Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis Induced by Chenopodium ambrosioides L. Essential Oil in Human Normal Liver Cell Line L02 via the Endogenous Mitochondrial Pathway Rather Than the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Culture
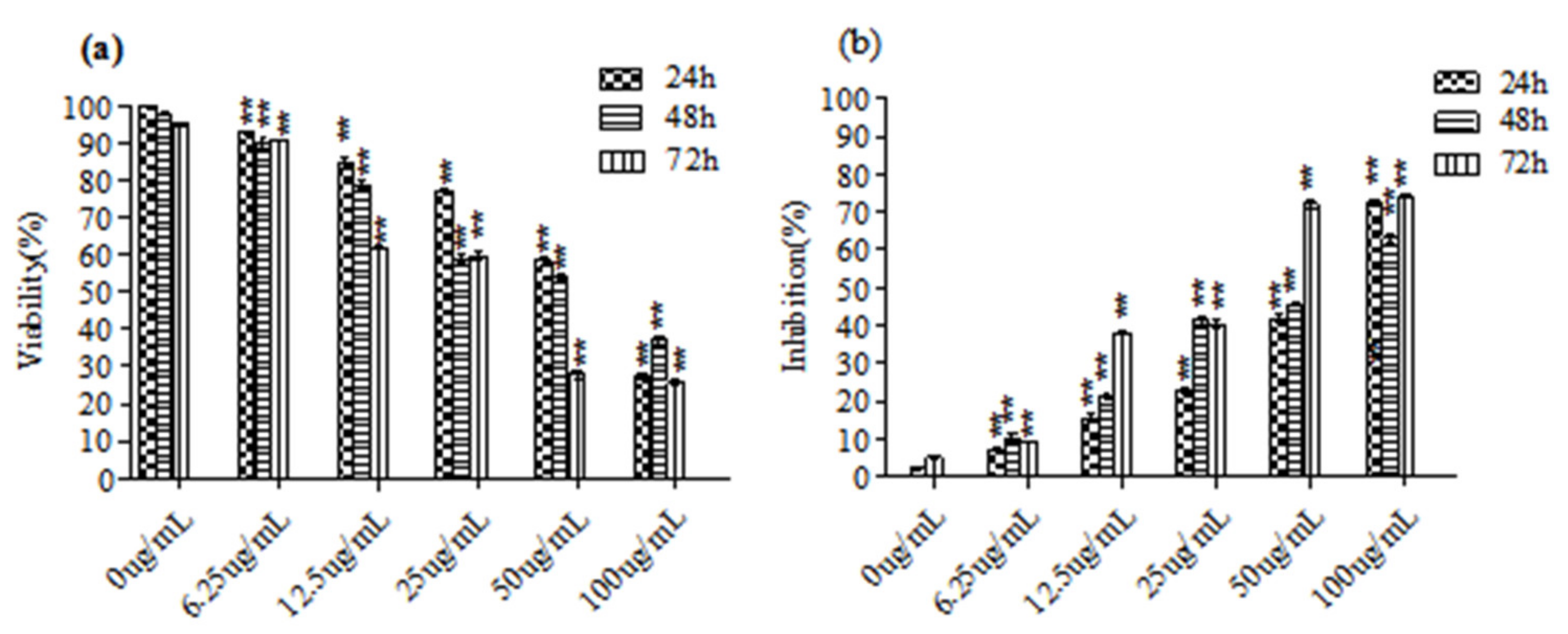
2.3. MTT Assay
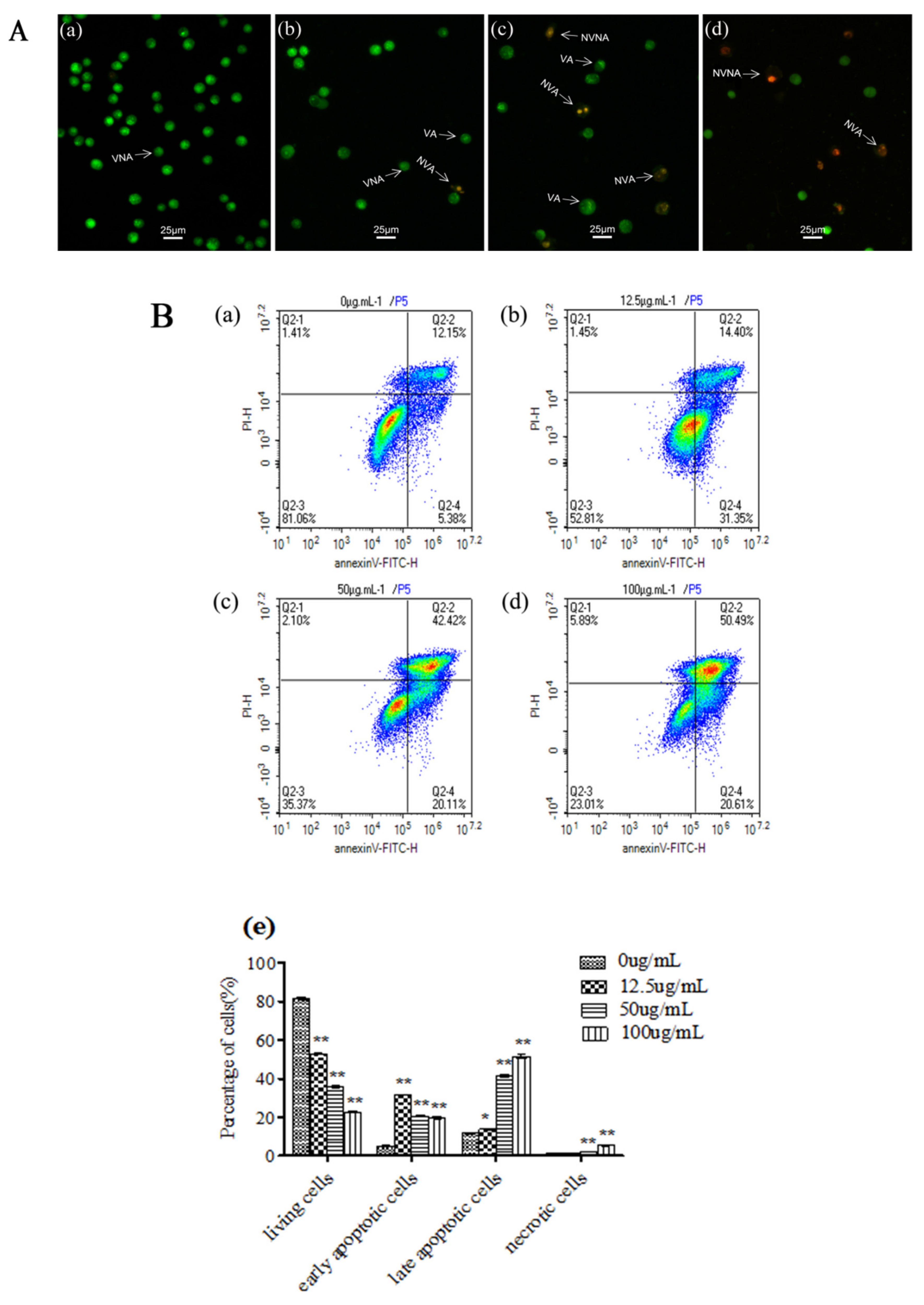
2.4. Apoptosis Observation by Fluorescence Microscope and Analysis by Flow Cytometry
2.5. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Assay
2.6. Cell Cycle Analysis by Flow Cytometry
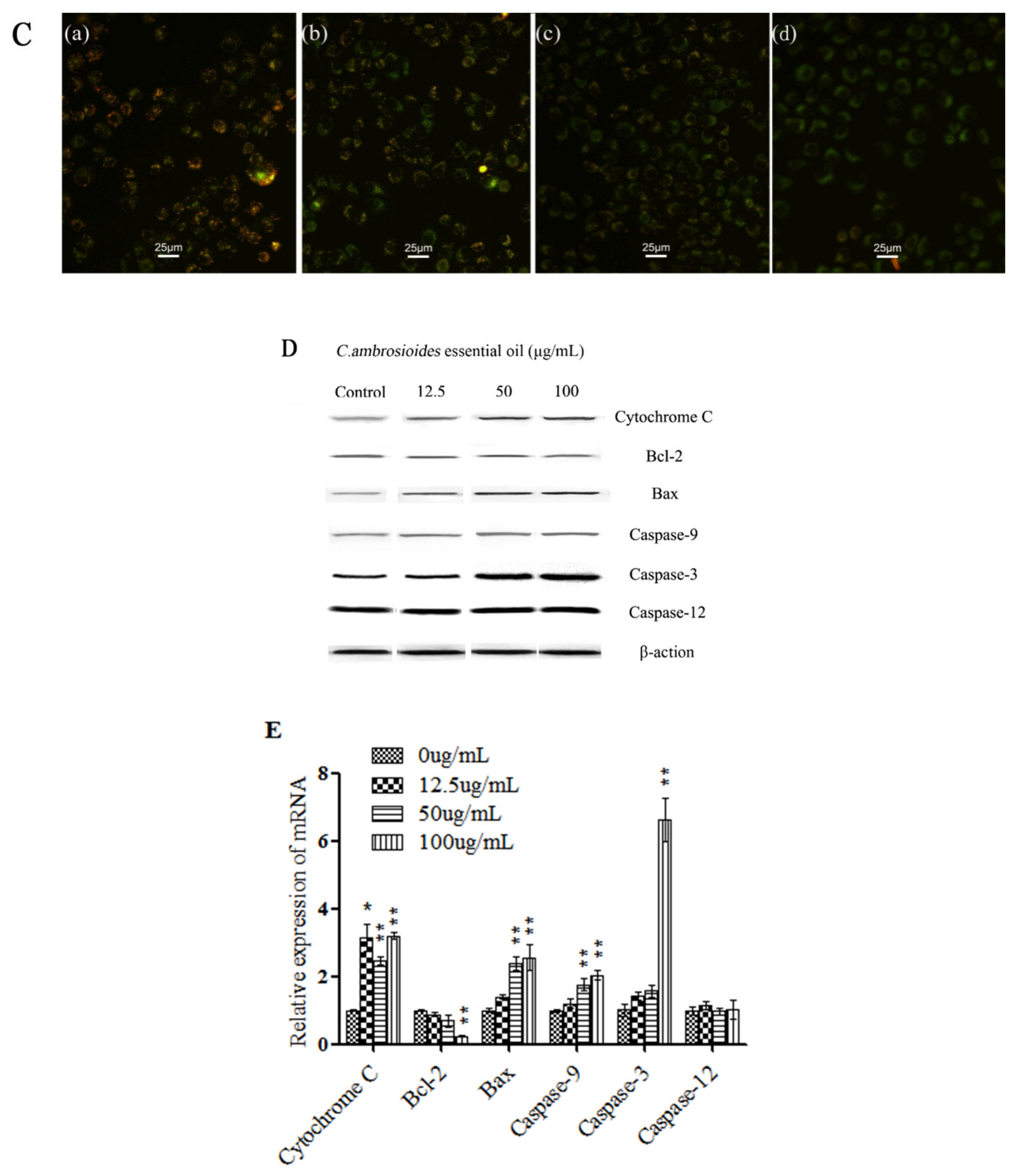
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. C. ambrosioides Essential Oil Inhibited the Proliferation of L02 Cells
3.2. C. ambrosioides Essential Oil Induced Apoptosis in L02 Cells
3.3. C. ambrosioides Essential Oil Induced Cell Cycle Arrest in L02 Cells
4. Discussion
4.1. Cytotoxic Effects of C. ambrosioides Essential Oil on L02 Cells
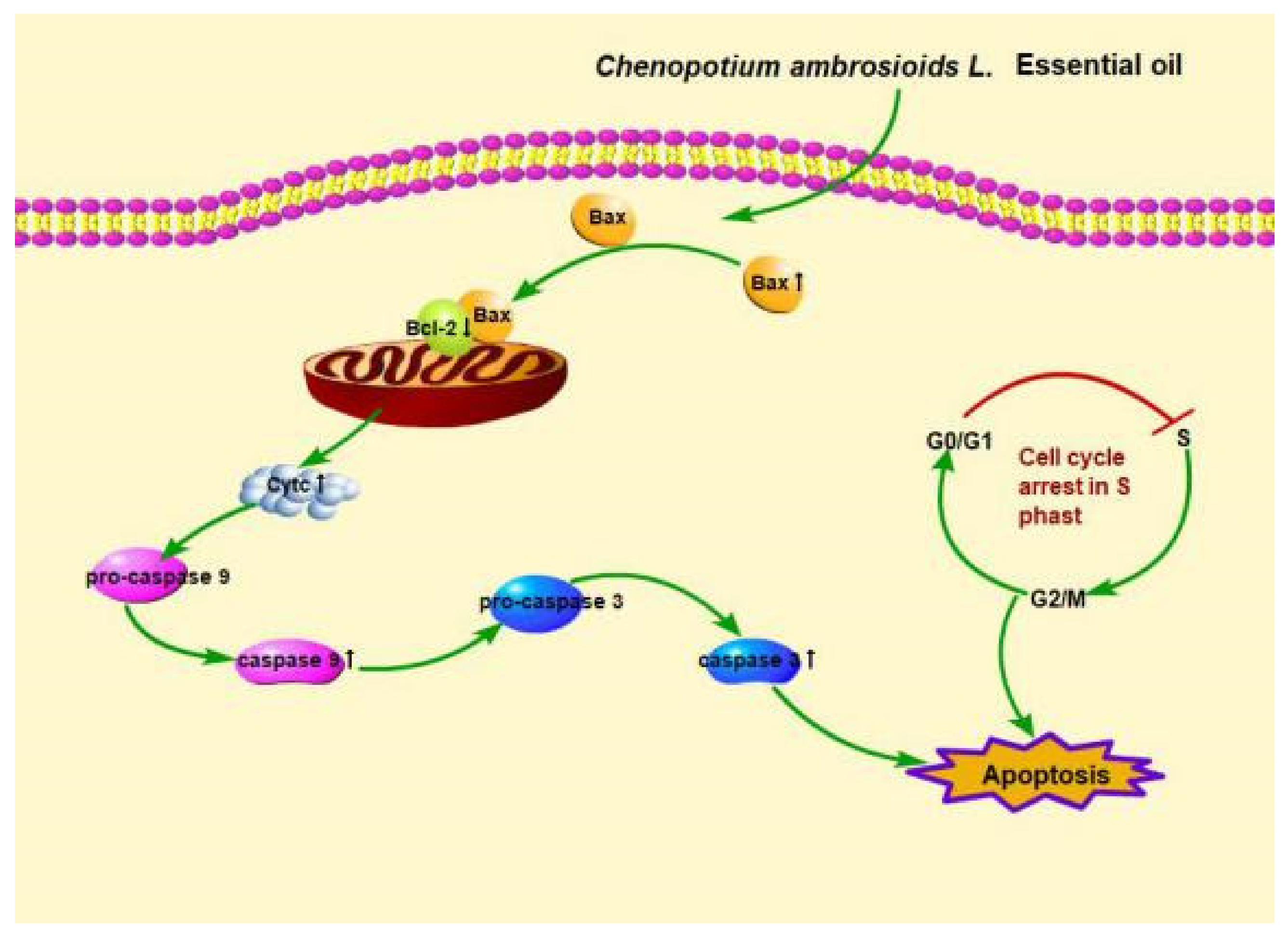
4.2. C. ambrosioides Essential Oil Induced L02 Cell Apoptosis through the Endogenous Mitochondrial Pathway
