Water Quality of the Mun River in Thailand—Spatiotemporal Variations and Potential Causes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Research Area and Methods
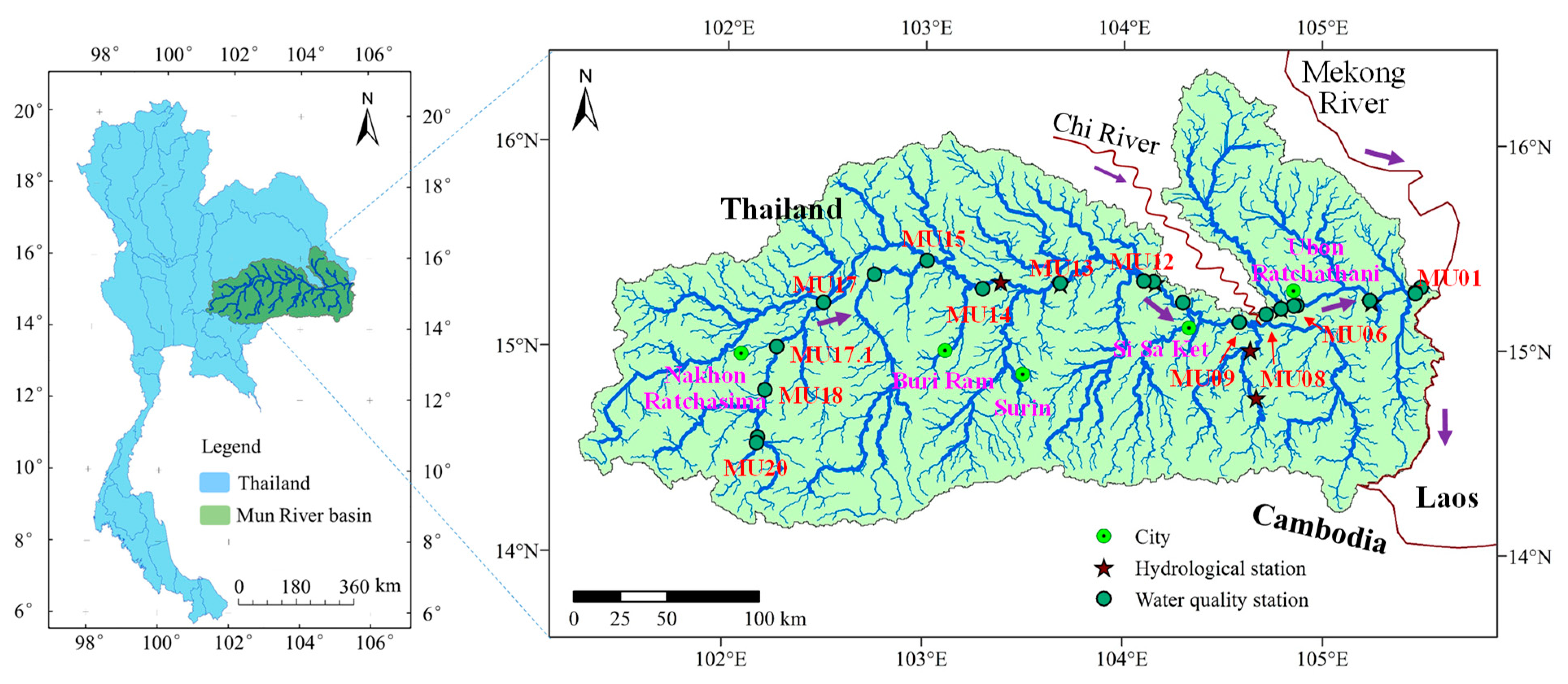
2.1. Research Area
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.3. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spatiotemporal Variation of Representative Water Quality Parameters
3.2. Spatiotemporal Variation of WQI
3.3. Potential Causes of the Spatiotemporal Variations of Water Quality
3.3.1. Correlation between Land Use Types and Water Quality
3.3.2. Impacts of Confluence from Chi River
3.3.3. Relationship between Soil Nutrient and Water Quality
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Parameter | Concentration Range (mg/L) | Score Rating Formula |
|---|---|---|
| DO | 0–4.0 | 15.25 × (DO concentration) + 0.1677 |
| 4.1–6.0 | 5 × (DO concentration) + 41 | |
| 6.1–8.4 | 12.083 × (DO concentration) − 1.5 | |
| 8.5–8.9 | 755.2 − 78 × (DO concentration) | |
| 9.0–11.2 | 177.09 − 13.043 × (DO concentration) | |
| 11.3–(≥15.3) | 115.68 − 7.561 × (DO concentration) | |
| BOD | 0–1.5 | 100 − 19.333 × (BOD concentration) |
| 1.6–2.0 | 101 − 20 × (BOD concentration) | |
| 2.1–4.0 | 91 − 15 × (BOD concentration) | |
| 4.1–(≥8.8) | 56.833 − 6.4583 × (BOD concentration) | |
| TCB | 0.0–5000 | 100 − 0.0058 × (TCB concentration) |
| 5001–20,000 | 74.333 − 0.0007 × (TCB concentration) | |
| 20,001–160,000 | 65.286 − 0.0002 × (TCB concentration) | |
| >160,000 | 32.292 − 8 × 10−6 × (TCB concentration) | |
| FCB | 0.0–1000 | 100 − 0.029 × (FCB concentration) |
| 1001–4000 | 74.333 − 0.0033 × (FCB concentration) | |
| 4001–90,000 | 62.395 − 0.0003 × (FCB concentration) | |
| >90,000 | 32.208 − 10−5 × (FCB concentration) | |
| TP | 0–1.48 | e(−2.5 × (TP concentration)) × 100 |
| >1.48 | 2 | |
| NO3-N | 0–23 | e(−0.16 × (NO3-N concentration)) × 100 |
| >23 | 2 | |
| NH3-N | 0.0–0.22 | 100 − 131.82 × (NH3 concentration) |
| 0.23–0.50 | 78.857 − 35.714 × (NH3 concentration) | |
| 0.51–1.83 | 72.278 − 22.556 × (NH3 concentration) | |
| >1.83 | 42.167 − 6.1024 × (NH3 concentration) | |
| SS | 0–4 | 100 |
| 4.1–75 | 0.0043 × (SS concentration)2 − 1.1687 × (SS concentration) + 105.03 | |
| 75.1–230 | 0.0007 × (SS concentration)2 − 0.4647 × (SS concentration) + 72.208 | |
| ≥230 | 2 |
References
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, R.; Hu, M.; Luo, J.; Li, J.; Liang, Q. Combining citizen science and land use data to identify drivers of eutrophication in the Huangpu River system. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 651–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, A.; Singh, A.; Mahato, M. Assessment of groundwater quality of Pratapgarh district in India for suitability of drinking purpose using water quality index (WQI) and GIS technique. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 4, 601–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Han, G.; Liu, M.; Yang, K.; Li, X.; Liu, J. Distribution, Sources, and Water Quality Assessment of Dissolved Heavy Metals in the Jiulongjiang River Water, Southeast China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, B.; Han, G.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Song, C.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, K. Spatial and Temporal Variation of Dissolved Heavy Metals in the Mun River, Northeast Thailand. Water 2019, 11, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Mazumder, M.; Al-Attas, O.; Husain, T. Heavy metals in drinking water: Occurrences, implications, and future needs in developing countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Gu, B.; Lin, Q.; Gu, J.; Han, B. Stable isotope composition of suspended particulate organic matter in twenty reservoirs from Guangdong, southern China: Implications for pelagic carbon and nitrogen cycling. Water Res. 2013, 47, 3610–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, A.; Babel, M. Hydrological modeling of the Mun River basin in Thailand. J. Hydrol. 