Assessing the Perceived Exertion in Elite Soccer Players during Official Matches According to Situational Factors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Perceived Exertion (PE)
2.4. Statistical Procedures
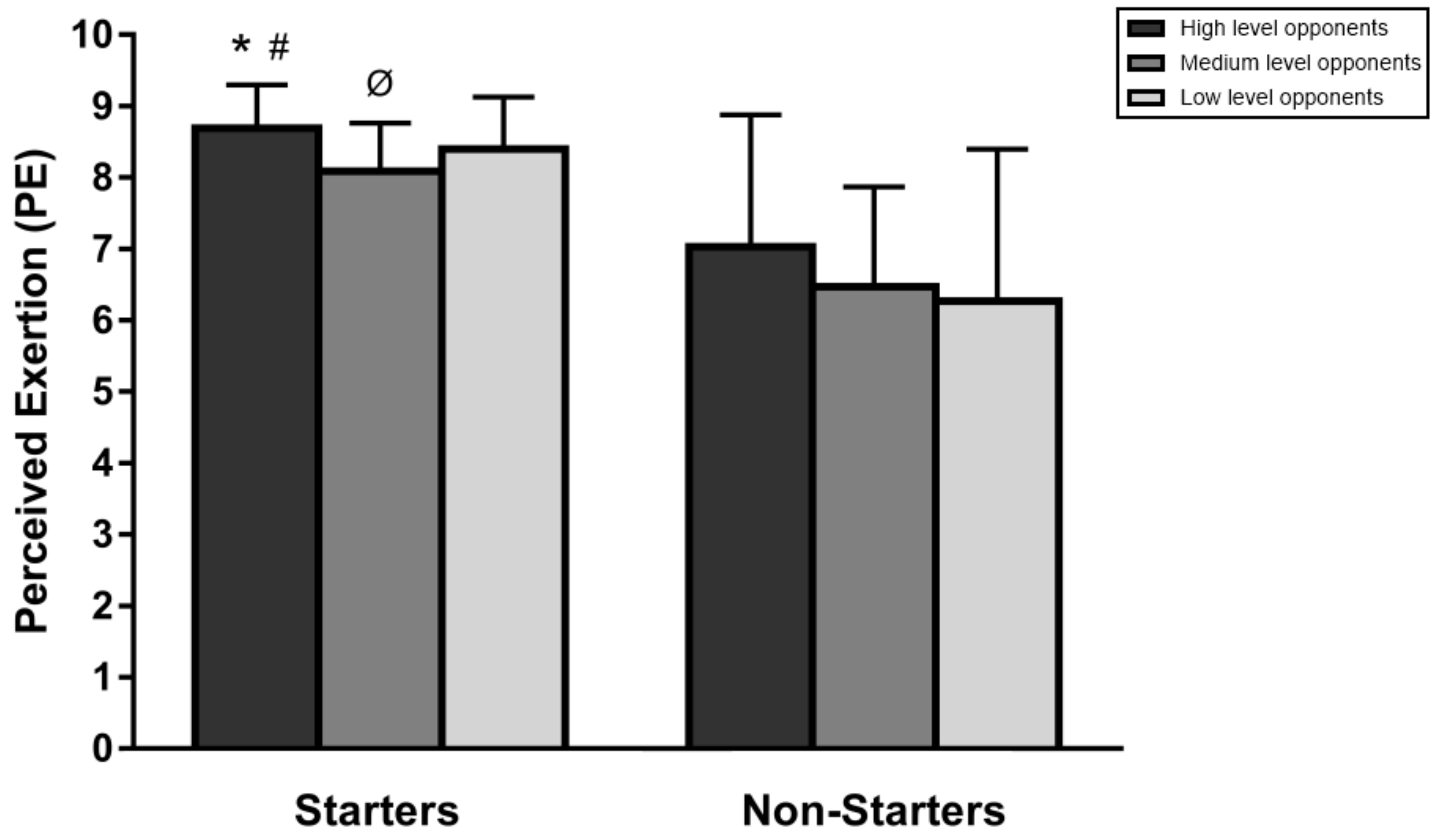
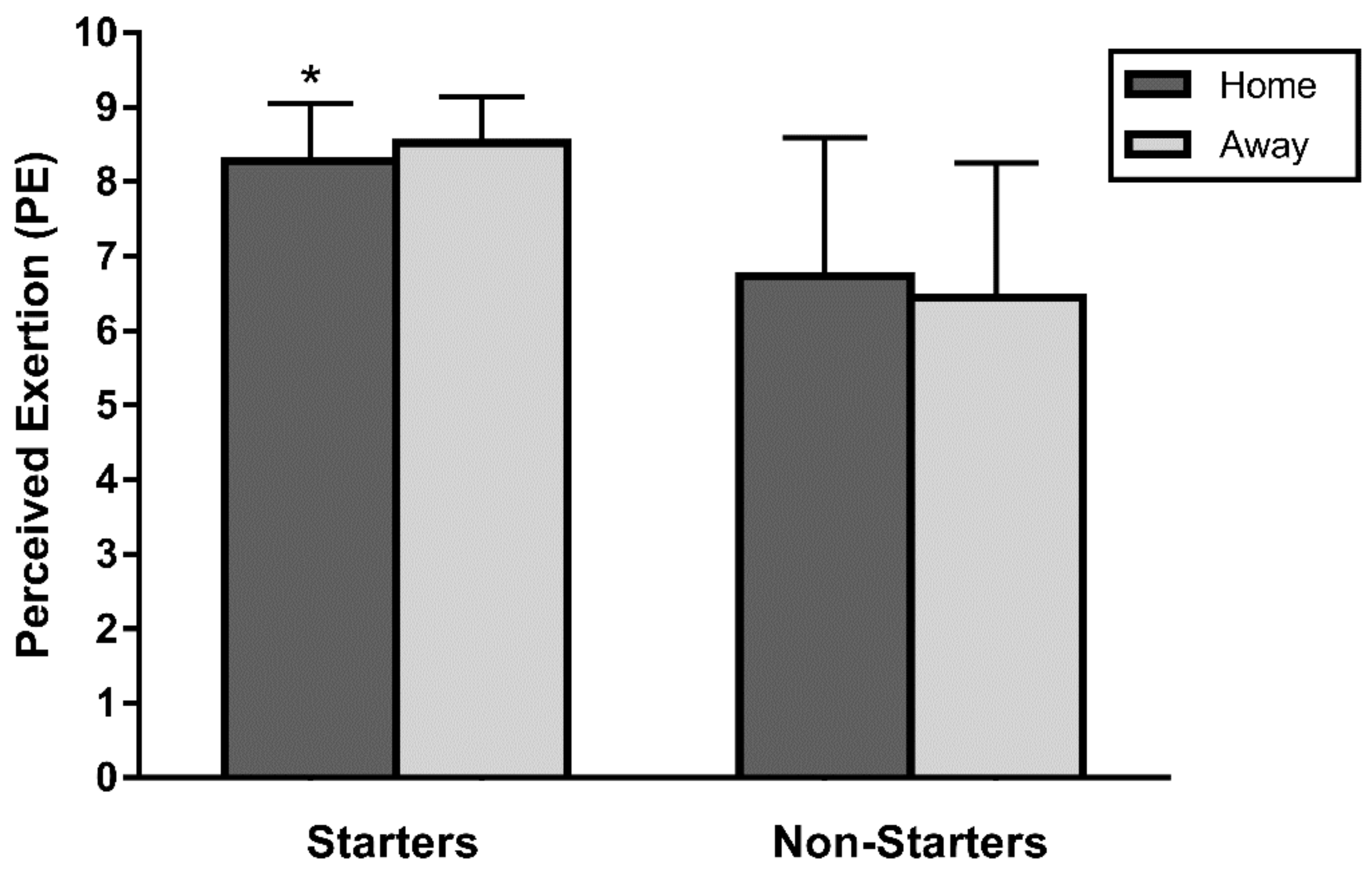
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reilly, T. An ergonomics model of the soccer training process. J. Sports Sci. 2005, 23, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, C.; Archer, D.; Hogg, B.; Bush, M.; Bradley, P. The evolution of physical and technical performance parameters in the English Premier League. Int. J. Sports Med. 2014, 35, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoff, J.; Wisløff, U.; Engen, L.C.; Kemi, O.J.; Helgerud, J. Soccer specific aerobic endurance training. Br. J. Sports Med. 2002, 36, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangsbo, J.; Mohr, M.; Krustrup, P. Physical and metabolic demands of training and match-play in the elite football player. J. Sports Sci. 2006, 24, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmento, H.; Marcelino, R.; Anguera, M.T.; CampaniÇo, J.; Matos, N.; LeitÃo, J.C. Match analysis in football: A systematic review. J. Sports Sci. 2014, 32, 1831–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castellano, J.; Blanco-Villaseñor, A.; Álvarez, D. Contextual variables and time-motion analysis in soccer. Int. J. Sports Med. 2011, 32, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castellano, J.; Alvarez-Pastor, D.; Bradley, P.S. Evaluation of research using computerised tracking systems (Amisco® and Prozone®) to analyse physical performance in elite soccer: A systematic review. Sport. Med. 2014, 44, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, G.A. Perceived exertion: A note on “history” and methods. Med. Sci. Sports 1973, 5, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Los Arcos, A.; Yanci, J.; Mendiguchia, J.; Gorostiaga, E.M. Rating of muscular and respiratory perceived exertion in professional soccer players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 3280–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexiou, H.; Coutts, A.J. A comparison of methods used for quantifying internal training load in women soccer players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2008, 3, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casamichana, D.; Castellano, J.; Calleja-Gonzalez, J.; San Román, J.; Castagna, C. Relationship between indicators of training load in soccer players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, B.R.; Lockie, R.G.; Knight, T.J.; Clark, A.C.; Janse