Anemia and Nutritional Status of Syrian Refugee Mothers and Their Children under Five Years in Greater Beirut, Lebanon
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Sampling Method
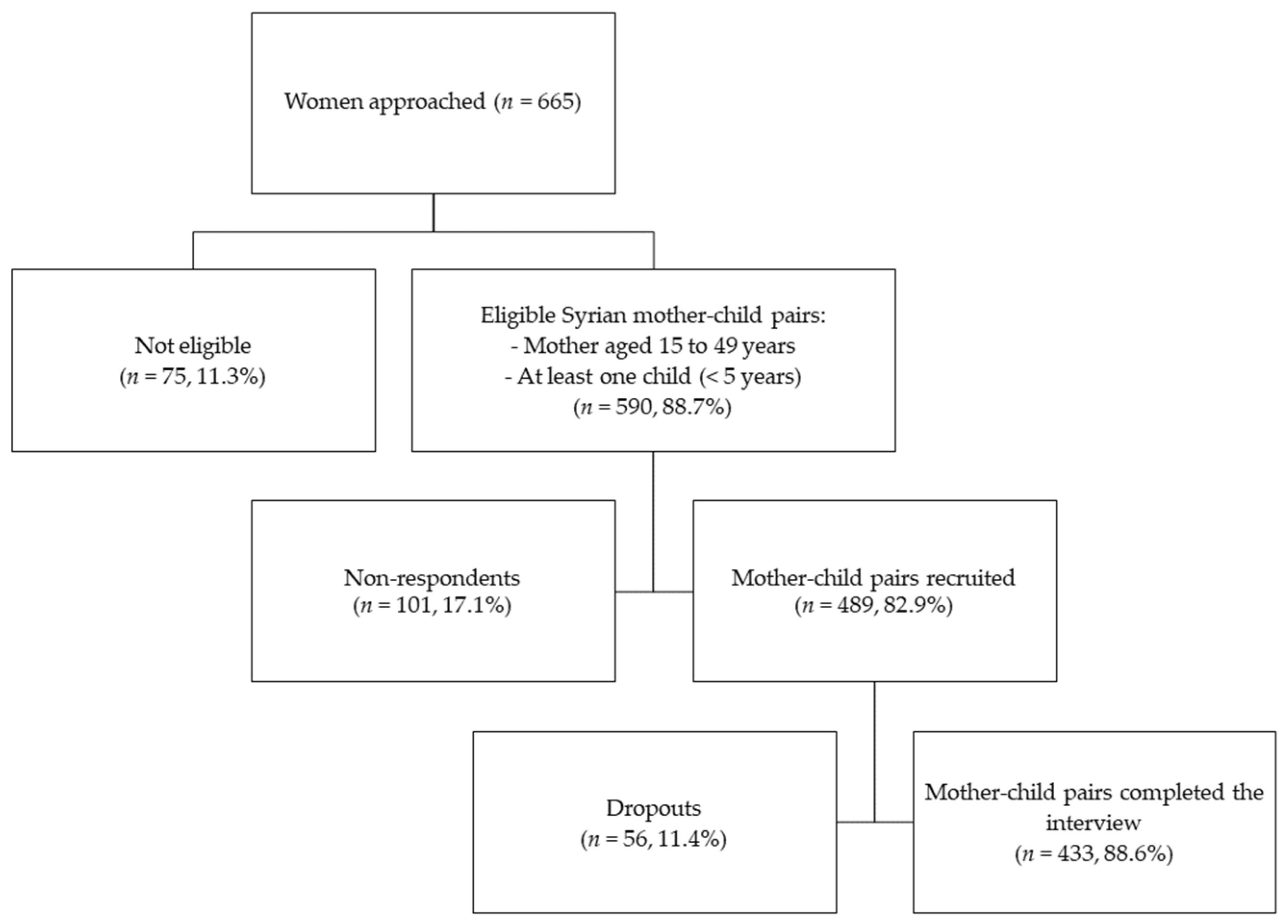
2.2. Recruitment Strategy
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Anthropometric Assessment
2.5. Biochemical Assessment
2.6. Dietary Assessment
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Pregnant Mothers | Lactating Mothers | Non-Pregnant Non-Lactating Mothers | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy and macronutrients | |||
| Energy (kcal/d) | 2200–2652 | 2600–2700 | 2200 |
| Carbohydrates (%EI/d) | 45–65 | 45–65 | 45–65 |
| Protein (%EI/d) | 10–35 | 10–35 | 10–35 |
| Total fat (%EI/d) | 20–35 | 20–35 | 20–35 |
| MUFA (%EI/d) | 15–20 | 15–20 | 15–20 |
| Linoleic acid (%EI/d) | 5–10 | 5–10 | 5–10 |
| Linolenic acid (%EI/d) | 0.6–1.2 | 0.6–1.2 | 0.6–1.2 |
| PUFA (%EI/d) | 6–11 | 6–11 | 6–11 |
| SFA (%EI/d) | 8–10 | 8–10 | 8–10 |
| TFA (%EI/d) | <1 | <1 | <1 |
| Cholesterol (mg/d) | <200 | <200 | <200 |
| Total sugar (%EI/d) | <10 | <10 | <10 |
| Macronutrients | |||
| Carbohydrates (g/d) | 175 | 210 | 130 |
| Protein (g/d) | 71 | 71 | 46 |
| Linoleic acid (g/d) | 13 * | 13 * | 11–12 * |
| Linolenic acid (g/d) | 1.4 * | 1.3 * | 1.1 * |
| Fibers (g/d) | 28 * | 29 * | 25–26 * |
| Micronutrients | |||
| Iron (mg/d) | 27 | 9–10 | 15–18 |
| Folate (µg/d) | 600 | 500 | 400 |
| Vitamin B12 (µg/d) | 2.6 | 2.8 | 2.4 |
| Vitamin C (mg/d) | 80–85 | 115–120 | 65–75 |
| Vitamin A (µg/d) | 750–770 | 1200–1300 | 700 |
| Vitamin D (µg/d) | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Vitamin E (mg/d) | 15 | 19 | 15 |
| Vitamin K (µg/d) | 75–90 * | 75–90 * | 75–90 * |
| Thiamin (mg/d) | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1–1.1 |
| Riboflavin (mg/d) | 1.4 | 1.6 | 1–1.1 |
| Niacin (mg/d) | 18 | 17 | 14 |
| Pantothenic acid (mg/d) | 6 * | 7 * | 5 * |
| Vitamin B6 (mg/d) | 1.9 | 2 | 1.2–1.3 |
| Zinc (mg/d) | 11–12 | 12–13 | 8–9 |
| Copper (mg/d) | 1 | 1.3 | 0.9 |
| Calcium (mg/d) | 1000–1300 | 1000–1300 | 1000–1300 |
| Magnesium (mg/d) | 350–400 | 310–360 | 310–360 |
| Sodium (mg/d) | 1500 * | 1500 * | 1500 * |
| Potassium (mg/d) | 4700 * | 5100 * | 4700 * |
| Phosphorus (mg/d) | 700–1250 | 700–1250 | 700–1250 |
| Manganese (mg/d) | 2.0 * | 2.6 * | 1.6–1.8 * |
| Selenium (µg/d) | 60 | 55 | 70 |
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization; International Fund for Agricultural Development; United Nations Children’s Fund; World Food Programme; World Health Organization. In Brief to The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2020. Transforming Food Systems for Affordable Healthy Diets; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020; p. 320. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 15 January 2021).
- World Health Organization. WHO Global Anaemia Estimates, 2021 Edition. Available online: https://www.who.int/data/maternal-newborn-child-adolescent-ageing/advisory-groups/gama/gama-advisory-group-members (accessed on 5 June 2021).
