Assessing the Impact of Lockdown on Atmospheric Ozone Pollution Amid the First Half of 2020 in Shenyang, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
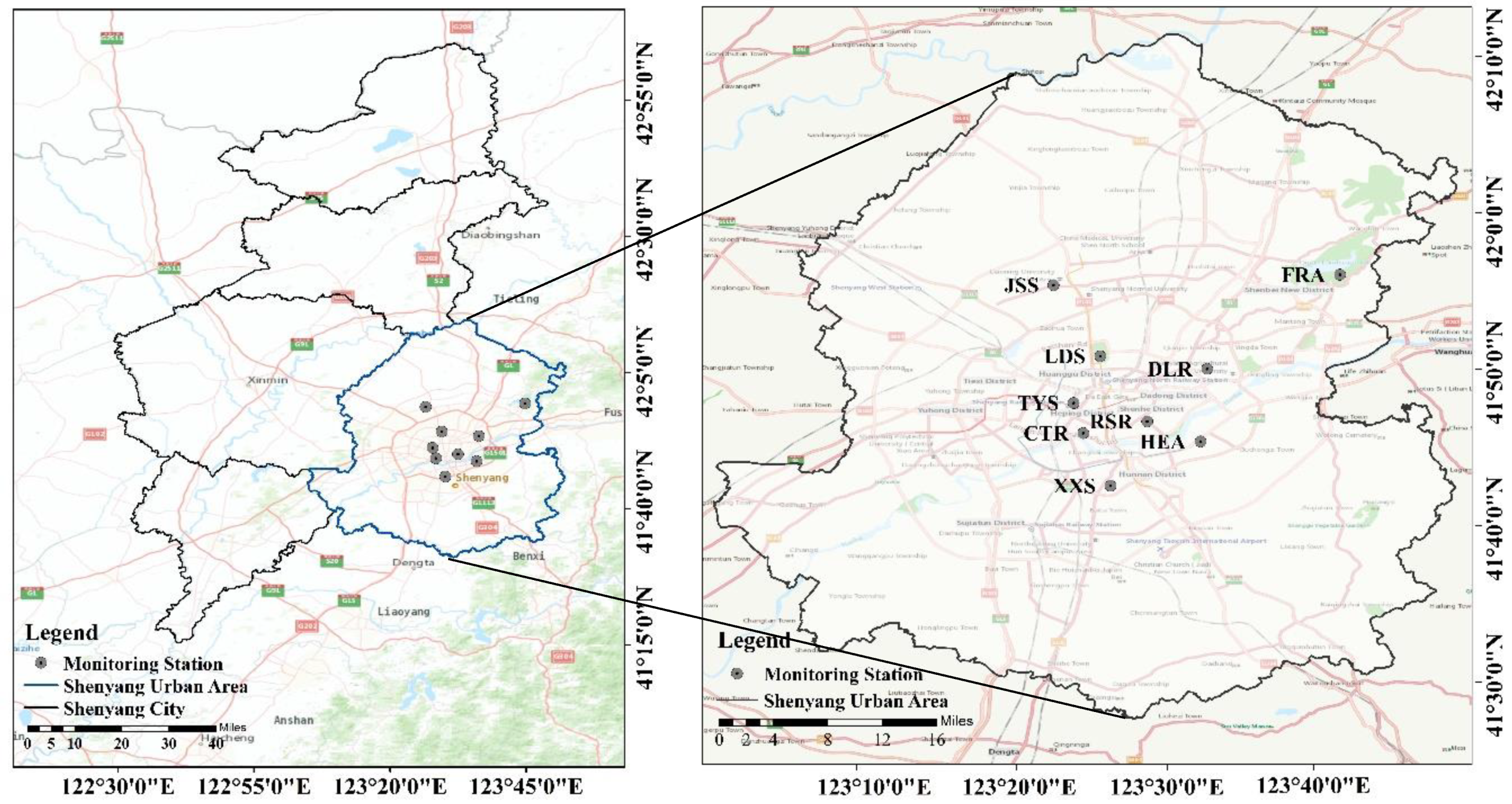
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Acquisition and Processing
2.3. Trajectory Clustering and Transmission Channel Establishment
2.4. Research Period Setting
2.4.1. Division of the Lockdown Period
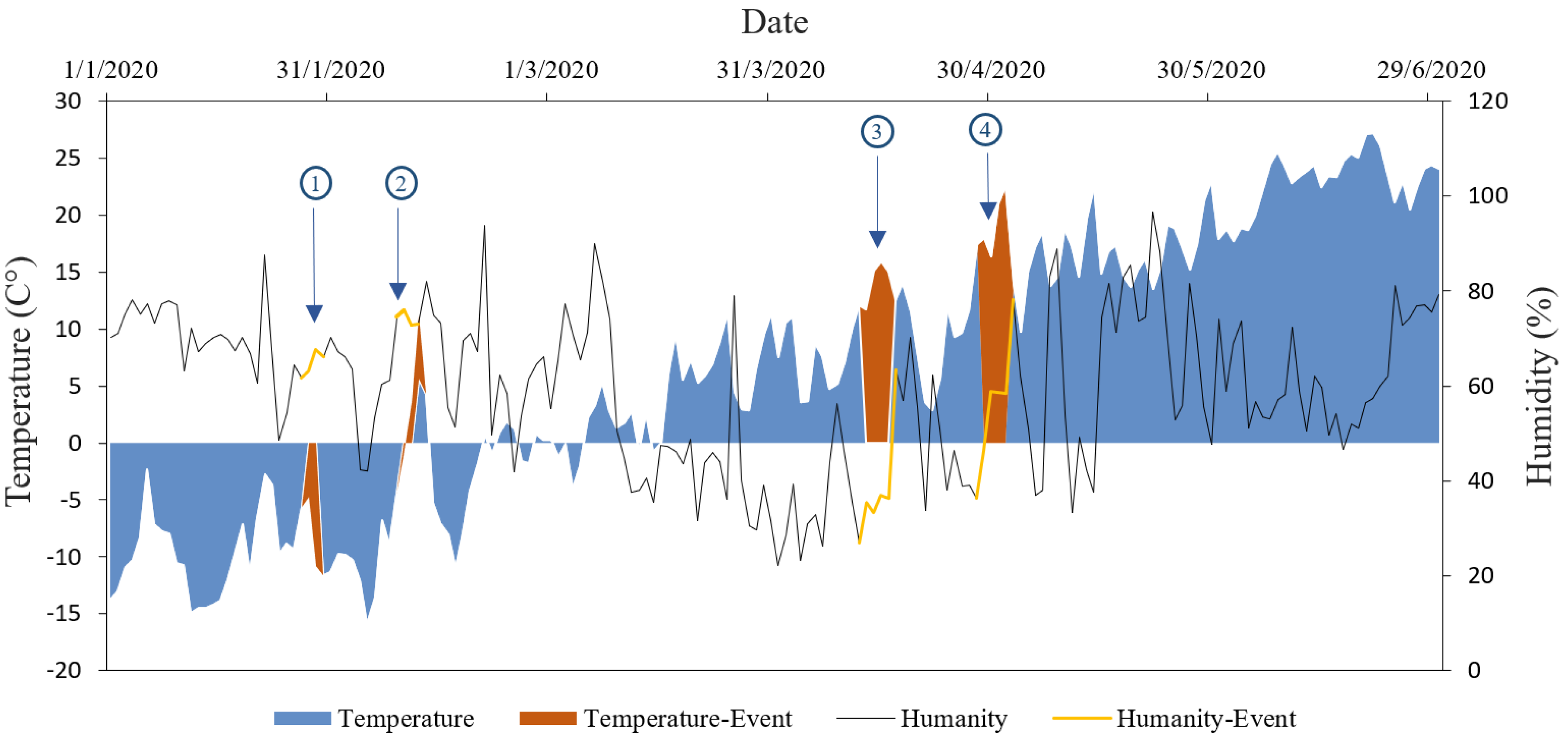
2.4.2. Division of Ozone Pollution Events
3. Results
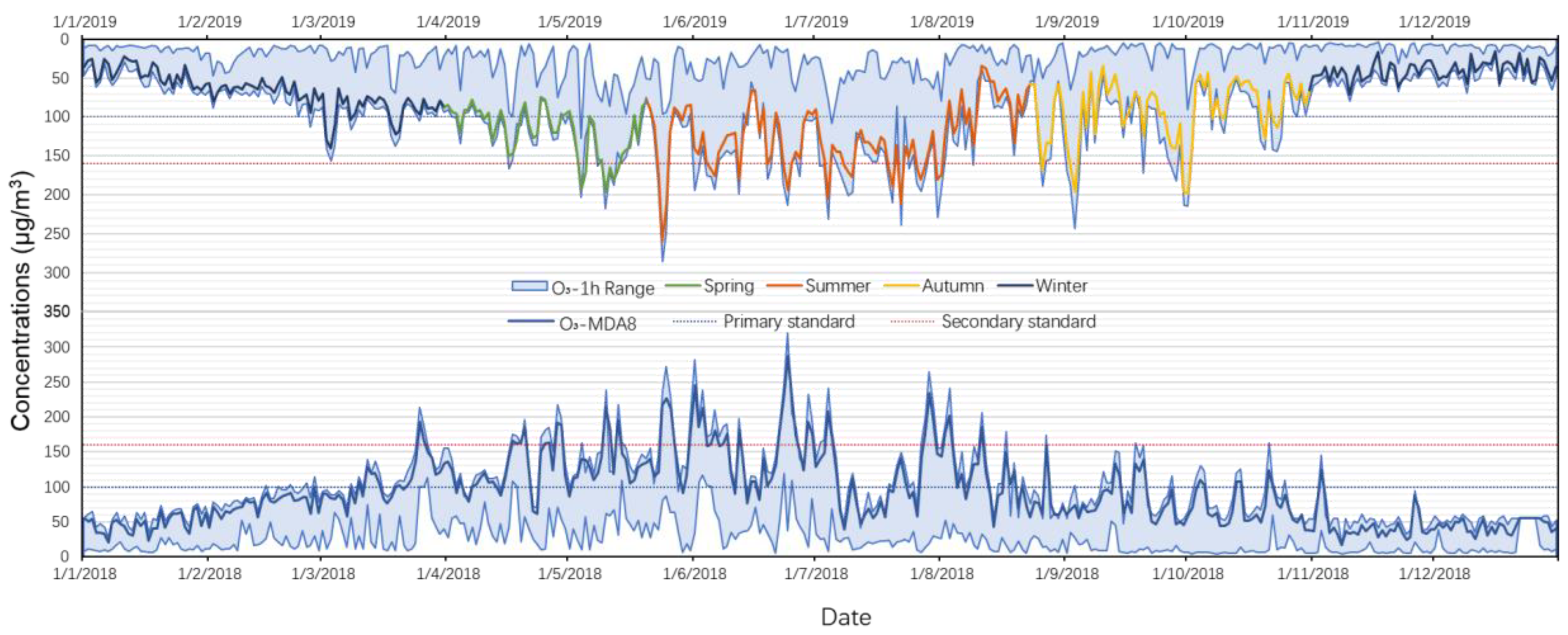
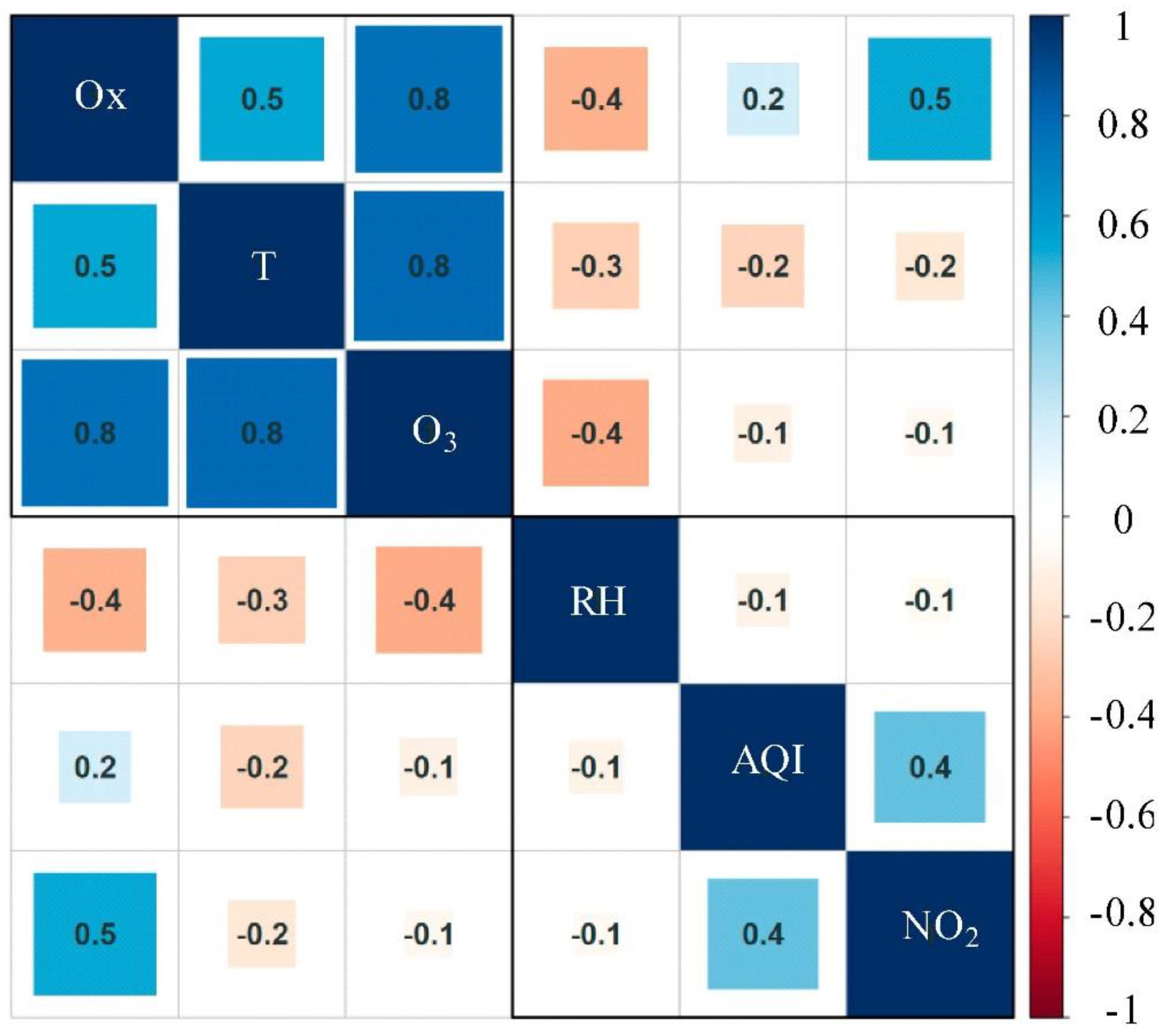
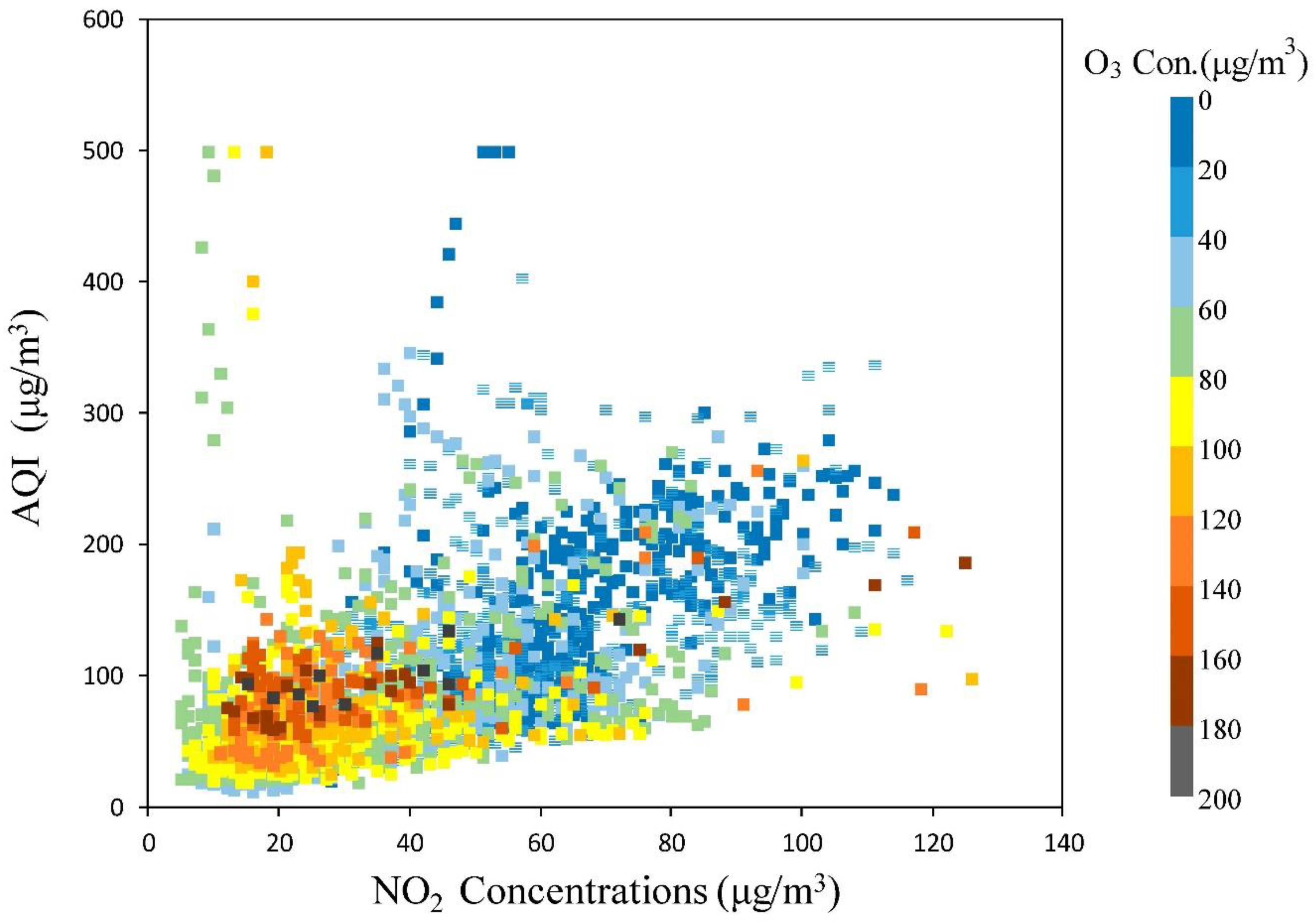
3.1. Analysis of Ozone Pollution in Shenyang in the First Half of 2020
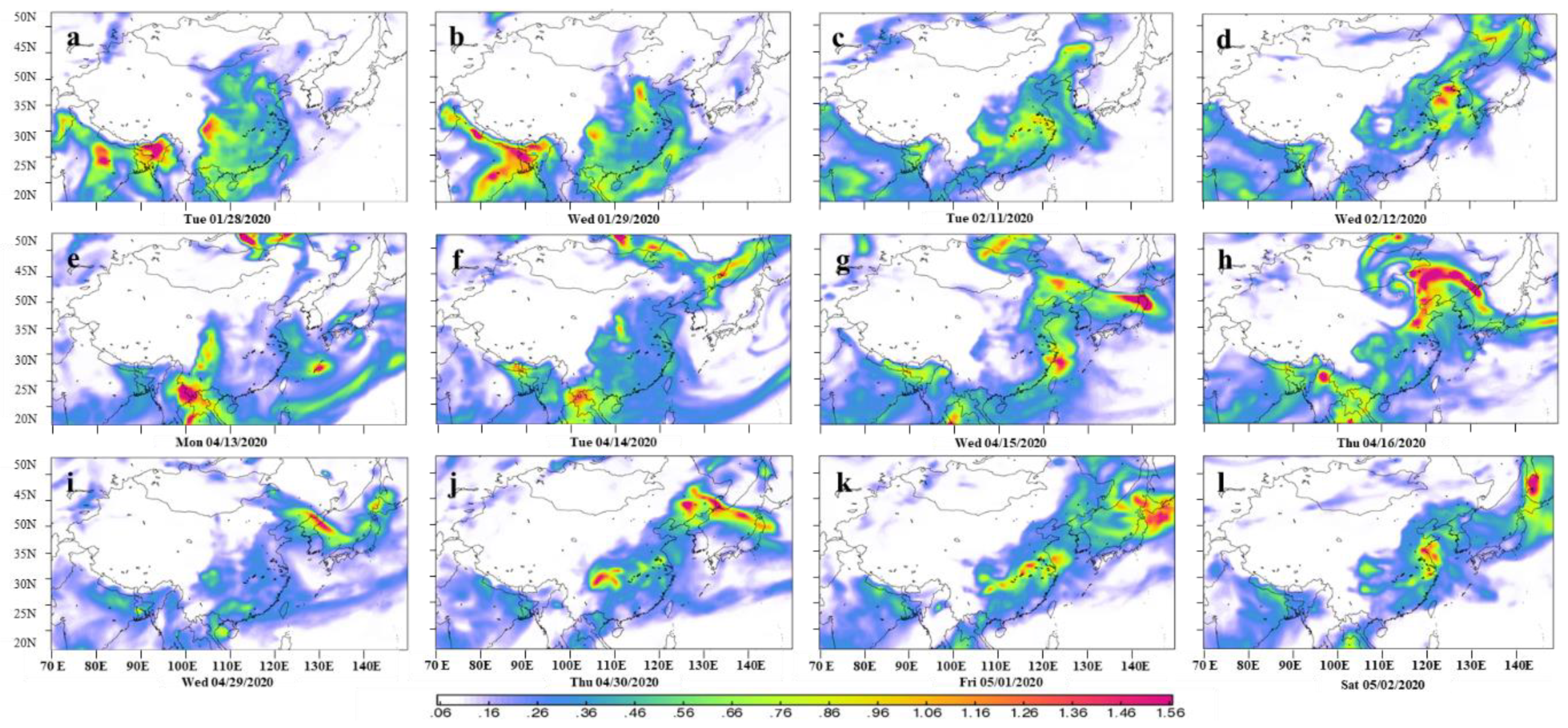
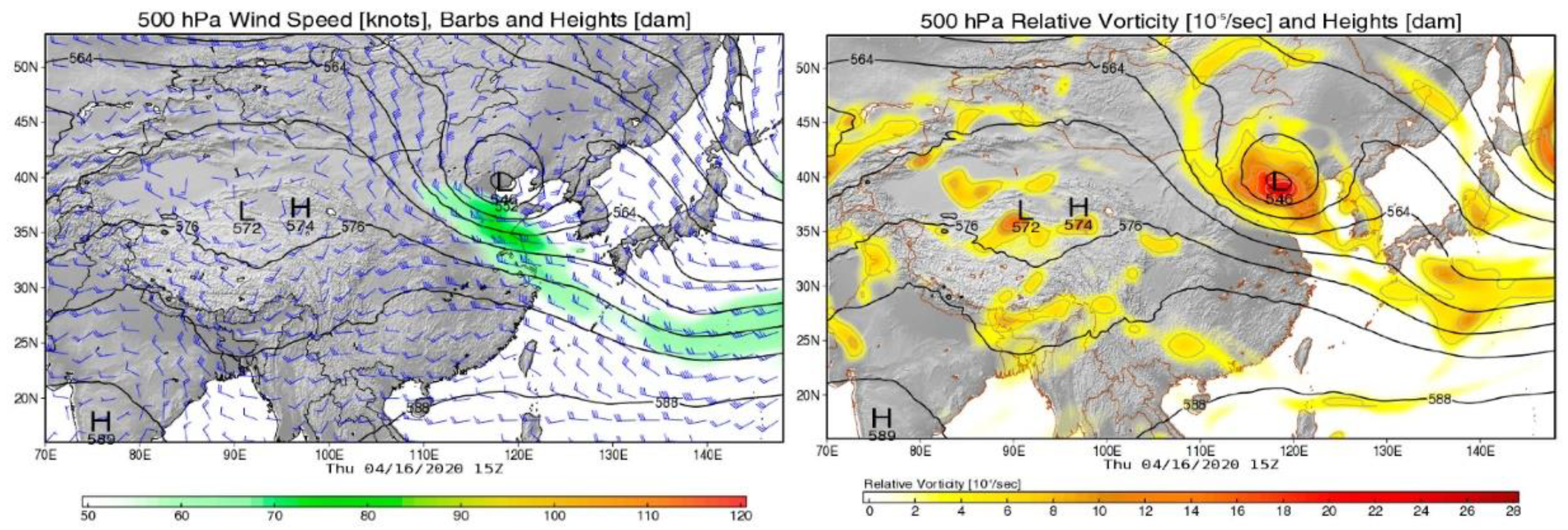
3.2. Analysis of Typical Ozone Pollution Events
3.3. Evolution of the Ozone Pollution in Shenyang Affected by the Lockdown of the Epidemic