de Jonge, X.A.K. A comparison of methods to quantify the in-season training load of professional soccer players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2013, 8, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Los Arcos, A.; Méndez-Villanueva, A.; Yanci, J.; Martínez-Santos, R. Respiratory and muscular perceived exertion during official games in professional soccer players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2016, 11, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, J.; Hertzog, M.; Nassis, G.P. Do match-related contextual variables influence training load in highly trained soccer players? J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azcárate, U.; Yanci, J.; Los Arcos, A. Influence of match playing time and the length of the between-match microcycle in Spanish professional soccer players’ perceived training load. Sci. Med. Footb. 2018, 2, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fessi, M.S.; Moalla, W. Post-match perceived exertion, feeling and wellness in professional soccer players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2018, 26, 262–275. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo, D.; Castagna, C.; Cámara, J.; Iturricastillo, A.; Yanci, J. Influence of team’s rank on soccer referees’ external and internal match loads during official matches. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018, 32, 1715–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, M.; Siegler, J.; Bahnert, A.; McBrien, J.; Lovell, R. The application of differential ratings of perceived exertion to Australian Football League matches. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2015, 18, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foster, C.; Florhaug, J.A.; Franklin, J.; Gottschall, L.; Hrovatin, L.A.; Parker, S.; Doleshal, P.; Dodge, C. A new approach to monitoring exercise training. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2001, 15, 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- Arcos, A.L.; Martínez-Santos, R.; Yanci, J.; Mendiguchia, J.; Méndez-Villanueva, A. Negative associations between perceived training load, volume and changes in physical fitness in professional soccer players. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2015, 14, 394–401. [Google Scholar]
- Algrøy, E.A.; Hetlelid, K.J.; Seiler, S.; Stray Pedersen, J.I. Quantifying training intensity distribution in a group of Norwegian professional soccer players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2011, 6, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Hillsdale, N.J., Ed.; L. Erlbaum Associates: New York, NY, USA, 1988; ISBN 9780805802832. [Google Scholar]
