Dimensions of the Complexity of Health Interventions: What Are We Talking about? A Review
Abstract
1. Background
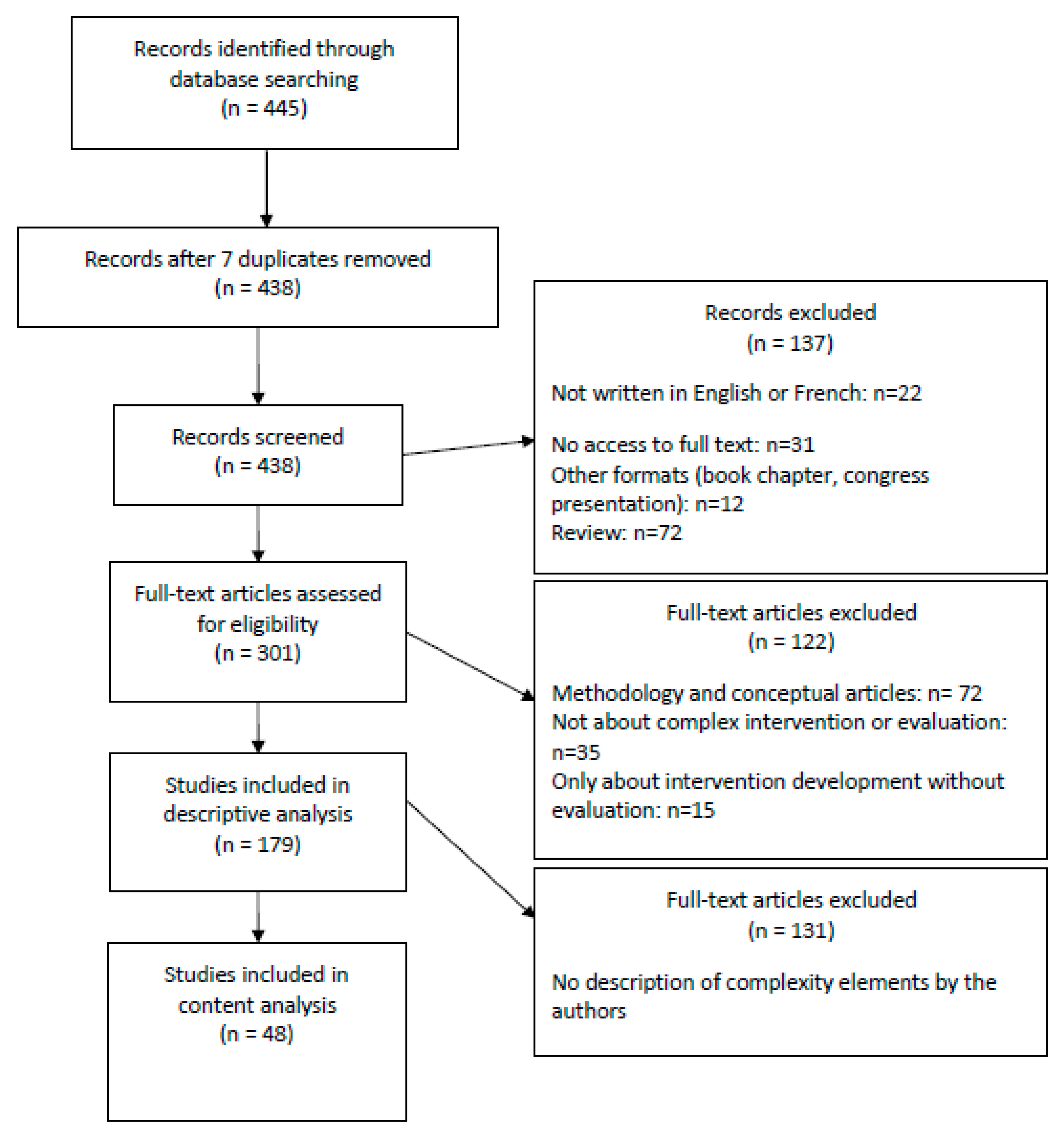
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Article Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Description of the Published Articles
3.2. The Dimensions of Complexity
3.2.1. Characteristics of Intervention Stakeholders
“Health care interventions […] are typically complex: they may […] seek to achieve outcomes that are difficult to influence, such as changes in individual patient or professional behaviour.”(article 8)
3.2.2. The Multimodality of an Intervention
3.2.3. The Intervention Context
“To describe the contexts in which the intervention was delivered and explore contextual factors that may influence the delivery or impact of the intervention, and the outcomes. […] It may also explain intentional and unintentional differences in delivery. Reflecting on the relationship between organisational context and how each agency used the program to address local needs may have implications for future program design and delivery. […] We conceptualised context as incorporating the social, structural and political environment of each participating organisation.”(article 41)
3.3. The Level of Detail in Descriptions of Dimensions of Complexity
3.3.1. Minimalist Descriptions
3.3.2. Intermediate Descriptions
“The intervention is “complex” according to the MRC definition because it comprises a number of, and interactions between, components within the intervention that subsequently impact on a number of variable outcomes. The components are: psychoeducation and peer support, each of which is a complex intervention in its own right, and each may work independently as well as inter-dependently in exerting their effects. […]. Another issue for consideration in complex interventions is the number and difficulty of performing behaviours required by those delivering and/or receiving the intervention, such as those involved in this intervention by the sibling-participants.”(article 38)
3.3.3. In-Depth Descriptions
3.4. Recognising Complexity When Considering Interventions and Evaluations
“This complexity makes a classical randomized controlled trial (RCT) design […] inappropriate for evaluating the effectiveness of public health interventions in a real-life setting [15,16]. […] Therefore, an evaluation approach is proposed that includes a combination of quantitative and qualitative evaluation methods to answer the three research questions of this study. To answer the first and second question, a quasi-experimental pre-test post-test study design […] is used. […] intervention inputs, activities, and outputs are recorded to assess the implementation process.“(article 10)
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Craig, P.; Dieppe, P.; Macintyre, S.; Michie, S.; Nazareth, I.; Petticrew, M. Medical Research Council Guidance. Developing and evaluating complex interventions: The new Medical Research Council guidance. BMJ 2008, 337, a1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawe, P.; Shiell, A.; Riley, T. Theorising interventions as events in systems. Am. J. Community Psychol. 2009, 43, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, J.; Petticrew, M. Challenges to Evaluating Complex Interventions: A Content Analysis of Published Papers. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cambon, L.; Minary, L.; Ridde, V.; Alla, F. Transferability of interventions in health education: A review. BMC Public Health 2012, 12, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Moss, J.R.; Hiller, J.E. Applicability and transferability of interventions in evidence-based public health. Health Promot. Int. 2006, 21, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarons, G.A.; Sklar, M.; Mustanski, B.; Benbow, N.; Brown, C.H. “Scaling-out” evidence-based interventions to new populations or new health care delivery systems. Implement. Sci. 