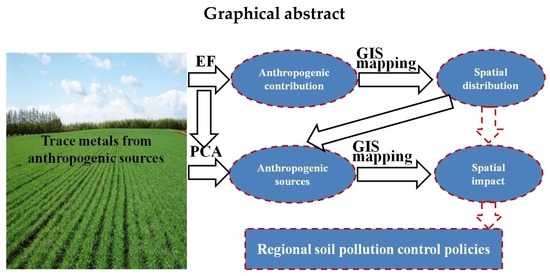
Spatial Assessment of Anthropogenic Impact on Trace Metal Accumulation in Farmland Soils from a Rapid Industrializing Region, East China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Soil Samples Collection
2.3. Trace and Major Metals Determination
2.4. Enrichment Factor Calculation
2.5. Statistical and Spatial Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Total Concentrations of the Trace Metals
3.2. Enrichment Factors of the Trace Metals
3.2.1. Selection of Reference Metal
3.2.2. Calculation of Enrichment Factor
3.2.3. Estimation of Anthropogenic Contribution
3.3. Principal Component Analysis
3.4. Spatial Distribution Maps
4. Discussion
4.1. Assessment of the Anthropogenic Trace Metal Accumulation in Regional Soils
4.2. Identification of the Major Anthropogenic Sources and Their Spatial Impacts
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Niu, L.L.; Yang, F.X.; Xu, C.; Yang, H.Y.; Liu, W.P. Status of metal accumulation in farmland soils across China: From distribution to risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 176, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.Y.; Chang, Q.; Yuan, X.Y.; Li, J.Z.; Ayoko, G.A.; Frost, R.L.; Chen, H.Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Song, Y.X.; Song, W.Z. Cadmium transfer from contaminated soils to the human body through rice consumption in southern Jiangsu Province, China. Environ. Sci.-Process Impacts 2017, 19, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghrefat, H.A.; Yusuf, N.; Jamarh, A.; Nazzal, J. Fractionation and risk assessment of heavy metals in soil samples collected along Zerqa River, Jordan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 66, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.A.; Cheng, H.F. A method for apportionment of natural and anthropogenic contributions to heavy metal loadings in the surface soils across large-scale regions. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, F.A.; Smith, S.R.; Alloway, B.J.; Carlton-Smith, C.; Chambers, B.J. An inventory of heavy metals inputs to agricultural soils in England and Wales. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 311, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benke, M.B.; Indraratne, S.P.; Hao, X.Y.; Chang, C.; Goh, T.B. Trace element changes in soil after long-term cattle manure applications. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37, 798–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atafar, Z.; Mesdaghinia, A.; Nouri, J.; Homaee, M.; Yunesian, M.; Ahmadimoghaddam, M.; Mahvi, A.H. Effect of fertilizer application on soil heavy metal concentration. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 160, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, W.; Ouyang, W.; Hao, F.H.; Wang, F.L.; Liu, B. Long-term cultivation impact on the heavy metal behavior in a reclaimed wetland, Northeast China. J. Soils Sediments 2014, 14, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Ma, Y.B.; Zhang, S.Z.; Wei, D.P.; Zhu, Y.G. An inventory of trace element inputs to agricultural soils in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2524–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.C.; Wang, Z.G.; Sun, W.X.; Huang, B.; Shi, X.Z.; Ji, J.F. Spatial interrelations and multi-scale sources of soil heavy metal variability in a typical urban–rural transition area in Yangtze River Delta region of China. Geoderma 2010, 156, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mico, C.; Recatala, L.; Peris, A.; Sanchez, J. Assessing heavy metal sources in agricultural soils of an European Mediterranean area by multivariate analysis. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, Y.S.; Tysklind, M.; Hao, F.H.; Ouyang, W.; Chen, S.Y.; Lin, C.Y. Identification of sources of heavy metals in agricultural soils using multivariate analysis and GIS. J. Soils Sediments 2013, 13, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, M.; Dumanoğlu, Y.; Altıok, H.; Elbir, T.; Odabası, M.; Bayram, A. Spatial distribution and source identification of trace elements in topsoil from heavily industrialized region, Aliaga, Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 6017–6038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Wang, W.Y.; Li, Y.H.; Yang, L.S. Heavy metals in soil and crops of an intensively farmed area: A case study in Yucheng City, Shandong Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.Y.; Hu, K.L.; An, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, G.D. Spatial distribution and source apportionment of the heavy metals in the agricultural soil in a regional scale. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 852–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauret, G.