Measuring the Environmental Efficiency and Technology Gap of PM2.5 in China’s Ten City Groups: An Empirical Analysis Using the EBM Meta-Frontier Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Model
- (1)
- .
- (2)
- if and , then .
- (3)
- if , then for , .
- (4)
- if , then for , .
- (5)
- if , then .
Measure of the Group Technology Gap
4. Data
4.1. City Group Classification
4.2. Data Sources
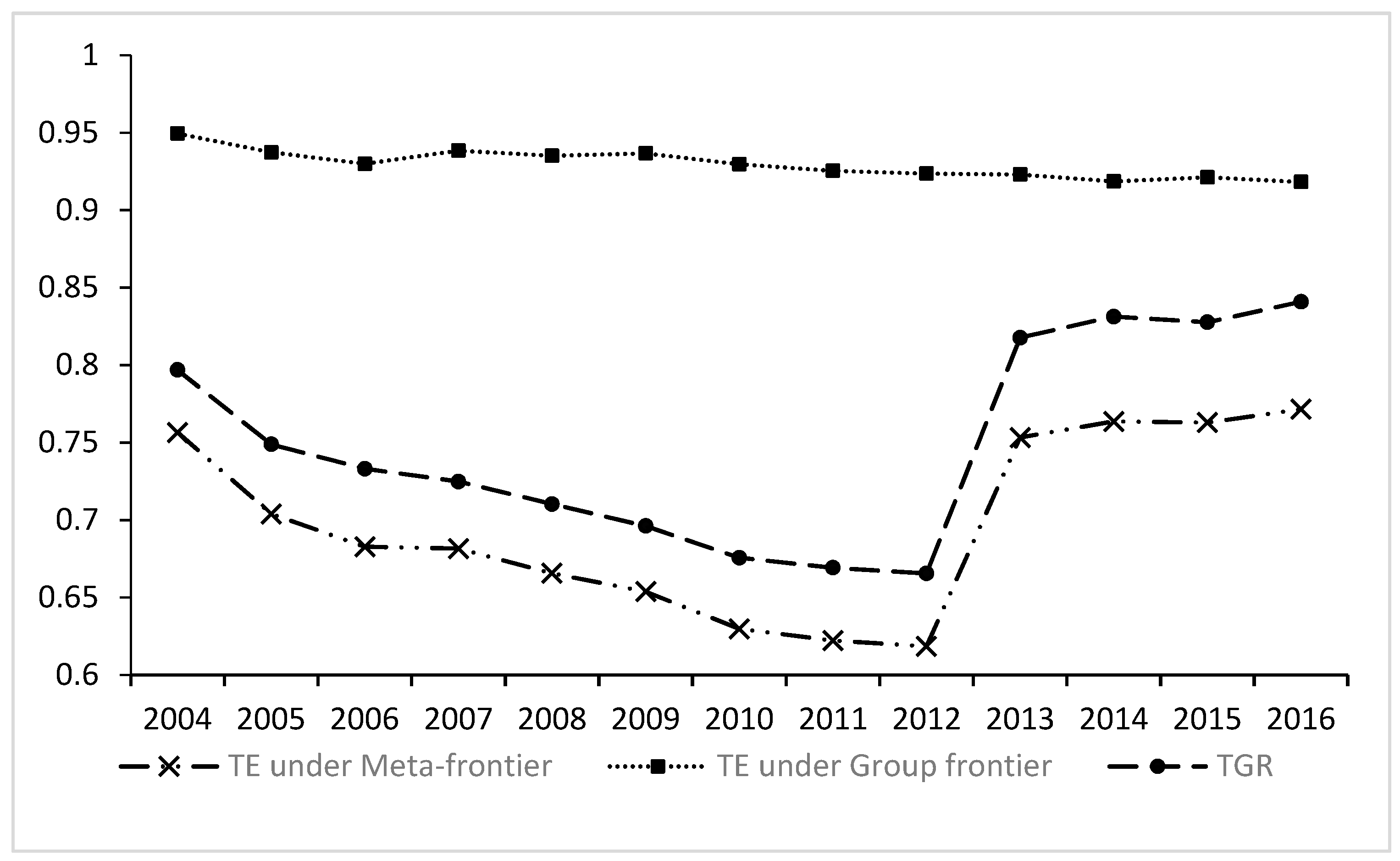
5. Results and Discussions
5.1. Environmental Efficiency of the EBM Model
5.2. PM2.5 Environmental Efficiency
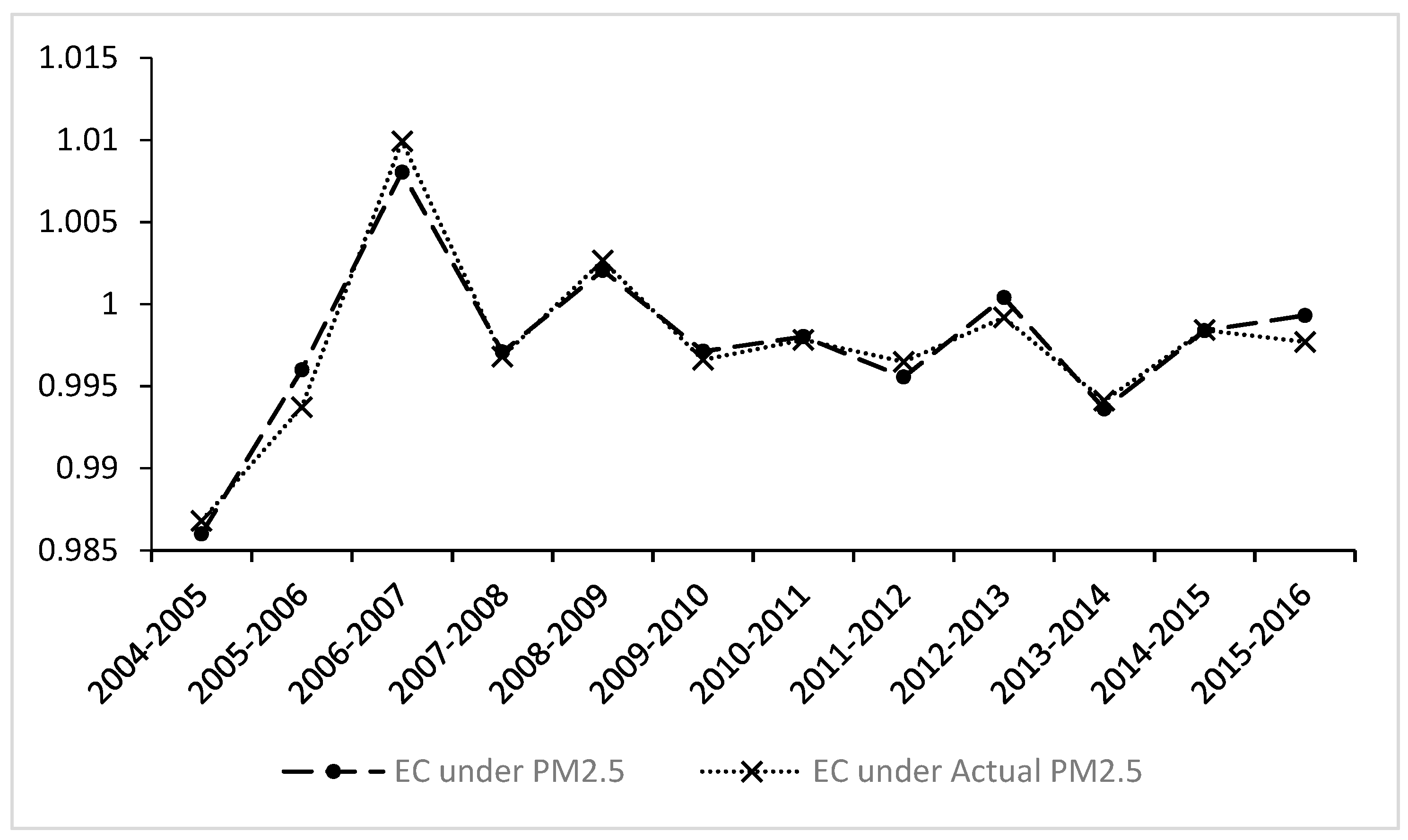
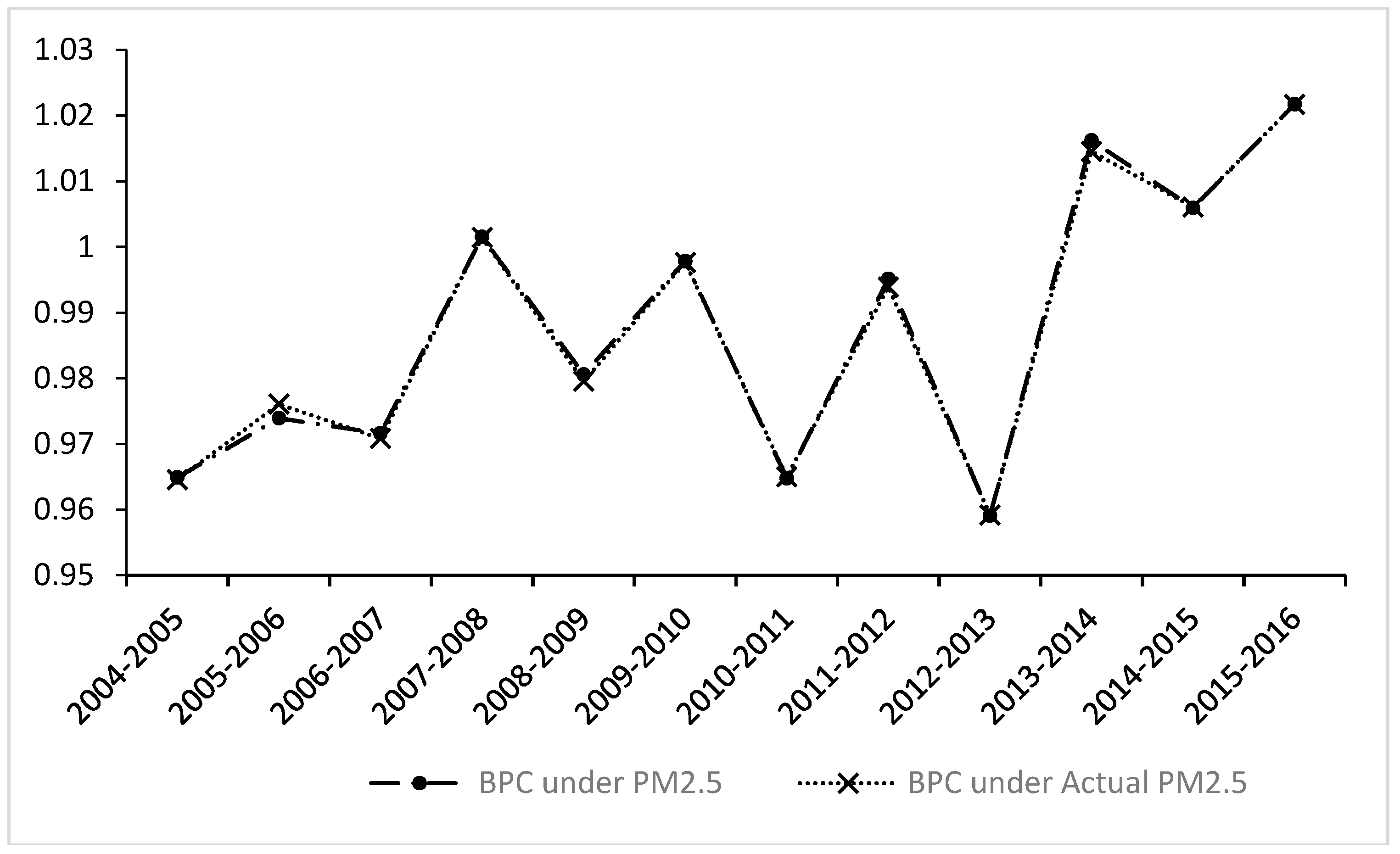
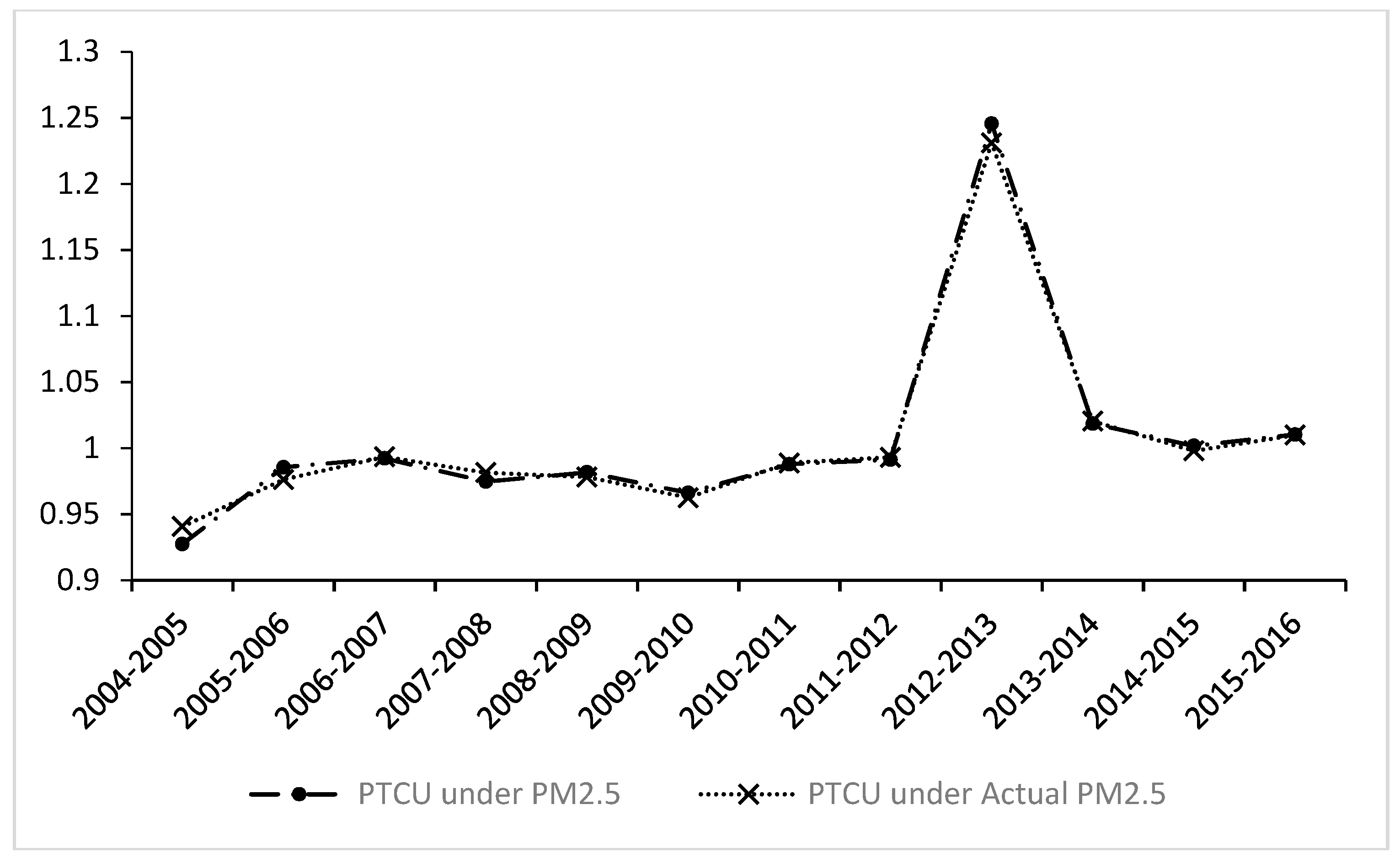
5.3. Analysis of the Meta-Frontier Malmquist Productivity Index
5.4. Analysis of the Driving Factors of Meta-Frontier Malmquist Productivity Index
5.5. Further Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, D.; Bai, K.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, R.; Ren, H. Estimating Ground-Level Concentrations of Multiple Air Pollutants and Their Health Impacts in the Huaihe River Basin in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ebenstein, A.; Greenstone, M.; Li, H. Evidence on the impact of sustained exposure to air pollution on life expectancy from China’s Huai River policy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12936–12941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Chen, S. Particulate air pollution and real estate valuation: Evidence from 286 Chinese prefecture-level cities over 2004–2013. Energy Policy 2017, 109, 884–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, B.; Chen, Z. Carbon emissions reductions and technology gaps in the world’s factory, 1990–2012. Energy Policy 2016, 91, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Cao, J.; Managi, S. Decomposition of Productivity Considering Multi-environmental Pollutants in Chinese Industrial Sector. Rev. Dev. Econ. 2015, 19, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Li, T.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L. The Relationships between PM2.5 and Meteorological Factors in China: Seasonal and Regional Variations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Ang, B.W.; Poh, K.L. A survey of data envelopment analysis in energy and environmental studies. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2008, 189, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueyoshi, T.; Yuan, Y.; Goto, M. A literature study for DEA applied to energy and environment. Energy Econ. 2017, 62, 104–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.H.; Färe, R.; Grosskopf, S. Productivity and Undesirable Outputs: A Directional Distance Function Approach. J. Environ. Manag. 1997, 51, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Choi, Y. A note on the evolution of directional distance function and its development in energy and environmental studies 1997–2013. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 33, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, R.G.; Chung, Y.; Färe, R. Profit, Directional Distance Functions, and Nerlovian Efficiency. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 1998, 98, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Zhou, X.; Fan, L.W. On estimating shadow prices of undesirable outputs with efficiency models: A literature review. Appl. Energy 2014, 130, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Tanaka, K. Efficiency analysis of Chinese industry: A directional distance function approach. Energy Policy 2007, 35, 6323–6331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Cheng, S.; Sun, J.; Liang, W. Measuring the environmental efficiency of the Chinese industrial sector: A directional distance function approach. Math. Comput. Model. 