Apoptotic Effect of 1800 MHz Electromagnetic Radiation on NIH/3T3 Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Exposure System
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Cell Apoptosis Assay
2.5. Real-Time qPCR to Detect p53 Expression
2.6. Western Blot to Detect p53 Protein Expression
2.7. Confocal Microscopy to Analyze p53 Expression
2.8. Analysis of Mitochondrial Structure by Electron Microscope
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. NIH/3T3 Cell Viability and Apoptosis
3.2. p53 Expression Analysis
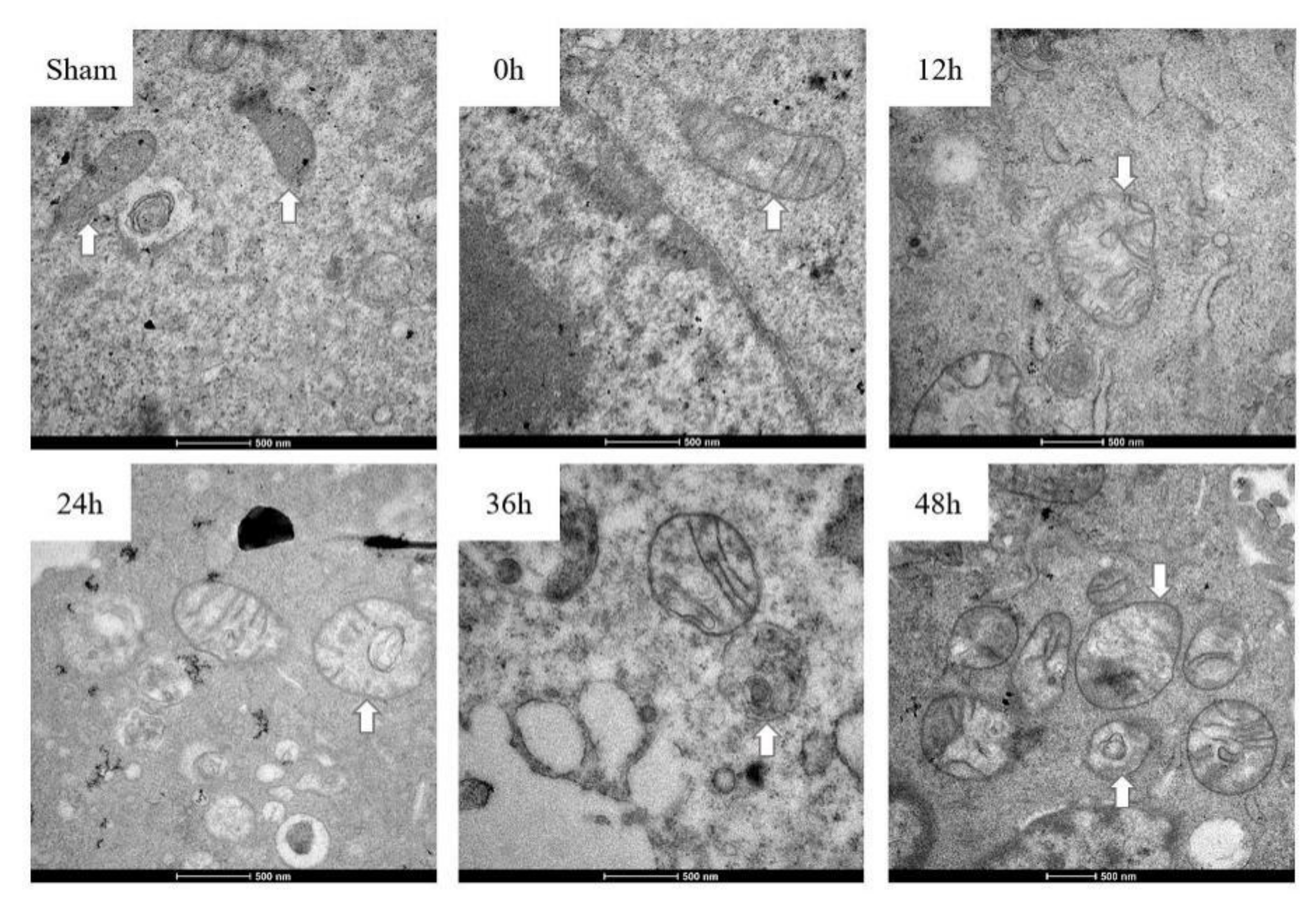
3.3. Mitochondria Imaging
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Non-ionizing radiation, Part 2: Radiofrequency electromagnetic fields. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 2013, 102, 1–460. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.C. Malignant brain tumors from cellular mobile telephone radiation. IEEE Antenna Propag. Mag. 2007, 49, 212–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, V.G.; Teo, C.; Kundi, M.; Hardell, L.; Carlberg, M. Cell phones and brain tumors: A review including the long-term epidemiologic data. Surg. Neurol. 2009, 72, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strumylaite, L.; Mechonosina, K.; Tamasauskas, S. Environmental factors and breast cancer. Medicina (Kaunas) 2010, 46, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hardell, L.; Carlberg, M. Comments on the US National Toxicology Program technical reports on toxicology and carcinogenesis study in rats exposed to whole-body radiofrequency radiation at 900 MHz and in mice exposed to whole-body radiofrequency radiation at 1900 MHz. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, H.G.; Kim, K.B.; Kim, H.R. Possible Effects of Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Field Exposure on Central Nerve System. Biomol. Ther. 2019, 27, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffar, F.H.F.; Osman, K.; Ismail, N.H.; Chin, K.; Ibrahim, S.F. Adverse Effects of Wi-Fi Radiation on Male Reproductive System: A Systematic Review. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2019, 248, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wdowiak, A.; Mazurek, P.A.; Wdowiak, A.; Bojar, I. Effect of electromagnetic waves on human reproduction. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2017, 24, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.K.; Patel, S.K.; Tomard, M.S.; Singh, S.K.; Mesharam, M.K.; Krishnamurthy, S. Long-term exposure of 2450 MHz electromagnetic radiation induces stress and anxiety like behavior in rats. Neurochem. Int. 2019, 128, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.J.; Son, Y.; Han, N.K.; Choi, H.D.; Pack, J.K.; Kim, N.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, H.J. Impact of Long-Term RF-EMF on Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation in Aging Brains of C57BL/6 Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joubert, V.; Leveque, P.; Cueille, M.; Bourthoumieu, S.; Yardin, C. No apoptosis is induced in rat cortical neurons exposed to GSM phone fields. Bioelectromagnetics 2007, 28, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falzone, N.; Huyser, C.; Franken, D.R.; Leszczynski, D. Mobile Phone Radiation Does Not Induce Pro-apoptosis Effects in Human Spermatozoa. Radiat. Res. 2010, 174, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, A.M.; Streckert, J.; Bitz, A.K.; Hansen, V.W.; Lerchl, A. No effects of GSM-modulated 900 MHz electromagnetic fields on survival rate and spontaneous development of lymphoma in female AKR/J mice. BMC Cancer 2004, 4, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.P.; Zhang, K.Y.; Guo, L.; Chen, Q.L.; Gao, P.; Wang, T.; Li, J.; Guo, G.Z.; Ding, G.R. Effects of 1.8 GHz Radiofrequency Fields on the Emotional Behavior and Spatial Memory of Adolescent Mice. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ziegelberger, G. Icnirp statement on the “guidelines for limiting exposure to time-varying electric, magnetic, and electromagnetic fields (up to 300 ghz)”. Health Phys. 2009, 97, 257–258. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, W.; Wei, Z.; Zhiqiang, C.; Zheng, F. X-ray-induced apoptosis of BEL-7402 cell line enhanced by extremely low frequency electromagnetic field in vitro. Bioelectromagnetics 2009, 30, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.J.; Traitcheva, N.; Gothe, G.; Gomez, J.; Berg, H. ELF-electromagnetic fields inhibit the proliferation of human cancer cells and induce apoptosis. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2002, 21, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarnejad, Z.; Eskandary, H.; Dini, L.; Vergallo, C.; Nematollahi-Mahani, S.N.; Farsinejad, A.; Abadi, M.; Ahmadi, M. Cytotoxicity of temozolomide on human glioblastoma cells is enhanced by the concomitant exposure to an extremely low-frequency electromagnetic field (100 Hz, 100 G). Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 92, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Si, T.; Xu, X.; Liang, F.; Wang, L.; Pan, S. Electromagnetic radiation at 900 MHz induces sperm apoptosis through bcl-2, bax and caspase-3 signaling pathways in rats. Reprod. Health 2015, 12, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, A.J. p53, the cellular gatekeeper for growth and division. Cell 1997, 88, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merritt, A.J.; Potten, C.S.; Kemp, C.J.; Hickman, J.A.; Balmain, A.; Lane, D.P.; Hall, P.A. The role of p53 in spontaneous and radiation-induced apoptosis in the gastrointestinal tract of normal and p53-deficient mice. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 614–617. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.G.; Williams, J.; Munoz-Pinedo, C.; Perkins, G.A.; Brown, J.M.; Ellisman, M.H.; Green, D.R.; Frey, T.G. Correlated three-dimensional light and electron microscopy reveals transformation of mitochondria during apoptosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuderer, J.; Samaras, T.; Oesch, W.; Spat, D.; Kuster, N. High peak SAR exposure unit with tight exposure and environmental control for in vitro experiments at 1800 MHz. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory 2004, 52, 2057–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Wang, M.; Wu, S.; Ma, X.; An, G.; Liu, H.; Xie, F. Oxidative changes and apoptosis induced by 1800-MHz electromagnetic radiation in NIH/3T3 cells. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2015, 34, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.X.; Tai, J.L.; Li, G.Q.; Zhang, Z.W.; Xue, J.H.; Liu, H.S.; Zhu, H.; Cheng, J.D.; Liu, Y.L.; Li, A.M.; et al. Exposure to 1950-MHz TD-SCDMA electromagnetic fields affects the apoptosis of astrocytes via caspase-3-dependent pathway. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.Y.; Wu, T.; Liu, J.Y.; Gao, P.; Li, K.C.; Guo, Q.Y.; Yuan, M.; Lang, H.Y.; Zeng, L.H.; Guo, G.Z. 1950MHz Radio Frequency Electromagnetic Radiation Inhibits Testosterone Secretion of Mouse Leydig Cells. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cig, B.; Naziroglu, M. Investigation of the effects of distance from sources on apoptosis, oxidative stress and cytosolic calcium accumulation via TRPV1 channels induced by mobile phones and Wi-Fi in breast cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1848, 2756–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kesari, K.K.; Meena, R.; Nirala, J.; Kumar, J.; Verma, H.N. Effect of 3G cell phone exposure with computer controlled 2-D stepper motor on non-thermal activation of the hsp27/p38 MAPK stress pathway in rat brain. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 68, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttiglione, M.; Roca, L.; Montemurno, E.; Vitiello, F.; Capozzi, V.; Cibelli, G. Radiofrequency radiation (900 MHz) induces Egr-1 gene expression and affects cell-cycle control in human neuroblastoma cells. J. Cell Physiol. 2007, 213, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Xie, R.; Liu, R.; Lu, Y. Mitochondria-derived reactive oxygen species play an important role in Doxorubicin-induced platelet apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 11087–11100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, X.M. Signal transduction mediated by Bid, a pro-death Bcl-2 family proteins, connects the death receptor and mitochondria apoptosis pathways. Cell Res. 2000, 10, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Peng, R.Y.; Wang, S.M.; Wang, L.F.; Gao, Y.B.; Dong, J.; Li, X.; Su, Z.T. Relationship between cognition function and hippocampus structure after long-term microwave exposure. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2012, 25, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Von Niederhausern, N.; Ducray, A.; Zielinski, J.; Murbach, M.; Mevissen, M. Effects of radiofrequency electromagnetic field exposure on neuronal differentiation and mitochondrial function in SH-SY5Y cells. Toxicol In Vitro 2019, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, F.; Zhan, Q.; He, Y.; Cui, J.; He, S.; Wang, G. 1800MHz Microwave Induces p53 and p53-Mediated Caspase-3 Activation Leading to Cell Apoptosis In Vitro. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e163935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solek, P.; Majchrowicz, L.; Bloniarz, D.; Krotoszynska, E.; Koziorowski, M. Pulsed or continuous electromagnetic field induce p53/p21-mediated apoptotic signaling pathway in mouse spermatogenic cells in vitro dand thus may affect male fertility. Toxicology 2017, 382, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, H.; Sakuma, N.; Kaji, N.; Suhara, T.; Sekijima, M.; Nojima, T.; Miyakoshi, J. Phosphorylation and gene expression of p53 are not affected in human cells exposed to 2.1425 GHz band CW or W-CDMA modulated radiation allocated to mobile radio base stations. Bioelectromagnetics 2006, 27, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.; Hilly, O.; Strenov, Y.; Tzabari, C.; Hauptman, Y.; Feinmesser, R. Effect of cell phone-like electromagnetic radiation on primary human thyroid cells. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2016, 92, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.-Y.; Song, J.-D.; Liang, Z.-Y.; Oskouei, K.; Xiao, X.-Q.; Hou, W.-Z.; Li, J.-T.; Yang, Y.-S.; Wang, M.-L.; Murbach, M. Apoptotic Effect of 1800 MHz Electromagnetic Radiation on NIH/3T3 Cells. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17030819
Li D-Y, Song J-D, Liang Z-Y, Oskouei K, Xiao X-Q, Hou W-Z, Li J-T, Yang Y-S, Wang M-L, Murbach M. Apoptotic Effect of 1800 MHz Electromagnetic Radiation on NIH/3T3 Cells. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(3):819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17030819
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Dan-Yang, Jing-Dong Song, Zhao-Yuan Liang, Kiana Oskouei, Xiang-Qian Xiao, Wen-Zhe Hou, Jin-Tao Li, Yi-Shu Yang, Ming-Lian Wang, and Manuel Murbach. 2020. "Apoptotic Effect of 1800 MHz Electromagnetic Radiation on NIH/3T3 Cells" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 3: 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17030819
APA StyleLi, D.-Y., Song, J.-D., Liang, Z.-Y., Oskouei, K., Xiao, X.-Q., Hou, W.-Z., Li, J.-T., Yang, Y.-S., Wang, M.-L., & Murbach, M. (2020). Apoptotic Effect of 1800 MHz Electromagnetic Radiation on NIH/3T3 Cells. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(3), 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17030819




