A Review of Environmental Contamination and Health Risk Assessment of Wastewater Use for Crop Irrigation with a Focus on Low and High-Income Countries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Current Global Scenario of Wastewater Use for Crop Irrigation
3. The Wastewater Use and Treatment in Low and High Income Countries
4. Potential Impacts of Wastewater Irrigation on Crops
5. The Effect of Wastewater on the Physico-Chemical Properties of Soil
5.1. The Effect of Wastewater on Soil pH
5.2. The Effect of Wastewater on Soil Organic Matter
5.3. The Effect of Wastewater on Soil Cations and Anions
6. The Effect of Wastewater on Soil Microbial Community
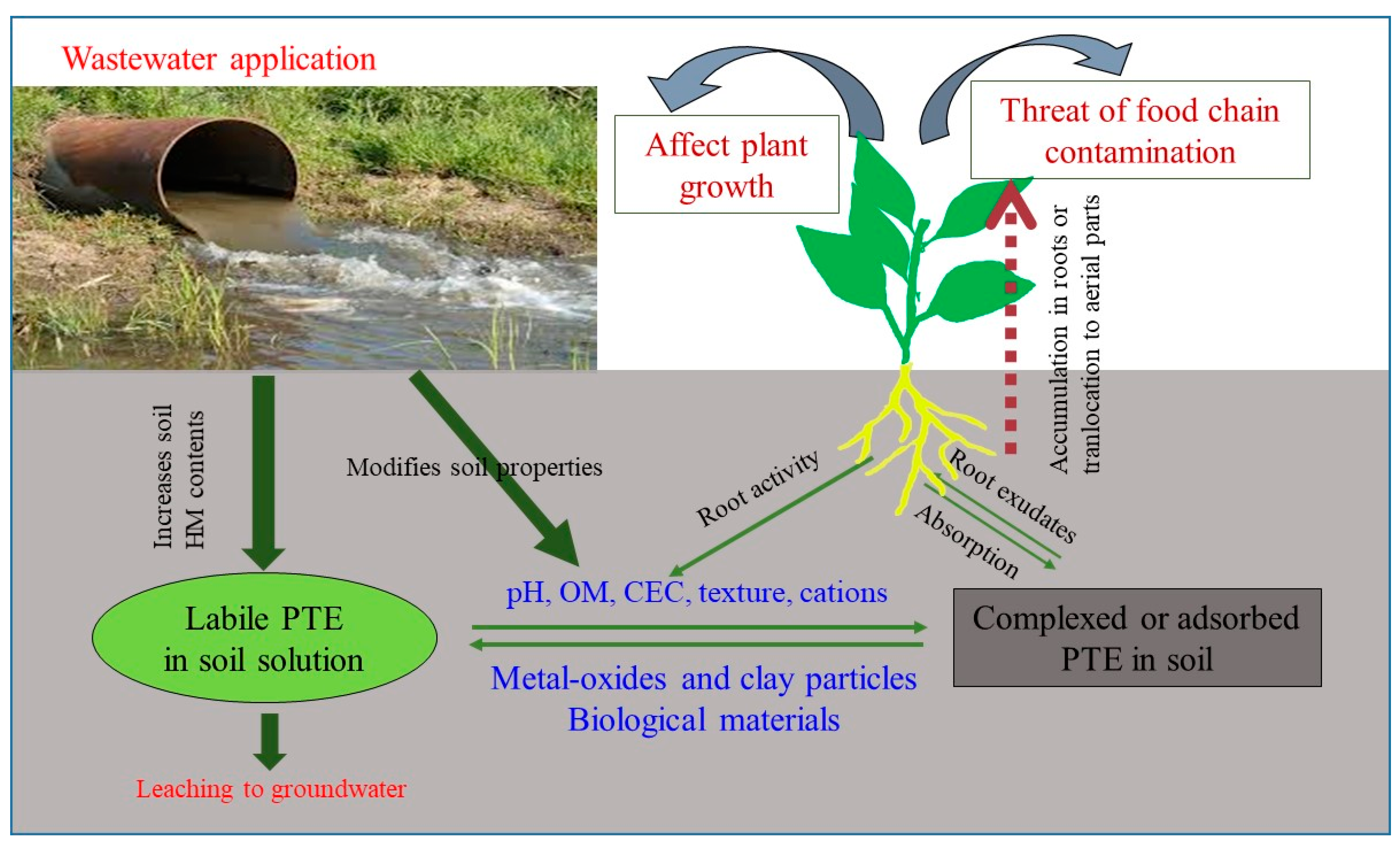
7. The Effect of Wastewater on Potentially Toxic Elements in the Soil-Plant System
7.1. The Effect of Wastewater on the Concentration of Potentially Toxic Elements in the Soil
7.2. The Effect of Wastewater on Potentially Toxic Element Accumulation in Plants
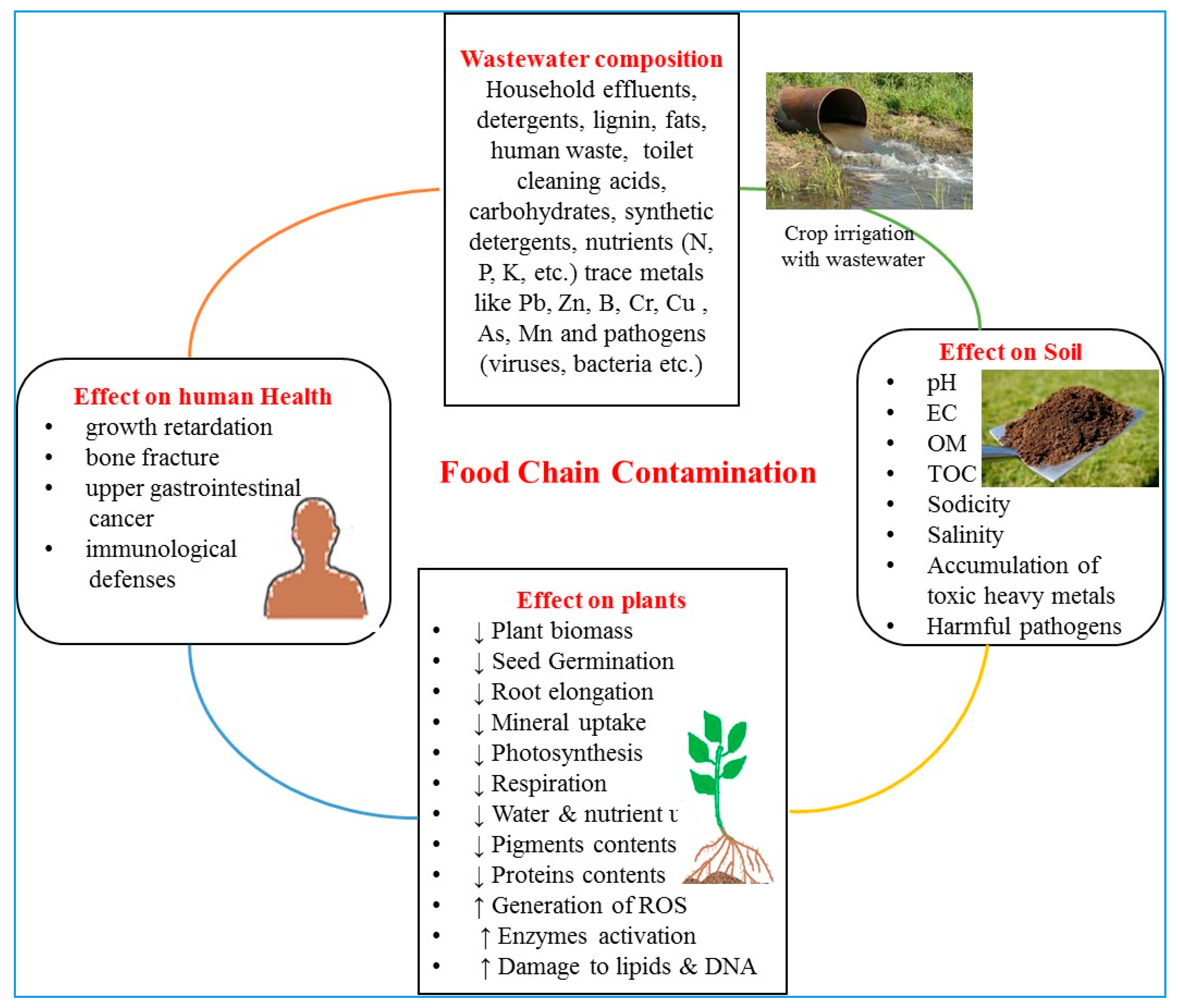
7.3. The Effect of Wastewater Irrigation on Food Chain Contamination and Human Health
8. Health Risk Assessment after Food Chain Contamination by Wastewater Irrigation
9. Future Perspectives
- The environmental protection laws and their proper implementation totally differ in developing and developed countries. Generally, the cities in developed countries have well-established and adopted environmentally friendly practices and environmentally sustainable approaches regarding wastewater disposal, treatment, and reuse in the agricultural sector. However, the scenario is very much alarming in developing countries, especially in highly populated areas of the Indo-Pak Sub-continent. In future, more wastewater will be produced/disposed and more environmental and health risks will appear due to the rapid urbanization, industrialization, increase in the world’s population, food demand, economic development, and increase in living standards. Therefore, there will be a need for more systematic approaches in industrial and agricultural sectors to tackle this environmental and health dilemma. At the industrial level, the use of environmental-friendly processes and techniques with minimal use/production of waste material can be highly effective.
- Similarly, the treatment of industrial wastewater before its discharge is also a key prerequisite to effectively alleviate its negative environmental effects. The proper establishment of wastewater treatment techniques can address the growing demands both in terms of quantity and quality. In the agricultural sector, the development of suitable irrigation approaches can be highly effective for its safe use. It is well-established that environmental contamination can be greatly controlled using a proper irrigation method. For example, drip irrigation has been regarded as the most environmentally friendly approach, which can mitigate up to 70% of environmental risks and leaching rates.
- Climate change has recently emerged as a key environmental challenge. The uncertainty of this anthropogenic-assisted natural phenomena and irregularity of the environment has to be faced and tacked properly. The scattered pattern of droughts and rainfall over the temporal scale will aggravate water shortages in some areas while flooding other areas. Under such conditions, there will be a need for appropriate techniques and wastewater disposal infrastructure to collect, recycle, and distribute wastewater, protect the soil, and optimize the management.
- In areas (arid, semi-arid) where fresh water supply is short, the mixing of wastewater with ground or surface water can greatly dilute the PTE concentrations in the applied (mixed) irrigation water. In this way, the risk of PTEs accumulating in soil and crops, as well as the associated health hazards, can be minimized. Similarly, the choice of vegetables/crops (low metal-accumulating species) cultivated using wastewater irrigation can also be a management strategy in areas where farmers have no choice but to use untreated wastewater for crop irrigation.
