Abstract
Naturally occurring 210Pb and artificial 137Cs fallouts are widely used as radioactive tracers for the determination of water-induced soil erosion for different time scales equal to 50 and 100 years, respectively. There exist several calibration models useful to convert the variation of the inventory of these radiotracers in cultivated soil compared to its value on non-disturbed soil to a soil erosion rate. The most comprehensive calibration models are based on a mass balance approach. In the present work, a new calibration model is proposed. It consists on the generalization of the mass balance approach to a cultivated soil subject to two successive and continuous periods of cultivation. The proposed model combines 210Pb and 137Cs fallouts for the same time scale by relaxing the constraint on 210Pb fallout from being used for 100 years’ time scale. The model was applied successfully to hypothetical cases and can be used to measure soil erosion rates for practical cases. It is important to note that the proposed model has two main advantages. First, the complementarity between 210Pb and 137Cs fallouts is for the same time scale and not for different time scales, as usually considered and believed in this field. Second, 210Pb fallout is used for time scales less than 100 years. This makes the model useful to estimate soil erosion rates for two successive periods of cultivation. To the best knowledge of the authors, the combination of 210Pb and 137Cs fallouts for the determination of soil erosion rate variation due to change in cultivation practices for the same time scale has never been developed or applied in the past.
1. Introduction
Rates of soil loss from agricultural land and associated soil degradation are important requirements for a successful environmental management. Rates of soil loss are strongly related to longer-term sustainability of soil resources [1]. Fallouts of 137Cs and210Pb are widely used to estimate rates of soil loss in the landscape [2,3,4,5,6,7,8]. 137Cs is used to produce information on erosion rates over the past 50 years [9] and 210Pb fallout (or 210Pb excess, noted as 210Pbex) is used to provide information relating to a longer period of up to 100 years [10]. To the best knowledge of the authors, there exists only one published work estimating the change in erosion rate due to change of cultivation practices using radioactive fallouts [11]. In this work, the change of cultivation practice consisted on a shift from conventional tillage to non-tillage and the estimation of soil erosion rate change was based on 137Cs only and then was constrained to the time scale relative to 137Cs (50 years). In the present work,210Pbex and 137Cs are combined using a mass balance approach for the determination of the change in soil erosion rate due to the change in cultivation practices. Two successive and continuous periods of cultivations are assumed. To develop the model, it is necessary to relax the commonly adopted constraint on 210Pbex from being used for a period of 100 years. This allows for the formulation of a mass balance mathematical model using 210Pbex and relating its inventory at the year of measurement to the two values of erosion rates relative to the recent (after the change of cultivation practice) and the old (before the change of cultivation practice) period of cultivation. The recent period of cultivation is assumed to be comparable to 50 years. The old period can be less than 100 years. The developed mathematical model can be resolved without the need to write the corresponding complicated differential equations because each mathematical term in its solution has a clear physical meaning. This fact simplifies the use of the model in spite of the complexity of its mathematical formulation. The resolution of the model uses as input the value of the measured inventory of 210Pbex on the eroded location and its reference value (inventory of 210Pbexon a non-perturbed site). If the model has a mathematical solution then the output is the erosion rate value for the recent and the old period of cultivation. Otherwise, soil deposition happened during the old and/or the recent period of cultivation. This corresponds to five different cases where 210Pbex has to be combined with 137Cs for the same time scale (50 years) to allow for the resolution of the model and to produce the soil redistribution rate (erosion or deposition rates) for each of the two periods. The proposed model was tested successfully for different hypothetical cases and can be applied on practical measurement. To the best knowledge of the authors, the procedure described in this work, which permits the estimation of the variation of the redistribution rate associated with a change in cultivation practices, represents a novel application of 210Pbex and 137Cs measurements in soil erosion investigations. This model can be re-formulated for the case of non-cultivated soils or for the case of change from cultivation to non-cultivation practice or vice versa.