2012, 452–453, 232–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A. Factors affecting the export of nitrate-nitrogen from drainage basins in southern Ontario. Water Res. 1978, 12, 1045–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correll, D.; Jordan, T.; Weller, D. Transport of nitrogen and phosphorus from Rhode River Watersheds during storm events. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 2513–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraco, N.; Col, J. Human impact on nitrate export: An analysis using major world rivers. Ambio 1999, 28, 167–170. [Google Scholar]
- Bledsoe, B.; Watson, C. Effects of urbanization on channel instability. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2001, 37, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, C.; Xu, C.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, T. Observed trends of annual maximum water level and streamflow during past 130 years in the Yangtze River basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2006, 324, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundzewicz, Z.; Robson, A. Change detection in hydrological records—A review of the methodology. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2004, 49, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libiseller, C.; Grimvall, A. Performance of partial Mann–Kendall test for trend detection in the presence of covariants. Environmetrics 2002, 13, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H. Spatial analysis of water quality trends in the Han River basin, South Korea. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3285–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouza-Deaño, R.; Ternero-Rodríguez, M.; Fernández-Espinosa, A. Trend study and assessment of surface water quality in the Ebro River (Spain). J. Hydrol. 2008, 361, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Bhang, K.; Park, S. Effective visualization for the spatiotemporal trend analysis of the water quality in the Nakdong River of Korea. Ecol. Inform. 2010, 5, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, T.; Srivastava, R. Application of water quality index for assessment of surface water quality surrounding integrated industrial estate-Pantnagar. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 2041–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, X.; Shao, D.; Xiao, Y.; Zhong, H. Spatio-Temporal Characterization Analysis and Water Quality Assessment of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project of China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Malik, A.; Sinha, S. Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources of Gomti river (India) using multivariate statistical techniques—A case study. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 538, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Y. Eutrophication prediction using a markov chain model: Application to lakes in the Yangtze River basin, China. Environ. Model. Assess. 2016, 21, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, N.; Wang, J. Water quality management of a cold climate region watershed in changing climate. J. Environ. Inform. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Schmalz, B.; Fohrer, N. Development and testing of a phytoplankton index of biotic integrity (P-IBI) for a German lowland river. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 13, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, F.; Moreira, A.; Bisinoti, M.; Gimenez, S.; Yabe, M. Water quality index as a simple indicator of aquaculture effects on aquatic bodies. Ecol. Indic. 2008, 8, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Dua, A. Water quality index for assessment of water quality of river Ravi at Madhopur (India). Glob. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 8, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srebotnjak, T.; Carr, G.; Sherbinin, A.; Rickwood, C. A global water quality Index and hot-deck imputation of missing data. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 17, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumb, A.; Sharma, T.; Bibeault, J. A review of genesis and evolution of water quality index (WQI) and some future directions. Water Qual. Expo. Health 2011, 3, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, S.; Sharma, B.; Singh, P.; Dobhal, R. Water quality assessment in terms of water quality index. Am. J. Water Resour. 2013, 1, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, W.; Sun, S.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, N.; Xin, X.; Sun, L.; Li, W.; Jia, R. Assessing water quality of five typical reservoirs in lower reaches of Yellow River, China: Using a water quality index method. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 61, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Cai, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y. Water quality assessment based on the water quality index method in Lake Poyang: The largest freshwater lake in China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AEP. Alberta River Water Quality Index Results (2015–2016); Alberta Environment and Parks (AEP): Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kachroud, M.; Trolard, F.; Kefi, M.; Jebari, S.; Bourrié, G. Water Quality Indices: Challenges and Application Limits in the Literature. Water 2019, 11, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.; Gawande, S. Review paper on development of water quality index. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2016, 5, 765–767. [Google Scholar]
- Massoud, M. Assessment of water quality along a recreational section of the Damour River in Lebanon using the water quality index. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 184, 4151–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, M.; Xing, X. A dynamic water quality index model based on functional data analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 57, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alobaidy, A.; Abid, H.; Maulood, B. Application of water quality index for assessment of Dokan lake ecosystem, Kurdistan region, Iraq. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2010, 2, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbal, F.; Gürel, L.; Bahadır, T.; Güler, İ.; Bakan, G.; Büyükgüngör, H. Multivariate statistical techniques for the assessment of surface water quality at the mid-black sea coast of Turkey. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 216, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goher, M.; Hassan, A.; Abdel-Moniem, I.; Fahmy, A.; El-sayed, S. Evaluation of surface water quality and heavy metal indices of Ismailia Canal, Nile River, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2014, 40, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lobato, T.; Hauser-Davis, R.; Oliveira, T.; Silveira, A.; Silva, H.; Tavares, M.; Saraiva, A. Construction of a novel water quality index and quality indicator for reservoir water quality evaluation: A case study in the Amazon region. J. Hydrol. 2015, 522, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangabam, R.D.; Govindaraju, M. Anthropogenic activity-induced water quality degradation in the Loktak lake, a Ramsar site in the Indo-Burma biodiversity hotspot. Environ. Technol. 2019, 40, 2232–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, O.; Tanji, H.; Somura, H.; Higuchi, K.; Yoshida, K. Evaluation of tributaries contribution in the Mekong River Basins during rainy and dry season. In Proceedings of the 2nd Asia Pacific Association of Hydrology and Water Resources Conference, Singapore, 5–8 July 2004; pp. 239–248. [Google Scholar]
- Hydro and Agro Informatics Institute (HAII), Ministry of Science and Technology 2012 Data Collection and Analysis under the Project on Developing 25 Basins Data Archive and Water Extreme Simulations: The Mun River Basin, 74 pp. Available online: http://www.thaiwater.net/web/attachments/25basins/05-moon.pdf (accessed on 9 December 2018). (In Thai).