2017, 12, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, S.E.; West, B.T.; Veliz, P.; Frank, K.A.; Boyd, C.J. Social contexts of substance use among U.S. high school seniors: A multicohort national study. J. Adolesc. Health 2014, 55, 842–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoveller, J.; Viehbeck, S.; Di Ruggiero, E.; Greyson, D.; Thomson, K.; Knight, R. A critical examination of representations of context within research on population health interventions. Crit. Public Health 2016, 26, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiell, A.; Hawe, P.; Gold, L. Complex interventions or complex systems? Implications for health economic evaluation. BMJ 2008, 336, 1281–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, M.; Fitzpatrick, R.; Haines, A.; Kinmonth, A.L.; Sandercock, P.; Spiegelhalter, D.; Tyrer, P. Framework for design and evaluation of complex interventions to improve health. BMJ 2000, 321, 694–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, G.F.; Audrey, S.; Barker, M.; Bond, L.; Bonell, C.; Hardeman, W.; Moore, L.; O’Cathain, A.; Tinati, T.; Wight, D.; et al. Process evaluation of complex interventions: Medical Research Council guidance. BMJ 2015, 350, h1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawe, P.; Shiell, A.; Riley, T. Complex interventions: How “out of control” can a randomised controlled trial be? BMJ 2004, 328, 1561–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poland, B.; Frohlich, K.L.; Cargo, M. Context as a Fundamental Dimension of Health Promotion Program Evaluation; Potvin, L., McQueen, D.V., Hall, M., Anderson, L.M., Eds.; Health Promotion Evaluation Practices in the Americas; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 299–317. [Google Scholar]
- Cambon, L.; Terral, P.; Alla, F. From intervention to interventional system: Towards greater theorization in population health intervention research. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minary, L.; Trompette, J.; Kivits, J.; Cambon, L.; Tarquinio, C.; Alla, F. Which design to evaluate complex interventions? Toward a methodological framework through a systematic review. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2019, 19, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petticrew, M.; Knai, C.; Thomas, J.; Rehfuess, E.A.; Noyes, J.; Gerhardus, A.; Grimshaw, J.M.; Rutter, H.; McGill, E. Implications of a complexity perspective for systematic reviews and guideline development in health decision making. BMJ Glob. Health 2019, 4 (Suppl. 1), e000899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfadenhauer, L.M.; Gerhardus, A.; Mozygemba, K.; Lysdahl, K.B.; Booth, A.; Hofmann, B.; Wahlster, P.; Polus, S.; Burns, J.; Brereton, L.; et al. Making sense of complexity in context and implementation: The Context and Implementation of Complex Interventions (CICI) framework. Implement. Sci. 2017, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Cathain, A.; Croot, L.; Duncan, E.; Rousseau, N.; Sworn, K.; Turner, K.M.; Yardley, L.; Hoddinott, P. Guidance on how to develop complex interventions to improve health and healthcare. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e029954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, K.; Booth, A.; Garside, R.; Tunçalp, Ö.; Noyes, J. Qualitative evidence synthesis for complex interventions and guideline development: Clarification of the purpose, designs and relevant methods. BMJ Glob. Health 2019, 4 (Suppl. 1), e000882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candy, B.; Vickerstaff, V.; Jones, L.; King, M. Description of complex interventions: Analysis of changes in reporting in randomised trials since 2002. Trials 2018, 19, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Government of Canada, Canadian Institutes of Health Research. (2010) A Guide to Knowledge Synthesis. CIHR. 2010. Available online: http://www.cihr-irsc.gc.ca/e/41382.html (accessed on 25 January 2018).
