Creating a Collaborative Platform for the Development of Community Interventions to Prevent Non-Communicable Diseases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Non-Communicable Diseases and Community Interventions
1.2. Articulating Non-Governmental Institutions
1.3. Inspiring Principles
- Social Determinants of Health. The social determinants of health are the conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work and get old, including the health system [21,22]. These conditions are crucial because of their influence on other health determinants (biological factors, health system factors, environmental factors, lifestyle factors). At the community level, all the elements from the environment that can help make the healthy choice the easy choice are especially important. We wanted to extend our approach by creating the right conditions, so our community interventions could influence the social determinants of health.
- The Health Impact Pyramid. Describes the impact of different public health actions and the gradient of personal effort needed in each action. It says for example, that counseling and education requires much more individual effort and has less population impact than changing the context to make default decisions healthy [23]. A greater number of non-governmental institutions have been working for a long time in health education and counseling, looking to inform and raise awareness about different risk factors or diseases. In this sense, refocusing the activities to complement what it´s done with actions that change context should be the way to go.
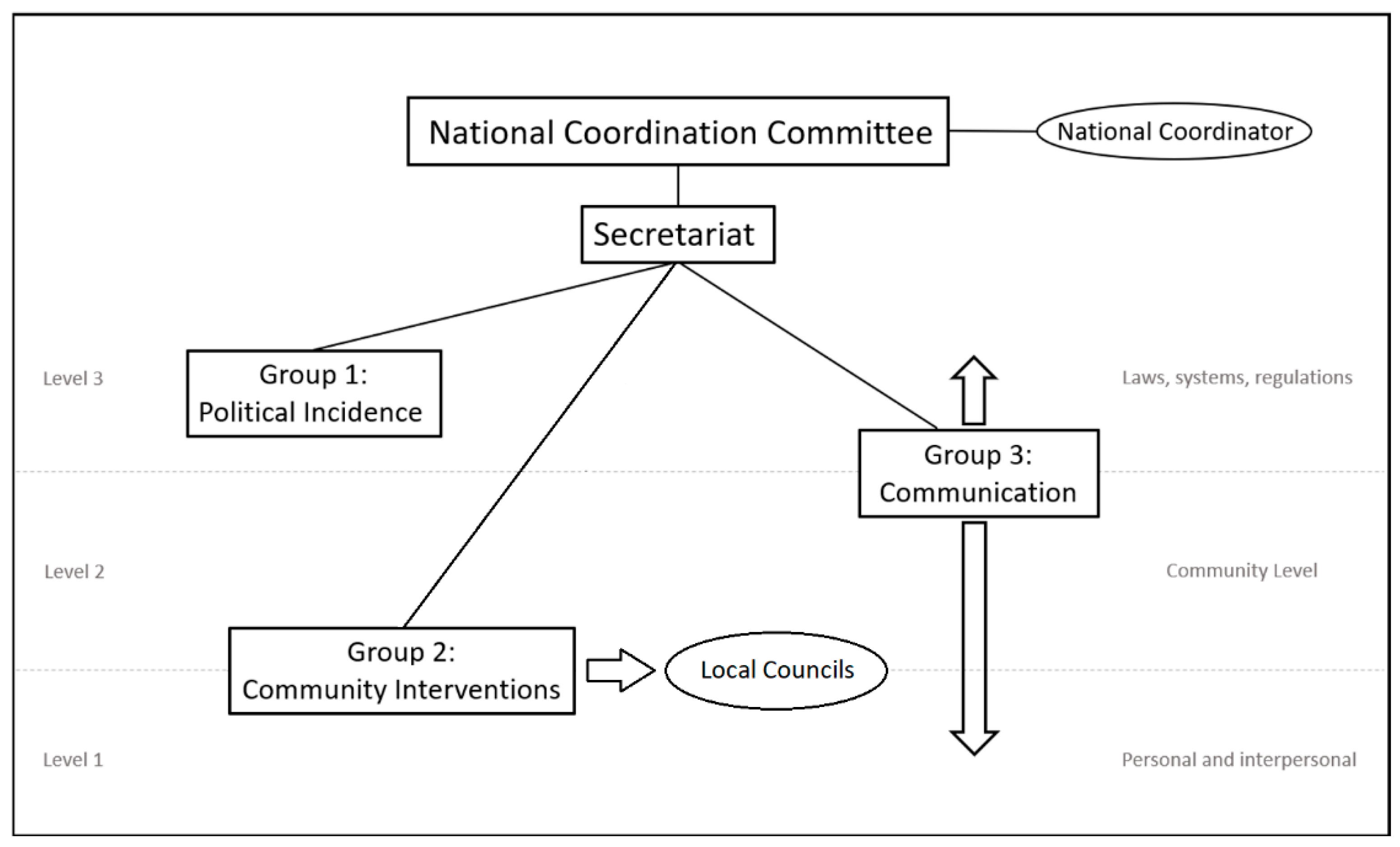
- Socio-ecological approach—Levels of intervention. The socio-ecological approach explains the interaction between different factors that lead to healthy or unhealthy behavior and decisions. This approach also organizes these factors in different levels [24,25].Level 3: Factors determined by governmental structures, production systems, laws and politics.Level 2: Factors determined by the conditions in which people´s day to day activities take place. Communities, common environments, workplaces, schools.Level 1: Factors determined by social norms, family, educations and the components of personal decision (expectations, motivation, self-efficacy, acceptance).Different health promotion initiatives have been structured by this approach [26] and, in this case, the working groups have been structured in the three levels with the intention of working harmonized actions to enhance the impact.
- Proportional Universalism. Proportional universalism, according to Sir Michael Marmot, means that even though health promotion actions must be universal, these actions must follow a scale and intensity that is proportional to the level of disadvantage. Dedicating the best efforts to those with more disadvantage without disregarding the rest [27]. This is a key concept that we had in mind to establish priorities in the design of the interventions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Theoretical Appproach