- Popkin, B.M.; Corvalan, C.; Grummer-Strawn, L.M. Dynamics of the Double Burden of Malnutrition and the Changing Nutrition Reality. Lancet 2020, 395, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, J.C.; Sawaya, A.L.; Wibaek, R.; Mwangome, M.; Poullas, M.S.; Yajnik, C.S.; Demaio, A. The Double Burden of Malnutrition: Aetiological Pathways and Consequences for Health. Lancet 2020, 395, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langley-Evans, S.C. Nutrition in Early Life and the Programming of Adult Disease: A Review. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2015, 28, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, R.E.; Victora, C.G.; Walker, S.P.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Christian, P.; de Onis, M.; Ezzati, M.; Grantham-McGregor, S.; Katz, J.; Martorell, R.; et al. Maternal and Child Undernutrition and Overweight in Low-Income and Middle-Income Countries. Lancet 2013, 382, 427–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, P.; Stewart, C.P. Maternal Micronutrient Deficiency, Fetal Development, and the Risk of Chronic Disease. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biesalski, H.K. The 1,000-Day Window and Cognitive Development. Hidden Hunger 2016, 115, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowensohn, R.I.; Stadler, D.D.; Naze, C. Current Concepts of Maternal Nutrition. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2016, 71, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Georgieff, M.K. Iron Deficiency in Pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 223, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juul, S.E.; Derman, R.J.; Auerbach, M. Perinatal Iron Deficiency: Implications for Mothers and Infants. Neonatology 2019, 115, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasricha, S.-R.; Low, M.; Thompson, J.; Farrell, A.; De-Regil, L.-M. Iron Supplementation Benefits Physical Performance in Women of Reproductive Age: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization. Regional Overview of Food Security and Nutrition—Building Resilience for in Times of Conflict and Crisis: Food Security and Nutrition a Perspective from the Near East and North Africa (NENA) Region; FAO: Cairo, Egypt, 2017; p. 62. [Google Scholar]
- Tanumihardjo, S.A.; Anderson, C.; Kaufer-Horwitz, M.; Bode, L.; Emenaker, N.J.; Haqq, A.M.; Satia, J.A.; Silver, H.J.; Stadler, D.D. Poverty, Obesity, and Malnutrition: An International Perspective Recognizing the Paradox. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2007, 107, 1966–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasreddine, L.; Ayoub, J.J.; Al Jawaldeh, A. Review of the Nutrition Situation in the Eastern Mediterranean Region. East. Mediterr. Health J. 2018, 24, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwalla, N.; Al Dhaheri, A.S.; Radwan, H.; Alfawaz, H.A.; Fouda, M.A.; Al-Daghri, N.M.; Zaghloul, S.; Blumberg, J.B. The Prevalence of Micronutrient Deficiencies and Inadequacies in the Middle East and Approaches to Interventions. Nutrients 2017, 9, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasreddine, L.; Chamieh, M.C.; Ayoub, J.; Hwalla, N.; Sibai, A.-M.; Naja, F. Sex Disparities in Dietary Intake across the Lifespan: The Case of Lebanon. Nutr. J. 2020, 19, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goverment of Lebanon. The United Nations Lebanon Crisis Response Plan 2017–2020 (2020 Update); Goverment of Lebanon: Beirut, Lebanon, 2020.
- United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs. Humanitarian Bulletin Lebanon (Issue 33, 1 August–31 October 2018); OCHA: Beirut, Lebanon, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. Refugees from Syria: Lebanon; UNHCR: Beirut, Lebanon, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs. Lebanon Overview (May 2016); OCHA: Beirut, Lebanon, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees; United Nations Children’s Fund; World Food Programme. VASYR 2018—Vulnerability Assessment of Syrian Refugees in Lebanon—Lebanon; UNHCR: Beirut, Lebanon, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, S.M.M.; Leidman, E.; Kingori, J.; Al Harun, A.; Bilukha, O.O. Nutritional Situation among Syrian Refugees Hosted in Iraq, Jordan, and Lebanon: Cross Sectional Surveys. Confl. Health 2016, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- United Nations Children’s Fund. 2013 Joint Nutrition Assessment Syrian Refugees in Lebanon—Lebanon; UNICEF: Beirut, Lebanon, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs. Lebanon: Beirut and Mount Lebanon Governorates Profile (May 2016); OCHA: Beirut, Lebanon, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- International Labour Organization. Syrian Refugees in Lebanon Face Harsh Working Conditions. Available online: http://www.ilo.org/global/about-the-ilo/newsroom/news/WCMS_240126/lang--en/index.htm (accessed on 7 August 2020).
- World Health Organization. WHO Housing and Health Guidelines; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- International Physical Activity Questionnaire Guidelines for Data Processing and Analysis of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ)—Short and Long Forms; YouthREX: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2005.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES)—Anthropometry Procedures Manual; CDC: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 2017; p. 95.
- World Health Organization. Training Course on Child Growth Assessment, WHO Child Growth Standards—B. Measuring a Child’s Growth; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Fakier, A.; Petro, G.; Fawcus, S. Mid-Upper Arm Circumference: A Surrogate for Body Mass Index in Pregnant Women. S. Afr. Med. J. 2017, 107, 606–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumilowicz, A. Guide to Screening for Food and Nutrition Services Among Adolescents and Adults Living with HIV; Food and Nutrition Technical Assistance III Project (FANTA); FHI 360: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; p. 20. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Nutrition Technical Assistance; United States Agency for International Development; FHI 360. Global MUAC Cutoffs for Adults: A Technical Consultation; FANTA Project: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; p. 6. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. World Food Programme Guidelines for Selective Feeding: The Management of Malnutrition in Emergencies; UNHCR: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- National Institutes of Health. Clinical Guidelines on the Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults—The Evidence Report. Obes. Res. 1998, 6 (Suppl. S2), 51S–209S. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Waist Circumference and Waist–Hip Ratio Report of a WHO Expert Consultation, Geneva, 8–11 December 2008; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Training Course on Child Growth Assessment, WHO Child Growth Standards—C. Intepreting Growth Indicators; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO Anthro for Personal Computers, Version 3.2.2, 2011: Software for Assessing Growth and Development of the World’s Children; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Haemoglobin Concentrations for the Diagnosis of Anaemia and Assessment of Severity. Vitamin and Mineral Nutrition Information System; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, R.F.S.V.; Taddei, J.A.A.C.; Lopez, F.A.; Braga, J.A.P. Breastfeeding Exclusively and Iron Deficiency Anemia during the First 6 Months of Age. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2014, 60, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Millen, B.E.; Morgan, J.L. The 2D Food Portion Visual; Nutrition Consulting Enterprises: Framingham, MA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Conway, J.M.; Ingwersen, L.A.; Moshfegh, A.J. Accuracy of Dietary Recall Using the USDA Five-Step Multiple-Pass Method in Men: An Observational Validation Study. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2004, 104, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.K. Dietary Intake—How Do We Measure What People Are Really Eating? Obes. Res. 2002, 10 (Suppl. S1), 63S–68S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erhardt, J. Nutrition Surveys and Assessment—NutriSurvey Software 2007. Available online: http://www.nutrisurvey.de/index.html (accessed on 7 August 2020).
- Pellett, P.L.; Shadarevian, S. Food Composition: Tables for Use in the Middle East; American University of Beirut: Beirut, Lebanon, 2013; ISBN 978-9953-586-02-1. [Google Scholar]
- National Research Council. Recommended Dietary Allowances, 10th ed.; The National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National Institutes of Health; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; ISBN 978-0-309-04633-6. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D; Ross, A.C., Taylor, C.L., Yaktine, A.L., Del Valle, H.B., Eds.; The National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National Institutes of Health; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization. WHO|Fats and Fatty Acids in Human Nutrition; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP). Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) Final Report. Circulation 2002, 106, 3143–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guideline: Sugars Intake for Adults and Children; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Harvard Humanitarian Initiative. KoBoToolbox—Data Collection Tools for Challenging Environments. Available online: https://kobotoolbox.org/ (accessed on 7 August 2020).
