Trade-in Strategy and Competition between Two Independent Remanufacturers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Reverse Logistics Management
2.2. Competition in Remanufacturing
2.3. Trade-in Strategy
2.4. Uniqueness and Contributions
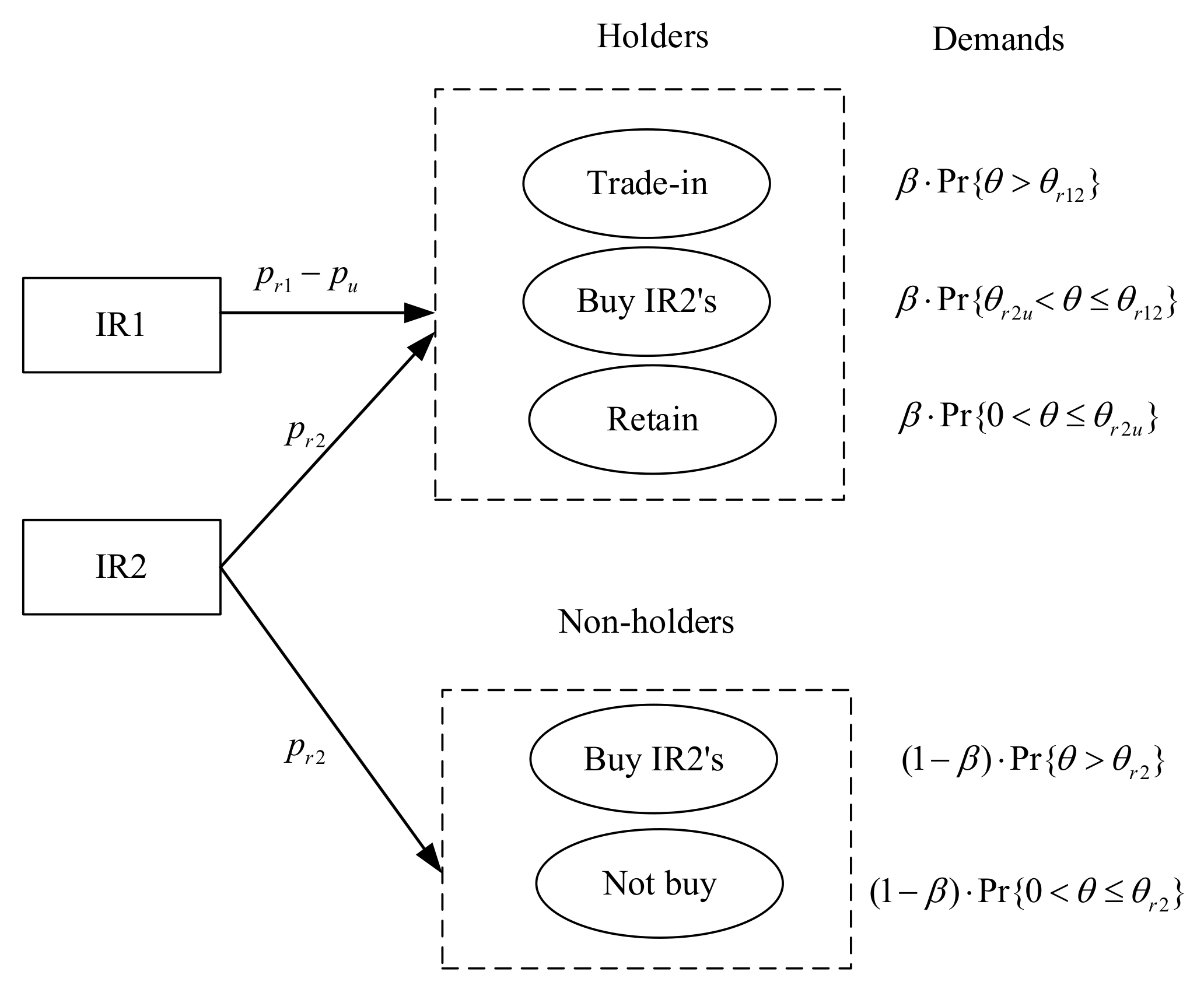
3. The Basic Model
4. Equilibrium Analysis
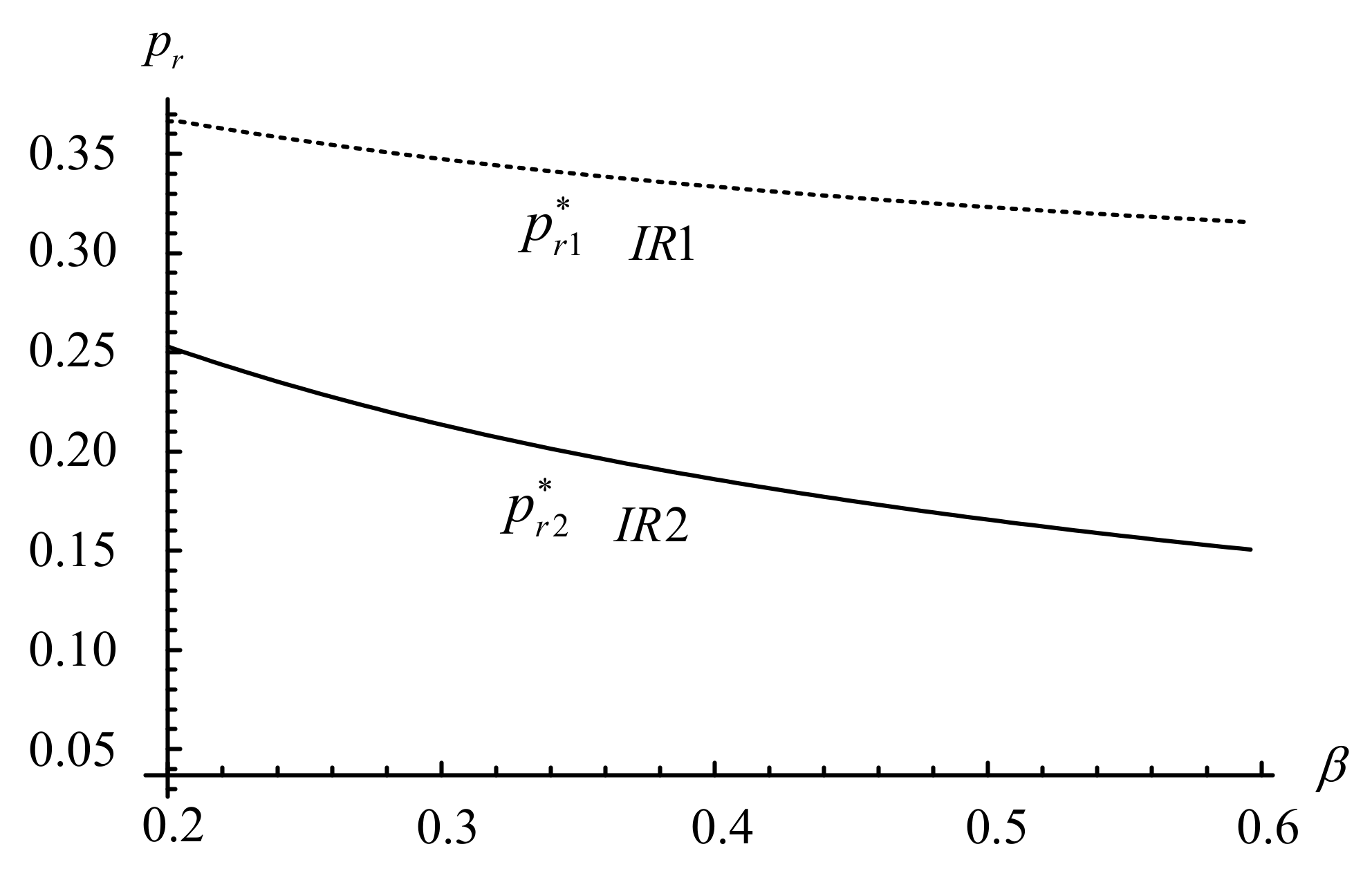
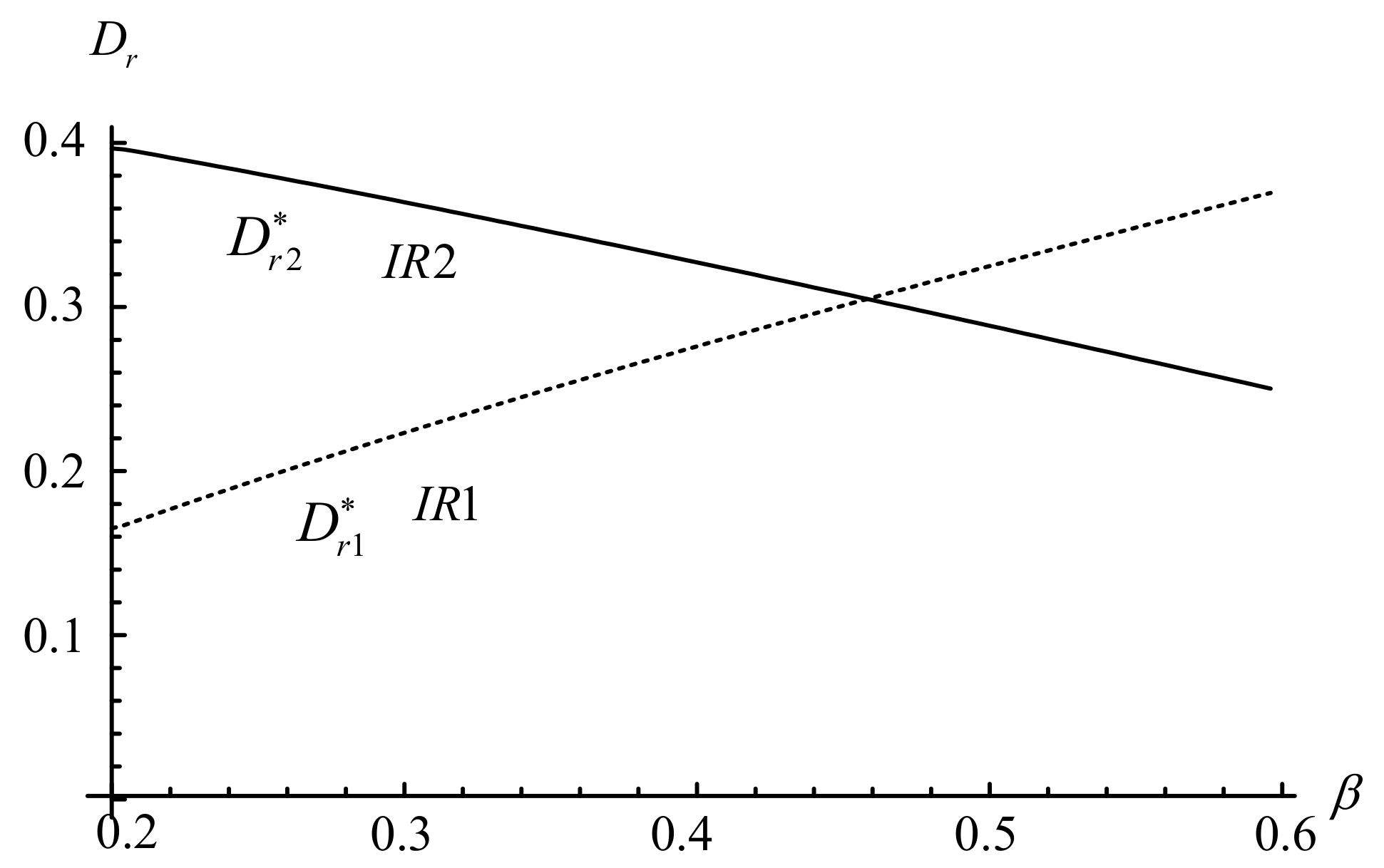
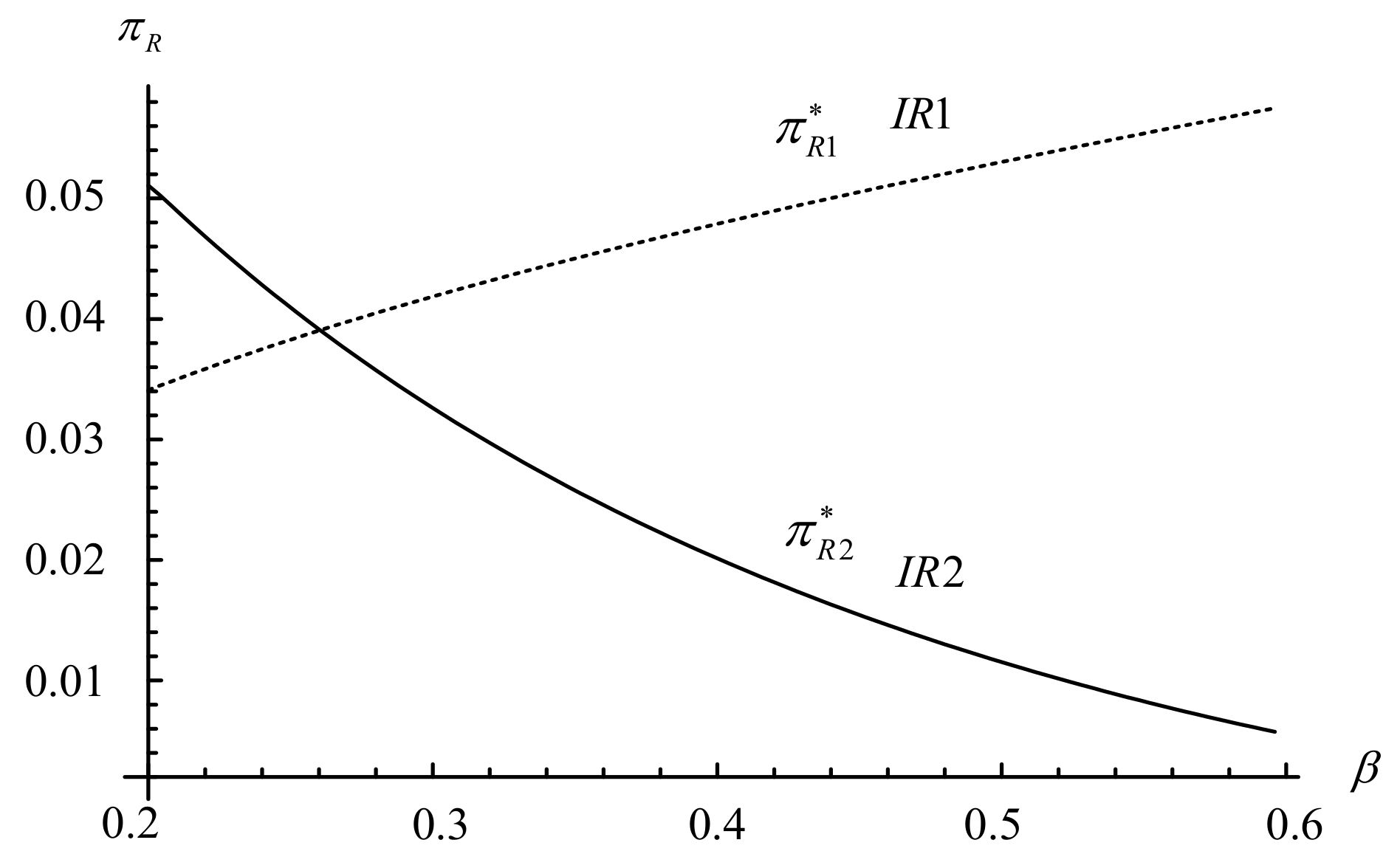
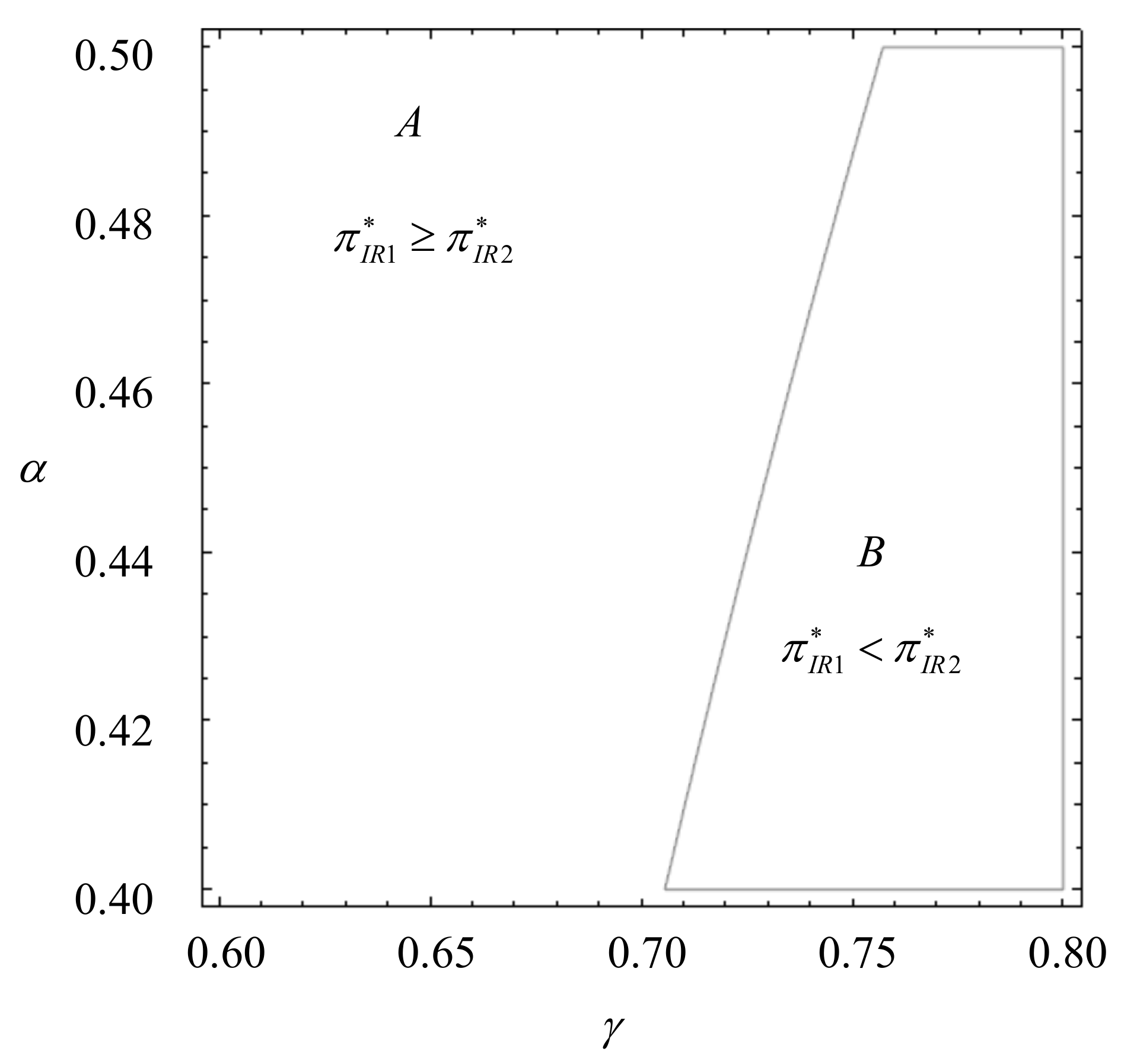
5. Numerical Experiments
6. Conclusions