- In order to effectively manage this environmental and health issue, there is need to properly implement laws and regulations on wastewater discharge and use in the agricultural sector, especially in less developed countries. The reports show that farmers in less developed countries do not pay enough attention to such laws and regulations, which results in environmental and health issue. Therefore, there is a need for strict regulatory systems, at the local, national, and international level, for effectively managing wastewater irrigation in the agricultural sector. Although abutment data are available regarding the wastewater use for crop irrigation, its effect (both positive and negative) on the soil, on plants, and on humans, there is limited data available with respect to the chemical speciation of the different contaminants (especially PTEs) in wastewater generated from different sectors at different time periods. Similarly, the plant physiological responses (overproduction of reactive oxygen species, lipid peroxidation) and tolerance mechanisms (activation of antioxidative enzymes, production of phytochelatins, glutathione, and so forth) remain unexplored under the wastewater crop irrigation scenario. It is possible that wastewater composition and chemical speciation of a contaminant may greatly vary in different municipal/industrial wastewaters during different seasons (summer and winter). Consequently, the environmental and health risk of that contaminant can vary under these circumstances. Further research work is needed in this regard.
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rijsberman, F.R. Water scarcity: Fact or fiction? Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 80, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y. Wastewater irrigation: Past, present, and future. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, M.F.; Restrepo, I. Wastewater Reuse in Agriculture: A Review about Its Limitations and Benefits. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, S.; Shahid, M.; Dumat, C.; Niazi, N.K.; Bibi, I.; Gul Bakhat, H.F.S.; Abbas, G.; Murtaza, B.; Javeed, H.M.R. Influence of groundwater and wastewater irrigation on lead accumulation in soil and vegetables: Implications for health risk assessment and phytoremediation. Int. J. Phytoremed. 2017, 19, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alobaidy, A.H.M.J.; Abid, H.S.; Maulood, B.K. Application of water quality index for assessment of Dokan lake ecosystem, Kurdistan region, Iraq. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2010, 2, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalavrouziotis, I. The reuse of Municipal Wastewater in soils. Glob. Nest J. 2015, 17, 474–486. [Google Scholar]
- Abaidoo, R.C.; Keraita, B.; Drechsel, P.; Dissanayake, P.; Maxwell, A.S. Soil and crop contamination through wastewater irrigation and options for risk reduction in developing countries. In Soil Biology and Agriculture in the Tropics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 275–297. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez, B. Irrigation in developing countries using wastewater. Int. Rev. Environ. Strateg. 2006, 6, 229–250. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. AquaStat, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. 2017. Available online: http://www.fao.org/nr/water/aquastat/data/query/results.html (accessed on 22 January 2018).
- Murtaza, G.; Ghafoor, A.; Qadir, M.; Owens, G.; Aziz, M.; Zia, M. Disposal and use of sewage on agricultural lands in Pakistan: A review. Pedosphere 2010, 20, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, C.A.; Drechsel, P.; Raschid-Sally, L.; Bahri, A.; Mara, D.; Redwood, M.; Jiménez, B. Wastewater irrigation and health: Challenges and outlook for mitigating risks in low-income countries. In Wastewater Irrigation and Health: Assessing and Mitigating Risk in Low-Income Countries; Earthscan: London, UK, 2010; pp. 381–394. [Google Scholar]
- Qadir, M.; Wichelns, D.; Raschid-Sally, L.; McCornick, P.G.; Drechsel, P.; Bahri, A.; Minhas, P. The challenges of wastewater irrigation in developing countries. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, Y.-A.; Philip, A.; Nelson, A.W.; Muspratt, A.; Aikins, S. Safety assessment on microbial and heavy metal concentration in Clarias gariepinus (African catfish) cultured in treated wastewater pond in Kumasi, Ghana. Environ. Technol. 2017, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azimi, A.; Azari, A.; Rezakazemi, M.; Ansarpour, M. Removal of Heavy Metals from Industrial Wastewaters: A Review. ChemBioEng Rev. 2016, 4, 37–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M. Biogeochemical Behavior of Heavy Metals in Soil-Plant System; Higher Education Commssion: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2017; pp. 1–196. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Tang, J.; Wang, T.; Wu, D.; Jiao, R.; Ren, X. Impacts of Sewage Irrigation on Soil Properties of Farmland in China: A Review. Yellow River 2017, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muamar, A.; Zouahri, A.; Tijane, M.; El Housni, A.; Mennane, Z.; Yachou, H.; Bouksaim, M. Evaluation of heavy metals pollution in groundwater, soil and some vegetables irrigated with wastewater in the Skhirat region “Morocco”. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2014, 5, 961–966. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, M.; Sabir, M.; Arif Ali, M.; Ghafoor, A. Effect of organic amendments on phytoavailability of nickel and growth of berseem (Trifolium alexandrinum) under nickel contaminated soil conditions. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab. 2014, 26, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattan, R.; Datta, S.; Chhonkar, P.; Suribabu, K.; Singh, A. Long-term impact of irrigation with sewage effluents on heavy metal content in soils, crops and groundwater—A case study. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 109, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Cao, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, Y. Health risks of heavy metals in contaminated soils and food crops irrigated with wastewater in Beijing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 152, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Sharma, R.K.; Agrawal, M.; Marshall, F.M. Health risk assessment of heavy metals via dietary intake of foodstuffs from the wastewater irrigated site of a dry tropical area of India. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Aijun, L.; Zhang, S.; Hu, Q.; Zhu, Y.-G. Accumulation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and heavy metals in lettuce grown in the soils contaminated with long-term wastewater irrigation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mapanda, F.; Mangwayana, E.; Nyamangara, J.; Giller, K. The effect of long-term irrigation using wastewater on heavy metal contents of soils under vegetables in Harare, Zimbabwe. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 107, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mombo, S.; Foucault, Y.; Deola, F.; Gaillard, I.; Goix, S.; Shahid, M.; Schreck, E.; Pierart, A.; Dumat, C. Management of human health risk in the context of kitchen gardens polluted by lead and cadmium near a lead recycling company. J. Soils Sediment. 2016, 16, 1214–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Khalid, M.; Dumat, C.; Khalid, S.; Niazi, N.K.; Imran, M.; Bibi, I.; Ahmad, I.; Hammad, M.; Tabassum, R.A. Arsenic level and risk assessment of groundwater in Vehari, Punjab Province, Pakistan. Exposure Health 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, T.; Dumat, C.; Pierart, A.; Shahid, M.; Kang, Y.; Li, N.; Bertoni, G.; Laplanche, C. Measurement of metal bioaccessibility in vegetables to improve human exposure assessments: Field study of soil–plant–atmosphere transfers in urban areas, South China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2016, 38, 1283–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, T.; Leveque, T.; Shahid, M.; Foucault, Y.; Mombo, S.; Dumat, C. Lead and cadmium phytoavailability and human bioaccessibility for vegetables exposed to soil or atmospheric pollution by process ultrafine particles. J. Environ. Qual. 2014, 43, 1593–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, A.; Malik, R.N. Human health risk assessment of heavy metals via consumption of contaminated vegetables collected from different irrigation sources in Lahore, Pakistan. Arab. J. Chem. 2014, 7, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järup, L. Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br. Med. Bull. 2003, 68, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumat, C.; Xiong, T.; Shahid, M. Agriculture Urbaine Durable: Opportunité Pour la Transition Écologique; Presses Universitaires Européennes: Saarbrücken, Germany, 2016; pp. 1–88. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, M.; Rafiq, M.; Niazi, N.K.; Dumat, C.; Shamshad, S.; Khalid, S.; Bibi, I. Arsenic accumulation and physiological attributes of spinach in the presence of amendments: An implication to reduce health risk. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 16097–16106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller-Robbie, L.; Ramaswami, A.; Amerasinghe, P. Wastewater treatment and reuse in urban agriculture: Exploring the food, energy, water, and health nexus in Hyderabad, India. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 075005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecosse, D. Techniques Alternatives en vue de Subvenir à la Pénurie D’eau Dans le Monde; Sciences: Amiens, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W. A critical review on the end uses of recycled water. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 43, 1446–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, F.; Farissi, M. Reuse of Treated Wastewater in Agriculture: Solving Water Deficit Problems in Arid Areas. Ann. West Univ. Timisoara Ser. Biol. 2014, 17, 95. [Google Scholar]
- Winpenny, J.; Heinz, I.; Koo-Oshima, S.; Salgot, M.; Collado, J.; Hernandez, F. The Wealth of Waste; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Roma, Italy, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Thebo, A.L.; Drechsel, P.; Lambin, E.; Nelson, K. A global, spatially-explicit assessment of irrigated croplands influenced by urban wastewater flows. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 074008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for the Safe Use of Wastewater, Excreta and Greywater; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Huibers, F.P.; Moscoso, O.; Durán, A.; van Lier, J.B. Use of wastewate rin agriculture: The water chain approach. Irrig. Drain. 2005, 54, S3–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, P.; Nishida, J.; Afzal, J.; Akbar, S.; Damania, R.; Hanrahan, D. Pakistan Strategic Country Environmental Assessment; World Bank: South Asia Region, 2006; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Valipour, M.; Singh, V.P. Global experiences on wastewater irrigation: Challenges and prospects. In Balanced Urban Development: Options and Strategies for Liveable Cities; Springer: Gewerbestrasse, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 289–327. [Google Scholar]
- Drechsel, P.; Evans, A.E. Wastewater use in irrigated agriculture. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2010, 24, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Tan, D.; Lazareva, I. 8 Facts on China’s Wastewater. Available online: http://chinawaterrisk.org/resources/analysis-reviews/8-facts-on-china-wastewater/ (accessed on 30 April 2018).
- NPSCB. 1st National Pollutant Source Census Bulletin; China Press: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H. A study of the permissible toxicant level in agricultural utilization of sludge. Chin. Environ. Sci. 1983, 3, 56–59. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, C.A.; Faruqui, N.I.; Raschid-Sally, L. Wastewater Use in Irrigated Agriculture: Management Challenges in Developing Countries. In Wastewater Use in Irrigated Agriculture: Confronting the Livelihood and Environmental Realities; CABI Publishing: Oxfordshire, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Villalobos, G.; Gamez, G.; Herrera, F. Program for the reuse of wastewater in Mexico. In Municipal Wastewater in Agriculture; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1981; pp. 105–144. [Google Scholar]
- Keraita, B.; Drechsel, P. Agricultural use of untreated urban wastewater in Ghana. In Wastewater Use in Irrigated Agriculture: Confrontin the Livelihood and Environmental Realities; CABI Publishing: Oxfordshire, UK, 2004; pp. 101–112. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The United Nations World Water Development Report 2017. Wastewater, The Untapped Resource. Available online: www.unwater.org/publications/world-water-development-report-2017/ (accessed on 30 April 2018).
- MOHURD, Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. 2017. Available online: https://translate.google.com.pk/translate?hl=en&sl=zh-CN&u=http://www.mohurd.gov.cn/&prev=search (accessed on 30 April 2018).