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, G.; Liu, Q.; Huang, C.; Li, H. Studies on the Spatiotemporal Variability of River Water Quality and its Relationships with Soil and Precipitation: A Case Study of the Mun River Basin in Thailand. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, G.; Liu, Q.; Huang, C.; Li, H.; Wu, C. Distribution Characteristics and Seasonal Variation of Soil Nutrients in the Mun River Basin, Thailand. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosa, P.; Kulworawanichpong, T.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Chinkulkijiwat, A.; Srivoramas, R.; Teaumroong, N. Potential micro-hydropower assessment in Mun River Basin, Thailand. In Proceedings of the 2011 Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference (APPEEC), Wuhan, China, 25–28 March 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch, R.; Slack, J. A nonparametric trend test for seasonal data with serial dependence. Water Resour. Res. 1984, 20, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, R.; Slack, J.; Smith, R. Techniques of trend analysis for monthly water quality data. Water Resour. Res. 1982, 18, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, G.; Tang, Z.; Xiao, X. Trend analysis of water quality of Sanmenxia Reservoir of the Yellow River. Geogr. Geo Inf. Sci. 2004, 5, 86–88. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, X.; Xia, J.; Zhang, Y. Water quality variation in the highly disturbed Huai River Basin, China from 1994 to 2005 by multi-statistical analyses. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 496, 594–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollution Control Department, Water Quality Management Bureau. General Water Quality Index; Pollution Control Department, Water Quality Management Bureau: Bangkok, Thailand, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Pollution Control Department (PCD). Combination Score of Water Quality from 5 Parameter (New WQI Calculation Method). Available online: Iwis.pcd.go.th/module/wqi_calculate (accessed on 20 February 2019). (In Thai).
- Singkran, N. Determining overall water quality related to anthropogenic influences across freshwater systems of Thailand. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2017, 33, 132–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singkran, N.; Yenpiem, A.; Sasitorn, P. Determining water conditions in the Northeastern rivers of Thailand using time series and water quality index models. J. Sustain. Energy Environ. 2010, 1, 47–58. [Google Scholar]
- Dojlido, J.; Raniszewski, J.; Woyciechowska, J. Water quality index applied to rivers in the Vistula river basin in Poland. Environ. Monit. Assess. 1994, 33, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Environment Board. Notification No. 8: Surface water quality standard. The 1992 Thailand enhancement and conservation of national environmental quality act. R. Thai Gov. Gaz. 1994, 111, 73–81. (In Thai) [Google Scholar]
- Cai, H.; He, Z.; An, Y.; Zhang, C.; Deng, H. Response relationship between land use and water quality in Chishui River Basin based on RS and GIS. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2015, 24, 286–291. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, R.; Amin, M.G.M.; Zhai, L.; Lu, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Water quality in irrigated paddy systems. In Irrigation in Agroecosystem; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 105–121. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Lin, Q.; Yan, M.; Kong, Q. Studies on N, P and K absorption characteristics of rice root system and its simulation model. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2011, 42, 117–122. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xia, B.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, Y.; Huang, M.; Ao, H.; Zou, Y. Characteristics of grain yield and nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium uptake and accumulation of super hybrid rice grown in different locations. J. Zhejiang Univ. (Agric. Life Sci.) 2015, 41, 547–557. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Ma, K.; Guo, Q.; Zhao, J. Impacts of the urbanization on waters non-point source pollution. Environ. Sci. 2004, 25, 32–39. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA), Historical El Niño and La Niña Events. Available online: http://ds.data.jma.go.jp/tcc/tcc/products/elnino/ensoevents.html (accessed on 20 February 2019).
