Effects of Sediment Chemical Properties on Phosphorus Release Rates in the Sediment-Water Interface of the Steppe Wetlands
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Analysis Method of Water and Sediments
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Characters of Sediment in Types of Wetlands
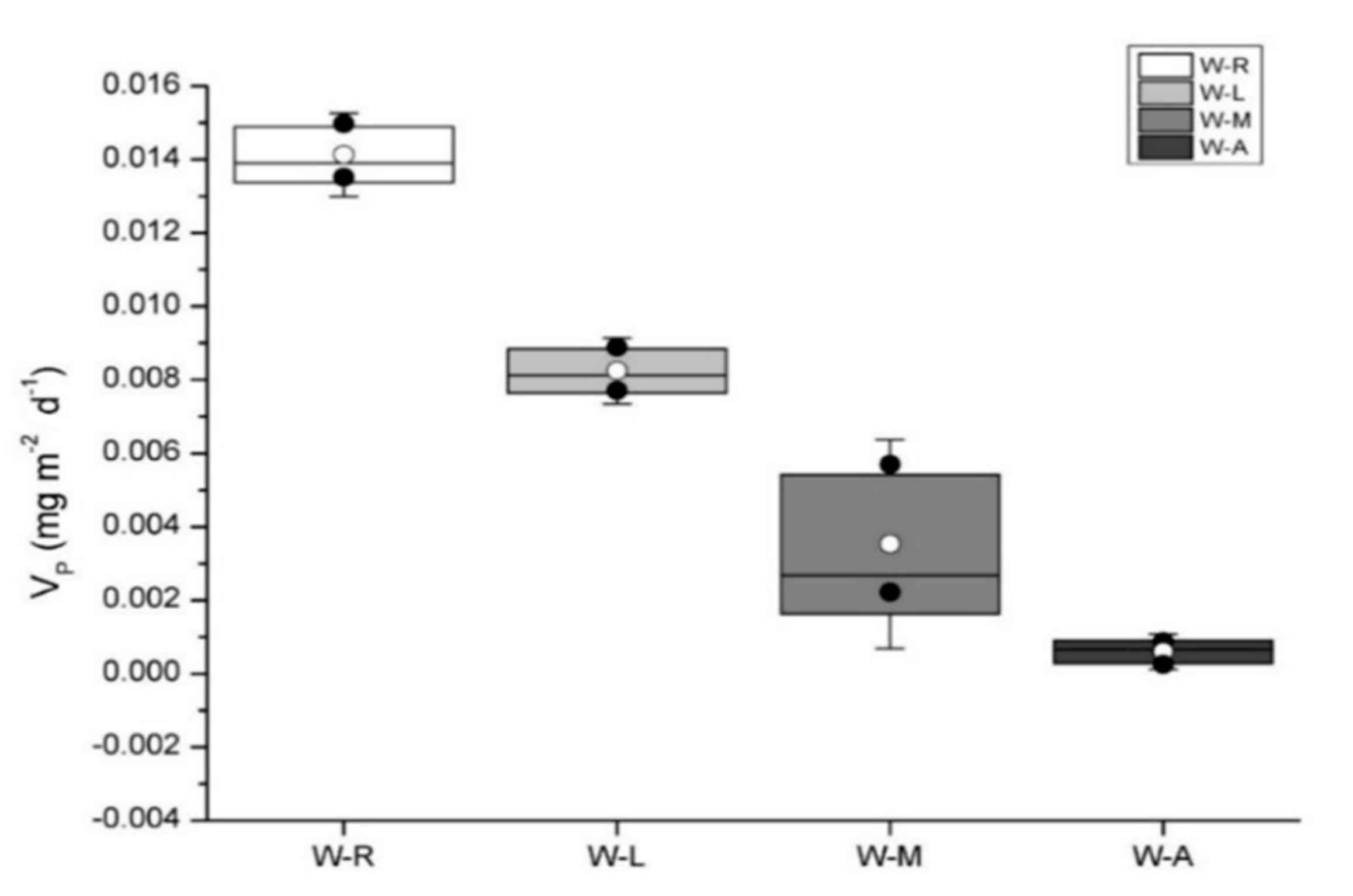
3.2. Phosphorus Release Rates in Sediment Surface Water of Types of Wetlands
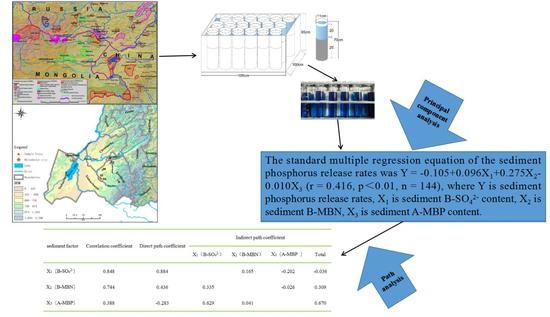
3.3. Main Factors Affecting Phosphorus Release Rates
4. Discussion
4.1. Phosphorus Release Rates
4.2. Factors Affecting Phosphorus Release Rate in Sediment–Water Interface
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kexia, X.; Huaicheng, G.; Yanfeng, S.; Yongtai, H. Assessment of the spatial-temporal eutrophic character in the Lake Dianchi. J. Geogr. Sci. 2005, 15, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, V.H.; Schindler, D.W. Eutrophication science: Where do we go from here? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, V.H.; Tilman, G.D.; Nekola, J.C. Eutrophication: Impacts of excess nutrient inputs on freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 1999, 100, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, R.G. Limnology: Lake and River Ecosystems, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2001; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Tang, L. Study prospect on removing and transforming characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus in sediment-water interface. J. Yunnan Agric. Univ. 2005, 20, 527–533. [Google Scholar]
- Oladosu, N.O.; Abayomi, A.A.; Olayinka, K.O.; Alo, B.I. Wet nitrogen and phosphorus deposition in the eutrophication of the Lagos Lagoon, Nigeria. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 8645–8657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correll, D.L. The role of phosphorus in the eutrophication of receiving waters: A review. J. Environ. Qual. 1998, 27, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Sondergaard, M.; Jensen, J.P.; Havens, K.E.; Anneville, O.; Carvalho, L.; Coveney, M.F.; Deneke, R.; Dokulil, M.T.; Foy, B.; et al. Lake responses to reduced nutrient loading—An analysis of contemporary long-term data from 35 case studies. Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 1747–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.W.; Hecky, R.E.; Findlay, D.L.; Stainton, M.P.; Parker, B.R.; Paterson, M.J.; Beaty, K.G.; Lyng, M.; Kasian, S.E. Eutrophication of lakes cannot be controlled by reducing nitrogen input: Results of a 37-year whole-ecosystem experiment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11254–11258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, L.; McDonald, C.; de Hoyos, C.; Mischke, U.; Phillips, G.; Borics, G.; Poikane, S.; Skjelbred, B.; Solheim, A.L.; Van Wichelen, J.; et al. Sustaining recreational quality of European lakes: Minimizing the health risks from algal blooms through phosphorus control. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 50, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rydin, E. Potentially mobile phosphorus in Lake Erken sediment. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2037–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundby, B. The phosphorus cycle in coastal marine sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1992, 37, 1129–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.L.; Zhou, W.B. Phosphorus forms and distribution in the sediments of Poyang Lake, China. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2011, 26, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndergaard, M.S.; Jensen, J.P.; Jeppesen, E. Role of sediment and internal loading of phosphorus in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Ye, T.R.; Krumholz, L.R.; Jiang, H.L. Temperature and cyanobacterial bloom biomass influence phosphorous cycling in eutrophic lake sediments. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Liu, L.; Li, M.; Zhang, X. Effects of pH, temperature, dissolved oxygen, and flow rate on phosphorus release processes at the sediment and water interface in storm sewer. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2013, 2013, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penn, M.R.; Auer, M.T.; Doerr, S.M.; Driscoll, C.T.; Brooks, C.M. Seasonality in phosphorus release rates from the sediments of a hypereutrophic lake under a matrix of pH and redox conditions. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2000, 57, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraguchi, A. Phosphorus Release from Sediments in a Riparian phragmites australis Community at the Estuary of the Chikugogawa River, Western Japan. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, P.A.; Ruddy, K.R.; Graetz, D.A. Phosphorus geochemistry in the sediment-water column of a hypereutrophic lake. J. Environ. Qual. 1991, 20, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, O.; Balla, D.; Kalettka, T.; Maassen, S. Sink or source—The effect of hydrology on phosphorus release in the cultivated riverine wetland Spreewald (Germany). Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 58, 1813–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirbahman, A.; Lake, B.A.; Norton, S.A. Seasonal phosphorus dynamics in the surficial sediment of two shallow temperate lakes: A solid-phase and pore-water study. Hydrobiologia 2013, 701, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsev, S.; Tsandev, I.; L’Heureux, I.; Rancourt, D.G. Factors controlling long-term phosphorus efflux from lake sediments: Exploratory reactive-transport modeling. Chem. Geol. 2006, 234, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slomp, C.; Raaphorst, W. Phophate adsorption in oxidized marine sediments. Chem. Geol. 1993, 107, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Bochove, E.V.; Auclair, J.C.; Thériault, G.; Denault, J.T.; Bossé, C.; Li, X.; Hu, C. Phosphorus algal availability and release potential in suspended and streambed sediments in relation to sediment and catchment characteristics. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 188, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, D.; Cheng, P.; Fan, J.; Zhong, B. Effects of sediment physical properties on the phosphorus release in aquatic environment. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2015, 58, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Ding, S.; Zhong, J.; Fan, C.; Chen, Q.; Yin, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation of simulated dredging to control internal phosphorus release from sediments: Focused on phosohorus transfer and resupply across the sediment-water interface. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 592, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonov, E.; Goroshko, O.; Tatiana, T. Daurian Steppe Wetlands of the Amur-Heilong River Basin (Russia, China, and Mongolia). In The Wetland Books; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y. The Impact of Climate Change on Vegetation Productivity Pattern in Hulunbuir Forest-Steppe Ecotone; Ludong University: Yantai, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Ding, S.; Luo, J.; Xu, Y. Effects of temperature on phosphorus release in sediments of Hongfeng Lake, southwest China: An experimental study using diffusive gradients in thin-films (DGT) technique. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 5885–5894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genkai-Kato, M.; Carpenter, S.R. Eutrophication due to phosphorus recycling in relation to lake morphometry, temperature, and macrophytes. Ecology 2005, 86, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmaeus, J.M.; Rydin, E. A time-dynamic phosphorus model for the profundal sediments of Lake Erken, Sweden. Aquat. Sci. 2006, 68, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Jin, X.; Yao, Y.; Li, L.; Wu, F. Effects of biological activity, light, temperature and oxygen on phosphorus release processes at the sediment and water interface of Taihu Lake, China. Water Res. 2008, 42, 2251–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; He, F.; Kong, L.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, Z. Release characteristics of sediment P in all fractions of Donghu Lake, Wuhan, China. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, R.; Larousse, A.; Jacquet, M.A.; Marin, M.; Reiss, C. Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: A rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1985, 17, 837–842. [Google Scholar]
- Vance, E.D.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, P.C.; Powlson, D.S.; Jenkinson, D.S. Measurement of microbial biomass phosphorus in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1982, 14, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joergensen, R.G.; Kübler, H.; Meyer, B.; Wolters, V. Microbial biomass phosphorus in soils of beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) forests. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1995, 19, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Joergensen, R.G.; Pommerening, B.; Chaussod, R.; Brookes, P.C. Measurement of soil microbial biomass C by fumigation-extraction—An automated procedure. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1990, 22, 1167–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, G.; Ying, W.; Tao, D.; Wanli, K.; Dan, Z.; Ying, W. Determination of Cl− and SO42− in the soil by ion chromatography. Chin. J. Spectrosc. Lab. 2010, 27, 1840–1843. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Wang, S.; Yan, P.; Feng, C.W. Phosphorus fractions and the effect of pH on the phosphorus release of the sediments from different trophic areas in Taihu Lake, China. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 139, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, P.; Gupta, A.; Satya, S. Vermicomposting of different types of waste using Eisenia foetida: A comparative study. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, T.W.; Neubauer, C.; Glatzel, G. Factors controlling soil carbon and nitrogen stores in pure stands of Norway spruce (Picea abies) and mixed species stands in Austria. For. Ecol. Manag. 