2.2. Participants and Intervention Design
3. Results
3.1. Organizational Structure
- Makes recommendations, offers guidance and support to the Secretariat since the foundation of the platform about the coordination of the work groups.
- Analyzes and approves the work plan of each group including the evaluation system.
- Works as ambassadors of the initiative, spreading the word and communicating it in all their institutional and professional channels.
3.2. Functional Structure
- Group 1: Political incidence
- Influence decision-makers to make permanent decisions and changes that promote healthy habits.
- Create political structures and networks that support health promotion through community interventions.
- Group 2: Community InterventionsThis group is the one in charge of working with local councils to:
- Promote the implementation of the National Prevention and Health Promotion Strategy.
- Promote the local implementation of the strategy (community interventions).
- Design and implement community interventions to promote healthy lifestyles (health education and changes in the context).
- Design and offer toolboxes and resources for the implementation of these local actions.
- Group 3: Social Marketing and Communication
- Design health promotion interventions through social marketing and communications.
- Create an internet repository of all the successful experiences.
- Perform as communications team for the platform.
3.3. Developing Community Interventions to Prevent NCDs—National Prevention and Health Promotion Strategy
3.3.1. Part 1. Recruiting Local Councils and Disseminating the Initiative
3.3.2. Part 2. Establishing an Inter-Sectorial Round table and Identifying Community Resources
- Creating the multi-sectorial round table. Our community interventions team (group 2) will support local councils in the creation of the round tables and will be a part of these tables. These tables will be led by the local council´s health promotion team.
- Identifying community resources. Health asset mapping [34] is done to get all of the information of health assets of the community (institutions, associations, physical resources or local activities that promote health). Health promotion based on asset mapping helps to introduce concepts like health equity and participation to all the processes [35]. Also, having all the health promotion resources identified helps a great deal in the design and implementation of new health promotion community interventions, whether it is promoting some resources that already exist, or generating new ones.