- Kaur, R.; Wani, S.; Singh, A.; Lal, K. Wastewater Production, Treatment and Use in India. Presented at the 2nd Regional workshop on Safe Use of Wastewater in Agriculture, New Delhi, India, 16–18 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ensink, J.H.; Mahmood, T.; van der Hoek, W.; Raschid-Sally, L.; Amerasinghe, F.P. A nationwide assessment of wastewater use in Pakistan: An obscure activity or a vitally important one? Water Policy 2004, 6, 197–206. [Google Scholar]
- Minhas, P.; Samra, J. Quality Assessment of Water Resources in the Indo-Gangetic Basin Part in India; Central Soil Salinity Research Inst.: Karnal, India, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Drechsel, P.; Graefe, S.; Sonou, M.; Cofie, O.O. Informal Irrigation in Urban West Africa: An Overview; International Water Management Institute (IWMI): Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2006; Volume 102. [Google Scholar]
- Bokhari, S.H.; Mahmood-ul-Hassan, M.; Riaz, Y.; Munir, A.; Ali, Z. Baseline water quality of municipal ponds and metal removal ability of Typha latifolia L. from sewage and industrial wastewaters. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2017, 19, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ensink, J.H.; Simmons, R.; van der Hoek, W. Wastewater use in Pakistan: The cases of Haroonabad and Faisalabad. In Wastewater use in Irrigated Agriculture: Confronting the Livelihood and Environmental Realities; CABI Publishing: Oxfordshire, UK, 2004; pp. 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Morugán-Coronado, A.; García-Orenes, F.; Mataix-Solera, J.; Arcenegui, V.; Mataix-Beneyto, J. Short-term effects of treated wastewater irrigation on Mediterranean calcareous soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 112, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Khalid, S.; Abbas, G.; Shahid, N.; Nadeem, M.; Sabir, M.; Aslam, M.; Dumat, C. Heavy metal stress and crop productivity. In Crop Production and Global Environmental Issues; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Uyttendaele, M.; Jaykus, L.A.; Amoah, P.; Chiodini, A.; Cunliffe, D.; Jacxsens, L.; Holvoet, K.; Korsten, L.; Lau, M.; McClure, P. Microbial hazards in irrigation water: Standards, norms, and testing to manage use of water in fresh produce primary production. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2015, 14, 336–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mireles, A.; Solís, C.; Andrade, E.; Lagunas-Solar, M.; Piña, C.; Flocchini, R.G. Heavy metal accumulation in plants and soil irrigated with wastewater from Mexico city. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2004, 219–220, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbano, V.R.; Mendonça, T.G.; Bastos, R.G.; Souza, C.F. Effects of treated wastewater irrigation on soil properties and lettuce yield. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 181, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghobar, M.A.; Suresha, S. Effect of wastewater irrigation on growth and yield of rice crop and uptake and accumulation of nutrient and heavy metals in soil. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2016, 4, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Lal, K.; Kaur, R.; Rosin, K.; Patel, N. Low-Cost Remediation and On-Farm Management Approaches for Safe Use of Wastewater in Agriculture. In Innovative Saline Agriculture; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016; pp. 265–275. [Google Scholar]
- Nafchi, R.A. Evaluation of Wastewater Quality Compared to Well Water in Irrigation. Ecology 2017, 7, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassama, U.M.; Puteh, A.B.; Abd-Halim, M.R.; Kargbo, B. Influence of municipal wastewater on rice seed germination, seedling performance, nutrient uptake, and chlorophyll content. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 18, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galal, T.M.; Shehata, H.S. Impact of nutrients and heavy metals capture by weeds on the growth and production of rice (Oryza sativa L.) irrigated with different water sources. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 54, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, R.; Zaman, M.; Mondol, A.; Islam, M.; Hossain, M. Effects of textile industrial waste water and uptake of nutrients on the yield of rice. Bangladesh J. Agric. Res. 2011, 36, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.J.; Jan, M.T.; Farhatullah, N.; Khan, M.A.; Perveen, S.; Alam, S.; Jan, A.U. The effect of using waste water for tomato. Pak. J. Bot. 2011, 43, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar]
- Abdoulkader, B.A.; Mohamed, B.; Nabil, M.; Alaoui-Sossé, B.; Eric, C.; Aleya, L. Wastewater use in agriculture in Djibouti: Effectiveness of sand filtration treatments and impact of wastewater irrigation on growth and yield of Panicum maximum. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 84, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, N.-U.; Ahmad, T. Contamination of soil with heavy metals from industrial effluent and their translocation in green vegetables of Peshawar, Pakistan. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 14322–14329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Khan, S.; Khan, M.A.; Qamar, Z.; Waqas, M. The uptake and bioaccumulation of heavy metals by food plants, their effects on plants nutrients, and associated health risk: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 13772–13799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farahat, E.; Linderholm, H.W. The effect of long-term wastewater irrigation on accumulation and transfer of heavy metals in Cupressus sempervirens leaves and adjacent soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, A.; Alamzeb, S.; Begum, S. Accumulation of heavy metals in edible parts of vegetables irrigated with waste water and their daily intake to adults and children, District Mardan, Pakistan. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar]
- Shilpi, S.; Seshadri, B.; Sarkar, B.; Bolan, N.; Lamb, D.; Naidu, R. Comparative values of various wastewater streams as a soil nutrient source. Chemosphere 2018, 192, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.; Khan, D.; Santra, S. Heavy metal accumulation in vegetables grown in a long-term wastewater-irrigated agricultural land of tropical India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 6673–6682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.U.; Malik, R.N.; Muhammad, S. Human health risk from heavy metal via food crops consumption with wastewater irrigation practices in Pakistan. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2230–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Nahhal, Y.; Tubail, K.; Safi, M.; Safi, J. Effect of treated waste water irrigation on plant growth and soil properties in Gaza Strip, Palestine. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 1736–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavadil, J. The effect of municipal wastewater irrigation on the yield and quality of vegetables and crops. Soil Water Res. 2009, 4, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, K.; Singh, N.; Patel, M.; Tiwari, M.; Rai, U. Metal contamination of soil and translocation in vegetables growing under industrial wastewater irrigated agricultural field of Vadodara, Gujarat, India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 1670–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becerra-Castro, C.; Lopes, A.R.; Vaz-Moreira, I.; Silva, E.F.; Manaia, C.M.; Nunes, O.C. Wastewater reuse in irrigation: A microbiological perspective on implications in soil fertility and human and environmental health. Environ. Int. 2015, 75, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M.; Pinelli, E.; Dumat, C. Review of Pb availability and toxicity to plants in relation with metal speciation; role of synthetic and natural organic ligands. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 219, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M.; Pinelli, E.; Dumat, C. Tracing trends in plant physiology and biochemistry: Need of databases from genetic to kingdom level. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Niazi, N.K.; Khalid, S.; Murtaza, B.; Bibi, I.; Rashid, M.I. A critical review of selenium biogeochemical behavior in soil-plant system with an inference to human health. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 915–934. [Google Scholar]
- Kunhikrishnan, A.; Bolan, N.S.; Müller, K.; Laurenson, S.; Naidu, R.; Kim, W.-I. The influence of wastewater irrigation on the transformation and bioavailability of heavy metal (loid) s in soil. Adv. Agron. 2012, 115, 215. [Google Scholar]
- Vaseghi, S.; Afyouni, M.; Shariat Madari, H.; Mobli, M. Effect of sewage sludge on same macronutrients concentration and soil chemical properties. J. Water Wastewater 2005, 53, 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Khai, N.M.; Öborn, I.; Hillier, S.; Gustafsson, J.P. Modeling of metal binding in tropical Fluvisols and Acrisols treated with biosolids and wastewater. Chemosphere 2008, 70, 1338–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanli, A.M.; Javan, M.; Saadat, Y. Reuse of municipal effluent with drip irrigation and evaluation the effect on soil properties in a semi-arid area. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 144, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, C.; Lin, H. Soil property changes after four decades of wastewater irrigation: A landscape perspective. Catena 2008, 73, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, A.; Eliadou, E.; Michael, C.; Hapeshi, E.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Assessment of long-term wastewater irrigation impacts on the soil geochemical properties and the bioaccumulation of heavy metals to the agricultural products. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 4857–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabie Ahmed Usman, A.; Ghallab, A. Heavy-metal fractionation and distribution in soil profiles short-term-irrigated with sewage wastewater. Chem. Ecol. 2006, 22, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapliyal, A.; Vasudevan, P.; Dastidar, M.; Tandon, M.; Mishra, S. Irrigation with domestic wastewater: Responses on growth and yield of ladyfinger Abelmoschus esculentus and on soil nutrients. J. Environ. Biol. 2011, 32, 645. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Galal, H.A. Long-term Effect of Mixed Wastewater Irrigation on Soil Properties, Fruit Quality and Heavy Metal Contamination of Citrus. Am. J. Environ. Prot. 2015, 3, 100–105. [Google Scholar]