- Greenland, S.; Senn, S.J.; Rothman, K.J.; Carlin, J.B.; Poole, C.; Goodman, S.N.; Altman, D.G. Statistical Tests, P Values, Confidence Intervals, and Power: A Guide to Misinterpretations. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 31, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moyé, L.; Cohen, M. Liberation From the p Value’s Tyranny. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 1046–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Worldwide Prevalence of Anaemia 1993–2005: WHO Global Database on Anaemia; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ghattas, H.; Sassine, A.J.; Seyfert, K.; Nord, M.; Sahyoun, N.R. Food Insecurity among Iraqi Refugees Living in Lebanon, 10 Years after the Invasion of Iraq: Data from a Household Survey. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kern, J. Nutrition Interventions Syria 2017; WFP: Aleppo, Syria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Al Khatib, L.; Obeid, O.; Sibai, A.-M.; Batal, M.; Adra, N.; Hwalla, N. Folate Deficiency Is Associated with Nutritional Anaemia in Lebanese Women of Childbearing Age. Public Health Nutr. 2006, 9, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Food and Agriculture Organization. The State of Food and Agriculture: Food Systems for Better Nutrition; The State of Food and Agriculture Series; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2013; ISBN 978-92-5-107671-2. [Google Scholar]
- Hwalla, N. Nutrition Country Profile: Lebanese Republic; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2007; p. 32. [Google Scholar]
- Hwalla, N.; Adra, N.; Jackson, R.T. Iron Deficiency Is an Important Contributor to Anemia Among Reproductive Age Women in Lebanon. Ecol. Food Nutr. 2004, 43, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khader, A.; Madi, H.; Riccardo, F.; Sabatinelli, G. Anaemia among Pregnant Palestinian Women in the Occupied Palestinian Territory. Public Health Nutr. 2009, 12, 2416–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Mehaisen, L.; Khader, Y.; Al-Kuran, O.; Abu Issa, F.; Amarin, Z. Maternal Anemia in Rural Jordan: Room for Improvement. Anemia 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saaka, M.; Oladele, J.; Larbi, A.; Hoeschle-Zeledon, I. Dietary Diversity Is Not Associated with Haematological Status of Pregnant Women Resident in Rural Areas of Northern Ghana. J. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Anaemia Reduction Efforts among Women of Reproductive Age: Impact, Achievement of Targets and the Way Forward for Optimizing Efforts; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mawani, M.; Ali, S.A.; Bano, G.; Ali, S.A. Iron Deficiency Anemia among Women of Reproductive Age, an Important Public Health Problem: Situation Analysis. Reprod. Syst. Sex. Disord. 2016, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, R.M.; Leon, J.S.; Suchdev, P.S. Identification, Prevention and Treatment of Iron Deficiency during the First 1000 Days. Nutrients 2014, 6, 4093–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scholl, T.O. Maternal Iron Status: Relation to Fetal Growth, Length of Gestation, and Iron Endowment of the Neonate. Nutr. Rev. 2011, 69, S23–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agbozo, F.; Abubakari, A.; Der, J.; Jahn, A. Maternal Dietary Intakes, Red Blood Cell Indices and Risk for Anemia in the First, Second and Third Trimesters of Pregnancy and at Predelivery. Nutrients 2020, 12, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees; United Nations Children’s Fund; World Food Programme. VASYR 2019—Vulnerability Assessment of Syrian Refugees in Lebanon—Lebanon; UNHCR: Beirut, Lebanon, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. Protection—UNHCR Lebanon; UNHCR: Beirut, Lebanon, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Truppa, C.; Leresche, E.; Fuller, A.F.; Marnicio, A.S.; Abisaab, J.; El Hayek, N.; Zmeter, C.; Toma, W.S.; Harb, H.; Hamadeh, R.S.; et al. Utilization of Primary Health Care Services among Syrian Refugee and Lebanese Women Targeted by the ICRC Program in Lebanon: A Cross-Sectional Study. Confl. Health 2019, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christian, A.K.; Marquis, G.S.; Colecraft, E.K.; Lartey, A.; Sakyi-Dawson, O.; Ahunu, B.K.; Butler, L.M. Caregivers’ Nutrition Knowledge and Attitudes Are Associated with Household Food Diversity and Children’s Animal Source Food Intake across Different Agro-Ecological Zones in Ghana. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 115, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hashmi, A.H.; Paw, M.K.; Nosten, S.; Darakamon, M.C.; Gilder, M.E.; Charunwatthana, P.; Carrara, V.I.; Wickramasinghe, K.; Angkurawaranon, C.; Plugge, E.; et al. “Because the Baby Asks for It”: A Mixed-Methods Study on Local Perceptions toward Nutrition during Pregnancy among Marginalised Migrant Women along the Myanmar-Thailand Border. Glob. Health Action 2018, 11, 1473104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmeer, K.K.; Piperata, B.A.; Herrera Rodríguez, A.; Salazar Torres, V.M.; Centeno Cárdenas, F.J. Maternal Resources and Household Food Security: Evidence from Nicaragua. Public Health Nutr. 2015, 18, 2915–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Onis, M.; Borghi, E.; Arimond, M.; Webb, P.; Croft, T.; Saha, K.; De-Regil, L.M.; Thuita, F.; Heidkamp, R.; Krasevec, J.; et al. Prevalence Thresholds for Wasting, Overweight and Stunting in Children under 5 Years. Public Health Nutr. 2019, 22, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nasreddine, L.M.; Kassis, A.N.; Ayoub, J.J.; Naja, F.A.; Hwalla, N.C. Nutritional Status and Dietary Intakes of Children amid the Nutrition Transition: The Case of the Eastern Mediterranean Region. Nutr. Res. 2018, 57, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jawaldeh, A.A.; Doggui, R.; Borghi, E.; Aguenaou, H.; Ammari, L.E.; Abul-Fadl, A.; McColl, K. Tackling Childhood Stunting in the Eastern Mediterranean Region in the Context of COVID-19. Children 2020, 7, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, R.E.; Allen, L.H.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Caulfield, L.E.; de Onis, M.; Ezzati, M.; Mathers, C.; Rivera, J. Maternal and Child Undernutrition: Global and Regional Exposures and Health Consequences. Lancet 2008, 371, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Islam, M.M.; Mubarak, E.; Haque, M.A.; Choudhury, N.; Ahmed, T. Mother’s Dietary Diversity and Association with Stunting among Children <2 Years Old in a Low Socio-Economic Environment: A Case-Control Study in an Urban Care Setting in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Matern. Child. Nutr. 2019, 15, e12665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Global Health Observatory Data Repository. Body Mass Index (BMI). Available online: https://www.who.int/data/maternal-newborn-child-adolescent/monitor (accessed on 28 November 2020).
- Jomaa, L.; Naja, F.; Cheaib, R.; Hwalla, N. Household Food Insecurity Is Associated with a Higher Burden of Obesity and Risk of Dietary Inadequacies among Mothers in Beirut, Lebanon. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naja, F.; Nasreddine, L.; Itani, L.; Chamieh, M.C.; Adra, N.; Sibai, A.M.; Hwalla, N. Dietary Patterns and Their Association with Obesity and Sociodemographic Factors in a National Sample of Lebanese Adults. Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 1570–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, P.H.; Macfarlane, D.J.; Lam, T.H.; Stewart, S.M. Validity of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire Short Form (IPAQ-SF): A Systematic Review. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2011, 8, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chamieh, M.C.; Moore, H.J.; Summerbell, C.; Tamim, H.; Sibai, A.M.; Hwalla, N. Diet, Physical Activity and Socio-Economic Disparities of Obesity in Lebanese Adults: Findings from a National Study. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghattas, H. Food Security and Nutrition in the Context of the Global Nutrition Transition; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2014; p. 21. [Google Scholar]
- Nasreddine, L.; Naja, F.; Chamieh, M.C.; Adra, N.; Sibai, A.-M.; Hwalla, N. Trends in Overweight and Obesity in Lebanon: Evidence from Two National Cross-Sectional Surveys (1997 and 2009). BMC Public Health 2012, 12, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naja, F.; Nasreddine, L.; Itani, L.; Adra, N.; Sibai, A.M.; Hwalla, N. Association between Dietary Patterns and the Risk of Metabolic Syndrome among Lebanese Adults. Eur. J. Nutr. 2013, 52, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darmon, N.; Drewnowski, A. Contribution of Food Prices and Diet Cost to Socioeconomic Disparities in Diet Quality and Health: A Systematic Review and Analysis. Nutr. Rev. 2015, 73, 643–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerson, J.A.; Tol, W.; Caulfield, L.E.; Doocy, S. Maternal Psychological Distress and Perceived Impact on Child Feeding Practices in South Kivu, DR Congo. Food Nutr. Bull. 2017, 38, 319–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmudiono, T.; Segalita, C.; Rosenkranz, R.R. Socio-Ecological Model of Correlates of Double Burden of Malnutrition in Developing Countries: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wirth, J.P.; Rajabov, T.; Petry, N.; Woodruff, B.A.; Shafique, N.B.; Mustafa, R.; Tyler, V.Q.; Rohner, F. Micronutrient Deficiencies, Over- and Undernutrition, and Their Contribution to Anemia in Azerbaijani Preschool Children and Non-Pregnant Women of Reproductive Age. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aigner, E.; Feldman, A.; Datz, C. Obesity as an Emerging Risk Factor for Iron Deficiency. Nutrients 2014, 6, 3587–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaparro, C.M.; Suchdev, P.S. Anemia Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Etiology in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1450, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghose, B.; Tang, S.; Yaya, S.; Feng, Z. Association between Food Insecurity and Anemia among Women of Reproductive Age. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ford, N.D.; Patel, S.A.; Narayan, K.M.V. Obesity in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Burden, Drivers, and Emerging Challenges. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2017, 38, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scagliusi, F.B.; Polacow, V.O.; Artioli, G.G.; Benatti, F.B.; Lancha, A.H. Selective Underreporting of Energy Intake in Women: Magnitude, Determinants, and Effect of Training. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2003, 103, 1306–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subar, A.F.; Kipnis, V.; Troiano, R.P.; Midthune, D.; Schoeller, D.A.; Bingham, S.; Sharbaugh, C.O.; Trabulsi, J.; Runswick, S.; Ballard-Barbash, R.; et al. Using Intake Biomarkers to Evaluate the Extent of Dietary Misreporting in a Large Sample of Adults: The OPEN Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2003, 158, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, J.; Taren, D.L.; Teixeira, P.J.; Thomson, C.A.; Lohman, T.G.; Going, S.B.; Houtkooper, L.B. The Psychosocial and Behavioral Characteristics Related to Energy Misreporting. Nutr. Rev. 2006, 64, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. 2015–2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 8th ed.; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Washinton, DC, USA, 2015.
