Association between Area-Level Socioeconomic Deprivation and Prehospital Delay in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients: An Ecological Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Setting
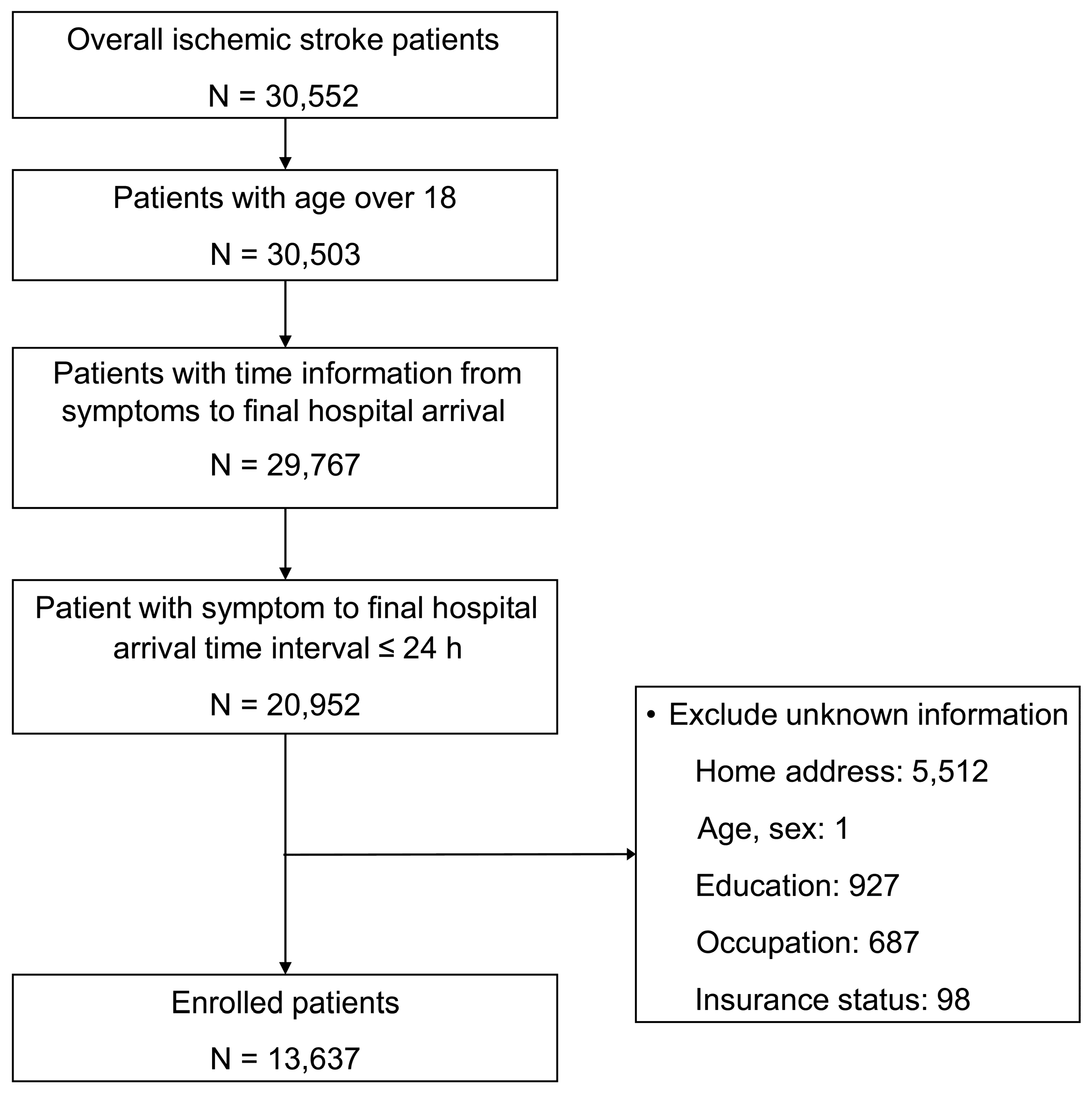
2.2. Study Participants
2.3. Data Collection
2.3.1. Area-Level Socioeconomic Index
2.3.2. Individual-Level Socioeconomic Variables
2.3.3. Patient Characteristics
2.3.4. Outcome Variables
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethical Approval
3. Results
3.1. Participants’ Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Correlation between Area-Level and Individual-Level SES
3.3. Associations between Area-Level SES and Prehospital Delay
3.4. Stratified Analysis by Urbanization Status
4. Discussion
5. Strength and Limitation of the Study
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mukherjee, D.; Patil, C.G. Epidemiology and the global burden of stroke. World Neurosurg. 2011, 76, S85–S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marler, J.R.; Tilley, B.C.; Lu, M.; Brott, T.G.; Lyden, P.C.; Grotta, J.C.; Broderick, J.P.; Levine, S.R.; Frankel, M.P.; Horowitz, S.H.; et al. Early stroke treatment associated with better outcome: The NINDS rt-PA stroke study. Neurology 2000, 55, 1649–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroke Unit Trialists Collaboration. How do stroke units improve patient outcomes? A collaborative systematic review of the randomized trials. Stroke 1997, 28, 2139–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 333, 1581–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleindorfer, D.; Lindsell, C.J.; Brass, L.; Koroshetz, W.; Broderick, J.P. National US estimates of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator use: ICD-9 codes substantially underestimate. Stroke 2008, 39, 924–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleindorfer, D.; de los Rios La Rosa, F.; Khatri, P.; Kissela, B.; Mackey, J.; Adeoye, O. Temporal trends in acute stroke management. Stroke 2013, 44, S129–S131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abilleira, S.; Lucente, G.; Ribera, A.; Permanyer-Miralda, G.; Gallofré, M. Patient-related features associated with a delay in seeking care after stroke. Eur. J. Neurol. 2011, 18, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macleod, M.R.; Lewis, S.C.; Dennis, M.S. Effect of deprivation on time to hospital in acute stroke. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2003, 74, 545–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cox, A.M.; McKevitt, C.; Rudd, A.G.; Wolfe, C.D.A. Socioeconomic status and stroke. Lancet Neurol. 