus insuetus, which was isolated from the Mediterranean sponge Psammocinia sp. []. Compound 844 exhibited weak anti-fungal activity towards N. crassa with an MIC value of 140 μM. Meanwhile, compound 846 showed mild cytotoxicity towards MOLT-4 human leukemia cells. The chemical structures of compounds 816–846 are depicted in Figure 22.
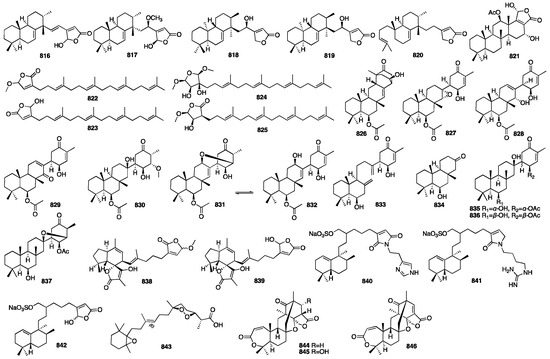
Figure 22.
Chemical structures of compounds 816–846.
Seven new phenylspirodrimanes (847–853) were isolated from the fungus Stachybotrys chartarum MXH-X73, which was obtained from the sponge Xestospongia testudinaris collected from Xisha Island, China []. All the compounds were tested for their antiviral activity against wild-type HIV-1 replication. Only 847 exhibited an inhibitory effect on HIV-1 replication with an EC50 value of 8.4 μM at a final concentration of 10 μM. A further study showed that 847 could block NNRTI-resistant strains (HIV-1RT-K103N, HIV-1RT-L100I, K103N, HIV-1RT-K103N, V108I, HIV-1RT-K103N, G190A, HIV-1RT-K103N, and P225H) and wild-type HIV-1 (HIV-1wt) with EC50 values of 7.0, 23.8, 13.3, 14.2, 6.2, and 8.4 μM, respectively. Shin and colleagues from Seoul National University reported five suvanine-lactam derivatives (854–858) from the Korean marine sponge Coscinoderma sp., which was collected from Chuuk Island, Micronesia []. All the compounds showed cytotoxicity against two cancer cell lines (K562 and A549). Researchers from Peking University reported six new DMOA-related meroterpenoids (859–864) from an EtOAc extract of the unidentified sponge-associated fungus Penicillium brasilianum []. Additionally, biological tests revealed that only 859 significantly stimulated the expression of filaggrin and caspase-14 in HaCaT cells in a dose-dependent manner, while compounds 860 and 861 displayed moderate inhibition against NO production in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages. It was indicated that 859 could reduce UVB-induced cell damage. In addition, compounds 861–864 also inhibited the DNA expression of the HBV virus in HepG2.2.15 cells with inhibitory rates of 25, 15, and 10%, respectively. One year later, six additional bioinformatics (865–870) were isolated from the same fungus []. Brasilianoid L (870) exhibited significant inhibition against bacteria invasion into host cells. An investigation of the sponge Dysidea villosa collected from the South China Sea resulted in the isolation of four unusual merosesterterpenoids (871–874) []. Dysivillosins A-D are the first natural products of terpenepolyketide–pyridine hybrid metabolites. An anti-allergic activity evaluation showed that compounds 871–874 potently inhibited the release of β-hexosaminidase with IC50 values ranging from 8.2 to 19.9 μM. Additionally, these four meroterpenoids could downregulate the production of lipid mediator leukotrienes B4 (LTB4) and the pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-4 (IL-4) in the antigen-stimulated RBL-2H3 mast cells. Further biological investigations exhibited that dysivillosin A (871) could suppress the phosphorylation of Syk and PLCγ1 in the IgE/FcɛRI/Syk signaling pathway.
A diketopiperazine-indole alkaloid that was isolated from the marine sponge Ircinia variabilis-derived fungus Eurotium sp. was named fintiamin (875) []. Fintiamin was composed of amino acid and terpenoid moieties resulting in a terpenoid–dipeptide derivative, which shows affinity for the cannabinoid CB1 receptor. Reiko Tanaka and colleagues from the Osaka University of Pharmaceutical Sciences reported six decalin derivatives (876–881) isolated from the strain of Trichoderma harzianum OUPS-111D-4 originally derived from the marine sponge Halichondria okadai [,,,]. In addition, compounds 879–880 exhibited the most inhibitory activity against the P388, HL-60, and LI210 cell lines with IC50 values of less than 10 μM, followed by 876–878 with IC50 values of 54.5, 42.2, and 41.3 μM, respectively. A chemical investigation of the Red Sea Spongia sp. led to the isolation of a new furanyl trinorsesterpenoid, 16-epi-irciformonin G (882) []. Two new meroterpenoids, hyrtamide A (883) and hyrfarnediol A (884), were isolated from the South China Sea sponge Hyrtios sp. in Wang’s group []. They found that compound 883 exhibited weak cytotoxicity against HCT-116 with an IC50 value of 41.6 μM. The sponge Ircinia felix was selected for the significant anti-human adenovirus (HAdV) activity displayed by its organic extracts []. Its chemical analysis yielded three novel sesterterpene lactams, ircinialactams J-L (885–887). Ircinialactam J displayed significant antiviral activity against HAdV without significant cytotoxicity, showing an effectiveness 11 times greater than that of the standard treatment, cidofovir®.
The chemical structures of compounds 847–887 are depicted in Figure 23, and the remaining information for compounds 617–887, including names and marine sources, is presented in Table S3.
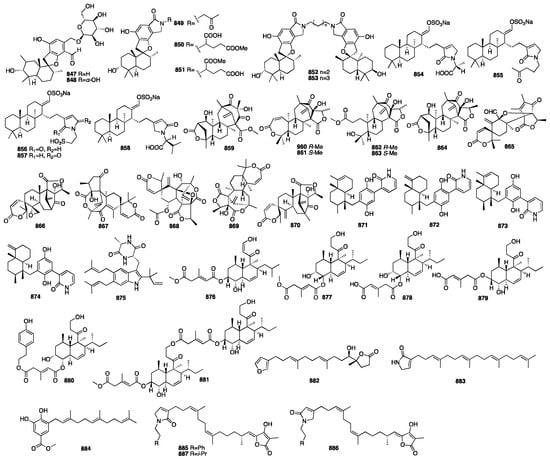
Figure 23.
Chemical structures of compounds 847–887.
3.4. Triterpenes
Common triterpenoids belong to tetra- and/or pentacyclic compounds, and some are usually combined with one or several carbohydrate chains. The isomalabaricane triterpenoids, constructed of tricyclic core systems with long side chains, represent those with a marine origin []. In 2009, nine new terpenoids (888–896) were obtained from the Red Sea sponge Callyspongia (=Siphonochalina) siphonella []. The identification of the isolated compounds was achieved using X-ray crystallography and extensive spectral analyses. Additionally, all the compounds were evaluated for their ability to reverse P-glycoprotein (P-gp)-mediated multidrug resistance in human epidermoid cancer cells. At a noncytotoxic concentration of 10 μM, sipholenone E (889) displayed better activity than a positive control in reversing P-gp-mediated MDR to colchicine. Sipholenol L (893) and siphonellinol D (895) also showed P-gp modulatory activity. A year later, seven new isomalabaricane derivatives (897–903) and a new monocyclic triterpene glycoside (904) were isolated from a MeOH extract of Rhabdastrella globostellata collected from Amamioshima, Japan []. Compounds 900–903, possessing a cyclopentane side chain, exhibited weak activity against the proliferation of promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells with IC50 values of 21, 29, 44, and 11 μM.
Five unique isomalabaricane-type triterpenoids (905–909) were isolated from the Okinawan marine sponge Rhabdastrella cf. globostellata []. In 2012, a chemical investigation of the marine sponge Rhabdastrella globostellata yielded nine unprecedented isomalabaricane-type triterpenoids (910–918) []. Globostelletins J–R (910–918) were characterized as an unusual cyclopentane unit linked at different positions of their side chains. Compounds 910 and 911 showed more potent inhibitory effects against ALK, FAK, IGF-1R, SRC, and VEGF-R2 human tumor-related protein kinases than the other compounds. These findings indicated that these two compounds may be developed as protein kinase-targeted inhibitors. A new isomalabaricane triterpene (919) was isolated from the crude Et2O-soluble extract of the Hainan sponge Stelletta sp. []. A chemical investigation of the marine sponge Jaspis stellifera yielded seven new isomalabaricane-type triterpenoid derivatives (920–926) [,]. In 2021, Kolesnikova and colleagues isolated two new isomalabaricane triterpenoids, stellettins Q and R (927 and 928), from a Vietnamese collection of the Stelletta sp. sponge []. Lai isolated two new isomalabaricane-type triterpenes, rhabdastin H (929) and rhabdastin I (930), from the marine sponge Rhabdastrella collected in Kenting, Taiwan []. Both compounds 929 and 930 showed activity against K562 (with IC50 values of 11.7 and 9.8 μM) and Molt4 (with IC50 values of 16.5 and 11.0 μM) leukemic cells in an MTT cell proliferation assay.
The chemical structures of compounds 888–930 are depicted in Figure 24, and the remaining information, including names and marine sources, is presented in Table S4.
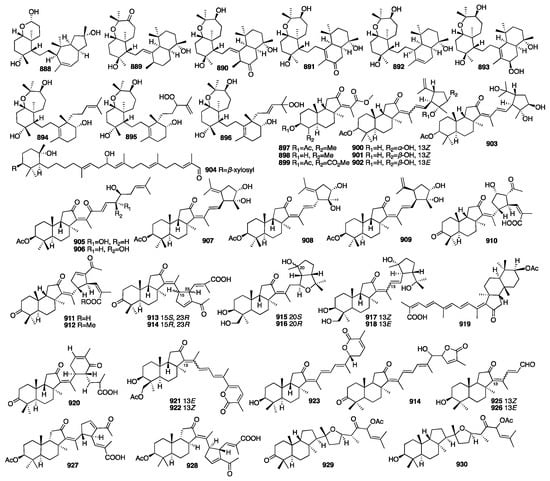
Figure 24.
Chemical structures of compounds 888–930.
In 2022, Chen and colleagues isolated nine new isomalabaricane terpenoids (931–939) from the sponge zza globostellata from Ximao Island []. Seven new triterpene glycosides (940–946) were isolated from the sponges Erylus formosus and Penares spp. []. The chemical structures of compounds 931–946 are depicted in Figure 25.
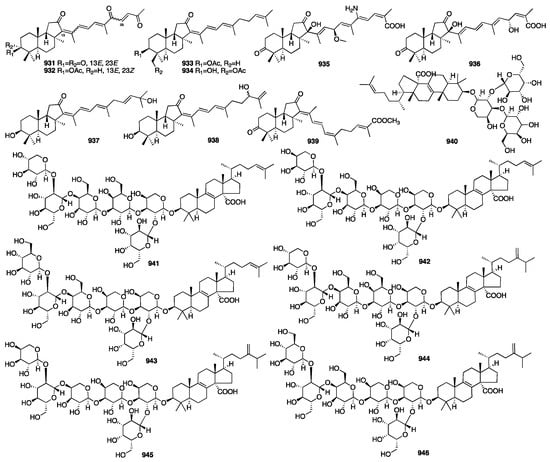
Figure 25.
Chemical structures of compounds 931–946.
Five new nortriterpene glycosides (947–951) were isolated from the tropical sponge Lipastrotethya sp. collected from Chuuk in Micronesia []. Several compounds exhibited cytotoxicity against the A549 and K562 cell lines, as well as weak inhibitory activity against Na+/K+-ATPase. The first C3-pyranosyl 4-hydroxypyrone structure (952) was isolated from the fungus Epicoccum sp. JJY40, obtained from the sponge Callyspongia sp. collected offshore at Sanya in China []. Compound 952 showed both a significant inhibitory effects in the CPE inhibition assay with an IC50 value of 91.5 μM and a weak NF-κB inhibitory effect with an IC50 value of 40 μM. Compounds 953–955 were isolated from the Caribbean marine sponge Ectyoplasia ferox []. Unexpectedly, all these saponin derivatives showed very low activity against the Jurkat and CHO cell lines in an MTT in vitro assay, as well as a hemolysis assay. Nine new triterpene galactosides and aglycones (956–964) were isolated from the tropical sponge Lipastrotethya sp. collected from Micronesia []. These compounds exhibited weak-to-no activity against the K562 human erythroleukemia cell line with IC50 values of 17.0, 12.5, >100, >100, 14.8, 38.9, 14.6, >100, and 27.5 μM, respectively. The chemical structures of compounds 947–964 are depicted in Figure 26.