- Satia-Abouta, J. Dietary Acculturation: Definition, Process, Assessment, and Implications. Int. J. Hum. Ecol. 2003, 4, 71–86. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Fischer, L.; Ghaziani, S.; Jeremias, T.; Scherbaum, V. Nutritional Habits of Asylum Seekers Living in Communal Accomodation in Stuttgart, Germany. Ernahr. Umsch. 2019, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, R.; Fülle, J.; Abou-Rizk, J.; Al-Sayed, L.; Masserrat, N.; Schüle, E.; Scherbaum, V. Nutritional Habits of Female Asylum Seekers—From Tradition to Adaptation. Ernahr. Umsch. 2019, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilter, R.W. Essential Nutrients in the Management of Hematopoietic Disorders of Human Beings: A Résumé. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1955, 3, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dror, D.K.; Allen, L.H. Overview of Nutrients in Human Milk. Adv. Nutr. 2018, 9, 278S–294S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bzikowska, A.; Czerwonogrodzka-Senczyna, A.; Weker, H.; Wesołowska, A. Correlation between Human Milk Composition and Maternal Nutritional Status. Rocz. Panstw. Zakl. Hig. 2018, 69, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherbaum, V.; Srour, M.L. The Role of Breastfeeding in the Prevention of Childhood Malnutrition. World Rev. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 115, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.E.; Talegawkar, S.A.; Merialdi, M.; Caulfield, L.E. Dietary Intakes of Women during Pregnancy in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Public Health Nutr. 2013, 16, 1340–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harika, R.; Faber, M.; Samuel, F.; Kimiywe, J.; Mulugeta, A.; Eilander, A. Micronutrient Status and Dietary Intake of Iron, Vitamin A, Iodine, Folate and Zinc in Women of Reproductive Age and Pregnant Women in Ethiopia, Kenya, Nigeria and South Africa: A Systematic Review of Data from 2005 to 2015. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumfield, M.; Hure, A.; Macdonald-Wicks, L.; Smith, R.; Collins, C. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Micronutrient Intakes during Pregnancy in Developed Countries. Nutr. Rev. 2013, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachir, R.; Chaaya, M. Maternal Smoking: Determinants and Associated Morbidity in Two Areas in Lebanon. Matern. Child. Health J. 2008, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Z.; Cogswell, M.E.; Looker, A.C.; Pfeiffer, C.M.; Cusick, S.E.; Lacher, D.A.; Grummer-Strawn, L.M. Assessment of Iron Status in US Pregnant Women from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), 1999–2006. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 1312–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Food Programme. Assessing the Impact of the Economic and COVID-19 Crises in Lebanon—June 2020—Lebanon; WFP: Beirut, Lebanon, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- World Food Programme. Beirut Port Explosion: Impact on Key Economic and Food Security Indicators—August 2020—Lebanon; WFP: Beirut, Lebanon, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Moshfegh, A.J.; Rhodes, D.G.; Baer, D.J.; Murayi, T.; Clemens, J.C.; Rumpler, W.V.; Paul, D.R.; Sebastian, R.S.; Kuczynski, K.J.; Ingwersen, L.A.; et al. The US Department of Agriculture Automated Multiple-Pass Method Reduces Bias in the Collection of Energy Intakes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 88, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Agriculture Organization. Dietary Assessment: A Resource Guide to Method Selection and Application in Low Resource Settings; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes, C.; Ruel, M.T.; Salm, L.; Sinclair, B.; Branca, F. Double-Duty Actions: Seizing Programme and Policy Opportunities to Address Malnutrition in All Its Forms. Lancet 2020, 395, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables a | PM n = 77 | LM n = 204 | NPNLM n = 152 | Total b n = 433 | p-Value c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Socio-economic characteristics | |||||
| Age of the mothers (years) | 27.0 ± 5.2 | 26.7 ± 5.8 | 28.7 ± 6.1 | 27.4 ± 5.9 | 0.005 0.013 |
| <25 years | 32 (41.6) | 90 (44.1) | 48 (31.8) | 170 (39.4) | |
| 25 to 29 years | 18 (23.4) | 59 (28.9) | 41 (27.2) | 118 (27.3) | |
| 30 to 34 years | 22 (28.6) | 39 (19.1) | 35 (23.2) | 96 (22.2) | |
| ≥35 years | 5 (6.5) | 16 (7.8) | 27 (17.9) | 48 (11.1) | |
| Age of the children (months) | 23.0 ± 13.0 | 7.6 ± 6.3 | 25.9 ± 15.1 | 16.7 ± 14.3 | <0.001 <0.001 |
| <6 months | 4 (5.2) | 100 (49.0) | 10 (6.6) | 114 (26.3) | |
| 6 to 23 months | 41 (53.2) | 99 (48.5) | 75 (49.3) | 215 (49.7) | |
| 24 to 59 months | 32 (41.6) | 5 (2.5) | 67 (44.1) | 104 (24.0) | |
| Child’s sex | 0.372 | ||||
| Male | 35 (46.1) | 107 (52.5) | 85 (55.9) | 227 (52.5) | |
| Female | 41 (53.9) | 97 (47.5) | 67 (44.1) | 205 (47.5) | |
| Marital status of the mother | 0.948 | ||||
| Engaged/ Divorced/Widowed | 1 (1.3) | 2 (1.0) | 2 (1.3) | 5 (1.2) | |
| Married | 75 (98.7) | 202 (99.0) | 150 (98.7) | 427 (98.8) | |
| Mother’s education level | 0.519 | ||||
| No schooling/Illiterate | 9 (11.7) | 35 (17.2) | 26 (17.4) | 70 (16.3) | |
| Primary, Intermediate school | 44 (57.1) | 122 (60.1) | 83 (55.7) | 249 (58.1) | |
| Secondary school and higher | 24 (31.2) | 46 (22.7) | 40 (26.8) | 110 (25.6) | |
| Father’s education level | 0.401 | ||||
| No schooling/Illiterate | 10 (13.0) | 30 (14.9) | 31 (20.4) | 71 (16.5) | |
| Primary, Intermediate school | 52 (67.5) | 140 (69.7) | 102 (67.1) | 294 (68.4) | |
| Secondary school and higher | 15 (19.5) | 31 (15.4) | 19 (12.5) | 65 (15.1) | |
| Mother’s employment status | 0.969 | ||||
