Effect of a Multidimensional Physical Activity Intervention on Body Mass Index, Skinfolds and Fitness in South African Children: Results from a Cluster-Randomised Controlled Trial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Area and Population
2.2. Study Design and Randomisation
2.3. Interventions
2.4. Ethics Statement
2.5. Procedures
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marshall, S.J. Developing countries face double burden of disease. Bull. World Health Organ. 2004, 82, 556. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.S.; Vos, T.; Flaxman, A.D.; Danaei, G.; Shibuya, K.; Adair-Rohani, H.; Amann, M.; Anderson, H.R.; Andrews, K.G.; Aryee, M.; et al. A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2224–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, C.L.; Carroll, M.D.; Curtin, L.R.; McDowell, M.A.; Tabak, C.J.; Flegal, K.M. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the United States, 1999–2004. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2006, 295, 1549–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, T.N. Reducing children’s television viewing to prevent obesity: A randomized controlled trial. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1999, 282, 1561–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekelund, U.; Sardinha, L.B.; Anderssen, S.A.; Harro, M.; Franks, P.W.; Brage, S.; Cooper, A.R.; Andersen, L.B.; Riddoch, C.; Froberg, K. Associations between objectively assessed physical activity and indicators of body fatness in 9- to 10-y-old European children: A population-based study from 4 distinct regions in Europe (the European Youth Heart Study). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, P.H.; Nobre, M.R.; Silveira, J.A.; Taddei, J.A. The effect of school-based physical activity interventions on body mass index: A meta-analysis of randomized trials. Clinics 2013, 68, 1263–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Lin, S.; Guo, H.; Huang, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, J.; Wang, H.J. Effectiveness of a school-based physical activity intervention on obesity in school children: A nonrandomized controlled trial. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steyn, K.; Damasceno, A. Lifestyle and related risk factors for chronic diseases. In Disease and Mortality in Sub-Saharan Africa, 2nd ed.; Jamison, D.T., Feachem, R.G., Makgoba, M.W., Bos, E.R., Baingana, F.K., Hofman, K.J., Rogo, K.O., Eds.; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kipping, R.R.; Jago, R.; Lawlor, D.A. Obesity in children. Part 1: Epidemiology, measurement, risk factors, and screening. BMJ 2008, 337, a1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draper, C.E.; Tomaz, S.A.; Bassett, S.H.; Burnett, C.; Christie, C.J.; Cozett, C.; de Milander, M.; Krog, S.; Monyeki, A.; Naidoo, N.; et al. Results from South Africa’s 2018 Report Card on Physical Activity for Children and Youth. J. Phys. Act. Health 2018, 15, S406–S408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, I.; Yap, P.; Steinmann, P.; Damons, B.P.; Schindler, C.; Seelig, H.; Htun, N.S.N.; Probst-Hensch, N.; Gerber, M.; du Randt, R.; et al. Intestinal parasites, growth and physical fitness of schoolchildren in poor neighbourhoods of Port Elizabeth, South Africa: A cross-sectional survey. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, S.; Müller, I.; Walter, C.; Seelig, H.; Steenkamp, L.; Pühse, U.; du Randt, R.; Smith, D.; Adams, L.; Nqweniso, S.; et al. Associations between selective attention and soil-transmitted helminth infections, socioeconomic status, and physical fitness in disadvantaged children in Port Elizabeth, South Africa: An observational study. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, S.L.; Müller, I.; Mertens, P.; Herrmann, M.; Zondie, L.; Beyleveld, L.; Gerber, M.; du Randt, R.; Pühse, U.; Walter, C.; et al. PCR-based verification of positive rapid diagnostic tests for intestinal protozoa infections with variable test band intensity. Acta Trop. 2017, 174, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, P.; Müller, I.; Walter, C.; Seelig, H.; Gerber, M.; Steinmann, P.; Damons, B.P.; Smith, D.; Gall, S.; Bänninger, D.; et al. Disease, Activity and Schoolchildren’s Health (DASH) in Port Elizabeth, South Africa: A study protocol. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, K.; Giese, S. Addressing Quality through School Fees and School Funding; South African Child Gauge: Pretoria, South Africa, 2009; pp. 