Concentrations, Possible Sources and Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Multi-Media Environment of the Songhua River, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
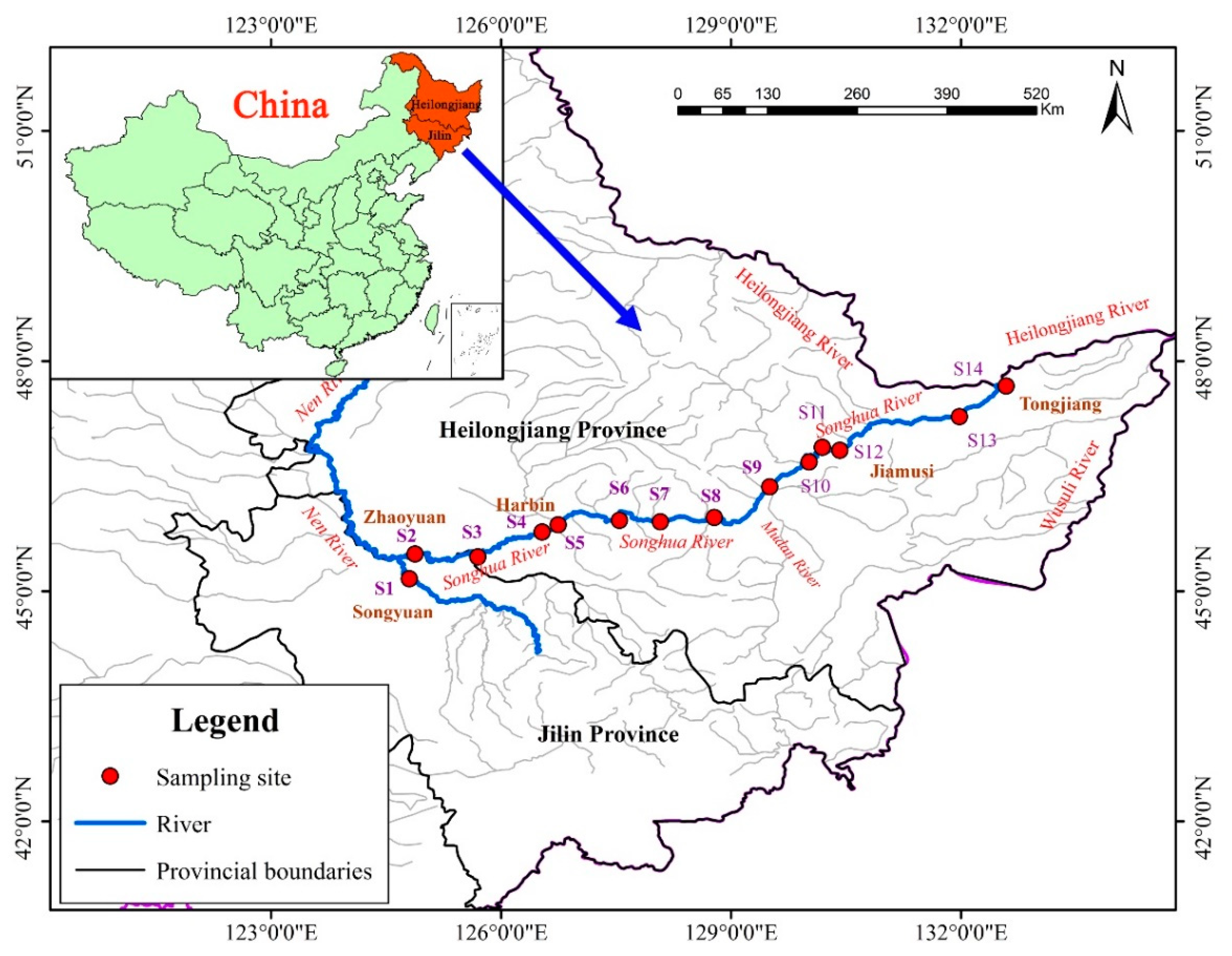
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Heavy Metal Analysis
2.2.1. Sample Collection and Processing
2.2.2. Quality Assurance and Quality Control (QA/QC)
2.3. Evaluation Pollution of Heavy Metals
2.3.1. Heavy Metal Pollution Index
2.3.2. Nemerow Pollution Index
2.3.3. Human Health Risk Assessment
2.3.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Concentrations and Spatial Distribution of Heavy Metals
3.1.1. Concentration
3.1.2. Spatial Distribution
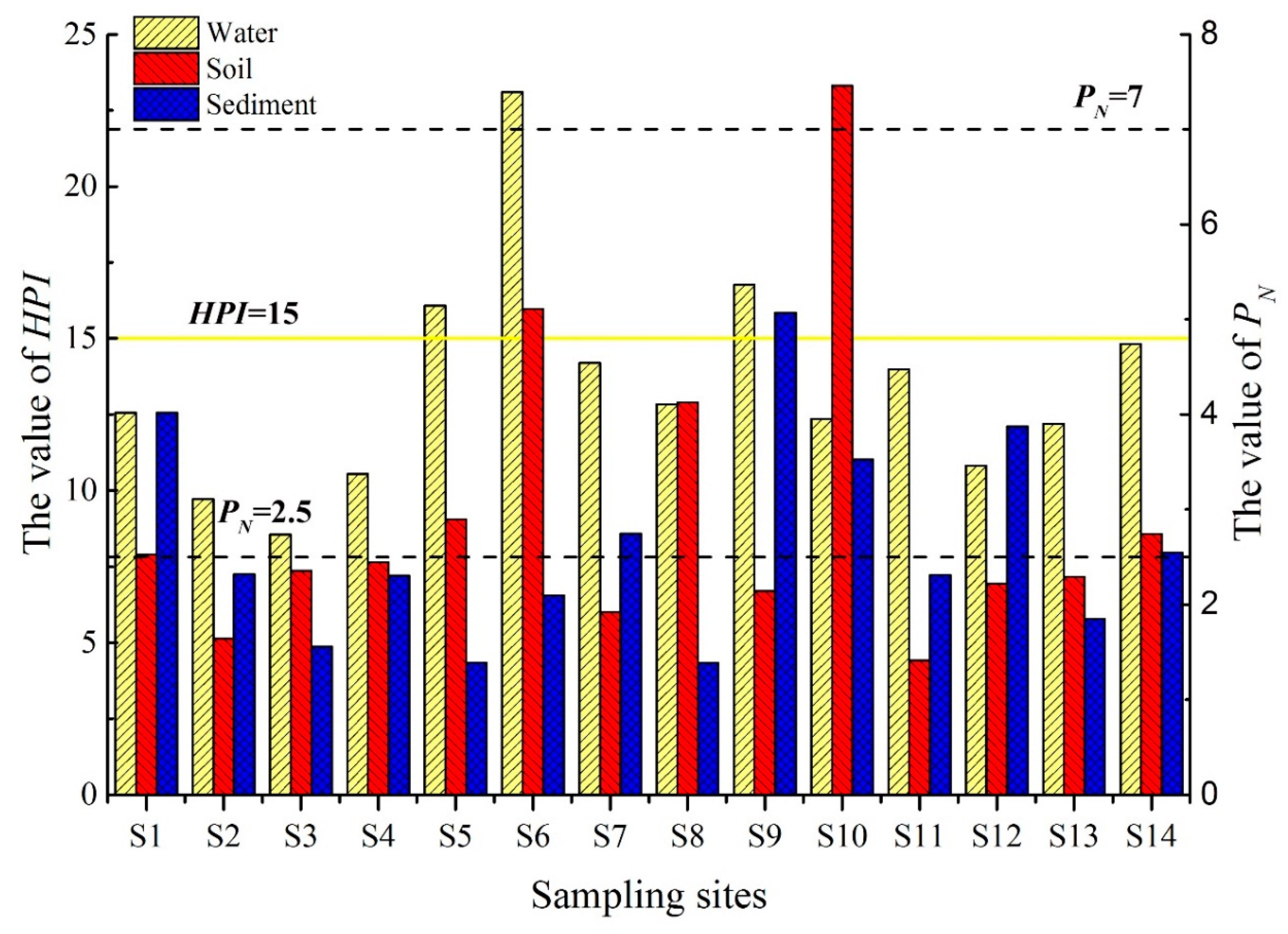
3.2. Pollution Assessment of Heavy Metals
3.3. Human Health Risk Assessment
3.4. Analysis of Sources of Heavy Metal Pollution
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, X.; Karki, K.; Zeng, C.; Aastha, R.B.; Zhang, F. Heavy metals in surface sediments in the trans-Himalayan Koshi River catchment: Distribution, source identification and pollution assessment. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, B.; Xu, D.; Chen, T.; Yan, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, M. Leachability characteristic of heavy metals and associated health risk study in typical copper mining-impacted sediments. Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, L.; Huang, H.; Xia, F.; Liu, Y.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Zhang, M.; Mei, K. Risk analysis of heavy metal concentration in surface waters across the rural-urban interface of the Wen-Rui Tang River, China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeng, X.; Liu, Y.; You, S.; Zeng, G.; Li, F. Spatial distribution, health risk assessment and statistical source identification of the trace elements in surface water from the Xiangjiang river, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 9400–9412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Wang, L.; Deng, L.; Jin, Z. Characteristics, sources, water quality and health risk assessment of trace elements in river water and well water in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2004–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Feng, X.; Li, G.; Bi, X.; Zhu, J.; Qin, H.; Dai, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Sun, G. Distributions, sources and pollution status of 17 trace metal/metalloids in the street dust of a heavily industrialized city of central China. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 182, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Gong, D.; Zhao, W.; Lin, L.; Yang, W.; Guo, W.; Tang, X.; Li, Q. Spatial-temporal distribution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in surface water of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 134883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Zhang, F.; Hu, P.; Hough, R.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; An, L.; Li, Y.; Li, K.; Liu, D.; et al. Heavy metals in sediment from the urban and rural rivers in Harbin City, Northeast China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, N.; Liu, W.; Xie, H.; Gao, L.; Han, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, H. Distribution and assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediment of Yellow River, China. J. Environ. Sci. China 2016, 39, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Chen, H.; Song, L.; Yao, Z.; Meng, F.; Teng, Y. Characterization and source apportionment of heavy metals in the sediments of Lake Tai (China) and its surrounding soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Feng, H.; Chang, J.; Qu, J.; Xie, H.; Yu, L. Heavy metal contamination in surface sediments of Yangtze River intertidal zone: An assessment from different indexes. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1533–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, H.; Mou, L.; Ru, J.; Zhao, J.; Xiao, S. Long-term and high-concentration heavy-metal contamination strongly influences the microbiome and functional genes in Yellow River sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637, 1400–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, L.; Li, H.; Yang, Z.; Min, X.; Liao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Men, S.; Yan, Y.; Xu, J. Heavy metals and metalloids in the surface sediments of the Xiangjiang River, Hunan, China: Distribution, contamination, and ecological risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, W.; Zhang, Y.; Quan, X. Health risk assessment of heavy metals and pesticides: A case study in the main drinking water source in Dalian, China. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, W.M.; Ghanim, E.H.; Duliu, O.G.; El Samman, H.; Frontasyeva, M.V. Major and trace element distribution in soil and sediments from the Egyptian central Nile Valley. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2017, 131, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turer, D.; Maynard, J.B.; Sansalone, J.J. Heavy metal contamination in soils of urban highways: Comparison between runoff and soil concentrations at Cincinnati, Ohio. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2001, 132, 293–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Huang, C.; Chen, Z.; Bao, K. Distribution, ecological risk assessment, and bioavailability of cadmium in soil from Nansha, Pearl River Delta, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minh, N.D.; Hough, R.L.; Nyberg, Y.; Vinh, N.C.; Khai, N.M.; Öborn, I. Assessing dietary exposure to cadmium in a metal recycling community in Vietnam: Age and gender aspects. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 416, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Liu, L.; Qi, H.; Zhang, Z.; Song, W.; Shen, J.; Chen, Z.; Ren, N.; Grabuski, J.; Li, Y. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water, sediment and soil of the Songhua River Basin, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 8399–8409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Zou, Z.; Li, R. Water quality assessment in the Harbin Reach of the Songhuajiang River (China) based on a fuzzy rough set and an attribute recognition theoretical model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 3507–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, C.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, H.; Xu, M.; Xu, L. Concentrations, speciation, and ecological risk of heavy metals in the sediment of the Songhua River in an urban area with petrochemical industries. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; He, M.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, W.; Yang, Z. Distribution and contamination assessment of heavy metals in sediment of the Second Songhua River, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 137, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Tan, L.; Shan, P.; Cao, H.; Deng, H. Analysis of the potential contamination risk of riverside key monitored enterprises on the aquatic environment of the Songhua River Basin. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 36, 2732–2739. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- State Environmental Protection Administration of China (SEPAC). Technical Specifications for Surface Water and Wastewater Monitoring; HJ_T91-2002; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002.