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.F.; Sahuquillo, A.; Rubio, R.; Davidson, C.; Ure, A.; Quevauviller, P. Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials. J. Environ. Monit. 1999, 1, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chester, R.; Stoner, J.H. Pb in particulates from the lower atmosphere of the eastern Atlantic. Nature 1973, 245, 27–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N’guessan, Y.M.; Probst, J.L.; Bur, T.; Probst, A. Trace elements in stream bed sediments from agricultural catchments (Gascogne region, S-W France): Where do they come from? Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2939–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ye, C.; Li, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, Q.F. Assessing soil heavy metal pollution in the water-level-fluctuation zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 191, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaser, P.; Zimmermann, S.; Luster, J.; Shotyk, W. Critical examination of trace element enrichments and depletions in soils: As, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn in Swiss forest soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 249, 257–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Guo, H.C.; Liu, L. Quantitative identification and source apportionment of anthropogenic heavy metals in marine sediment of Hong Kong. Environ. Geol. 2007, 53, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.B.; Ma, J.; Wang, X.L.; Hou, H. Heavy metals in soils from a typical county in Shanxi Province, China: Levels, sources and spatial distribution. Chemosphere 2016, 14, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.Y.; Jia, Z.M. Heavy metals in soils from a representative rapidly developing megacity (SW China): Levels, source identification and apportionment. Catena 2018, 163, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.X.; Chao, S.H.; Liu, J.W.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Zhang, A.C.; Cao, H.B. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil for a township in Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 1658–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.X.; Yu, Y.; Yang, Z.F.; Shen, Z.Y.; Wang, X.; Cai, Y.P. A comparison of metal distribution in surface dust and soil among super city, town, and rural area. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 7849–7860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Y.; Liu, L.J.; Wang, Y.G.; Luo, G.P.; Chen, X.; Yang, X.L.; Hall, M.H.P.; Guo, R.C.; Wang, H.J.; Cui, J.H.; et al. Heavy metal contamination of urban soil in an old industrial city (Shenyang) in Northeast China. Geoderma 2013, 192, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.K.; Li, W.D.; Zhang, C.R.; Wang, S.Q.; Yang, Y.; He, L.Y. Source apportionment of heavy metals in soils using multivariate statistics and geostatistics. Pedosphere 2013, 23, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhu, F.; Chen, J.; Gan, H.; Guo, Y. Chemical fractionation of heavy metals in urban soils of Guangzhou, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 134, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SEPAC (State Environmental Protection Administration of China). Environmental Quality Standard for Soils (GB 15618–1995); State Environmental Protection Administration of China: Beijing, China, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Christakos, G.; Guo, M.W.; Xiao, L.; Huang, W. Space-time quantitative source apportionment of soil heavy metal concentration increments. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.P. Heavy metal pollution in China: Origin, pattern and control. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2003, 10, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, L.B.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Hu, Y.; Su, B.Y.; Fang, G.L.; Wang, L.; Xiang, B. A review of heavy metal pollution levels and health risk assessment of urban soils in Chinese cities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 1055–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, W.; Ouyang, W.; Hao, F.H.; Lin, C.Y. Anthropogenic impact on diffuse trace metal accumulation in river sediments from agricultural reclamation areas with geochemical and isotopic approaches. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 536, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, W.; Ouyang, W.; Hao, F.H.; Liu, B.; Wang, F.L. Geochemical variability of heavy metals in soil after land use conversions in Northeast China and its environmental applications. Environ. Sci.