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. BMJ 2009, 339, b2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, N.C.; Murray, E.; Darbyshire, J.; Emery, J.; Farmer, A.; Griffiths, F.; Guthrie, B.; Lester, H.; Wilson, P.; Kinmonth, A.L. Designing and evaluating complex interventions to improve health care. BMJ 2007, 334, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oakley, A.; Strange, V.; Bonell, C.; Allen, E.; Stephenson, J. RIPPLE Study Team. Process evaluation in randomised controlled trials of complex interventions. BMJ 2006, 332, 413–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohn, S.; Clinch, M.; Bunn, C.; Stronge, P. Entangled complexity: Why complex interventions are just not complicated enough. J. Health Serv. Res. Policy 2013, 18, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, P.; Di Ruggiero, E.; Frohlich, K.L.; Mykhalovskiy, E.; White, M. On behalf of the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR)–National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Context Guidance Authors Group. In Taking Account of Context in Population Health Intervention Research: Guidance for Producers, Users and Funders of Research; NIHR Evaluation, Trials and Studies Coordinating Centre: Southampton, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Movsisyan, A.; Arnold, L.; Evans, R.; Hallingberg, B.; Moore, G.; O’Cathain, A.; Pfadenhauer, L.M.; Segrott, J.; Rehfuess, E. Adapting evidence-informed complex population health interventions for new contexts: A systematic review of guidance. Implement. Sci. 2019, 14, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minary, L.; Alla, F.; Cambon, L.; Kivits, J.; Potvin, L. Addressing complexity in population health intervention research: The context/intervention interface. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2018, 72, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durlak, J.A. Why Program Implementation Is Important. J. Prev. Interv. Community 1998, 17, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbraith, J.S.; Herbst, J.H.; Whittier, D.K.; Jones, P.L.; Smith, B.D.; Uhl, G.; Fisher, H.H. Taxonomy for strengthening the identification of core elements for evidence-based behavioral interventions for HIV/AIDS prevention. Health Educ. Res. 2011, 26, 872–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.M. What Are the Components of Complex Interventions in Healthcare? Theorizing Approaches to Parts, Powers and the Whole Intervention. Soc. Sci. Med. 2013, 93, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, T.C.; Glasziou, P.P.; Boutron, I.; Milne, R.; Perera, R.; Moher, D.; Altman, D.G.; Barbour, V.; Macdonald, H.; Johnston, M.; et al. Better reporting of interventions: Template for intervention description and replication (TIDieR) checklist and guide. BMJ 2014, 348, g1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michie, S.; Wood, C.E.; Johnston, M.; Abraham, C.; Francis, J.J.; Hardeman, W. Behaviour change techniques: The development and evaluation of a taxonomic method for reporting and describing behaviour change interventions (a suite of five studies involving consensus methods, randomised controlled trials and analysis of qualitative data). Health Technol. Assess. 2015, 19, 1–188. [Google Scholar]
- Lewin, S.; Hendry, M.; Chandler, J.; Oxman, A.D.; Michie, S.; Shepperd, S.; Reeves, B.C.; Tugwell, P.; Hannes, K.; Rehfuess, E.A.; et al. Assessing the complexity of interventions within systematic reviews: Development, content and use of a new tool (iCAT_SR). BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2017, 17, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| N | Articles Included |
|---|---|
| 1 | Power R, Langhaug LF, Nyamurera T, Wilson D, Bassett MT, Cowan FM. Developing complex interventions for rigorous evaluation—a case study from rural Zimbabwe. Health Educ Res. 2004 Oct;19(5):570–575. |
| 2 | Byrne M, Cupples ME, Smith SM, Leathem C, Corrigan M, Byrne MC, et al. Development of a complex intervention for secondary prevention of coronary heart disease in primary care using the UK Medical Research Council framework. Am J Manag Care. 2006 May;12(5):261–266. |
| 3 | Sturt J, Whitlock S, Hearnshaw H. Complex intervention development for diabetes self-management. J AdvNurs. 2006 May;54(3):293–303. |