| No paid job/Housewife | 75 (97.4) | 192 (97.0) | 147 (97.4) | 414 (97.2) | |
| Paid job (daily/part-/full-time) | 2 (2.6) | 6 (3.0) | 4 (2.6) | 12 (2.8) | |
| Father’s employment status | 0.627 | ||||
| No job/Part-time job | 39 (52.7) | 91 (46.4) | 73 (49.7) | 203 (48.7) | |
| Full-time job/ Self-employed | 35 (47.3) | 105 (53.6) | 74 (50.3) | 214 (51.3) | |
| Monthly household income | 0.455 | ||||
| ≤750,000 LBP | 51 (71.8) | 123 (63.7) | 95 (64.6) | 269 (65.5) | |
| >750,000 LBP | 20 (28.2) | 70 (36.3) | 52 (35.4) | 142 (34.5) | |
| Length of stay in Lebanon (years) | 3.2 ± 1.9 | 4.0 ± 3.8 | 4.0 ±2.2 | 3.8 ±3.0 | 0.130 |
| UNHCR refugee registration status | 0.313 | ||||
| No | 18 (23.7) | 35 (17.4) | 23 (15.5) | 76 (17.9) | |
| Yes | 58 (76.3) | 166 (82.6) | 125 (84.5) | 349 (82.1) | |
| If yes, received WFP food assistance (e-vouchers) * | 0.784 | ||||
| No | 53 (91.4) | 151 (91.5) | 112 (90.3) | 316 (91.1) | |
| Yes | 5 (8.6) | 14 (8.5) | 12 (9.7) | 31 (8.9) | |
| Receipt of any cash or food assistance | 0.243 | ||||
| No assistance | 68 (88.3) | 180 (88.7) | 125 (82.8) | 373 (86.5) | |
| Any type of assistance | 9 (11.7) | 23 (11.3) | 26 (17.2) | 58 (13.5) | |
| Reliance on savings or subsidies | 0.251 | ||||
| No reliance | 76 (98.7) | 192 (94.6) | 147 (96.7) | 415 (96.1) | |
| Any type of savings/subsidies | 1 (1.3) | 11 (5.4) | 5 (3.3) | 17 (3.9) | |
| Perception of safety | 0.012 | ||||
| Very to reasonably safe | 60 (77.9) | 151 (75.1) | 95 (62.5) | 306 (71.2) | |
| Somewhat to very unsafe | 17 (22.1) | 50 (24.9) | 57 (37.5) | 124 (28.8) | |
| Household characteristics | |||||
| Household type | 0.187 | ||||
| Nuclear family | 37 (48.1) | 102 (50.0) | 89 (58.6) | 228 (52.7) | |
| Extended family | 40 (51.9) | 102 (50.0) | 63 (41.4) | 205 (47.3) | |
| Decision-making/Head of household | 0.199 | ||||
| Father/ Family-in-law | 75 (97.4) | 194 (97.5) | 141 (94.0) | 410 (96.2) | |
| Mother/ Both parents | 2 (2.6) | 2 (2.5) | 9 (6.0) | 16 (3.8) | |
| Crowding index score | 4.0 ±2.0 | 3.6 ±1.6 | 3.7 ±1.5 | 3.7 ±1.6 | 0.189 |
| Number of children < 5 years per household | 2.4 ±1.8 | 2.7 ±1.5 | 2.8 ±1.5 | 2.7 ±1.5 | 0.327 0.024 |
| 1 to 2 | 53 (68.8) | 104 (51.2) | 75 (49.7) | 232 (53.8) | |
| 3 to 4 | 14 (18.2) | 76 (37.4) | 54 (35.8) | 144 (33.4) | |
| ≥5 | 10 (13.0) | 23 (11.3) | 22 (14.6) | 55 (12.8) |
| Variables a | PM n = 77 | LM n = 204 | NPNLM n = 152 | Total b n = 433 | p-Value c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare service utilization | |||||
| Health insurance | 0.493 | ||||
| Uninsured | 70 (92.1) | 190 (93.6) | 143 (94.7) | 403 (93.7) | |
| Public insurance | 2 (2.6) | 3 (1.5) | 0 (0.0) | 5 (1.2) | |
| Other | 4 (5.3) | 10 (4.9) | 8 (5.3) | 22 (5.1) | |
| Type of healthcare usually sought | 0.287 | ||||
| Public healthcare only | 51 (66.2) | 147 (73.1) | 99 (66.0) | 297 (69.4) | |
| Public, private, and/or other healthcare | 26 (33.8) | 54 (26.9) | 51 (34.0) | 131 (30.6) | |
| Number of antenatal care visits | 0.699 | ||||
| 0 times | 16 (21.1) | 32 (16.1) | 23 (15.1) | 71 (16.6) | |
| 1 to 3 times | 17 (22.4) | 40 (20.1) | 34 (22.4) | 91 (21.3) | |
| ≥4 times | 43 (56.6) | 127 (63.8) | 95 (62.5) | 265 (62.1) | |
| Sources of health and nutrition messages | 0.538 | ||||
| Healthcare professionals exclusively d | 13 (16.9) | 30 (14.7) | 17 (11.3) | 60 (13.9) | |
| Family, friends, media, and/or other | 51 (66.2) | 126 (61.8) | 96 (63.6) | 273 (63.2) | |
| Multiple sources e | 13 (16.9) | 48 (23.5) | 38 (25.2) | 99 (22.9) | |
| Maternal health characteristics | |||||
| Self-reported previous diagnosis with anemia | 0.040 | ||||
| No | 16 (21.1) | 66 (32.8) | 57 (37.7) | 139 (32.5) | |
| Yes | 60 (78.9) | 135 (67.2) | 94 (62.3) | 289 (67.5) | |
| Suffering from a flu (self-reported) | 0.030 | ||||
| No | 66 (88.0) | 178 (88.6) | 145 (96.0) | 389 (91.1) | |
| Yes | 9 (12.0) | 23 (11.4) | 6 (4.0) | 38 (8.9) | |
| Suffering from symptoms f | 0.438 | ||||
| No | 10 (13.0) | 29 (14.3) | 16 (10.8) | 55 (12.9) | |
| 1 to 2 symptoms | 24 (31.2) | 77 (37.9) | 47 (31.8) | 148 (34.6) | |
| ≥3 symptoms | 43 (55.8) | 97 (47.8) | 85 (57.4) | 225 (52.6) | |
| Health problems during previous pregnancy g | 0.537 | ||||
| No health problem | 45 (58.4) | 100 (49.5) | 86 (57.0) | 231 (53.7) | |
| 1 health problem | 26 (33.8) | 82 (40.6) | 50 (33.1) | 158 (36.7) | |
| ≥2 health problems | 6 (7.8) | 20 (9.9) | 15 (9.9) | 41 (9.5) | |
| Mother’s use of micronutrient supplements | |||||
| No | 29 (37.7) | 145 (72.9) | 125 (82.2) | 299 (69.9) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 48 (62.3) | 54 (27.1) | 27 (17.8) | 129 (30.1) | |
| If yes, what kind of supplement? | |||||
| Iron/Iron-folic acid | 33 (68.8) | 32 (62.7) | 18 (66.7) | 83 (65.9) | 0.816 0.210 0.068 0.006 0.234 |
| Multivitamins | 14 (29.2) | 8 (15.7) | 8 (29.6) | 30 (23.8) | |
| Calcium | 9 (18.8) | 15 (29.4) | 2 (7.4) | 26 (20.6) | |
| Vitamin D | 1 (2.1) | 3 (5.9) | 6 (22.2) | 10 (7.9) | |
| Other | 6 (12.5) | 4 (7.8) | 3 (11.1) | 13 (10.3) | |
| If yes, in what frequency? | |||||
| Not compliant | 3 (10.7) | 11 (25.6) | 3 (20.0) | 17 (19.8) | 0.307 |
| Weekly or daily | 25 (89.3) | 32 (74.4) | 12 (80.0) | 69 (80.2) |
| Variables a | PM n = 77 | LM n = 204 | NPNLM n = 152 | Total b n = 433 | p-Value c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maternal daily meal pattern | |||||
| Have breakfast every day | 0.022 | ||||
| No | 20 (26.0) | 51 (25.2) | 57 (38.3) | 128 (29.9) | |
| Yes | 57 (74.0) | 151 (74.8) | 92 (61.7) | 300 (70.1) | |
| Main meals per day | 2.1 ± 0.6 | 2.2 ± 0.6 | 2.0 ± 0.6 | 2.1 ± 0.6 | 0.018 |
| Snacks per day | 1.5 ± 1.1 | 1.3 ± 1.0 | 1.2 ± 1.0 | 1.3 ± 1.0 | 0.155 |
