Composition of Metallic Elements and Size Distribution of Fine and Ultrafine Particles in a Steelmaking Factory
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- the sampling of inhalable fraction, the measurement of their concentration, and their chemical characterization in terms of ME;
- (2)
- the measurement of number concentrations and particle size distributions carried out by ELPI.
2. Materials and Methods
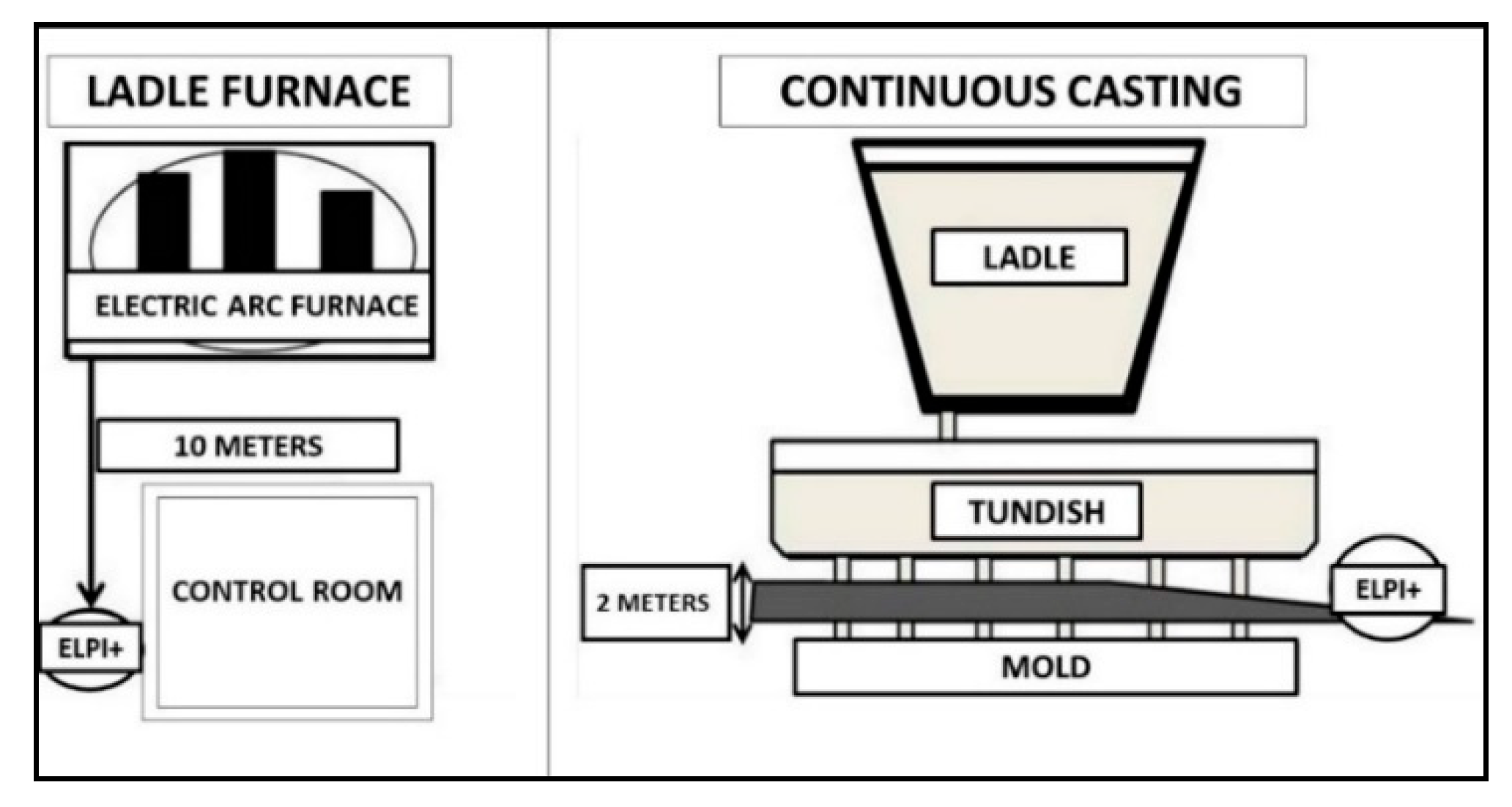
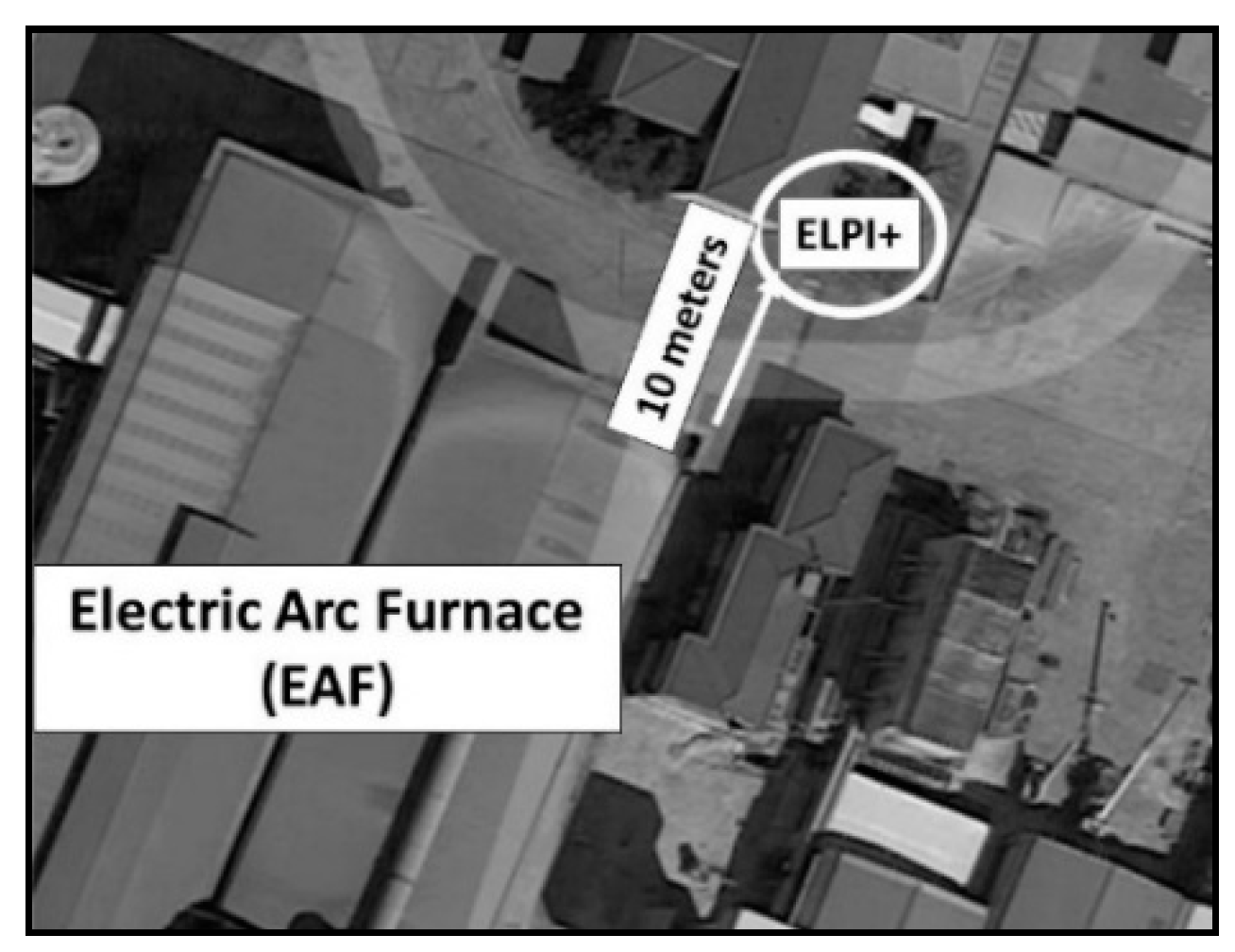
2.1. Sampling Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sampling Equipment
2.4. Chemical Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Determination and Chemical Characterization of Inhalable Fraction
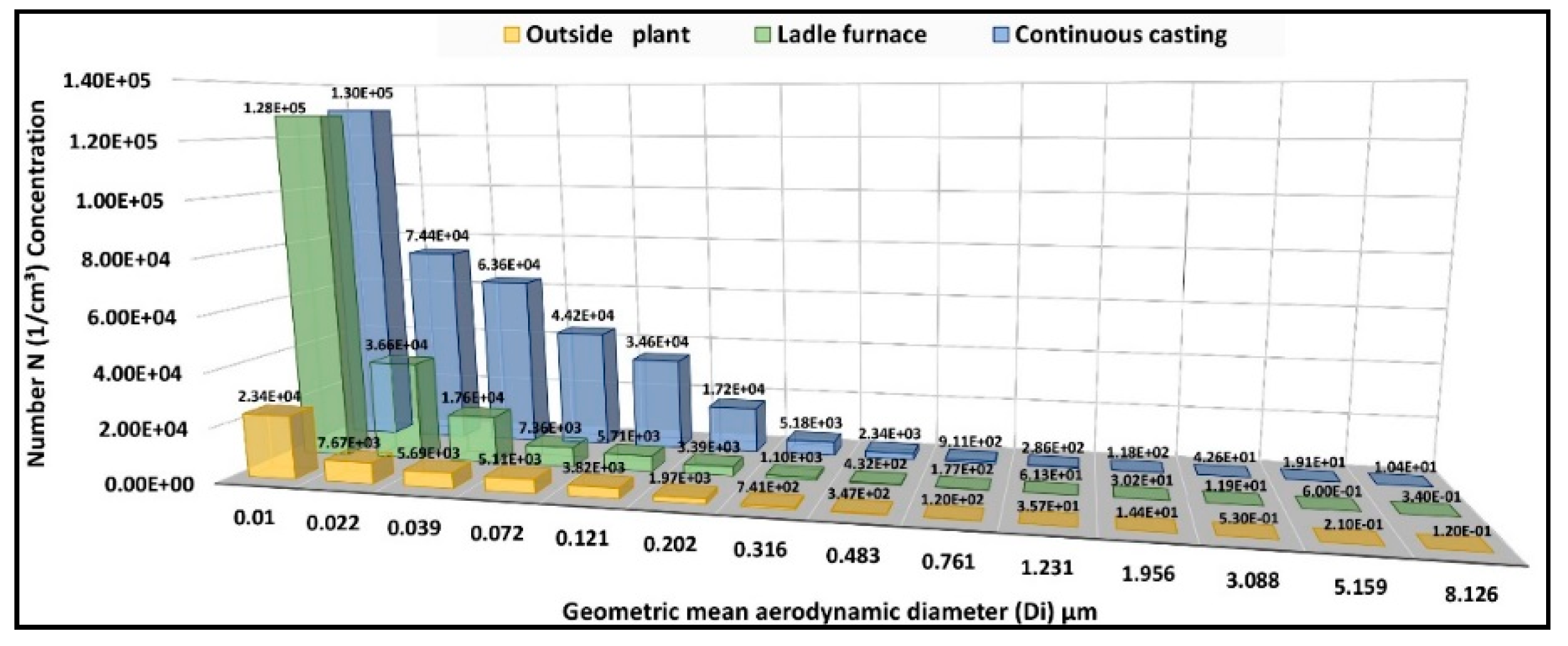
3.2. Particle Number Concentrations
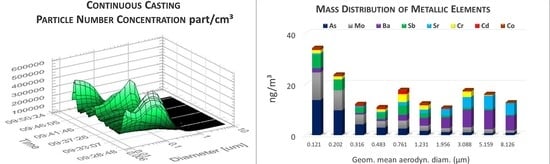
3.3. Particle Number and Mass Size Distribution
3.4. Chemical Characterization of Particles Collected by ELPI+
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hobbesland, A.; Kjuus, H.; Thelle, D.S. Study of cancer incidence among 8530 male workers in eight Norwegian plants producing ferrosilicon and silicon metal. Occup. Environ. Med. 1999, 56, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kjuus, H.; Andersen, A.; Langård, S.; Knudsen, K.E. Cancer incidence among workers in the Norwegian ferroalloy industry. Br. J. Ind. Med. 1986, 43, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, T.; Fine, J.M. Metal fume fever. Occup. Med. 1993, 8, 504–517. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Başaran, N.; Shubair, M.; Ündeğer, Ü.; Canpınar, H.; Kars, A. Alterations in immune parameters in foundry and pottery workers. Toxicology 2002, 178, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, H.-W.; Chang, C.-L.; Lai, J.-S.; Lee, F.-C.; Chung, B.-C.; Chen, C.-J. Prevalence of and factors related to pneumoconiosis among foundry workers in central Taiwan. Sci. Total Environ. 1998, 222, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tossavainen, A. Estimated risk of lung cancer attributable to occupational exposures in iron and steel foundries. IARC Sci. Publ. 1990, 104, 363–367. [Google Scholar]