| 4 | Sturt J, Hearnshaw H, Farmer A, Dale J, Eldridge S. The Diabetes Manual trial protocol—a cluster randomized controlled trial of a self-management intervention for type 2 diabetes [ISRCTN06315411]. BMC Fam Pract. 2006;7:45. |
| 5 | Panella M, Marchisio S, Gardini A, Di Stanislao F. A cluster randomized controlled trial of a clinical pathway for hospital treatment of heart failure: study design and population. BMC Health Serv Res. 2007;7:179. |
| 6 | Paul G, Smith SM, Whitford D, O’Kelly F, O’Dowd T. Development of a complex intervention to test the effectiveness of peer support in type 2 diabetes. BMC Health Serv Res. 2007;7:136. |
| 7 | Protheroe J, Bower P, Chew-Graham C. The use of mixed methodology in evaluating complex interventions: identifying patient factors that moderate the effects of a decision aid. Fam Pract. 2007 Dec;24(6):594–600. |
| 8 | Redfern J, Rudd AD, Wolfe CDA, McKevitt C. Stop Stroke: development of an innovative intervention to improve risk factor management after stroke. Patient EducCouns. 2008 Aug;72(2):201–209. |
| 9 | Lenz M, Kasper J, Mühlhauser I. Development of a patient decision aid for prevention of myocardial infarction in type 2 diabetes—rationale, design and pilot testing. Psycho-Soc Med. 2009;6:Doc05. |
| 10 | deVlaming R, Haveman-Nies A, Van’t Veer P, de Groot LC. Evaluation design for a complex intervention program targeting loneliness in non-institutionalized elderly Dutch people. BMC Public Health. 2010;10:552. |
| 11 | Freund T, Wensing M, Mahler C, Gensichen J, Erler A, Beyer M, et al. Development of a primary care-based complex care management intervention for chronically ill patients at high risk for hospitalization: a study protocol. Implement Sci IS. 2010;5:70. |
| 12 | Lemmens KMM, Nieboer AP, Rutten-Van Mölken MPMH, van Schayck CP, Asin JD, Dirven JAM, et al. Application of a theoretical model to evaluate COPD disease management. BMC Health Serv Res. 2010;10:81. |
| 13 | Protheroe J, Blakeman T, Bower P, Chew-Graham C, Kennedy A. An intervention to promote patient participation and self-management in long term conditions: development and feasibility testing. BMC Health Serv Res. 2010;10:206. |
| 14 | Siddiqi K, Khan A, Ahmad M, Shafiq-ur-Rehman. An intervention to stop smoking among patients suspected of TB—evaluation of an integrated approach. BMC Public Health. 2010;10:160. |
| 15 | Vanhaecht K, Sermeus W, Peers J, Lodewijckx C, Deneckere S, Leigheb F, et al. The impact of care pathways for exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: rationale and design of a cluster randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2010;11:111. |
| 16 | Brady MC, Stott DJ, Norrie J, Chalmers C, St George B, Sweeney PM, et al. Developing and evaluating the implementation of a complex intervention: using mixed methods to inform the design of a randomised controlled trial of an oral healthcare intervention after stroke. Trials. 2011;12:168. |
| 17 | Glaucoma screening Platform Study group, Burr JM, Campbell MK, Campbell SE, Francis JJ, Greene A, et al. Developing the clinical components of a complex intervention for a glaucoma screening trial: a mixed methods study. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2011;11:54. |
| 18 | Greenhalgh T, Campbell-Richards D, Vijayaraghavan S, Collard A, Malik F, Griffin M, et al. New models of self-management education for minority ethnic groups: pilot randomized trial of a story-sharing intervention. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2011 Jan;16(1):28–36. |
| 19 | Hartveit M, Biringer E, Vanhaeht K, Haug K, Aslaksen A. The Western Norway mental health interface study: a controlled intervention trial on referral letters between primary care and specialist mental health care. BMC Psychiatry. 2011;11:177. |
| 20 | Hirsch O, Keller H, Krones T, Donner-Banzhoff N. Acceptance of shared decision making with reference to an electronic library of decision aids (arriba-lib) and its association to decision making in patients: an evaluation study. Implement Sci IS. 2011;6:70. |
| 21 | Treweek S, Ricketts IW, Francis J, Eccles M, Bonetti D, Pitts NB, et al. Developing and evaluating interventions to reduce inappropriate prescribing by general practitioners of antibiotics for upper respiratory tract infections: a randomised controlled trial to compare paper-based and web-based modelling experiments. Implement Sci IS. 2011;6:16. |