2013, 58, 936–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wei, Y.-M.; Zhang, X. Energy and emissions efficiency patterns of Chinese regions: A multi-directional efficiency analysis. Appl. Energy 2013, 104, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Zhang, Q.; Lei, J.; Fu, W.; Xu, X. Energy efficiency and productivity change of China’s iron and steel industry: Accounting for undesirable outputs. Energy Policy 2013, 54, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Choi, Y. Total-factor carbon emission performance of fossil fuel power plants in China: A metafrontier non-radial Malmquist index analysis. Energy Econ. 2013, 40, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.W.; Rhodes, E. Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1978, 2, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banker, R.D.; Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.W. Some Models for Estimating Technical and Scale Inefficiencies in Data Envelopment Analysis. Manag. Sci. 1984, 30, 1078–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueyoshi, T.; Goto, M. Returns to scale and damages to scale on U.S. fossil fuel power plants: Radial and non-radial approaches for DEA environmental assessment. Energy Econ. 2012, 34, 2240–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 130, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of super-efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 143, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Liang, D.; Xing, X. Environmental efficiency of industrial sectors in China: An improved weighted SBM model. Math. Comput. Model. 2013, 58, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Fang, K.; Yang, W.; Wang, D.; Hong, X. Regional environmental efficiency evaluation in China: Analysis based on the Super-SBM model with undesirable outputs. Math. Comput. Model. 2013, 58, 1018–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Choi, Y. Environmental energy efficiency of China’s regional economies: A non-oriented slacks-based measure analysis. Soc. Sci. J. 2013, 50, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Kong, F.; Kung, C.-C. On Modeling Environmental Production Characteristics: A Slacks-Based Measure for China’s Poyang Lake Ecological Economics Zone. Comput. Econ. 2015, 46, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Li, L.; Song, Y. Provincial water use efficiency measurement and factor analysis in China: Based on SBM-DEA model. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 69, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K.; Tsutsui, M. An epsilon-based measure of efficiency in DEA – A third pole of technical efficiency. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 207, 1554–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Zhen, W.; Wei, Y.-M. Air emissions perspective on energy efficiency: An empirical analysis of China’s coastal areas. Appl. Energy 2017, 185, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Li, Y. Airline efficiency measures using a Dynamic Epsilon-Based Measure model. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2017, 100, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Cui, Q. Evaluating airline energy efficiency: An integrated approach with Network Epsilon-based Measure and Network Slacks-based Measure. Energy 2017, 122, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caves, D.W.; Christensen, L.R.; Diewert, W.E. Multilateral Comparisons of Output, Input, and Productivity Using Superlative Index Numbers. Econ. J. 1982, 92, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fare, R.; Grosskopf, S.; Norris, M.; Zhongyang, Z. Productivity growth, technical progress, and efficiency change in industrialized countries. Am. Econ. Rev. 1994, 84, 66–83. [Google Scholar]
- Färe, R.; Grosskopf, S.; Lovell, C.A.K.; Yaisawarng, S. Derivation of Shadow Prices for Undesirable Outputs: A Distance Function Approach. Rev. Econ. Stat. 1993, 75, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.-H. A metafrontier approach for measuring an environmentally sensitive productivity growth index. Energy Econ. 2010, 32, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.-H.; Lee, J.-D. A metafrontier approach for measuring Malmquist productivity index. Empir. Econ. 2010, 38, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.-H.; Yang, H.-Y. A cross-country comparison of productivity growth using the generalised metafrontier Malmquist productivity index: With application to banking industries in Taiwan and China. J. Prod. Anal. 2011, 35, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munisamy, S.; Arabi, B. Eco-efficiency change in power plants: Using a slacks-based measure for the meta-frontier Malmquist–Luenberger productivity index. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 105, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Guo, C.; Shao, S.; Jiang, Z. Total-factor CO2 emission performance of China’s provincial industrial sector: A meta-frontier non-radial Malmquist index approach. Appl. Energy 2016, 184, 1142–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, G.-C. Decomposition of energy efficiency and energy-saving potential in China: A three-hierarchy meta-frontier approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 176, 1054–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Wu, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J. Environmental efficiency for 192 thermal power plants in the Yangtze River Delta considering heterogeneity: A metafrontier directional slacks-based measure approach. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 3962–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zhang, A.; Huang, H.; Yao, X. Measuring unified efficiency of fossil fuel power plants across provinces in China: An analysis based on non-radial directional distance functions. Energy 2018, 152, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Chen, J.; Yao, S.; Chang, Y.-C. A meta-frontier DEA approach to efficiency comparison of carbon reduction technologies on project level. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 2606–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, R.; Lin, B. Technology gap and CO2 emission reduction potential by technical efficiency measures: A meta-frontier modeling for the Chinese agricultural sector. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 73, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Huang, J.