2002, 159, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Tang, H.; Wang, D. Phosphorus adsorption on natural sediments: Modeling and effects of pH and sediment composition. Water Res. 2005, 39, 1245–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Q.; Du, J.; Chen, H.; Yu, Z. Particle-size distribution and phosphorus forms as a function of hydrological forcing in the Yellow River. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 3385–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, M.; Xu, S.; Hou, L.; Ou, D. Distribution feature of inorganic phosphorus in tidal sediments of different grain sizes taken from Shanghai coastal zone. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2002, 21, 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, X.; Chu, J. Study on the phosphate sorption of the different particle size fractions in the sediments from wuli lake and gonghu lake. Res. Environ. Sci. 2004, 17, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Xu, F.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, W. Distributional characteristics of grain sizes of surface sediments in the Zhujiang River Estuary. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2014, 33, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Han, S.; Huang, T. The influences of environmental factors on phosphate sorption by sediments in Lake Dianchi. Shuili Xuebao 1998, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainswin, B.E.; House, W.A.; Leadbeater, B.S.; Armitage, P.D.; Patten, J. The effects of sediment size fraction and associated algal biofilms on the kinetics of phosphorus release. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 360, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, L.H.; Choi, E.; Stenstrom, M.K. Sediment characteristics, phosphorus types and phosphorus release rates between river and lake sediments. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Ahmed, M.K.; Raknuzzaman, M.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Islam, M.K. Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: A preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Qiu, X.; Chen, B.; Yu, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhong, G.; Li, H.; Chen, M.; Sun, G.; Huang, H.; et al. Antibiotics pollution in Jiulong River estuary: Source, distribution and bacterial resistance. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 1677–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohiuddin, K.M.; Zakir, H.M.; Otomo, K.; Sharmin, S.; Shikazono, N. Geochemical distribution of trace metal pollutants in water and sediments of downstream of an urban river. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 7, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balls, P. Nutrient behavior in 2 contrasting Scottish estuaries, the Forth and Tay. Oceanol. Acta 1992, 15, 261–277. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Hua, Z. The effect of vegetation on sediment resuspension and phosphorus release under hydrodynamic disturbance in shallow lakes. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 69, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, J.; Xu, S.; Qin, G.; Sun, Y.; Wang, F. Spatial distribution, adsorption/release characteristics, and environment influence of phosphorus on sediment in reservoir. Water 2017, 9, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, H.S.; Nielsen, O.I.; Koch, M.S.; Vicentea, I.D. Phosphorus release with carbonate dissolution coupled to sulfide oxidation in Florida Bay seagrass sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 1753–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schippers, A.; Bo, B.J. Biogeochemistry of pyrite and iron sulfide oxidation in marine sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2002, 66, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravina, M.D.; Acea, M.J.; Carballas, T. Seasonal changes in microbial biomass and nutrient flush in forest soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1995, 19, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, D.S.; Ladd, J.N. Microbial biomass in soil: Measurement and turnover. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1981, 451–471. [Google Scholar]
- Demaria, P.; Sinaj, S.; Flisch, R.; Frossard, E. Soil properties and phosphorus isotopic exchangeability in cropped temperate soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2013, 44, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.C.; He, Z.L.; Huang, C.Y. Microbial biomass phosphorus and its significance in predicting phosphorus availability in red soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2000, 31, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberson, A.; Friesen, D.K.; Rao, I.M.; Bühler, S.; Frossard, E. Phosphorus transformations in an oxisol under contrasting land-use systems: The role of the soil microbial biomass. Plant Soil 2001, 237, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.L.; Yang, X.E.; Baligar, V.C.; Calvert, D.V. Microbiological and biochemical indexing system for assessing quality of acid soils. Adv. Agron. 2003, 78, 89–138. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, F.W. The phosphate uptake mechanism. Plant Soil 2002, 245, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.S.; Raghubanshi, A.S.; Singh, R.S.; Srivastava, S.C. Microbial biomass acts as a source of plant nutrients in dry tropical forest and savanna. Nature 1989, 338, 499–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.C.; Singh, J.S. Microbial C, N and P in dry trophical forest soils: Effects of alternate land-uses and nutrient flux. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1991, 23, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mary, B.; Recous, S.; Robin, D. A model for calculating nitrogen fluxes in soil using 15N tracing. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1998, 30, 1963–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, C.C.; Liptzin, D. C:N:P stoichiometry in soil: Is there a “Redfield ratio” for the microbial biomass? Biogeochemistry 2007, 85, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Name of Sampling Place | Abbreviation | Latitude and Longitude | Statues of the Wetland | Average Water Depth (m) | Wetland Types |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HuiheMuqiao | R1 | 119°02′21.89″ E | The surroundings are grazing steppe. | 1.0–2.5 | River wetland (W–R) |
| 48°27′14.42″ N | |||||
| Interchange of Huihe and Yimin River | R2 | 119°44′09.23″ E | The surroundings are grazing steppe. | 1.0–2.5 | |
| 49°01′50.27″ N | |||||
| Hulun Lake | L1 | 117°27′31.25″ E | The surroundings are grazing steppe. | 4.0–5.5 | Lake wetland (W–L) |
| 49°11′23.88″ N | |||||
| Swan Lake | L2 | 119°04′21.99″ E | The surroundings are grazing steppe. | 2.0–3.0 | |
| 48°28′43.62″ N | |||||
| HuiheXiboqiao | M | 119°13′50.42″ E | The surroundings are grazing steppe. | 1.0–2.5 | Grassy Marsh wetland (W–M) |
| 48°49′13.25″ N | |||||
| Midstream of Yimin River | A | 120°01′44.28″ E | Water sources protection area. | 0.–2.5 | Reservoir wetland (W–A) |
| 48°16′59.52″ N |