2006, 5, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, M.; Glader, E.-L.; Norrving, B.; Stegmayr, B.; Asplund, K. Acute stroke alert activation, emergency service use, and reperfusion therapy in Sweden. Brain Behav. 2017, 7, e00654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iosif, C.; Papathanasiou, M.; Staboulis, E.; Gouliamos, A. Social factors influencing hospital arrival time in acute ischemic stroke patients. Neuroradiology 2012, 54, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niklasson, A.; Herlitz, J.; Jood, K. Socioeconomic disparities in prehospital stroke care. Scand. J. Trauma Resusc. Emerg. Med. 2019, 27, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleindorfer, D.O.; Lindsell, C.J.; Broderick, J.P.; Flaherty, M.L.; Woo, D.; Ewing, I.; Schmit, P.; Moomaw, C.; Alwell, K.; Pancioli, A.; et al. Community socioeconomic status and prehospital times in acute stroke and transient ischemic attack: Do poorer patients have longer delays from 911 call to the emergency department? Stroke 2006, 37, 1508–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, M.; Imtiyaz, I. Social Impact of Urbanization on the Institution of Family in Kashmir: A Study of Srinagar City. Communications 2016, 24, 109. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.A.; Ahn, K.O.; Shin, S.D.; Cha, W.C.; Ro, Y.S. The Effect of Emergency Medical Service Use and Inter-hospital Transfer on Prehospital Delay among Ischemic Stroke Patients: A Multicenter Observational Study. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2016, 31, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics Korea. 10% Sample of 2010 Population and Housing Census. MDIS, RAS. 20190215 Provided. Available online: http://mdis.kostat.go.kr (accessed on 19 July 2019).
- Choi, M.H.; Cheong, K.S.; Cho, B.M.; Hwang, I.K.; Kim, C.H.; Kim, M.H.; Hwang, S.S.; Lim, J.H.; Yoon, T.H. Deprivation and mortality at the town level in Busan, Korea: An ecological study. J. Prev. Med. Public Health 2011, 44, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benach, J.; Yasui, Y.; Borrell, C.; Sáez, M.; Pasarin, M.I. Material deprivation and leading causes of death by gender: Evidence from a nationwide small area study. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2001, 55, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics Korea. Korean Standard Statistical Classification [Internet]. Classification of Occupations. Available online: https://kssc.kostat.go.kr:8443/ksscNew_web/ekssc/main/main.do (accessed on 19 July 2019).