| 22 | Bath B, Pahwa P. A physiotherapy triage assessment service for people with low back disorders: evaluation of short-term outcomes. Patient Relat Outcome Meas. 2012 Jul;3:9–19. |
| 23 | Bench SD, Day TL, Griffiths P. Developing user centred critical care discharge information to support early critical illness rehabilitation using the Medical Research Council’s complex interventions framework. Intensive Crit Care Nurs Off J Br AssocCrit Care Nurses. 2012 Apr;28(2):123–131. |
| 24 | Chan CWH, Richardson A, Richardson J. Evaluating a complex intervention: a process evaluation of a psycho-education program for lung cancer patients receiving palliative radiotherapy. Contemp Nurse. 2012 Feb;40(2):234–244. |
| 25 | Cresswell KM, Sadler S, Rodgers S, Avery A, Cantrill J, Murray SA, et al. An embedded longitudinal multi-faceted qualitative evaluation of a complex cluster randomized controlled trial aiming to reduce clinically important errors in medicines management in general practice. Trials. 2012;13:78. |
| 26 | Irvine L, Falconer DW, Jones C, Ricketts IW, Williams B, Crombie IK. Can text messages reach the parts other process measures cannot reach: an evaluation of a behavior change intervention delivered by mobile phone? PloS One. 2012;7(12):e52621. |
| 27 | Jack SM, Ford-Gilboe M, Wathen CN, Davidov DM, McNaughton DB, Coben JH, et al. Development of a nurse home visitation intervention for intimate partner violence. BMC Health Serv Res. 2012;12:50. |
| 28 | Walsh TS, Salisbury LG, Boyd J, Ramsay P, Merriweather J, Huby G, et al. A randomised controlled trial evaluating a rehabilitation complex intervention for patients following intensive care discharge: the RECOVER study. BMJ Open. 2012;2(4). |
| 29 | Yam PS, Morrison R, Penpraze V, Westgarth C, Ward DS, Mutrie N, et al. Children, parents, and pets exercising together (CPET) randomised controlled trial: study rationale, design, and methods. BMC Public Health. 2012;12:208. |
| 30 | Chandler CI, DiLiberto D, Nayiga S, Taaka L, Nabirye C, Kayendeke M, et al. The PROCESS study: a protocol to evaluate the implementation, mechanisms of effect and context of an intervention to enhance public health centres in Tororo, Uganda. Implement Sci. 2013;8:113. |
| 31 | Clyne B, Bradley MC, Hughes CM, Clear D, McDonnell R, Williams D, et al. Addressing potentially inappropriate prescribing in older patients: development and pilot study of an intervention in primary care (the OPTI-SCRIPT study). BMC Health Serv Res. 2013;13:307. |
| 32 | Geaney F, Scotto Di Marrazzo J, Kelly C, Fitzgerald AP, Harrington JM, Kirby A, et al. The food choice at work study: effectiveness of complex workplace dietary interventions on dietary behaviours and diet-related disease risk - study protocol for a clustered controlled trial. Trials. 2013;14:370. |
| 33 | Higginson IJ, Koffman J, Hopkins P, Prentice W, Burman R, Leonard S, et al. Development and evaluation of the feasibility and effects on staff, patients, and families of a new tool, the Psychosocial Assessment and Communication Evaluation (PACE), to improve communication and palliative care in intensive care and during clinical uncertainty. BMC Med. 2013;11:213. |
| 34 | Hinrichs T, Brach M, Bucchi C, Moschny A, Wilm S, Thiem U, et al. An exercise programme for community-dwelling, mobility-restricted and chronically ill older adults with structured support by the general practitioner’s practice (HOMEfit). From feasibility to evaluation. Z FürGerontolGeriatr. 2013 Jan;46(1):56, 58–63. |
| 35 | Mars T, Ellard D, Carnes D, Homer K, Underwood M, Taylor SJC. Fidelity in complex behaviour change interventions: a standardised approach to evaluate intervention integrity. BMJ Open. 2013;3(11):e003555. |
| 36 | Poston L, Briley AL, Barr S, Bell R, Croker H, Coxon K, et al. Developing a complex intervention for diet and activity behaviour change in obese pregnant women (the UPBEAT trial); assessment of behavioural change and process evaluation in a pilot randomised controlled trial. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2013 Jul 15;13(1):148. |
| 37 | Round J, Drake R, Kendall E, Addicott R, Agelopoulos N, Jones L. Evaluating a complex system-wide intervention using the difference in differences method: the Delivering Choice Programme. BMJ Support Palliat Care. 2013 Aug 27;bmjspcare-2012-000285. |
| 38 | Sin J, Henderson C, Pinfold V, Norman I. The E Sibling Project—exploratory randomised controlled trial of an online multi-component psychoeducational intervention for siblings of individuals with first episode psychosis. BMC Psychiatry. 2013;13:123. |
