Sensation Seeking and Gambling Behavior in Adolescence: Can Externalizing Problems Moderate this Relationship?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Measures
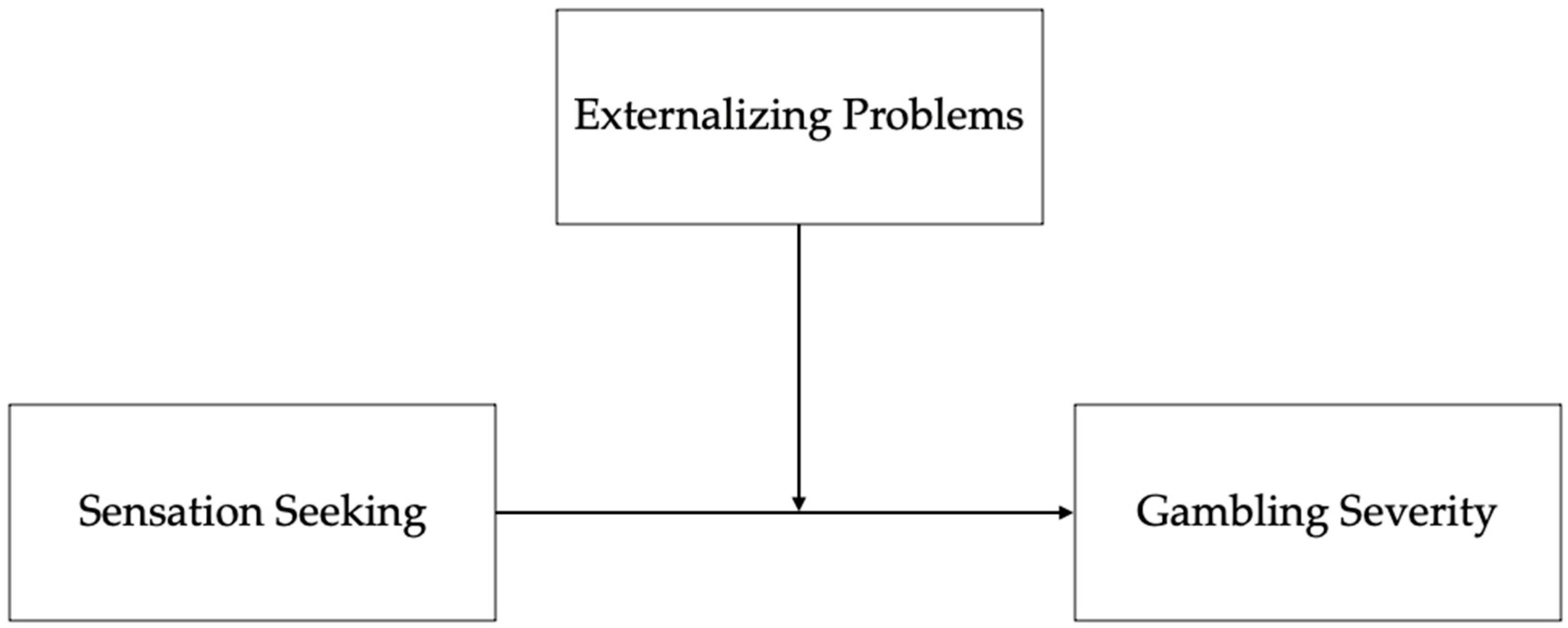
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Erikson, E.H. Identity: Youth and Crisis; Norton: New York, NY, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Corsano, P.; Majorano, M.; Musetti, A.; Antonioni, M.C. Autonomia emotiva e solitudine in adolescenti con abuso di sostanze Emotional autonomy and solitude in adolescent substance abusers. Psicologia Clinica dello Sviluppo 2014, 18, 257–278. [Google Scholar]
- Derevensky, J.L.; Gilbeau, L. Preventing adolescent gambling problems. In Gambling Disorder; Heinz, A., Romanczuk-Seiferth, N., Potenza, M.N., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 297–311. [Google Scholar]
- Guzzo, G.; Cascio, V.L.; Pace, U. The role of individual and relational characteristics on alcohol consumption among Italian adolescents: A discriminant function analysis. Child Ind. Res. 2013, 6, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derevensky, J.L.; Gupta, R.; Winters, K. Prevalence rates of youth gambling problems: Are the current rates inflated? J. Gambl. Stud. 2003, 19, 405–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potenza, M.N. Neurobiology of gambling behaviors. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2013, 23, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reyna, V.F.; Chapman, S.B.; Dougherty, M.R.; Confrey, J. The Adolescent Brain: Learning, Reasoning, and Decision Making; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tozzi, L.; Akre, C.; Fleury-Schubert, A.; Surís, J.C. Gambling among youths in Switzerland and its association with other addictive behaviours: A population-based study. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2013, 143, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.J.; Volberg, R.A.; Stevens, R.M.G.; Williams, L.A.; Arthur, J.N. The Definition, Dimensionalization, and Assessment of Gambling Participation; Report for the Canadian Consortium for Gambling Research: Guelph, ON, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Andrie, E.K.; Tzavara, C.K.; Tzavela, E.; Richardson, C.; Greydanus, D.; Tsolia, M.; Tsitsika, A.K. Gambling involvement and problem gambling correlates among European adolescents: Results from the European Network for Addictive Behavior study. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2019, 54, 1429–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calado, F.; Alexandre, J.; Griffiths, M.D. Prevalence of adolescent problem gambling: A systematic review of recent research. J. Gambl. Stud. 2017, 33, 397–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Floros, G.D. Gambling disorder in adolescents: Prevalence, new developments, and treatment challenges. Adolesc. Health Med. Ther. 2018, 9, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tani, F.; Ponti, L.; Ghinassi, S. Gambling behaviors in adolescent male and female regular and non-regular gamblers: A study of Central Italian adolescents. J. Gambl. Stud. 2020, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Derevensky, J. Reflections on underage gambling. Responsible Gambl. Rev. 2014, 1, 37–50. [Google Scholar]