- Marine Department, Water Quality Report for the Chi River from Vachasart Bridge to Ban Wang Yao in May 24. 2016. Available online: www.md.go.th/md/index.php/2014-01-19-05-02-28/2016-07-25-03-15-33/2016-11-23-07-42-29/-131/-2559-4/-14-2559/11-4 (accessed on 20 February 2019). (In Thai)
- Vanni, M.; Renwick, W.; Headworth, J.; Auch, J.; Schaus, M. Dissolved and particulate nutrient flux from three adjacent agricultural watersheds: A five-year study. Biogeochemistry 2001, 54, 85–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Location | Monitoring Sites | DO | BOD | TCB | FCB | TP | NO3-N | NH3-N | SS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper reaches | MU17 | NS | NS | ↓ * | ↓ ** | NS | NS | ↓ * | NS |
| MU14 | NS | NS | NS | ↓ ** | NS | NS | ↓ ** | ↓ ** | |
| MU12 | NS | NS | NS | ↓ ** | NS | NS | NS | NS | |
| MU09 | NS | NS | ↓ * | ↓ ** | NS | NS | ↓ * | ↓ ** | |
| Lower reaches | MU08 | ↓ ** | NS | ↑ ** | NS | NS | ↑ ** | ↑ ** | ↓ ** |
| MU06 | ↓ ** | NS | NS | ↓ ** | NS | ↑ ** | ↑ ** | ↓ * | |
| MU03 | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | ↑ ** | NS | NS | |
| MU01 | NS | NS | ↑ ** | ↑ * | NS | ↑ ** | ↑ ** | NS |
| Location | Statistical Parameters | TP (mg/L) | NO3-N (mg/L) | NO2-N (mg/L) | NH3-N (mg/L) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NF | F | NF | F | NF | F | NF | F | ||
| Upstream MU09 | Min | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Median | 0.13 | 0.24 | 0.11 | 0.20 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 | |
| Mean | 0.23 | 0.46 | 0.25 | 0.60 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.16 | 0.11 | |
| Max | 3.40 | 12.80 | 5.00 | 10.28 | 2.11 | 1.25 | 8.73 | 1.28 | |
| cv | 1.47 | 2.44 | 1.70 | 1.94 | 3.09 | 2.18 | 4.12 | 1.80 | |
| cs | 5.05 | 9.74 | 5.24 | 5.08 | 8.78 | 7.29 | 9.47 | 3.09 | |
| Downstream MU08 | Min | 0 | 0.01 | 0 | 0.06 | 0 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.03 |
| Median | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.26 | 0.31 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.21 | 0.34 | |
| Mean | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.48 | 0.55 | 0.15 | 0.28 | 0.34 | 0.43 | |
| Max | 6.82 | 0.35 | 2.68 | 2.37 | 15.40 | 3.45 | 2.60 | 1.51 | |
| cv | 4.28 | 0.53 | 1.10 | 0.94 | 6.24 | 2.70 | 1.04 | 0.73 | |
| cs | 16.14 | 0.70 | 1.72 | 1.58 | 14.44 | 3.06 | 1.91 | 0.98 | |
| Location | Parameters | February | May | August | November | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper reaches | DO | 4.53 | 5.49 | 2.75 | 10.99 | 23.76 |
| BOD | 6.59 | 6.46 | 3.30 | 6.59 | 22.94 | |
| TCB | 0.69 | 0.14 | 0.27 | 0.69 | 1.79 | |
| FCB | 1.24 | 0.41 | 0.14 | 0.55 | 2.34 | |
| TP | 9.48 | 5.22 | 9.20 | 6.73 | 30.63 | |
| NO3-N | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.82 | 0.14 | 0.96 | |
| NH3-N | 1.37 | 0.41 | 0.00 | 0.82 | 2.61 | |
| SS | 3.98 | 3.16 | 4.67 | 3.16 | 14.97 | |
| Lower reaches | DO | 2.12 | 5.19 | 3.65 | 4.23 | 15.19 |
| BOD | 5.77 | 5.00 | 2.88 | 6.35 | 20.00 | |
| TCB | 2.88 | 1.15 | 0.96 | 1.54 | 6.54 | |
| FCB | 3.85 | 2.50 | 0.77 | 2.69 | 9.81 | |
| TP | 0.19 | 1.92 | 2.50 | 1.92 | 6.54 | |
| NO3-N | 0.38 | 0.19 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.58 | |
| NH3-N | 11.15 | 4.81 | 5.38 | 9.81 | 31.15 | |
| SS | 1.15 | 0.96 | 5.58 | 2.50 | 10.19 |