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Gall, S.; Adams, L.; Joubert, N.; Ludyga, S.; Müller, I.; Nqweniso, S.; Pühse, U.; du Randt, R.; Seelig, H.; Smith, D.; et al. Effect of a 20-week physical activity intervention on selective attention and academic performance in children living in disadvantaged neighborhoods: A cluster randomized control trial. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Onis, M.; Onyango, A.W.; Borghi, E.; Siyam, A.; Nishida, C.; Siekmann, J. Development of a WHO growth reference for school-aged children and adolescents. Bull. World Health Organ. 2007, 85, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederer, I.; Kriemler, S.; Zahner, L.; Bürgi, F.; Ebenegger, V.; Hartmann, T.; Meyer, U.; Schindler, C.; Nydegger, A.; Marques-Vidal, P.; et al. Influence of a lifestyle intervention in preschool children on physiological and psychological parameters (Ballabeina): Study design of a cluster randomized controlled trial. BMC Public Health 2009, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puder, J.J.; Marques-Vidal, P.; Schindler, C.; Zahner, L.; Niederer, I.; Bürgi, F.; Ebenegger, V.; Nydegger, A.; Kriemler, S. Effect of multidimensional lifestyle intervention on fitness and adiposity in predominantly migrant preschool children (Ballabeina): Cluster randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2011, 343, d6195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Léger, L.A.; Mercier, D.; Gadoury, C.; Lambert, J. The multistage 20 meter shuttle run test for aerobic fitness. J. Sports Sci. 1988, 6, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Léger, L.; Lambert, J.; Goulet, A.; Rowan, C.; Dinelle, Y. Capacité aérobie des Québécois de 6 à 17 ans—Test navette de 20 mètres avec paliers de 1 minute. Can. J. Appl. Sport Sci. 1984, 9, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gwetu, T.P.; Chhagan, M.K.; Taylor, M.; Kauchali, S.; Craib, M. Anaemia control and the interpretation of biochemical tests for iron status in children. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, N.; Chaves, A.; Pellegrino, J. A simple device for quantitative stool thick-smear technique in schistosomiasis mansoni. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 1972, 14, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Müller, I.; Beyleveld, L.; Gerber, M.; Pühse, U.; du Randt, R.; Utzinger, J.; Zondie, L.; Walter, C.; Steinmann, P. Low efficacy of albendazole against Trichuris trichiura infection in schoolchildren from Port Elizabeth, South Africa. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 110, 676–678. [Google Scholar]
- Vyas, S.; Kumaranayake, L. Constructing socio-economic status indices: How to use principal components analysis. Health Policy Plan. 2006, 21, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woringer, V.; Schutz, Y. Obesity in Switzerland: Body mass index (BMI) percentiles of a child and adolescent population born in 1980 in Lausanne and comparison with Swiss norms (1955). Soz. Präventivmed. 2003, 48, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Sluijs, E.M.; McMinn, A.M.; Griffin, S.J. Effectiveness of interventions to promote physical activity in children and adolescents: Systematic review of controlled trials. BMJ 2007, 335, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, G.F.; Nicolás, J.; Díaz, A. Effects of a vigorous physical activity program on blood pressure and heart rate of schoolchildren aged 10–11 years. J. Sport Health Res. 2018, 10, 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Resaland, G.K.; Aadland, E.; Nilsen, A.K.O.; Bartholomew, J.B.; Andersen, L.B.; Anderssen, S.A. The effect of a two-year school-based daily physical activity intervention on a clustered CVD risk factor score—The Sogndal school-intervention study. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2018, 28, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, C.E.; de Villiers, A.; Lambert, E.V.; Fourie, J.; Hill, J.; Dalais, L.; Abrahams, Z.; Steyn, N.P. HealthKick: A nutrition and physical activity intervention for primary schools in low-income settings. BMC Public Health 2010, 10, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. World-Wide Survey of School Physical Education—Final Report. 1–130; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2013; pp. 1–130. Available online: https://library.olympic.org/Default/doc/SYRACUSE/65300/world-wide-survey-of-school-physical-education-final-report-2013-united-nations-educational-scientif?_lg=fr-FR (accessed on 17 November 2018).
