Youth Engaged Participatory Air Monitoring: A ‘Day in the Life’ in Urban Environmental Justice Communities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Participants
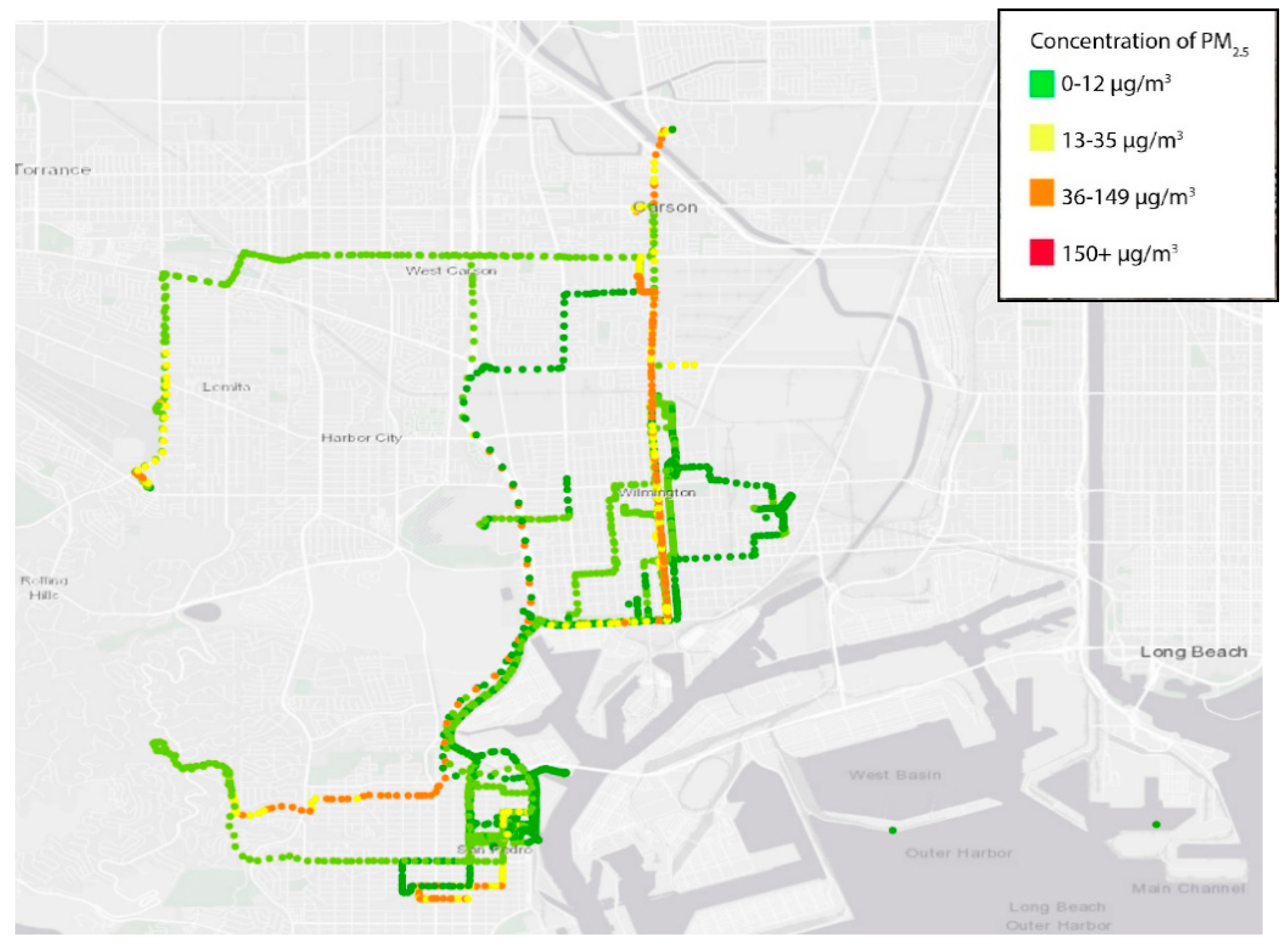
3.2. Air Monitoring Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Landrigan, P.J.; Fuller, R.; Acosta, N.J.; Adeyi, O.; Arnold, R.; Baldé, A.B.; Bertollini, R.; Bose-O’Reilly, S.; Boufford, J.I.; Breysse, P.N. The Lancet Commission on pollution and health. Lancet 2018, 391, 462–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delfino, R.J.; Gong, H., Jr.; Linn, W.S.; Pellizzari, E.D.; Hu, Y. Asthma symptoms in Hispanic children and daily ambient exposures to toxic and criteria air pollutants. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gauderman, W.J.; Urman, R.; Avol, E.; Berhane, K.; McConnell, R.; Rappaport, E.; Chang, R.; Lurmann, F.; Gilliland, F. Association of improved air quality with lung development in children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gauderman, W.J.; Vora, H.; McConnell, R.; Berhane, K.; Gilliland, F.; Thomas, D.; Lurmann, F.; Avol, E.; Kunzli, N.; Jerrett, M.; et al. Effect of exposure to traffic on lung development from 10 to 18 years of age: A cohort study. Lancet 2007, 369, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, C.G.; Eckel, S.P.; Habre, R.; Girguis, M.S.; Gao, L.; Lurmann, F.W.; Gilliland, F.D.; Breton, C.V. Association of Prenatal Exposure to Ambient and Traffic-Related Air Pollution With Newborn Thyroid Function: Findings From the Children’s Health Study. JAMA Netw. Open 2018, 1, e182172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Ren, C.; Delfino, R.J.; Chung, J.; Wilhelm, M.; Ritz, B. Association between Local Traffic-Generated Air Pollution and Preeclampsia and Preterm Delivery in the South Coast Air Basin of California. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 1773–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, R.; Berhane, K.; Yao, L.; Jerrett, M.; Lurmann, F.; Gilliland, F.; Künzli, N.; Gauderman, J.; Avol, E.; Thomas, D.; et al. Traffic, Susceptibility, and Childhood Asthma. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gan, W.Q.; Koehoorn, M.; Davies, H.W.; Demers, P.A.; Tamburic, L.; Brauer, M. Long-Term Exposure to Traffic-Related Air Pollution and the Risk of Coronary Heart Disease Hospitalization and Mortality. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 119, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasheminassab, S.; Daher, N.; Saffari, A.; Wang, D.; Ostro, B.; Sioutas, C. Spatial and temporal variability of sources of ambient fine particulate matter (PM 2.5) in California. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 12085–12097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lurmann, F.; Avol, E.; Gilliland, F. Emissions reduction policies and recent trends in Southern California’s ambient air quality. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2015, 65, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trasande, L.; Thurston, G.D. The role of air pollution in asthma and other pediatric morbidities. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, E.; Berhane, K.T.; Islam, T.; McConnell, R.; Urman, R.; Chen, Z.; Gilliland, F.D. Association of changes in air quality with incident asthma in children in California, 1993–2014. JAMA 2019, 321, 1906–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bateson, T.F.; Schwartz, J. Children’s response to air pollutants. J. Toxicol. Environ. Heal. A 2007, 71, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, F.P. Multiple threats to child health from fossil fuel combustion: Impacts of air pollution and climate change. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 125, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikati, I.; Benson, A.F.; Luben, T.J.; Sacks, J.D.; Richmond-Bryant, J. Disparities in distribution of particulate matter emission sources by race and poverty status. Am. J. Public Health 2018, 108, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brulle, R.J.; Pellow, D.N. Environmental justice: Human health and environmental inequalities. Public Health 2006, 27, 103–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wing, S.; Horton, R.A.; Muhammad, N.; Grant, G.R.; Tajik, M.; Thu, K. Integrating epidemiology, education, and organizing for environmental justice: Community health effects of industrial hog operations. Am. J. Public Health 2008, 98, 1390–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scammell, M.K.; Senier, L.; Darrah-Okike, J.; Brown, P.; Santos, S. Tangible evidence, trust and power: Public perceptions of community environmental health studies. Soc. Sci. Med. 2009, 68, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnston, J.E.; Kramer, A.J.; MacDonald Gibson, J. Community Perspectives on the Risk of Indoor Air Pollution Arising from Contaminated Groundwater. New Solut. A J. Environ. Occup. Health Policy 2015, 25, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullard, R.D. Dumping in Dixie: Race, Class, and Environmental Quality; Westview Press: Boulder, CO, USA, 2000; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Fals-Borda, O.; Rahman, M.A. Action and Knowledge: Breaking the Monopoly with Participatory Action-Research; Apex Press: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Corburn, J. Street Science: Community Knowledge and Environmental Health Justice; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- English, P.B.; Richardson, M.J.; Garzon-Galvis, C. From Crowdsourcing to Extreme Citizen Science: Participatory Research for Environmental Health. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2018, 39, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shepard, P.M. Advancing environmental justice through community-based participatory research. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conrad, C.C.; Hilchey, K.G. A review of citizen science and community-based environmental monitoring: Issues and opportunities. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 176, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, E.G.; Watkins, T.H.; Solomon, P.A.; Thoma, E.D.; Williams, R.W.; Hagler, G.S.W.; Shelow, D.; Hindin, D.A.; Kilaru, V.J.; Preuss, P.W. The Changing Paradigm of Air Pollution Monitoring. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11369–11377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerrett, M.; Arain, A.; Kanaroglou, P.; Beckerman, B.; Potoglou, D.; Sahsuvaroglu, T.; Morrison, J.; Giovis, C. A review and evaluation of intraurban air pollution exposure models. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2005, 15, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, A.L.; Griswold, W.G.; Johnston, J.E.; Herting, M.M.; Thorson, J.; Collier-Oxandale, A.; Hannigan, M. Low-Cost Air Quality Monitoring Tools: From Research to Practice (A Workshop Summary). Sensors 2017, 17, 2478. [Google Scholar]