-Process Impacts 2014, 16, 924–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, D.Y.; O’Connor, D.; Nathanail, P.; Tian, L.; Ma, Y. Integrated GIS and multivariate statistical analysis for regional scale assessment of heavy metal soil contamination: A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 1188–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.S.; Xue, Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Long, C.; Xu, B.; Ding, J. Source identification and apportionment of heavy metals in urban soil profiles. Chemosphere 2015, 127, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dach, J.; Starmans, D. Heavy metals balance in Polish and Dutch agronomy: Actual state and previsions for the future. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 107, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, C.A.; Sheppard, S.C. Fertilizer impacts on cadmium availability in agricultural soils and crops. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2008, 14, 210–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.T.; Chen, W.P.; Chang, A.C.; Page, A.L. Environmental risks of trace elements associated with long-term phosphate fertilizers applications: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 168, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Trace Metals (mg/kg) | Parameters | Pb | Cd | Cu | Zn | Cr | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study area | Minimum | 33.10 | 0.15 | 23.54 | 68.09 | 41.13 | 24.41 |
| (Topsoil, n = 97) | Maximum | 56.10 | 0.22 | 42.13 | 131.30 | 68.81 | 40.69 |
| Mean | 43.34 | 0.19 | 30.51 | 94.74 | 53.23 | 34.75 | |
| S.D a | 8.34 | 0.03 | 5.73 | 21.85 | 9.27 | 7.21 | |
| V.C b | 19.24 | 15.79 | 18.78 | 23.06 | 17.41 | 20.75 | |
| Study area | Minimum | 18.95 | 0.08 | 16.17 | 43.80 | 27.46 | 15.72 |
| (Subsoil, n = 25) | Maximum | 26.69 | 0.12 | 20.96 | 63.75 | 35.81 | 26.19 |
| Mean | 24.46 | 0.11 | 18.83 | 55.59 | 31.62 | 21.33 | |
| S.D a | 2.48 | 0.02 | 2.84 | 8.81 | 3.19 | 4.11 | |
| V.C b | 10.14 | 18.18 | 15.08 | 15.85 | 10.09 | 19.27 | |
| A county in Northwest China [22] | Mean | 24 | 0.20 | 30 | 83 | 71 | 32 |
| A county in Southwest China [23] | Mean | 29.41 | 0.38 | 26.55 | 91.20 | 76.48 | 35.79 |
| A town in East China [24] | Mean | 31.41 | 0.11 | 31.60 | 61.13 | 86.38 | 34.93 |
| A town in North China [25] | Mean | 28.29 | 0.24 | 35.98 | 93.31 | 100.73 | 38.14 |
| Shenyang [26] | Mean | 116.76 | 1.10 | 92.45 | 234.80 | 67.90 | — |
| Wuhan [27] | Mean | 301.70 | 3.98 | 60.85 | 86.40 | 152.78 | 52.87 |
| Guangzhou [28] | Mean | 109 | 0.5 | 63 | 117 | — | 26 |
| Chinese environmental quality standard for soils c | 250 | 0.3 | 50 | 200 | 150 | 40 |
| Metal | Spearman Correlation Coefficients | Chemical Fractions % (Mean ± S.D) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Cd | Cu | Zn | Cr | Ni | Acid-Soluble | Reducible | Oxidizable | Residual | |
| Fe | 0.573 | 0.611 | 0.458 | 0.418 | 0.526 | 0.406 | 6.23 ± 0.71 | 18.21 ± 1.35 | 12.36 ± 1.21 | 63.20 ± 5.17 |
| Al | 0.813 | 0.876 | 0.795 | 0.729 | 0.842 | 0.704 | 2.68 ± 0.28 | 8.13 ± 1.14 | 5.06 ± 0.53 | 84.13 ± 7.75 |
| Initial Eigenvalues | Element | Rotated Component Matrix | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Component | Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | PC1 | PC2 | |
| Explanation of Total Variance | Component Matrixes | |||||
| 1 | 3.191 | 53.182 | 53.182 | Pb | 0.974 | −0.140 |
| 2 | 2.364 | 39.402 | 92.584 | Cd | −0.235 | 0.866 |
| 3 | 0.275 | 4.585 | 97.170 | Cu | 0.092 | 0.961 |
| 4 | 0.077 | 1.279 | 98.449 | Zn | −0.073 | 0.967 |
| 5 | 0.061 | 1.024 | 99.472 | Cr | 0.975 | 0.060 |
| 6 | 0.032 | 0.528 | 100.000 | Ni | 0.967 | −0.135 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiao, W.; Niu, Y.; Niu, Y.; Hu, H.; Li, R. Spatial Assessment of Anthropogenic Impact on Trace Metal Accumulation in Farmland Soils from a Rapid Industrializing Region, East China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2052. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15092052
Jiao W, Niu Y, Niu Y, Hu H, Li R. Spatial Assessment of Anthropogenic Impact on Trace Metal Accumulation in Farmland Soils from a Rapid Industrializing Region, East China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(9):2052. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15092052
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiao, Wei, Yong Niu, Yuan Niu, Hengyu Hu, and Ruiping Li. 2018. "Spatial Assessment of Anthropogenic Impact on Trace Metal Accumulation in Farmland Soils from a Rapid Industrializing Region, East China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 9: 2052. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15092052
APA StyleJiao, W., Niu, Y., Niu, Y., Hu, H., & Li, R. (2018). Spatial Assessment of Anthropogenic Impact on Trace Metal Accumulation in Farmland Soils from a Rapid Industrializing Region, East China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(9), 2052. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15092052