- Wrigley, R.; Drust, B.; Stratton, G.; Scott, M.; Gregson, W. Quantification of the typical weekly in-season training load in elite junior soccer players. J. Sports Sci. 2012, 30, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalen, T.; Lorås, H. Monitoring training and match physical load in junior soccer players: Starters versus substitutes. Sports 2019, 7, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Los Arcos, A.; Mendez-Villanueva, A.; Martínez-Santos, R. In-season training periodization of professional soccer players. Biol. Sport 2017, 34, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carling, C.; Bradley, P.; McCall, A.; Dupont, G. Match-to-match variability in high-speed running activity in a professional soccer team. J. Sports Sci. 2016, 34, 2215–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, M.D.; Archer, D.T.; Hogg, R.; Bradley, P.S. Factors influencing physical and technical variability in the English Premier League. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2015, 10, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregson, W.; Drust, B.; Atkinson, G.; Salvo, V. Match-to-match variability of high-speed activities in premier league soccer. Int. J. Sports Med. 2010, 31, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raya-González, J.; Castillo, D.; Yanci, J.; Los Arcos, A. Assessing the Perceived Exertion in Elite Soccer Players during Official Matches According to Situational Factors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17020410
Raya-González J, Castillo D, Yanci J, Los Arcos A. Assessing the Perceived Exertion in Elite Soccer Players during Official Matches According to Situational Factors. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(2):410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17020410
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaya-González, Javier, Daniel Castillo, Javier Yanci, and Asier Los Arcos. 2020. "Assessing the Perceived Exertion in Elite Soccer Players during Official Matches According to Situational Factors" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 2: 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17020410
APA StyleRaya-González, J., Castillo, D., Yanci, J., & Los Arcos, A. (2020). Assessing the Perceived Exertion in Elite Soccer Players during Official Matches According to Situational Factors. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(2), 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17020410