2. Materials and Methods
The basic form of the mass balance model for an eroding location is described in detail in [9,10]. Briefly, it consists on the following differential equation:
where is the time (y), the annual deposited flux (Bq m−2 y−1), (y−1) the decay constant of the radioactive tracer (y−1), the soil erosion rate (kg m−2 y−1), the plow depth (kg m−2), and the inventory (Bq m−2) of the radiotracer on the location at time (year of the measurement). This equation assumes only one time period of cultivation, during which soil was eroded by a rate (kg m−2 y−1) with a plow depth (kg m−2). If 137Cs is used to determine soil erosion rate, the mass balance approach provides an estimation of the erosion rate for a window of about 50 years because the onset of 137Cs fallout is at 1953. If 210Pbex is used, it is generally constrained to provide an estimation of erosion rate for a period of about 100 years. It is, however, possible to use 210Pbex for shorter time periods of cultivation if needed [9,12,13]. The solution of Equation (1) is:
in this equation represents the reference inventory. In case of 210Pbex, which is characterized by a constant flux , the reference inventory is equal to and Equation (2) becomes:
In Equation (3), it is assumed that cultivation begins at some year (y) (). The right-hand side of Equation (3) contains two terms. Their meaning is the following.
- Inventory of 210Pbex contained on the location before the beginning of cultivation decreased by radioactive decay and by soil erosion during the cultivation period .
- : Inventory of 210Pbex accumulated on the location during the cultivation period decreased by radioactive decay and by soil erosion.
It is important to note that each of these terms has a clear physical meaning and a specific expression. They can be written directly based on their meaning. This is very useful when dealing with multiple successive cultivation periods because it simplifies the development and the resolution of the relative complex mass balance model. In case of two successive and continuous cultivation periods, cultivation would begin from some year to some year with erosion rate and plow depth for the old cultivation period and from the year to the year of measurement () with erosion rate and plow depth for the recent cultivation period. The inventory of 210Pbex in this case can be expressed directly as follows.