| Study Scale | Land Types | Period | DO | BOD | TCB | FCB | TP | NO3-N | NH3-N | SS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 km | A1 | F | 0.03 | 0.30 | −0.31 | −0.45 | 0.62 ** | −0.59 ** | −0.73 ** | −0.15 |
| NF | −0.22 | 0.14 | −0.40 | −0.51 * | 0.56 * | −0.59 * | −0.56 * | 0.36 | ||
| A2 | F | −0.29 | 0.07 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.28 | −0.10 | −0.23 | 0.19 | |
| NF | −0.21 | 0.21 | −0.18 | −0.02 | 0.39 | −0.32 | −0.19 | 0.23 | ||
| A3 | F | −0.05 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 0.26 | 0.29 | −0.33 | −0.30 | 0.28 | |
| NF | −0.08 | 0.00 | −0.26 | 0.00 | 0.34 | −0.26 | −0.35 | 0.16 | ||
| F | F | 0.48 * | −0.24 | 0.09 | −0.09 | −0.72 ** | 0.27 | 0.50 * | 0.29 | |
| NF | 0.69 ** | −0.58 * | 0.11 | 0.24 | −0.43 | 0.21 | 0.48 * | −0.48 * | ||
| U | F | −0.46 | 0.29 | 0.29 | 0.41 | −0.05 | 0.40 | 0.14 | −0.21 | |
| NF | −0.38 | 0.51 * | 0.59 ** | 0.48 * | −0.22 | 0.33 | 0.04 | −0.03 | ||
| W | F | 0.16 | 0.07 | −0.11 | 0.08 | −0.37 | 0.22 | 0.48 * | 0.05 | |
| NF | 0.02 | −0.07 | 0.04 | 0.21 | −0.51 * | 0.46 | 0.45 | −0.43 | ||
| M | F | 0.25 | −0.70 ** | 0.20 | 0.20 | −0.31 | 0.44 | 0.49 * | −0.25 | |
| NF | 0.17 | −0.16 | 0.15 | 0.06 | −0.53 * | 0.65 ** | 0.58 * | −0.23 | ||
| 2 km | A1 | F | 0.27 | 0.18 | −0.14 | −0.24 | 0.69 ** | −0.63 ** | −0.79 ** | −0.14 |
| NF | 0.03 | 0.05 | −0.28 | −0.47 | 0.67 ** | −0.70 ** | −0.54 * | 0.32 | ||
| A2 | F | −0.19 | 0.23 | −0.22 | −0.10 | 0.00 | −0.14 | −0.09 | 0.50 * | |
| NF | −0.32 | 0.15 | 0.05 | −0.07 | 0.44 | −0.18 | −0.20 | 0.38 | ||
| A3 | F | −0.07 | 0.25 | −0.17 | −0.02 | 0.44 | −0.61 ** | −0.53 * | 0.20 | |
| NF | −0.17 | 0.11 | −0.22 | −0.15 | 0.36 | −0.31 | −0.38 | 0.39 | ||
| F | F | 0.38 | −0.34 | −0.05 | −0.14 | −0.62 ** | 0.24 | 0.35 | 0.13 | |
| NF | 0.49 | −0.55 | −0.23 | 0.12 | −0.45 | 0.20 | 0.36 | −0.47 | ||
| U | F | −0.16 | −0.02 | 0.49 * | 0.27 | −0.25 | 0.63 ** | 0.37 | −0.24 | |
| NF | −0.13 | 0.40 | 0.59 ** | 0.55 * | −0.42 | 0.55 * | 0.24 | −0.19 | ||
| W | F | −0.03 | 0.35 | −0.26 | 0.08 | −0.26 | 0.01 | 0.24 | 0.09 | |
| NF | −0.05 | 0.05 | −0.01 | 0.22 | −0.24 | 0.14 | 0.13 | −0.35 | ||
| M | F | −0.14 | −0.46 | 0.10 | 0.28 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.08 | −0.31 | |
| NF | −0.18 | 0.12 | 0.13 | −0.08 | −0.14 | 0.34 | 0.20 | 0.17 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, H.; Yu, G.-A.; Tong, L.; Li, R.; Huang, H.Q.; Bridhikitti, A.; Prabamroong, T. Water Quality of the Mun River in Thailand—Spatiotemporal Variations and Potential Causes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3906. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16203906
Tian H, Yu G-A, Tong L, Li R, Huang HQ, Bridhikitti A, Prabamroong T. Water Quality of the Mun River in Thailand—Spatiotemporal Variations and Potential Causes. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(20):3906. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16203906
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Haoyu, Guo-An Yu, Ling Tong, Renzhi Li, He Qing Huang, Arika Bridhikitti, and Thayukorn Prabamroong. 2019. "Water Quality of the Mun River in Thailand—Spatiotemporal Variations and Potential Causes" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 20: 3906. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16203906