-B.; Wang, M. Analysis of green total-factor productivity in China’s regional metal industry: A meta-frontier approach. Resourc. Policy 2018, 58, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Lin, B. Regional technology gap in energy utilization in China’s light industry sector: Non-parametric meta-frontier and sequential DEA methods. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 178, 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueyoshi, T.; Yuan, Y. China’s regional sustainability and diversified resource allocation: DEA environmental assessment on economic development and air pollution. Energy Econ. 2015, 49, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Luo, L.; Lin, B. A dynamic analysis of air pollution emissions in China: Evidence from nonparametric additive regression models. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 63, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Gu, J.; Wang, H.; Yao, T.; Wu, Z. Uncovering the culprits of air pollution: Evidence from China’s economic sectors and regional heterogeneities. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 1481–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Guo, X.; Wu, H.; Yu, J. Evaluating air quality in China based on daily data: Application of integer data envelopment analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 198, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Färe, R.; Grosskopf, S.; Noh, D.-W.; Weber, W. Characteristics of a polluting technology: Theory and practice. J. Econom. 2005, 126, 469–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, C.J.; Rao, D.S.P.; Battese, G.E. Metafrontier frameworks for the study of firm-level efficiencies and technology ratios. Empir. Econ. 2008, 34, 231–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, J.T.; Lovell, C.A.K. A global Malmquist productivity index. Econ. Lett. 2005, 88, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yu, Y.; Yu, J.; Chen, J.; Niu, Z.; Yin, L.; Zhang, F.; Liao, X.; Chen, Y. Spatial distribution and sources identification of elements in PM2.5 among the coastal city group in the Western Taiwan Strait region, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 442, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Jin, M.; Li, H. Exploring Spatial Influence of Remotely Sensed PM2.5 Concentration Using a Developed Deep Convolutional Neural Network Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD. Measuring Capital—OECD Manual; OECD: Paris, France, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Measuring Productivity—OECD Manual; OECD: Paris, France, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Coe, D.T.; Helpman, E. International R&D spillovers. Eur. Econ. Rev. 1995, 39, 859–887. [Google Scholar]
- Coe, D.T.; Helpman, E.; Hoffmaister, A.W. International R&D spillovers and institutions. Eur. Econ. Rev. 2009, 53, 723–741. [Google Scholar]
- Pui, D.Y.H.; Chen, S.-C.; Zuo, Z. PM2.5 in China: Measurements, sources, visibility and health effects, and mitigation. Particuology 2014, 13, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Hu, X.; Sayer, A.M.; Levy, R.; Zhang, Q.; Xue, Y.; Tong, S.; Bi, J.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y. Satellite-Based Spatiotemporal Trends in PM(2.5) Concentrations: China, 2004–2013. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Meng, X.; Yu, X.; Lei, M.; Li, W.; Shi, F.; Yang, W.; Zhang, S.; Xie, S. Characteristics of trace elements in PM2.5 and PM10 of Chifeng, northeast China: Insights into spatiotemporal variations and sources. Atmos. Res. 2018, 213, 550–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.B.; Fu, F.; Wang, J.N.; Tang, G.Q.; Lei, Y.; Yang, J.T.; Wang, Y.S. Numerical study on the characteristics of regional transport of PM2.5 in China. China Environ. Sci. 2014, 34, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, A.; Li, A. Regional energy efficiency, carbon emission performance and technology gaps in China: A meta-frontier non-radial directional distance function analysis. Energy Policy 2015, 84, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| City Group | Group ID | Cities Included in the City Group |
|---|---|---|
| Yangtze River Delta | 1 | Zhenjiang, Taizhou (in Jiangsu), Hangzhou, Huzhou, Shaoxing, Suzhou, Hefei, Taizhou (in Zhejiang), Changzhou, Nantong, Wuxi, Jiaxing, Yangzhou, Yancheng, Shanghai Jinhua, Nanjing, Zhoushan, Ningbo |
| Pearl River Delta | 2 | Zhaoqing, Jiangmen, Shenzhen Huizhou, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Zhuhai, Foshan |
| Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei | 3 | Cangzhou, Handan, Beijing, Langfang, Tianjin, Shijiazhuang, Zhangjiakou, Xingtai, Tangshan, Chengde, Hengshui, Baoding, Qinhuangdao |
| Central and southern Liaoning | 4 | Benxi, Tieling, Shenyang, Liaoyang, Panjin, Dandong, Dalian Fushun, Anshan, Yingkou |
| Shandong Peninsula | 5 | Weihai, Jinan, Dongying, Qingdao Zibo, Rizhao, Weifang, Yantai |
| Cheng Yu | 6 | Chengdu, Deyang, Chongqing, Mianyang, Neijiang, Zigong, bSuining, Luzhou |
| West coast of the Taiwan Strait | 7 | Zhangzhou, Ningde, Putian, Xiamen, Quanzhou, Fuzhou |
| Central Henan | 8 | Pingdingshan, Xinxiang, Jiaozuo, Luohe, Zhengzhou, Xuchang, Kaifeng, Luoyang |
| Middle reaches of the Yangtze River | 9 | Ezhou, Suizhou, Yueyang, Jingmen, Huanggang, Jingzhou, Huangshi, Xianning, Wuhan, Xinyang, Jiujiang, Xiaogan |
| Guanzhong | 10 | Weinan, Shangluo, Xianyang, Tongchuan, Baoji, Xi’an |
| Province | Contribution | Province | Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 37 | Hubei | 42 |
| Tianjin | 42 | Hunan | 39 |
| Hebei | 36 | Guangdong | 35 |
| Shanxi | 31 | Guangxi | 46 |
| Inner Mongolia | 22 | Hainan | 71 |
| Liaoning | 33 | Chongqing | 31 |
| Jilin | 48 | Sichuan | 28 |
| Heilongjiang | 20 | Guizhou | 37 |
| Shanghai | 54 | Yunnan | 36 |
| Jiangsu | 50 | Tibet | 1 |
| Zhejiang | 48 | Shaanxi | 31 |
| Anhui | 42 | Gansu | 33 |
| Fujian | 41 | Qinghai | 13 |
| Jiangxi | 48 | Ningxia | 35 |
| Shandong | 41 | Xinjiang | 0 |
| Henan | 37 | National Mean | 36 |
| Variable | Unit | Obs | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRP | Billion yuan | 1287 | 2254.01 | 2782.91 | 58.90 | 23,423.39 |
| Capital stock | Billion yuan | 1287 | 741,092.30 | 896,380.40 | 6078.33 | 6,892,826.00 |
| Labour | 10 thousand persons | 1287 | 83.58 | 112.85 | 9.07 | 986.87 |
| PM2.5 Concentration | μg/m3 | 1287 | 68.89 | 21.39 | 23.14 | 125.33 |
| Actual PM2.5 Concentration | μg/m3 | 1287 | 42.24 | 14.17 | 12.83 | 80.22 |
| DMU | PM2.5 | Rank | Actual PM2.5 | Rank | DMU | PM2.5 | Rank | Actual PM2.5 | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anshan | 0.625 | 18 | 0.624 | 21 | Qinhuangdao | 0.498 | 53 | 0.498 | 55 |
| Baoji | 0.435 | 80 | 0.434 | 82 | Qingdao | 0.712 | 13 | 0.727 | 13 |
| Baoding | 0.371 | 95 | 0.372 | 95 | Quanzhou | 0.872 | 5 | 0.889 | 5 |
| Beijing | 0.685 | 14 | 0.670 | 15 | Rizhao | 0.533 | 40 | 0.534 | 42 |
| Benxi | 0.435 | 81 | 0.435 | 81 | Shangluo | 0.402 | 88 | 0.401 | 90 |