- Mulidzi, A.R. The Effect of Winery Wastewater Irrigation on the Properties of Selected Soils from the South African Wine Region. Ph.D. Thesis, Stellenbosch University, Stellenbosch, South Africa, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Abegunrin, T.; Awe, G.; Idowu, D.; Onigbogi, O.; Onofua, O. Effect of kitchen wastewater irrigation on soil properties and growth of cucumber (Cucumis sativus). J. Soil Sci. Environ. Manag. 2013, 4, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, P.C.P.; Gloaguen, T.V.; Gonçalves, R.A.B.; Santos, D.L.; Couto, C.F. Soil Chemistry after Irrigation with Treated Wastewater in Semiarid Climate. Rev. Bras. Ciênc. Solo 2016, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Muamar, A.-J.; Tijane, M.H.; Shawqi, E.-A.; El Housni, A.; Zouahri, A.; Bouksaim, M. Assessment of the Impact of Wastewater Use on Soil Properties. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2014, 5, 747–752. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; Yang, P.; Ren, S.; Li, Y.; Su, Y. Effects of Municipal Reclaimed Wastewater Irrigation on Soil Biochemical Properties. In Proceedings of the 2010 4th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering (iCBBE), Chengdu, China, 18–20 June 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Mojiri, A. Effects of municipal wastewater on physical and chemical properties of saline soil. J. Biol. Environ. Sci. 2011, 5, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, M.; Dumat, C.; Silvestre, J.; Pinelli, E. Effect of fulvic acids on lead-induced oxidative stress to metal sensitive Vicia faba L. plant. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2012, 48, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, T.; Bibi, I.; Shahid, M.; Niazi, N.K.; Murtaza, B.; Wang, H.; Ok, Y.S.; Sarkar, B.; Javed, M.T.; Murtaza, G. Effect of compost addition on arsenic uptake, morphological and physiological attributes of maize plants grown in contrasting soils. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 178, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Lu, Q.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Mao, X.; He, Z. Inhibition of the bioavailability of heavy metals in sewage sludge biochar by adding two stabilizers. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M.; Shamshad, S.; Rafiq, M.; Khalid, S.; Bibi, I.; Niazi, N.K.; Dumat, C.; Rashid, M.I. Chromium speciation, bioavailability, uptake, toxicity and detoxification in soil-plant system: A review. Chemosphere 2017, 178, 513–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linkhorst, A.; Dittmar, T.; Waska, H. Molecular Fractionation of Dissolved Organic Matter in a Shallow Subterranean Estuary: The Role of the Iron Curtain. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 1312–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lori, M.; Symnaczik, S.; Mäder, P.; De Deyn, G.; Gattinger, A. Organic farming enhances soil microbial abundance and activity—A meta-analysis and meta-regression. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Błońska, E.; Lasota, J.; Gruba, P. Enzymatic activity and stabilization of organic matter in soil with different detritus inputs. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2017, 63, 242–247. [Google Scholar]
- Chahal, S.S.; Choudhary, O.P.; Mavi, M.S. Organic amendments decomposability influences microbial activity in saline soils. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2017, 63, 1875–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedbabis, S.; Rouina, B.B.; Boukhris, M.; Ferrara, G. Effect of irrigation with treated wastewater on soil chemical properties and infiltration rate. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 133, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qadir, M.; Scott, C.A. Non-pathogenic trade-offs of wastewater irrigation. In Wastewater Irrigation and Health Assessing and Mitigating Risk in Low-Income Countries; IWMI: Colombo, SriLanka, 2010; pp. 101–126. [Google Scholar]
- Sou, M.Y.; Mermoud, A.; Yacouba, H.; Boivin, P. Impacts of irrigation with industrial treated wastewater on soil properties. Geoderma 2013, 200, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, I.C.C.; Fernandes, R.B.A.; Neves, J.C.L.; Ruiz, H.A.; Lima, T.L.B.D.; Hoogmoed, W. Soil Quality after Six Years of Paper Mill Industrial Wastewater Application. Rev. Bras. Ciênc. Solo 2017, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.V.; de Lima, V.L.; Pearson, H.W.; Silva, T.T.; Maciel, C.L.; Sofiatti, V. Chemical properties of a Haplustalf soil under irrigation with treated wastewater and nitrogen fertilization. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agrícola Ambient. 2016, 20, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tabatabaei, S.H.; Najafi, P.; Amini, H. Assessment of change in soil water content properties irrigated with industrial sugar beet wastewater. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. PJBS 2007, 10, 1649–1654. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Connor, R.; Renata, A.; Ortigara, C.; Koncagül, E.; Uhlenbrook, S.; Lamizana-Diallo, B.M.; Zadeh, S.M.; Qadir, M.; Kjellén, M.; Sjödin, J. The United Nations World Water Development Report 2017; The Untapped Resource: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Alghobar, M.A.; Suresha, S. Evaluation of Nutrients and Trace Metals and Their Enrichment Factors in Soil and Sugarcane Crop Irrigated with Wastewater. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2015, 3, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blok, C.; Jackson, B.E.; Guo, X.; De Visser, P.H.; Marcelis, L.F. Maximum Plant Uptakes for Water, Nutrients, and Oxygen Are Not Always Met by Irrigation Rate and Distribution in Water-based Cultivation Systems. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusan, M.J.M.; Hinnawi, S.; Rousan, L. Long term effect of wastewater irrigation of forage crops on soil and plant quality parameters. Desalination 2007, 215, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christen, E.; Quayle, W.; Marcoux, M.; Arienzo, M.; Jayawardane, N. Winery wastewater treatment using the land filter technique. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 1665–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosse, K.; Patti, A.; Christen, E.; Cavagnaro, T. Winery wastewater quality and treatment options in Australia. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2011, 17, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, M.; Aghajanzadeh, T.; Helm, J.; Parmar, S.; Hawkesford, M.J.; De Kok, L.J. Chloride and sulfate salinity differently affect biomass, mineral nutrient composition and expression of sulfate transport and assimilation genes in Brassica rapa. Plant Soil 2017, 411, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadaf, J.; Shah, G.A.; Shahzad, K.; Ali, N.; Shahid, M.; Ali, S.; Hussain, R.A.; Ahmed, Z.I.; Traore, B.; Ismail, I.M. Improvements in wheat productivity and soil quality can accomplish by co-application of biochars and chemical fertilizers. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balkhair, K.S.; El-Nakhlawi, F.S.; Ismail, S.M.; Al-Solimani, S.G. Treated wastewater use and its effect on water conservation, vegetative yeild, yield components and water use efficiency of some vegetable crops grown under two different irrigation systems in western region, Saudi Arabia. Eur. Sci. J. ESJ 2013, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, E.A. The contribution of manure and fertilizer nitrogen to atmospheric nitrous oxide since 1860. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubiello, F.N.; Salvatore, M.; Rossi, S.; Ferrara, A.; Fitton, N.; Smith, P. The FAOSTAT database of greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 015009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergé, X.; Dyer, J.; Desjardins, R.; Worth, D. Greenhouse gas emissions from the Canadian dairy industry in 2001. Agric. Syst. 2007, 94, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatta, G.; Libutti, A.; Gagliardi, A.; Beneduce, L.; Brusetti, L.; Borruso, L.; Disciglio, G.; Tarantino, E. Treated agro-industrial wastewater irrigation of tomato crop: Effects on qualitative/quantitative characteristics of production and microbiological properties of the soil. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 149, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatta, G.; Libutti, A.; Gagliardi, A.; Disciglio, G.; Beneduce, L.; d’Antuono, M.; Rendina, M.; Tarantino, E. Effects of treated agro-industrial wastewater irrigation on tomato processing quality. Ital. J. Agron. 2015, 10, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghtape, A.A.; Ghanbari, A.; Sirousmehr, A.; Siahsar, B.; Asgharipour, M.; Tavssoli, A. Effect of irrigation with wastewater and foliar fertilizer application on some forage characteristics of foxtail millet (Setaria italica). Int. J. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 3, 34–42. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Li, Z. In situ nutrient removal from aquaculture wastewater by aquatic vegetable Ipomoea aquatica on floating beds. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 59, 1937–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirelli, G.; Consoli, S.; Licciardello, F.; Aiello, R.; Giuffrida, F.; Leonardi, C. Treated municipal wastewater reuse in vegetable production. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 104, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rashidi, R.; Rusan, M.; Obaid, K. Changes in plant nutrients, and microbial biomass in different soil depths after long-term surface application of secondary treated wastewater. Sci. J. Riga Tech. Univ. Environ. Clim. Technol. 2013, 11, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Najafi, P.; Shams, J.; Shams, A. The effects of irrigation methods on some of soil and plant microbial indices using treated municipal wastewater. Int. J. Recycl. Organ. Waste Agric. 2015, 4, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkhair, K.S.; Ashraf, M.A. Field accumulation risks of heavy metals in soil and vegetable crop irrigated with sewage water in western region of Saudi Arabia. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 23, S32–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.; Dimbu, P. Research Article Effect of Abbatoir Waste Water on Soil Microbial Communities. Sch. Acad. J. Biosci. 2015, 5, 452–455. [Google Scholar]
- Adesemoye, A.; Opere, B.; Makinde, S. Microbial content of abattoir wastewater and its contaminated soil in Lagos, Nigeria. African J. Biotechnol. 2006, 5, 1963–1968. [Google Scholar]
- Disciglio, G.; Gatta, G.; Libutti, A.; Gagliardi, A.; Carlucci, A.; Lops, F.; Cibelli, F.; Tarantino, A. Effects of irrigation with treated agro-industrial wastewater on soil chemical characteristics and fungal populations during processing tomato crop cycle. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2015, 15, 765–780. [Google Scholar]
- Ahemad, M.; Malik, A. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals by zinc resistant bacteria isolated from agricultural soils irrigated with wastewater. Bacteriol. J. 2011, 2, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-lan, X.; Cui-ying, Z.; Shu-ming, Q.; Xu, M.; Ming-xia, G. Characterization of microorganisms in the soils with sewage irrigations. African J. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 6, 7168–7175. [Google Scholar]