3.3.3. Part 3. Implementing Specific Community Interventions
3.4. The Importance of Sustainability
4. Discussion
Main Challenges and Opportunities
- Complexity and variability of the different contexts that the work is done, guaranteed long-time sustainability of partnerships and resources limitation. Our platform allows great variability and flexibility of actions inside the general conceptual framework. It allows for the implementation of different kinds of community interventions depending on what the situation requires or the community needs.
- Institutional differences between partners (structural, resources, procedures) that generate very complicated legal and bureaucratic barriers. We have been very careful with the creation process, trying to make it very participative and everything has been done by consensus. Having the objectives in mind, a common agenda was made to make easier the interaction between partners.
- Reaching an agreement on the roles and responsibilities when defining the platform was also an important issue between partners. In our collaborative platform, every institution established from the beginning in a questionnaire their possibilities and resources (human resources, communication efforts, branding) for the platform. This was added to the terms of reference that we all approved.
- Management of economic resources. From the beginning each institution contributed professional or different resources, avoiding any money exchange between partners.
5. Conclusions
- Institutional support and recognition.
- Multi-component community interventions.
- Collaboration between different agents and local authorities.
- Planning based on community needs.
- Evidence-based actions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Phase | Actor | Objectives | Methodology Description | Done | Planned 2019 | To be Planned |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organizational | AECC All partners | Creating a collaborative platform by articulating non-governmental institutions | Mapping and evaluation of potential partners. | X | ||
| Meetings with potential partners. | X | |||||
| Defining an organizational and functional structure | X | |||||
| Defining roles, responsibilities, resources, etc. | X | |||||
| Signing Terms of Reference | X | |||||
| Functional | Work group 1 | Influence decision-makers to make permanent decisions and changes that promote healthy habits. | Political Incidence | X | ||
| Create political structures and networks that support health promotion through community interventions. | ||||||
| Work group 2 | Promote the implementation of the National Prevention and Health Promotion Strategy. | Community Interventions | X | |||
| Promote the local implementation of the strategy (community interventions). | ||||||
| Design and implement community interventions to promote healthy lifestyles (health education and changes in the context). | ||||||
| Work group 3 | Design health promotion interventions through social marketing and communications. | Communication | X | |||
| Perform as a communications team for the platform. | ||||||
| Evaluation | All partners and each work group | Evaluating the implementation process of the initiative. | Qualitative evaluation | X | ||
| Evaluating the political incidence actions. | Quantitative evaluation | X | ||||
| Evaluating the results of each community intervention. | Quantitative evaluation | X | ||||
| Evaluating health promotion interventions through communications. | Quantitative evaluation | X |
References
- Organización Mundial de la Salud. Factsheet. Country Profile. Spain. 2014. Available online: http://www.who.int/nmh/countries/esp_en.pdf?ua=1 (accessed on 14 October 2018).
- Estévez, J.; Guerrero, M. Soluciones Para la Gestión de la Cronicidad. Foro de Debate. Sociedad Española de Directivos de Salud (Sedisa), 2015. Available online: https://www.redaccionmedica.com/contenido/images/INFORME%20SEDISA.compressed.pdf (accessed on 14 October 2018).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global Observatory Data. Noncommunicable Disease. Available online: http://www.who.int/gho/ncd/en/ (accessed on 14 October 2018).
- Organización Mundial de la Salud (OMS). Cáncer. Available online: http://www.who.int/cancer/en/ (accessed on 14 October 2018).