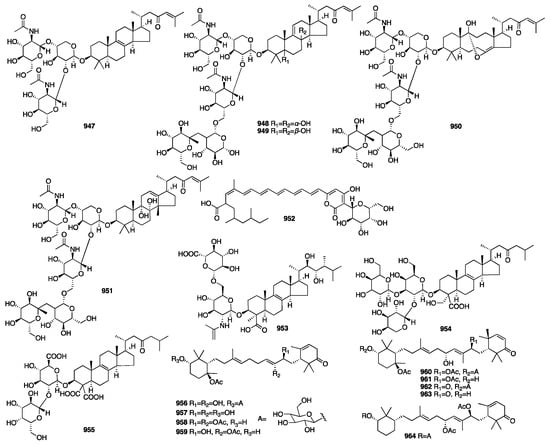
Figure 26.
Chemical structures of compounds 947–964.
Seven new triterpene glycosides (965–971) were isolated from an EtOH extract of the Caribbean sponge Erylus goffrilleri collected from the Caribbean Sea near the Arrecife–Seco reef []. Compound 967 showed moderately active hemolytic and significant cytotoxic activities, whereas 969 possessed moderate cytotoxic and low hemolytic activities. In 2020, two new triterpene galactosides, melophluosides A85 (972) and B86 (973), were successfully isolated from Melophlus sarassinorum collected in Siladen, North Sulawesi [,]. Both compounds exhibited moderate cytotoxic activity against HeLa cells with IC50 values of 11.6 and 9.7 mM, respectively. A simultaneous report on the same marine sponge Clathria gombawuiensis revealed the isolation of an additional new nortriterpene, saponin (974) []. Compound 974 exhibited moderate activity against the K562 and A549 cell lines with LC50 values of 2.1 and 1.8 μM, respectively, and against the bacteria Bacillus subtilis and Proteus hauseri, with MIC values of 1.6 and 3.1 μg/mL, respectively. Ten new norterpene alkaloids, coscinoderines A–J (975–984), were isolated from the marine sponge Coscinoderma bakusi []. Each coscinoderine contains a 1,2,5-trisubstituted pyridinium moiety bearing a terpene unit at the C-2 position. Mama and colleagues isolated two new sarasinosides, 5,8-epoxysarasinoside (985) and 8,9-epoxysarasinoside (986), from the marine sponge Petrosia nigricans, collected off the coast of Lipata, Philippines []. Both compounds exhibited low cytotoxicity against the HCT116 (colon) and A549 (lung) cancer cell lines. Six new triterpenoids (987–992) were isolated from the sponges Erylus formosus and Penares spp., respectively []. The isolated triterpenoid 992 was cytotoxic against human leukemia HL-60 cells (IC50 = 9.7 μM). New nor-isomalabaricanic acids, Stellettins W–X (993–994), were isolated from polar fractions of an EtOH extract of the Vietnamese sponge Rhabdastrella globostellata. Stellettin W was the first isomalabaricane derivative with a 13,14-epoxide group in its structure [].
The chemical structures of compounds 965–994 are depicted in Figure 27, while the remaining information for compounds 931–994, including names and marine sources, is presented in Table S4.
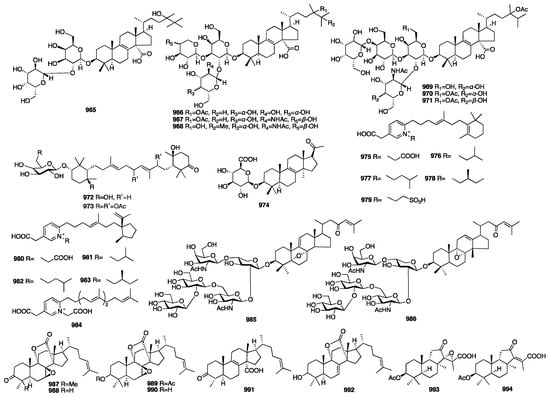
Figure 27.
Chemical structures of compounds 965–994.
3.5. Tetraterpenes
Tetraterpenoids consist of eight isoprene units and usually have a series of conjugated double bond chromophores in the molecule; therefore, these compounds usually have a color. In 2010, two new tetraterpenoids (995–996) were isolated from the Korean marine sponge Phorbas gukulensis []. They both had an unprecedented skeleton with a bis-tropolone moiety. In addition, compounds 995 and 996 exhibited significant cytotoxicity against the human pharynx, stomach, colon, and renal cancer cell lines with IC50 values ranging from 0.05 to 0.80 μM. Luo and coworkers isolated one polyprenylbenzaldehyde derivative (997) from the sponge Luffariella variabilis collected in the South China Sea []. Compound 997 demonstrated cytotoxic activity against several human cancer cell lines with IC50 values ranging from 3.5 to 21 μM.
The chemical structures of compounds 995–997 are depicted in Figure 28, while the remaining information, including names and marine sources, is presented in Table S4.
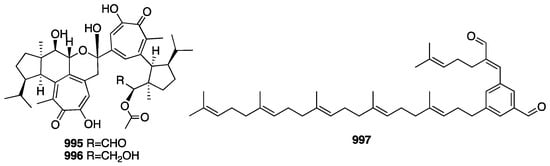
Figure 28.
Chemical structures of compounds 995–997.
4. Conclusions
Terpenes, as a broadly distributed class of MNPs within sponges, exhibit a diverse array of structures and activities, demonstrating substantial medicinal potential. This paper reports 997 sponge-derived terpenes, including sesquiterpenes, diterpenes, sesterterpenes, and triterpenes, as well as tetraterpenoids, over the past fifteen years (from January 2009 to December 2024).
Among the sesquiterpenes, the quinone/hydroquinone sesquiterpenes of the drimane (90–152, etc.), arenarol, and arenarone types (153–164, etc.) share a common rearranged drimane skeleton (1–39, etc.). The relative positions of the C-4 carbon double bond and/or the stereochemical configuration with respect to C-5 are different. The C-9 position is decorated with hydroxylated or heteroatom-substituted benzoquinone side chains. They often possess antibacterial, cytotoxic, and antioxidant activities. It is speculated that, when there are multiple hydroxyl and carboxyl groups in the structure, the active hydrogen atoms on these two types of groups can be easily released. As a result, they can react with free hydroxyl radicals (•OH), endowing them with significant antioxidant properties. Bisabolane-type sesquiterpenes (69–89, etc.) are a class of sesquiterpenes with a simple skeleton, and oxygen bridges and three-membered oxygen rings are often seen in the structure. Nitrogen-containing bisabolane-type sesquiterpenes (69, 78–79, 81–83) have only been reported from marine organisms. They often have anti-inflammatory and cytotoxic activities. For instance, the terminal ethylene group or the dienone group enhances anti-inflammatory activity. Conversely, the oxidation of the C-15 position or the methylation of the OH-7 group leads to a decline in this activity. The aromatization of the six-membered ring, as well as the oxidation of C-10/11, exerts a substantial influence on cytotoxicity.
Spongian diterpene (321–367, etc.) is a large class of diterpenes, most of which have a 6,6,6,5-tetracyclic ring system carbon skeleton and are highly oxidized, especially at the C-17 and C-19 positions and on all A–D rings. That gives them numerous biological activities, such as cytotoxicity, osteoclast inhibitory activity, and antiparasitic activity. Sesterterpenes are commonly found in the secondary metabolites of sponges. Scalarane-type sesterterpenes (564–665, etc.) often have a tetracyclic structure or a few pentacyclic structures. Compounds with hydroxyl or acetoxy groups in the C ring often have higher activity. On this basis, if the D ring also has a furan or lactone ring, it has better antitumor activity. The common triterpenes are isomalabaricane alkanes (897–939, etc.), and some triterpenes with linked carbohydrate chains (940–973, etc.). Isomalabaricane alkanes have limited structural diversity, usually with side chain variations, while the linked carbohydrate chains give the compounds better water solubility and are more amenable to bioavailability and transformation. Terpenes are widespread in nature, with an extremely diverse range of species and highly variable structures, resulting in a wide variety of biological activities. This is related not only to the structure of the compounds themselves but also to the test items selected by researchers. For example, with meroterpenes, another classification of terpenoids, this category contains a large number of compounds whose biological activities are greatly affected by structural units other than the terpene moiety, such as alkaloids and polyketides. More importantly, current research has only revealed a fraction of the biological activity of terpenes, far from all their potential activities, and a considerable portion of their biological activities remains to be discovered. Therefore, it is a huge challenge to find out the structure–activity relationship laws applicable to all terpenes.
5. Discussion
In contemporary research, marine natural products (MNPs) have remained a critical resource for new drug discovery. The number of studies on Porifera has been increasing worldwide, demonstrating their importance and research value []. Marine sponge-derived terpenes have a wide range of activities, including anti-fouling and antimalarial activities, in addition to the main activities, such as antioxidant, antibacterial, antifungal, and antitumoral activities, which are illustrated in Figure 1. Most of these compounds have only been tested for in vitro bioactivity, and the mechanism of pharmacological activity remains unclear. Consequently, further comprehensive and objective assessments must be made in conjunction with in vivo and in vitro tests. Furthermore, the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and safety of these terpenes do not meet the requirements of drug resistance. In this context, those compounds with remarkable effects should be selected to carry out structural modification and structure–activity relationship studies, which will hopefully provide strong support for drug discovery.
In addition to terpenes, alkaloids are another major class of metabolites from marine sponges and their associated microorganisms. Alkaloids are typically a group of nitrogen-containing natural organic compounds, featuring complex structures and diverse biological activity []. However, in terms of quantity, they are fewer than terpenes. Only about 413 alkaloids were discovered from marine sponges during the period from 2000 to 2023 []. When terpenes combine with alkaloids, the demarcation is less clear. Many meroterpenes contain both the structure of terpenoids and the parts of alkaloids [,,,,,,]. Among the various compounds, meroterpenes are large in number and diverse in activity. The classification and identification of meroterpenes are not easy [,,]. Therefore, the classification in this paper is broadly based on the number of isoprenoids, the structural unit of the terpenes, and the number of carbons. In conclusion, these marine natural products all exhibit remarkable activities and can be used, either directly or indirectly, as the lead compounds for derivatization synthesis [].
On the other hand, traditional separation methods, such as the OSMAC (one strain many compounds) strategy, are no longer sufficient for today’s separation needs, because they are time-consuming and mostly purposeless, making them inefficient when used alone. As a matter of fact, the boundaries between disciplines have been gradually blurred in the continuous development of scientific research. More often than not, we need interdisciplinary co-operation in order to achieve our research goals with less effort. For example, the creation of databases by collecting the key annotation information and contributions of known MNPs can provide an important database for drug mining and screening []. The use of MS/MS-based molecular networking (GNPS) to guide extract selection is growing rapidly, and many papers have specifically used the technique to select extracts for investigation [,]. Traditional biology mainly takes living organisms in the natural world as research objects; applies scientific methods such as observation, experiment, analysis, and reasoning; and adopts a variety of technological means to obtain and process a large amount of biological data, establishing and verifying biological models and theories with the main goal of exploring the nature and laws of life. The development of technology makes it possible to carry out systematic engineering modifications of living organisms []. Synthetic biology is an emerging intersection of the biological and chemical disciplines, with the aim of creating, controlling, and reprogramming the artificial biosystems that operate like electrical circuits [,]. It is possible to obtain a certain component in a targeted manner or to increase its yield by this means, solving the disadvantage of the low yield of MNPs.
It is encouraging to see that there is sustained interest in innovative drug discovery and development based on MNPs. In future research, interdisciplinary collaboration between chemical synthesis, biosynthesis, bioactivities, ecological studies, genomic studies, and other related fields should be emphasized to enhance the success rate of new drug discovery. Social and scientific progress follows the Cannikin law that no discipline can exist separately from all others. The development of human civilization requires the combined efforts of all our disciplines and all their researchers.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/md23030096/s1, Table S1: Sesquiterpenes isolated from the marine sponges; Table S2: Diterpenes isolated from the marine sponges; Table S3: Sesterterpenes isolated from the marine sponges; Table S4: Triterpenes and tetraterpenes (marked *) isolated from the marine sponges.