| Drinks coffee/tea between meals d | 0.065 | ||||
| No | 55 (72.4) | 118 (59.3) | 84 (56.8) | 257 (60.8) | |
| Yes | 21 (27.6) | 81 (40.7) | 64 (43.2) | 166 (39.2) | |
| Drinks coffee/tea during a meal e | 0.122 | ||||
| No | 33 (43.4) | 75 (37.7) | 72 (48.6) | 180 (42.6) | |
| Yes | 43 (56.6) | 124 (62.3) | 76 (51.4) | 243 (57.3) | |
| Lifestyle characteristics | |||||
| Physical activity f | 0.033 | ||||
| Low-intensity activity | 27 (35.1) | 85 (41.7) | 40 (26.3) | 152 (35.1) | |
| Moderate-intensity activity | 21 (27.3) | 56 (27.5) | 44 (28.9) | 121 (27.9) | |
| High-intensity activity | 29 (37.7) | 63 (30.9) | 68 (44.7) | 160 (37.0) | |
| Currently smoking cigarettes or shisha | 0.001 | ||||
| No | 68 (88.3) | 171 (83.8) | 105 (70.5) | 344 (80.0) | |
| Yes | 9 (11.7) | 33 (16.2) | 44 (29.5) | 86 (20.0) | |
| Currently drinking any type of alcohol | 0.260 | ||||
| No | 77 (100.0) | 194 (96.5) | 144 (97.3) | 415 (97.4) | |
| Yes | 0 (0.0) | 7 (3.5) | 4 (2.7) | 11 (2.6) |
| Variables a | PM n = 77 | LM n = 204 | NPNLM n = 152 | Total b n = 433 | p-Value c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anemia among mothers | |||||
| Hemoglobin concentration (g/dL) | 11.8 ± 1.3 | 12.9 ± 1.1 | 12.7 ± 1.3 | 12.6 ± 1.3 | <0.001 |
| Total anemia d | 0.199 | ||||
| Not anemic | 63 (81.8) | 162 (80.6) | 111 (73.5) | 336 (78.3) | |
| Anemic | 14 (18.2) | 39 (19.4) | 40 (26.5) | 93 (21.7) | |
| Classification of anemia e | 0.043 | ||||
| Not anemic | 63 (81.8) | 162 (80.6) | 111 (73.5) | 336 (78.3) | |
| Mild anemia | 6 (7.8) | 32 (15.9) | 28 (18.5) | 66 (15.4) | |
| Moderate anemia | 8 (10.4) | 7 (3.5) | 12 (7.9) | 27 (6.3) | |
| Anemia among children | |||||
| Hemoglobin concentration (g/dL) | 11.7 ± 1.3 | 11.3 ± 1.2 | 11.6 ± 1.2 | 11.4 ± 1.3 | 0.008 |
| Total anemia (0–59 months) d | 0.060 | ||||
| Not anemic | 60 (77.9) | 130 (64.4) | 109 (72.2) | 299 (69.5) | |
| Anemic | 17 (22.1) | 72 (35.6) | 42 (27.8) | 131 (30.5) | |
| Classification of anemia (6–59 months; n = 318) e | 0.001 | ||||
| Not anemic | 57 (78.1) | 52 (50.0) | 101 (71.6) | 210 (66.0) | |
| Mild anemia | 10 (13.7) | 39 (37.5) | 28 (19.9) | 77 (24.2) | |
| Moderate anemia | 6 (8.2) | 13 (12.5) | 12 (8.5) | 31 (9.8) | |
| Nutritional status of mothers | |||||
| MUAC (cm) | 28.6 ± 3.9 | 29.4 ± 4.1 | 29.9 ± 4.8 | 29.4 ± 4.4 | 0.148 |
| Classification of malnutrition using MUAC | 0.056 | ||||
| Undernourished (<23.0 cm) | 2 (2.6) | 8 (3.9) | 10 (6.6) | 20 (4.6) | |
| Normal weight (23.0–27.9 cm) | 32 (42.1) | 72 (35.5) | 42 (27.6) | 146 (33.9) | |
| Overweight (28.0–30.9 cm) | 25 (32.9) | 54 (26.6) | 37 (24.3) | 116 (26.9) | |
| Obese (≥31.0 cm) | 17 (22.4) | 69 (34.0) | 63 (41.4) | 149 (34.6) | |
| Nutritional status of non-pregnant mothers f | |||||
| BMI | 0.142 | ||||
| Underweight (<18.5 kg/m2) | - | 2 (1.0) | 7 (4.6) | 9 (2.5) | |
| Normal weight (18.5–24.9 kg/m2) | 76 (37.3) | 55 (36.2) | 131 (36.8) | ||
| Overweight (25.0–29.9 kg/m2) | 68 (33.3) | 43 (28.3) | 111 (31.2) | ||
| Obese (≥30.0 kg/m2) | 58 (28.4) | 47 (30.9) | 105 (29.5) | ||
| Waist circumference | 0.362 | ||||
| Normal (≤79 cm) | - | 67 (32.8) | 57 (37.5) | 124 (34.8) | |
| At-risk (>80 cm) | 137 (67.2) | 95 (62.5) | 232 (65.2) | ||
| Waist–hip ratio | 0.066 | ||||
| Normal (<0.85 cm) | - | 94 (46.1) | 85 (55.9) | 179 (50.3) | |
| Substantially increased risk (≥0.85 cm) | 110 (53.9) | 67 (44.1) | 177 (49.7) | ||
| Nutritional status of the children (0–59 months) | |||||
| Length/Height-for-age Z-score (L/HAZ) | 0.458 | ||||
| No stunting (L/HAZ ≥ −2) | 69 (90.8) | 189 (92.6) | 135 (88.8) | 393 (91.0) | |
| Stunting (L/HAZ < −2) | 7 (9.2) | 15 (7.4) | 17 (11.2) | 39 (9.0) | |
| Weight-for-age Z-score (WAZ) | 0.327 | ||||
| No underweight (WAZ ≥ −2) | 73 (96.1) | 192 (94.1) | 148 (97.4) | 413 (95.6) | |
| Underweight (WAZ < −2) | 3 (3.9) | 12 (5.9) | 4 (2.6) | 19 (4.4) | |
| Weight-for-length/height Z-score (WHZ) | 0.050 | ||||
| No wasting (WHZ ≥ −2) | 69 (90.8) | 191 (94.1) | 149 (98.0) | 409 (94.9) | |
| Wasting (WHZ < −2) | 7 (9.2) | 12 (5.9) | 3 (2.0) | 22 (5.1) | |
| BMI-for-age Z-score (BAZ) | 0.086 | ||||
| Wasting (BAZ < −2) | 7 (9.2) | 13 (6.4) | 2 (1.3) | 22 (5.1) | |
| Normal weight (−2 ≤ BAZ ≤ +2) | 66 (86.8) | 181 (88.7) | 144 (94.7) | 391 (90.5) | |
| Overweight/obese (BAZ > +2) | 3 (3.9) | 10 (4.9) | 6 (3.9) | 19 (4.4) |
| Variables | OR (95% CI) a Reference Group: NPNLM | aOR (95% CI) b Reference Group: NPNLM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pregnant mothers | Lactating mothers | Pregnant mothers | Lactating mothers | |
| Age | ||||
| Age of the mother (years) | 0.95 (0.91–0.99) * | 0.94 (0.91–0.98) ** | 0.92 (0.86–0.99) * | 0.97 (0.91–1.05) |
| Age of the children (months) | 0.99 (0.97–1.00) | 0.83 (0.79–0.86) α | 1.01 (0.98–1.03) | 0.82 (0.78–0.86) α |
| Health and lifestyle characteristics | ||||
| Self-reported previous diagnosis with anemia | ||||
| No | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Yes | 2.27 (1.20–4.32) * | 1.24 (0.80–1.93) | 2.60 (1.21–5.55) * | 1.75 (0.90–3.40) |
| Suffering from the flu (self-reported) | ||||
| No | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Yes | 3.30 (1.13–9.64) * | 3.12 (1.24–7.87) * | 3.66 (1.08–12.42) * | 2.63 (0.72–9.58) |
| Mother’s use of supplements | ||||
| No | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Yes | 7.66 (4.12–14.26) α | 1.72 (1.02–2.90) * | 12.47 (5.64–27.55) α | 2.37 (1.05–5.35) * |
| Have breakfast every day | ||||
| No | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Yes | 1.77 (0.96–3.24) | 1.83 (1.16–2.90) ** | 2.14 (1.05–4.40) * | 2.28 (1.14–4.56) * |
| Currently smokes cigarettes or shisha | ||||
| No | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Yes | 0.32 (0.14–0.69) ** | 0.46 (0.28–0.77) ** | 0.34 (0.14–0.83) * | 0.41 (0.20–0.86) * |