- Malkawi, H.I.; Mohammad, M.J. Survival and accumulation of microorganisms in soils irrigated with secondary treated wastewater. J. Basic Microbiol. 2003, 43, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibekwe, A.; Gonzalez-Rubio, A.; Suarez, D. Impact of treated wastewater for irrigation on soil microbial communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 622–623, 1603–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, A.; Pampulha, M.E. Effects of long-term heavy metal contamination on soil microbial characteristics. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2006, 102, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadi, I.; Laor, Y.; Raviv, M.; Medina, S. Land spreading of olive mill wastewater: Effects on soil microbial activity and potential phytotoxicity. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Mar Alguacil, M.; Torrecillas, E.; Torres, P.; García-Orenes, F.; Roldán, A. Long-term effects of irrigation with waste water on soil AM fungi diversity and microbial activities: The implications for agro-ecosystem resilience. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mechri, B.; Mariem, F.B.; Baham, M.; Elhadj, S.B.; Hammami, M. Change in soil properties and the soil microbial community following land spreading of olive mill wastewater affects olive trees key physiological parameters and the abundance of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechri, B.; Chehab, H.; Attia, F.; Mariem, F.; Braham, M.; Hammami, M. Olive mill wastewater effects on the microbial communities as studied in the field of olive trees by analysis of fatty acid signatures. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2010, 46, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covarrubias, S.A.; de-Bashan, L.E.; Moreno, M.; Bashan, Y. Alginate beads provide a beneficial physical barrier against native microorganisms in wastewater treated with immobilized bacteria and microalgae. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 2669–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daims, H.; Nielsen, J.L.; Nielsen, P.H.; Schleifer, K.-H.; Wagner, M. In Situ Characterization ofNitrospira-Like Nitrite-Oxidizing Bacteria Active in Wastewater Treatment Plants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 5273–5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanjra, M.A.; Blackwell, J.; Carr, G.; Zhang, F.; Jackson, T.M. Wastewater irrigation and environmental health: Implications for water governance and public policy. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2012, 215, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duran, N.; Esposito, E. Potential applications of oxidative enzymes and phenoloxidase-like compounds in wastewater and soil treatment: A review. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2000, 28, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wu, L.; Frankenberger, W.T.; Chang, A.C. Soil enzyme activities of long-term reclaimed wastewater-irrigated soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37 (Suppl. S5), S36–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meli, S.; Porto, M.; Belligno, A.; Bufo, S.A.; Mazzatura, A.; Scopa, A. Influence of irrigation with lagooned urban wastewater on chemical and microbiological soil parameters in a citrus orchard under Mediterranean condition. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 285, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.-C.; Zhang, H.-B.; Ma, S.-T.; Wang, R.; Wang, G.-X.; Shao, Y.; Li, C.-X. Effects of mine wastewater irrigation on activities of soil enzymes and physiological properties, heavy metal uptake and grain yield in winter wheat. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 113, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenk, S.; Hadar, Y.; Minz, D. Resilience of soil bacterial community to irrigation with water of different qualities under Mediterranean climate. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niazi, N.K.; Bibi, I.; Shahid, M.; Ok, Y.S.; Burton, E.D.; Wang, H.; Shaheen, S.M.; Rinklebe, J.; Lüttge, A. Arsenic removal by perilla leaf biochar in aqueous solutions and groundwater: An integrated spectroscopic and microscopic examination. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 232, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niazi, N.K.; Bibi, I.; Shahid, M.; Ok, Y.S.; Shaheen, S.M.; Rinklebe, J.; Wang, H.; Murtaza, B.; Islam, E.; Nawaz, M.F. Arsenic removal by Japanese oak wood biochar in aqueous solutions and well water: Investigating arsenic fate using integrated spectroscopic and microscopic techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 621, 1642–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakoor, M.B.; Bibi, I.; Niazi, N.K.; Shahid, M.; Nawaz, M.F.; Farooqi, A.; Naidu, R.; Rahman, M.M.; Murtaza, G.; Lüttge, A. The evaluation of arsenic contamination potential, speciation and hydrogeochemical behaviour in aquifers of Punjab, Pakistan. Chemosphere 2018, 199, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakoor, M.B.; Niazi, N.K.; Bibi, I.; Murtaza, G.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; Seshadri, B.; Shahid, M.; Ali, S.; Bolan, N.S.; Ok, Y.S. Remediation of arsenic-contaminated water using agricultural wastes as biosorbents. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 46, 467–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabassum, R.A.; Shahid, M.; Dumat, C.; Niazi, N.K.; Khalid, S.; Shah, N.S.; Imran, M.; Khalid, S. Health risk assessment of drinking arsenic-containing groundwater in Hasilpur, Pakistan: Effect of sampling area, depth, and source. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, N.; Zia, Z.; Shahid, M.; Faiq Bakhat, H.; Anwar, S.; Mustafa Shah, G.; Rizwan Ashraf, M. Assessing Drinking Water Quality in Punjab, Pakistan. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 24, 2597–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Pourrut, B.; Dumat, C.; Nadeem, M.; Aslam, M.; Pinelli, E. Heavy-metal-induced reactive oxygen species: Phytotoxicity and physicochemical changes in plants. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; Volume 232, pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Zia, Z.; Bakhat, H.F.; Saqib, Z.A.; Shah, G.M.; Fahad, S.; Ashraf, M.R.; Hammad, H.M.; Naseem, W.; Shahid, M. Effect of water management and silicon on germination, growth, phosphorus and arsenic uptake in rice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 144, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woldetsadik, D.; Drechsel, P.; Keraita, B.; Itanna, F.; Gebrekidan, H. Heavy metal accumulation and health risk assessment in wastewater-irrigated urban vegetable farming sites of Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Int. J. Food Contam. 2017, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekki, A.; Sayadi, S. Study of heavy metal accumulation and residual toxicity in soil saturated with phosphate processing wastewater. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Wu, L.; Chang, A.C.; Zhang, Y. Impact of long-term reclaimed wastewater irrigation on agricultural soils: A preliminary assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 183, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silveira, M.L.A.; Alleoni, L.R.F.; Guilherme, L.R.G. Biosolids and heavy metals in soils. Sci. Agri. 2003, 60, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierart, A.; Shahid, M.; Séjalon-Delmas, N.; Dumat, C. Antimony bioavailability: Knowledge and research perspectives for sustainable agricultures. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 289, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourrut, B.; Shahid, M.; Dumat, C.; Winterton, P.; Pinelli, E. Lead uptake, toxicity, and detoxification in plants. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; Volume 213, pp. 113–136. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, M.; Dumat, C.; Khalid, S.; Niazi, N.K.; Antunes, P.M. Cadmium bioavailability, uptake, toxicity and detoxification in soil-plant system. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 241, 73–137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M.; Dumat, C.; Khalid, S.; Schreck, E.; Xiong, T.; Niazi, N.K. Foliar heavy metal uptake, toxicity and detoxification in plants: A comparison of foliar and root metal uptake. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 325, 36–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ma, Z.; van der Kuijp, T.J.; Yuan, Z.; Huang, L. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: Pollution and health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, S. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in fishes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River basin. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2575–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.-S.; Lee, J.-S.; Chon, H.-T.; Sager, M. Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment in the vicinity of the abandoned Songcheon Au–Ag mine in Korea. J. Geochem. Explor. 2008, 96, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.-S.; Ding, J.; Xu, B.; Wang, Y.-J.; Li, H.-B.; Yu, S. Incorporating bioaccessibility into human health risk assessments of heavy metals in urban park soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 424, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Javid, S.; Muhmood, A.; Mjeed, T.; Niaz, A.; Majeed, A. Heavy metal status of soil and vegetables grown on peri-urban area of Lahore district. Soil Environ. 2013, 32, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Jin, Q.; Kavan, P. A study of heavy metal pollution in China: Current status, pollution-control policies and countermeasures. Sustainability 2014, 6, 5820–5838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi-Koupai, J.; Mollaei, R.; Eslamian, S.S. The effect of pumice on reduction of cadmium uptake by spinach irrigated with wastewater. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2015, 15, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdu, N.; Abdulkadir, A.; Agbenin, J.O.; Buerkert, A. Vertical distribution of heavy metals in wastewater-irrigated vegetable garden soils of three West African cities. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2011, 89, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Wang, Z.; Hu, B.; Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Goodman, R.C. Heavy metals in soil and plants after long-term sewage irrigation at Tianjin China: A case study assessment. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 171, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qishlaqi, A.; Moore, F.; Forghani, G. Impact of untreated wastewater irrigation on soils and crops in Shiraz suburban area, SW Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 141, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, A.M.; Iqbal, J.; Khan, M.A.; Shah, M.H. Health risk assessment and multivariate apportionment of trace metals in wild leafy vegetables from Lesser Himalayas, Pakistan. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 92, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, B.; Song, C.; Park, B.; Cho, J. Heavy metals in brown rice (Oryza sativa L.) and soil after long-term irrigation of wastewater discharged from domestic sewage treatment plants. Pedosphere 2011, 21, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.S.; Hussain, M.I.; Ismail, S.; Khan, Q.M. Evaluating heavy metal accumulation and potential health risks in vegetables irrigated with treated wastewater. Chemosphere 2016, 163, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodda, N.; Salukazana, L.; Jackson, S.; Smith, M. Use of domestic greywater for small-scale irrigation of food crops: Effects on plants and soil. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2011, 36, 1051–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Melo, W.J.; de Stefani Aguiar, P.; de Melo, G.M.P.; de Melo, V.P. Nickel in a tropical soil treated with sewage sludge and cropped with maize in a long-term field study. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akoto, O.; Addo, D.; Baidoo, E.; Agyapong, E.A.; Apau, J.; Fei-Baffoe, B. Heavy metal accumulation in untreated wastewater-irrigated soil and lettuce (Lactuca sativa). Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 6193–6198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, R.; Khan, M.; Masab, M.; Rehman, H.U.; Rauf, N.U.; Shahab, S.; Ameer, N.; Sajed, M.; Ullah, M.; Rafeeq, M. Accumulation of heavy metals (Ni, Cu, Cd, Cr, Pb, Zn, Fe) in the soil, water and plants and analysis of physico-chemical parameters of soil and water collected from Tanda Dam Kohat. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2015, 7, 89–97. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Yao, H.; Shan, D.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yang, J. Heavy metal residues in soil and accumulation in maize at long-term wastewater irrigation area in Tongliao, China. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 628280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.K.; Agrawal, M.; Marshall, F. Heavy metal contamination of soil and vegetables in suburban areas of Varanasi, India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2007, 66, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamali, M.; Kazi, T.; Arain, M.; Afridi, H.; Jalbani, N.; Memon, A. Heavy metal contents of vegetables grown in soil, irrigated with mixtures of wastewater and sewage sludge in Pakistan, using ultrasonic-assisted pseudo-digestion. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2007, 193, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, N.T.L.; Ohtsubo, M.; Li, L.; Higashi, T.; Kanayama, M. Heavy-Metal Contamination of Soil and Vegetables in Wastewater-Irrigated Agricultural Soil in a Suburban Area of Hanoi, Vietnam. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2010, 41, 390–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masona, C.; Mapfaire, L.; Mapurazi, S.; Makanda, R. Assessment of heavy metal accumulation in wastewater irrigated soil and uptake by maize plants (Zea mays L.) at Firle Farm in Harare. J. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 4, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nguyen, T.L.H.; Kanayama, M.; Higashi, T.; Le, V.C.; Doan, T.H.; Daochu, A. Heavy Metal of Soil in Wastewater–Irrigated Agricultural Soil in a Surrounding Area of the Nhue River, Vietnam. J. Fac. Agric. Kyushu Univ. 2014, 59, 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Oyeku, O.; Eludoyin, A. Heavy metal contamination of groundwater resources in a Nigerian urban settlement. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 4, 201–214. [Google Scholar]