| Wetland Types | SOC g·kg−1 | TN g·kg−1 | TP mg·kg−1 | IP mg·kg−1 | SO42− mg·kg−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W–R | 145.78 ± 2.01 a | 7.16 ± 0.39 bc | 507.53 ± 13.79 d | 407.08 ± 9.60 d | 5.39 ± 1.29 b |
| W–L | 76.38 ± 48.91 ab | 5.73 ± 0.61 c | 747.13 ± 32.27 c | 584.36 ± 13.29 c | 2.83 ± 0.86 b |
| W–M | 59.11 ± 18.83 b | 31.85 ± 7.86 a | 1057.56 ± 51.81 a | 766.99 ± 8.75 a | 23.83 ± 5.95 a |
| W–A | 146.08 ± 61.36 a | 15.10 ± 2.96 b | 894.65 ± 15.54 b | 629.13 ± 9.58 b | 0.87 ± 0.11 b |
| Item | Vp (mg/m−2/d−1) | A-Al-P | A-Fe-P | A-Ca-P | A-Oc-P | A-MBP | A-MBC | A-MBN | A-TP | B-SO42− | B-Al-P | B-Fe-P | B-Ca-P | B-Oc-P | B-MBP | B-MBC | B-MBN | B-TP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vp (mg/m−2/d−1) | 1.000 | 0.015 | −0.499 * | −0.654 ** | 0.336 | 0.388 | −0.236 | −0.069 | −0.538 * | 0.848 ** | −0.230 | −0.684 ** | −0.362 | −0.191 | 0.160 | −0.560 * | 0.744 ** | −0.546 * |
| A-Al-P | 1.000 | −0.349 | 0.226 | −0.225 | −0.174 | −0.484 * | −0.536 * | 0.235 | −0.241 | 0.844 ** | 0.595 ** | −0.296 | 0.653 ** | −0.512 * | −0.295 | 0.399 | 0.231 | |
| A-Fe-P | 1.000 | 0.313 | 0.445 | −0.225 | 0.870 ** | 0.683 ** | 0.614 ** | −0.267 | −0.511 * | 0.042 | 0.797 ** | −0.177 | 0.623 ** | 0.678 ** | −0.648 ** | 0.612 ** | ||
| A-Ca-P | 1.000 | 0.051 | −0.859 ** | 0.050 | −0.166 | 0.878 ** | −0.885 ** | 0.322 | 0.353 | 0.593 ** | 0.460 | −0.462 | 0.619 ** | −0.276 | 0.882 ** | |||
| A-Oc-P | 1.000 | −0.149 | 0.382 | 0.557 * | 0.361 | 0.366 | −0.506 * | −0.608 ** | 0.464 | 0.133 | 0.590 ** | 0.089 | −0.036 | 0.360 | ||||
| A-MBP | 1.000 | −0.047 | 0.158 | −0.787 ** | 0.712 ** | −0.214 | −0.150 | −0.572 * | −0.363 | 0.414 | −0.520 * | 0.093 | −0.790 ** | |||||
| A-MBC | 1.000 | 0.573 * | 0.358 | −0.042 | −0.678 ** | −0.166 | 0.721 ** | −0.469 * | 0.632 ** | 0.635 ** | −0.408 | 0.361 | ||||||
| A-MBN | 1.000 | 0.093 | 0.272 | −0.677 ** | −0.315 | 0.412 | −0.286 | 0.834 ** | 0.160 | −0.513 * | 0.106 | |||||||
| A-TP | 1.000 | −0.701 ** | 0.111 | 0.262 | 0.779 ** | 0.398 | −0.097 | 0.677 ** | −0.285 | 0.998 ** | ||||||||
| B-SO42− | 1.000 | −0.439 | −0.646 ** | −0.425 | −0.315 | 0.550 * | −0.607 ** | 0.379 | −0.704 ** | |||||||||
| B-Al-P | 1.000 | 0.749 ** | −0.492 * | 0.750 ** | −0.739 ** | −0.367 | 0.153 | 0.111 | ||||||||||
| B-Fe-P | 1.000 | −0.189 | 0.469 * | −0.393 | 0.006 | −0.348 | 0.262 | |||||||||||
| B-Ca-P | 1.000 | −0.227 | 0.251 | 0.890 ** | −0.267 | 0.780 ** | ||||||||||||
| B-Oc-P | 1.000 | −0.370 | −0.329 | −0.102 | 0.397 | |||||||||||||
| B-MBP | 1.000 | 0.025 | −0.373 | −0.100 | ||||||||||||||
| B-MBC | 1.000 | −0.292 | 0.673 ** | |||||||||||||||
| B-MBN | 1.000 | −0.287 | ||||||||||||||||
| B-TP | 1.000 |
| Component | Initial Eigenvalues | Extraction Sums of Squared Loadings | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Variance (%) | Cumulative (%) | Total | Variance (%) | Cumulative (%) | |
| 1 | 6.432 | 37.835 | 37.835 | 6.432 | 37.835 | 37.835 |
| 2 | 5.787 | 34.04 | 71.875 | 5.787 | 34.04 | 71.875 |
| 3 | 1.744 | 10.259 | 82.134 | 1.744 | 10.259 | 82.134 |
| 4 | 1.687 | 9.924 | 92.057 | 1.687 | 9.924 | 92.057 |
| 5 | 0.787 | 4.63 | 96.687 | |||
| 6 | 0.254 | 1.497 | 98.184 | |||
| 7 | 0.177 | 1.039 | 99.223 | |||
| 8 | 0.081 | 0.479 | 99.702 | |||
| 9 | 0.021 | 0.126 | 99.829 | |||
| 10 | 0.014 | 0.083 | 99.912 | |||
| 11 | 0.009 | 0.053 | 99.965 | |||
| 12 | 0.004 | 0.022 | 99.987 | |||
| 13 | 0.001 | 0.007 | 99.993 | |||
| 14 | 0.001 | 0.005 | 99.998 | |||
| 15 | 0 | 0.001 | 100 | |||