- Oberdörster, G. Pulmonary effects of inhaled ultrafine particles. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2001, 74, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilmour, P.S.; Ziesenis, A.; Morrison, E.R.; Vickers, M.A.; Drost, E.M.; Ford, I.; Karg, E.; Mossa, C.; Schroeppel, A.; Ferron, G.A.; et al. Pulmonary and systemic effects of short-term inhalation exposure to ultrafine carbon black particles. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004, 195, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanzinger, S.; Schneider, A.; Breitner, S.; Stafoggia, M.; Erzen, I.; Dostal, M.; Pastorkova, A.; Bastian, S.; Cyrys, J.; Zscheppang, A.; et al. Associations between ultrafine and fine particles and mortality in five central European cities—Results from the UFIREG study. Environ. Int. 2016, 88, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennig, F.; Quass, U.; Hellack, B.; Küpper, M.; Kuhlbusch, T.A.J.; Stafoggia, M.; Hoffmann, B. Ultrafine and Fine Particle Number and Surface Area Concentrations and Daily Cause-Specific Mortality in the Ruhr Area, Germany, 2009–2014. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delfino, R.J.; Sioutas, C.; Malik, S. Potential role of ultrafine particles in associations between airborne particle mass and cardiovascular health. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 934–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nel, A. Atmosphere. Air pollution-related illness: Effects of particles. Science 2005, 308, 804–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donaldson, K.; Brown, D.; Clouter, A.; Duffin, R.; MacNee, W.; Renwick, L.; Tran, L.; Stone, V. The Pulmonary Toxicology of Ultrafine Particles. J. Aerosol Med. 2002, 15, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiser, M.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Kapp, N.; Schürch, S.; Kreyling, W.; Schulz, H.; Semmler, M.; Im Hof, V.; Heyder, J.; Gehr, P. Ultrafine particles cross cellular membranes by nonphagocytic mechanisms in lungs and in cultured cells. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 1555–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geys, J.; Coenegrachts, L.; Vercammen, J.; Engelborghs, Y.; Nemmar, A.; Nemery, B.; Hoet, P.H.M. In vitro study of the pulmonary translocation of nanoparticles: A preliminary study. Toxicol. Lett. 2006, 160, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.S.; Zeman, K.L.; Bennett, W.D. Ultrafine Particle Deposition and Clearance in the Healthy and Obstructed Lung. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 1240–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberdörster, G.; Oberdörster, E.; Oberdörster, J. Nanotoxicology: An emerging discipline evolving from studies of ultrafine particles. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 823–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, J.H.; Clement, C.F. Ultrafine particles in workplace atmospheres. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2000, 358, 2673–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wake, D.; Mark, D.; Northage, C. Ultrafine Aerosols in the Workplace. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2002, 46, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peters, T.M.; Heitbrink, W.A.; Evans, D.E.; Slavin, T.J.; Maynard, A.D. The Mapping of Fine and Ultrafine Particle Concentrations in an Engine Machining and Assembly Facility. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2005, 50, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heitbrink, W.A.; Evans, D.E.; Peters, T.M.; Slavin, T.J. Characterization and Mapping of Very Fine Particles in an Engine Machining and Assembly Facility. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2007, 4, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonanno, G.; Fuoco, F.C.; Stabile, L. Influential parameters on particle exposure of pedestrians in urban microenvironments. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 1434–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Morawska, L.; Birmili, W.; Paasonen, P.; Hu, M.; Kulmala, M.; Harrison, R.M.; Norford, L.; Britter, R. Ultrafine particles in cities. Environ. Int. 2014, 66, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Gilio, A.; Ventrella, G.; Giungato, P.; Tutino, M.; Giua, R.; Assennato, G.; de Gennaro, G. An intensive monitoring campaign of PAHs for assessing the impact of a steel plant. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dales, R.; Kauri, L.M.; Cakmak, S.; Mahmud, M.; Weichenthal, S.A.; Van Ryswyk, K.; Kumarathasan, P.; Thomson, E.; Vincent, R.; Broad, G.; et al. Acute changes in lung function associated with proximity to a steel plant: A randomized study. Environ. Int. 2013, 55, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cakmak, S.; Dales, R.; Kauri, L.M.; Mahmud, M.; Van Ryswyk, K.; Vanos, J.; Liu, L.; Kumarathasan, P.; Thomson, E.; Vincent, R.; et al. Metal composition of fine particulate air pollution and acute changes in cardiorespiratory physiology. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 189, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harris, G.K.; Shi, X. Signaling by carcinogenic metals and metal-induced reactive oxygen species. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2003, 533, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lee, S.; Pisaniello, D. Measurement of fine and ultrafine dust exposure in an iron foundry in South Australia. J. Heal. 2010, 26, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Marris, H.; Deboudt, K.; Augustin, P.; Flament, P.; Blond, F.; Fiani, E.; Fourmentin, M.; Delbarre, H. Fast changes in chemical composition and size distribution of fine particles during the near-field transport of industrial plumes. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 427–428, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohiuddin, K.; Strezov, V.; Nelson, P.F.; Stelcer, E.; Evans, T. Mass and elemental distributions of atmospheric particles nearby blast furnace and electric arc furnace operated industrial areas in Australia. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 487, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, W.-S.; Duffin, R.; Poland, C.A.; Howie, S.E.M.; MacNee, W.; Bradley, M.; Megson, I.L.; Donaldson, K. Metal Oxide Nanoparticles Induce Unique Inflammatory Footprints in the Lung: Important Implications for Nanoparticle Testing. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietroiusti, A. Health implications of engineered nanomaterials. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manke, A.; Wang, L.; Rojanasakul, Y. Mechanisms of nanoparticle-induced oxidative stress and toxicity. Biomed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 942916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sioutas, C.; Delfino, R.J.; Singh, M. Exposure assessment for atmospheric ultrafine particles (UFPs) and implications in epidemiologic research. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.C.; Lippmann, M. Effects of Metals within Ambient Air Particulate Matter (PM) on Human Health. Inhal. Toxicol. 2009, 21, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viitanen, A.-K.; Uuksulainen, S.; Koivisto, A.J.; Hämeri, K.; Kauppinen, T. Workplace Measurements of Ultrafine Particles—A Literature Review. Ann. Work Expo. Heal. 2017, 61, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwer, D.H.; Gijsbers, J.H.J.; Lurvink, M.W.M. Personal Exposure to Ultrafine Particles in the Workplace: Exploring Sampling Techniques and Strategies. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2004, 48, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bemer, D.; Regnier, R.; Subra, I.; Sutter, B.; Lecler, M.T.; Morele, Y. Ultrafine Particles Emitted by Flame and Electric Arc Guns for Thermal Spraying of Metals. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2010, 54, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kero, I.; Naess, M.K.; Tranell, G. Particle size distributions of particulate emissions from the ferroalloy industry evaluated by electrical low pressure impactor (ELPI). J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2015, 12, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debia, M.; Weichenthal, S.; Tardif, R.; Dufresne, A. Ultrafine Particle (UFP) Exposures in an Aluminium Smelter: Soderberg vs. Prebake Potrooms. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meléndez, A.; García, E.; Carnicer, P.; Pena, E.; Larrión, M.; Legarreta, J.A.; Gutiérrez-Cañas, C. Fine and Ultrafine Emission Dynamics from a Ferrous Foundry Cupola Furnace. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2010, 60, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kero, I.T.; Jørgensen, R.B. Comparison of Three Real-Time Measurement Methods for Airborne Ultrafine Particles in the Silicon Alloy Industry. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNI EN 481:1994—Atmosfera Nell’ambiente di Lavoro. Definizione Delle Frazioni Granulometriche per la Misurazione Delle Particelle Aerodisperse, 1994, Italy. Available online: http://store.uni.com/catalogo/index.php/uni-en-481-1994.html (accessed on 26 April 2018).