- Livazović, G.; Bojčić, K. Problem gambling in adolescents: What are the psychological, social and financial consequences? BMC Psychiatry 2019, 19, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiesi, F.; Donati, M.A.; Galli, S.; Primi, C. The suitability of the South Oaks Gambling Screen–Revised for Adolescents (SOGS-RA) as a screening tool: IRT-based evidence. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2013, 27, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canale, N.; Vieno, A.; Griffiths, M.D.; Marino, C.; Francesca Chieco, F.; Disperati, F.; Andriolo, S.; Santinello, M. The efficacy of a web-based gambling intervention program for high school students: A preliminary randomized study. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 55, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cosenza, M.; Ciccarelli, M.; Nigro, G. The steamy mirror of adolescent gamblers: Mentalization, impulsivity, and time horizon. Addict. Behav. 2019, 89, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allami, Y.; Vitaro, F.; Brendgen, M.; Carbonneau, R.; Tremblay, R.E. Identifying at-risk profiles and protective factors for problem gambling: A longitudinal study across adolescence and early adulthood. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2018, 32, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowling, N.A.; Merkouris, S.S.; Greenwood, C.J.; Oldenhof, E.; Toumbourou, J.W.; Youssef, G.J. Early risk and protective factors for problem gambling: A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2017, 51, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Passanisi, A.; D’Urso, G.; Pace, U. The Interplay Between Maladaptive Personality Traits and Mindfulness Deficits Among Adolescent Regular Gamblers: A Mediation Model. J. Gambl. Stud. 2019, 35, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passanisi, A.; D’Urso, G.; Schimmenti, A.; Ruggieri, S.; Pace, U. Coping Strategies, Creativity, Social Self-Efficacy, and Hypercompetitiveness in Gambling Behaviors: A Study on Male Adolescent Regular Gamblers. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuckerman, M. Behavioral Expression and Biosocial Bases of Sensation Seeking; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Donati, M.A.; Chiesi, F.; Primi, C. A model to explain at-risk/problem gambling among male and female adolescents: Gender similarities and differences. J. Adolesc. 2013, 36, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevez, A.; Herrero-Fernández, D.; Sarabia, I.; Jauregui, P. The impulsivity and sensation-seeking mediators of the psychological consequences of pathological gambling in adolescence. J. Gambl. Stud. 2015, 31, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, K.W.; Wang, M.; Neighbors, C.; Tackett, J.L. The Personality Context of Adolescent Gambling: Better Explained by the Big Five or Sensation-Seeking? J. Psychopathol. Behav. Assess. 2019, 41, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hollén, L.; Dörner, R.; Griffiths, M.D.; Emond, A. Gambling in young adults aged 17-24 years: A population-based study. J. Gambl. Stud. 2020, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donati, M.A.; Primi, C.; Mazzarese, M.; Sanson, F.; Leone, L. Immigrant status and problem-gambling severity in adolescents: Evidence for moderation by sensation seeking. Addict. Behav. 2020, 107, 106395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tani, F.; Ilari, A. Il gioco d’azzardo tra attività ludica e patologia The spiral of the game. Gambling between ludic activity and pathology. In La Spirale Del Gioco; University Press: Florence, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman, M. Faites vos jeux anouveau: Still another look at sensation seeking and pathological gambling. Pers. Individ. Differ. 