- Møller, N.C.; Tarp, J.; Kamelarczyk, E.F.; Brond, J.C.; Klakk, H.; Wedderkopp, N. Do extra compulsory physical education lessons mean more physically active children--findings from the childhood health, activity, and motor performance school study Denmark (The CHAMPS-study DK). Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2014, 11, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frémeaux, A.E.; Mallam, K.M.; Metcalf, B.S.; Hosking, J.; Voss, L.D.; Wilkin, T.J. The impact of school-time activity on total physical activity: The activitystat hypothesis (EarlyBird 46). Int. J. Obes. 2011, 35, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, C.M. In-school physical activity patterns of primary school learners from disadvantaged schools in South Africa. Afr. J. Phys. Health Educ. 2011, 17, 780–789. [Google Scholar]
- Kimani-Murage, E.W.; Kahn, K.; Pettifor, J.M.; Tollman, S.M.; Dunger, D.B.; Gomez-Olive, X.F.; Norris, S.A. The prevalence of stunting, overweight and obesity, and metabolic disease risk in rural South African children. BMC Public Health 2010, 10, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, C.M.; Du Randt, R.; Venter, D.J.L. The physical activity and health status of two generations of black South African professional women. Health S A Gesondheid 2011, 16, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.L.; Olsen, L.W.; Sorensen, T.I. Childhood body-mass index and the risk of coronary heart disease in adulthood. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2329–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hürlimann, E.; Houngbedji, C.A.; N’Dri, P.B.; Bänninger, D.; Coulibaly, J.T.; Yap, P.; Silué, K.D.; N’Goran, E.K.; Raso, G.; Utzinger, J. Effect of deworming on school-aged children’s physical fitness, cognition and clinical parameters in a malaria-helminth co-endemic area of Côte d’Ivoire. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, P.; Wu, F.W.; Du, Z.W.; Hattendorf, J.; Chen, R.; Jiang, J.Y.; Kriemler, S.; Krauth, S.J.; Zhou, X.N.; Utzinger, J.; et al. Effect of deworming on physical fitness of school-aged children in Yunnan, China: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriemler, S.; Zahner, L.; Schindler, C.; Meyer, U.; Hartmann, T.; Hebestreit, H.; Brunner-La Rocca, H.P.; van Mechelen, W.; Puder, J.J. Effect of school based physical activity programme (KISS) on fitness and adiposity in primary schoolchildren: Cluster randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2010, 340, c785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imhof, K.; Faude, O.; Donath, L.; Bean-Eisenhut, S.; Hanssen, H.; Zahner, L. The