- Zusman, M.; Schumacher, C.S.; Gassett, A.J.; Spalt, E.W.; Austin, E.; Larson, T.V.; Carvlin, G.; Seto, E.; Kaufman, J.D.; Sheppard, L. Calibration of low-cost particulate matter sensors: Model development for a multi-city epidemiological study. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nazelle, A.; Seto, E.; Donaire-Gonzalez, D.; Mendez, M.; Matamala, J.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J.; Jerrett, M. Improving estimates of air pollution exposure through ubiquitous sensing technologies. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 176, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, C.C.; Kim, H.; Vilcassim, M.J.R.; Thurston, G.D.; Gordon, T.; Chen, L.-C.; Lee, K.; Heimbinder, M.; Kim, S.-Y. Mapping urban air quality using mobile sampling with low-cost sensors and machine learning in Seoul, South Korea. Environ. Int. 2019, 131, 105022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apparicio, P.; Carrier, M.; Gelb, J.; Séguin, A.-M.; Kingham, S. Cyclists’ exposure to air pollution and road traffic noise in central city neighbourhoods of Montreal. J. Transp. Geogr. 2016, 57, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Steinle, S.; Reis, S.; Sabel, C.E.; Semple, S.; Twigg, M.M.; Braban, C.F.; Leeson, S.R.; Heal, M.R.; Harrison, D.; Lin, C. Personal exposure monitoring of PM2. 5 in indoor and outdoor microenvironments. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 508, 383–394. [Google Scholar]
- Sloan, C.D.; Philipp, T.J.; Bradshaw, R.K.; Chronister, S.; Barber, W.B.; Johnston, J.D. Applications of GPS-tracked personal and fixed-location PM2.5 continuous exposure monitoring. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2016, 66, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hubbell, B.J.; Kaufman, A.; Rivers, L.; Schulte, K.; Hagler, G.; Clougherty, J.; Cascio, W.; Costa, D. Understanding social and behavioral drivers and impacts of air quality sensor use. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 886–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morello-Frosch, R.; Pastor, M., Jr.; Porras, C.; Sadd, J. Environmental justice and regional inequality in southern California: Implications for future research. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gunier, R.B.; Hertz, A.; Von Behren, J.; Reynolds, P. Traffic density in California: Socioeconomic and ethnic differences among potentially exposed children. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2003, 13, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McConnell, R.; Berhane, K.; Gilliland, F.; London, S.J.; Islam, T.; Gauderman, W.J.; Avol, E.; Margolis, H.G.; Peters, J.M. Asthma in exercising children exposed to ozone: A cohort study. Lancet 2002, 359, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauderman, W.J.; Avol, E.; Gilliland, F.; Vora, H.; Thomas, D.; Berhane, K.; McConnell, R.; Kuenzli, N.; Lurmann, F.; Rappaport, E.; et al. The Effect of Air Pollution on Lung Development from 10 to 18 Years of Age. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jerrett, M.; McConnell, R.; Wolch, J.; Chang, R.; Lam, C.; Dunton, G.; Gilliland, F.; Lurmann, F.; Islam, T.; Berhane, K. Traffic-related air pollution and obesity formation in children: A longitudinal, multilevel analysis. Environ. Health 2014, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brandt, S.J.; Perez, L.; Kunzli, N.; Lurmann, F.; McConnell, R. Costs of childhood asthma due to traffic-related pollution in two California communities. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 40, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Herting, M.M.; Chatzi, L.; Belcher, B.R.; Alderete, T.L.; McConnell, R.; Gilliland, F.D. Regional and traffic-related air pollutants are associated with higher consumption of fast food and trans fat among adolescents. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 109, 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, J.; Zandbergen, P.A. Children at risk: Measuring racial/ethnic disparities in potential exposure to air pollution at school and home. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2007, 61, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Green, R.S.; Smorodinsky, S.; Kim, J.J.; McLaughlin, R.; Ostro, B. Proximity of California public schools to busy roads. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gaffron, P.; Niemeier, D. School locations and traffic emissions—Environmental (in) justice findings using a new screening method. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 2009–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mirabelli, M.C.; Wing, S.; Marshall, S.W.; Wilcosky, T.C. Race, poverty, and potential exposure of middle-school students to air emissions from confined swine feeding operations. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 114, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pastor, J.M.; Sadd, J.L.; Morello-Frosch, R. Who’s Minding the Kids? Pollucion, Public Schools, and Environmental Justice in Los Angeles. Soc. Sci. Q. 2002, 83, 263–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- California Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment. California Communities Environmental Health Screening Tool; Version 3.0 (CalEnviroScreen 3.0); California Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2018.
- Heimbinder, M.; Yap, R.; Lim, C.C. AirBeam Device Description. Available online: http://www.takingspace.org/aircasting/airbeam/ (accessed on 7 October 2019).
- Mazaheri, M.; Clifford, S.; Yeganeh, B.; Viana, M.; Rizza, V.; Flament, R.; Buonanno, G.; Morawska, L. Investigations into factors affecting personal exposure to particles in urban microenvironments using low-cost sensors. Environ. Int. 2018, 120, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilcassim, M.R.; Thurston, G.D.; Chen, L.-C.; Lim, C.C.; Gordon, T. Exposure to Greater Air Pollution when Traveling Abroad is Associated with Decreased Lung Function. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Stanton, L.G.; Graham, A.R.; Roberts, P.T. Assessing the Utility of Low-Cost Particulate Matter Sensors over a 12-Week Period in the Cuyama Valley of California. Sensors 2017, 17, 1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiao, W.; Hagler, G.; Williams, R.; Sharpe, R.; Brown, R.; Garver, D.; Judge, R.; Caudill, M.; Rickard, J.; Davis, M. Community Air Sensor Network (CAIRSENSE) project: Evaluation of low-cost sensor performance in a suburban environment in the southeastern United States. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 5281–5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sousan, S.; Koehler, K.; Hallett, L.; Peters, T.M. Evaluation of consumer monitors to measure particulate matter. J. Aerosol Sci. 2017, 107, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutschow, W. Participatory Community Air Monitoring: Using AirBeams and Viewing Data on AirCasting.org. Available online: https://envhealthcenters.usc.edu/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/AirCasting_AirBeams_HowTo_USCEHC.pdf (accessed on 7 October 2019).
- Heimbinder, M.; Yap, R.; Lim, C.C. AirCasting.org Map. Available online: http://aircasting.org/fixed_map (accessed on 7 October 2019).
- Gutschow, W. A Day in the Life: A Community Science Air Monitoring Program. Available online: http://arcg.is/CXfen (accessed on 7 October 2019).