- Alia, N.; Sardar, K.; Said, M.; Salma, K.; Sadia, A.; Sadaf, S.; Toqeer, A.; Miklas, S. Toxicity and bioaccumulation of heavy metals in spinach (Spinacia oleracea) grown in a controlled environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 7400–7416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, R.; Suthar, S. Lead and cadmium removal from water using duckweed–Lemna gibba L.: Impact of pH and initial metal load. Alex. Eng. J. 2015, 54, 1297–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, M.H.; Watts, M.J.; Niaz, A.; Middleton, D.R.; Kim, A.W. Health risk assessment of potentially harmful elements and dietary minerals from vegetables irrigated with untreated wastewater, Pakistan. Environ. Geochem. Health 2017, 39, 707–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feenstra, S.; Hussain, R.; van der Hoek, W. Health Risks of Irrigation with Untreated Urban Wastewater in the Southern Punjab, Pakistan; International Water Management Institute: Lahore, Pakistan, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Aslam, M.M.; Malik, M.; Baig, M.; Qazi, I.; Iqbal, J. Treatment performances of compost-based and gravel-based vertical flow wetlands operated identically for refinery wastewater treatment in Pakistan. Ecol. Eng. 2007, 30, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensink, J.H.; Van der Hoek, W. Implementation of the WHO guidelines for the safe use of wastewater in Pakistan: Balancing risks and benefits. J. Water Health 2009, 7, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sheikh, K.H.; Irshad, M. Wastewater effluents from a tannery: Their effects on soil and vegetation in Pakistan. Environ. Conserv. 1980, 7, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, N.; Ibrar, D.; Alam, S. Heavy metals accumulation in soil irrigated with industrial effluents of Gadoon Industrial Estate, Pakistan and its comparison with fresh water irrigated soil. J. Agric. Chem. Environ. 2014, 3, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cecchi, M.; Dumat, C.; Alric, A.; Felix-Faure, B.; Pradère, P.; Guiresse, M. Multi-metal contamination of a calcic cambisol by fallout from a lead-recycling plant. Geoderma 2008, 144, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, R.; Zahra, Z.; Virk, N.; Shahid, M.; Pinelli, E.; Park, T.J.; Kallerhoff, J.; Arshad, M. Dose-dependent physiological responses of Triticum aestivum L. to soil applied TiO2 nanoparticles: Alterations in chlorophyll content, H2O2 production, and genotoxicity. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 255, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, S.; Shahid, M.; Niazi, N.K.; Rafiq, M.; Bakhat, H.F.; Imran, M.; Abbas, T.; Bibi, I.; Dumat, C. Arsenic behaviour in soil-plant system: Biogeochemical reactions and chemical speciation influences. In Enhancing Cleanup of Environmental Pollutants; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017; pp. 97–140. [Google Scholar]
- Saifullah; Shahid, M.; Zia-Ur-Rehman, M.; Sabir, M.; Ahmad, H.R. Chapter 14—Phytoremediation of Pb-Contaminated Soils Using Synthetic Chelates. In Soil Remediation and Plants; Mermut, K.R.H.S.Ö.R., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 397–414. [Google Scholar]
- Muchuweti, M.; Birkett, J.; Chinyanga, E.; Zvauya, R.; Scrimshaw, M.D.; Lester, J. Heavy metal content of vegetables irrigated with mixtures of wastewater and sewage sludge in Zimbabwe: Implications for human health. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 112, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, A.; Pathak, C. Accumulation of heavy metals in the vegetables grown in wastewater irrigated areas of Dehradun, India with reference to human health risk. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiziloglu, F.; Turan, M.; Sahin, U.; Kuslu, Y.; Dursun, A. Effects of untreated and treated wastewater irrigation on some chemical properties of cauliflower (Brassica olerecea L. var. botrytis) and red cabbage (Brassica olerecea L. var. rubra) grown on calcareous soil in Turkey. Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Agrawal, M. Potential benefits and risks of land application of sewage sludge. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Agrawal, M. Variations in heavy metal accumulation, growth and yield of rice plants grown at different sewage sludge amendment rates. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, M.; Anwar, F.; Rashid, U. Appraisal of heavy metal contents in different vegetables grown in the vicinity of an industrial area. Pak. J. Bot. 2008, 40, 2099–2106. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, M.; Ferrand, E.; Schreck, E.; Dumat, C. Behavior and impact of zirconium in the soil–plant system: Plant uptake and phytotoxicity. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; Volume 221, pp. 107–127. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, M.; Dumat, C.; Pourrut, B.; Sabir, M.; Pinelli, E. Assessing the effect of metal speciation on lead toxicity to Vicia faba pigment contents. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 144, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, M.; Shahid, M.; Abbas, G.; Shamshad, S.; Khalid, S.; Niazi, N.K.; Dumat, C. Comparative effect of calcium and EDTA on arsenic uptake and physiological attributes of Pisum sativum. Int. J. Phytoremed. 2017, 19, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafiq, M.; Shahid, M.; Shamshad, S.; Khalid, S.; Niazi, N.K.; Abbas, G.; Saeed, M.F.; Ali, M.; Murtaza, B. A comparative study to evaluate efficiency of EDTA and calcium in alleviating arsenic toxicity to germinating and young Vicia faba L. seedlings. J. Soils Sedim. 2017, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Arshad, M.; Kaemmerer, M.; Pinelli, E.; Probst, A.; Baque, D.; Pradere, P.; Dumat, C. Long-term field metal extraction by Pelargonium: Phytoextraction efficiency in relation to plant maturity. Int. J. Phytoremed. 2012, 14, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M.; Pinelli, E.; Pourrut, B.; Dumat, C. Effect of organic ligands on lead-induced oxidative damage and enhanced antioxidant defense in the leaves of Vicia faba plants. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 144, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Dumat, C.; Aslam, M.; Pinelli, E. Assessment of lead speciation by organic ligands using speciation models. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab. 2012, 24, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foucault, Y.; Lévêque, T.; Xiong, T.; Schreck, E.; Austruy, A.; Shahid, M.; Dumat, C. Green manure plants for remediation of soils polluted by metals and metalloids: Ecotoxicity and human bioavailability assessment. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 1430–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austruy, A.; Shahid, M.; Xiong, T.; Castrec, M.; Payre, V.; Niazi, N.K.; Sabir, M.; Dumat, C. Mechanisms of metal-phosphates formation in the rhizosphere soils of pea and tomato: Environmental and sanitary consequences. J. Soils Sedim. 2014, 14, 666–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niazi, N.K.; Bibi, I.; Fatimah, A.; Shahid, M.; Javed, M.T.; Wang, H.; Ok, Y.S.; Bashir, S.; Murtaza, B.; Saqib, Z.A. Phosphate-assisted phytoremediation of arsenic by Brassica napus and Brassica juncea: Morphological and physiological response. Int. J. Phytoremed. 2017, 19, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.-B.; Zhou, Q.-X.; An, J.; Liu, W.-T.; Liu, R. Chelator-enhanced phytoextraction of heavy metals from contaminated soil irrigated by industrial wastewater with the hyperaccumulator plant (Sedum alfredii Hance). Geoderma 2009, 150, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhir, B.; Srivastava, S. Heavy metal removal from a multi-metal solution and wastewater by Salvinia Natans. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 893–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennicelli, R.; Stępniewska, Z.; Banach, A.; Szajnocha, K.; Ostrowski, J. The ability of Azolla caroliniana to remove heavy metals (Hg (II), Cr (III), Cr (VI)) from municipal waste water. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niazi, N.K.; Singh, B.; Van Zwieten, L.; Kachenko, A.G. Phytoremediation potential of Pityrogramma calomelanos var. austroamericana and Pteris vittata L. grown at a highly variable arsenic contaminated site. Int. J. Phytoremed. 2011, 13, 912–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshad, M.; Silvestre, J.; Pinelli, E.; Kallerhoff, J.; Kaemmerer, M.; Tarigo, A.; Shahid, M.; Guiresse, M.; Pradère, P.; Dumat, C. A field study of lead phytoextraction by various scented Pelargonium cultivars. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 2187–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niazi, N.K.; Bashir, S.; Bibi, I.; Murtaza, B.; Shahid, M.; Javed, M.T.; Shakoor, M.B.; Saqib, Z.A.; Nawaz, M.F.; Aslam, Z. Phytoremediation of Arsenic-Contaminated Soils Using Arsenic Hyperaccumulating Ferns. In Phytoremediation; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016; pp. 521–545. [Google Scholar]
- Niazi, N.K.; Singh, B.; Van Zwieten, L.; Kachenko, A.G. Phytoremediation of an arsenic-contaminated site using Pteris vittata L. and Pityrogramma calomelanos var. austroamericana: A long-term study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 3506–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabir, M.; Waraich, E.A.; Hakeem, K.R.; Öztürk, M.; Ahmad, H.R.; Shahid, M. Phytoremediation: Mechanisms and adaptations. Soil Remediat. Plants Prospects Chall. 2014, 85, 85–105. [Google Scholar]
- Mombo, S.; Dumat, C.; Shahid, M.; Schreck, E. A socio-scientific analysis of the environmental and health benefits as well as potential risks of cassava production and consumption. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 24, 5207–5221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, T.; Austruy, A.; Pierart, A.; Shahid, M.; Schreck, E.; Mombo, S.; Dumat, C. Kinetic study of phytotoxicity induced by foliar lead uptake for vegetables exposed to fine particles and implications for sustainable urban agriculture. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 46, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, A.; Bibi, I.; Niazi, N.K.; Ok, Y.S.; Murtaza, G.; Shahid, M.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; Li, D.; Mahmood, T. Chromium (VI) sorption efficiency of acid-activated banana peel over organo-montmorillonite in aqueous solutions. Int. J. Phytoremed. 2017, 19, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, G.; Murtaza, B.; Bibi, I.; Shahid, M.; Niazi, N.; Khan, M.; Amjad, M.; Hussain, M. Arsenic Uptake, Toxicity, Detoxification, and Speciation in Plants: Physiological, Biochemical, and Molecular Aspects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, M.; Cheng, Y.; Kanwar, M.K.; Chu, X.-Y.; Ahammed, G.J.; Qi, Z.-Y. Responses of Plant Proteins to Heavy Metal Stress—A Review. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, B. Identification of a rice metal tolerance protein OsMTP11 as a manganese transporter. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Chai, T.; Sun, T. Heavy metal absorption, transportation and accumulation mechanisms in hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens. Sheng wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 561–568. [Google Scholar]