- Emerson, E.; Hatton, C.; Robertson, J.; Baines, S. The association between non-standard employment, job insecurity and health among British adults with and without intellectual impairments: Cohort study. SSM Popul. Health 2018, 4, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, W.J.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Ackerson, T.; Adeoye, O.M.; Bambakidis, N.C.; Becker, K.; Biller, J.; Brown, M.; Demaerschalk, B.M.; Hoh, B.; et al. 2018 guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: A guideline for healthcare professionals from the american heart association/american stroke association. Stroke 2018, 49, e46–e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addo, J.; Ayerbe, L.; Mohan, K.M.; Crichton, S.; Sheldenkar, A.; Chen, R.; Wolfe, C.D.; McKevitt, C. Socioeconomic status and stroke: An updated review. Stroke 2012, 43, 1186–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carstairs, V.; Morris, R. Deprivation and mortality: An alternative to social class? Community Med. 1989, 11, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kothari, R.; Sauerbeck, L.; Jauch, E.; Broderick, J.; Brott, T. Patients’ awareness of stroke signs, symptoms, and risk factors. Stroke 1997, 28, 1871–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, A.T.; Pancioli, A.M.; Khoury, J.C.; Rademacher, E.; Tuchfarber, A.; Miller, R.; Woo, D.; Kissela, B.; Broderick, J.P. Trends in community knowledge of the warning signs and risk factors for stroke. JAMA 2003, 289, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barsan, W.G.; Brott, T.G.; Broderick, J.P.; Haley, E.C.; Levy, D.E.; Marler, J.R. Time of hospital presentation in patients with acute stroke. Arch. Intern. Med. 1993, 153, 2558–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kothari, R.; Jauch, E.; Broderick, J.; Brott, T.; Sauerbeck, L.; Khoury, J.; Liu, T. Acute stroke: Delays to presentation and emergency department evaluation. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1999, 33, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, C.R.; Suh, D.C.; Bueno, M.; Kostis, J.B. Delay in presentation and evaluation for acute stroke: Stroke Time Registry for Outcomes Knowledge and Epidemiology (S.T.R.O.K.E.). Stroke 2001, 32, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Total | Affluent | Middle | Deprived | p | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | ||
| 13,637 | 4489 | 4615 | 4533 | ||||||
| Sex (female) | 7822 | 57.4 | 2637 | 58.7 | 2665 | 57.7 | 2520 | 55.6 | 0.01 |
| Age group (years) | <0.001 | ||||||||
| 19–40 | 352 | 2.58 | 141 | 3.14 | 126 | 2.73 | 85 | 1.88 | |
| 40–65 | 4290 | 31.5 | 1614 | 36.0 | 1471 | 31.9 | 1205 | 26.6 | |
| ≥65 | 8995 | 66.0 | 2734 | 60.9 | 3018 | 65.4 | 3243 | 71.5 | |
| Education level | <0.001 | ||||||||
| Below high school | 8228 | 60.3 | 2282 | 50.8 | 2615 | 56.7 | 3331 | 73.5 | |
| ≥High school graduate | 5409 | 39.7 | 2207 | 49.2 | 2000 | 43.3 | 1202 | 26.5 | |
| Occupation type | <0.001 | ||||||||
| Non-manual | 565 | 4.14 | 226 | 5.03 | 220 | 4.77 | 119 | 2.63 | |
| Manual | 3656 | 26.8 | 1138 | 25.4 | 1052 | 22.8 | 1466 | 32.3 | |