- Minkler, M.; Vásquez, V.B.; Tajik, M.; Petersen, D. Promoting environmental justice through community-based participatory research: The role of community and partnership capacity. Health Educ. Behav. Off. Publ. Soc. Public Health Educ. 2008, 35, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickenbacker, H.; Brown, F.; Bilec, M. Creating environmental consciousness in underserved communities: Implementation and outcomes of community-based environmental justice and air pollution research. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 47, 101473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, M.; Maurana, C.A. Building effective community—Academic partnerships to improve health: A qualitative study of perspectives from communities. Acad. Med. 2001, 76, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, S.; O’Fallon, L. The Emergence of Environmental Health Literacy—From Its Roots to Its Future Potential. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madrigal, D.S.; Salvatore, A.; Casillas, G.; Casillas, C.; Vera, I.; Eskenazi, B.; Minkler, M. Health in my community: Conducting and evaluating PhotoVoice as a tool to promote environmental health and leadership among Latino/a youth. Prog. Community Health Partnersh. Res. Educ. Action 2014, 8, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peréa, F.C.; Sayles, N.R.; Reich, A.J.; Koomas, A.; McMann, H.; Sprague Martinez, L.S. “Mejorando Nuestras Oportunidades”: Engaging Urban Youth in Environmental Health Assessment and Advocacy to Improve Health and Outdoor Play Spaces. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bloom, B.S. Taxonomy of educational objectives. Vol. 1: Cognitive domain. N. Y. Mckay 1956, 1, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Sadd, J.; Morello-Frosch, R.; Pastor, M.; Matsuoka, M.; Prichard, M.; Carter, V. The truth, the whole truth, and nothing but the ground-truth: Methods to advance environmental justice and researcher–community partnerships. Health Educ. Behav. 2014, 41, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinberg, S.; Williams, R.; Hagler, G.S.; Rickard, J.; Brown, R.; Garver, D.; Harshfield, G.; Stauffer, P.; Mattson, E.; Judge, R. Long-term evaluation of air sensor technology under ambient conditions in Denver, Colorado. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 4605–4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Youth * | Organization | Minutes | Mean PM2.5 (μg/m3) | Standard Deviation (μg/m3) | % of Time PM2.5 Exposure >12 μg/m3 ** | Minimum (μg/m3) | Maximum (μg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | CBE | 7547 | 8.55 | 13.52 | 11.1 | 0.59 | 96.62 |
| B | SCYLC | 7677 | 8.25 | 7.64 | 17.1 | 0.77 | 92.36 |
| C | CBE | 8111 | 6.02 | 10.21 | 12.8 | 0.54 | 62.05 |
| D | CBE | 5686 | 8.00 | 9.08 | 19.3 | 0.61 | 110.09 |
| E | CBE | 15,002 | 17.97 | 33.43 | 33.2 | 0.55 | 186.85 |
| F | CBE | 7853 | 15.89 | 17.58 | 45.2 | 0.54 | 120.96 |
| G | PYA | 12,382 | 8.99 | 11.10 | 13.6 | 0.77 | 89.14 |
| H | CBE | 8779 | 7.23 | 9.75 | 10.2 | 0.74 | 114.99 |
| I | PYA | 14,748 | 13.10 | 21.83 | 22.9 | 0.98 | 128.82 |
| J | PYA | 6932 | 4.59 | 2.54 | 2.1 | 1.24 | 50.43 |
| All | 94,717 | 10.73 | 18.82 | 20.0 | 0.54 | 186.85 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Johnston, J.E.; Juarez, Z.; Navarro, S.; Hernandez, A.; Gutschow, W. Youth Engaged Participatory Air Monitoring: A ‘Day in the Life’ in Urban Environmental Justice Communities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010093
Johnston JE, Juarez Z, Navarro S, Hernandez A, Gutschow W. Youth Engaged Participatory Air Monitoring: A ‘Day in the Life’ in Urban Environmental Justice Communities. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(1):93. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010093
Chicago/Turabian StyleJohnston, Jill E., Zully Juarez, Sandy Navarro, Ashley Hernandez, and Wendy Gutschow. 2020. "Youth Engaged Participatory Air Monitoring: A ‘Day in the Life’ in Urban Environmental Justice Communities" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 1: 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010093
APA StyleJohnston, J. E., Juarez, Z., Navarro, S., Hernandez, A., & Gutschow, W. (2020). Youth Engaged Participatory Air Monitoring: A ‘Day in the Life’ in Urban Environmental Justice Communities. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(1), 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010093