2005, 39, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canale, N.; Scacchi, L.; Griffiths, M.D. Adolescent gambling and impulsivity: Does employment during high school moderate the association? Addict. Behav. 2016, 60, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leeman, R.F.; Hoff, R.A.; Krishnan-Sarin, S.; Patock-Peckham, J.A.; Potenza, M.N. Impulsivity, sensation-seeking, and part-time job status in relation to substance use and gambling in adolescents. J. Adolesc. Health 2014, 54, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caldeira, K.M.; Arria, A.M.; O’Grady, K.E.; Vincent, K.B.; Robertson, C.; Welsh, C.J. Risk factors for gambling and substance use among recent college students. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017, 179, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achenbach, T.M. Manual for The Youth Self-Report and 1991 Profile; Department of Psychiatry, University of Vermont: Burlington, VT, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Masten, A.S.; Roisman, G.I.; Long, J.D.; Burt, K.B.; Obradović, J.; Riley, J.R.; Boelcke-Stennes, K.; Tellegen, A. Developmental cascades: Linking academic achievement and externalizing and internalizing symptoms over 20 years. Dev. Psychol. 2005, 41, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moffitt, T.E. Adolescence-limited and life-course-persistent antisocial behavior: A developmental taxonomy. Psychol. Rev. 1993, 100, 674–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuckerman, M. Sensation Seeking and Risky Behavior; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, F.D.; Engelhardt, L.; Briley, D.A.; Grotzinger, A.D.; Patterson, M.W.; Tackett, J.L.; Statham, D.J.; Heath, A.; Lynskey, M.T.; Slutske, W.G.; et al. Sensation seeking and impulsive traits as personality endophenotypes for antisocial behavior: Evidence from two independent samples. Pers. Individ. Differ. 2017, 105, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mann, F.D.; Kretsch, N.; Tackett, J.L.; Harden, K.P.; Tucker-Drob, E.M. Person× environment interactions on adolescent delinquency: Sensation seeking, peer deviance and parental monitoring. Pers. Individ. Differ. 2015, 76, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peach, H.D.; Gaultney, J.F. Sleep, impulse control, and sensation-seeking predict delinquent behavior in adolescents, emerging adults, and adults. J. Adolesc. Health 2013, 53, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, S.S.; Liu, W.; Hedden, S.L.; Goldweber, A.; Storr, C.L.; Derevensky, J.L.; Stinchfield, R.; Ialongo, N.S.; Petras, H. Youth aggressive/disruptive behavior trajectories and subsequent gambling among urban male youth. J. Clin. Child Adolesc. Psychol. 2013, 42, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Winters, K.C.; Stinchfield, R.; Fulkerson, J. Patterns and characteristics of adolescent gambling. J. Gambl. Stud. 1993, 9, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, D.; Mallery, P. SPSS for Windows Step by Step: A Simple Guide and Reference. 11.0 Update, 4th ed.; Allyn & Bacon: Boston, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pastorelli, C.; Gerbino, M.; Vecchio, G.M.; Steca, P.; Picconi, L.; Paciello, M. School failure: Risk and protective factors during preadolescence. Età Evol. 2002, 71, 84–91. [Google Scholar]