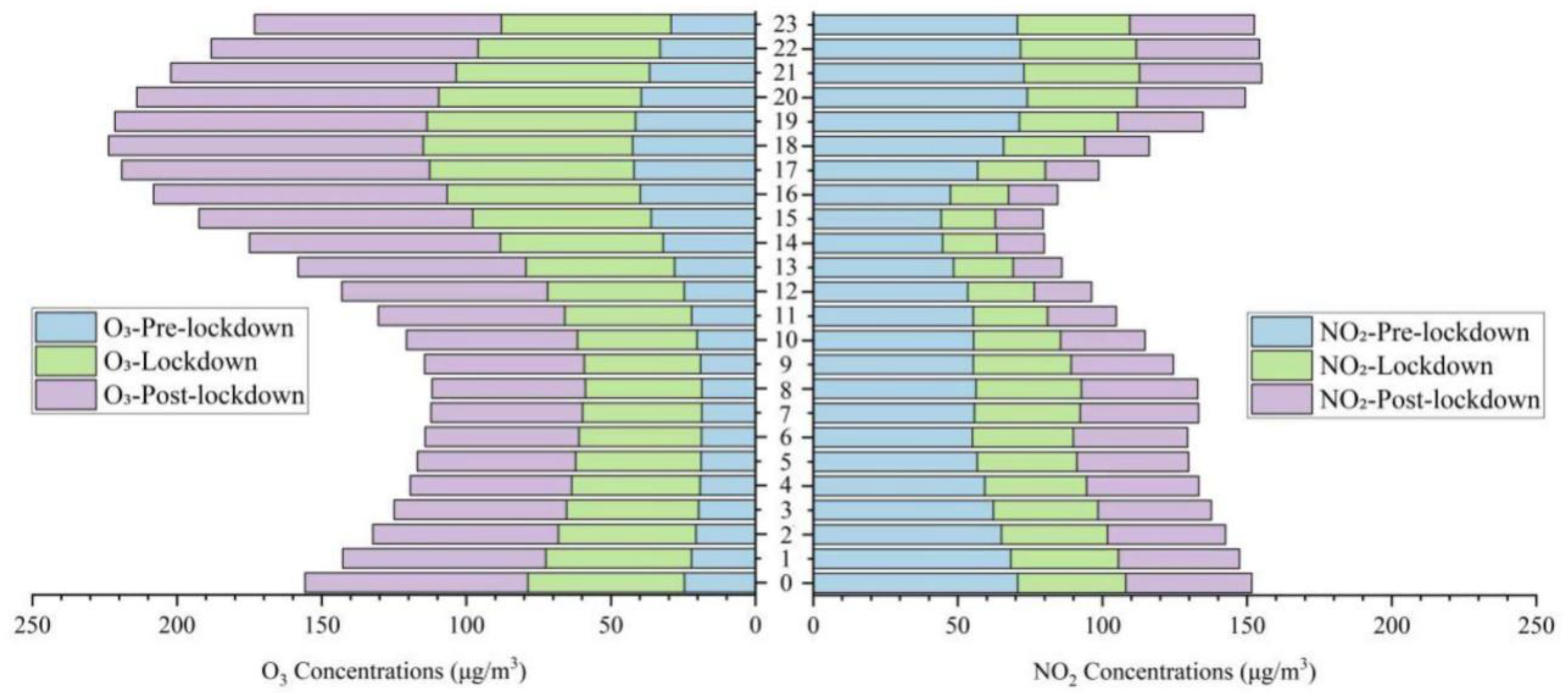
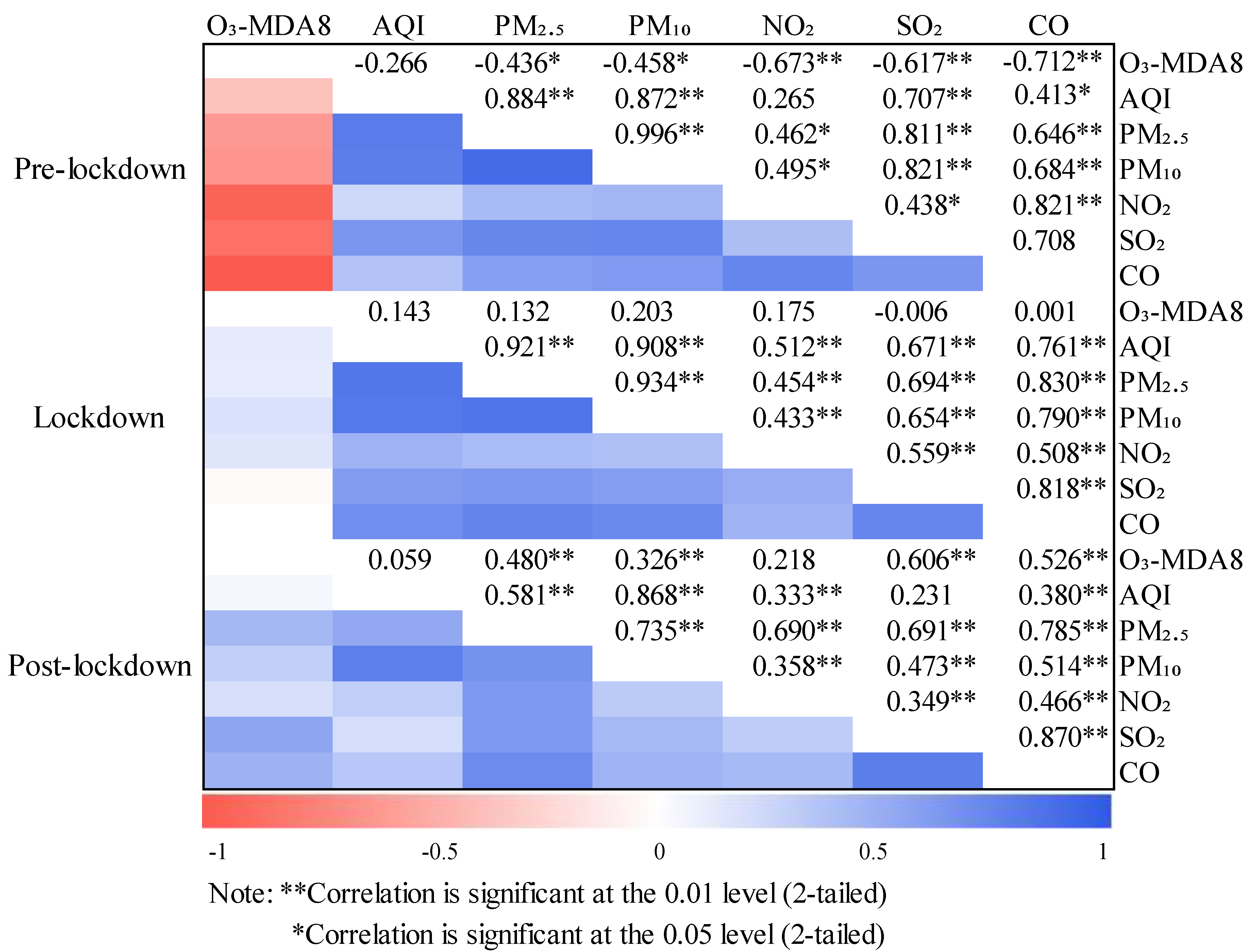
3.3.1. Evolution of Ozone and Other Basic Pollutants during the Preset Periods
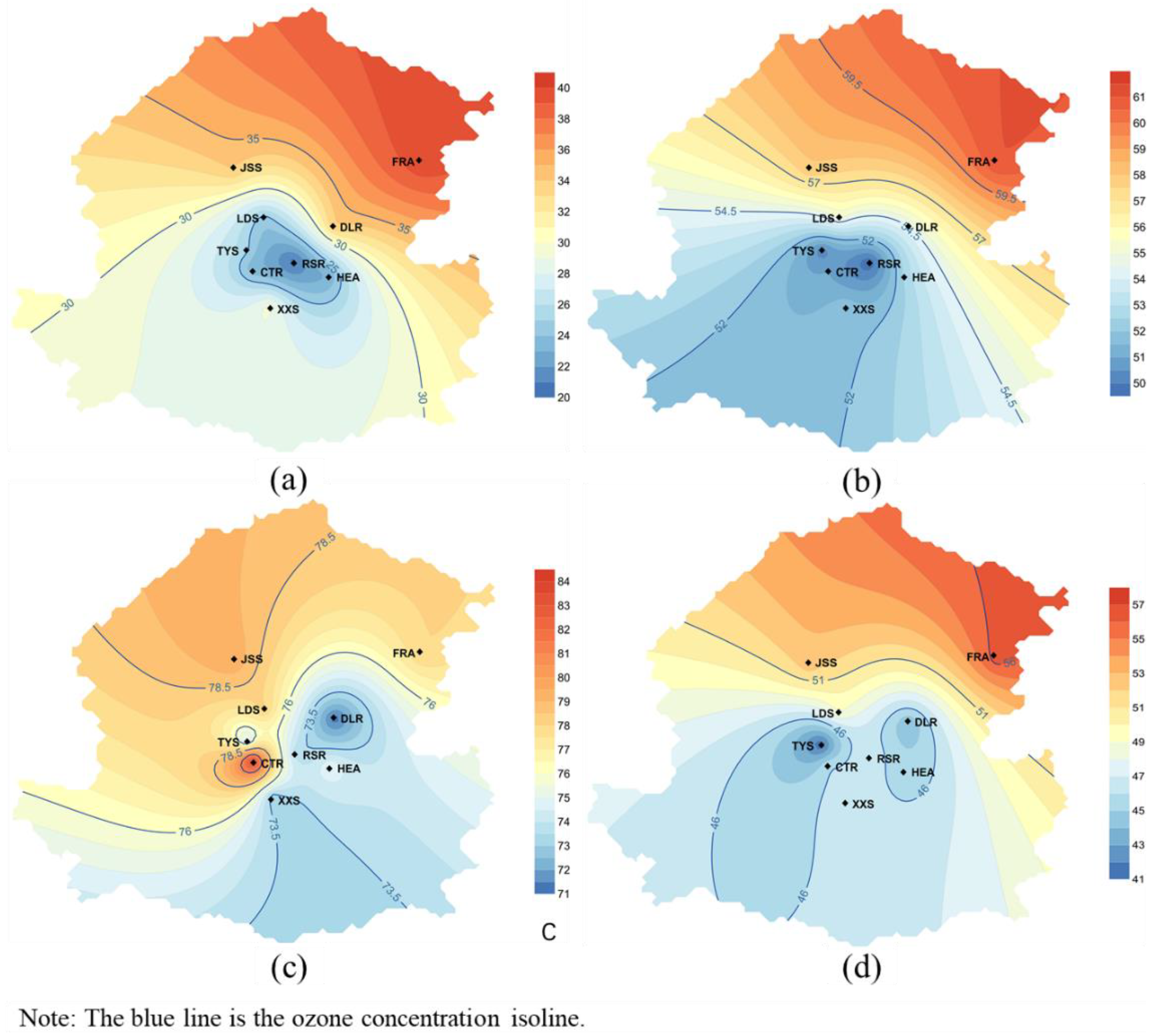
3.3.2. Spatial Distinction and Long-Distance Transport of Ozone in Shenyang during the Preset Period
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Variable Category | Pre-Lockdown | Lockdown | Post-Lockdown | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Mean | Min | SD | Max | Mean | Min | SD | Max | Mean | Min | SD | |
| AQI | 500.0 | 208.0 | 83.0 | 80.3 | 346.0 | 130.9 | 42.0 | 73.1 | 500.0 | 138.9 | 25.0 | 104.2 |
| NO2 | 116.0 | 82.5 | 53.0 | 18.6 | 88.0 | 54.2 | 13.0 | 18.9 | 126.0 | 60.4 | 12.0 | 26.0 |
| O3-MDA8 | 75.3 | 44.6 | 21.6 | 16.5 | 121.8 | 75.7 | 51.1 | 14.6 | 258.0 | 121.4 | 55.8 | 37.9 |