| 39 | Yuen WW-Y, Wong WC-W, Tang CS-K, Holroyd E, Tiwari AF-Y, Fong DY-T, et al. Evaluating the effectiveness of personal resilience and enrichment programme (PREP) for HIV prevention among female sex workers: a randomised controlled trial. BMC Public Health. 2013 Jul 26;13:683. |
| 40 | Ettema R, Schuurmans MJ, Schutijser B, van Baar M, Kamphof N, Kalkman CJ. Feasibility of a nursing intervention to prepare frail older patients for cardiac surgery: a mixed-methods study. Eur J CardiovascNurs J Work Group CardiovascNursEurSocCardiol. 2015 Aug;14(4):342–351. |
| 41 | Haynes A, Brennan S, Carter S, O’Connor D, Schneider CH, Turner T, et al. Protocol for the process evaluation of a complex intervention designed to increase the use of research in health policy and program organisations (the SPIRIT study). Implement Sci IS. 2014;9:113. |
| 42 | Kwamie A, van Dijk H, Agyepong IA. Advancing the application of systems thinking in health: realist evaluation of the Leadership Development Programme for district manager decision-making in Ghana. Health Res Policy SystBioMed Cent. 2014;12:29. |
| 43 | Lawton R, Mceachan R, Jackson C, West R, Conner M. Intervention fidelity and effectiveness of a UK worksite physical activity intervention funded by the BUPA Foundation, UK. Health Promot Int. 2015 Mar;30(1):38–49. |
| 44 | Leamy M, Clarke E, Le Boutillier C, Bird V, Janosik M, Sabas K, et al. Implementing a complex intervention to support personal recovery: a qualitative study nested within a cluster randomised controlled trial. PloS One. 2014;9(5):e97091. |
| 45 | Leo SD, Bono L, Romoli V, West E, Ambrosio R, Gallucci M, et al. Implementation of the Liverpool Care Pathway (LCP) for the dying patient in the inpatient hospice setting: development and preliminary assessment of the Italian LCP program. Am J HospPalliat Care. 2014 Feb;31(1):61–68. |
| 46 | Nayiga S, DiLiberto D, Taaka L, Nabirye C, Haaland A, Staedke SG, et al. Strengthening patient-centred communication in rural Ugandan health centres: A theory-driven evaluation within a cluster randomized trial. EvalLondEngl 1995. 2014 Oct;20(4):471–491. |
| 47 | Rees K, Zweigenthal V, Joyner K. Implementing intimate partner violence care in a rural sub-district of South Africa: a qualitative evaluation. Glob Health Action. 2014;7:24588. |
| 48 | Watson DP, Young J, Ahonen E, Xu H, Henderson M, Shuman V, et al. Development and testing of an implementation strategy for a complex housing intervention: protocol for a mixed-methods study. Implement Sci IS. 2014;9:138. |
| N | Reference | Description of Complexity | Refence(s) to Complexity | Part of Article Where Complexity Is Identified | Influence of Complexity Identification in Development/Evaluation of the Intervention | Type of Study | Evaluation Approach | Methodology Approach |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Power R 2004 | Minimalist | Campbell 2000 | Background | In evaluation | Pilot study | - Quasi experimental trial- Process evaluation | Qualitative |
| 2 | Byrne M 2006 | Minimalist | - Bradley 1999 - Medical research Council (MRC) 2000 - Campbell 2000 - Michie 2004 - Rowlands 2005 - Wong 2005 | Background | In development | Pilot study | Formative/developmental evaluation | Mixed |
| 3 | Sturt J, J AdvNurs. 2006 | Minimalist | MRC 2000 | Background Methods | - In development - In evaluation | Pilot study | - Quasi experimental trial - Formative/developmental evaluation | Mixed |
| 4 | Sturt J, BMC Fam Pract. 2006 | Minimalist | MRC 2000 | Discussion | No | Evaluation | - RCT Cluster randomized controlled trial (RCT) - Process evaluation | Mixed |
| 5 | Panella M, 2007 | Intermediate | - Campbell 2000 - Hawe 2004 | Discussion | No | Evaluation | - Cluster RCT - Process evaluation | Quantitative |
| 6 | Paul G, S2007 | Minimalist | - MRC 2000 - Campbell 2000 - Van-Meijel 2004 | Background Discussion | In development | Pilot study | Formative evaluation/development | Mixed |
| 7 | Protheroe J, 2007 | Intermediate | - MRC 2000 - Campbell 2000 - Oakley 2006 - Campbell 2007 - Vanhaecht 2007 - Panella 2009 | Background | In evaluation | Evaluation | - Pragmatic trial - Process evaluation | Mixed |
| 8 | Redfern J, 2008 | Intermediate | Campbell 2000 | Background Methods Results Discussion | - In development - In evaluation | Pilot study | - Formative/developmental evaluation - Process evaluation | Mixed |