- State Environmental Protection Administration of China (SEPAC). Environmental Quality Standard for Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land; GB15618-2018; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2018.
- State Environmental Protection Administration of China (SEPAC). Water and Wastewater Monitoring and Analysis Methods; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Mohan, S.V.; Nithila, P.; Reddy, S.J. Estimation of heavy metals in drinking water and development of heavy metal pollution index. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 1996, 31, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Ministry of Health (CMH), National Standardization Administration of China. Standards for Drinking Water Quality; GB5749-2006; Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Nemerow, N.L.C. Scientific Stream Pollution Analysis; Scripta Book Company: Washington, DC, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Memoli, V.; Esposito, F.; Panico, S.C.; De Marco, A.; Barile, R.; Maisto, G. Evaluation of tourism impact on soil metal accumulation through single and integrated indices. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 682, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, A.; Iqbal, J.; Hussain, S. Adaptive geospatial modeling of soil contamination by selected heavy metals in the industrial area of Sheikhupura, Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 4447–4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China National Environmental Monitoring Centre (CNEMC). Background Values of Soil Elements in China; China Environmental Press: Beijing, China, 1990.
- US Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA). Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund. Volume I. Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part A); US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington DC, USA, 1989.
- State Environmental Protection Administration of China (SEPAC). Technical Guidelines for Risk Assessment of Contaminated Sites; HJ35.3-2104; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2014.
- US Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA). Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund. Volume I. Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part E, Supplemental Guidance for Dermal Risk Assessment); US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2004.
- US Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA). Supplemental Guidance for Developing Soil Screening Levels for Superfund Sites. Office of Soild Waste and Emergency Response; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2001.
- Li, J.; Zheng, C. Environmental Background Data Handbook; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1989.
- Wu, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, H.; Gao, M.; Bi, R.; Klerks, P.; Wang, H.; Luo, Y.; et al. Assessment of metal contamination in the Hun River, China, and evaluation of the fish Zacco platypus and the snail Radix swinhoei as potential biomonitors. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 6512–6522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Environmental Protection Administration of China (SEPAC). Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water; GB 3838-2002; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Zhang, F.; Yan, B.; Zhu, L. Speciation of heavy metals in sediment of the Songhua River, Northeast of China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2010, 29, 163–167. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- LeCloatec, M.F.; Bonete, P.H.; Lestel, L.I.; Ayrault, S. Sedimentary record of metal contamination in the Seine River during the last century. Phys. Chem. Earth 2011, 36, 515–529. [Google Scholar]