| PM2.5 | 267.5 | 101.2 | 40.3 | 51.2 | 210.6 | 54.3 | 10.9 | 42.1 | 121.2 | 77.3 | 8.0 | 29.2 |
| PM10 | 329.8 | 133.1 | 57.6 | 63.1 | 241.1 | 80.5 | 30.8 | 46.3 | 257.6 | 89.5 | 19.4 | 50.3 |
| SO2 | 77.5 | 32.8 | 16.8 | 15.3 | 43.8 | 17.9 | 7.0 | 8.0 | 38.4 | 15.8 | 4.7 | 8.1 |
| CO | 3.3 | 1.6 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 2.8 | 0.9 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| T | 2.5 | −9.9 | −20.4 | 5.8 | 18.5 | −2.0 | −21.3 | 7.3 | 30.0 | 12.8 | −7.0 | 7.1 |
| Po | 775.5 | 766.0 | 757.2 | 3.4 | 775.8 | 762.2 | 744.3 | 5.6 | 767.8 | 755.0 | 743.1 | 5.2 |
| RH | 94.0 | 70.3 | 27.0 | 16.1 | 98.0 | 60.7 | 17.0 | 20.6 | 99.0 | 52.0 | 9.0 | 25.9 |
| WS | 6.0 | 1.3 | 0.0 | 1.1 | 9.0 | 2.2 | 0.0 | 1.6 | 9.0 | 2.5 | 0.0 | 1.6 |
| VV | 30.0 | 6.3 | 0.6 | 6.9 | 30.0 | 14.4 | 0.3 | 10.2 | 30.0 | 18.5 | 1.0 | 9.7 |