6.1. Theoretical Implications
6.2. Managerial Implications
- When there are all holders exist in the market, independent manufacturers who adopt trade-in strategy obtain more benefit than others no matter for the demand or profit;
- The higher the proportion of holders in the market, the lower the prices of remanufactured goods, irrespective of whether independent manufacturers offer trade-in schemes or not;
- Independent manufacturers driven by self-serving goals will be inclined to adopt a “trade-old-for remanufactured” strategy when the proportion of holders is sufficiently high;
- If remanufactured goods are very popular with holders and original new products are not durable, independent manufacturers who are seeking maximum benefits should adopt a trade-in strategy.
6.3. Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Proof of the Demand
Appendix B. Proof of Lemma 1
Appendix C. Proof of Proposition 1
Appendix D. Proof of Proposition 2
References
- The United Nations Reports that Global Amounts of e-Waste Reached an All-Time High of 45 Million Tons in 2016. Available online: https://www.sohu.com/a/210631724_162522 (accessed on 30 May 2021).
- How to Deal with 160 Million Home Appliances “Expired” in One Year? Available online: https://new.qq.com/omn/20210330/20210330A09GH200.html (accessed on 30 May 2021).
- Mokhtar, A.; Genovese, A.; Brint, A.; Kumar, N. Improving reverse supply chain performance: The role of supply chain leadership and governance mechanisms. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 216, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atasu, A.; Sarvary, M.; Van Wassenhove, L.N. Remanufacturing as a marketing strategy. Manag. Sci. 2008, 54, 1731–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, Z.; Xiao, T.; Robb, D. Environmentally responsible closed-loop supply chain models with outsourcing and authorization options. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 01 Computer System’s participation in HP Planet Partners Program. Available online: https://www.01computer.com/hp-planet-partners-program (accessed on 30 May 2021).