| Anemia and nutritional status of mothers | ||||
| Classification of anemia c | ||||
| Not anemic | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Mild anemia | 0.38 (0.15–0.96) * | 0.78 (0.45–1.37) | 0.26 (0.08–0.82) * | 1.09 (0.43–2.71) |
| Moderate anemia | 1.18 (0.46–3.03) | 0.40 (0.15–1.05) | 2.75 (0.70–10.84) | 0.93 (0.20–4.45) |
| Classification of malnutrition using MUAC | ||||
| Normal weight (23.0–27.9 cm) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Undernourished (<23.0 cm) | 0.26 (0.05–1.28) | 0.47 (0.17–1.27) | 0.26 (0.05–1.50) | 0.36 (0.09–1.48) |
| Overweight (28.0–30.9 cm) | 0.89 (0.45–1.76) | 0.85 (0.48–1.50) | 0.82 (0.36–1.86) | 0.94 (0.41–2.16) |
| Obese (≥31.0 cm) | 0.35 (0.18–0.72) ** | 0.64 (0.38–1.06) | 0.25 (0.10–0.60)** | 0.86 (0.39–1.92) |
| Anemia and nutritional status of children | ||||
| Total anemia (0–59 months) c | ||||
| Not anemic | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Anemic | 0.74 (0.39–1.40) | 1.44 (0.91–2.27) | 0.66 (0.30–1.45) | 2.11 (1.07–4.17) * |
| Classification of anemia (6–59 months) d | ||||
| Not anemic | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Mild anemia | 0.63 (0.29–2.49) | 2.70 (1.50–4.88) ** | 0.75 (0.21–2.62) | 2.98 (1.26–7.04) ** |
| Moderate anemia | 0.89 (0.32–1.40) | 2.10 (0.90–4.94) | 0.52 (0.20–1.36) | 2.67 (0.83–8.57) |
| BMI-for-age Z-score (BAZ) (0–59 months) | ||||
| Normal weight (−2 ≤ BAZ ≤ +2) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Wasting (BAZ < −2) | 7.64 (1.54–37.76) * | 5.17 (1.15–23.28) * | 5.90 (1.02–34.18) * | 2.37 (0.44–11.90) |
| Overweight/obese (BAZ > +2) | 1.09 (0.26–4.50) | 1.33 (0.47–3.73) | 3.01 (0.54–16.79) | 0.58 (0.07–4.82) |
| Variables a | Not Anemic | Anemic | Maternal Anemia | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Socio-economic and household characteristics (n = 433) | n= 334 | n= 93 | OR (95% CI) b | aOR (95% CI) c |
| Crowding index score | 3.6 ±1.5 | 4.1 ±2.0 | 1.2 (1.03–1.34) * | 1.09 (0.88–1.35) |
| Receipt of WFP food assistance (e-vouchers) | ||||
| No | 311 (94.0) | 77 (87.5) | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Yes | 20 (6.0) | 11 (12.5) | 2.22 (1.02–4.83) * | 1.56 (0.55–4.44) d |
| Number of children < 5 years per household | ||||
| 1 to 2 | 188 (56.0) | 41 (45.1) | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| 3 to 4 | 115 (34.2) | 28 (30.8) | 1.12 (0.66–1.90) | 0.62 (0.28–1.39) |
| ≥5 | 33 (9.8) | 22 (24.2) | 3.06 (1.62–5.78)** | 1.73 (0.58–5.10) |
| Health characteristics of mothers (n = 433) | n= 334 | n= 93 | OR (95% CI) b | aOR (95% CI) c |
| Self-reported previous diagnosis with anemia | ||||
| No | 118 (35.6) | 20 (21.5) | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Yes | 213 (64.4) | 73 (78.5) | 2.02 (1.17–3.48) * | 2.27 (1.14–4.52) * |
| Sources of health and nutrition messages | ||||
| Healthcare professionals exclusively e | 38 (11.3) | 22 (23.9) | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Family, friends, media, and/or other | 219 (65.2) | 52 (56.5) | 0.41 (0.22–0.75) ** | 0.42 (0.19–0.94) * |
| Multiple sources f | 79 (23.5) | 18 (19.6) | 0.39 (0.19–0.82) * | 0.23 (0.08–0.66) ** |
| Anemia status among children (0–59 months) (n = 433) | n= 333 | n= 93 | OR (95% CI) b | aOR (95% CI) c |
| Total anemia (0–59 months) g | ||||
| Not anemic | 239 (71.8) | 56 (60.2) | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Anemic | 94 (28.2) | 37 (39.8) | 1.68 (1.04–2.71) * | 2.67 (1.42–5.02) ** |
| Classification of anemia (6–59 months) (n = 318) | n= 242 | n= 75 | OR (95% CI) b | aOR (95% CI) c |
| Classification of anemia (6–59 months) h | ||||
| Not anemic | 165 (68.2) | 44 (58.7) | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Mild anemia | 55 (22.7) | 22 (29.3) | 1.50 (0.83–2.72) | 4.40 (1.79–10.80) α |
| Moderate anemia | 22 (9.1) | 9 (12.0) | 1.53 (0.66–3.57) | 2.39 (0.72–7.97) |
| Nutritional status of non-pregnant mothers i (n = 356) | n= 273 | n= 79 | OR (95% CI) b | aOR (95% CI) j |
| Waist circumference | ||||
| Normal | 104 (38.1) | 20 (25.3) | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| At-risk (>80 cm) | 169 (61.9) | 59 (74.7) | 1.82 (1.03–3.19) * | 3.05 (1.34–6.92) ** |
| Nutritional status of NPNLM (n = 152) | n= 111 | n= 40 | OR (95% CI) b | aOR (95% CI) k |
| Waist circumference | ||||
| Normal | 49 (44.1) | 8 (20.0) | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| At-risk (>80 cm) | 62 (55.9) | 32 (80.0) | 3.16 (1.34–7.48) ** | 10.90 (2.74–43.38)** |
| BMI for the mother | ||||
| Normal weight | 46 (41.4) | 9 (22.5) | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Underweight | 4 (3.6) | 3 (7.5) | 3.83 (0.73–20.13) | 13.39 (1.52–118.12) * |
| Overweight/Obese | 61 (55.0) | 28 (70.0) | 2.35 (1.01–5.45) * | 14.68 (3.22–66.96) ** |
| Consumption of coffee and tea (n = 375) | n= 294 | n= 81 | OR (95% CI) b | aOR (95% CI) c |
| Drinks coffee/tea between meals l | ||||
| No | 140 (47.6) | 35 (43.2) | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Yes | 154 (52.4) | 46 (56.8) | 0.82 (0.48–1.39) | 0.87 (0.44–1.73) |
| Drinks coffee/tea during a meal m | ||||
| No | 140 (47.6) | 35 (43.2) | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Yes | 154 (52.4) | 46 (56.8) | 1.20 (0.73–1.96) | 1.38 (0.73–2.62) |
| Variables | Intake/Day (Mean ± SD) | <2/3rd DRIs (n, %) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy and Macronutrients (%EI) | PM n = 77 | LM n = 204 | NPNLM n = 152 | Total n = 433 | PM n = 77 | LM n = 204 | NPNLM n = 152 | Total n = 433 |
| Energy (kcal/d) | 1622.6 ± 872.9 a | 1555.5 ± 729.4 b | 1341.5 ± 685.2 c | 1492.3 ± 749.0 | - | - | - | - |