All the terms at the right-hand side of Equation (4) are comprehensive, and this is the reason their expressions can be written directly. Their meaning is explained in the following.
- : Inventory of 210Pbex existing on the location before the beginning of cultivation decreased by radioactive decay and by soil erosion during the old and the recent time periods of cultivation.
- : Inventory of 210Pbex accumulated on the location during the old period of cultivation decreased by radioactive decay and by soil erosion during its accumulation along the old period and decreased during the recent period by radioactive decay and by soil erosion.
- : Inventory of 210Pbex accumulated on the location during the old time period of cultivation decreased by radioactive decay and by soil erosion during this period.
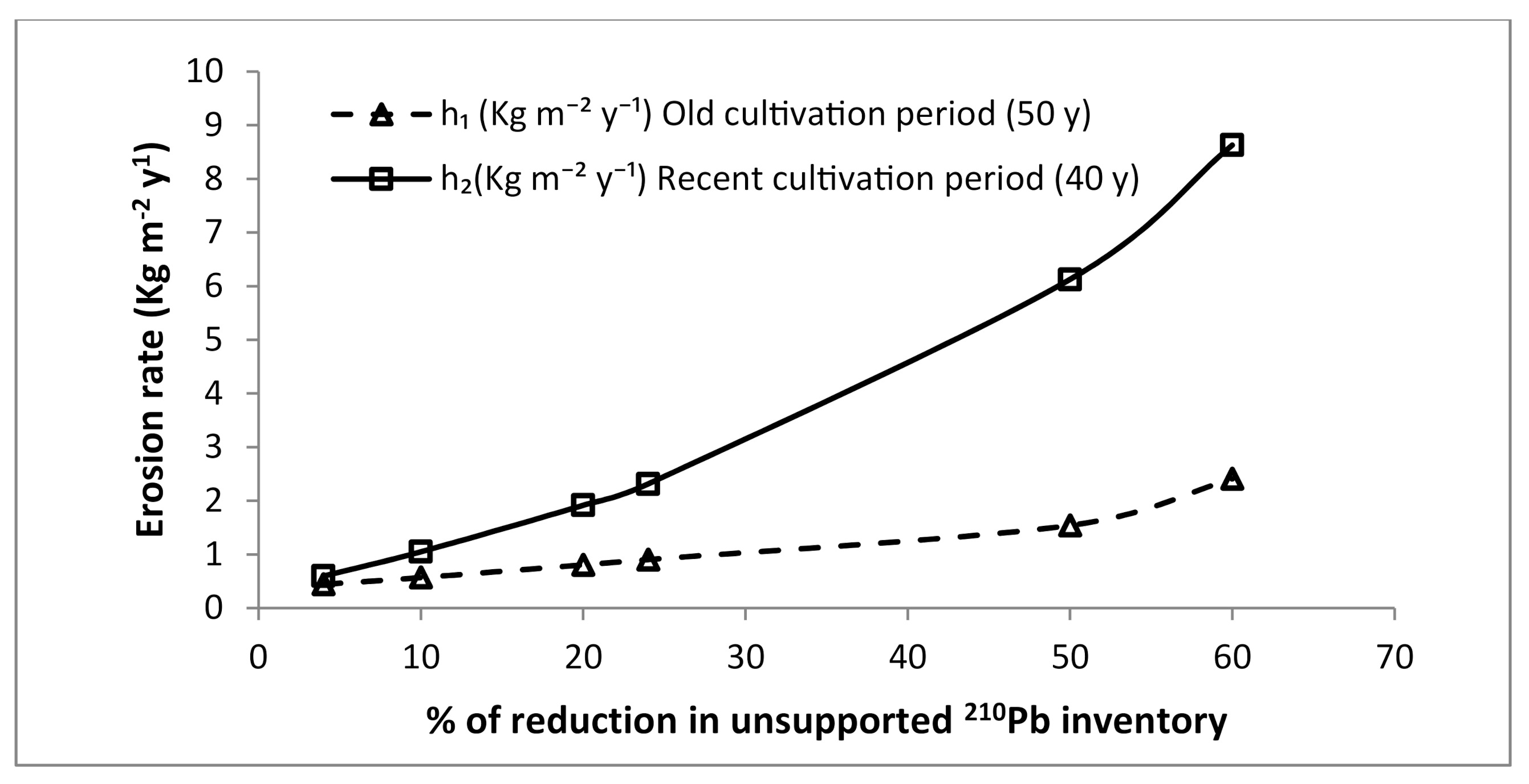
If during the two cultivation periods, only erosion happened on the location, 210Pbex is sufficient as radiotracer to determine the value of erosion rate during each period using Equation (4). Figure 1 illustrates the result of a numerical test of the model (Equation (4)). The figure shows the obtained relationships between soil erosion rate and the percentage reduction in 210Pbex inventory relative to the local reference inventory for a hypothetical eroding soil. The old and the recent period of cultivation are assumed equal to 50 and 40 years, respectively ( y and y). The following values of the employed relevant parameters were considered: kg m−2(plow depth of the old period), kg m−2 (plow depth of the recent period), and Bq m−2.
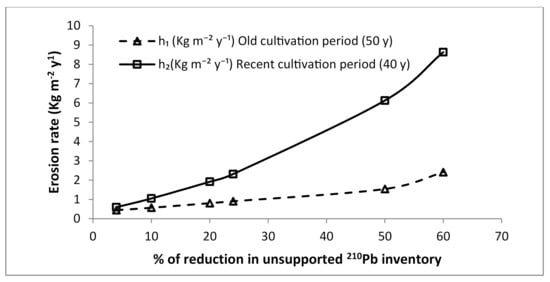
Figure 1.
Erosion rate as a function of percentage reduction in 210Pbex obtained using the mass balance model (Equation (4)) for a hypothetical eroding soil subject to two successive periods of continuous cultivation.