association of socio-economic factors with physical fitness and activity behaviours, spinal posture and retinal vessel parameters in first graders in urban Switzerland. J. Sports Sci. 2016, 34, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.J.; Tremblay, M.S.; Léger, L.; Olds, T.; Tomkinson, G.R. International variability in 20 m shuttle run performance in children and youth: Who are the fittest from a 50-country comparison? A systematic literature review with pooling of aggregate results. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomkinson, G.R.; Lang, J.J.; Tremblay, M.S.; Dale, M.; LeBlanc, A.G.; Belanger, K.; Ortega, F.B.; Leger, L. International normative 20 m shuttle run values from 1142026 children and youth representing 50 countries. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southern Africa Development RaTI. One Community Many Communities: A Nelson Mandela Bay Heritage and History Project (NMBHHP): Forced Removals in South End, North End, Salisbury Park, Fairview, Willowdene and Korsten; Southern Africa Development RaTI: Gaborone, Botswana, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kamath, C.C.; Vickers, K.S.; Ehrlich, A.; McGovern, L.; Johnson, J.; Singhal, V.; Paulo, R.; Hettinger, A.; Erwin, P.J.; Montori, V.M. Clinical review: Behavioral interventions to prevent childhood obesity: A systematic review and metaanalyses of randomized trials. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 4606–4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erturan-Ilker, G.; Yu, C.; Alemdaroğlu, U.; Köklü, Y. Basic psychological needs and self-determined motivation in PE to predict health-related fitness level. J. Sport Health Res. 2018, 10, 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, U.; Roth, R.; Zahner, L.; Gerber, M.; Puder, J.J.; Hebestreit, H.; Kriemler, S. Contribution of physical education to overall physical activity. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2013, 23, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustinduy, A.L.; Thomas, C.L.; Fiutem, J.J.; Parraga, I.M.; Mungai, P.L.; Muchiri, E.M.; Mutuku, F.; Kitron, U.; King, C.H. Measuring fitness of Kenyan children with polyparasitic infections using the 20-meter shuttle run test as a morbidity metric. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
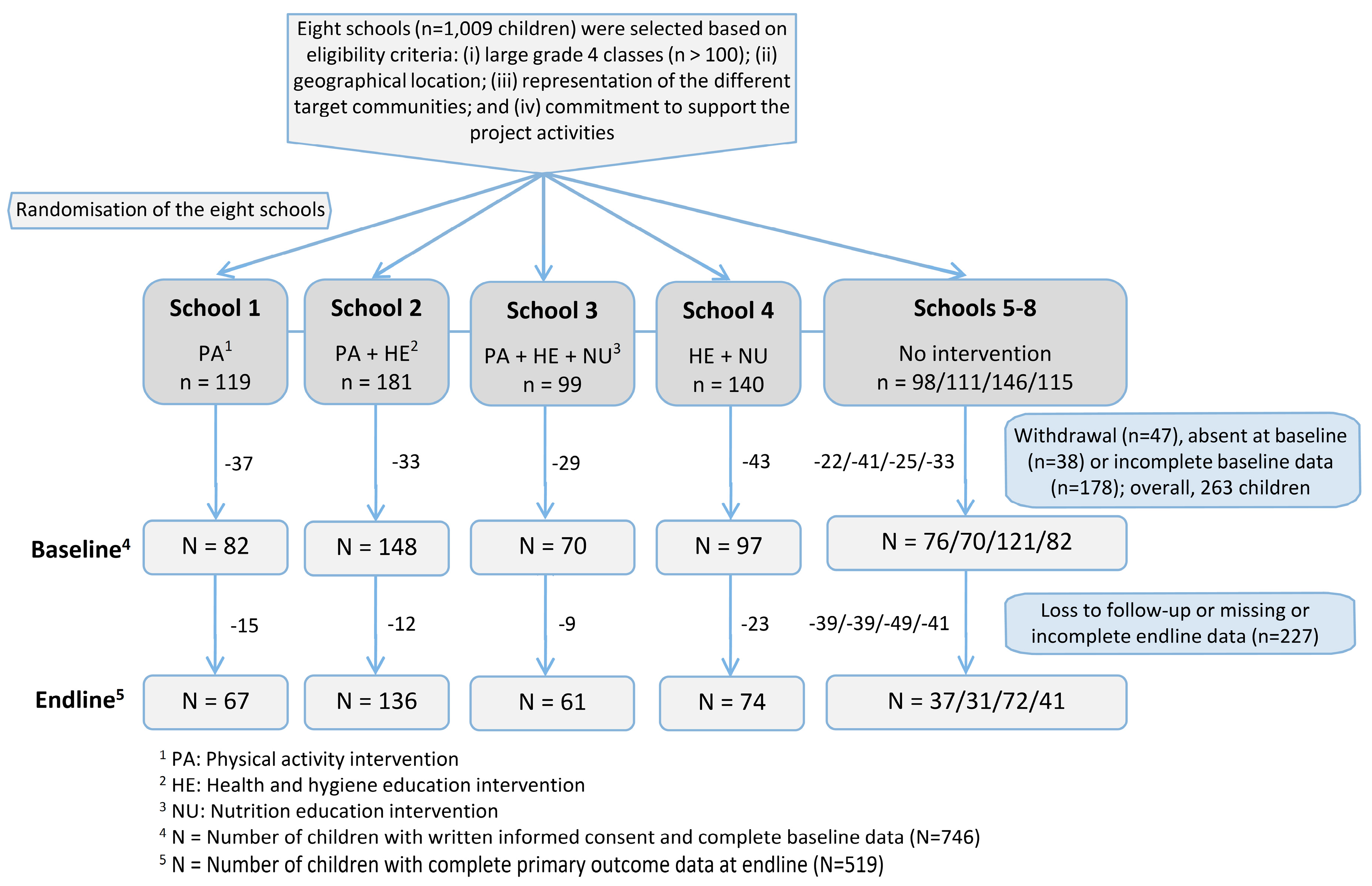


| Total (n = 746) | Schools with Physical Activity Intervention (n = 300) | Schools without Physical Activity Intervention (n = 446) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| In numbers (percentages) | |||
| Girls | 372 (49.9) | 150 (50.0) | 222 (49.8) |