| RRR | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 13.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 29.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 3.8 |
| Variable Category | Variable Definition |
|---|---|
| AQI | Hourly air quality index |
| O3-MDA8 | Hourly concentrations of the daily maximum 8-h moving average (MDA8) |
| CO | Hourly concentrations (mg/m3) |
| Other | Hourly concentrations (μg/m3) |
| T | Air temperature (°C) at 2 m height above the earth’s surface |
| Po | Atmospheric pressure at weather station level (millimeters of mercury) |
| RH | Relative humidity (%) at the height of 2 m above the earth’s surface |
| WS | Mean wind speed at 10–12 m above the earth’s surface over 10-min preceding the observation(m/s) |
| VV | Horizontal visibility (km) |
| RRR | Precipitation (mm) |
References
- Hart, O.E.; Halden, R.U. Computational analysis of SARS-COV-2/COVID-19 surveillance by waste water-based epidemiology locally and globally: Feasibility, economy, opportunities and challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 138875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunus, A.P.; Masago, Y.; Hijioka, Y. COVID-19 and surface water quality: Improved lake water quality during the lockdown. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 139012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atalan, A. Is the lockdown important to prevent the COVID-19 pandemic? Effects on psychology, environment and economy-perspective. Ann. Med. Surg. 2020, 56, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earth Observatory. Airborne Nitrogen Dioxide Plummets over China. 2020. Available online: https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/images/146362/airborne-nitrogen-dioxide-plummets-over-China (accessed on 20 April 2020).