- Satoh-Nagasawa, N.; Mori, M.; Nakazawa, N.; Kawamoto, T.; Nagato, Y.; Sakurai, K.; Takahashi, H.; Watanabe, A.; Akagi, H. Mutations in rice (Oryza sativa) heavy metal ATPase 2 (OsHMA2) restrict the translocation of zinc and cadmium. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011, 53, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papoyan, A.; Kochian, L.V. Identification of Thlaspi caerulescens genes that may be involved in heavy metal hyperaccumulation and tolerance. Characterization of a novel heavy metal transporting ATPase. Plant Physiol. 2004, 136, 3814–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Kim, Y.-Y.; Lee, Y.; An, G. Rice P1B-type heavy-metal ATPase, OsHMA9, is a metal efflux protein. Plant Physiol. 2007, 145, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, S.; Shahid, M.; Niazi, N.K.; Murtaza, B.; Bibi, I.; Dumat, C. A comparison of technologies for remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 182, 247–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerinot, M.L. The ZIP family of metal transporters. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembranes 2000, 1465, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer, U.; Talke, I.N.; Hanikenne, M. Transition metal transport. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 2263–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montanini, B.; Blaudez, D.; Jeandroz, S.; Sanders, D.; Chalot, M. Phylogenetic and functional analysis of the Cation Diffusion Facilitator (CDF) family: Improved signature and prediction of substrate specificity. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guffanti, A.A.; Wei, Y.; Rood, S.V.; Krulwich, T.A. An antiport mechanism for a member of the cation diffusion facilitator family: Divalent cations efflux in exchange for K+ and H+. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 45, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pottier, M.; Oomen, R.; Picco, C.; Giraudat, J.; Scholz-Starke, J.; Richaud, P.; Carpaneto, A.; Thomine, S. Identification of mutations allowing Natural Resistance Associated Macrophage Proteins (NRAMP) to discriminate against cadmium. Plant J. 2015, 83, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourrut, B.; Shahid, M.; Douay, F.; Dumat, C.; Pinelli, E. Molecular mechanisms involved in lead uptake, toxicity and detoxification in higher plants. In Heavy Metal Stress in Plants; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 121–147. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, M.; Xiong, T.; Masood, N.; Leveque, T.; Quenea, K.; Austruy, A.; Foucault, Y.; Dumat, C. Influence of plant species and phosphorus amendments on metal speciation and bioavailability in a smelter impacted soil: A case study of food-chain contamination. J. Soils Sedim. 2014, 14, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Dumat, C.; Pourrut, B.; Silvestre, J.; Laplanche, C.; Pinelli, E. Influence of EDTA and citric acid on lead-induced oxidative stress to Vicia faba roots. J. Soils Sedim. 2014, 14, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Xiong, T.; Castrec-Rouelle, M.; Leveque, T.; Dumat, C. Water extraction kinetics of metals, arsenic and dissolved organic carbon from industrial contaminated poplar leaves. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 2451–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamverdian, A.; Ding, Y.; Mokhberdoran, F.; Xie, Y. Heavy metal stress and some mechanisms of plant defense response. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 756120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M.; Dumat, C.; Pourrut, B.; Abbas, G.; Shahid, N.; Pinelli, E. Role of metal speciation in lead-induced oxidative stress to Vicia faba roots. Rus. J. Plant Physiol. 2015, 62, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Austruy, A.; Echevarria, G.; Arshad, M.; Sanaullah, M.; Aslam, M.; Nadeem, M.; Nasim, W.; Dumat, C. EDTA-enhanced phytoremediation of heavy metals: A review. Soil Sedim. Contam. Int. J. 2014, 23, 389–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshad, S.; Shahid, M.; Rafiq, M.; Khalid, S.; Dumat, C.; Sabir, M.; Murtaza, B.; Farooq, A.B.U.; Shah, N.S. Effect of organic amendments on cadmium stress to pea: A multivariate comparison of germinating vs young seedlings and younger vs older leaves. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 151, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M.; Pinelli, E.; Pourrut, B.; Silvestre, J.; Dumat, C. Lead-induced genotoxicity to Vicia faba L. roots in relation with metal cell uptake and initial speciation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuhrimann, S.; Winkler, M.S.; Kabatereine, N.B.; Tukahebwa, E.M.; Halage, A.A.; Rutebemberwa, E.; Medlicott, K.; Schindler, C.; Utzinger, J.; Cissé, G. Risk of intestinal parasitic infections in people with different exposures to wastewater and fecal sludge in Kampala, Uganda: A cross-sectional study. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuhrimann, S.; Winkler, M.S.; Schneeberger, P.H.; Niwagaba, C.B.; Buwule, J.; Babu, M.; Medlicott, K.; Utzinger, J.; Cissé, G. Health risk assessment along the wastewater and faecal sludge management and reuse chain of Kampala, Uganda: A visualization. Geospat. Health 2014, 9, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yapo, R.; Koné, B.; Bonfoh, B.; Cissé, G.; Zinsstag, J.; Nguyen-Viet, H. Quantitative microbial risk assessment related to urban wastewater and lagoon water reuse in Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire. J. Water Health 2014, 12, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuhrimann, S.; Winkler, M.S.; Stalder, M.; Niwagaba, C.B.; Babu, M.; Kabatereine, N.B.; Halage, A.A.; Utzinger, J.; Cissé, G.; Nauta, M. Disease burden due to gastrointestinal pathogens in a wastewater system in Kampala, Uganda. Microb. Risk Anal. 2016, 4, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, E. Sick Water? The Central Role of Wastewater Management in Sustainable Development: A Rapid Response Assessment; UNEP/Earthprint: Nairobi, Kenya, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Prüss-Ustün, A.; Bartram, J.; Clasen, T.; Colford, J.M.; Cumming, O.; Curtis, V.; Bonjour, S.; Dangour, A.D.; De France, J.; Fewtrell, L. Burden of disease from inadequate water, sanitation and hygiene in low-and middle-income settings: A retrospective analysis of data from 145 countries. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2014, 19, 894–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, J.; Prüss-Ustün, A.; Cumming, O.; Bartram, J.; Bonjour, S.; Cairncross, S.; Clasen, T.; Colford, J.M.; Curtis, V.; France, J. Systematic review: Assessing the impact of drinking water and sanitation on diarrhoeal disease in low-and middle-income settings: Systematic review and meta-regression. Trop.Med. Int. Health 2014, 19, 928–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, H.F.; Hamilton, A.J. Exposure factors for wastewater-irrigated Asian vegetables and a probabilistic rotavirus disease burden model for their consumption. Risk Anal. 2014, 34, 602–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakoor, M.B.; Niazi, N.K.; Bibi, I.; Rahman, M.M.; Naidu, R.; Dong, Z.; Shahid, M.; Arshad, M. Unraveling health risk and speciation of arsenic from groundwater in rural areas of Punjab, Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 12371–12390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mara, D.; Sleigh, A. Estimation of Ascaris infection risks in children under 15 from the consumption of wastewater-irrigated carrots. J. Water Health 2010, 8, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hien, B.T.T.; Scheutz, F.; Cam, P.D.; Mølbak, K.; Dalsgaard, A. Diarrhoeagenic Escherichia coli and other causes of childhood diarrhoea: A case–control study in children living in a wastewater-use area in Hanoi, Vietnam. J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 56, 1086–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotruvo, J.A.; Dufour, A.; Rees, G.; Bartram, J.; Carr, R.; Cliver, D.O.; Craun, G.F.; Fayer, R.; Gannon, V.P. Waterborne Zoonoses; Iwa Publishing: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Parasidis, T.; Vorou, E.; Theodoropoulou-Rodiou, G.; Katsantridou, G.; Stamatopoulou, G.; Vantarakis, A. Outbreak of gastroenteritis occurred in North-Eastern Greece associated with several waterborne strains of noroviruses. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 12, e104–e105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Muller, E.; Grabow, W.; Ehlers, M. Immunomagnetic separation of Escherichia coli O157: H7 from environmental and wastewater in South Africa. Water SA 2003, 29, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Seguí Amórtegui, L.A. Sistemas de Regeneración y Reutilización de Aguas Residuales. Metodología Para el Análisis Técnico-Económico y Casos; Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya: Barcelona, Spain, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Vilar, J.L.B.; Bernabeu-Mestre, J. La Salud y el Estado: El Movimiento Sanitario Internacional y la Administración Española (1851–1945); Universitat de València: València, Spain, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Angelakis, A.N.; Snyder, S.A. Wastewater treatment and reuse: Past, present, and future. Water 2015, 7, 4887–4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Health Guidelines for the Use of Wastewater in Agriculture and Aquaculture: Report of a WHO Scientific Group [Meeting held in Geneva from 18 to 23 November 1987]; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, T.; Dumat, C.; Dappe, V.; Vezin, H.; Schreck, E.; Shahid, M.; Pierart, A.; Sobanska, S. Copper oxide nanoparticle foliar uptake, phytotoxicity, and consequences for sustainable urban agriculture. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 5242–5251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farahat, E.A.; Galal, T.M.; Elawa, O.E.; Hassan, L.M. Health risk assessment and growth characteristics of wheat and maize crops irrigated with contaminated wastewater. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoniadis, V.; Levizou, E.; Shaheen, S.M.; Ok, Y.S.; Sebastian, A.; Baum, C.; Prasad, M.N.; Wenzel, W.W.; Rinklebe, J. Trace elements in the soil-plant interface: Phytoavailability, translocation, and phytoremediation–A review. Earth Sci. Rev. 2017, 171, 621–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhat, H.F.; Zia, Z.; Fahad, S.; Abbas, S.; Hammad, H.M.; Shahzad, A.N.; Abbas, F.; Alharby, H.; Shahid, M. Arsenic uptake, accumulation and toxicity in rice plants: Possible remedies for its detoxification: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 9142–9158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabir, R.; Abbas, G.; Saqib, M.; Shahid, M.; Shah, G.; Akram, M.; Niazi, N.; Naeem, M.; Hussain, M.; Ashraf, F. Cadmium tolerance and phytoremediation potential of acacia (Acacia nilotica L.) under salinity stress. Int. J. Phytoremed. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijani, M.N.; Onodera, S. Hydrogeochemical assessment of metals contamination in an urban drainage system: A case study of Osogbo township, SW-Nigeria. J. Water Resour. Protect. 2009, 1, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oti, W.O. Bioaccumulation factors and pollution indices of heavy metals in selected fruits and vegetables from a derelict mine and their associated health implications. Int. J. Environ. Sustain. 2015, 4, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirola, R.; Megharaj, M.; Palanisami, T.; Aryal, R.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Naidu, R. Evaluation of metal uptake factors of native trees colonizing an abandoned copper mine—A quest for phytostabilization. J. Sustain. Min. 2015, 14, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Country | Total Area (1000 ha) | Cultivated Area (1000 ha) | Total Cultivated Area (%) | Produced Municipal Wastewater (109 m3/year) | Collected Municipal Wastewater (109 m3/year) | Treated Municipal Wastewater (109 m3/year) | Use of Treated Wastewater for Irrigation (109 m3/year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Australia | 774,122 | 47,307 | 6.11 | - | - | 2 | 0.28 |