| Cangzhou | 0.657 | 15 | 0.658 | 16 | Shanghai | 0.964 | 3 | 1.000 | 1 |
| Changzhou | 0.553 | 34 | 0.589 | 26 | Shaoxing | 0.463 | 72 | 0.497 | 57 |
| Chengdu | 0.486 | 62 | 0.467 | 72 | Shenzhen | 0.991 | 1 | 0.984 | 2 |
| Chengde | 0.469 | 68 | 0.470 | 70 | Shenyang | 0.570 | 29 | 0.562 | 34 |
| Dalian | 0.747 | 10 | 0.730 | 12 | Shijiazhuang | 0.489 | 60 | 0.490 | 62 |
| Dandong | 0.492 | 56 | 0.492 | 60 | Suzhou | 0.790 | 8 | 0.852 | 7 |
| Deyang | 0.586 | 27 | 0.585 | 28 | Suizhou | 0.551 | 35 | 0.553 | 37 |
| Dongguan | 0.906 | 4 | 0.906 | 4 | Suining | 0.464 | 71 | 0.464 | 74 |
| Dongying | 0.577 | 28 | 0.580 | 29 | Xiamen | 0.541 | 39 | 0.552 | 38 |
| Ezhou | 0.465 | 70 | 0.466 | 73 | Taizhou (in Zhejiang) | 0.506 | 50 | 0.550 | 41 |
| Foshan | 0.871 | 6 | 0.871 | 6 | Taizhou (in Jiangsu) | 0.480 | 64 | 0.488 | 64 |
| Fuzhou | 0.615 | 21 | 0.633 | 19 | Tangshan | 0.783 | 9 | 0.787 | 10 |
| Fushun | 0.525 | 42 | 0.525 | 45 | Tianjin | 0.728 | 12 | 0.755 | 11 |
| Guangzhou | 0.966 | 2 | 0.958 | 3 | Tieling | 0.443 | 77 | 0.443 | 78 |
| Handan | 0.512 | 49 | 0.513 | 51 | Tongchuan | 0.369 | 96 | 0.369 | 96 |
| Hangzhou | 0.619 | 20 | 0.645 | 18 | Weihai | 0.459 | 75 | 0.473 | 69 |
| Hefei | 0.445 | 76 | 0.450 | 77 | Weifang | 0.441 | 78 | 0.457 | 76 |
| Hengshui | 0.254 | 99 | 0.254 | 99 | Weinan | 0.428 | 83 | 0.428 | 84 |
| Huzhou | 0.350 | 98 | 0.360 | 97 | Wuxi | 0.729 | 11 | 0.816 | 8 |
| Huanggang | 0.395 | 90 | 0.397 | 92 | Wuhan | 0.554 | 33 | 0.577 | 30 |
| Huangshi | 0.490 | 58 | 0.491 | 61 | Xi’an | 0.357 | 97 | 0.351 | 98 |
| Huizhou | 0.498 | 54 | 0.498 | 56 | Xianning | 0.436 | 79 | 0.437 | 79 |
| Jinan | 0.514 | 48 | 0.519 | 46 | Xianyang | 0.403 | 87 | 0.402 | 89 |
| Jiaxing | 0.386 | 93 | 0.418 | 86 | Xiaogan | 0.410 | 86 | 0.411 | 88 |
| Jiangmen | 0.594 | 25 | 0.594 | 25 | Xinxiang | 0.375 | 94 | 0.375 | 94 |
| Jiaozuo | 0.463 | 73 | 0.463 | 75 | Xinyang | 0.391 | 92 | 0.391 | 93 |
| Jinhua | 0.393 | 91 | 0.432 | 83 | Xingtai | 0.420 | 84 | 0.421 | 85 |
| Jingmen | 0.491 | 57 | 0.493 | 58 | Xuchang | 0.551 | 36 | 0.552 | 39 |
| Jingzhou | 0.478 | 66 | 0.479 | 67 | Yantai | 0.598 | 23 | 0.614 | 22 |
| Jiujiang | 0.431 | 82 | 0.435 | 80 | Yancheng | 0.489 | 59 | 0.501 | 53 |
| Kaifeng | 0.566 | 31 | 0.567 | 33 | Yangzhou | 0.506 | 51 | 0.515 | 50 |
| Langfang | 0.481 | 63 | 0.481 | 65 | Yingkou | 0.478 | 67 | 0.477 | 68 |
| Liaoyang | 0.595 | 24 | 0.595 | 24 | Yueyang | 0.623 | 19 | 0.625 | 20 |
| Luzhou | 0.493 | 55 | 0.492 | 59 | Zhangjiakou | 0.480 | 65 | 0.480 | 66 |
| Luoyang | 0.524 | 43 | 0.525 | 44 | Zhangzhou | 0.646 | 17 | 0.654 | 17 |
| Luohe | 0.517 | 47 | 0.517 | 49 | Zhaoqing | 0.551 | 37 | 0.551 | 40 |
| Mianyang | 0.501 | 52 | 0.499 | 54 | Zhenjiang | 0.542 | 38 | 0.554 | 36 |
| Neijiang | 0.587 | 26 | 0.586 | 27 | Zhengzhou | 0.487 | 61 | 0.489 | 63 |
| Nanjing | 0.523 | 44 | 0.571 | 32 | Zhongshan | 0.529 | 41 | 0.529 | 43 |
| Nantong | 0.466 | 69 | 0.518 | 48 | Chongqing | 0.520 | 45 | 0.502 | 52 |
| Ningbo | 0.647 | 16 | 0.677 | 14 | Zhoushan | 0.415 | 85 | 0.418 | 87 |
| Ningde | 0.569 | 30 | 0.571 | 31 | Zhuhai | 0.517 | 46 | 0.518 | 47 |
| Panjin | 0.397 | 89 | 0.397 | 91 | Zibo | 0.461 | 74 | 0.467 | 71 |
| Pingdingshan | 0.558 | 32 | 0.559 | 35 | Zigong | 0.792 | 7 | 0.791 | 9 |
| Putian | 0.603 | 22 | 0.607 | 23 | Mean | 0.525 | --- | 0.531 | --- |
| City Group | Group ID | City |
|---|---|---|
| Yangtze River Delta | 1 | Shanghai |