- Kerimray, A.; Baimatova, N.; Ibragimova, O.P.; Bukenov, B.; Karaca, F. Assessing air quality changes in large cities during COVID-19 lockdowns: The impacts of traffic-free urban conditions in Almaty, Kazakhstan. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 139179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otmani, A.; Benchrif, A.; Tahri, M.; Bounakhla, M.; Krombi, M. Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on PM10, SO2 and NO2 concentrations in Salé City (Morocco). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masum, M.H.; Pal, S. Statistical evaluation of selected air quality parameters influenced by COVID-19 lockdown. Glob. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2020, 6, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, P.; Marco, A.D.; Agathokleous, E.; Feng, Z.; Calatayud, V. Amplified ozone pollution in cities during the COVID-19 lockdown. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, X.; Huang, J.; Huang, R.; Liu, C.; Zhang, T. Impact of city lockdown on the air quality of COVID-19-hit of Wuhan city. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collivignarelli, M.C.; Abbà, A.; Bertanza, G.; Pedrazzani, R.; Ricciardi, P.; Miino, M.C. Lockdown for COVID-2019 in Milan: What are the effects on air quality? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, G.; Siciliano, B.; França, B.B.; Silva, C.M.; Arbilla, G. The impact of COVID-19 partial lockdown on the air quality of the city of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 139085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, R.; Zhang, A. Does lockdown reduce air pollution? Evidence from 44 cities in northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 139052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, X.; Lei, Y.; Zhou, H.; Liu, Z.; Hu, S.; Cai, Z.; Lin, J.; Jiang, Z.; Liao, H. Changes in China’s man-made carbon emissions and air pollutants during the COVID-19 epidemic. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 2, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, S.; Xing, J.; Wang, Y.; Hao, J. Progress of air pollution control in China and its challenges and opportunities in the ecological civilization era. Engineering 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Wang, S.; Gong, Z.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Y. Characteristics of ozone pollution in pilot cities for ozone monitoring from 2008 to 2016. China Environ. Monit. 2017, 33, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Q.; Liu, M.; Ma, Y.; Du, B.; Du, Y.; Wang, C.; Jin, S. Simulation Study on Time Series Curves of Ambient Air Ozone Concentration and Accumulation Rate in Shenyang. China Environ. Monit. 2019, 35, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, J. Analysis of the spatial–temporal variation of the surface ozone concentration and its associated meteorological factors in Changchun. Environments 2019, 6, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, X.; Shi, N.; Lu, M. CEEMD-subset-OASVR-GRNN for ozone forecasting: Xiamen and Harbin as cases. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, S. Characteristics of Ozone Pollution Trend and Temporal and Spatial Distribution in Central of Liaoning Province. Environ. Prot. Circ. Econ. 2018, 38, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, X.; Shi, S.; Shen, L.; Luan, L.; Ma, Y. Spatiotemporal Variations and Regional Transport of Air Pollutants in Two Urban Agglomerations in Northeast China Plain. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 917–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Hong, Y.; Ma, Y. Characteristics of pollutants and boundary layer structure during two haze events in summer and autumn 2014 in Shenyang, northeast China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 18, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Chen, J.; Sun, B.; Zhou, B.; Li, X. Temporal trends in respiratory mortality and short-term effects of air pollutants in Shenyang, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 11468–11479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, A.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.; Stunder, B.; Cohen, M.D.; Ngan, F. NOAA’s HYSPLIT atmospheric transport and dispersion modeling system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Wang, J.; Li, T.; Fang, C. Pollution Characteristics, Transport Pathways, and Potential Source Regions of PM2.5 and PM10 in Changchun City in 2018. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.; Petrik, L.; Wichmann, J. PM2.5 chemical composition and geographical origin of air masses in Cape Town, South Africa. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wespes, C.; Hurtmans, D.; Clerbaux, C.; Boynard, A.; Coheur, P.-F. Decrease in tropospheric O3 levels of the Northern Hemisphere 1 observed by IASI. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iván, Y.H.; Lopez-Farias, R.; José, J.P.; Pichardo-Corpus, J.A.; Delgadillo-Ruiz, O.; Flores-Torres, A.; García-Reynoso, A.; Ruiz-Suárez, L.G.; Mendoza, A. Increasing weekend effect in ground-level O3 in metropolitan areas of Mexico during 1988–2016. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Foy, B.; William, H.B.; James, J.S. Changes in ozone photochemical regime in Fresno, California from 1994 to 2018 deduced from changes in the weekend effect. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notario, A.; Bravo, I.; Adame, J.A.; Díaz-de-Mera, Y.; Aranda, A.; Rodríguez, A.; Rodríguez, D. Analysis of NO, NO2, NOx, O3 and oxidant (Ox = O3 + NO2) levels measured in a metropolitan area in the southwest of Iberian Peninsula. Atmos. Res. 2012, 104–105, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notario, A.; Bravo, I.; Adame, J.A.; Díaz-de-Mera, Y.; Aranda, A.; Rodríguez, A.; Rodríguez, D. Behaviour and variability of local and regional oxidant levels (Ox = O3 + NO2) measured in a polluted area in central-southern of Iberian Peninsula. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faustini, A.; Stafoggia, M.; Williams, M.; Davoli, M.; Forastiere, F. The effect of short-term exposure to O3, NO2, and their combined oxidative potential on mortality in Rome. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2019, 12, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xia, L.; Zang, K.; Xu, W.; Mu, Y. The abundance and inter-relationship of atmospheric peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN), peroxy propionyl nitrate (PPN), O3, and NOy during the wintertime in Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 137388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q. Research on Temporal and Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Ozone Concentration in Shenyang; Shenyang Aerospace University: Shenyang, China, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xing, J.; Mathur, R.; Liu, S.; Wang, S.; Hao, J. Quantification of the enhancement of PM2.5 concentration by the downward transport of ozone from the stratosphere. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 126907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Yin, L.; Gu, F.; Sun, R. Study on PM2.5 emission characteristics before and after the outbreak of COVID-19 in Tianjin City in the first quarter of 2020. Low Carbon World 2020, 10, 14–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Fang, N.; Xiong, T.; Wang, X.; Ye, C. Analysis of characteristics of atmospheric pollution in typical cities along the Yangtze River during the period of COVID-19 epidemic. Environ. Technol. 2020, 33, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Ren, W.; Li, X.; Ma, X.; Li, B. Distribution and urban–suburban differences in ground-level ozone and its precursors over Shenyang, China. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2018, 131, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Duan, F.; He, K.; Qin, Y.; Tong, D.; Geng, G.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Yang, S.; Ye, S.; et al. Air pollution characteristics and their relationship with emissions and meteorology in the Yangtze river delta region during 2014–2016. Environ. Sci. 2019, 83, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, M.G.; Schröder, S.; Lyapina, O.; Cooper, O.; Galbally, I.; Petropavlovskikh, I.; von Schneidemesser, E.; Tanimoto, H.; Elshorbany, Y.; Naja, M.; et al. Tropospheric Ozone Assessment Report: Database and Metrics Data of Global Surface Ozone Observations. Elem. Sci. Anth. 2017, 5, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, Z.L.; Doherty, R.M.; von Schneidemesser, E.; Malley, C.S.; Cooper, O.R.; Pinto, J.P.; Colette, A.; Xu, X.; Simpson, D.; Schultz, M.G.; et al. Tropospheric Ozone Assessment Report: Presentday ozone distribution and trends relevant to human health. Elem Sci. Anth. 2018, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, P.J.; Naik, V.; Fiore, A.M.; Gaudel, A.; Guo, J.; Lin, M.Y.; Neu, J.; Parrish, D.; Reider, H.E.; Schnell, J.L.; et al. Tropospheric Ozone Assessment Report: Assessment of global-scale model performance for global and regional ozone distributions, variability, and trends. Elem. Sci. Anth. 2018, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudel, A.; Cooper, O.R.; Ancellet, G.; Barret, B.; Boynard, A.; Burrows, J.P.; Clerbaux, C.; Coheur, P.-F.; Cuesta, J.; Cuevas Agulló, E.; et al. Tropospheric Ozone Assessment Report: Present-day distribution and trends of tropospheric ozone relevant to climate and global atmospheric chemistry model evaluation. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2018, 6, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbrecht, W.; Froidevaux, L.; Fuller, R.; Wang, R.; Anderson, J.; Roth, C.; Bourassa, A.; Degenstein, D.; Damadeo, R.; Zawodny, J.; et al. An update on ozone profile trends for the period 2000 to 2016. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 10675–10690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, Y.; Petetin, H.; Thouret, V.; Marécal, V.; Josse, B.; Clark, H.; Sauvage, B.; Fontaine, A.; Athier, G.; Blot, R.; et al. Climatology and long-term evolution of ozone and carbon monoxide in the UTLS at northern mid-latitudes, as seen by IAGOS from 1995 to 2013. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 5415–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belan, B.D.; Savkin, D.E. The Role of Air Humidity in Variations in Near-Surface Ozone Concentration. Atmos. Ocean Opt. 2019, 32, 586–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Yang, B.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, M. Study on the Influence of Meteorological Conditions on the Ambient Air Ozone Concentration in Shenyang. China Environ. Monit. 2015, 31, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romer, P.S.; Duffey, K.C.; Wooldridge, P.J.; Edgerton, E.; Baumann, K.; Feiner, P.A.; Miller, D.O.; Brune, W.H.; Koss, A.R.; de Gouw, J.A.; et al. Effects of temperature-dependent NOx emissions on continental ozone production. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 2601–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.M.; Ismail, M.; Yuen, F.S.; Abdullah, S.; Elhadi, R.E. The Relationship between Daily Maximum Temperature and Daily Maximum Ground Level Ozone Concentration. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2017, 26, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Wang, T.; Xie, M.; Han, Y. A case study of the impact of atmospheric particles on surface ozone in Nanjing area. Clim. Environ. Res. 2013, 18, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Zhao, C.; Yang, Y. A comprehensive analysis of the spatial-temporal variation of urban air pollution in China during 2014–2018. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 220, 117066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellano, P.; Reynoso, J.; Quaranta, N.; Bardach, A.; Ciapponi, A. Short-term exposure to particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and ozone (O3) and all-cause and cause-specific mortality: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Feng, X.; Heal, M.R. Temporal persistence of intra-urban spatial contrasts in ambient NO2, O3 and Ox in Edinburgh, UK. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2016, 7, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Guan, Q.; Lin, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, N. Air pollution characteristics and human health risks in key cities of northwest China. Environ. Manag. 2020, 269, 110791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstone, M.E. Review of evidence on health aspects of air pollution—REVIHAAP Project. Air Qual. Clim. Chang. 2015, 49, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, S.; He, S.; He, P. Heterogeneous effects of COVID-19 lockdown measures on air quality in Northern China. Appl. Energy 2021, 282, 116179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, D.; Shen, F.; Wang, J.; Ma, X.; Li, Z.; Ge, P.; Ou, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, M.; Chen, M.; et al. Changes of air quality and its associated health and economic burden in 31 provincial capital cities in China during COVID-19 pandemic. Atmos. Res. 2021, 249, 105328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Gou, X.; Yang, J.; Zhao, W.; Xu, Q.; Liu, Y. Characteristics of Ozone Variation in Typical Cities in China and Its Relationship with Meteorological Conditions. Plateau Weather 2020, 39, 416–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



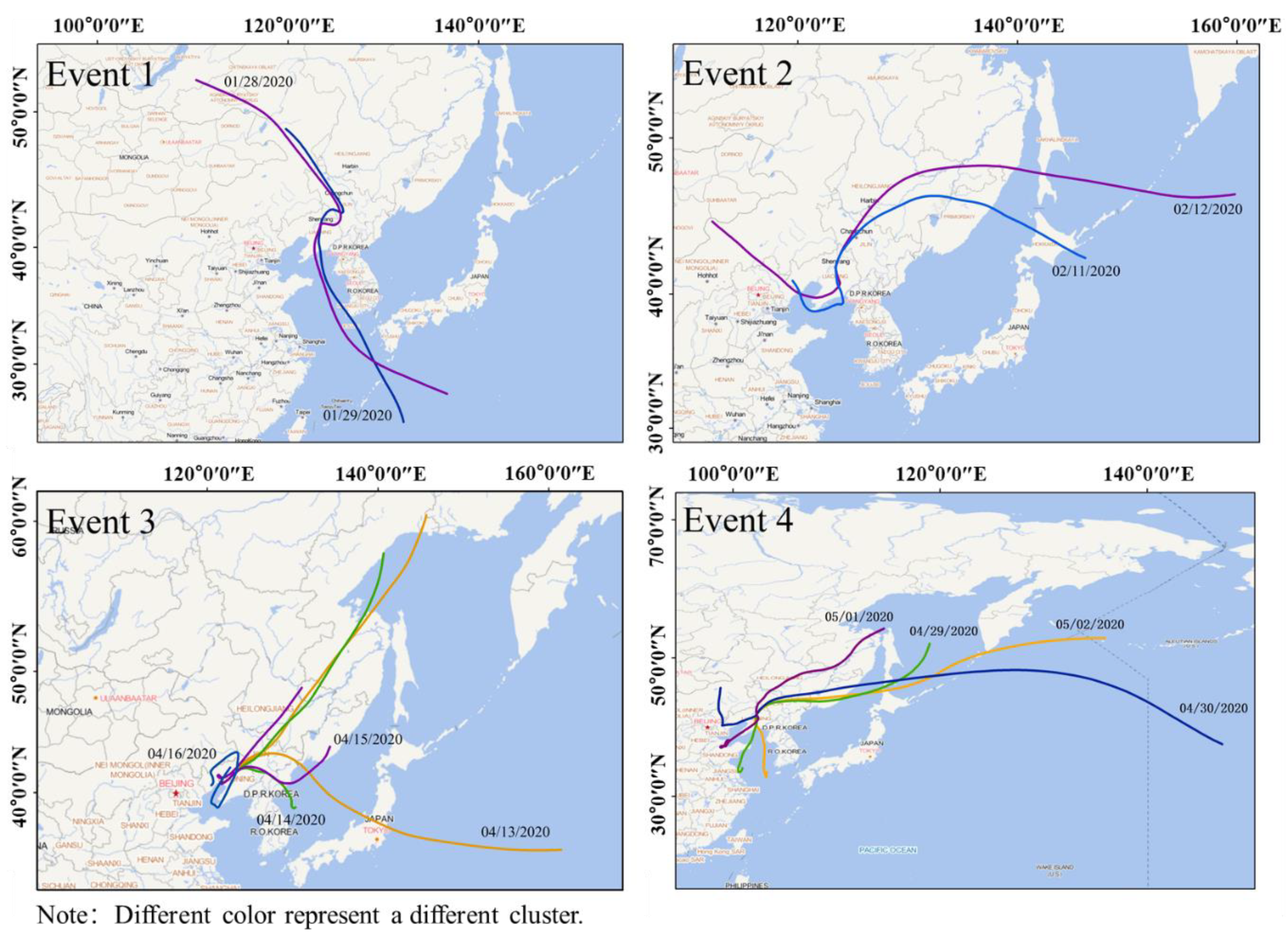

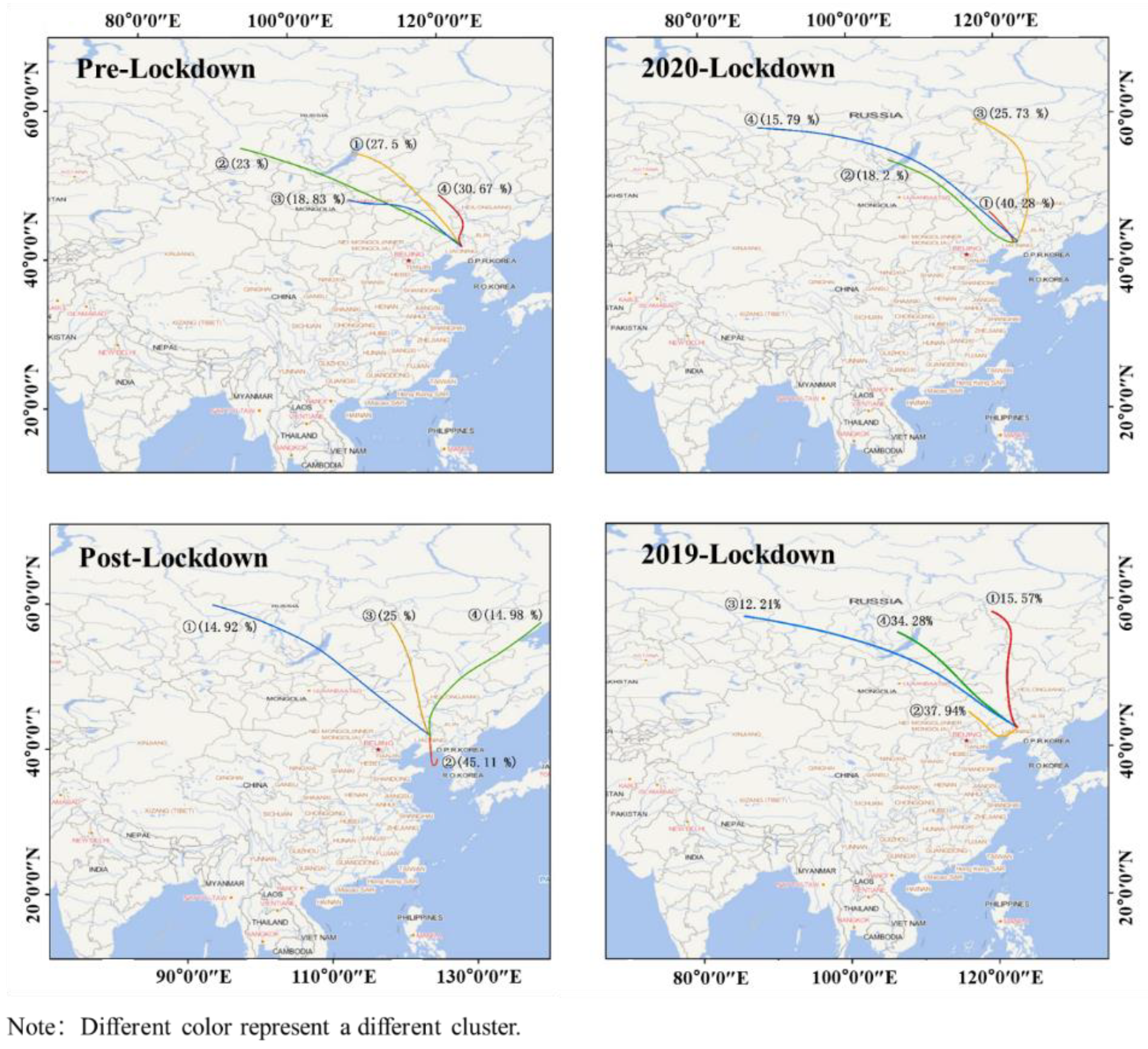
| Period | Cluster NO. | Direction | Areas of Pathways | Percentage of Total Trajectory (%) | Trajectory Length (km) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre lockdown | 1 | NW | Lake Baikal, Yabnorov and Borshov Mountains, Eastern Mongolia, Inner Mongolia Plateau, Greater Khingan Range, Horqin Sandy Land | 27.50 | 1857.13 |
| 2 | WNW | East Sayan Mountain in Russia, Northeast Kent Mountain in Mongolia, Yanshan Mountains | 23.00 | 2862.09 | |
| 3 | WNW | Kent Mountain, Inner Mongolia Plateau, Horqin Sandy Land | 18.83 | 1439.85 | |
| 4 | NNW | Northern Greater Khingan Range, Northeast Plain, Western Heilongjiang, Northwest Jilin, Northern Liaoning | 30.67 | 808.62 | |
| 2020 lockdown | 1 | NW | Huolingole in Inner Mongolia, Songliao Watershed, Northwest Liaoyang, Western Horqin Sandy Land, Southwest Shenyang | 40.28 | 569.22 |
| 2 | WNW | Yabnorov and Borshov Mountains, Northeast Mongolia, Northeast Xilinguole League in Inner Mongolia, Chifeng City, Southwest Fuxin, Northeast Jinzhou | 18.20 | 1962.43 | |
| 3 | NNW | Outer Hinggan Mountains in Russia, Middle Greater and Lesser Khingan Range, West Heilongjiang Province, Central Jilin Province, Northeast Plain | 25.73 | 1973.17 | |
| 4 | WNW | South Russia, Lake Baikal, Eastern Mongolia, Southwest Hulunbeir, Northeast Xilinguole League, Central Tongliao, Northwest Shenyang | 15.79 | 3489.30 | |
| Post lockdown | 1 | WNW | Eastern Mongolia, Lake Baikal, Southwest Hulunbeir, Northeast Xilinguole League, central Tongliao, Northwest Shenyang | 14.92 | 3150.11 |
| 2 | S | Yellow Sea, Bohai Sea, Liaodong Peninsula, Northeast Dalian, Southeast Anshan, Liaoyang | 45.11 | 355.11 | |
| 3 | NNW | South Russia, Great Khingan Mountains, Northeast Plain, Horqin Desert | 25.00 | 1766.78 | |
| 4 | NE | Ayano meisky, Turana and Buleya Mountains, Lesser Khingan Range, Northwest Heilongjiang Province, West side of the Northeast Plain | 14.98 | 2114.64 | |
| 2019 lockdown | 1 | N | Southeast Russia, Northeast Inner Mongolia, Northeast Plain, Tongliao | 15.57 | 1772.01 |
| 2 | WNW | Xilin Gol League, Chifeng, Huludao, Liaodong Bay, Panjin | 37.94 | 843.95 | |
| 3 | WNW | South Russia, East Sayan Mountain, Lake Baikal, Yabnorov and Borshov Mountains, East Mongolia, Northeast Inner Mongolia, Horqin Sandy Land | 12.21 | 4177.31 | |
| 4 | NW | Lake Baikal, Yabnorov and Borshov mountains, East Mongolia, Northeast Inner Mongolia, Horqin Sandy Land | 34.28 | 2150.36 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Fang, C. Assessing the Impact of Lockdown on Atmospheric Ozone Pollution Amid the First Half of 2020 in Shenyang, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9004. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17239004
Wang L, Wang J, Fang C. Assessing the Impact of Lockdown on Atmospheric Ozone Pollution Amid the First Half of 2020 in Shenyang, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(23):9004. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17239004
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Liyuan, Ju Wang, and Chunsheng Fang. 2020. "Assessing the Impact of Lockdown on Atmospheric Ozone Pollution Amid the First Half of 2020 in Shenyang, China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 23: 9004. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17239004
APA StyleWang, L., Wang, J., & Fang, C. (2020). Assessing the Impact of Lockdown on Atmospheric Ozone Pollution Amid the First Half of 2020 in Shenyang, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(23), 9004. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17239004