Author Contributions
Writing—review and editing: Y.Y.; writing—original draft preparation: Y.L.; resources: M.X.; and funding acquisition and supervision: B.Z. and S.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of this manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Department of Natural Resources of Guangdong Province (no. [2024]28), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 42376085), and Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities (no. 21623210).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Liu, Y.H.; Yang, B.; Dong, J.D. Secondary Metabolites of Sponges of the Genus Melissa and Their Biological Activities. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2008, 6, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.M.; Tang, X.L.; Sun, Y.T.; Song, D.Y.; Cheng, Y.J.; Liu, H.; Li, P.L.; Li, G.Q. Biological and Chemical Diversity of Marine Sponge-Derived Microorganisms over the Last Two Decades from 1998 to 2017. Molecules 2020, 25, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.W.; Radax, R.; Steger, D.; Wagner, M. Sponge-Associated Microorganisms: Evolution, Ecology, and Biotechnological Potential. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2007, 71, 295–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, N.S.; Taylor, M.W. Marine Sponges and Their Microbial Symbionts: Love and other Relationships. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hentschel, U.; Piel, J.; Degnan, S.M.; Taylor, M.W. Genomic Insights into the Marine Sponge Microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, R.J. Sponging off Nature for New Drug Leads. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 139, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B. The Study Progress on Clinical Application of Cytarabine. Guangdong Huagong 2014, 41, 111–113. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Glaser, K.B.; Cuevas, C.; Jacobs, R.S.; Kem, W.; Little Daniel, R.; Mclntosh Michael, J.; Newman, J.D.; Potts, C.B.; Shuster, E.D. The Odyssey of Marine Pharmaceuticals: A Current Pipeline Perspective. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 31, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanjooloo, A.; Andersen, R.J.; Bhaw-Luximon, A. Marine Sponge-Derived/Inspired Drugs and Their Applications in Drug Delivery Systems. Future Med. Chem. 2021, 13, 487–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.C.; Wu, W.T.; Lin, J.J.; Su, J.H.; Wu, Y.J. Stellettin B Isolated from Stelletta Sp. Reduces Migration and Invasion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells through Reducing Activation of the MAPKs and FAK/PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2022, 2022, 4416611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.A.; Zhou, Q.; Guo, W.Z.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, R.; Jin, M.; Zhang, W.; Li, K.; Yamori, T.; Dan, S.; et al. In Vitro Antitumor Activity of Stellettin B, a Triterpene from Marine Sponge Jaspis stellifera, on Human Glioblastoma Cancer SF295 Cells. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4200–4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, X.; Zhou, C.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, X.; Qiu, Y.; Jin, M.; Gong, M.; Kong, D. Stellettin B Induces G1 Arrest, Apoptosis and Autophagy in Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer A549 Cells via Blocking PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, Y.; Fan, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, R.; Jin, M.; Qiu, Y.; Kong, D. Stellettin B Induces Apoptosis in Human Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Cells via Targeting PI3K and Stat5. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 28906–28921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Chen, X.; Li, G.; Qiu, P.; Wang, W.; Shao, Z. A Review of Sponge-Derived Diterpenes: 2009–2022. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Souza, G.G.; Gonçalves Castro, J.W.; Nascimento, L.L.L.; Pereira da Silva, M.; Ferreira Viturino, J.J.; Inácio da Silva, M.; do Nascimento, J.B.; Janaine Camilo, C.; Martins da Costa, J.G. Chemical and Biological Prospection of Marine Sponges Belonging to the Class Demospongiae: A Review. Chem. Biodivers. 2024; e202401711, Epub ahead of printing. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xin, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, F.; Niu, C.; Liu, S. Terpenoids from Marine Sources: A Promising Avenue for New Antimicrobial Drugs. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.L.; Wang, B.W.; Sun, Z.C.; Yang, J.S.; Xu, X.D.; Ma, G.X. Natural Nitrogenous Sesquiterpenoids and Their Bioactivity: A Review. Molecules 2020, 25, 2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elissawy, A.M.; El-Shazly, M.; Ebada, S.S.; Singab, B.A.; Proksch, P. Bioactive Terpenes from Marine-Derived Fungi. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1966–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinin, V.I.; Ivanchina, N.V.; Krasokhin, V.B.; Makarieva, T.N.; Stonik, V.A. Glycosides from Marine Sponges (Porifera, Demospongiae): Structures, Taxonomical Distribution, Biological Activities and Biological Roles. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1671–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Edrada-Ebel, R.A.; Ebel, R.; Wang, Y.; Schulz, B.; Draeger, S.; Muller, W.E.G.; Wray, V.; Lin, W.H.; Proksch, P. Drimane Sesquiterpenoids from the Fungus Aspergillus ustus Isolated from the Marine Sponge Suberites domuncula. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1585–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, E.; Koch, L.; Thu, K.M.; Rahamin, Y.; Aluma, Y.; Ilan, M.; Yarden, O.; Carmeli, S. Novel Terpenoids of the Fungus Aspergillus insuetus Isolated from the Mediterranean Sponge Psammocinia sp. Collected Along the Coast of Israel. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 6587–6593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, S.J.; Hoobler, E.K.; Riener, M.; Loveridge, S.T.; Tenney, K.; Valeriote, F.A.; Holman, T.R.; Crews, P. Using Enzyme Assays to Evaluate the Structure and Bioactivity of Sponge-Derived Meroterpenes. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1857–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, I.H.; Oh, J.; Zhou, W.; Park, S.; Kim, J.H.; Chittiboyina, A.G.; Ferreira, D.; Song, G.Y.; Oh, S.; Na, M.; et al. Cytotoxic Activity of Rearranged Drimane Meroterpenoids against Colon Cancer Cells via Down-Regulation of β-Catenin Expression. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.K.; Woo, J.K.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, E.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, H.S.; Sim, C.J.; Oh, D.C.; Oh, K.B.; Shin, J. Meroterpenoids from a Tropical Dysidea sp. Sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2814–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Cheng, Z.; Huang, J.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Chartarolides A–C, Novel Meroterpenoids with Antitumor Activities. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017, 58, 1826–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebada, S.S.; de Voogd, N.; Kalscheuer, R.; Müller, W.E.; Chaidir; Proksch, P. Cytotoxic Drimane Meroterpenoids from the Indonesian Marine Sponge Dactylospongia elegans. Phytochem. Lett. 2017, 22, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Han, X.; Cui, Y.; Fu, A.; Liu, K.; Zhang, W.; Tang, X.; Li, G. Pseudoceranoids A–J, Sesquiterpene-Based Meroterpenoids with Cytotoxicity from the Sponge Pseudoceratina purpurea. J. Nat. Prod. 2023, 86, 2710–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daletos, G.; de Voogd, N.J.; Müller, W.E.; Wray, V.; Lin, W.; Feger, D.; Kubbutat, M.; Aly, A.H.; Proksch, P. Cytotoxic and Protein Kinase Inhibiting Nakijiquinones and Nakijiquinols from the Sponge Dactylospongia metachromia. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 21–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Zhou, Y.D.; Nagle, D.G. Inducers of Hypoxic Response: Marine Sesquiterpene Quinones Activate HIF-1. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Mu, F.R.; Jiao, W.H.; Huang, J.; Hong, L.L.; Yang, F.; Xu, Y.; Wang, S.P.; Sun, F.; Lin, H.W. Meroterpenoids with Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Inhibitory Activity from a Hyrtios sp. Marine Sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2509–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, W.H.; Li, J.; Wang, D.; Zhang, M.M.; Liu, L.Y.; Sun, F.; Li, J.Y.; Capon, R.J.; Lin, H.W. Cinerols, Nitrogenous Meroterpenoids from the Marine Sponge Dysidea cinerea. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 2586–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, T.A.; Amagata, T.; Sashidhara, K.V.; Oliver, A.G.; Tenney, K.; Matainaho, T.; Ang, K.K.H.; McKerrow, J.H.; Crews, P. The Aignopsanes, a New Class of Sesquiterpenes from Selected Chemotypes of the Sponge Cacospongia mycofijiensis. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 1975–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondempudi, C.M.; Singanaboina, R.; Manchala, N.; Gunda, V.G.; Janapala, V.R.; Yenamandra, V. Chemical Examination of the Sponge Phycopsis sp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 57, 990–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.Z.; Chen, K.S.; Liu, H.L.; van Soest, R.; Guo, Y.W. New Epoxy-Substituted Nitrogenous Bisabolene-Type Sesquiterpenes from a Hainan Sponge Axinyssa sp. Helv. Chim. Acta 2010, 93, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xu, Y.; Shao, C.L.; Yang, R.Y.; Zheng, C.J.; Chen, Y.Y.; Fu, X.M.; Qian, P.Y.; She, Z.G.; Voogd, N.J.; et al. Antibacterial Bisabolane-Type Sesquiterpenoids from the Sponge-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sp. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.L.; Shao, C.L.; Chen, J.F.; Guo, Z.Y.; Fu, X.M.; Chen, M.; Chen, Y.Y.; Li, R.; de Voogd, N.J.; She, Z.G.; et al. New Bisabolane Sesquiterpenoids from a Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sp. Isolated from the Sponge Xestospongia testudinaria. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 1326–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liang, K.J.; Chiang, C.Y.; Lu, M.C.; Su, J.H. New Nitrogenous Bisabolene-Type Sesquiterpenes from a Formosan Sponge Axinyssa sp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 62, 392–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.L.; Xue, D.Q.; Chen, S.H.; Li, X.W.; Guo, Y.W. New Highly Oxidized Formamidobisabolene-Derived Sesquiterpenes from a Hainan Sponge Axinyssa variabilis. Helv. Chim. Acta 2016, 99, 650–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitora, Y.; Ogura, K.; El-Desoky, A.H.H.; Ise, Y.; Angkouw, E.D.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; Tsukamoto, S. Halichonic Acid B, a Rearranged Nitrogenous Bisabolene-Type Sesquiterpene from a Marine Sponge Axinyssa sp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 69, 802–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Hong, L.L.; Zhan, K.X.; Lin, Z.J.; Jiao, W.H.; Lin, H.W. New Bisabolane-Type Phenolic Sesquiterpenoids from the Marine Sponge Plakortis simplex. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2021, 19, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.H.; Hong, L.L.; Jiao, W.H.; Lin, H.W. Natural Sesquiterpene Quinone/Quinols: Chemistry, Biological Activity, and Synthesis. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2023, 40, 718–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suna, H.; Arai, M.; Tsubotani, Y.; Hayashi, A.; Setiawan, A.; Kobayashi, M. Dysideamine, A New Sesquiterpene Aminoquinone, Protects Hippocampal Neuronal Cells Against Iodoacetic Acid-Induced Cell Death. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 3968–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, X.; Guo, Y.W. A Novel Sesquiterpene Quinone from Hainan Sponge Dysidea villosa. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 390–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Kubota, T.; Kobayashi, J. Nakijiquinones E and F, New Dimeric Sesquiterpenoid Quinones from Marine Sponge. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 2185–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Ushio, M.; Kubota, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Fromont, J.; Kobayashi, J. Nakijiquinones J-R, Sesquiterpenoid Quinones with an Amine Residue from Okinawan Marine Sponges. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.H.; Huang, X.J.; Yang, J.S.; Yang, F.; Piao, S.J.; Gao, H.; Li, J.; Ye, W.C.; Yao, X.S.; Chen, W.S.; et al. Dysidavarones A–D, New Sesquiterpene Quinones from the Marine Sponge Dysidea avara. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmalzbauer, B.; Herrmann, J.; Mueller, R.; Menche, D. Total Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of Dysidavarone A. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 964–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shubina, L.K.