| 16 | 0 | 0 | 100 | |||
| 17 | 0 | 0 | 100 | |||
| Sediment Factor | Component | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| A-Al-P mg/kg | 0.018 | −0.020 | 0.233 | 0.066 |
| A-Fe-P mg/kg | 0.036 | 0.227 | 0.014 | −0.045 |
| A-Ca-P mg/kg | 0.165 | −0.052 | 0.019 | −0.010 |
| A-Oc-P mg/kg | 0.058 | 0.039 | 0.179 | 0.420 |
| A-MBP mg/kg | −0.182 | 0.131 | 0.008 | −0.088 |
| A-MBC mg/g | 0.032 | 0.127 | −0.114 | −0.047 |
| A-MBN mg/g | −0.054 | 0.252 | 0.080 | 0.067 |
| A-TP mg/kg | 0.158 | 0.024 | 0.089 | 0.090 |
| B-SO42− mg/kg | −0.113 | −0.001 | 0.056 | 0.234 |
| B-Al-P mg/kg | −0.009 | 0.008 | 0.201 | −0.089 |
| B-Fe-P mg/kg | −0.047 | 0.204 | 0.138 | −0.322 |
| B-Ca-P mg/kg | 0.158 | −0.037 | −0.126 | 0.073 |
| B-Oc-P mg/kg | 0.011 | 0.111 | 0.375 | 0.140 |
| B-MBP mg/kg | −0.090 | 0.249 | 0.082 | 0.094 |
| B-MBC mg/g | 0.151 | −0.073 | −0.242 | −0.108 |
| B-MBN mg/g | 0.064 | −0.350 | −0.090 | 0.245 |
| B-TP mg/kg | 0.158 | 0.025 | 0.089 | 0.089 |
| Model | Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | B | Std. Error | Beta | t | Sig. | |
| 1 | (Constant) | −0.087 | 0.027 | −3.25 | 0.005 | |
| B-SO42−mg/kg | 0.092 | 0.014 | 0.848 | 6.396 | 0 | |
| 2 | (Constant) | −0.1 | 0.014 | −7.009 | 0 | |
| B-SO42−mg/kg | 0.072 | 0.008 | 0.661 | 8.807 | 0 | |
| B-MBN mg/g | 0.312 | 0.047 | 0.494 | 6.585 | 0 | |
| 3 | (Constant) | −0.105 | 0.01 | −10.017 | 0 | |
| B-SO42−mg/kg | 0.096 | 0.009 | 0.884 | 10.973 | 0 | |
| B-MBN mg/g | 0.275 | 0.036 | 0.436 | 7.669 | 0 | |
| A-MBP mg/kg | −0.01 | 0.003 | −0.283 | −3.776 | 0.002 | |
| Sediment Factor | Correlation Coefficient | Direct Path Coefficient | Indirect Path Coefficient | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 (B-SO42−) | X2 (B-MBN) | X3 (A-MBP) | Total | |||
| X1 (B-SO42−) | 0.848 | 0.884 | 0.165 | −0.202 | −0.036 | |
| X2 (B-MBN) | 0.744 | 0.436 | 0.335 | −0.026 | 0.309 | |
| X3 (A-MBP) | 0.388 | −0.283 | 0.629 | 0.041 | 0.670 | |
| Sediment Factor | X1 (B-SO42−) | X2 (B-MBN) | X3 (A-MBP) |
|---|---|---|---|
| X1 (B-SO42−) | 0.7815 | 0.2922 | −0.3562 |
| X2 (B-MBN) | 0.1901 | −0.0230 | |
| X3 (A-MBP) | 0.0801 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, J.; Su, D.; Lv, S.; Diao, Z.; Xie, J.; Luo, Y. Effects of Sediment Chemical Properties on Phosphorus Release Rates in the Sediment-Water Interface of the Steppe Wetlands. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1430. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14111430
He J, Su D, Lv S, Diao Z, Xie J, Luo Y. Effects of Sediment Chemical Properties on Phosphorus Release Rates in the Sediment-Water Interface of the Steppe Wetlands. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2017; 14(11):1430. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14111430
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Jing, Derong Su, Shihai Lv, Zhaoyan Diao, Jingjie Xie, and Yan Luo. 2017. "Effects of Sediment Chemical Properties on Phosphorus Release Rates in the Sediment-Water Interface of the Steppe Wetlands" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 14, no. 11: 1430. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14111430
APA StyleHe, J., Su, D., Lv, S., Diao, Z., Xie, J., & Luo, Y. (2017). Effects of Sediment Chemical Properties on Phosphorus Release Rates in the Sediment-Water Interface of the Steppe Wetlands. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(11), 1430. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14111430