| Pearl River Delta | 2 | Shenzhen |
| Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei | 3 | Beijing, Tangshan, Tianjin |
| Central and southern Liaoning | 4 | Dalian |
| Shandong Peninsula | 5 | Dongying, Jinan, Qingdao |
| Cheng Yu | 6 | Chengdu, Deyang, Chongqing, Zigong |
| West Coast of Taiwan Straits | 7 | Quanzhou, Zhangzhou |
| Central Henan | 8 | Kaifeng, Luoyang, Xuchang, Zhengzhou |
| Middle reaches of the Yangtze River | 9 | Wuhan, Yueyang |
| Guanzhong | 10 | Baoji, Xi’an |
| City Group | Group ID | TGR (PM2.5) | TGR (Actual PM2.5) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yangtze River Delta | 1 | 0.695 | 0.735 |
| Pearl River Delta | 2 | 0.990 | 0.988 |
| Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei | 3 | 0.712 | 0.713 |
| Central and southern Liaoning | 4 | 0.692 | 0.689 |
| Shandong Peninsula | 5 | 0.588 | 0.598 |
| Cheng Yu | 6 | 0.599 | 0.593 |
| West coast of Taiwan Strait | 7 | 0.699 | 0.709 |
| Central Henan | 8 | 0.559 | 0.560 |
| Middle reaches of the Yangtze River | 9 | 0.646 | 0.647 |
| Guanzhong | 10 | 0.434 | 0.432 |
| Mean | 0.661 | 0.666 |
| Group ID | Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | Group 4 | Group 5 | Group 6 | Group 7 | Group 8 | Group 9 | Group 10 | Mean | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | ||||||||||||
| 2004–2005 | 0.9890 | 1.0296 | 0.9372 | 0.9390 | 0.9749 | 0.9201 | 0.8975 | 0.8552 | 0.8495 | 0.9282 | 0.9305 | |
| 2005–2006 | 1.0198 | 1.0034 | 0.9431 | 0.8658 | 1.0138 | 0.9587 | 0.9974 | 0.8582 | 0.9123 | 0.8983 | 0.9453 | |
| 2006–2007 | 0.9522 | 1.0076 | 0.9138 | 0.9097 | 1.0466 | 0.9619 | 0.9184 | 0.8677 | 0.9006 | 0.9182 | 0.9383 | |
| 2007–2008 | 0.9819 | 1.0243 | 0.9644 | 0.9185 | 1.0306 | 0.9401 | 0.9768 | 0.9143 | 0.9313 | 0.9165 | 0.9590 | |
| 2008–2009 | 1.0246 | 1.0142 | 0.9042 | 0.8732 | 0.9719 | 0.8745 | 1.0441 | 0.8550 | 0.8919 | 0.9328 | 0.9363 | |
| 2009–2010 | 1.0170 | 1.0918 | 0.9608 | 0.9824 | 1.0113 | 0.9345 | 1.0124 | 0.8918 | 0.8863 | 0.9009 | 0.9669 | |
| 2010–2011 | 0.9776 | 0.9326 | 0.9380 | 0.9323 | 0.9794 | 0.9490 | 0.9263 | 0.9274 | 0.8992 | 0.8862 | 0.9344 | |
| 2011–2012 | 0.9947 | 1.0243 | 1.0125 | 0.9506 | 1.0173 | 0.9445 | 0.9566 | 0.9180 | 0.9391 | 0.9709 | 0.9722 | |
| 2012–2013 | 0.9133 | 0.8813 | 0.9941 | 0.9777 | 0.9785 | 0.8755 | 0.9585 | 0.8938 | 0.9293 | 0.8858 | 0.9278 | |
| 2013–2014 | 1.0288 | 1.0121 | 1.0319 | 0.9723 | 1.1102 | 1.0662 | 0.9802 | 1.0137 | 0.9744 | 1.0453 | 1.0227 | |
| 2014–2015 | 1.0479 | 1.0436 | 1.0482 | 1.0394 | 1.0641 | 0.9936 | 1.0612 | 0.9941 | 0.9993 | 1.0220 | 1.0310 | |
| 2015–2016 | 1.0588 | 0.9869 | 1.0549 | 1.0575 | 1.0370 | 1.0113 | 1.0434 | 1.0070 | 1.0310 | 0.9754 | 1.0259 | |
| Mean | 0.9997 | 1.0030 | 0.9740 | 0.9499 | 1.0189 | 0.9511 | 0.9798 | 0.9147 | 0.9274 | 0.9387 | 0.9651 | |
| Group ID | Group ID | Group 2 | Group 3 | Group 4 | Group 5 | Group 6 | Group 7 | Group 8 | Group 9 | Group 10 | Mean | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | ||||||||||||
| Year | 1.0364 | 0.9416 | 0.9328 | 0.9691 | 0.9174 | 0.9074 | 0.8529 | 0.8547 | 0.9279 | 0.9318 | ||
| 2005–2006 | 1.0216 | 1.0082 | 0.9480 | 0.8724 | 0.9989 | 0.9566 | 0.9926 | 0.8568 | 0.9128 | 0.8881 | 0.9439 | |
| 2006–2007 | 0.9514 | 1.0124 | 0.9166 | 0.9134 | 1.0466 | 0.9612 | 0.9208 | 0.8535 | 0.9034 | 0.9090 | 0.9373 | |
| 2007–2008 | 0.9848 | 1.0219 | 0.9635 | 0.9128 | 1.0362 | 0.9378 | 0.9827 | 0.9118 | 0.9331 | 0.9135 | 0.9588 | |