| Overweight a | 102 (13.7) | 38 (12.7) | 64 (14.3) |
| Obese b | 39 (5.3) | 15 (5.0) | 24 (5.4) |
| Stunted c | 86 (11.5) | 46 (15.3) | 40 (9.0) |
| Anaemic d | 138 (18.5) | 67 (22.3) | 71 (15.9) |
| Infected with intestinal protozoa e | 120 (16.1) | 61 (20.3) | 59 (13.2) |
| Infected with soil-transmitted helminths (STHs) f | 235 (31.5) | 132 (44.0) | 103 (23.1) |
| In means (SD) | |||
| Age in years | 10.0 (0.9) | 10.1 (0.9) | 9.9 (1.0) |
| Height in cm | 133.3 (7.1) | 132.6 (7.1) | 133.8 (7.0) |
| Skinfolds in mm | 9.0 (4.5) | 9.0 (4.5) | 9.0 (4.4) |
| Shuttle run in laps | 36.3 (17.3) | 35.6 (17.0) | 36.8 (17.4) |
| VO2max g in mL × kg−1 × min−1 | 46.1 (4.3) | 45.8 (4.1) | 46.3 (4.3) |
| Overall SES index h | 0.0 (2.8) | −0.1 (2.7) | 0.0 (2.9) |
| Poorest | −4.8 (2.3) | −4.5 (2.5) | −5.0 (2.1) |
| Second quintile | −0.3 (0.6) | −0.2 (0.6) | −0.4 (0.6) |
| Less poor | 1.0 (0.2) | 1.0 (0.2) | 1.0 (0.2) |
| Fourth quintile | 1.7 (0.2) | 1.7 (0.2) | 1.7 (0.2) |
| Least poor | 2.3 (0.2) | 2.3 (0.2) | 2.3 (0.2) |
| Score of self-reported physical activity | 8.4 (3.8) | 9.1 (3.7) | 7.8 (3.8) |
| Variables | Schools with Physical Activity Intervention | Schools without Physical Activity Intervention | Intervention Effect a | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Endline | Baseline | Endline | Estimate b (95% CI) | p-Value | ICC c | |
| (n = 300) | (n = 264) | (n = 446) | (n = 255) | ||||
| Cardiorespiratory fitness | |||||||
| Shuttle run (laps) | 35.6 | 34.5 | 36.8 | 35.3 | −0.56 (−4.67 to 3.56) | 0.79 | 0.04 |
| (17.0) | (17.9) | (17.4) | (18.7) | ||||
| VO2max d (mL × kg−1 × min−1) | 45.8 | 43.5 | 46.3 | 44 | −0.14 (−1.17 to 0.88) | 0.78 | 0.03 |
| (4.1) | (4.7) | (4.3) | (4.8) | ||||
| Obesity | |||||||
| BMIZ e | −0.1 | −0.1 | 0 | 0.2 | −0.17 (−0.24 to −0.09) | <0.001 | <0.01 |
| (1.2) | (1.3) | (1.2) | (1.3) | ||||
| Skinfolds f (mm) | 9.0 | 9.6 | 9 | 10.1 | −1.06 (−1.83 to −0.29) | 0.007 | 0.02 |
| (4.5) | (4.6) | (4.4) | (5.9) | ||||
| Mean of self-reported physical activity g | 9.1 | 9.0 | 7.8 | 9.9 | −1.08 (−2.36 to 0.18) | 0.09 | 0.04 |
| (3.7) | (3.1) | (3.8) | (3.4) | ||||
| Binary Variables | Schools with Physical Activity Intervention | Schools without Physical Activity Intervention | Intervention Effect a | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Endline | Baseline | Endline | Odds Ratio b | (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| (n = 300) | (n = 264) | (n = 446) | (n = 255) | ||||
| Stunted c | 46 (15.3) | 47 (17.8) | 40 (9.0) | 48 (12.8) | New occurrence | 0.68 (0.23 to 2.07) | 0.50 |
| Re-occurrence | 0.68 (0.12 to 3.96) | 0.67 | |||||