| Other | 1834 | 13.4 | 626 | 13.9 | 739 | 16.0 | 469 | 10.3 | |
| Inactive | 7582 | 55.6 | 2499 | 55.7 | 2604 | 56.4 | 2479 | 54.7 | |
| Insurance type | <0.001 | ||||||||
| National Health Insurance | 12,953 | 95.0 | 4322 | 96.3 | 4373 | 94.8 | 4258 | 93.9 | |
| Medicaid | 684 | 5.02 | 167 | 3.72 | 242 | 5.24 | 275 | 6.07 | |
| Past medical history | |||||||||
| Diabetes | 3521 | 25.8 | 1224 | 27.3 | 1245 | 27.0 | 1052 | 23.2 | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 7985 | 58.6 | 2694 | 60.0 | 2760 | 59.8 | 2531 | 55.8 | <0.001 |
| Cardiovascular disease | 2689 | 19.7 | 879 | 19.6 | 978 | 21.2 | 832 | 18.4 | <0.001 |
| Exercise (yes) | 2673 | 19.6 | 972 | 21.7 | 984 | 21.3 | 717 | 15.8 | <0.001 |
| Smoker | 0.12 | ||||||||
| No | 8020 | 58.8 | 2646 | 58.9 | 2652 | 57.5 | 2722 | 60.0 | |
| Former | 2248 | 16.5 | 732 | 16.3 | 803 | 17.4 | 713 | 15.7 | |
| Current | 3369 | 24.7 | 1111 | 24.7 | 1160 | 25.1 | 1098 | 24.2 | |
| Alcohol consumption | 0.02 | ||||||||
| Never | 9320 | 68.3 | 2998 | 66.8 | 3200 | 69.3 | 3122 | 68.9 | |
| Yes | 4317 | 31.7 | 1491 | 33.2 | 1415 | 30.7 | 1411 | 31.1 | |
| Onset | 0.03 | ||||||||
| Day | 9105 | 66.8 | 3063 | 68.2 | 3037 | 65.8 | 3005 | 66.3 | |
| Night | 4532 | 33.2 | 1426 | 31.8 | 1578 | 34.2 | 1528 | 33.7 | |
| Loss of consciousness | 2237 | 16.4 | 654 | 14.6 | 723 | 15.7 | 860 | 19.0 | <0.001 |
| Recognition of symptoms | 11,319 | 83.0 | 3662 | 81.6 | 3767 | 81.6 | 3890 | 85.8 | <0.001 |
| EMS use | 9232 | 67.7 | 3014 | 67.1 | 2938 | 63.7 | 3280 | 72.4 | <0.001 |
| Interhospital transfer | 4052 | 29.7 | 1086 | 24.2 | 1032 | 22.4 | 1934 | 42.7 | <0.001 |
| Prehospital delay | 8096 | 59.4 | 2557 | 57.0 | 2699 | 58.5 | 2840 | 62.7 | <0.001 |
| ED outcome | <0.001 | ||||||||
| Discharge | 264 | 1.94 | 78 | 1.74 | 112 | 2.43 | 74 | 1.63 | |
| Transfer | 417 | 3.06 | 85 | 1.89 | 109 | 2.36 | 223 | 4.92 | |
| Admission | 12,916 | 94.7 | 4314 | 96.1 | 4383 | 95.0 | 4219 | 93.1 | |
| Death | 27 | 0.20 | 7 | 0.16 | 6 | 0.13 | 14 | 0.31 | |
| Unknown | 13 | 0.10 | 5 | 0.11 | 5 | 0.11 | 3 | 0.07 | |
| Residence | <0.001 | ||||||||
| Urban | 8463 | 62.1 | 3637 | 81.0 | 3519 | 76.3 | 1307 | 28.8 | |
| Rural | 5174 | 37.9 | 852 | 19.0 | 1096 | 23.7 | 3226 | 71.2 | |
| Variable | Total | Affluent | Middle | Deprived | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total patients | |||||
| Symptom onset to final hospital (hours) | 4.3 (1.7–10.4) | 4.0 (1.4–10.0) | 4.2 (1.4–10.6) | 4.6 (2.0–10.8) | <0.001 |
| Patients who were transferred | |||||
| Symptom onset to first hospital (hours) | 2.9 (1.0–8.8) | 3.0 (1.0–8.7) | 3.0 (1.0–9.2) | 2.8 (1.0–8.4) | 0.03 |
| Patients who used EMS | |||||
| Symptom onset to call (min) | 60 (12–288) | 52 (10–261) | 60 (12–282) | 67 (15–349) | 0.04 |
| Call to EMS arrival (min) | 6 (4–10) | 7 (5–10) | 5 (4–8) | 6 (4–10) | <0.001 |
| Call to hospital arrival (min) | 32 (24–48) | 33 (25–46) | 30 (23–40) | 40 (26–66) | <0.001 |
| Variable | Unadjusted | Basic | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p | Model | p | aOR | 95% CI | p | aOR | 95% CI | p | aOR | 95% CI | p | |
| Fixed effects | ||||||||||||||
