High Risk of Peritonsillar Abscess in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients: A Nationwide Real-World Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Source of Study Data
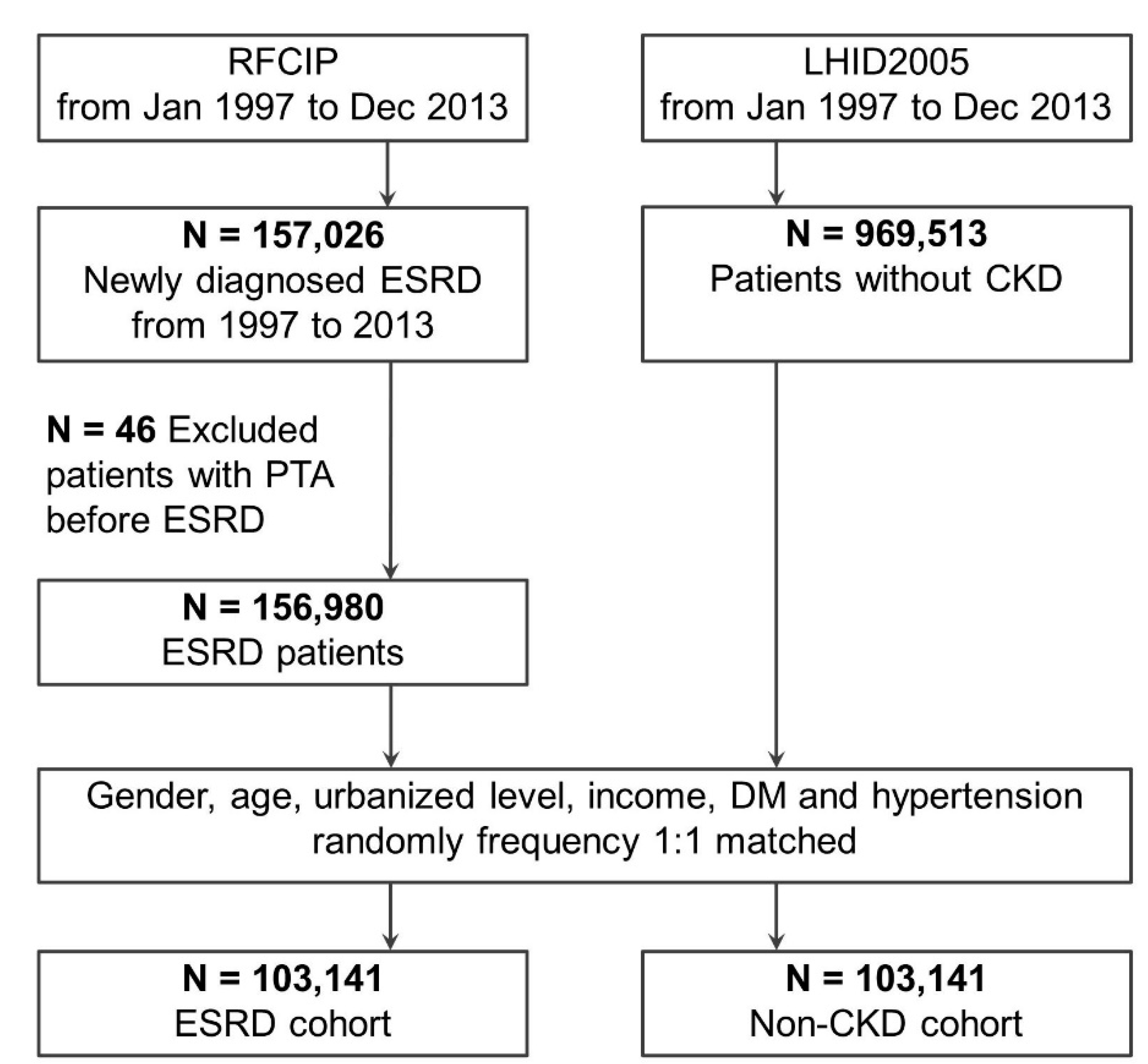
2.2. Study Cohort
2.3. Comparison Cohort
2.4. Matching Process
2.5. PTA Incidence as Main Study Outcome
2.6. Comorbidities
2.7. Treatment Modalities and Prognosis Evaluation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klug, T.E.; Rusan, M.; Fuursted, K.; Ovesen, T. Peritonsillar Abscess: Complication of Acute Tonsillitis or Weber’s Glands Infection? Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2016, 155, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, J.K.; Seikaly, H.R.; Harris, J.R.; Villa-Roel, C.; Brick, C.; Rowe, B.H. Corticosteroids in peritonsillar abscess treatment: A blinded placebo-controlled clinical trial. Laryngoscope 2014, 124, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galioto, N.J. Peritonsillar Abscess. Am. Fam. Physician 2017, 95, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Berry, S.; Pascal, I.; Whittet, H.B. Tonsillectomy à chaud for quinsy: Revisited. Eur. Arch. Oto Rhino Laryngol. 2008, 265, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mejzlik, J.; Celakovsky, P.; Tucek, L.; Kotulek, M.; Vrbacky, A.; Matousek, P.; Stanikova, L.; Hoskova, T.; Pazs, A.; Mittu, P. Univariate and multivariate models for the prediction of life-threatening complications in 586 cases of deep neck space infections: Retrospective multi-institutional study. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2017, 131, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, J.; Barth, I.; Wigand, M.C.; Mayer, B.; Hoffmann, T.K.; Greve, J. The Surgical Treatment of Peritonsillar Abscess: A Retrospective Analysis in 584 Patients. Laryngoscope 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottin, R.; Marioni, G.; Rinaldi, R.; Boninsegna, M.; Salvadori, L.; Staffieri, A. Deep neck infection: A present-day complication. A retrospective review of 83 cases (1998–2001). Eur. Arch. Oto Rhino Laryngol. 2003, 260, 576–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.T.; Liu, T.C.; Chen, P.R.; Tseng, F.Y.; Yeh, T.H.; Chen, Y.S. Deep neck infection: Analysis of 185 cases. Head Neck 2004, 26, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftekharian, A.; Roozbahany, N.A.; Vaezeafshar, R.; Narimani, N. Deep neck infections: A retrospective review of 112 cases. Eur. Arch. Oto Rhino Laryngol. 2009, 266, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Hu, L.; Wang, Z.; Nie, G.; Li, X.; Lin, D.; Luo, J.; Qin, H.; Wu, J.; Wen, W.; et al. Deep Neck Infection: A Review of 130 Cases in Southern China. Medicine 2015, 94, e994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, G.H.; Ding, M.