To resolve Equation (4), it is possible to assume that the values of erosion rates and are two unknown zeros of the function equal to the difference between the calculated inventory of 210Pbex and the measured inventory on the location. Excel software (Microsoft, Redmond, WA, United States), through its well-known Solver numerical tool, can be used to find these zeros which determine the values of erosion rates.
The previous studied case (Will be called case-0) where 210Pbex is sufficient as a radiotracer to determine the erosion rate of each cultivation period is not unique. There exist five other cases where 210Pbex alone is not sufficient to determine the redistribution rates and where another radiotracer has to be used. If the recent cultivation period is in the range 40–50 years or less, 137Cs would be the best candidate. If the measured inventory of 210Pbex on the location is less than the reference inventory and Equation (4) does not have a solution, this means that the location was subject to a deposition during one of the two periods of cultivation. This corresponds to two cases:
- Case 1: Deposition during the old period of cultivation and erosion during the recent period with reduction of 210Pbex inventory.
- Case 2: Erosion during the old period of cultivation and deposition during the recent period with reduction of 210Pbex inventory.
- If the measured inventory of210Pbex on the location is greater than the reference inventory, there could be deposition during the two periods of cultivation or deposition during only one period and/or erosion during the other. This corresponds to three cases:
- Case 3: Deposition during the old period of cultivation and erosion during the recent period with excess of 210Pbexinventory.
- Case 4: Erosion during the old period of cultivation and deposition during the recent period with excess of 210Pbexinventory.
- Case 5: Deposition during the old period of cultivation and deposition during the recent period with excess of 210Pbex inventory.
One may think that 210Pbex can be re-used (in place of 137Cs) with a mass balance approach restricted to the recent period of cultivation to provide the redistribution rate of the location during the old period. This, however, is not possible because the inventory of 210Pbex at the beginning of cultivation of the recent period is not known, since it was altered by the cultivation during the old period.
3. Results and Discussion
In the following, the combination of 210Pbex and 137Cs for the determination of the redistribution rate during the old and recent periods of cultivation is explained for each of the five described cases.
3.1. Case 1: Deposition during the Old Period of Cultivation and Erosion during the Recent Period with Reduction of 210PbexInventory
In this case,137Cs provides the value of erosion rate during the recent period using the usual mass balance approach corresponding to one period of cultivation (the recent period). can be used to determine 210Pbex inventory at the end of the old period of cultivation (at year ) by resolving the equation:
where is the measured inventory of 210Pbex on the location. It is important to note that Equation (5) is a 210Pbex mass balance model applied to the recent period and which uses the erosion rate produced by the use of 137Cs during a time period comparable to the time scale appropriate for the use of 137Cs. It is in that sense that the combination of 210Pbex and 137Cs for the same time scale is understood in the present approach. All the combination sof 210Pbex and 137Cs relative to each of the five different cases described previously are for the same time scale in that sense. As a numerical test of the model for this case, Table 1 shows the obtained erosion rate values for the recent period from the resolution of Equation (5) for three different hypothetical values of and . It is clear from the three examples illustrated in Table 1 that erosion rate during the recent period was sufficiently high to reduce the inventory.

Table 1.
Examples of possible values of the inventories , , and the erosion rates compatible with Equation (2), assuming is equal to 170 kg m−2.
The calculation procedure of the deposition rate during the old period is well known [9,10] and is described briefly here. It is based on the calculation of the concentration of 210Pbex in the mobilized sediment (Bq kg−1), which depends on the erosion of a proportion of the annually deposited 210Pb fallout from the eroding soil profile (from the up slope in general) prior to its incorporation by tillage, and on the removal of the accumulated fallout 210Pb that is stored in the plow layer. The knowledge of allows for the estimation of 210Pbex concentration of deposited sediment at year t’(y) on the location. The relation between and depends on the erosion rate and on the particle-size correction factor that reflects differences in grain-size compositions of mobilized and deposited sediment and is defined as the ratio of 210Pbex concentration of deposited sediment to that of the mobilized sediment. The correction factor is generally less than 1 [9].