- Ambienti di Lavoro—Determinazione Della Frazione Inalabile Delle Particelle Aerodisperse—Metodo Gravimetrico—UNICHIM—Associazione Per l’Unificazione Nel Settore Dell’industria Chimica, federato All’UNI (Ente Nazionale di Unificazione, Italy). Available online: http://www.uni.com/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=454&Itemid=2448&lang=it (accessed on 26 April 2018).
- MarjamaK ki, M.; Jorma Keskinen, R.; Da-Ren Chen, S.A.; Pui, D.Y. Performance Evaluation of the Electrical low-Pressure Impactor (ELPI). J. Aerosol Sci 2000, 31, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekati Ltd. ELPIVI Software Manual; Version 4.1 0; Dekati Ltd.: Kangasala, Finland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Apostoli, P.; De Palma, G.; Catalani, S.; Bortolotti, F.; Tagliaro, F. Multielemental analysis of tissues from Cangrande della Scala, Prince of Verona, in the 14th century. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2009, 33, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D.lgs. 9 Aprile 2008, n. 81 Testo Coordinato con il D.Lgs. 3 Agosto 2009, n. 106, Italy, 2008. Available online: http://www.regione.fvg.it/rafvg/export/sites/default/RAFVG/formazione-lavoro/formazione/FOGLIA12/documentazione/04_ART_73_DGLS812008.pdf (accessed on 26 April 2018).
- ACGIH. 2017. TLVs® and BEIs®: Threshold Limit Values for Chemical Substances and Physical Agents Biological Exposure Indices; American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH): Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, D.E.; Heitbrink, W.A.; Slavin, T.J.; Peters, T.M. Ultrafine and Respirable Particles in an Automotive Grey Iron Foundry. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2007, 52, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Y.-H.; Chao, Y.-C.; Wu, C.-H.; Tsai, C.-J.; Uang, S.-N.; Shih, T.-S. Measurements of ultrafine particle concentrations and size distribution in an iron foundry. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 158, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.-C.O.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Glowacki, C.; Sheya, S.A.; Prabhu, A. Characterization of Fine Particulate Emissions from Casting Processes. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 947–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buonanno, G.; Stabile, L.; Avino, P.; Belluso, E. Chemical, dimensional and morphological ultrafine particle characterization from a waste-to-energy plant. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 2253–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyersmann, D. Effects of carcinogenic metals on gene expression. Toxicol. Lett. 2002, 127, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostoli, P.; Catalani, S. Carcinogenicity of metallic elements: General considerations about their identification and monitoring and about their main mechanisms of action. Part 1: General aspects. G. Ital. Med. Lav. Ergon. 2008, 30, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brunner, T.J.; Wick, P.; Manser, P.; Spohn, P.; Grass, R.N.; Limbach, L.K.; Bruinink, A.; Stark, W.J. In Vitro Cytotoxicity of Oxide Nanoparticles: Comparison to Asbestos, Silica, and the Effect of Particle Solubility. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grass, R.N.; Limbach, L.K.; Athanassiou, E.K.; Stark, W.J. Exposure of aerosols and nanoparticle dispersions to in vitro cell cultures: A review on the dose relevance of size, mass, surface and concentration. J. Aerosol Sci. 2010, 41, 1123–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raemy, D.O.; Grass, R.N.; Stark, W.J.; Schumacher, C.M.; Clift, M.J.D.; Gehr, P.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Effects of flame made zinc oxide particles in human lung cells—A comparison of aerosol and suspension exposures. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2012, 9, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.; Demokritou, P.; Shafer, M.; Christiani, D. Physicochemical and toxicological characteristics of welding fume derived particles generated from real time welding processes. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2013, 15, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
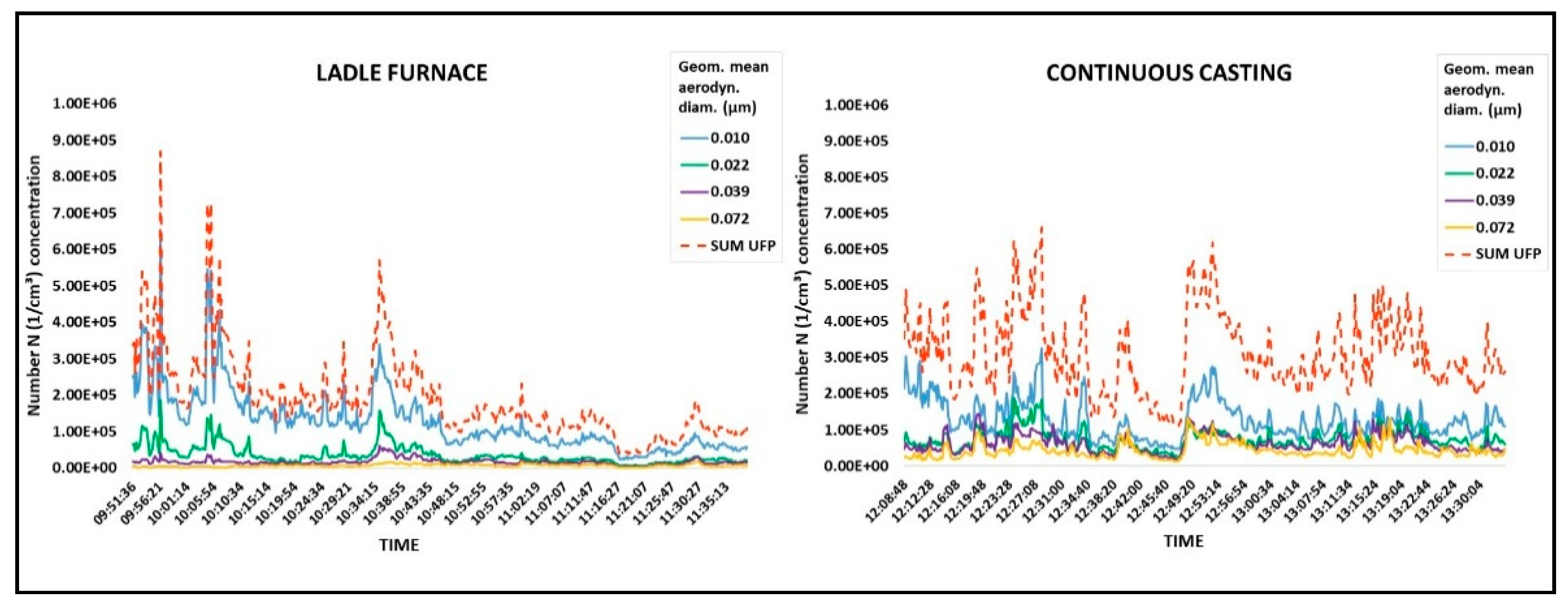
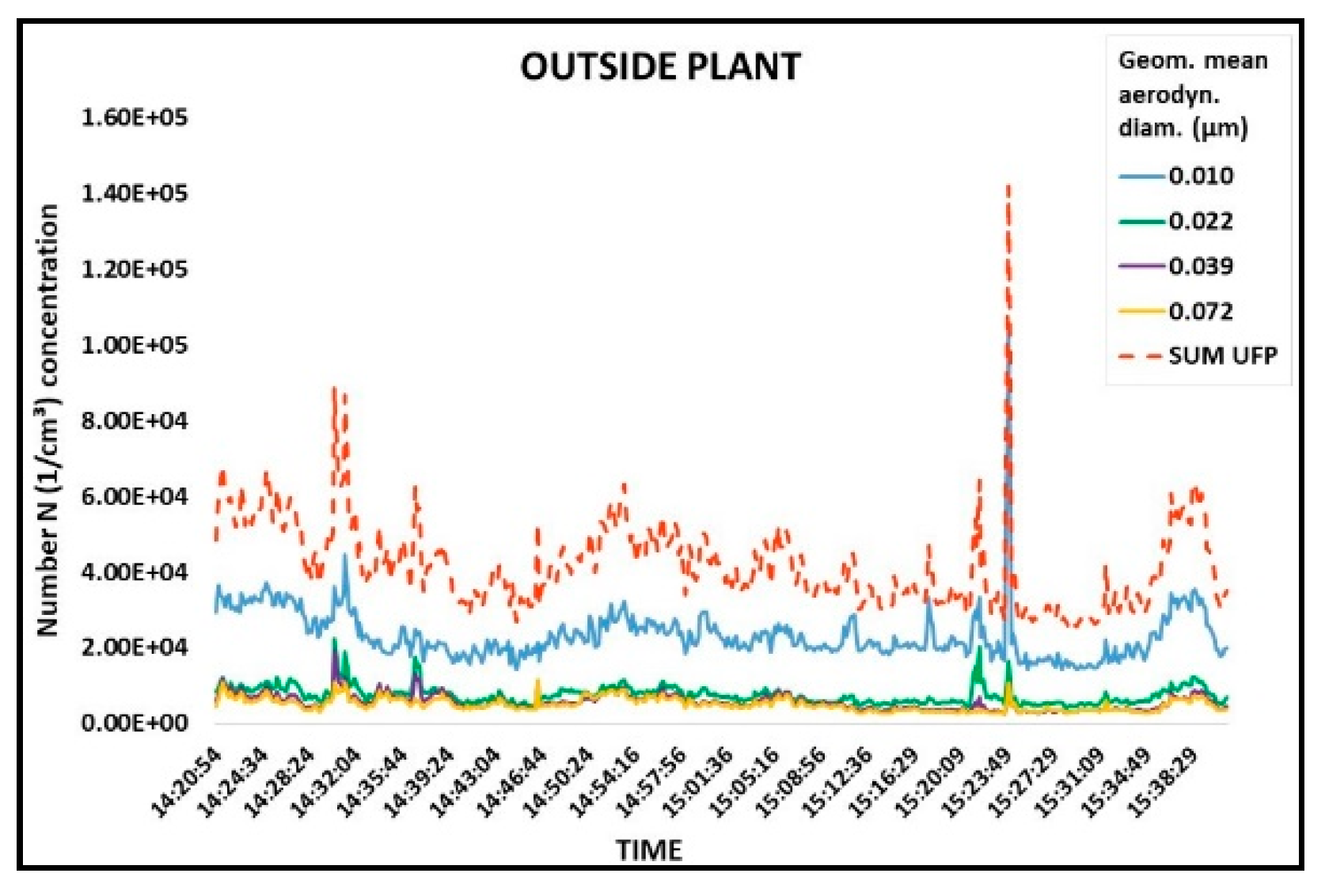
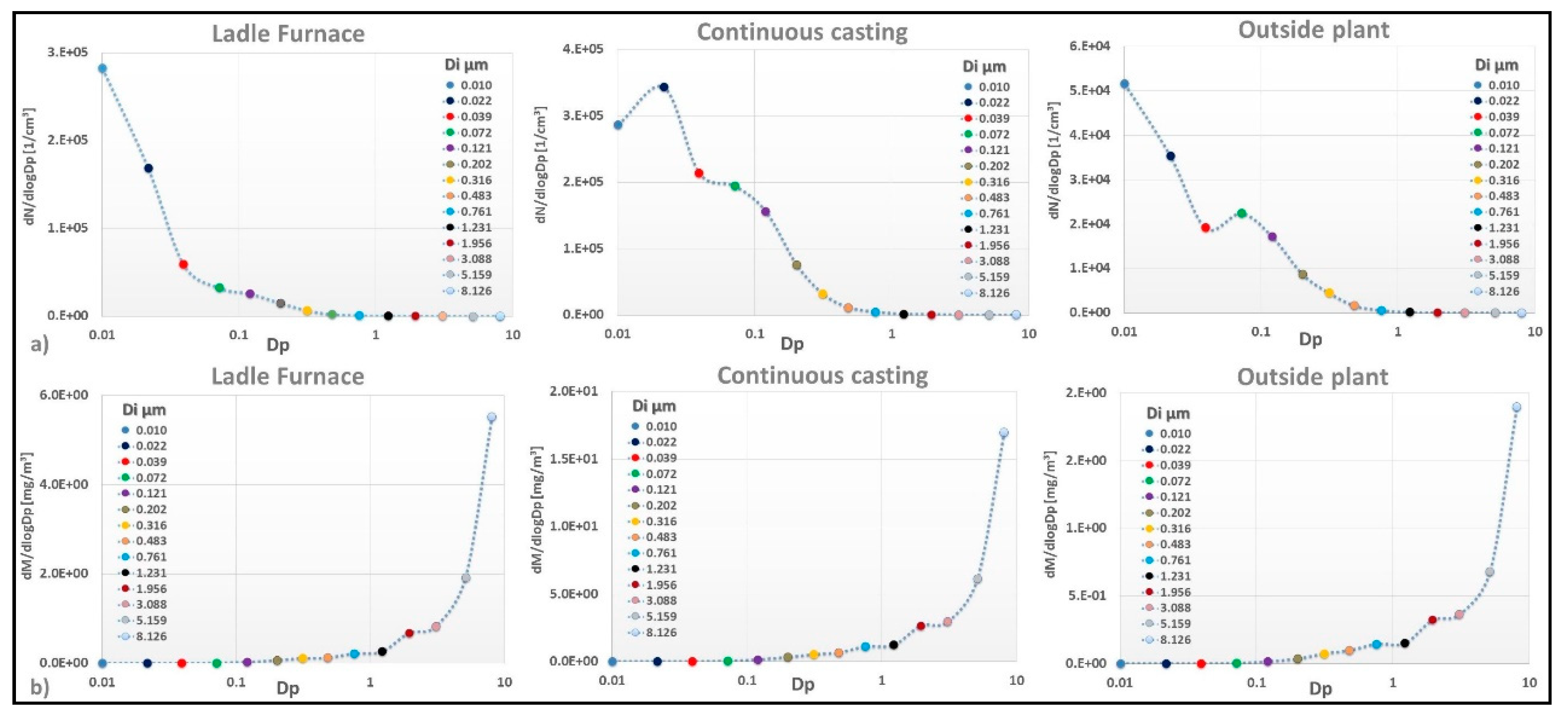

| Sampling Sites | Ladle Furnace | Continuous Casting | Outside Plant | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inhalable Fraction Concentration | 0.81 | 1.19 | 0.4 | ||||
| Metallic Elements | Sampling Sites | Metallic Elements | Sampling Sites | ||||