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Yang, Y.H.; Liu, C.Y.; Chang, P.J.; Lee, C.P.; Lin, M.H.; Hsu, C.M.; Wu, C.Y.; et al. Real-world evidence for increased deep neck infection risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Laryngoscope 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, J.; Wilson, J.A. An evidence-based review of peritonsillar abscess. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2012, 37, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, G.H.; Tsai, M.S.; Liu, C.Y.; Lin, M.H.; Tsai, Y.T.; Hsu, C.M.; Yang, Y.H. End-stage renal disease: A risk factor of deep neck infection—A nationwide follow-up study in Taiwan. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, Y.T.; Huang, E.I.; Chang, G.H.; Tsai, M.S.; Hsu, C.M.; Yang, Y.H.; Lin, M.H.; Liu, C.Y.; Li, H.Y. Risk of acute epiglottitis in patients with preexisting diabetes mellitus: A population-based case-control study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, M.S.; Lee, L.A.; Tsai, Y.T.; Yang, Y.H.; Liu, C.Y.; Lin, M.H.; Hsu, C.M.; Chen, C.K.; Li, H.Y. Sleep apnea and risk of vertigo: A nationwide population-based cohort study. Laryngoscope 2018, 128, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.-Y.; Su, C.-C.; Shao, S.-C.; Sung, S.-F.; Lin, S.-J.; Yang, Y.-H.K.; Lai, E.C.-C. Taiwan’s national health insurance research database: Past and future. Clin. Epidemiol. 2019, 11, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, G.H.; Ding, M.C.; Yang, Y.H.; Lin, Y.H.; Liu, C.Y.; Lin, M.H.; Wu, C.Y.; Hsu, C.M.; Tsai, M.S. High Risk of Deep Neck Infection in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.-S.; Lai, M.-S.; Gau, S.S.-F.; Wang, S.-C.; Tsai, H.-J. Concordance between patient self-reports and claims data on clinical diagnoses, medication use, and health system utilization in Taiwan. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsieh, C.Y.; Chen, C.H.; Li, C.Y.; Lai, M.L. Validating the diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke in a National Health Insurance claims database. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2015, 114, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-C.; Chen, P.-C.; Hsu, C.-W.; Chang, S.-L.; Lee, C.-C. Validity of the age-adjusted charlson comorbidity index on clinical outcomes for patients with nasopharyngeal cancer post radiation treatment: A 5-year nationwide cohort study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e117323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, L.M.; Matijasec, J.W.; Perry, A.P.; Kakade, A.; Walvekar, R.R.; Kluka, E.A. Pediatric peritonsillar abscess: Quinsy ie versus interval tonsillectomy. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2013, 77, 1355–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Kong, I.G.; Min, C.; Choi, H.G. Association of air pollution with increased risk of peritonsillar abscess formation. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 145, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsai, M.S.; Chang, G.H.; Chen, W.M.; Liu, C.Y.; Lin, M.H.; Chang, P.J.; Huang, T.Y.; Tsai, Y.T.; Wu, C.Y.; Hsu, C.M.; et al. The Association between Decompensated Liver Cirrhosis and Deep Neck Infection: Real-World Evidence. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chonchol, M. Neutrophil dysfunction and infection risk in end-stage renal disease. Semin. Dial. 2006, 19, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalrymple, L.S.; Go, A.S. Epidemiology of Acute Infections among Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 3, 1487–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cahuayme-Zuniga, L.J.; Brust, K.B. Mycobacterial Infections in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Kidney Transplantation. Adv. Chronic. Kidney Dis. 2019, 26, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndlovu, K.C.Z.; Swe Swe-Han, K.; Assounga, A. Association of Staphylococcus nasal colonization and HIV in end-stage renal failure patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis. Ren. Fail. 2019, 41, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, S.; Papanikolaou, V.; Keogh, I. Appraisal of the peri-hospital management and evolving microbiology of peritonsillar abscess disease. B-ENT 2014, 10, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Ozbek, C.; Aygenc, E.; Unsal, E.; Ozdem, C. Peritonsillar abscess: A comparison of outpatient i.m. clindamycin and inpatient i.v. ampicillin/sulbactam following needle aspiration. Ear. Nose Throat J. 2005, 84, 366–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brook, I. Microbiology and management of peritonsillar, retropharyngeal, and parapharyngeal abscesses. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2004, 62, 1545–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celakovsky, P.; Kalfert, D.; Tucek, L.; Mejzlik, J.; Kotulek, M.; Vrbacky, A.; Matousek, P.; Stanikova, L.; Hoskova, T.; Pasz, A. Deep neck infections: Risk factors for mediastinal extension. Eur. Arch. Oto Rhino Laryngol. 2014, 271, 1679–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa Menezes, A.; Ribeiro, D.C.; Guimaraes, J.R.; Lima, A.F.; Dias, L. Management of pediatric peritonsillar and deep neck infections- cross- sectional retrospective analysis. World J. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 5, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Lim, H.; Choi, H.G. Smoking and alcohol consumption are associated with the increased risk of peritonsillar abscess. Laryngoscope 2020, 130, 2833–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristic | ESRD | Non-CKD | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | ||