| Area-level SES (Affluent) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||
| Middle | 1.06 | (0.98–1.16) | 0.14 | 1.01 | (0.85–1.18) | 0.95 | 1.04 | (0.90–1.20) | 0.62 | |||||
| Deprived | 1.27 | (1.17–1.38) | <0.01 | 1.25 | (1.08–1.45) | 0.003 | 1.03 | (0.89–1.20) | 0.7 | |||||
| Individual-level SES | ||||||||||||||
| High school graduate (below high school) | 0.88 | (0.82–0.95) | <0.01 | 0.91 | (0.84–0.98) | 0.02 | 0.92 | (0.86–1.00) | 0.04 | 0.93 | (0.85–1.32) | 0.07 | ||
| Occupation (non-manual) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Manual | 1.14 | (0.95–1.36) | 0.15 | 1.09 | (0.90–1.30) | 0.39 | 1.08 | (0.90–1.29) | 0.4299 | 1.09 | (0.90–1.32) | 0.39 | ||
| Other | 1.00 | (0.83–1.21) | 1.00 | 0.95 | (0.78–1.16) | 0.61 | 0.96 | (0.78–1.16) | 0.64 | 1.04 | (0.84–1.27) | 0.73 | ||
| Inactive | 1.12 | (0.94–1.33) | 0.20 | 1.07 | (0.90–1.28) | 0.44 | 1.07 | (0.90–1.29) | 0.44 | 1.17 | (0.97–1.42) | 0.11 | ||
| National Health Insurance (Medicaid) | 0.99 | (0.84–1.16) | 0.88 | 1.00 | (0.85–1.18) | 1.00 | 1.01 | (0.86–1.18) | 0.93 | 0.94 | (0.79–1.11) | 0.45 | ||
| Covariates | ||||||||||||||
| EMS use (no) | 0.32 | (0.30–0.35) | <0.001 | 0.39 | (0.36–0.42) | <0.001 | ||||||||
| Interhospital transfer (no) | 2.29 | (2.11–2.48) | <0.001 | 1.85 | (1.69–2.03) | <0.001 | ||||||||
| Age group (years) (19–39) | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||
| 40–65 | 1.12 | (0.90–1.40) | 0.30 | 1.13 | (0.90–1.43) | 0.31 | ||||||||
| ≥65 | 1.17 | (0.94–1.45) | 0.15 | 1.29 | (1.01–1.63) | 0.04 | ||||||||
| Male (female) | 0.99 | (0.92–1.06) | 0.70 | |||||||||||
| Previous diabetes (no) | 1.21 | (1.12–1.31) | <0.001 | 1.25 | (1.14–1.35) | <0.001 | ||||||||
| Previous hypertension (no) | 1.01 | (0.94–1.08) | 0.76 | |||||||||||
| Previous cardiovascular disease (no) | 0.79 | (0.74–0.85) | <0.001 | 0.83 | (0.77–0.90) | <0.001 | ||||||||
| Exercise (no) | 0.88 | (0.81–0.96) | <0.001 | 0.92 | (0.83–1.01) | 0.08 | ||||||||
| Smoker (never) | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Former | 1.08 | (1.00–1.18) | 0.05 | |||||||||||
| Current | 0.99 | (0.90–1.09) | 0.79 | |||||||||||
| Alcohol consumption (never) | 1.05 | (0.80–0.92) | 0.21 | |||||||||||
| Onset (day) | 0.86 | (0.80–0.92) | <0.001 | 0.85 | (0.79–0.92) | <0.001 | ||||||||
| Loss of consciousness (no) | 0.55 | (0.50–0.60) | <0.001 | 0.58 | (0.52–0.64) | <0.001 | ||||||||
| Recognition of symptoms (no) | 1.28 | (1.17–1.40) | <0.001 | 1.04 | (0.94–1.15) | 0.48 | ||||||||
| Urbanization | 0.74 | (0.69–0.80) | <0.001 | 0.90 | (0.78–1.04) | 0.17 | ||||||||
| Random effects | ||||||||||||||
| Area-level variance | 0.147 | <0.001 | 0.143 | <0.001 | 0.133 | <0.001 | 0.08 | <0.001 | ||||||
| Intraclass correlation | 4.27 | 4.15 | 3.88 | 2.37 | ||||||||||
| AUC | 0.599 | (0.599–0.609) | 0.599 | (0.589–0.608) | 0.693 | (0.684–0.702) | ||||||||
| AUC change | <0.001 | 0.095 | ||||||||||||
| Model fitness | ||||||||||||||
| AIC | 18,310.3 | 18,308.2 | 18,300.6 | 17,104.3 | ||||||||||
| BIC | 18,317.1 | 18,332.2 | 18,331.4 | 17,172.7 | ||||||||||
| Variable | Urban | Rural | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aOR | 95% CI | p | aOR | 95% CI | p | |