| 2008–2009 | 1.0251 | 1.0070 | 0.9024 | 0.8701 | 0.9672 | 0.8738 | 1.0371 | 0.8529 | 0.8891 | 0.9286 | 0.9331 | |
| 2009–2010 | 1.0292 | 1.0621 | 0.9572 | 0.9687 | 1.0073 | 0.9275 | 1.0082 | 0.8911 | 0.8876 | 0.8977 | 0.9619 | |
| 2010–2011 | 0.9748 | 0.9406 | 0.9390 | 0.9219 | 0.9795 | 0.9487 | 0.9302 | 0.9259 | 0.8918 | 0.8852 | 0.9333 | |
| 2011–2012 | 0.9883 | 1.0154 | 1.0147 | 0.9418 | 1.0219 | 0.9325 | 0.9612 | 0.9177 | 0.9436 | 0.9578 | 0.9688 | |
| 2012–2013 | 0.9289 | 0.8804 | 0.9842 | 0.9593 | 0.9829 | 0.8717 | 0.9763 | 0.8922 | 0.9316 | 0.8887 | 0.9287 | |
| 2013–2014 | 1.0299 | 1.0126 | 1.0362 | 0.9740 | 1.1077 | 1.0533 | 0.9889 | 1.0095 | 0.9669 | 1.0186 | 1.0190 | |
| 2014–2015 | 1.0594 | 1.0294 | 1.0412 | 1.0402 | 1.0566 | 0.9802 | 1.0731 | 0.9886 | 0.9889 | 1.0251 | 1.0278 | |
| 2015–2016 | 1.0706 | 0.9710 | 1.0488 | 1.0568 | 1.0434 | 1.0167 | 1.0289 | 0.9999 | 1.0199 | 0.9744 | 1.0225 | |
| Mean | 1.0039 | 0.9987 | 0.9733 | 0.9454 | 1.0173 | 0.9468 | 0.9828 | 0.9111 | 0.9259 | 0.9334 | 0.9632 | |
| Group ID | PM2.5 | Actual PM2.5 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC (PM2.5) | BPC (PM2.5) | PTCU (PM2.5) | FCU (PM2.5) | EC (APM2.5) | BPC (APM2.5) | PTCU (APM2.5) | FCU (APM2.5) | |
| Group 1 | 0.9930 | 1.0050 | 1.0100 | 0.9918 | 0.9929 | 1.0043 | 1.0068 | 1.0000 |
| Group 2 | 1.0004 | 0.9905 | 1.0070 | 1.0051 | 1.0004 | 0.9905 | 1.0075 | 1.0003 |
| Group 3 | 1.0004 | 0.9835 | 1.0096 | 0.9806 | 1.0004 | 0.9834 | 1.0101 | 0.9794 |
| Group 4 | 1.0008 | 0.9778 | 0.9961 | 0.9745 | 1.0008 | 0.9778 | 0.9963 | 0.9698 |
| Group 5 | 0.9988 | 1.0075 | 1.0227 | 0.9901 | 0.9988 | 1.0075 | 1.0215 | 0.9897 |
| Group 6 | 0.9986 | 0.9913 | 1.0035 | 0.9575 | 0.9986 | 0.9911 | 1.0040 | 0.9529 |
| Group 7 | 0.9955 | 0.9988 | 0.9980 | 0.9873 | 0.9955 | 0.9988 | 0.9951 | 0.9933 |
| Group 8 | 0.9983 | 0.9723 | 0.9883 | 0.9536 | 0.9983 | 0.9723 | 0.9884 | 0.9496 |
| Group 9 | 0.9932 | 0.9665 | 1.0068 | 0.9597 | 0.9921 | 0.9652 | 1.0075 | 0.9596 |
| Group 10 | 0.9973 | 0.9834 | 1.0025 | 0.9548 | 0.9973 | 0.9834 | 1.0026 | 0.9493 |
| Mean | 0.9976 | 0.9876 | 1.0044 | 0.9753 | 0.9975 | 0.9873 | 1.0040 | 0.9742 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, S.; Xie, J.; Xiao, D.; Zhang, Y. Measuring the Environmental Efficiency and Technology Gap of PM2.5 in China’s Ten City Groups: An Empirical Analysis Using the EBM Meta-Frontier Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16040675
Cheng S, Xie J, Xiao D, Zhang Y. Measuring the Environmental Efficiency and Technology Gap of PM2.5 in China’s Ten City Groups: An Empirical Analysis Using the EBM Meta-Frontier Model. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(4):675. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16040675
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Shixiong, Jiahui Xie, De Xiao, and Yun Zhang. 2019. "Measuring the Environmental Efficiency and Technology Gap of PM2.5 in China’s Ten City Groups: An Empirical Analysis Using the EBM Meta-Frontier Model" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 4: 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16040675
APA StyleCheng, S., Xie, J., Xiao, D., & Zhang, Y. (2019). Measuring the Environmental Efficiency and Technology Gap of PM2.5 in China’s Ten City Groups: An Empirical Analysis Using the EBM Meta-Frontier Model. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(4), 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16040675