| Total | 103,141 | 103,141 | |||
| Sex | 1.000 | ||||
| Male | 51,306 | 49.7 | 51,306 | 49.7 | |
| Female | 51,835 | 50.3 | 51,835 | 50.3 | |
| Age (years) | 1.000 | ||||
| <65 | 60,364 | 58.5 | 60,364 | 58.5 | |
| ≥65 | 42,777 | 41.5 | 42,777 | 41.5 | |
| Urbanized level | 1.000 | ||||
| 1 (City) | 25,742 | 25.0 | 25,742 | 25.0 | |
| 2 | 45,506 | 44.1 | 45,506 | 44.1 | |
| 3 | 19,407 | 18.8 | 19,407 | 18.8 | |
| 4 (Village) | 12,486 | 12.1 | 12,486 | 12.1 | |
| Income (NTD/month) | 1.000 | ||||
| 0 | 25,950 | 25.2 | 25,950 | 25.2 | |
| 1–15,840 | 21,737 | 21.1 | 21,737 | 21.1 | |
| 15,841–25,000 | 43,320 | 42.0 | 43,320 | 42.0 | |
| ≥25,001 | 12,134 | 11.8 | 12,134 | 11.8 | |
| Comorbidities | |||||
| Chronic tonsillitis | 88 | 0.1 | 213 | 0.2 | <0.001 |
| DM | 51,292 | 49.7 | 51,292 | 49.7 | 1.000 |
| Hypertension | 93,712 | 90.9 | 93,712 | 90.9 | 1.000 |
| COPD | 24,631 | 23.9 | 24,701 | 24.0 | 0.718 |
| LC | 10,381 | 10.1 | 4244 | 4.1 | <0.001 |
| Autoimmune | 4387 | 4.3 | 3232 | 3.1 | <0.001 |
| Dyslipidemia | 48,067 | 46.6 | 49,688 | 48.2 | <0.001 |
| Outcome | |||||
| PTA | 72 | 0.070 | 48 | 0.047 | 0.028 |
| ESRD | Non-CKD | IRR (95% CI) | p-Value | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | PTA | PYs | Rate † | N | PTA | PYs | Rate † | |||
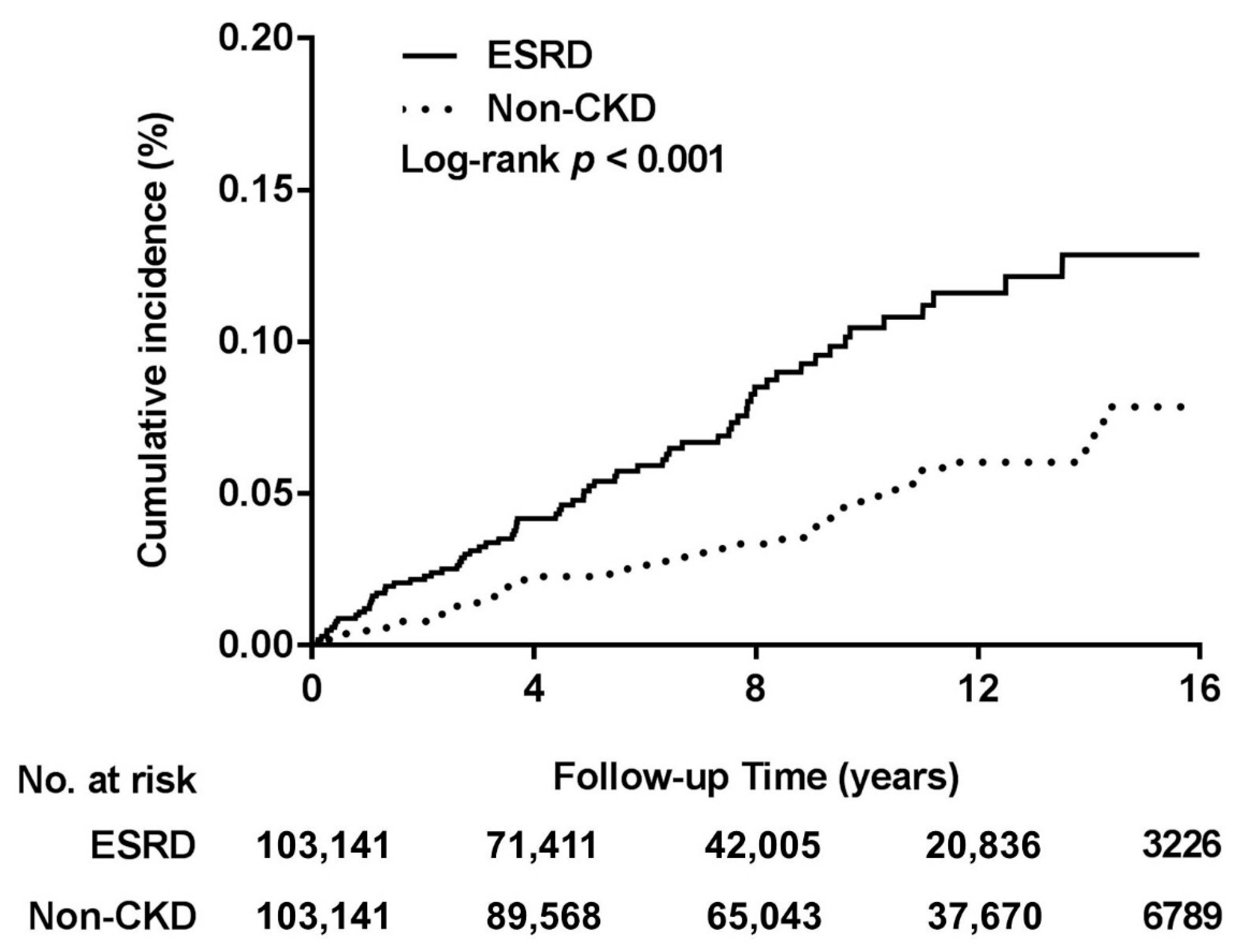
| Overall follow-up years | 103,141 | 72 | 745,775 | 9.7 | 103,141 | 48 | 1002,588 | 4.8 | 2.02 (1.40–2.91) | <0.0001 |
| <1 | 103,141 | 12 | 99,510 | 12.1 | 103,141 | 5 | 102,687 | 4.9 | 2.48 (0.87–7.03) | 0.0884 |
| 1–5 | 95,513 | 32 | 317,802 | 10.1 | 101,912 | 17 | 376,309 | 4.5 | 2.23 (1.24–4.01) | 0.0076 |
| >5 | 63,109 | 28 | 328,463 | 8.5 | 83,810 | 26 | 523,593 | 5.0 | 1.72 (1.01–2.93) | 0.0472 |
| Variables | Adjusted HR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Multivariable Regression Analysis | ||
| Non-CKD | Reference | |
| ESRD (main model *) | 1.98 (1.37–2.86) | <0.001 |
| Sensitivity analysis † | ||
| Main model + Chronic tonsillitis | 1.99 (1.38–2.88) | <0.001 |
| Main model + DM | 2.01 (1.39–2.90) | <0.001 |
| Main model + Hypertension | 2.00 (1.39–2.89) | <0.001 |
| Main model + COPD | 1.99 (1.38–2.87) | <0.001 |
| Main model + LC | 2.01 (1.39–2.90) | <0.001 |
| Main model + Autoimmune | 2.01 (1.39–2.90) | <0.001 |
| Main model + Dyslipidemia | 1.98 (1.37–2.86) | <0.001 |
| Subgroup analysis | ||
| Sex | ||
| Female | 2.38 (1.28–4.24) | 0.006 |
| Male | 1.79 (1.12–2.85) | 0.015 |
| Age | ||
| <65 | 2.22 (1.41–3.50) | 0.001 |
| ≥65 | 1.56 (0.83–2.95) | 0.167 |
| Chronic tonsillitis | ||
| No | 1.94 (1.35–2.81) | <0.001 |
| Yes | – | – |