| 9 | Lenz M, 2009 | Intermediate | - Campbell 2000 - Campbell 2007 - Lenz 2007 - Craig 2008 | Methods Discussion | - In development - In evaluation | Pilot study | Formative /developmental evaluation | Qualitative |
| 10 | deVlaming R, 2010 | Intermediate | - MRC 2000 - Craig 2008 | Background Discussion | In evaluation | Evaluation | - Quasi experimental trial - Process evaluation | Mixed |
| 11 | Freund T, 2010 | Minimalist | - Campbell 2000 - Campbell 2007 - Craig 2008 | Background Methods | In development | Feasibility study | Formative/developmental evaluation | Mixed |
| 12 | Lemmens KMM, 2010 | Intermediate | - Campbell 2000 - Campbell 2007 - Epping-Jordan 2005 - May 2006 - Lemmens 2008 | Background Methods | In evaluation | Evaluation | - Quasi experimental trial - Process evaluation | Quantitative |
| 13 | Protheroe J, 2010 | Minimalist | MRC 2000 | Background Discussion | In development | Pilot study | Formative/developmental evaluation | Qualitative |
| 14 | Siddiqi K, 2010 | Intermediate | - MRC 2000 - Campbell 2000 | Background Methods | - In development - In evaluation | Pilot study Evaluation | - Cluster RCT - Process evaluation | Mixed |
| 15 | Vanhaecht K, 2010 | Minimalist | - Campbell 2000 - Hawe 2004 - Oakley 2006 - Vanhaecht 2007 - Craig 2008 - Panella 2009 - Panella 2010 | Background Methods Discussion | No | Evaluation | - Cluster RCT - Realistic evaluation - Process evaluation | Mixed |
| 16 | Brady MC, 2011 | In-depth | - MRC 2008 - Shiell 2008 | Background Methods Discussion | - In development - In evaluation | Pilot study | - Quasi experimental trial - Formative/developmental evaluation | Mixed |
| 17 | Burr JM, 2011 | Minimalist | Craig 2008 | Background Discussion | In development | Pilot study | Formative/developmental evaluation | Mixed |
| 18 | Greenhalgh T, 2011 | Intermediate | - Hawe 2004 - Craig 2008 | Background Discussion | - In development - In evaluation | Feasibility study | - RCT - Process evaluation | Mixed |
| 19 | Hartveit M, 2011 | Intermediate | - MRC 2000 - Campbell 2000 - Craig 2008 - Vanhaecht 2011 | - Background Methods Discussion | - In development - In evaluation | Pilot study | - Quasi experimental trial - Formative/developmental evaluation | Mixed |
| 20 | Hirsch O, 2011 | Minimalist | - Craig 2008 - Protheroe 2007 | Background Methods | In evaluation | Pilot study | Process evaluation | Mixed |
| 21 | Treweek S, 2011 | Minimalist | MRC 2008 | Background Discussion | In evaluation | Feasibility study | - RCT - process evaluation | Mixed |
| 22 | Bath B, 2012 | Minimalist | Campbell 2000 | Background Discussion | No | Pilot study | Quasi-experimental trial | Mixed |
| 23 | Bench SD, 2012 | Minimalist | Campbell 2007 | Background Methods Discussion | - In development - In evaluation | Pilot study | - Pragmatic and clustered trial - Formative/developmental evaluation | Mixed |
| 24 | Chan CWH, 2012 | Intermediate | Campbell 2000 | Background | In evaluation | Evaluation | - Pragmatic trial - Process evaluation | Mixed |
| 25 | Cresswell KM, 2012 | Minimalist | - Bradley 1999 - MRC 2000 - Campbell 2000 - NIH 2004 - VanMeijel 2004 - Lindsay 2004 - Lewin 2009 | Background Discussion | In evaluation | Evaluation | - Pragmatic and clustered trial - Process evaluation | Mixed |
| 26 | Irvine L, 2012 | Minimalist | Oakley 2006 | Background | - In development - In evaluation | Pilot study | - RCT - process evaluation | Mixed |
| 27 | Jack SM, 2012 | Minimalist | - Campbell 2000 - Van-Meijel 2004 - Ford-Gilboe 2011 | Background Results Discussion | In development | Feasibility study | Process evaluation | Qualitative |
| 28 | Walsh TS, 2012 | In-depth | - Campbell 2000 - MRC 2000 | Methods | In evaluation | Evaluation | - RCT - process evaluation | Mixed |
| 29 | Yam PS, 2012 | Minimalist | Craig 2008 | Background Methods | In development - In evaluation | Evaluation | - RCT - process evaluation | Mixed |
| 30 | Chandler CI, 2013 | Minimalist | - Chen 1989 - Weiss 1995 - Power 2004 - Stame 2004 - MRC 2008 - Lewin 2009 - Bonell 2012 - Marchal 2012 | Methods | In evaluation | Evaluation | - Cluster RCT - Process evaluation | Mixed |
| 31 | Clyne B, 2013 | In-depth | - MRC 2000 - Grimshaw 2001 - Majumdar 2003 - Spinewine 2007 - Campbell 2007 - Craig 2008 - Kaur 2009 - Marcum 2010 - Loganathan 2011 | Background Methods Results Discussion | In development | Pilot study | Formative/developmental evaluation | Qualitative |