- Roig, N.; Sierra, J.; Moreno Garrido, I.; Nieto, E.; Gallego, E.P.; Schuhmacher, M.; Blasco, J. Metal bioavailability in freshwater sediment samples and their influence on ecological status of river basins. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 540, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Yang, Z.; Cui, Y.; Li, Y.; Hou, Q.; Yu, T. Soil heavy metal concentrations and their typical input and output fluxes on the southern Songnen Plain, Heilongjiang Province, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 139, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Pu, L.; Zhu, M.; Liao, Q.; Wang, H.; Cai, F. Spatial pattern of heavy metal concentration in the soil of rapid urbanization area: A case of Ehu Town, Wuxi City, Eastern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 3355–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Zhao, D.; Jia, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, S. Preliminary risk assessment of trace metal pollution in surface water from Yangtze River in Nanjing Section, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 82, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, G.; Liu, H.; Lam, P.K.S. Multivariate statistical evaluation of dissolved trace elements and a water quality assessment in the middle reaches of Huaihe River, Anhui, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 583, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xiong, J.; Deng, C.; Wang, X. The assessment of the heavy metal pollution and health risks in the Liujiang River, Xijiang Region. Guangxi Sci. 2018, 25, 393–399. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Albasel, N.; Cottenie, A. Heavy metal contamination near major highways, industrial and urban areas in Belgian grassland. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1985, 24, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuana, R.A.; Okieimen, F.E. Heavy metals in contaminated soils: A review of sources, chemistry, risks and best available strategies for remediation. ISRN Ecol. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, S.; Tao, B.; Tao, R.; He, X.; Qu, L.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Fu, Z. Chromium alters lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses both in vivo and in vitro. Chemosphere 2016, 148, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. Heavy Metal Concentration, Speciation and Ecological Risk Assessment of Surface Sediments in Songhua River. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou University of Technology, Lanzhou, China, March 2019. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]


| Exposure Parameter | Water | Soil | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit | Reference | Unit | Reference | |
| Ingestion rate (IR) [19,34] | L d−1 | 1.227 | mg d−1 | 100 |
| Exposure frequency (EF) | day | 365 | day | 365 |
| Exposure duration (ED) [21] | a | 74.8 | a | 74.8 |
| Daily exposure time (SL) [35] | hr day−1 | 0.6 | - | - |
| Average weight Body weight (BW) [19] | kg | 63.1 | kg | 63.1 |
| Average life time (AT) [21] | d | 27,302 | d | 27,302 |
| Conversion factor Conversion factor (CF) | L cm−3 | 10−6 | mg kg−1 | 10−6 |
| Skin exposed area Skin-surface area (SA) [35] | cm2 | 18,100 | cm2 | 18,100 |
| Permeability coefficient (Kp) [35] | cm hr−1 | Pb:10−4; Cd: 10−3; Cr: 2 × 10−3; Zn: 6 × 10−4; Ni: 2 × 10−4; Cu: 10−3 | - | - |
| Gastrointestinal absorption factor (ABSg) [35] | - | Pb:0.117; Cd:0.05; Cu:0.3; Zn:0.2; Ni:0.2; Cr:0.038 | - | - |
| Skin adhesion factor (SL) [35] | - | - | mg cm−2 d−1 | 0.2 |
| Dermal absorption factor (ABSd) [35] | - | 0.001 | - | - |
| Medium | Element | Range | Average | Median | Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation | Background Values [32,37] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water μg L−1 | Cu | 0.75–7.55 | 4.27 | 4.06 | 1.90 | 44.5% | 1.46 |