| DM | ||
| No | 2.31 (1.33–3.99) | 0.003 |
| Yes | 1.79 (1.09–2.95) | 0.022 |
| Hypertension | ||
| No | 1.31 (0.50–3.42) | 0.587 |
| Yes | 2.15 (1.44–3.21) | <0.001 |
| COPD | ||
| No | 1.96 (1.30–2.95) | 0.001 |
| Yes | 2.16 (0.92–5.05) | 0.076 |
| LC | ||
| No | 2.03 (1.39–2.97) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 1.39 (0.28–6.97) | 0.687 |
| Autoimmune | ||
| No | 2.06 (1.43–2.99) | <0.001 |
| Yes | – | – |
| Dyslipidemia | ||
| No | 1.86 (1.13–3.04) | 0.014 |
| Yes | 2.18 (1.25–3.78) | 0.006 |
| ESRD-PTA | Non-CKD-PTA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 72 | N = 48 | ||||
| N | % | N | % | p-Value | |
| Treatment | |||||
| Antibiotic | 72 | 100.0 | 46 | 95.8 | - # |
| Aspiration | 27 | 37.5 | 25 | 52.1 | 0.135 |
| Tonsillectomy | 1 | 1.4 | 0 | 0.0 | - # |
| Prognosis | |||||
| Hospitalization (days) | 8.1 ± 10.3 | 5.7 ± 4.6 | 0.090 | ||
| Progress to DNI | 3 | 4.2 | 3 | 6.3 | 0.682 |
| Progress to mediastinitis | 1 | 1.4 | 1 | 2.1 | 0.773 |
| Mortality rate | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | - # |
| Recurrence within 3 months | 1 | 1.4 | 0 | 0.0 | - # |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, G.-H.; Lu, A.; Yang, Y.-H.; Liu, C.-Y.; Chang, P.-J.; Lee, C.-P.; Tsai, Y.-T.; Hsu, C.-M.; Wu, C.-Y.; Shih, W.-T.; et al. High Risk of Peritonsillar Abscess in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients: A Nationwide Real-World Cohort Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6775. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18136775
Chang G-H, Lu A, Yang Y-H, Liu C-Y, Chang P-J, Lee C-P, Tsai Y-T, Hsu C-M, Wu C-Y, Shih W-T, et al. High Risk of Peritonsillar Abscess in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients: A Nationwide Real-World Cohort Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(13):6775. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18136775
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Geng-He, Ang Lu, Yao-Hsu Yang, Chia-Yen Liu, Pey-Jium Chang, Chuan-Pin Lee, Yao-Te Tsai, Cheng-Ming Hsu, Ching-Yuan Wu, Wei-Tai Shih, and et al. 2021. "High Risk of Peritonsillar Abscess in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients: A Nationwide Real-World Cohort Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 13: 6775. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18136775
APA StyleChang, G.-H., Lu, A., Yang, Y.-H., Liu, C.-Y., Chang, P.-J., Lee, C.-P., Tsai, Y.-T., Hsu, C.-M., Wu, C.-Y., Shih, W.-T., & Tsai, M.-S. (2021). High Risk of Peritonsillar Abscess in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients: A Nationwide Real-World Cohort Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(13), 6775. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18136775