| Ladle Furnace | Continuous Casting | Outside Plant | Ladle Furnace | Continuous Casting | Outside Plant | ||
| Al | 6.243 | 7.223 | 2.88 | Hg | 0.0012 | 0.0018 | <0.0005 1 |
| As | 0.0565 | 0.2856 | 0.0035 | Mn | 41.016 | 15.16 | 0.6973 |
| Ba | 0.1947 | 0.3034 | 0.2142 | Mo | 0.0487 | 0.2737 | 0.0212 |
| Be | <0.0006 1 | <0.0006 1 | <0.0006 1 | Ni | 0.2467 | 0.833 | 0.1107 |
| Cd | 0.0043 | 0.0134 | 0.0024 | Pb | 3.122 | 5.093 | 0.3094 |
| Co | 0.0143 | 0.0274 | 0.0041 | Sb | 0.0208 | 0.1095 | 0.0093 |
| Cr | 0.095 | 0.158 | 0.044 | Sn | 0.1181 | 0.595 | 0.0357 |
| Cu | 0.7983 | 4.272 | 0.1785 | Sr | 0.1188 | 0.1737 | 0.0821 |
| Fe | 2.132 | 40.579 | 0.0405 | Zn | 6.827 | 8.794 | 1.82 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marcias, G.; Fostinelli, J.; Catalani, S.; Uras, M.; Sanna, A.M.; Avataneo, G.; De Palma, G.; Fabbri, D.; Paganelli, M.; Lecca, L.I.; et al. Composition of Metallic Elements and Size Distribution of Fine and Ultrafine Particles in a Steelmaking Factory. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15061192
Marcias G, Fostinelli J, Catalani S, Uras M, Sanna AM, Avataneo G, De Palma G, Fabbri D, Paganelli M, Lecca LI, et al. Composition of Metallic Elements and Size Distribution of Fine and Ultrafine Particles in a Steelmaking Factory. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(6):1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15061192
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarcias, Gabriele, Jacopo Fostinelli, Simona Catalani, Michele Uras, Andrea Maurizio Sanna, Giuseppe Avataneo, Giuseppe De Palma, Daniele Fabbri, Matteo Paganelli, Luigi Isaia Lecca, and et al. 2018. "Composition of Metallic Elements and Size Distribution of Fine and Ultrafine Particles in a Steelmaking Factory" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 6: 1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15061192
APA StyleMarcias, G., Fostinelli, J., Catalani, S., Uras, M., Sanna, A. M., Avataneo, G., De Palma, G., Fabbri, D., Paganelli, M., Lecca, L. I., Buonanno, G., & Campagna, M. (2018). Composition of Metallic Elements and Size Distribution of Fine and Ultrafine Particles in a Steelmaking Factory. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(6), 1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15061192