The excess inventory of 210Pbex at the end of the old period of cultivation is equal to the subtraction of the reference inventory from the inventory determined from Equation (5). It is used to determine the deposition rate (kg m−2 y−1) according to Equation (6) [9,10].
3.2. Case 2: Erosion during the Old Period of Cultivation and Deposition during the Recent Period with Reduction of210PbexInventory
In this case, the combination of 137Cs and 210Pbex is as follows. The deposition rate is determined using 137Cs based on the knowledge of the erosion rate at the up slope of the transect (determined using 137Cs or 210Pbex, or both, depending on the situation). The 210Pbex inventory accumulated during the recent period of cultivation is determined using the equation [9,10]:
where is the 210Pbex concentration of deposited sediment at time t’(y) on the location determined using the concentration of 210Pbex on the mobilized sediment due to erosion at the up slope of the transect. The subtraction of from the measured inventory of210Pbex at the time of measurement increased by decay correction with the time length of the recent period (multiplied by ) provides the inventory of 210Pbex at the end of the old period. The inventory at the end of the old period should be less than the reference inventory because the soil was eroded during the recent period in the present case. Erosion rate during the old period is obtained by resolving the following mass balance equation restricted to the recent period.
The first term on the right-hand side of Equation (8) represents the reference inventory of210Pbex decreased by decay and by erosion during the old period, and the second term represents the accumulated 210Pbex during the old period decreased by decay and by erosion. It is clear in this case that 137Cs and 210Pbex are used for the same time scale. Table 2 shows hypothetical values of and obtained erosion rates relative to the old period (satisfying Equation (8)).

Table 2.
Obtained erosion rate values for the old period according to case 2 assuming is equal to 270 kg m−2.
3.3. Case 3: Deposition during the Old Period of Cultivation and Erosion during the Recent Period with Excess of 210Pbex Inventory
In this case, a reduction of 137Cs inventory should be observed since soil was eroded during the recent period. 137Cs is then used to determine the erosion rate during the recent period. The inventory of 210Pbex at the end of the old period can be calculated by solving the equation:
where is the measured 210Pbex inventory at the end of the recent period. is expected to be greater than the reference inventory in the present case. The deposition rate during the old period is determined based on the knowledge of the erosion rate at the up slope and after calculating the concentration of 210Pbex of the mobilized sediment as done in case 2 for the recent period.
3.4. Case 4: Erosion during the Old Period of Cultivation and Deposition during the Recent Period with Excess of 210PbexInventory
In this case,137Cs is used to determine deposition rate on the location during the recent period.210Pbex inventory accumulated on the location during the recent period of cultivation is determined using Equation (7). The subtraction of from the measured inventory of 210Pbex at the year of measurement, increased by decay correction with the time length of the recent period (multiplied by ), provides the inventory of 210Pbex at the end of the old period . The determination of erosion rate during the old period is obtained using Equation (8).
3.5. Case 5: Deposition during the Old Period of Cultivation and Deposition during the Recent Period with Excess of 210PbexInventory
In this case,137Cs is used to determine 210Pbex inventory at the end of the old period , as described in case 2. is then subtracted to the reference inventory of 210Pbex to estimate the 210Pbex inventory on the location at time . is expected to be greater than the reference inventory, indicating that the situation is corresponding to case 5.
Using the erosion rate at the up slope of the transect during the recent period and 210Pbex concentration of deposited sediment at time t’, the deposition rate during the old period can be determined on the location through Equation (10).