- Frieden, T.R. Six components necessary for effective public health program implementation. Am. J. Public Health 2014, 104, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Marchand, S.; Corcoran, C.; DiBiasio, H.; Clough, R.; Dyer, C.S.; Nobles, J.; White, J.; Greaney, M.L.; Greene, G.W. A Community-Based Nutrition and Physical Activity Intervention for Children Who Are Overweight or Obese and Their Caregivers. J. Obes. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, K.R.; Dwyer, J.J.M.; MacGillivray, A.; Hawrychuk, S. A Review of Workplace and Community Interventions for Adults: Effects of Physical Activity, Eating Behaviours and BMI—Risk factors for Diabetes; Ontario Agency for Health Protection and Promotion: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Heath, G.W.; Parra, D.C.; Sarmiento, O.L.; Andersen, L.B.; Owen, N.; Goenka, S.; Montes, F.; Brownson, R.C.; Lancet Physical Activity Series Working Group. Evidence-based intervention in physical activity: Lessons from around the world. Lancet 2012, 380, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, A.; Ekowati, R.; Baridalyne, N.; Kusumawardani, N.; Suhardi Kapoor, S.K.; Leowski, J. Evaluation of community-based interventions for non-communicable diseases: Experiences from India and Indonesia. Health Promot. Int. 2011, 26, 276–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rinsum, C.E.; Gerards, S.M.P.L.; Rutten, G.M.; van de Goor, I.A.M.; Kremers, S.P.J. The coaching on lifestyle (CooL) intervention for obesity, a study protocol for an action-oriented mixed-methods study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyson, P.A.; Anthony, D.; Fenton, B.; Stevens, D.E.; Champagne, B.; Li, L.-M.; Lv, J.; Hernández, J.R.; Thankappan, K.R.; Matthews, D.R.; et al. Successful Up-Scaled Population Interventions to Reduce Risk Factors for Non-Communicable Disease in Adults: Results from the International Community Interventions for Health (CIH) Project in China, India and Mexico. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niccolai, L.M.; Hansen, C.E. Practice- and Community-Based Interventions to Increase Human Papillomavirus Vaccine Coverage: A Systematic Review. JAMA Pediatr. 2015, 169, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grady, M.; Goldblatt, P. Addressing the Social Determinants of Health: The Urban Dimension and the Role of Local Government; World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2012; Available online: http://www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0005/166136/UrbanDimensions.pdf?ua=1 (accessed on 16 October 2018).
- López Ruiz, V.; Segura del Pozo, J.; Pires, M.P.; Malmusi, D.; Vergara Duarte, M.; Pérez Sanz, E. Municipalismo y salud comunitaria: Transformar desde los ayuntamientos. Informe SESPAS 2018. Gac. Sanit. 2018, 32 (Suppl. 1), 1–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases 2013–2020; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013; Available online: https://www.who.int/nmh/events/ncd_action_plan/en/ (accessed on 16 October 2018).
- Arora, M.; Chauhan, K.; John, S.; Mukhopadhyay, A. Multi-sectoral action for addressing social determinants of noncommunicable diseases and mainstreaming health promotion in national health programmes in India. Indian J. Community Med. 2011, 36 (Suppl. 1), S43–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez Cía, N.; Pérez, M.; Heras-Mosteiro, J.; Gutierrez Ávila, G.; Diaz-Olalla, J.M.; Ruiz-Giménez Aguilar, J.L. Encuentros y desencuentros entre salud comunitaria y sistema sanitario español. Informe SESPAS 2018. Gac. Sanit. 2018, 32 (Suppl. 1), 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor-Robinson, D.C.; Lloyd-Williams, F.; Orton, L.; Moonan, M.; O’Flaherty, M.; Capewell, S. Barriers to partnership working in public health: A qualitative study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, D.; Perkins, N. Partnership Working in Public Health: The Implications for Governance of a Systems Approach. J. Health Serv. Res. Policy 2012, 17 (Suppl. 2), 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Red de Actividades Comunitarias. Programa de Actividades Comunitarias en Atención Primaria. Sociedad Española de Medicina Familiar y Comunitaria. Available online: http://www.pacap.net/pacap/que-es-la-red-pacap/ (accessed on 17 November 2018).
- Determinantes Sociales de la Salud. Organización Mundial de la Salud. Available online: http://www.who.int/social_determinants/es/ (accessed on 17 November 2018).