| Carbohydrates (%EI/d) | 51.8 ± 10.6 | 51.9 ± 11.2 | 53.1 ± 11.7 | 52.3 ± 11.3 | - | - | - | - |
| Protein (%EI/d) | 12.2 ± 5.1 | 12.3 ± 3.9 | 12.8 ± 4.6 | 12.4 ± 4.4 | - | - | - | - |
| Total fat (%EI/d) | 37.2 ± 11.0 | 36.8 ± 11.3 | 35.5 ± 11.3 | 36.4 ± 11.2 | - | - | - | - |
| MUFA (%EI/d) | 13.5 ± 8.4 | 12.8 ± 8.0 | 12.6 ± 9.4 | 12.9 ± 8.6 | - | - | - | - |
| Linoleic acid (%EI/d) | 8.9 ± 4.3 | 9.0 ± 5.1 | 8.7 ± 4.7 | 8.9 ± 4.8 | - | - | - | - |
| Linolenic acid (%EI/d) | 1.6 ± 3.8 | 1.4 ± 2.7 | 1.4 ± 2.8 | 1.4 ± 3.0 | - | - | - | - |
| PUFA (%EI/d) | 12.2 ± 13.0 | 12.1 ± 14.3 | 12.7 ± 21.3 | 12.3 ± 16.9 | - | - | - | - |
| SFA (%EI/d) | 9.4 ± 10.7 | 9.2 ± 7.0 | 8.2 ± 4.2 | 8.9 ± 7.0 | - | - | - | - |
| TFA (%EI/d) | 0.1 ± 0.22 | 0.2 ± 0.4 | 0.2 ± 0.4 | 0.2 ± 0.3 | - | - | - | - |
| Cholesterol (mg/d) | 146.4 ± 158.0 a | 162.5 ± 186.5 b | 116.9 ± 130.7 c | 143.6 ± 164.7 | - | - | - | - |
| Total sugar (%EI/d) | 12.8 ± 8.5 | 13.8 ± 7.79 | 15.0 ± 7.8 | 14.0 ± 8.0 | - | - | - | - |
| Macronutrient intake | ||||||||
| Carbohydrates (g/d) | 205.9 ± 104.8 a | 197.0 ± 90.6 b | 171.4 ± 81.4 c | 189.6 ± 91.1 | 16 (20.8) d | 60 (29.4) e | 21 (13.8) f | 97 (22.4) |
| Protein (g/d) | 45.3 ± 21.7 | 46.7 ± 26.3 | 41.4 ± 24.5 | 44.6 ± 25.0 | 46 (59.7) d | 121 (59.3) e | 58 (38.2) f | 225 (52.0) |
| Linoleic acid (g/d) | 17.1 ± 12.5 | 16.2 ± 12.7 | 13.9 ± 11.2 | 15.6 ± 12.2 | 24 (31.2) | 65 (31.9) | 55 (36.4) | 144 (33.3) |
| Linolenic acid (g/d) | 4.3 ± 13.2 | 2.3 ± 4.4 | 2.2 ± 4.8 | 2.6 ± 6.9 | 43 (55.8) | 110 (53.9) | 90 (59.2) | 243 (56.1) |
| Fibers (g/d) | 16.8 ± 12.0 | 15.5 ± 11.0 | 14.5 ± 10.7 | 15.3 ± 11.1 | 51 (66.2) d | 148 (72.5) e | 107 (70.9) f | 306 (70.8) |
| Micronutrient intake | ||||||||
| Iron (mg/d) | 10.2 ± 9.8 | 8.2 ± 6.2 | 8.0 ± 6.1 | 8.5 ± 7.0 | 63 (81.8) d | 92 (45.1) e | 121 (80.1) f | 276 (63.9) |
| Folate (µg/d) | 238.8 ± 222.0 | 221.3 ± 204.5 | 203.8 ± 178.3 | 218.2 ± 199.0 | 65 (84.4) | 161 (78.9) | 116 (76.3) | 342 (79.0) |
| Vitamin B12 (µg/d) | 1.4 ± 3.3 | 1.4 ± 2.4 | 1.2 ± 1.8 | 1.4 ± 2.4 | 59 (76.6) | 160 (78.4) | 117 (77.0) | 336 (77.6) |
| Vitamin C (mg/d) | 62.9 ± 65.1 | 64.4 ± 58.6 | 52.9 ± 43.0 | 60.1 ± 55.1 | 46 (59.7) | 140 (68.6) | 86 (57.0) | 272 (63.0) |
| Vitamin A (µg/d) | 418.6 ± 668.8 | 425.6 ± 530.7 | 329.8 ± 397.3 | 390.7 ± 517.9 | 57 (74.0) d | 182 (89.2) e | 126 (82.9) f | 365 (84.3) |
| Vitamin D (µg/d) | 0.7 ± 0.8 a | 0.8 ± 1.1 b | 0.4 ± 0.6 c | 0.6 ± 0.9 | 77 (100.0) | 204 (100.0) | 152 (100.0) | 433 (100.0) |
| Vitamin E (mg/d) | 9.1 ± 9.2 | 7.7 ± 5.9 | 7.1 ± 6.5 | 7.8 ± 6.8 | 53 (68.8) d | 175 (85.8) e | 120 (78.9) f | 348 (80.4) |
| Vitamin K (µg/d) | 132.1 ± 194.5 | 133.6 ± 276.9 | 111.0 ± 174.7 | 125.4 ± 231.2 | 35 (45.5) | 90 (44.1) | 84 (55.6) | 209 (48.4) |
| Thiamin (mg/d) | 1.3 ± 0.8 a | 1.3 ± 0.7 b | 1.1 ± 0.6 c | 1.2 ± 0.7 | 24 (31.2) | 65 (31.9) | 40 (26.5) | 129 (29.9) |
| Riboflavin (mg/d) | 1.1 ± 0.7 a | 1.1 ± 0.6 b | 0.9 ± 0.5 c | 1.0 ± 0.6 | 37 (48.1) | 111 (54.4) | 70 (46.4) | 218 (50.5) |
| Niacin (mg/d) | 13.7 ± 7.1 | 13.8 ± 8.3 | 11.9 ± 6.9 | 13.1 ± 7.6 | 35 (45.5) | 86 (42.2) | 63 (41.4) | 184 (42.5) |
| Pantothenic acid (mg/d) | 3.4 ± 2.4 | 3.3 ± 2.1 | 2.9 ± 1.9 | 3.2 ± 2.1 | 55 (71.4) d | 171 (83.8) e | 111 (73.0) f | 337 (77.8) |
| Vitamin B6 (mg/d) | 1.0 ± 0.6 a | 0.9 ± 0.6 b | 0.8 ± 0.5 c | 0.9 ± 0.6 | 52 (67.5) d | 173 (84.8) e | 99 (65.6) f | 324 (75.0) |
| Zinc (mg/d) | 6.4 ± 4.3 | 6.0 ± 3.7 | 5.5 ± 3.5 | 5.9 ± 3.8 | 55 (71.4) d | 161 (78.9) e | 94 (62.3) f | 310 (71.8) |
| Copper (mg/d) | 1.3 ± 1.1 a | 1.0 ± 0.6 b | 0.9 ± 0.6 c | 1.0 ± 0.7 | 20 (26.0) d | 98 (48.0) e | 58 (38.2) f | 176 (40.6) |
| Calcium (mg/d) | 475.1 ± 386.1 | 449.6 ± 341.2 | 414.1 ± 325.9 | 441.7 ± 344.3 | 62 (80.5) | 166 (81.4) | 125 (82.8) | 353 (81.7) |
| Magnesium (mg/d) | 216.2 ± 140.9 a | 183.1 ± 99.6 b | 174.2 ± 105.4 c | 186.8 ± 110.7 | 52 (67.5) | 139 (68.1) | 108 (71.5) | 299 (69.2) |
| Sodium (mg/d) | 2088.9 ± 1235.6 | 2217.8 ± 1335.6 | 1948.2 ± 1170.1 | 2100.2 ± 1265.0 | 13 (16.9) | 33 (16.2) | 32 (21.1) | 78 (18.0) |
| Potassium (mg/d) | 744.6 ± 459.1 a | 1798.2 ± 956.4 b | 1600.4 ± 879.9 c | 1752.9 ± 972.2 | 66 (85.7) d | 195 (95.6) e | 144 (94.7) f | 405 (93.5) |
| Phosphorus (mg/d) | 744.6 ± 459.1 | 696.4 ± 437.9 | 621.4 ± 391.6 | 678.6 ± 427.6 | 20 (26.0) | 66 (32.4) | 61 (40.4) | 147 (34.0) |
| Manganese (mg/d) | 2.8 ± 1.6 | 2.5 ± 1.6 | 2.4 ± 1.5 | 2.5 ± 1.6 | 14 (18.2) d | 71 (34.8) e | 33 (21.9) f | 118 (27.3) |
| Selenium (µg/d) | 69.9 ± 39.0 a | 72.0 ± 37.9 b | 59.2 ± 34.0 c | 67.2 ± 37.2 | 18 (23.4) | 55 (27.0) | 40 (26.3) | 113 (26.1) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abou-Rizk, J.; Jeremias, T.; Nasreddine, L.; Jomaa, L.; Hwalla, N.; Tamim, H.; Frank, J.; Scherbaum, V. Anemia and Nutritional Status of Syrian Refugee Mothers and Their Children under Five Years in Greater Beirut, Lebanon. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6894. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18136894
Abou-Rizk J, Jeremias T, Nasreddine L, Jomaa L, Hwalla N, Tamim H, Frank J, Scherbaum V. Anemia and Nutritional Status of Syrian Refugee Mothers and Their Children under Five Years in Greater Beirut, Lebanon. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(13):6894. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18136894
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbou-Rizk, Joana, Theresa Jeremias, Lara Nasreddine, Lamis Jomaa, Nahla Hwalla, Hani Tamim, Jan Frank, and Veronika Scherbaum. 2021. "Anemia and Nutritional Status of Syrian Refugee Mothers and Their Children under Five Years in Greater Beirut, Lebanon" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 13: 6894. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18136894