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Makarieva, T.N.; Fedorov, S.N.; Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Kapustina, I.I.; Mollo, E.; Utkina, N.K.; Krasokhin, V.B.; et al. New Meroterpenoids from the Marine Sponge Aka coralliphaga. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2012, 7, 487–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prawat, H.; Mahidol, C.; Kaweetripob, W.; Wittayalai, S.; Ruchirawat, S. Iodo-Sesquiterpene Hydroquinone and Brominated Indole Alkaloids from the Thai Sponge Smenospongia sp. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 6881–6886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed Hamed, A.N.; Waetjen, W.; Schmitz, R.; Chovolou, Y.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Youssef, D.T.; Kamel, M.S.; Proksch, P. A New Bioactive Sesquiterpenoid Quinone from the Mediterranean Sea Marine Sponge Dysidea avara. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.H.; Xu, T.T.; Yu, H.B.; Chen, G.D.; Huang, X.J.; Yang, F.; Li, Y.S.; Han, B.N.; Liu, X.Y.; Lin, H.W. Dysideanones A–C, Unusual Sesquiterpene Quinones from the South China Sea Sponge Dysidea avara. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goethel, Q.; Koeck, M. New sesquiterpene hydroquinones from the Caribbean sponge Aka coralliphagum. Beilstein. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 10, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdjul, D.B.; Yamazaki, H.; Takahashi, O.; Kirikoshi, R.; Ukai, K.; Namikoshi, M. Sesquiterpene Hydroquinones with Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Inhibitory Activities from a Dysidea sp. Marine Sponge Collected in Okinawa. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1842–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.M.; Ito, T.; Win, N.N.; Vo, H.Q.; Nguyen, H.T.; Morita, H. New Antibacterial Sesquiterpene Aminoquinones from a Vietnamese Marine Sponge of Spongia sp. Phytochem. Lett. 2016, 17, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, H.Y.; Huang, A.M.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Cao, P.Y.; Yang, P.M. Antibacterial Meroterpenoids from the South China Sea Sponge Dysidea sp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 64, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gu, B.B.; Sun, F.; Xu, J.R.; Jiao, W.H.; Yu, H.B.; Han, B.N.; Yang, F.; Zhang, X.C.; Lin, H.W. Sesquiterpene Quinones/Hydroquinones from the Marine Sponge Spongia pertusa Esper. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1436–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitora, Y.; Sejiyama, A.; Honda, K.; Ise, Y.; Losung, F.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; Tsukamoto, S. Fluorescent Image-Based High-Content Screening of Extracts of Natural Resources for Cell Cycle Inhibitors and Identification of a New Sesquiterpene Quinone from the Sponge, Dactylospongia metachromia. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2021, 31, 115968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Zhao, Q.; Gu, Y.C.; Lan, L.; Wang, C.Y.; Guo, Y.W. Xishaeleganins A–D, Sesquiterpenoid Hydroquinones from Xisha Marine Sponge Dactylospongia elegans. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Zhou, M.; Shang, R.Y.; Hong, L.L.; Wang, G.H.; Tian, W.J.; Jiao, W.H.; Chen, H.F.; Lin, H.W. Dysideanones F–G and Dysiherbols D–E, Unusual Sesquiterpene Quinones with Rearranged Skeletons from the Marine Sponge Dysidea avara. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2022, 20, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.X.; Shang, R.Y.; Xie, D.D.; Luo, X.C.; Hu, T.Y.; Cheng, B.H.; Lin, H.W.; Jiao, W.H. Arenarialins A–F, Anti-Inflammatory Meroterpenoids with Rearranged Skeletons from the Marine Sponge Dysidea arenaria. J. Nat. Prod. 2024, 87, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Kubota, T.; Takahashi-Nakaguchi, A.; Fromont, J.; Gonoi, T.; Kobayashi, J. Nakijiquinone S and Nakijinol C, New Meroterpenoids from a Marine Sponge of the Family Spongiidae. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 62, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertiani, T.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Ortlepp, S.; van Soest, R.W.; de Voogd, N.J.; Wray, V.; Hentschel, U.; Kozytska, S.; Müller, W.E.; Proksch, P. From Anti-Fouling to Biofilm Inhibition: New Cytotoxic Secondary Metabolites from Two Indonesian Agelas sponges. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 1297–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkina, N.K.; Denisenko, V.A.; Krasokhin, V.B. Sesquiterpenoid Aminoquinones from the Marine Sponge Dysidea sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utkina, N.K.; Denisenko, V.A. Tauroarenarones A and B, New Taurine-containing Meroterpenoids from the Marine Sponge Dysidea sp. Nat. Prod. Com. 2014, 9, 757–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.H.; Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Xu, T.T.; Shi, G.H.; Yu, H.B.; Yang, F.; Han, B.N.; Li, M.; Lin, H.W. Dysidinoid A, An Unusual Meroterpenoid with Anti-MRSA Activity from the South China Sea Sponge Dysidea sp. Molecules 2014, 19, 18025–18032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, W.H.; Shi, G.H.; Xu, T.T.; Chen, G.D.; Gu, B.B.; Wang, Z.; Peng, S.; Wang, S.P.; Li, J.; Han, B.N.; et al. Dysiherbols A-C and Dysideanone E, Cytotoxic and NF-κB Inhibitory Tetracyclic Meroterpenes from a Dysidea sp. Marine Sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Bao, B.; Dang, H.T.; Hong, J.; Lee, H.J.; Yoo, E.S.; Bae, K.S.; Jung, J.H. Anti-Inflammatory Sesquiterpenoids from a Sponge-Derived Fungus Acremonium sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.E.; Marques, S.O.; Hajdu, E.; Peixinho, S.; Andersen, R.J.; Berlinck, R.G.S. Pyrodysinoic Acid Derivatives from the Marine Sponge Dysidea robusta. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1691–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.G.; Li, J.; Li, Z.Y.; Guo, Y.W. Two New Unprecedented Acetonyl-Bearing Sesquiterpenes from the Hainan Sponge Dysidea fragilis. Chem. Biodivers. 2009, 6, 858–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, C.H.; Chou, K.J.; Wang, G.H.; Wu, Y.C.; Wang, L.H.; Chen, J.P.; Sheu, J.H.; Sung, P.J. Norterpenoids and Related Peroxides from the Formosan Marine Sponge Negombata corticata. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1538–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovenden, S.P.B.; Nielson, J.L.; Liptrot, C.H.; Willis, R.H.; Tapiolas, D.M.; Wright, A.D.; Motti, C.A. Sesquiterpene Benzoxazoles and Sesquiterpene Quinones from the Marine Sponge Dactylospongia elegans. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovenden, S.P.B.; Nielson, J.L.; Liptrot, C.H.; Willis, R.H.; Tapiolas, D.M.; Wright, A.D.; Motti, C.A. Metachromins U–W: Cytotoxic Merosesquiterpenoids from an Australian Specimen of the Sponge Thorecta reticulata. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1335–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suto, S.; Tanaka, N.; Fromont, J.; Kobayashi, J. Halichonadins G-J, New Sesquiterpenoids from a Sponge Halichondria sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 3470–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suciati; Fraser, J.A.; Lambert, L.K.; Pierens, G.K.; Bernhardt, P.V.; Garson, M.J. Secondary Metabolites of the Sponge-Derived Fungus Acremonium persicinum. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1432–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiem, P.V.; Minh, C.V.; Nhiem, N.X.; Cuc, N.T.; Quang, N.V.; Tuan Anh, H.L.; Tai, B.H.; Yen, P.H.; Hoai, N.T.; Ho, K.Y.; et al. Muurolane-Type Sesquiterpenes from Marine Sponge Dysidea cinerea. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2014, 52, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, H.; Nakazawa, T.; Sumilat, D.A.; Takahashi, O.; Ukai, K.; Takahashi, S.; Namikoshi, M. Euryspongins A–C, Three New Unique Sesquiterpenes from a Marine Sponge Euryspongia sp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 2151–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, H.; Takahashi, O.; Kanno, S.; Nakazawa, T.; Takahashi, S.; Ukai, K.; Sumilat, D.A.; Ishikawa, M.; Namikoshi, M. Absolute Structures and Bioactivities of Euryspongins and Eurydiene Obtained from the Marine Sponge Euryspongia sp. Collected at Iriomote Island. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, D.; Chin, J.; Kim, H.; Yang, I.; Wan, D.W.; Ekins, M.; Choi, H.; Nam, S.J.; Kang, H. Sesquiterpenoids with PPARδ Agonistic Effect from a Korean Marine Sponge Ircinia sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 4716–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Liu, D.; Proksch, P.; Guo, P.; Lin, W. Punctaporonins H–M: Caryophyllene-Type Sesquiterpenoids from the Sponge-Associated Fungus Hansfordia sinuosae. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3904–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.M.; Meng, L.H.; Jiang, W.L.; Xu, G.M.; Huang, C.G.; Wang, B.G. Bisthiodiketopiperazines and Acorane Sesquiterpenes Produced by the Marine-Derived Fungus Penicillium adametzioides AS-53 on Different Culture Media. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1294–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.W.; Chen, S.H.; Ye, F.; Mollo, E.; Zhu, W.L.; Liu, H.L.; Guo, Y.W. Axiriabilines A-D, Uncommon Nitrogenous Eudesmane-Type Sesquiterpenes from the Hainan Sponge Axinyssa variabilis. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 5239–5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.H. The Secondery Metabolites of Carteriospongia foliascens and Kjellmaniella crassifolia and Their Bioactivies. Master’s Thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Torii, M.; Kato, H.; Hitora, Y.; Angkouw, E.D.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; de Voogd, N.J.; Tsukamoto, S. Lamellodysidines A and B, Sesquiterpenes Isolated from the Marine Sponge Lamellodysidea herbacea. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2536–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khushi, S.; Salim, A.A.; Elbanna, A.H.; Nahar, L.; Bernhardt, P.V.; Capon, R.J. Dysidealactams and Dysidealactones: Sesquiterpene Glycinyl-Lactams, Imides, and Lactones from a Dysidea sp. Marine Sponge Collected in Southern Australia. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1577–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, D.; Fan, A.; Huang, J.; Lin, W. Eremophilane-Type Sesquiterpenes from a Marine-Derived Fungus Penicillium copticola with Antitumor and Neuroprotective Activities. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohte, S.; Yamazaki, H.; Takahashi, O.; Rotinsulu, H.; Wewengkang, D.S.; Sumilat, D.A.; Abdjul, D.B.; Maarisit, W.; Kapojos, M.M.; Zhang, H.; et al. Inhibitory Effects of Sesquiterpene Lactones from the Indonesian Marine Sponge Lamellodysidea Cf. Herbacea on Bone Morphogenetic Protein-Induced Osteoblastic Differentiation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 35, 127783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkina, N.K.; Denisenko, V.A.; Krasokhin, V.B. Diplopuupehenone, a New Unsymmetrical Puupehenone-Related Dimer from the Marine Sponge Dysidea sp. Tetrahedron lett. 2011, 52, 3765–3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, K.; Garcia Hernandez, J.E.; Harper, M.K.; Carroll, A.; Motti, C.A.; Awaya, J.; Nguyen, H.Y.; Wright, A.D. Puupehenol, a Potent Antioxidant Antimicrobial Meroterpenoid from a Hawaiian Deep-Water Dactylospongia sp. Sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingavat, N.; Mahidol, C.; Ruchirawat, S.; Kittakoop, P. Asperaculin A, a Sesquiterpenoid from a Marine-Derived Fungus, Aspergillus aculeatus. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1650–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.Q.; Liao, X.J.; Zhao, B.X.; Xu, S.H. (+)- and (–)-Spongiterpene, a Pair of New Valerenane Sesquiterpene Enantiomers from the Marine Sponge Spongia sp. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 2178–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.Y.; Han, G.Y.; Yang, N.N.; Lan, L.F.; Li, X.W.; Guo, Y.W. Racemic Trinorsesquiterpenoids from the Beihai Sponge Spongia officinalis: Structure and Biomimetic Total Synthesis. Org. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 1022–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Luo, X.; Zhao, H.; Lu, J.; Dai, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lin, H.; Yang, F. New Spiro-Sesquiterpenoids from the Marine Sponge Myrmekioderma sp. Chem. Biodivers. 2022, 19, e202200455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, L.; Wang, J.; Guo, Y.; Li, X. Nitrogenous Sesquiterpenoids from the South China Sea Nudibranch Hexabranchus sanguineus and Its Possible Sponge-Prey Acanthella cavernosa: Chiral Separation, Stereochemistry and Chemical Ecology. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 40, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.M.; Yang, Q.; Zang, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Guo, Y.W. Anti-Inflammatory Aromadendrane- and Cadinane-Type Sesquiterpenoids from the South China Sea Sponge Acanthella cavernosa. Beilstein. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Wang, H.; Yan, M.; Sai, C.; Zhang, Z. Research Advances of Bioactive Sesquiterpenoids Isolated from Marine-Derived Aspergillus sp. Molecules 2022, 27, 7376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Liu, X.; Sun, N.; Zhang, X.; Shah, M.; Zhang, G.; Che, Q.; Zhu, T.; Li, J.; Li, D. Cytotoxic Nitrobenzoyl Sesquiterpenoids from an Antarctica Sponge-Derived Aspergillus insulicola. J. Nat. Prod. 2022, 85, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, X.; Lin, W.; He, S.; Ding, L. Molecular Networking-Guided Isolation of Undescribed Antifungal Odoriferous Sesquiterpenoids from a Marine Mesophotic Zone Sponge-Associated Streptomyces Sp. NBU3428. Phytochemistry 2023, 213, 113779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Wang, G.; Li, J.; Peng, Z.; Gan, M. Acremosides A–G, Sugar Alcohol-Conjugated Acyclic Sesquiterpenes from a Sponge-Derived Acremonium Species. J. Nat. Prod. 2024, 87, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Yang, T.; Li, J.; Li, K.; Zhuang, C.; Zhang, M.; Li, R.; Zhao, Y.; Song, Q.; Jiang, M.; et al. Identification of a Marine-derived Sesquiterpenoid, Compound-8, That Inhibits Tumour Necrosis Factor-induced Cell Death by Blocking Complex II Assembly. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 181, 2443–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiem, P.V.; Huyen, L.T.; Hang, D.T.; Nhiem, N.X.; Tai, B.H.; Anh, H.L.; Cuong, P.V.; Quang, T.H.; Minh, C.V.; Dau, N.V.; et al. Sesquiterpene Derivatives from Marine Sponge Smenospongia cerebriformis and Their Anti-inflammatory Activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 1525–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiso, A.; Kittiwisut, S.; Chantakul, R.; Yuenyongsawad, S.; Putchakarn, S.; Schäberle, T.F.; Temkitthaworn, P.; Ingkaninan, K.; Chaithirayanon, K.; Plubrukarn, A. Quintaquinone, a Merosesquiterpene from the Yellow Sponge Verongula cf. rigida Esper. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Li, P.; Wang, K.; De Voogd, N.J.; Tang, X.; Li, G. Cytotoxic Sesquiterpenoid Quinones from South China Sea Sponge Dysidea sp. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 2866–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Han, X.; Mi, Y.; Cui, Y.; Fu, A.; Liu, K.; Li, X.; Tang, X.; Li, G. Anti-Inflammatory and Cytotoxicity Nitrogenous MerosesQuiterpenoids from the Sponge Pseudoceratina purpurea. Phytochemistry 2024, 226, 114220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wattanapiromsakul, C.; Chanthathamrongsiri, N.; Bussarawit, S.; Yuenyongsawad, S.; Plubrukarn, A.; Suwanborirux, K. 8-Isocyanoamphilecta-11(20),15-diene, a New Antimalarial Isonitrile Diterpene from the Sponge Ciocalapata sp. Can. J. Chem. 2009, 87, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanthathamrongsiri, N.; Yuenyongsawad, S.; Wattanapiromsakul, C.; Plubrukarn, A. Bifunctionalized Amphilectane Diterpenes from the Sponge Stylissa cf. massa. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 789–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, M.H.; Hossain, M.K.; Nigar, M.; Roy, M.C.; Tanka, J. New Cytotoxic Spongian-Class Rearranged Diterpenes from a Marine Sponge. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2012, 48, 412–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shingaki, M.; Wauke, T.; Ahmadi, P.; Tanaka, J. Four Cytotoxic Spongian Diterpenes from the Sponge Dysidea cf. arenaria. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 64, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Salm, J.L.; Witowski, C.G.; Fleeman, R.M.; McClintock, J.B.; Amsler, C.D.; Shaw, L.N.; Baker, B.J. Darwinolide, a New Diterpene Scaffold That Inhibits Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm from the Antarctic Sponge Dendrilla membranosa. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 2596–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, M.C.A.; Williams, D.E.; Gubiani, J.R.; Parra, L.L.; Santos, M.F.; Ferreira, D.D.; Mesquita, J.T.; Tempone, A.G.; Ferreira, A.G.; Padula, V.; et al. Rearranged Terpenoids from the Marine Sponge Darwinella cf. oxeata and Its Predator, the Nudibranch Felimida grahami. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Desoky, A.H.; Kato, H.; Kagiyama, I.; Hitora, Y.; Losung, F.; Mangindaan, R.E.; de Voogd, N.J.; Tsukamoto, S. Ceylonins A–F, Spongian Diterpene Derivatives That Inhibit RANKL-Induced Formation of Multinuclear Osteoclasts, from the Marine Sponge Spongia ceylonensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Desoky, A.H.; Kato, H.; Tsukamoto, S. Ceylonins G–I: Spongian Diterpenes from the Marine Sponge Spongia ceylonensis. J. Nat. Med. 2017, 71, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Desoky, A.H.; Kato, H.; Angkouw, E.D.; Mangindaan, R.E.; de Voogd, N.J.; Tsukamoto, S. Ceylonamides A-F, Nitrogenous Spongian Diterpenes That Inhibit RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis, from the Marine Sponge Spongia ceylonensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1922–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.Y.; Sun, D.Y.; Liang, L.F.; Yao, L.G.; Chen, K.X.; Guo, Y.W. Spongian Diterpenes from Chinese Marine Sponge Spongia officinalis. Fitoterapia 2018, 127, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, M.; Fernández, R.; Pérez, M.; Thorsteinsdottir, M. Two New Spongian Diterpene Analogues Isolated from the Marine Sponge Acanthodendrilla sp. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bory, A.; Shilling, A.J.; Allen, J.; Azhari, A.; Roth, A.; Shaw, L.N.; Kyle, D.E.; Adams, J.H.; Amsler, C.D.; McClintock, J.B.; et al. Bioactivity of Spongian Diterpenoid Scaffolds from the Antarctic Sponge Dendrilla antarctica. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, C.J.; Ahmed, A.F.; Chao, C.H.; Yen, C.H.; Hwang, T.L.; Chang, F.R.; Huang, Y.M.; Sheu, J.H. Spongenolactones A–C, Bioactive 5,5,6,6,5-Pentacyclic Spongian Diterpenes from the Red Sea Sponge Spongia sp. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Shubina, L.K.; Makarieva, T.N.; Hauschild, J.; Strewinsky, N.; Guzii, A.G.; Menshov, A.S.; Popov, R.S.; Grebnev, B.B.; Busenbender, T.; et al. New Diterpenes from the Marine Sponge Spongionella Sp. Overcome Drug Resistance in Prostate Cancer by Inhibition of P-Glycoprotein. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Li, P.; Wang, C.; Tang, X.; Yv, X.; Li, K.; Luo, L.; Ou, H.; Li, G. Two New Spongian Diterpene Derivatives from the Aquaculture Sponge Spongia officinalis Linnaeus, 1759. Nat. Prod. Res. 2023, 37, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, C.J.; Chao, C.H.; Ahmed, A.F.; Yen, C.H.; Hwang, T.L.; Chang, F.R.; Huang, Y.M.; Sheu, J.H. New 3,4-Seco-3,19-Dinor- and Spongian-Based Diterpenoid Lactones from the Marine Sponge Spongia sp. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sala, S.; James, P.J.C.; Nealon, G.L.; Fromont, J.; Gomez, O.; Vuong, D.; Lacey, E.; Flematti, G.R. Dendrillic Acids A and B: Nitrogenous, Rearranged Spongian Nor-Diterpenes from a Dendrilla Sp. Marine Sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2023, 86, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pech-Puch, D.; Rodriguez, J.; Jimenez, C.; Sandoval-Castro, C.A.; Jiménez, C. Cytotoxic Furanoditerpenes from the Sponge Spongia tubulifera Collected in the Mexican Caribbean. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, H.; Wright, A.D.; Reinscheid, U.; König, G.M. Three New Spongian Diterpenes from the Fijian Marine Sponge Spongia sp. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2009, 4, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.H.; Tseng, S.W.; Lu, M.C.; Liu, L.L.; Chou, Y.; Sung, P.J. Cytotoxic C21 and C22 Terpenoid-Derived Metabolites from the Sponge Ircinia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 2005–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzo, E.; Ciavatta, M.L.; Villani, G.; Varcamonti, M.; Sayem, S.M.; van Soest, R.; Gavagnin, M. Bioactive Terpenes from Spongia officinalis. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.J.; Dattelbaum, J.D.; Field, J.J.; Smart, Z.; Woolly, E.F.; Barber, J.M.; Heathcott, R.; Miller, J.H.; Northcote, P.T. Structurally Diverse Hamigerans from the New Zealand Marine Sponge Hamigera tarangaensis: NMR-directed isolation, structure elucidation and antifungal activity. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 8041–8051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolly, E.F.; Singh, A.J.; Russell, E.R.; Miller, J.H.; Northcote, P.T. Hamigerans R and S: Nitrogenous Diterpenoids from the New Zealand Marine Sponge Hamigera tarangaensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dattelbaum, J.D.; Singh, A.J.; Field, J.J.; Miller, J.H.; Northcote, P.T. The Nitrogenous Hamigerans: Unusual Amino Acid-Derivatized Aromatic Diterpenoid Metabolites from the New Zealand Marine Sponge Hamigera tarangaensis. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojnar, J.M.; Dowle, K.O.; Northcote, P.T. The Oxeatamides: Nitrogenous Spongian Diterpenes from the New Zealand Marine Sponge Darwinella oxeata. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 2288–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, J.M.; Leahy, D.C.; Miller, J.H.; Northcote, P.T. Luakuliides A–C, Cytotoxic Labdane Diterpenes from a Tongan Dictyoceratid Sponge. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 6314–6318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, K.; Hamamoto, Y.; Eda, W.; Tamura, K.; Sawada, A.; Hoshino, A.; Mitome, H.; Kamaike, K.; Miyaoka, H. Amitorines A and B, Nitrogenous Diterpene Metabolites of Theonella swinhoei: Isolation, Structure Elucidation, and Asymmetric Synthesis. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Mao, Q.; Bao, M.; Mou, Y.; Fang, C.; Zhao, M.; Jiang, W.; Yu, X.; Wang, C.; Dai, L.; et al. Spongian Diterpenes Including One with a Rearranged Skeleton from the Marine Sponge Spongia officinalis. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1714–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, G.F.; Tang, X.L.; de Voogd, N.J.; Li, P.L.; Li, G.Q. Cytotoxic Components from the Xisha Sponge Fascaplysinopsis reticulata. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.C.; Wang, Q.; Tang, X.L.; Li, P.L.; Li, G.Q. One Cytotoxic Steroid and Other Two New Metabolites from the South China Sea Sponge Luffariella variabilis. Tetrahedron Lett. 2021, 65, 152762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Han, X.; Liu, G.; Zhang, D.; Hou, H.; Xiao, L.; De Voogd, N.J.; Tang, X.; Li, P.; Li, G. Kalihioxepanes A–G: Seven Kalihinene Diterpenoids from Marine Sponge Acanthella cavernosa Collected off the South China Sea. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 40, 1785–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Han, X.; Zhang, D.; Hou, H.; Xiao, L.; Li, G. Kalihiacyloxyamides A-H, α-Acyloxy Amide Substituted Kalihinane Diterpenes Isolated from the Sponge Acanthella cavernosa Collected in the South China Sea. Phytochemistry 2023, 206, 113512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wu, G.; Zhu, T.; Kurtán, T.; Mándi, A.; Jiao, J.; Li, J.; Qi, X.; Gu, Q.; Li, D. Meroterpenoids with Diverse Ring Systems from the Sponge-Associated Fungus Alternaria sp. JJY-32. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1946–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wu, C.; Liu, D.; Proksch, P.; Guo, P.; Lin, W. Chartarlactams A–P, Phenylspirodrimanes from the Sponge-Associated Fungus Stachybotrys chartarum with Antihyperlipidemic Activities. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, A.D.; Lang-Unnasch, N. Diterpene Formamides from the Tropical Marine Sponge Cymbastela hooperi and Their Antimalarial Activity in Vitro. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 492–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rateb, M.E.; Houssen, W.E.; Schumacher, M.; Harrison, W.T.; Diederich, M.; Ebel, R.; Jaspars, M. Bioactive Diterpene Derivatives from the Marine Sponge Spongionella sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1471–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agena, M.; Tanaka, C.; Hanif, N.; Yasumoto-Hirose, M.; Tanaka, J. New Cytotoxic Spongian Diterpenes from the Sponge Dysidea cf. arenaria. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 1495–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcul, L.; Tenney, K.; Ratnam, J.; McKerrow, J.H.; Crews, P. Structural Variations to the 9-N-Methyladeninium Diterpenoid Hybrid Commonly Isolated from Agelas Sponges. Aust. J. Chem. 2010, 63, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Sharma, U.; Schulz, T.C.; McLean, A.B.; Robins, A.J.; West, L.M. Bicyclic C21 Terpenoids from the Marine Sponge Clathria compressa. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1223–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katavic, P.L.; Jumaryatno, P.; Hooper, J.N.A.; Blanchfield, J.T.; Garson, M.J. Oxygenated Terpenoids from the Australian Sponges Coscinoderma matthewsi and Dysidea sp., and the Nudibranch Chromodoris albopunctata. Aust. J. Chem. 2012, 65, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, P.L.; Qin, G.F.; Li, S.; de Voogd, N.J.; Tang, X.L.; Li, G.Q. Isolation and Absolute Configurations of Diversiform C17, C21 and C25 Terpenoids from the Marine Sponge Cacospongia sp. Mar. Drugs 2018, 17, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettit, G.R.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Bourne, G.T.; Arm, C.A.; Leet, J.E.; Knight, J.C.; Pettit, R.K.; Chapuis, J.C.; Doubek, D.L.; et al. Isolation and Structures of Axistatins 1–3 from the Republic of Palau Marine Sponge Agelas axifera Hentschel. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Liao, L.; Kim, H.; Sim, C.J.; Oh, D.C.; Oh, K.B.; Shin, J. Cytotoxic Diterpenoid Pseudodimers from the Korean Sponge Phorbas gukhulensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1679–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trianto, A.; Hermawan, I.; de Voogd, N.J.; Tanaka, J. Halioxepine, a New Meroditerpene from an Indonesian Sponge Haliclona sp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 59, 1311–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centko, R.M.; Steinoe, A.; Rosell, F.I.; Patrick, B.O.; de Voogd, N.; Mauk, A.G.; Andersen, R.J. Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Inhibitors Isolated from the Sponge Xestospongia vansoesti: Structure Elucidation, Analogue Synthesis, and Biological Activity. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 6480–6483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elissawy, A.M.; Ebada, S.S.; Ashour, M.L.; Özkaya, F.C.; Ebrahim, W.; Singab, A.B.; Proksch, P. Spiroarthrinols A and B, Two Novel Meroterpenoids Isolated from the Sponge-Derived Fungus Arthrinium sp. Phytochem. Lett. 2017, 20, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomarenko, L.P.; Terent’eva, N.A.; Krasokhin, V.B.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Rasskazov, V.A. Terpenoid Metabolites from Spongia spp. and Their Effects on Nucleic Acid Biosynthesis in Sea Urchin Eggs. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2011, 6, 773–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebada, S.S.; Schulz, B.; Wray, V.; Totzke, F.; Kubbutat, M.H.; Müller, W.E.; Hamacher, A.; Kassack, M.U.; Lin, W.; Proksch, P. Arthrinins A-D: Novel Diterpenoids and Further Constituents from the Sponge Derived Fungus Arthrinium sp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 4644–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, H.; Rempel, V.; Kehraus, S.; Kaiser, M.; Hufendiek, P.; Müller, C.E.; König, G.M. Indoloditerpenes from a Marine-Derived Fungal Strain of Dichotomomyces cejpii with Antagonistic Activity at GPR18 and Cannabinoid Receptors. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrish, S.M.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Kondratyuk, T.P.; Park, E.J.; Pezzuto, J.M.; Kelly, M.; Williams, P.G. Spongiapyridine and Related Spongians Isolated from an Indonesian Spongia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 1644–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Abdjul, D.B.; Yamazaki, H.; Takahashi, O.; Kirikoshi, R.; Ukai, K.; Namikoshi, M. Strongylophorines, New Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Inhibitors, from the Marine Sponge Strongylophora strongilata Collected at Iriomote Island. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 3900–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, A.; Sakai, E.; Kato, H.; Losung, F.; Mangindaan, R.E.; de Voogd, N.J.; Yokosawa, H.; Tsukamoto, S. Strongylophorines, Meroditerpenoids from the Marine Sponge Petrosia corticata, Function as Proteasome Inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 2650–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Nehira, T.; Matsuo, K.; Kawabata, T.; Kobashigawa, Y.; Morioka, H.; Losung, F.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; de Voogd, N.; Yokasawa, H.; et al. Niphateolide A: Isolation from the Marine Sponge Niphates olemda and Determination of Its Absolute Configuration by an ECD Analysis. Tetrahedron 2015, 71, 6956–6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, H.; Li, F.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Li, D. Stachybotrin G, a Sulfate Meroterpenoid from a Sponge Derived Fungus Stachybotrys chartarum MXH-X73. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 7053–7055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dung, D.T.; Yen, P.H.; Nhiem, N.X.; Quang, T.H.; Tai, B.H.; Minh, C.V.; Kim, D.C.; Oh, H.; Kim, Y.C.; Kim, P.V. New Acetylated Terpenoids from Sponge Rhabdastrella providentiae Inhibit NO Production in LPS Stimulated BV2 Cells. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2018, 13, 934578X1801300602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.H.; Cheng, B.H.; Chen, G.D.; Shi, G.H.; Li, J.; Hu, T.Y.; Lin, H.W. Dysiarenone, a Dimeric C21 Meroterpenoid with Inhibition of COX-2 Expression from the Marine Sponge Dysidea arenaria. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 3092–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolesnikova, S.A.; Lyakhova, E.G.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Berdyshev, D.V.; Pislyagin, E.A.; Popov, R.S.; Grebnev, B.B.; Makarieva, T.N.; Minh, C.V.; Stonik, V.A. Cyclobutastellettolides A and B, C19 Norterpenoids from a Stelletta sp. Marine Sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 3196–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Y.H.; Jiao, W.H.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, D.Q.; Zhu, H.R.; Liu, K.C.; Sun, F.; Chen, H.F.; Lin, H.W. Septosones A–C, in Vivo Anti-inflammatory Meroterpenoids with Rearranged Carbon Skeletons from the Marine Sponge Dysidea septosa. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 767–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, C.; Cho, Y.; Son, A.; Shin, S.W.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, H.C. Therapeutic Potential of (–)-Agelamide D, a Diterpene Alkaloid from the Marine Sponge Agelas Sp., as a Natural Radiosensitizer in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Models. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolesnikova, S.A.; Lyakhova, E.G.; Kozhushnaya, A.B.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Berdyshev, D.V.; Popov, R.S.; Stonik, V.A. New Isomalabaricane-Derived Metabolites from a Stelletta Sp. Marine Sponge. Molecules 2021, 26, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wang, D.; Wilson, B.; Kang, U.; Bokesch, H.; Smith, E.; Wamiru, A.; Goncharova, E.; Voeller, D.; Lipkowitz, S.; et al. Agelasine Diterpenoids and Cbl-b Inhibitory Ageliferins from the Coralline Demosponge Astrosclera willeyana. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Sun, C.; Hou, X.; Che, Q.; Zhang, G.; Gu, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhu, T.; Li, D. Ascandinines A–D, Indole Diterpenoids, from the Sponge-Derived Fungus Aspergillus candidus HDN15-152. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 2431–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, C.J.; Huang, C.Y.; Ahmed, A.F.; Orfali, R.S.; Alarif, W.M.; Huang, Y.M.; Wang, Y.H.; Hwang, T.L.; Sheu, J.H. An Anti-Inflammatory 2,4-Cyclized-3,4-Secospongian Diterpenoid and Furanoterpene-Related Metabolites of a Marine Sponge Spongia Sp. from the Red Sea. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Wu, J.; Ding, L.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Lai, Q.; Lin, W.; Wang, T.; He, S. Guignardones Y–Z, Antiviral Meroterpenes from Penicillium Sp. NBUF154 Associated with a Crella Sponge from the Marine Mesophotic Zone. Chem. Biodivers. 2022, 19, e202200475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pech-Puch, D.; Forero, A.M.; Fuentes-Monteverde, J.C.; Lasarte-Monterrubio, C.; Martinez-Guitian, M.; González-Salas, C.; Guillén-Hernández, S.; Villegas-Hernández, H.; Beceiro, A.; Griesinger, C.; et al. Antimicrobial Diterpene Alkaloids from an Agelas citrina Sponge Collected in the Yucatán Peninsula. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.; Bawkar, C.; Hyun, J.M.; Song, M.J.; Jeong, K.; Lee, Y.J. Norterpene Cyclic Peroxides from the Marine Sponge Diacarnus spinipoculum, Inhibitors of Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin 1. J. Nat. Prod. 2024, 87, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, I.M.; Paola, A.; Pérez, M.; García, M.; Blustein, G.; Schejter, L.; Palermo, J.A. Antifouling Diterpenoids from the Sponge Dendrilla antarctica. Chem. Biodivers. 2022, 19, e202100618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.; Li, S.; Su, M.; Yao, L.; Appendino, G.; Guo, Y. Structurally Diverse Diterpenoids from the Sanya Bay Nudibranch Hexabranchus sanguineus and Its Sponge-Prey Chelonaplysilla sp. Chem. Eur. J. 2023, 29, e202203858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Wang, M.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Ma, J.; Li, G.; Li, P. Terpenoids from the Sponge Sarcotragus Sp. Collected in the South China Sea. J. Nat. Prod. 2023, 86, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Feng, Y.; Huang, J.; Wu, S.; Hu, K.; Wu, J.; Naman, C.B.; Wang, H.; Lin, W.; He, S. Pestanoid A, a Rearranged Pimarane Diterpenoid Osteoclastogenesis Inhibitor from a Marine Mesophotic Zone Chalinidae Sponge-Associated Fungus, Pestalotiopsis Sp. NBUF145. J. Nat. Prod. 2024, 87, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marino, S.; Festa, C.; D’Auria, M.V.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.; Petek, S.; Debitus, C.; Andres, R.M.; Terencio, M.C.; Paya, M.; Zampella, A. Coscinolactams A and B: New Nitrogen-Containing Sesterterpenoids from the Marine Sponge Coscinoderma mathewsi Exerting Anti-Inflammatory Properties. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 2905–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Meng, X.J.; Fan, W.Y.; Du, W.T.; Deng, W.P. Research Advances in the Biologically Active Scalarane SesterTerpenoid Marine Natural Products. J. Chin. Pharm. Univ. 2010, 41, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Tang, H.F.; Yi, Y.H.; Lin, H.W. Scalarane Sesterterpenes from the Chinese Sponge Phyllospongia foliascens. Helv. Chim. Acta 2009, 92, 762–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Yi, Y.H.; Yang, F.; Chen, W.S.; Lin, H.W. Sesterterpenes and a New Sterol from the Marine Sponge Phyllospongia foliascens. Molecules 2010, 15, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahidol, C.; Prawat, H.; Sangpetsiripan, S.; Ruchirawat, S. Bioactive Scalaranes from the Thai Sponge Hyrtios gumminae. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.E.; Hollander, I.; Feldberg, L.; Frommer, E.; Mallon, R.; Tahir, A.; van Soest, R.; Andersen, R.J. Scalarane-Based Sesterterpenoid RCE-Protease Inhibitors Isolated from the Indonesian Marine Sponge Carteriospongia foliascens. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1106–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.E.; Bae, J.M.; Lee, K.J.; Oh, K.B.; Shin, J. Scalarane Sesterterpenes from the Sponge Hyatella sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, D.; Won, D.H.; Mun, B.; Kim, H.; Han, C.; Wang, W.; Chun, T.; Park, S.; Yoon, D.; Choi, H.; et al. Cytotoxic Scalarane Sesterterpenes from a Korean Marine Sponge Psammocinia sp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 2336–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Festa, C.; Cassiano, C.; D’Auria, M.V.; Debitus, C.; Monti, M.C.; De Marino, S. Scalarane Sesterterpenes from Thorectidae Sponges as Inhibitors of TDP-43 Nuclear Factor. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 8646–8655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, X.; Qiu, Y. Two New Scaralane-Type Sesterterpenoids Isolated from the Marine Sponge Hyrtios erectus. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2014, 8, 417–421. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, M.H.A.; Rateb, M.E.; Hetta, M.; Abdelaziz, T.A.; Sleim, M.A.; Jaspars, M.; Mohammed, R. Scalarane Sesterterpenes from the Egyptian Red Sea Sponge Phyllospongia lamellosa. Tetrahedron 2015, 71, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.R.; Lai, K.H.; Chang, Y.C.; Chen, Y.Y.; Su, J.H.; Huang, Y.M.; Chen, P.J.; Yu, S.S.; Duh, C.Y.; Sung, P.J. Sponge-Derived 24-Homoscalaranes as Potent Anti-Inflammatory Agents. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, A.Y.; Son, A.; Choi, C.; Lee, J. Isolation of Scalarane-Type Sesterterpenoids from the Marine Sponge Dysidea Sp. and Stereochemical Reassignment of 12-Epi-Phyllactone D/E. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.B.; Hong, L.L.; Shang, R.Y.; Liu, H.Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, W.; Sun, F.; Jiao, W.H.; et al. Dysiscalarones A-E, Scalarane Sesterterpenoids with Nitric Oxide Production Inhibitory Activity from Marine Sponge Dysidea granulosa. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 111, 104791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, B.R.; Lai, K.H.; Lee, G.H.; Yu, S.S.F.; Duh, C.Y.; Su, J.H.; Zheng, L.G.; Hwang, T.L.; Sung, P.J. Scalarane-Type Sesterterpenoids from the Marine Sponge Lendenfeldia Sp. Alleviate Inflammation in Human Neutrophils. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, K.; Francis, P. Hyrtioscalaranes A and B, Two New Scalarane-Type Sesterterpenes from Hyrtios erectus with Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 5559–5570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, H.N.K.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, Y.J. Scalarane Sesterterpenoids Isolated from the Marine Sponge Hyrtios erectus and Their Cytotoxicity. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.B.; Hu, B.; Ning, Z.; He, Y.; Men, X.L.; Yin, Z.F.; Jiao, B.H.; Liu, X.Y.; Lin, H.W. Phyllofenones F–M, Scalarane Sesterterpenes from the Marine Sponge Phyllospongia foliascens. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.B.; Hu, B.; Wu, G.F.; Ning, Z.; He, Y.; Jiao, B.H.; Liu, X.Y.; Lin, H.W. Phyllospongianes A-E, Dinorscalarane Sesterterpenes from the Marine Sponge Phyllospongia foliascens. J. Nat. Prod. 2023, 86, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.C.; Tseng, S.W.; Liu, L.L.; Chou, Y.; Ho, Y.S.; Lu, M.C.; Su, J.H. Cytotoxic Sesterterpenoids from a Sponge Hippospongia sp. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 987–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Yang, L.; Luo, X.; de Voogd, N.J.; Tang, X.; Li, P.; Li, G. Bishomoscalarane Sesterterpenoids from the Sponge Dysidea granulosa Collected in the South China Sea. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Shao, Z.; Zhang, X. Sesterterpenes from the Sponge Dysidea sp. Z. Naturforschung B 2010, 65, 625–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, M.; Depree, C.; Thompson, K.J. Antifouling Sesterterpenes from the New Zealand Marine Sponge Semitaspongia bactriana. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2009, 4, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forestieri, R.; Merchant, C.E.; de Voogd, N.J.; Matainaho, T.; Kieffer, T.J.; Andersen, R.J. Alotaketals A and B, Sesterterpenoids from the Marine Sponge Hamigera Species that Activate the cAMP Cell Signaling Pathway. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 5166–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daoust, J.; Fontana, A.; Merchant, C.E.; de Voogd, N.J.; Patrick, B.O.; Kieffer, T.J.; Andersen, R.J. Ansellone A, a Sesterterpenoid Isolated from the Nudibranch Cadlina luteromarginata and the Sponge Phorbas sp., Activates the cAMP Signaling Pathway. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 320–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daoust, J.; Chen, M.; Wang, M.; Williams, D.E.; Garcia Chavez, M.A.; Wang, Y.A.; Merchant, C.E.; Fontana, A.; Kieffer, T.J.; Andersen, R.J. Sesterterpenoids Isolated from a Northeastern Pacific Phorbas sp. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 8267–8273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rho, J.R.; Hwang, B.S.; Sim, C.J.; Joung, S.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, H.J. Phorbaketals A, B, and C, Sesterterpenoids with a Spiroketal of Hydrobenzopyran Moiety Isolated from the Marine Sponge Phorbas sp. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 5590–5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Wang, W.; Kim, H.; Giri, A.G.; Won, D.H.; Hahn, D.; Baek, K.R.; Lee, J.; Yang, I.; Choi, H.; et al. Phorbaketals L-N, Cytotoxic Sesterterpenoids Isolated from the Marine Sponge of the Genus Phorbas. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 4095–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Mun, B.; Lee, Y.; Venkat Reddy, M.; Park, Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Hahn, D.; Chin, J.; Ekins, M.; et al. Bioactive Sesterterpenoids from a Korean Sponge Monanchora sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubert, J.G.; Furkert, D.P.; Brimble, M.A. Preparation of cis-γ-Hydroxycarvone Derivatives for Synthesis of Sesterterpenoid Natural Products: Total Synthesis of Phorbin, A. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 2231–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rho, J.R.; Hwang, B.S.; Joung, S.; Byun, M.R.; Hong, J.H.; Lee, H.Y. Phorbasones A and B, Sesterterpenoids Isolated from the Marine Sponge Phorbas sp. and Induction of Osteoblast Differentiation. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 884–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Lee, Y.; Lee, T.G.; Mun, B.; Giri, A.G.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Hahn, D.; Yang, I.; Chin, J.; et al. Phorone A and Isophorbasone A, Sesterterpenoids Isolated from the Marine Sponge Phorbas sp. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 4486–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.C.; Shih, P.S.; Lin, Y.S.; Lin, Y.C.; Kuo, Y.H.; Kuo, Y.C.; Khalil, A.T. Irciformonins E–K, C22-Trinorsesterterpenoids from the Sponge Ircinia formosana. Helv. Chim. Acta 2009, 92, 2101–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianese, G.; Silber, J.; Luciano, P.; Merten, C.; Erpenbeck, D.; Topaloglu, B.; Kaiser, M.; Tasdemir, D. Antiprotozoal Linear Furanosesterterpenoids from the Marine Sponge Ircinia oros. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2566–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afifi, A.H.; Kagiyama, I.; El-Desoky, A.H.; Kato, H.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; de Voogd, N.J.; Ammar, N.M.; Hifnawy, M.S.; Tsukamoto, S. Sulawesins A–C, Furanosesterterpene Tetronic Acids That Inhibit USP7, from a Psammocinia sp. Marine Sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2045–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, B.K.; Tenney, K.; Ang, K.H.; Abdulla, M.; Arkin, M.; McKerrow, J.H.; Crews, P. The Marine Sponge Diacarnus bismarckensis as a Source of Peroxiterpene Inhibitors of Trypanosoma brucei, the Causative Agent of Sleeping Sickness. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefranc, F.; Nuzzo, G.; Hamdy, N.A.; Fakhr, I.; Moreno, Y.; Banuls, L.; Van Goietsenoven, G.; Villani, G.; Mathieu, V.; van Soest, R.; et al. In Vitro Pharmacological and Toxicological Effects of Norterpene Peroxides Isolated from the Red Sea Sponge Diacarnus erythraeanus on Normal and Cancer Cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Al Haidari, R.A.; Mohamed, G.A. Megaspinoxide A: New Norterpene Cyclic Peroxide from the Sponge Diacarnus megaspinorhabdosa. Nat. Prod. J. 2014, 4, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.J.; Zhang, H.J.; Lu, H.Y.; Yang, F.; Jiao, W.H.; Yi, Y.H.; Chen, W.S.; Lin, H.W. Hippolides A–H, Acyclic Manoalide Derivatives from the Marine Sponge Hippospongia lachne. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1248–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.M.; Jeon, J.E.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, H.S.; Sim, C.J.; Oh, K.B.; Shin, J. Sesterterpenes from the Tropical Sponge Coscinoderma sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1805–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Gresa, M.P.; Cabedo, N.; González-Mas, M.C.; Ciavatta, M.L.; Avila, C.; Primo, J. Terretonins E and F, Inhibitors of the Mitochondrial Respiratory Chain from the Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus insuetus. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1348–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Khalil, Z.G.; Capon, R.J. Fascioquinols A-F: Bioactive Meroterpenes from a Deep-Water Southern Australian Marine Sponge, Fasciospongia sp. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 2591–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Mandi, A.; Debbab, A.; Wray, V.; Schulz, B.; Muller, W.E.G.; Lin, W.H.; Proksch, P.; Kurtan, T.; Aly, A.H. New Austalides from the Sponge-Associated Fungus Aspergillus sp. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 2011, 6009–6019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Li, D. Austalides S–U, New Meroterpenoids from the Sponge-Derived Fungus Aspergillus aureolatus HDN14-107. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diyabalanage, T.; Ratnayake, R.; Bokesch, H.R.; Ransom, T.T.; Henrich, C.J.; Beutler, J.A.; McMahon, J.B.; Gustafson, K.R. Flabelliferins A and B, Sesterterpenoids from the South Pacific Sponge Carteriospongia flabellifera. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1490–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Du, L.; Kelly, M.; Zhou, Y.D.; Nagle, D.G. Structures and Potential Antitumor Activity of Sesterterpenes from the Marine Sponge Hyrtios communis. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1492–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.J.; Jiao, W.H.; Yang, F.; Yi, Y.H.; Di, Y.T.; Han, B.N.; Lin, H.W. New Hippolide Derivatives with Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Inhibitory Activity from the Marine Sponge Hippospongia lachne. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4096–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, J.K.; Kim, C.K.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.; Oh, D.C.; Oh, K.B.; Shin, J. Gombaspiroketals A–C, Sesterterpenes from the Sponge Clathria gombawuiensis. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 2826–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prompanya, C.; Dethoup, T.; Bessa, L.J.; Pinto, M.M.; Gales, L.; Costa, P.M.; Silva, A.M.; Kijjoa, A. New Isocoumarin Derivatives and Meroterpenoids from the Marine Sponge-Associated Fungus Aspergillus similanensis sp. nov. KUFA 0013. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5160–5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdjul, D.B.; Yamazaki, H.; Takahashi, O.; Kirikoshi, R.; Mangindaan, R.E.; Namikoshi, M. Two New Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Inhibitors, Hyattellactones A and B, from the Indonesian Marine Sponge Hyattella sp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 904–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, J.K.; Kim, C.K.; Ahn, C.H.; Oh, D.C.; Oh, K.B.; Shin, J. Additional Sesterterpenes and a Nortriterpene Saponin from the Sponge Clathria gombawuiensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Tietjen, I.; Chen, M.; Williams, D.E.; Daoust, J.; Brockman, M.A.; Andersen, R.J. Sesterterpenoids Isolated from the Sponge Phorbas sp. Activate Latent HIV-1 Provirus Expression. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 11324–11334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.H.; Hong, L.L.; Sun, J.B.; Piao, S.J.; Chen, G.D.; Deng, H.; Wang, S.P.; Yang, F.; Lin, H.W. (±)-Hippolide J—A Pair of Unusual Antifungal Enantiomeric Sesterterpenoids from the Marine Sponge Hippospongia lachne. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 3421–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audoin, C.; Bonhomme, D.; Ivanisevic, J.; de la Cruz, M.; Cautain, B.; Monteiro, M.C.; Reyes, F.; Rios, L.; Perez, T.; Thomas, O.P. Balibalosides, an Original Family of Glucosylated Sesterterpenes Produced by the Mediterranean Sponge Oscarella balibaloi. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1477–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanki, D.; Imai, K.; Ise, Y.; Okada, S.; Matsunaga, S. Oshimalides A and B, Sesterterpenes of the Manoalide Class from a Luffariella Sp. Deep-Sea Marine Sponge: Application of Asymmetric Dihydroxylation in Structure Elucidation. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 84, 1676–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Wang, Q.; Tang, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, M.; Li, P.; Li, G. Cytotoxic Manoalide-Type Sesterterpenes from the Sponge Luffariella variabilis Collected in the South China Sea. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 84, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.B.; Gu, B.B.; Iwasaki, A.; Jiang, W.L.; Ecker, A.; Wang, S.P.; Yang, F.; Lin, H.W. Dactylospenes A–E, Sesterterpenes from the Marine Sponge Dactylospongia elegans. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, D.T.; Trang, D.T.; Tai, B.H.; Yen, P.H.; Thu, V.K.; Nhiem, N.X.; Kiem, P.V. Hippotulosas A-D: Four New Sesterterpenes from Marine Sponge Hippospongia fistulosa Lendenfeld, 1889. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 36, 5247–5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracegirdle, J.; Olsen, S.S.H.; Teng, M.N.; Tran, K.C.; Amsler, C.D.; McClintock, J.B.; Baker, B.J. Neosuberitenone, a New Sesterterpenoid Carbon Skeleton; New Suberitenones; and Bioactivity against Respiratory Syncytial Virus, from the Antarctic Sponge Suberites sp. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, H.; Angulo-Preckler, C.; Calabro, K.; Kaur, N.; Lasserre, P.; Cautain, B.; de la Cruz, M.; Reyes, F.; Avila, C.; Thomas, O.P. Suberitane Sesterterpenoids from the Antarctic Sponge Phorbas areolatus (Thiele, 1905). Tetrahedron Lett. 2018, 59, 3353–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majer, T.; Bhattarai, K.; Straetener, J.; Pohlmann, J.; Cahill, P.; Zimmermann, M.O.; Hübner, M.P.; Kaiser, M.; Svenson, J.; Schindler, M.; et al. Discovery of Ircinianin Lactones B and C—Two New Cyclic Sesterterpenes from the Marine Sponge Ircinia wistarii. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.; Kondratyuk, T.P.; Tan, G.T.; Pezzuto, J.M.; Chang, L.C. Bioactive Sulfated Sesterterpene Alkaloids and Sesterterpene Sulfates from the Marine Sponge Fasciospongia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Li, L.; Zhu, T.; Ba, M.; Li, G.; Gu, Q.; Guo, Y.; Li, D. Phenylspirodrimanes with Anti-HIV Activity from the Sponge-Derived Fungus Stachybotrys chartarum MXH-X73. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 2298–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.K.; Song, I.H.; Park, H.Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, H.S.; Sim, C.J.; Oh, D.C.; Oh, K.B.; Shin, J. Suvanine Sesterterpenes and Deacyl Irciniasulfonic Acids from a Tropical Coscinoderma sp. Sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 1396–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yuan, B.; Liu, D.; Gao, S.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Brasilianoids A-F, New Meroterpenoids from the Sponge-Associated Fungus Penicillium brasilianum. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 311–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, B.; Liu, D.; Zhu, K.; Huang, J.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. DMOA-Based Meroterpenoids with Diverse Scaffolds from the Sponge-Associated Fungus Penicillium brasilianum. Tetrahedron 2019, 75, 2193–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.H.; Cheng, B.H.; Shi, G.H.; Chen, G.D.; Gu, B.B.; Zhou, Y.J.; Hong, L.L.; Yang, F.; Liu, Z.Q.; Qiu, S.Q.; et al. Dysivillosins A–D, Unusual Anti-allergic Meroterpenoids from the Marine Sponge Dysidea villosa. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsebai, M.F.; Schoeder, C.T.; Müller, C.E. Fintiamin: A Diketopiperazine from the Marine Sponge-Derived Fungus Eurotium sp. Archiv Pharm. 2021, 354, 2100206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzue, M.; Kikuchi, T.; Tanaka, R.; Yamada, T. Tandyukisins E and F, Novel Cytotoxic Decalin Derivatives Isolated from a Marine Sponge-Derived Fungus. Tetrahedron Lett. 2016, 57, 5070–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Umebayashi, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Sugiura, Y.; Kikuchi, T.; Tanaka, R. Determination of the Chemical Structures of Tandyukisins B–D, Isolated from a Marine Sponge-Derived Fungus. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3231–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stonik, V.A.; Kolesnikova, S.A. Malabaricane and Isomalabaricane Triterpenoids, Including Their Glycoconjugated Forms. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, T.; Mizutani, Y.; Umebayashi, Y.; Inno, N.; Kawashima, M.; Kikuchi, T.; Tanaka, R. Tandyukisin, a Novel Ketoaldehyde Decalin Derivative, Produced by a Marine Sponge-Derived Trichoderma harzianum. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 662–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yan, Y.L.; Yu, X.Y.; Pan, J.Y.; Liu, X.L.; Hong, L.L.; Wang, B. Meroterpenoids from Marine Sponge Hyrtios Sp. and Their Anticancer Activity against Human Colorectal Cancer Cells. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Molina, A.; Pech-Puch, D.; Millán, R.E.; Ageitos, L.; Villegas-Hernández, H.; Pachón, J.; Pérez Sestelo, J.; Sánchez-Céspedes, J.; Rodríguez, J.; Jiménez, C. Uncovering the Potent Antiviral Activity of the Sesterterpenoids from the Sponge Ircinia Felix Against Human Adenoviruses: From the Natural Source to the Total Synthesis. Chemistry. 2024, 30, e202401844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Abraham, I.; Carvalho, P.; Kuang, Y.H.; Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.; Avery, M.A.; Chen, Z.S.; El Sayed, K.A. Sipholane Triterpenoids: Chemistry, Reversal of ABCB1/P-glycoprotein-Mediated Multidrug Resistance, and Pharmacophore Modeling. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirashima, M.; Tsuda, K.; Hamada, T.; Okamura, H.; Furukawa, T.; Akiyama, S.; Tajitsu, Y.; Ikeda, R.; Komatsu, M.; Doe, M.; et al. Cytotoxic Isomalabaricane Derivatives and a Monocyclic Triterpene Glycoside from the Sponge Rhabdastrella globostellata. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1512–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, N.; Momose, R.; Shibazaki, A.; Gonoi, T.; Fromont, J.; Kobayashi, J. Stelliferins J-N, Isomalabaricane-Type Triterpenoids from Okinawan Marine Sponge Rhabdastrella cf. globostellata. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 6689–6696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhu, H.; Ren, J.; Deng, Z.; de Voogd, N.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Globostelletins J-S (sic), Isomalabaricanes with Unusual Cyclopentane Sidechains from the Marine Sponge Rhabdastrella globostellata. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.Q.; Mao, S.C.; Yu, X.Q.; Guo, Y.W. Isomalabaricane Triterpenes with Potent Protein-tyrosine Phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) Inhibition from the Hainan Sponge Stelletta sp. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2013, 49, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wang, J.; Qiao, W.; Zhao, C.; Tang, S. Jaspiferins H-J, New Isomalabaricane-Type Terpenoids from the South China Sea Marine Sponge Jaspis stellifera. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2018, 54, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.J.; Tang, S.A.; Xing, G.S.; Zhao, W.J.; Zhao, C.; Duan, H.Q.; Lin, W.H. Jaspiferins C-F, Four New Isomalabaricane-Type Triterpenoids from the South China Sea Sponge Jaspis stellifera. J. Asian. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 16, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, K.H.; Huang, Z.H.; El-Shazly, M.; Peng, B.R.; Wei, W.C.; Su, J.H. Isomalabaricane Triterpenes from the Marine Sponge Rhabdastrella sp. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Qiu, P.; Xu, B.; Zhao, Q.; Gu, Y.C.; Fu, L.; Bi, S.; Lan, L.; Wang, C.Y.; Guo, Y.W. Cytotoxic and Antibacterial Isomalabaricane Terpenoids from the Sponge Rhabdastrella globostellata. J. Nat. Prod. 2022, 85, 1799–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonov, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Kalinin, V.I.; Stonik, V.A.; Mollo, E.; Cimino, G. New Triterpene Oligoglycosides from the Caribbean Sponge Erylus formosus. Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 2182–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Jeon, J.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, H.S.; Sim, C.J.; Oh, K.B.; Shin, J. Nortriterpene Glycosides of the Sarasinoside Class from the Sponge Lipastrotethya sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Jiao, J.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, T.; Li, D. Pyronepolyene C-glucosides with NF-κB Inhibitory and Anti-Influenza A viral (H1N1) Activities from the Sponge-Associated Fungus Epicoccum sp. JJY40. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 3188–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colorado, J.; Munoz, D.; Marquez, D.; Marquez, M.E.; Lopez, J.; Thomas, O.P.; Martinez, A. Ulososides and Urabosides-Triterpenoid Saponins from the Caribbean Marine Sponge Ectyoplasia ferox. Molecules 2013, 18, 2598–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Jang, K.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, H.S.; Sim, C.J.; Oh, K.B.; Shin, J. Triterpene Galactosides of the Pouoside Class and Corresponding Aglycones from the Sponge Lipastrotethya sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 2563–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonov, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Afiyatullov, S.S.; Leshchenko, E.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Yurchenko, E.A.; Kalinin, V.I.; Stonik, V.A. Erylosides F8, V1-V3, and W-W2—New triterpene oligoglycosides from the Carribean sponge Erylus goffrilleri. Carbohydr. Res. 2017, 449, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadahiro, Y.; Hitora, Y.; Fukumoto, A.; Ise, Y.; Angkouw, E.D.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; Tsukamoto, S. Melophluosides A and B, New Triterpene Galactosides from the Marine Sponge Melophlus sarasinorum. Tetrahedron Lett. 2020, 61, 151852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzati, F.; Warsito, M.F.; Bayu, A.; Prasetyoputri, A.; Atikana, A.; Sukmarini, L.; Rahmawati, S.I.; Putra, M.Y. Chemical Diversity and Biological Activity of Secondary Metabolites Isolated from Indonesian Marine Invertebrates. Molecules 2021, 26, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, H.N.K.; Kim, M.J.; Shin, A.Y.; Tran, L.V.H.; Lee, J.; Lee, Y.J. Coscinoderines A–J: Trisubstituted Pyridinium-Containing Norterpenoids Isolated from Coscinoderma bakusi, a Tropical Marine Sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2023, 86, 2145–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mama, R.L.; Gelani, C.D.; Daluz, J.M.T.; Uy, M.M.; Ohta, E.; Ohta, S. Two New Sarasinosides from Marine Sponge Petrosia nigricans. Nat. Prod. Res. 2024, 38, 2395–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolesnikova, S.A.; Lyakhova, E.G.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Afiyatullov, S.S.; Yurchenko, E.A.; Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Minh, C.V.; Stonik, V.A. Isolation, Structures, and Biological Activities of Triterpenoids from a Penares sp. Marine Sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1746–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozhushnaya, A.B.; Kolesnikova, S.A.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Popov, R.S.; Ivanchina, N.V. New Nor-Isomalabaricanic Acids from the Vietnamese Marine Sponge Rhabdastrella globostellata. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2024, 60, 1056–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Choi, H.; Hwang, H.; Kang, H.; Rho, J.R. Gukulenins A and B, Cytotoxic Tetraterpenoids from the Marine Sponge Phorbas gukulensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 734–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine Natural Products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2023, 40, 275–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wibowo, J.T.; Ahmadi, P.; Rahmawati, S.I.; Bayu, A.; Putra, M.Y.; Kijjoa, A. Marine-Derived Indole Alkaloids and Their Biological and Pharmacological Activities. Mar. Drugs 2021, 20, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afsona, K.; Kuntal, H.; Belarani, M.; Ritabrata, K.; Rajshekhar, G.; Anupam, A.; Biplab, D.; Shaileyee, D. Studies of Chemical Distribution and Pharmacological Activities of Porifera-Derived Alkaloids: A review (2000–2023). Eur. J. Med. Chem. Rep. 2024, 11, 100158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyer, E.; Lavaud, C.; Massiot, G. Meroterpenoids? A Historical and Critical Review of This Biogenetic Determinant. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2023, 40, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.; Saleem, M.; Tousif, M.I.; Anwar, M.A.; Surup, F.; Ali, I.; Wang, D.; Mamadalieva, N.Z.; Alshammari, E.; Ashour, M.L.; et al. Meroterpenoids: A Comprehensive Update Insight on Structural Diversity and Biology. Biomolecules. 2021, 11, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menna, M.; Imperatore, C.; D’Aniello, F.; Aiello, A. Meroterpenes from Marine Invertebrates: Structures, Occurrence, and Ecological Implications. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1602–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, D.; Pecoraro, C.; Panzeca, G.; Geng, X.; Margot, S.F.R.; Stella, C.; Elisa, G.; Patrizia, D.; Barbara, P. 1,3,4-Oxadiazole and 1,3,4-Thiadiazole Nortopsentin Derivatives against Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Synthesis, Cytotoxic Activity, and Inhibition of CDK1. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, T.; Li, J.; Wu, R. Natural Product Databases for Drug Discovery: Features and Applications. Pharm. Sci. Adv. 2024, 2, 100050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fu, X.; Zhang, X. A Brief Overview of Synthetic Biology. Chin. Biotechnol. 2024, 44, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, T.; Zhao, H. A Brief Overview of Synthetic Biology Research Programs and Roadmap Studies in the United States. Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 2016, 1, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Li, S.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Luo, Y.; Lv, C.; Wang, B.; Cheng, C.H.K.; Chen, H.; Yang, X. Genome Sequencing and Analysis of Thraustochytriidae sp. SZU445 Provides Novel Insights into the Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Pathway. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Yin, F.; Wang, X.; Kong, L. Progress in Approved Drugs from Natural Product Resources. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2024, 22, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).