| Brazil | 851,577 | 86,589 | 10.1 | - | - | 3.1 | 0.008 |
| China | 960,001 | 122,524 | 12.7 | 48.51 | 31.14 | 42.37 | 1.26 |
| Germany | 35,738 | 12,074 | 33.7 | - | 5.287 | 5.213 | 5.183 |
| India | 328,726 | 169,360 | 51.5 | - | - | 4.416 | - |
| Itlay | 30,134 | 9121 | 30.2 | 3.926 | - | 3.902 | 0.087 |
| Jordan | 8932 | 322 | 3.60 | - | 0.115 | 0.113 | 0.103 |
| Pakistan | 79,610 | 31,252 | 39.2 | 3.06 | - | - | - |
| South Africa | 121,909 | 12,913 | 10.5 | 3.542 | 2.769 | 1.919 | - |
| Turkey | 78,535 | 23,944 | 30.4 | 4.297 | - | 3.483 | - |
| UK | 24,361 | 6279 | 25.7 | 4.089 | 4.048 | 4.048 | - |
| USA | 983,151 | 157,205 | 15.9 | 60.41 | 47.24 | 45.35 | - |
| Canada | 998,467 | 50,846 | 5.09 | 6.613 | 5.819 | 5.632 | - |
| Sweden | 44,742 | 2608 | 5.82 | 0.671 | - | 0.436 | - |
| Nutrients and Heavy Metal | Vegetables/Crops | Concentration in Vegetables Irrigated by Fresh Water (mg/kg) | Concentration in Vegetables Irrigated by Wastewater (mg/kg) | % Decrease or Increase | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Lettuce | 39,500 | 42,880 | 8.56 | [61] |
| Rice | 296 | 453 | 53.04 | [62] | |
| Coriander | 402 | 499 | 24.13 | ||
| Wheat | 160 | 174 | 8.75 | [63] | |
| Rice | 135 | 142 | 5.185 | ||
| P | Lettuce | 4480 | 5530 | 23.44 | [61] |
| Rice | 28 | 38 | 35.71 | [62] | |
| Alfalfa | 0.26 | 0.27 | 3.85 | [64] | |
| Rice | 35 | 45 | 28.57 | [65] | |
| K | Rice | 1364 | 835 | −38.78 | [66] |
| Rice | 225 | 312 | 38.67 | [62] | |
| Coriander | 416 | 517 | 24.28 | ||
| Alfalfa | 2.2 | 2.5 | 13.64 | [64] | |
| Rice | 106 | 230 | 116.98 | [67] | |
| Pb | Tomato | 4.4 | 9.6 | 118.18 | [68] |
| Panicum | 0.01 | 0.09 | 800 | [69] | |
| Brinjal | 4 | 14.15 | 253.75 | [70] | |
| Radish | 1 | 2.5 | 150 | [71] | |
| Cypress | 1.6 | 3.2 | 100 | [72] | |
| Onion | 11.2 | 2.7 | 415 | [73] | |
| Garlic | 8.15 | 4.94 | 165 | ||
| Tomato | 12.7 | 4.45 | 285 | ||
| Brinjal | 14.15 | 4.35 | 325 | ||
| Cd | Tomato | 0.03 | 0.04 | 33.33 | [68] |
| Maize | 0.02 | 0.03 | 50 | [74] | |
| Cypress | 0.05 | 0.06 | 20 | [72] | |
| Radish | 3.4 | 5.1 | 50 | [75] | |
| Garlic | 20 | 30 | 50 | [76] | |
| vegetables, cereal crops | 3.12 | 1.49 | 209 | [21] | |
| Ni | Tomato | 4.67 | 8.33 | 78.37 | [68] |
| Cabbage | 0.77 | 0.88 | 14.29 | [77] | |
| Tomato | 1.6 | 5.65 | 253 | [73] | |
| Brinjal | 3 | 7.45 | 148 | ||
| Maize | 0.62 | 1.12 | 80.65 | [74] | |
| Lettuce | 1.31 | 1.47 | 12.21 | [78] | |
| vegetables, cereal crops | 23.64 | 9.06 | 261 | [21] | |
| As | Maize | 0.03 | 0.08 | 166.67 | [74] |
| Carrot | 0.12 | 0.15 | 25 | [78] | |
| Radish | 0.49 | 0.5 | 2.04 | [78] | |
| Radish | 0.13 | 5 | 3746.15 | [79] | |
| Cr | Onion | 5.05 | 1.05 | 481 | [73] |
| Garlic | 2.6 | 1 | 260 | ||
| Tomato | 6.1 | 6.1 | No | ||
| Brinjal | 12.55 | 7.5 | 167 | ||
| vegetables, cereal crops | 19.2 | 9.07 | 212 | [21] | |
| Fe | Tomato | 118 | 220 | 86.44 | [68] |
| Onion | 6.15 | 26.15 | 325.20 | [73] | |
| Brinjal | 300 | 370 | 23.33 | [62] | |
| Sunflower | 140 | 324 | 131.43 | [74] | |
| Lettuce | 510 | 430 | −15.69 | [61] |
| Microbes | Microbes Count | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Coliforms | 3.3 × 102 cfu/g | [130] |
| Coliforms Fecal Coliforms | 4.39 × 103/100 mL 7.5 × 107 cfu/g | [131] |
| Fecal streptococci Fecal coliform | 65 240 | [132] |
| Bacteria (Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus faecalis) | 7.6 × 107 cfu/g 4.6 × 107 cfu/g | [133] |
| Fungi (Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus fumigatus, Aspergillus flavus) | 6.0 × 106 cfu/g 9.0 × 106 cfu/g | |
| Bacteria (Lactobacillus plantarum, Pseudomonas aeruginosa) | 3.36 × 107 cfu/g | [134] |
| Salmonella Shigella Clostridium bacteria | 3.5 × 106 cfu/g 5.4 × 104 cfu/g 7.8 × 102 cfu/g 5.1 × 104 cfu/g | [135] |
| Penicillium expansum Aspergillus spp. | 5.45 × 104 cfu/g 1.30 ×105 cfu/g | [135] |
| Escherichia coli | 8.0 × 106 cfu/g 3.8 × 106 cfu/g | [136] |
| Bacteria Actinomycetes Fungi | 1.34 × 107 cfu/g 2.21 × 106 cfu/g 9.99 × 103 cfu/g | [137] |
| Total coliforms | 2.1 × 103 cfu/g 4.2 × 103 cfu/g | [138] |
| Fecal coliforms | 1.2 × 102 cfu/g 4.2 × 102 cfu/g |
| Metal | Vegetable | Concentration in Wastewater (mg/L) | Concentration in Soil (mg/kg) | Concentration in Plant (mg/kg) | Transfer Factor | Bioaccumulation Factor | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Cupressus sempervirens | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.5 | 2 | [72] |
| Cd | Raphanus sativus | - | 0.84 | 0.93 | - | 1.29 | [20] |
| Cd | Vicia faba | - | 0.11 | 0.1 | - | 0.9 | [173] |
| Cd | Oryza sativa | 0.01 | 3 | 1.1 | 300 | 0.4 | [174] |
| Cd | Spinacia oleracea | 10 | 5.8 | 15 | 0.6 | 2.6 | [175] |
| Cd | Lactuca sativa | 0.05 | 1 | 0.2 | 20 | 0.2 | [176] |
| Pb | Triticum | - | 41.56 | 2.77 | - | 0.1 | [177] |
| Pb | Raphanus sativus | 0.18 | 49.4 | 2.6 | 274.4 | 0.04 | [20] |
| Pb | Triticum | 0.585 | 411.7 | 26.23 | 703.8 | 0.064 | [178] |
| Pb | Convolvulus arvensis | - | 24.7 | 1.433 | - | 0.058 | [179] |
| Pb | Triticum | 0.1 | 33.4 | 2.3 | 334.0 | 0.069 | [151] |
| Pb | Oryza sativa | - | 5.1 | 0.37 | - | 0.073 | [180] |
| Pb | Cupressus sempervirens | 9.2 | 7.1 | 3.2 | 0.8 | 0.5 | [72] |
| Zn | Raphanus sativus | - | 157 | 57 | - | 0.41 | [20] |
| Zn | Daucus carota | 0.27 | 12.4 | 2.5 | 45.9 | 0.202 | [181] |
| Zn | Vicia faba | 0.36 | 0.42 | 0.07 | 1.2 | 0.2 | [76] |
| Zn | Amaranthus | 1 | 167 | 67 | 167.0 | 0.4 | [176] |
| Zn | Beta vulgaris | 0.24 | 1.7 | 25 | 7.1 | 14.7 | [182] |
| Zn | Hordeum vulgare | 0.19 | 1.4 | 32.2 | 7.4 | 23.0 | [116] |
| Zn | Citrus x sinensis | 0.02 | 134.22 | 4.15 | 6711.0 | 0.031 | [89] |
| Ni | Cupressus sepervirens | 7.1 | 11.3 | 4.7 | 1.6 | 0.4 | [72] |
| Ni | Oryza sativa | 1.03 | 35 | 1.8 | 34.0 | 0.051 | [174] |
| Ni | Raphanus sativus | - | 24.9 | 11 | - | 0.42 | [20] |
| Ni | Zea mays | - | 28.13 | 2.65 | - | 0.09 | [183] |
| Ni | Abelmoschus esculentus | 1.6 | 0.3 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 4.67 | [132] |
| Ni | Vicia faba | 0.04 | 0.55 | 0.09 | 13.8 | 0.2 | [76] |
| Ni | Triticum | 0.22 | 276.6 | 27.19 | 1257.3 | 0.098 | [178] |
| Cu | Cupressus sempervirens | 4.7 | 5.4 | 9.4 | 1.1 | 1.7 | [72] |
| Cu | Raphanus sativus | 0.2 | 5.4 | 1.2 | 27.0 | 0.222 | [181] |
| Cu | Raphanus sativus | - | 32.8 | 9 | - | 0.32 | [20] |
| Cu | Lactuca sativa | - | 7.4 | 8.05 | - | 1.088 | [184] |
| Cu | Xanthium strumarium | 0.616 | 0.768 | 0.791 | 1.2 | 1.0 | [185] |
| Cu | Vicia faba | 0.181 | 0.49 | 0.04 | 2.7 | 0.1 | [76] |
| Cu | Citrus x sinensis | 0.03 | 94.38 | 4.352 | 3146.0 | 0.046 | [89] |
| Metal | Vegetable | Estimated Daily Intake | Health Risk Index | Hazard Quotient | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Cupressus sempervirens | 0.00003 | 0.0315 | 0.000009 | [72] |
| Cd | Raphanus sativus | 0.00049 | 0.4879 | 0.000134 | [20] |
| Cd | Vicia faba | 0.00005 | 0.0525 | 0.000014 | [20] |
| Cd | Oryza sativa | 0.00058 | 0.5771 | 0.000158 | [174] |
| Cd | Spinach oleracea | 0.00787 | 7.8690 | 0.002156 | [175] |
| Cd | Lactuca sativa | 0.00011 | 0.1049 | 0.000029 | [176] |
| Pb | Triticum | 0.00145 | 0.4152 | 0.000398 | [177] |
| Pb | Raphanus sativus | 0.00136 | 0.3897 | 0.000374 | [20] |
| Pb | Triticum | 0.01380 | 3.9315 | 0.003770 | [178] |
| Pb | Convolvulus arvensis | 0.00075 | 0.2148 | 0.000206 | [179] |
| Pb | Triticum | 0.00121 | 0.3447 | 0.000331 | [151] |
| Pb | Oryza sativa | 0.00019 | 0.0555 | 0.000053 | [180] |
| Pb | Cupressus sempervirens | 0.00168 | 0.4796 | 0.000460 | [72] |
| Zn | Raphanus sativus | 0.02990 | 0.0997 | 0.008192 | [20] |
| Zn | Daucus carota | 0.00131 | 0.0044 | 0.000359 | [181] |
| Zn | Amaranthus | 0.03510 | 0.1172 | 0.009630 | [176] |
| Zn | Beta vulgaris | 0.01310 | 0.0437 | 0.003593 | [182] |
| Zn | Hordeum vulgare | 0.01690 | 0.0563 | 0.004628 | [116] |
| Zn | Citrus x sinensis | 0.00218 | 0.0073 | 0.000596 | [89] |
| Ni | Cupressus sempervirens | 0.00247 | 0.1233 | 0.000676 | [72] |
| Ni | Raphanus sativus | 0.00577 | 0.2885 | 0.001581 | [20] |
| Ni | Zea mays | 0.00139 | 0.0695 | 0.000381 | [183] |
| Ni | Abelmoschus esculentus | 0.00073 | 0.0367 | 0.000201 | [132] |
| Ni | Vicia faba | 0.00005 | 0.0024 | 0.000013 | [76] |
| Ni | Triticum | 0.01430 | 0.7132 | 0.003908 | [178] |
| Cu | Cupressus sempervirens | 0.00493 | 0.1233 | 0.001351 | [72] |
| Cu | Raphanus sativus | 0.00063 | 0.0157 | 0.000172 | [181] |
| Cu | Raphanus sativus | 0.00472 | 0.1180 | 0.001294 | [20] |
| Cu | Lactuca sativa | 0.00422 | 0.1056 | 0.001157 | [184] |
| Cu | Xanthium strumarium | 0.00042 | 0.0104 | 0.000114 | [185] |
| Cu | Vicia faba | 0.00002 | 0.0005 | 0.000006 | [76] |
| Cu | Citrus x sinensis | 0.00228 | 0.0571 | 0.000625 | [89] |
| Soil Contamination and Soil-Plant Transfer Indices | References | Risk Assessment Indices | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Degree of contamination (Cdeg) | [277] | Root-shoot translocation factor (TrF) | [215] |
| Geo-accumulation index (Igeo) | [274] | Plant pollution index (PPI) | [274] |
| Contamination factor (CF), Enrichment factors (EF) | [274] | Estimated daily intake (EDI) or Average daily intake (ADI) | [31] |
| Mobilization factor (MF) | [215] | Hazard quotient (HQ) | [31] |
| Bioaccumulation factor (BF) | [278] | Maximum allowable daily intake (MDI) | [4] |
| Bioconcentration factor (BCF) | [215] | Life time cancer risk (ILTCR) | [31] |
| Plant enrichment factors (PEF) | [25,279] | Health risk index (HRI) | [4] |
| Soil-plant transfer factor (TF) or transfer coefficient (TC) | [274] | Tolerance index (TI) | [274] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khalid, S.; Shahid, M.; Natasha; Bibi, I.; Sarwar, T.; Shah, A.H.; Niazi, N.K. A Review of Environmental Contamination and Health Risk Assessment of Wastewater Use for Crop Irrigation with a Focus on Low and High-Income Countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15050895
Khalid S, Shahid M, Natasha, Bibi I, Sarwar T, Shah AH, Niazi NK. A Review of Environmental Contamination and Health Risk Assessment of Wastewater Use for Crop Irrigation with a Focus on Low and High-Income Countries. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(5):895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15050895
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhalid, Sana, Muhammad Shahid, Natasha, Irshad Bibi, Tania Sarwar, Ali Haidar Shah, and Nabeel Khan Niazi. 2018. "A Review of Environmental Contamination and Health Risk Assessment of Wastewater Use for Crop Irrigation with a Focus on Low and High-Income Countries" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 5: 895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15050895
APA StyleKhalid, S., Shahid, M., Natasha, Bibi, I., Sarwar, T., Shah, A. H., & Niazi, N. K. (2018). A Review of Environmental Contamination and Health Risk Assessment of Wastewater Use for Crop Irrigation with a Focus on Low and High-Income Countries. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(5), 895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15050895