- Primi, C.; Narducci, R.; Benedetti, D.; Donati, M.; Chiesi, F. Validity and reliability of the Italian version of the Brief Sensation Seeking Scale (BSSS) and its invariance across age and gender. Test Psychom. Methodol. Appl. Psychol. 2011, 18, 231–241. [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman, M.; Eysenck, S.; Eysenck, H.J. Sensation seeking in England and America: Cross-cultural age and sex comparisons. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 1978, 46, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, P.J.; West, S.G.; Finch, J.F. The robustness of test statistics to nonnormality and specification error in confirmatory factor analysis. Psychol. Methods 1996, 1, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Erlbaum: Hillsdale, MI, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Aiken, L.S.; West, S.G. Multiple Regression: Testing and Interpreting Interactions; Sage: Newbury Park, CA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Joseé, P.E. Doing Statistical Mediation and Moderation, 1st ed.; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Donati, M.A.; Sottili, E.; Morsanyi, K.; Primi, C. Time perspectives and gambling in adolescent boys: Differential effects of present-and future-orientation. J. Gambl. Stud. 2019, 35, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans-Polce, R.J.; Schuler, M.S.; Schulenberg, J.E.; Patrick, M.E. Gender-and age-varying associations of sensation seeking and substance use across young adulthood. Addict. Behav. 2018, 84, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innamorati, M.; Parolin, L.; Tagini, A.; Santona, A.; Bosco, A.; De Carli, P.; Palmisano, G.L.; Pergola, F.; Sarracino, D. Attachment, social value orientation, sensation seeking, and bullying in early adolescence. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kiire, S.; Matsumoto, N.; Yoshida, E. Discrimination of Dark Triad traits using the UPPS-P model of impulsivity. Pers. Individ. Differ. 2020, 167, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionio, C.; Camisasca, E.; Milani, L.; Miragoli, S.; Di Blasio, P. Facing Death in Adolescence: What Leads to Internalization and Externalization Problems? J. Child Adolesc. Trauma 2018, 11, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca-Pedrero, E.; Sierra-Baigrie, S.; Lemos-Giráldez, S.; Paino, M.; Muñiz, J. Dimensional structure and measurement invariance of the Youth Self-Report across gender and age. J. Adolesc. Health 2012, 50, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rescorla, L.; Achenbach, T.M.; Ivanova, M.Y.; Dumenci, L.; Almqvist, F.; Bilenberg, N.; Bird, H.; Hector Broberg, A.; Dobrean, A.; Döpfner, M.; et al. Epidemiological comparisons of problems and positive qualities reported by adolescents in 24 countries. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 2007, 75, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canale, N.; Vieno, A.; Lenzi, M.; Griffiths, M.D.; Borraccino, A.; Lazzeri, G.; Lemma, P.; Scacchi, L.; Santinello, M. Income inequality and adolescent gambling severity: Findings from a large-scale Italian representative survey. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Svensson, J.; Sundqvist, K. Gambling among Swedish youth: Predictors and prevalence among 15-and 17-year-old students. Nord. Stud. Alcohol Drugs 2019, 36, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weidberg, S.; González-Roz, A.; Fernández-Hermida, J.R.; Martínez-Loredo, V.; Grande-Gosende, A.; García-Pérez, Á.; Secades-Villa, R. Gender differences among adolescent gamblers. Pers. Individ. Differ. 