- Agrawal, V.V.; Ferguson, M.; Souza, G.C. Trade-in rebates for price discrimination and product recovery. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2016, 63, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y. Choosing the right exchange-old-for-new programs for durable goods with a rollover. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 259, 512–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, R. Trade-in remanufacturing, customer purchasing behavior, and government policy. Manuf. Serv. Oper. Manag. 2018, 20, 601–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibben-Lembke, R.S. Life after death: Reverse logistics and the product life cycle. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logis. Manag. 2002, 32, 223–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savaskan, R.C.; Bhattacharya, S.; Van Wassenhove, L.N. Closed-loop supply chain models with product remanufacturing. Manag. Sci. 2004, 50, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, L.; Liu, W.; Guo, Q.; Gao, L.; Zhang, G.; Chen, X. Comparative life cycle assessment of manufactured and remanufactured loading machines in china. Resour. Conserv. Recyl. 2018, 131, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakayali, I.; Emir-Farinas, H.; Akcali, E. An analysis of decentralized collection and processing of end-of-life products. J. Oper. Manag. 2007, 25, 1161–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.-M.; Li, Y.; Xu, L. Channel leadership, performance and coordination in closed loop supply chains. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2013, 146, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wang, N.; Yang, Z.; He, Z.; Jiang, B. Competitive collection under channel inconvenience in closed-loop supply chain. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2019, 275, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Chu, J.; Jin, L.C. Recycling channel selection and coordination in dual sales channel closed-loop supply chains. Appl. Math. Model. 2021, 95, 484–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmykova, Y.; Berg, E.O.; Patrício, J.; Lisovskaja, V. Portable battery lifespans and new estimation method for battery collection rate based on a lifespan modeling approach. Resour. Conserv. Recyl. 2017, 120, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Xiao, T.; Chai, C. Recycling and pricing strategies of closed-loop supply chain by the leader of third-party recycler. Chin. J. Manag. Sci. 2018, 26, 118–127. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, H.; Xu, M.; Zhou, L. Collaborative collection effort strategies based on the “Internet + recycling” business model. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 241, 118120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Z. Values of information sharing: A comparison of supplier-remanufacturing and manufacturer-remanufacturing scenarios. Transp. Res. Part E 2017, 106, 20–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Xu, M. Dynamic game strategies of a two-stage remanufacturing closed-loop supply chain considering big data marketing, technological innovation and overconfidence. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 145, 106538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Marc, R.; Zhang, W. When remanufacturing meets product quality improvement: The impact of production cost. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 271, 913–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegoz, M.; Kaya, O.; Bayindir, Z.P. A comparison of pure manufacturing and hybrid manufacturing-remanufacturing systems under carbon tax policy. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2021, 294, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, P.; Groenevelt, H. Competition in remanufacturing. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2001, 10, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, M.E.; Toktay, L.B. The effect of competition on recovery strategies. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2006, 15, 351–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrer, G.; Swaminathan, J.M. Managing new and remanufactured products. Manag. Sci. 2006, 52, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Örsdemir, A.; Kemahlıo˘glu-Ziya, E.; Parlaktürk, A.K. Competitive quality choice and remanufacturing. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2014, 23, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oraiopoulos, N.; Ferguson, M.E.; Toktay, L.B. Relicensing as a secondary market strategy. Manag. Sci. 2012, 58, 1022–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, Z.; Wang, J.; Deng, G.; Chen, H. Third-party remanufacturing mode selection: Outsourcing or authorization? Transp. Res. Part E. 2016, 87, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleber, R.; Souza, G.C.; Reimann, M.; Zhang, W. Two-sided competition with vertical differentiation in both acquisition and sales in remanufacturing. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2020, 284, 572–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.S.; Narasimhan, O.; John, G. Understanding the role of trade-ins in durable goods markets: Theory and evidence. Mark. Sci. 2009, 28, 950–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, K.; Xu, X.; Bian, Y.; Sun, Y. Optimal trade-in strategy of business-to-consumer platform with dual-format retailing model. Omega 2019, 82, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Dai, Y.; Sheu, J.B. Optimal pricing decisions under the coexistence of “trade old for new” and “trade old for remanufactured” programs. Transp Res. Part E 2017, 106, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, L.; Govindan, K.; Xu, F. Effects of a secondary market on original equipment manufactures’ pricing, trade-in remanufacturing, and entry decisions. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2019, 279, 751–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Li, Y.; Fan, C. Optimization of pricing and quality choice with the coexistence of secondary market and trade-in program. Ann. Oper. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Dong, Z.; Li, G.; Zhao, H. Joint advertisement and trade-in marketing strategy in closed-loop supply chain. Sustainability 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Chang, C. Dynamic pricing for new and remanufactured products in a closed-loop supply chain. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2013, 146, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Tian, L. Collaborative consumption: Strategic and economic implications of product sharing. Manag. Sci. 2016, 64, 1171–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulmus, S.C.; Zhu, S.X.; Teunter, R. Competition for cores in remanufacturing. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2014, 233, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Studies | Consumer Perspective | Trade-in | Competition | Main Features of the Paper |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Savaskan et al. [11] | Not considered | Not considered | Not considered | Three options for remanufacturing |
| Ferrer and Swaminathan [26] | Consumer’s WTP | Not considered | New vs. Re | Two-period remanufacturing |
| Atasu et al. [4] | Consumer’s WTP and green segment | Not considered | New vs. Re | Existence of a green consumer segment |
| Choi et al. [14] | Consumer’s WTP | Not considered | New vs. Re | Channel leadership and coordination in CLSC |
| Örsdemir et al. [27] | Consumer’s WTP | Not considered | New vs. Re | Competitive in quality of products |
| Agrawal et al. [7] | Consumer’s WTP | TON | New vs. New | Impact of trade-in rebates on price discrimination |
| Ma et al. [33] | Consumer’s WTP | TON and TOR | New vs. Re | Comparison between two kinds of trade-ins |
| Xiao [8] | Consumer’s WTP | TON | New vs. Re | Exchange decisions and sharing mechanism |
| Zhang and Zhang [9] | Consumer’s WTP | TON | New vs. Re | Impact of strategic behavior on trade-in remanufacturing |
| Feng et al. [35] | Consumer’s WTP | TON | New vs. Re | Trade-in program in secondary market |
| Chen et al. [36] | Consumer’s WTP | TON | New vs. Re | Implement trade-in programs and advertising decisions in CLSC |
| Kleber et al. [30] | Consumer’s WTP | TON and TOR | New vs. Newand Re vs. Re | Competition between two remanufacturers |
| This study | Consumer’s WTP and holder segment | TOR | Re vs. Re | Trade-in between two IRs in presence of competition |
| Symbol | Definition |
|---|---|
| Model parameters | |
| Consumer’s willingness-to-pay (WTP) for remanufactured products from the IR1, | |
| Consumer’s WTP a discount rate for remanufactured products from the IR2, | |
| Proportion of holders, | |
| Durability of new products, | |
| Unit production cost of remanufactured products | |
| Total number of used products for acquisition, | |
| Collection quantities by the IR1, | |
| Collection quantities by the IR2, | |
| Price of used products under trade-in strategy by the IR1 | |
| Unit collection fee of used products by the IR2, | |
| Functions | |
| , | Utility and demand of remanufactured products from the IR1 |
| , | Utility and demand of remanufactured products from the IR2 |
| Utility of used products | |
| Decision variables | |
| Price of remanufactured products by the IR1 | |
| Price of remanufactured products by the IR2 |
| Demand | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cases | |||
| otherwise | 0 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, Z.; Luo, N.; Liu, Y. Trade-in Strategy and Competition between Two Independent Remanufacturers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6745. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18136745
Feng Z, Luo N, Liu Y. Trade-in Strategy and Competition between Two Independent Remanufacturers. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(13):6745. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18136745
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Zhangwei, Na Luo, and Yanping Liu. 2021. "Trade-in Strategy and Competition between Two Independent Remanufacturers" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 13: 6745. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18136745
APA StyleFeng, Z., Luo, N., & Liu, Y. (2021). Trade-in Strategy and Competition between Two Independent Remanufacturers. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(13), 6745. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18136745