| 32 | Geaney F, 2013 | In-depth | Craig 2008 | Background Methods | - In development - In evaluation | Evaluation | - Cluster RCT - Process evaluation | Mixed |
| 33 | Higginson IJ2013 | Minimalist | Craig 2008 | Methods | In development and evaluation | Pilot study | Formative/developmental evaluation | Mixed |
| 34 | Hinrichs T, 2013 | In-depth | - Campbell 2000 - Chen 2005 - Campbell 2007 - Craig 2008 - Thabane 2010 | Background Methods Results Discussion | - In development - In evaluation | Pilot study | Formative/developmental evaluation | Mixed |
| 35 | Mars T, 2013 | In-depth | - MRC 2008 - Craig 2008 | Background Discussion | - In development - In evaluation | Evaluation | - Pragmatic trial - Process evaluaiton | Quantitative |
| 36 | Poston L, 2013 | Minimalist | Craig 2008 | Background Discussion | In evaluation | Pilot study | -RCT - Evaluation process | Mixed |
| 37 | Round J, 2012 | Minimalist | MRC 2008 | Background Discussion | In development | Evaluation | - Quasi experimental trial - Process evaluation | Mixed |
| 38 | Sin J, 2013 | Intermediate | - Lancaster 2004 - MRC 2008 | Methods | - In development - In evaluation | Pilot study | RCT - Formative/developmental evaluation Process evaluation | Mixed |
| 39 | Yuen WW-Y, 2013 | Minimalist | MRC 2008 | Methods | In evaluation | Evaluation | RCT Evaluation process | Mixed |
| 40 | Ettema R, 2015 | Minimalist | MRC 2008 | Background Methods | - In development - In evaluation | Pilot study | Process evaluation | Mixed |
| 41 | Haynes A, 2014 | Intermediate | - Harachi 1999 - Sanderson 2000 - Oakley 2006 - Grimshaw 2007 - MRC 2008 - Shiell 2008 - Hawe 2009 - Bradley 2011 - Ling 2012 - Moore 2013 - Brennan 2013 | Background Methods Discussion | In evaluation | Evaluation | - Cluster RCT Process evaluation | Mixed |
| 42 | Kwamie A, 2014 | In-depth | - Pawson 1997 - Begun 2003 - Holland 2006 - Sterman 2006 - Foster-Fishman 2007 - De Savigny 2009 - Hawe 2009 - Frenk 2010 - Prashanth 2012 | Background Methods Discussion | In evaluation | Evaluation | Realistic evaluation -Process evaluation | Qualitative |
| 43 | Lawton R, 2015 | Minimalist | - Dane 1998 - Hawe 2004 - Bellg 2004 - Oakley 2006 - Craig 2008 | Background Discussion | In evaluation | Evaluation | - Cluster RCT Process evaluation | Mixed |
| 44 | Leamy M, 2014 | Intermediate | - MRC 2000 - MRC 2008 - Thompson 2009 - Datta 2013 | Background Methods Discussion | In evaluation | Evaluation | - Cluster RCT Process evaluation | Mixed |
| 45 | Leo SD, 2014 | Intermediate | - Campbell 2000 - Campbell 2007 | Methods Discussion | - In development - In evaluation | Pilot study | Formative/developmental evaluation | Mixed |
| 46 | Nayiga S, 2014 | Intermediate | - MRC 2000 - Hawe 2004 - Oakley 2006 - Cartwright 2011 - English 2011 | Methods | In evaluation | Evaluation | - Cluster RCT Process evaluation | Mixed |
| 47 | Rees K, 2014 | Minimalist | Atun 2010 | Methods Discussion | In evaluation | Feasibility study | Process evaluation | Qualitative |
| 48 | Watson DP, 2014 | Minimalist | May 2006 | Background Methods | No | Feasibility study | Process evaluation | Mixed |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trompette, J.; Kivits, J.; Minary, L.; Alla, F. Dimensions of the Complexity of Health Interventions: What Are We Talking about? A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3069. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17093069
Trompette J, Kivits J, Minary L, Alla F. Dimensions of the Complexity of Health Interventions: What Are We Talking about? A Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(9):3069. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17093069
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrompette, Justine, Joëlle Kivits, Laetitia Minary, and François Alla. 2020. "Dimensions of the Complexity of Health Interventions: What Are We Talking about? A Review" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 9: 3069. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17093069
APA StyleTrompette, J., Kivits, J., Minary, L., & Alla, F. (2020). Dimensions of the Complexity of Health Interventions: What Are We Talking about? A Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(9), 3069. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17093069