| Prevalence | 0.76 (0.09 to 6.53) | 0.81 | |||||
| Anaemic d | 67 (22.3) | 37 (14.0) | 71 (15.9) | 50 (13.4) | New occurrence | 1.36 (0.53 to 3.49) | 0.52 |
| Re-occurrence | 0.82 (0.25 to 2.62) | 0.73 | |||||
| Prevalence | 0.93 (0.38 to 2.30) | 0.87 | |||||
| Infected with soil-transmitted helminths (STHs) f | 132 (44.0) | 108 (40.9) | 103 (23.1) | 51 (13.6) | New occurrence | 2.33 (0.03 to 186.00) g | 0.71 |
| Re-occurrence | 3.44 (0.04 to 298.70) g | 0.59 | |||||
| Prevalence | 1.92 (0.47 to 7.80) | 0.36 | |||||
| Infected with intestinal protozoa e | 61 (20.3) | 54 (20.5) | 59 (13.2) | 38 (10.2) | New occurrence | 1.37 (0.65 to 2.90) | 0.41 |
| Re-occurrence | 1.55 (0.58 to 4.17) | 0.38 | |||||
| Prevalence | 1.23 (0.47 to 3.22) | 0.68 | |||||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Müller, I.; Schindler, C.; Adams, L.; Endes, K.; Gall, S.; Gerber, M.; Htun, N.S.N.; Nqweniso, S.; Joubert, N.; Probst-Hensch, N.; et al. Effect of a Multidimensional Physical Activity Intervention on Body Mass Index, Skinfolds and Fitness in South African Children: Results from a Cluster-Randomised Controlled Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16020232
Müller I, Schindler C, Adams L, Endes K, Gall S, Gerber M, Htun NSN, Nqweniso S, Joubert N, Probst-Hensch N, et al. Effect of a Multidimensional Physical Activity Intervention on Body Mass Index, Skinfolds and Fitness in South African Children: Results from a Cluster-Randomised Controlled Trial. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(2):232. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16020232
Chicago/Turabian StyleMüller, Ivan, Christian Schindler, Larissa Adams, Katharina Endes, Stefanie Gall, Markus Gerber, Nan S. N. Htun, Siphesihle Nqweniso, Nandi Joubert, Nicole Probst-Hensch, and et al. 2019. "Effect of a Multidimensional Physical Activity Intervention on Body Mass Index, Skinfolds and Fitness in South African Children: Results from a Cluster-Randomised Controlled Trial" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 2: 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16020232
APA StyleMüller, I., Schindler, C., Adams, L., Endes, K., Gall, S., Gerber, M., Htun, N. S. N., Nqweniso, S., Joubert, N., Probst-Hensch, N., du Randt, R., Seelig, H., Smith, D., Steinmann, P., Utzinger, J., Yap, P., Walter, C., & Pühse, U. (2019). Effect of a Multidimensional Physical Activity Intervention on Body Mass Index, Skinfolds and Fitness in South African Children: Results from a Cluster-Randomised Controlled Trial. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(2), 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16020232