- Dahlgren, G.; Whitehead, M. Policies and Strategies to Promote Social Equity in Health. Stockholm Institute for Futures Studies, 1991. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/6472456.pdf (accessed on 19 November 2018).
- Frieden, T.R. A Framework for Public Health Action: The Health Impact Pyramid. Am. J. Public Health 2010, 100, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Isobel Contento. Presentación: Evaluando la Efectividad de la Educación Nutricional. Red de Información, Comunicación y Educación Alimentaria y Nutricional para América Latina y el Caribe (Red ICEAN). Basado en el Modelo Ecológico de Bronfenbrenner. Available online: http://www.fao.org/ag/humannutrition/30497-0a4e500285ce056f28a16239bebb460ac.pdf (accessed on 14 October 2018).
- Torrence, C.; Griffin, F.S.; Rolke, L.; Kenison, K.; Marvin, A. Faithful Families Cooking and Eating Smart and Moving for Health: Evaluation of a Community Driven Intervention. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golden, S.D.; Earp, J.A. Social Ecological Approaches to Individuals and Their Contexts: Twenty Years of Health Education & Behavior Health Promotion Interventions. Health Educ. Behav. 2012, 39, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marmot, M.; Bell, R. Fair society, healthy lives: The Marmot Review: Strategic review of health inequalities in England post-2010. Public Health 2012, 126 (Suppl. 1), S4–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Think Tank. Cambridge Dictionary. Available online: https://dictionary.cambridge.org/es/diccionario/ingles/think-tank (accessed on 5 February 2019).
- Vilar, J. Ethical implications of working in networks and community action. Cult. Educ. 2008, 20, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubieto, J.R. Modelos de trabajo en red. Educ. Soc. 2013, 36, 26–39. [Google Scholar]
- NCD Alliance. Practical Guide on How to Build Effective National and Regional NCD Alliances. Sample 2. Potential Parters. P. 61. 2016. Available online: https://ncdalliance.org/resources/practical-guide-on-how-to-build-effective-national-and-regional-ncd-alliances (accessed on 22 October 2018).
- Project SoL—A Community-Based, Multi-Component Health Promotion Intervention to Improve Eating Habits and Physical Activity among Danish Families with Young Children. Part 1: Intervention Development and Implementation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1513. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministerio de Sanidad, Servicios Sociales e Igualdad. Guía Para la Implementación Local de la Estrategia de Promoción de la Salud y Prevención en el SNS. Madrid. 2015. Available online: https://www.mscbs.gob.es/profesionales/saludPublica/prevPromocion/Estrategia/docs/Guia_implementacion_local.pdf (accessed on 22 October 2018).
- Botello, B.; Palacio, S.; García, M.; Margolles, M.; Fernández, F.; Hernán, M.; Nieto, J.; Cofiño, R. Metodología para el mapeo de activos de salud en una comunidad. Gac. Sanit. 2013, 27, 101–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cofiño, R.; Avino, D.; Benede, C.B.; Botello, B.; Cubillo, J.; Morgan, A.; Paredes-Carbonell, J.J.; Hernán, M. Promoción de la salud basada en activos: Cómo trabajar con esta perspectiva en intervenciones locales? Gac. Sanit. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministerio de Sanidad, Servicios Sociales e Igualdad. Curso Online Sobre Salud Local. Available online: https://www.mscbs.gob.es/profesionales/saludPublica/prevPromocion/Estrategia/PlanCapacitacion/Curso_SaludLocal.htm (accessed on 22 October 2018).
- NCD Alliance. Our History. Available online: https://ncdalliance.org/who-we-are/about-ncd-alliance/our-history (accessed on 31 January 2019).
- NCD Alliance. NCD Civil Society ATLAS. National and Regional NCD Alliances in Action. NCD Alliance, November 2017. Available online: https://ncdalliance.org/resources/ncd-atlas (accessed on 14 November 2018).