| Fixed effects | ||||||
| Area-level SES (Affluent) | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Middle | 1.06 | (0.92–1.22) | 0.41 | 1.26 | (0.88–1.79) | 0.21 |
| Deprived | 1.24 | (1.04–1.47) | 0.02 | 1.04 | (0.78–1.38) | 0.81 |
| Individual-level SES | ||||||
| High school graduate (below high school) | 0.92 | (0.83–1.01) | 0.09 | 0.95 | (0.81–1.11) | 0.49 |
| Occupation (non-manual) | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Manual | 1.25 | (1.00–1.56) | 0.048 | 0.68 | (0.45–1.02) | 0.06 |
| Other | 1.21 | (0.95–1.53) | 0.12 | 0.64 | (0.41–0.99) | 0.046 |
| Inactive | 1.35 | (1.08–1.69) | 0.01 | 0.72 | (0.47–1.08) | 0.11 |
| National Health Insurance (Medicaid) | 1.03 | (0.82–1.28) | 0.83 | 0.83 | (0.64–1.07) | 0.15 |
| Covariates | ||||||
| EMS use (no) | 0.38 | (0.35–0.42) | <0.001 | 0.42 | (0.37–0.49) | <0.001 |
| Interhospital transfer (no) | 2.12 | (1.86–2.42) | <0.001 | 1.56 | (1.36–1.78) | <0.001 |
| Age group (years) (19–40) | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 40–65 | 1.12 | (0.85–1.48) | 0.44 | 1.17 | (0.76–1.81) | 0.48 |
| ≥65 | 1.22 | (0.92–1.62) | 0.18 | 1.46 | (0.94–2.28) | 0.09 |
| Previous diabetes (no) | 1.28 | (1.15–1.42) | <0.001 | 1.2 | (1.04–1.39) | 0.01 |
| Previous cardiovascular disease (no) | 0.84 | (0.76–0.92) | <0.001 | 0.84 | (0.73–0.95) | 0.01 |
| Exercise (no) | 0.94 | (0.84–1.06) | 0.31 | 0.88 | (0.73–1.05) | 0.15 |
| Onset (day) | 0.76 | (0.69–0.83) | <0.001 | 1.02 | (0.90–1.16) | 0.79 |
| Loss of consciousness (no) | 0.54 | (0.47–0.62) | <0.001 | 0.63 | (0.53–0.74) | <0.001 |
| Recognition of symptoms (no) | 1.12 | (0.98–1.28) | 0.1 | 0.89 | (0.75–1.06) | 0.19 |
| Random effects | ||||||
| Area-level variance | 0.03 | <0.05 | 0.16 | <0.001 | ||
| Intraclass correlation | 0.76 | 4.57 | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, H.A.; Lee, H.A.; Park, J.O. Association between Area-Level Socioeconomic Deprivation and Prehospital Delay in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients: An Ecological Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207392
Park HA, Lee HA, Park JO. Association between Area-Level Socioeconomic Deprivation and Prehospital Delay in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients: An Ecological Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(20):7392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207392
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Hang A, Hye Ah Lee, and Ju Ok Park. 2020. "Association between Area-Level Socioeconomic Deprivation and Prehospital Delay in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients: An Ecological Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 20: 7392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207392
APA StylePark, H. A., Lee, H. A., & Park, J. O. (2020). Association between Area-Level Socioeconomic Deprivation and Prehospital Delay in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients: An Ecological Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(20), 7392. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207392