| Cr | 5.71–28.23 | 12.01 | 10.10 | 6.16 | 51.3% | 0.85 | |
| Zn | 17.29–116.01 | 64.25 | 59.13 | 29.49 | 45.9% | 3.88 | |
| Pb | 1.66–6.27 | 3.02 | 2.92 | 1.04 | 34.4% | 1.76 | |
| Ni | 0.50–3.07 | 1.68 | 1.49 | 0.66 | 39.2% | 1.02 | |
| Cd | ND–0.46 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.09 | 42.1% | 0.06 | |
| Sediment mg kg−1 | Cu | 7.94–23.88 | 14.57 | 13.30 | 4.66 | 32.0% | 20 |
| Cr | 33.66–88.99 | 63.97 | 60.62 | 16.24 | 25.4% | 58.6 | |
| Zn | 100.69–326.14 | 175.76 | 159.35 | 64.11 | 36.5% | 70.7 | |
| Pb | 7.88–23.44 | 16.84 | 17.60 | 4.16 | 24.7% | 24.2 | |
| Ni | 13.47–35.41 | 22.71 | 21.77 | 5.77 | 25.4% | 22.8 | |
| Cd | 1.17–5.82 | 0.28 | 0.26 | 0.13 | 45.2% | 0.086 | |
| Riparian soil mg kg−1 | Cu | 10.83–30.78 | 18.27 | 18.52 | 5.19 | 28.4% | 20 |
| Cr | 16.79–105.90 | 74.26 | 77.20 | 21.66 | 29.2% | 58.6 | |
| Zn | 81.40–255.18 | 145.83 | 135.42 | 44.01 | 30.2% | 70.7 | |
| Pb | 9.27–28.41 | 18.82 | 18.54 | 4.15 | 22.0% | 24.2 | |
| Ni | 14.20–31.13 | 23.79 | 23.97 | 5.64 | 23.7% | 22.8 | |
| Cd | 0.37–0.87 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.20 | 66.2% | 0.086 |
| Element | RfDin | RfDderm | SF | CDIw-in | CDIs-in | CDIw-derm | CDIs-derm | CDIin | CDIderm | HQin | HQderm | HI | CRin | CRderm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | 0.04 | 0.012 | - | 2.49 × 10−5 | 2.89 × 10−5 | 7.34 × 10−10 | 1.05 × 10−6 | 5.38 × 10−5 | 1.05 × 10−6 | 1.35 × 10−3 | 8.74 × 10−5 | 1.43 × 10−3 | - | - |
| Cr | 0.003 | 0.015 | - | 8.87 × 10−6 | 1.18 × 10−4 | 4.13× 10−9 | 4.26 × 10−6 | 1.27 × 10−4 | 4.26 × 10−6 | 4.22 × 10−2 | 2.84 × 10−4 | 4.25 × 10−2 | - | - |
| Zn | 0.3 | 0.06 | - | 5.00 × 10−5 | 2.31 × 10−4 | 6.64× 10−9 | 8.37 × 10−6 | 2.81 × 10−4 | 8.37 × 10−6 | 9.37 × 10−4 | 1.40 × 10−4 | 1.08 × 10−3 | - | - |
| Pb | 0.001 | 4 × 10−4 | - | 6.88 × 10−6 | 2.98 × 10−5 | 5.20 × 10−11 | 1.08 × 10−6 | 3.76 × 10−5 | 1.08 × 10−6 | 3.67 × 10−2 | 2.70 × 10−3 | 3.94 × 10−2 | - | - |
| Ni | 0.02 | 0.005 | - | 6.51 × 10−6 | 3.77 × 10−5 | 5.76 × 10−11 | 1.36 × 10−6 | 4.42 × 10−5 | 1.36 × 10−6 | 2.21 × 10−3 | 2.73 × 10−4 | 2.48 × 10−3 | - | - |
| Cd | 5 × 10−4 | 5 × 10−6 | 6.1 | 2.62 × 10−7 | 4.89 × 10−7 | 4.65 × 10−11 | 1.77 × 10−8 | 7.51 × 10−7 | 1.77 × 10−8 | 1.50 × 10−3 | 3.54 × 10−3 | 5.05 × 10−3 | 4.58 × 10−6 | 1.08 × 10−7 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, K.; Cui, S.; Zhang, F.; Hough, R.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, S.; An, L. Concentrations, Possible Sources and Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Multi-Media Environment of the Songhua River, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17051766
Li K, Cui S, Zhang F, Hough R, Fu Q, Zhang Z, Gao S, An L. Concentrations, Possible Sources and Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Multi-Media Environment of the Songhua River, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(5):1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17051766
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Kunyang, Song Cui, Fuxiang Zhang, Rupert Hough, Qiang Fu, Zulin Zhang, Shang Gao, and Lihui An. 2020. "Concentrations, Possible Sources and Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Multi-Media Environment of the Songhua River, China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 5: 1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17051766
APA StyleLi, K., Cui, S., Zhang, F., Hough, R., Fu, Q., Zhang, Z., Gao, S., & An, L. (2020). Concentrations, Possible Sources and Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Multi-Media Environment of the Songhua River, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(5), 1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17051766