4. Conclusions
A new mass balance approach model useful for the determination of soil redistribution rates relative to two successive and continuous periods of soil cultivation is proposed. The model is based on the combination of 210Pbexand137Cs for the same time scale where excess or reduction of 210Pbexinventory at the year of measurement is known. The model can be applied on any soil subject to two successive and continuous time periods of cultivation where the recent period is comparable to the time scale appropriate to137Cs. 210Pbex is used without being constrained to 100 years, as commonly assumed, which allows for the use of the two radiotracers for the same time scale. Successful tests of the model for hypothetical cases were performed. The model can be applied in practical cases and can provide important information on soil redistribution rates needed to study the environmental impact of the change of soil cultivation procedures. The proposition of a model combining 210Pbex and 137Cs for the same time scale and predicting the variation of the redistribution rate of cultivated soils due to change of cultivation procedure in the present work constitutes a new method of estimation of soil redistributing rates with 210Pbex and 137Cs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.G. and T.H.A.; methodology, F.G.; software, R.B.A.; validation, F.G., T.H.A., and M.A.E.-N.; formal analysis, M.A.E.-N. and T.A.; investigation, R.B.A.; resources, M.A.E.-N.; data curation, F.G.; writing—original draft preparation, F.G.; writing—review and editing, R.B.A. and T.H.A.; visualization, supervision, M.A.E.-N.; project administration, M.A.E.-N. and R.B.A.; funding acquisition, F.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia, grant number IFT20097.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deputyship for Research & Innovation, Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia, for funding this research work through the project number IFT20097.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Montgomery, D.R. Soil erosion and agricultural sustainability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13268–13272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, J.C.; Ritchie, C.A. Bibliography of Publications of 137-Cesium Studies Related to Erosion and Sediment Deposition. USDA-ARS Hydrology and Remote Sensing Laboratory; Occasional Paper HRSL-2005-01. Available online: https://hrsl.ba.ars.usda.gov/cesium/Cesium137bib.htm (accessed on 5 November 2020).
- Mabit, L.; Benmansour, M.; Walling, D.E. Comparative advantages and limitations of fallout radionuclides (137Cs, 210Pb and 7Be) to assess soil erosion and sedimentation. J. Environ. Radioact. 2008, 99, 1799–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, D.E.; Zhang, Y. A national assessment of soil erosion based on caesium-137 measurements. Adv. Geoecol. 2010, 41, 89–97. [Google Scholar]
- Meliho, M.; Nouira, A.; Benmansour, M.; Boulmane, M.; Khattabi, A.; Mhammdi, N.; Benkdad, A. Assessment of soil erosion rates in a Mediterranean cultivated and uncultivated soils using fallout 137Cs. J. Environ. Radioact. 2019, 106021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damnati, B.; Brahim, D.; Radakovitch, O. Quantifying erosion using 137Cs and 210Pb in cultivated soils in three Mediterranean watershed: Synthesis study from El Hachef, Raouz and Nakhla (North West Morocco). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2013, 79, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto, P.; Walling, D.E.; Callegari, G.; Catona, F. Using Fallout lead-210 measurements to estimate soil erosion in three small catchments in southern Italy. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2006, 6, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienes Allas, R.; Alvarez Gonzalez, A.M.; Jimenez Ballesta, R. Preliminary Results of 137Cs Activity in a Soil Erosion Toposequence in Cuenca (Castilla-La Mancha, Central Spain). Available online: https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=3052345 (accessed on 4 October 2019).
- Walling, D.E.; He, Q. Improved Models for Erosion Rates from Cesium-137 Measurements. J. Environ. Qual. 1999, 28, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, D.; He, Q. Using Fallout Lead-210 Measurements to Estimate Soil Erosion on Cultivated Land. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1999, 63, 1404–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuller, P.; Walling, D.E.; Sepúlveda, A.; Castillo, A.; Pino, I. Changes in soil erosion associated with the shift from conventional tillage to a no-tillage system, documented using 137Cs measurements. Soil. Tillage. Res. 2007, 94, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashanoski, R.G.; de Jon, E. Predicting the temporal relationship between soil cesiom-137 and erosion rate. J. Environ. Qual. 1984, 13, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Yang, H.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, M.; Xu, L. Response of 210Pbex inventory to changes in soil erosion rates on uncultivated land. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 1725–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).