2018, 125, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinn-Pike, L.; Worthy, S.L.; Jonkman, J.N. Adolescent gambling: A review of an emerging field of research. J. Adolesc. Health 2010, 47, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoon, M.E.; Ingersoll, G.M. Parental modeling, attachment, and supervision as moderators of adolescent gambling. J. Gambl. Stud. 2006, 22, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonneau, R.; Vitaro, F.; Brendgen, M.; Tremblay, R.E. Trajectories of gambling problems from mid-adolescence to age 30 in a general population cohort. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2015, 29, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Granero, R.; Penelo, E.; Stinchfield, R.; Fernandez-Aranda, F.; Savvidou, L.G.; Fröberg, F.; Aymamì, N.; Gómez-Peña, M.; Pérez-Serrano, M.; del Pino-Gutiérrez, A.; et al. Is pathological gambling moderated by age? J. Gambl. Stud. 2014, 30, 475–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volberg, R.A.; Gupta, R.; Griffiths, M.D.; Olason, D.T.; Delfabbro, P. An international perspective on youth gambling prevalence studies. Int. J. Adolesc. Med. Health 2010, 2, 3–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| M | SD | Skewness | Kurtosis | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Externalizing problems | 10.91 | 6.75 | 1.00 | 1.17 | - | 0.44 ** | 0.29 ** |
| 2. Sensation seeking | 25.64 | 5.84 | −0.09 | −0.30 | - | 0.27 ** | |
| 3. Gambling | 0.82 | 1.48 | 2.05 | 3.74 | - |
| ß | t | p | 95% CI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | |||||
| Gender | −0.37 | −7.58 | 0.000 | −1.43 | −0.84 |
| Step 2 | |||||
| Gender | −0.33 | −6.67 | 0.024 | −1.30 | −0.71 |
| Sensation seeking | 0.20 | 4.00 | 0.000 | 0.03 | 0.07 |
| Step 3 | |||||
| Gender | −0.31 | −6.45 | 0.000 | −1.26 | −0.67 |
| Sensation seeking | 0.12 | 2.26 | 0.024 | 0.01 | 0.06 |
| Externalizing problems | 0.18 | 3.37 | 0.001 | 0.02 | 0.06 |
| Step 4 | |||||
| Gender | −0.31 | −0.46 | 0.000 | −1.25 | −0.66 |
| Sensation seeking | −0.08 | −0.88 | 0.382 | −0.07 | 0.03 |
| Externalizing problems | 0.13 | 2.43 | 0.016 | 0.01 | 0.05 |
| Sensation seeking X Externalizing problems | 0.26 | 2.72 | 0.007 | 0.00 | 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tani, F.; Ponti, L.; Ghinassi, S. Sensation Seeking and Gambling Behavior in Adolescence: Can Externalizing Problems Moderate this Relationship? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17238986
Tani F, Ponti L, Ghinassi S. Sensation Seeking and Gambling Behavior in Adolescence: Can Externalizing Problems Moderate this Relationship? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(23):8986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17238986
Chicago/Turabian StyleTani, Franca, Lucia Ponti, and Simon Ghinassi. 2020. "Sensation Seeking and Gambling Behavior in Adolescence: Can Externalizing Problems Moderate this Relationship?" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 23: 8986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17238986
APA StyleTani, F., Ponti, L., & Ghinassi, S. (2020). Sensation Seeking and Gambling Behavior in Adolescence: Can Externalizing Problems Moderate this Relationship? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(23), 8986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17238986