- OPEN. Obesity Prevention through European Network. Available online: http://openprogram.eu/ (accessed on 14 November 2018).
- Borys, J.-M.; Richard, P.; Ruault du Plessis, H.; Harper, P.; Levy, E. Tackling Health Inequities and Reducing Obesity Prevalence: The EPODE Community-Based Approach. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 68 (Suppl. 2), 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Red Española de Universidades Saludables (REUS). Available online: https://www.unisaludables.es/es/ (accessed on 14 November 2018).
- Ministerio de Sanidad, Consumo y Bienestar Social. Red Española de Universidades Saludables. Available online: https://www.mscbs.gob.es/profesionales/saludPublica/prevPromocion/promocion/UniversidadesSaludables/REUS.htm (accessed on 5 February 2019).
- Informe SESPAS 2018. Salud comunitaria y administración local. Gac. Sanit. 2018, 32 (Suppl. 1). Available online: http://www.gacetasanitaria.org/es-vol-32-num-s1-sumario-S0213911118X00053 (accessed on 5 February 2019).
- Dennis, S.; Hetherington, S.A.; Borodzicz, J.A.; Hermiz, O.; Zwar, N.A. Challenges to establishing successful partnerships in community health promotion programs: Local experiences from the national implementation of healthy eating activity and lifestyle (HEAL[TM]) program. Health Promot. J. Aust. 2015, 26, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riggs, E.; Block, K.; Warr, D.; Gibbs, L. Working better together: New approaches for understanding the value and challenges of organizational partnerships. Health Promot. Int. 2014, 29, 780–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leenaars, K.E.F.; Smit, E.; Wagemakers, A.; Molleman, G.R.; Koelen, M.A. Facilitators and barriers in the collaboration between the primary care and the sport sector in order to promote physical activity: A systematic literature review. Prev. Med. 2015, 81, 460–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalali, M.S.; Rahmandad, H.; Bullock, S.L.; Ammerman, A. Dynamics of Implementation and Maintenance of Organizational Health Interventions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Institution | Main Field | Type of Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Spanish Association Against Cancer (AECC) | Cancer | Prevention, Research, Political Incidence, Communication |
| Spanish Heart Foundation (FEC) | Heart Disease | Prevention, Health Promotion, Communication |
| Spanish Red Cross | General Health | Health Promotion, Political Incidence, Healthcare |
| Spanish Society of Family and Community Medicine (semFYC) | Primary Healthcare | Health Promotion, Healthcare, Research |
| Spanish Federation of Community Nursing Associations (FAECAP) | Primary Healthcare | Health Promotion, Healthcare, Research |
| Spanish Diabetes Association (SED) | Diabetes | Health Promotion, Healthcare, Research |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
del Busto, S.; Galindo, I.; Hernandez, J.J.; Camarelles, F.; Nieto, E.; Caballero, Á.; Sandín Vázquez, M. Creating a Collaborative Platform for the Development of Community Interventions to Prevent Non-Communicable Diseases. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16050676
del Busto S, Galindo I, Hernandez JJ, Camarelles F, Nieto E, Caballero Á, Sandín Vázquez M. Creating a Collaborative Platform for the Development of Community Interventions to Prevent Non-Communicable Diseases. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(5):676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16050676
Chicago/Turabian Styledel Busto, Sebastian, Inés Galindo, Juan Jesús Hernandez, Francisco Camarelles, Esther Nieto, Águeda Caballero, and María Sandín Vázquez. 2019. "Creating a Collaborative Platform for the Development of Community Interventions to Prevent Non-Communicable Diseases" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 5: 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16050676
APA Styledel Busto, S., Galindo, I., Hernandez, J. J., Camarelles, F., Nieto, E., Caballero, Á., & Sandín Vázquez, M. (2019). Creating a Collaborative Platform for the Development of Community Interventions to Prevent Non-Communicable Diseases. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(5), 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16050676