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reyes-Becerril, M.; Angulo, C.; Sánchez, V.; Vázquez-Martínez, J.; López, M.G. Antioxidant, intestinal immune status and anti-inflammatory potential of Chenopodium ambrosioides L. in fish: In vitro and in vivo studies. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 86, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, G.V.; Pereira, P.V.S.; Patrício, F.J.; Costa, G.C.; Sousa, S.M.; Frazão, J.B.; Aragão-Filho, W.C.; Maciel, M.C.; Silva, L.A.; Amaral, F.M.; et al. Increase of cellular recruitment, phagocytosis ability and nitric oxide production induced by hydroalcoholic extract from Chenopodium ambrosioides leaves. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 111, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos-Delgado, L.; González-Mondragón, E.; Ramírez-Andrade, J.; Salazar-Govea, A.; Santiago-Castro, J. Oxidative stability in raw, cooked, and frozen ground beef using Epazote (Chenopodium ambrosioides L.). Meat Sci. 2020, 168, 108187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Mishra, A.K.; Dubey, N.; Tripathi, Y. Evaluation of Chenopodium ambrosioides oil as a potential source of antifungal, antiaflatoxigenic and antioxidant activity. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 115, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harraz, F.M.; Hammoda, H.M.; El Ghazouly, M.G.; Farag, M.A.; El-Aswad, A.F.; Bassam, S.M. Chemical composition, antimicrobial and insecticidal activities of the essential oils of Conyza linifolia and Chenopodium ambrosioides. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 879–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.W. Toxicity of Chenopodium ambrosioides alkaloids to Musca domestica and influence on insecticides susceptibility. Entomol. J. East China 2007, 16, 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.Q.; Wei, H.; Liu, J.; Wei, W.U.; Zhan, Z.X. Toxic, antifeedant and growth inhibitory effects of Chenopodium ambrosioides essential oil against Pieris rapae larvae. Fujian J. Agric. Sci. 2007, 22, 266–270. [Google Scholar]
- Owolabi, M.S.; Lajide, L.; Oladimeji, M.O.; Setzer, W.N.; Palazzo, M.C.; Olowu, R.A.; Ogundajo, A. Volatile Constituents and Antibacterial Screening of the Essential Oil of Chenopodium ambrosioides L. Growing in Nigeria. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2009, 4, 989–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nie, X.N.; Liang, Z.S.; Duan, Q.M.; Lan, X.J. Chemical constituents and antibacterial activities of essential oils from Chenopodium ambrosioides L. J. Northwest A F Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2010, 38, 151–155. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, S.J.; Graças, C.; Roberto, B.L.; De Castro, E.M.; Luisa, T.M.; Rreira, P.M.F. Essential oil from Chenopodium ambrosioides L.: Secretory structures, antibacterial and antioxidant activities. Acta Sci. Biol. Sci. 2016, 38, 139. [Google Scholar]
- Degenhardt, R.T.; Farias, I.; Grassi, L.T.; Gilberto, C.F., Jr.; Nowill, A.E.; Bittencourt, C.M.D.S.; Wagner, T.M.; De Souza, M.M.; Cruz, A.B.; Malheiros, A. Characterization and evaluation of the cytotoxic potential of the essential oil of Chenopodium ambrosioides. Rev. Bras. Farm. 2016, 26, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.-N.; Zhu, X.-H.; Ma, H.; Du, R.-Y.; Li, D.-R.; Ma, D.-W. Essential Oil of Chenopodium ambrosioides Induced Caspase-Dependent Apoptosis in SMMC-7721 Cells. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2016, 39, 1124–1128. [Google Scholar]
- Nascimento, F.R.; Cruz, G.V.; Pereira, P.V.S.; Maciel, M.C.; Silva, L.A.; Azevedo-Santos, A.P.; Barroqueiro, E.S.; Guerra, R.N. Ascitic and solid Ehrlich tumor inhibition by Chenopodium ambrosioides L. treatment. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 2650–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, J.; Cavalli, J.; Tomi, F.; Bernardini, A. Combined analysis of the essential oil of Chenopodium ambrosioides by GC, GC-MS and13C-NMR spectroscopy: Quantitative determination of ascaridole, a heat-sensitive compound. Phytochem. Anal. 2004, 15, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ma, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; He, B.; Li, Q.; Zou, Z.; Feng, J. Cytotoxicity of Essential Oil of Chenopodium ambrosioides L against Human Breast Cancer MCF-7 Cells. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 12, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhong, S.; Ren, Q.; Wang, Y. The Effects of Ethanol Extract from Chenopodium ambrosioides on MCF-7 Cell Proliferation. J. Sichuan Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2017, 40, 531–535. [Google Scholar]
- Monzote, L.; García, M.; Montalvo, A.M.; Linares, R.; Scull, R. Effect of oral treatment with the essential oil from Chenopodium ambrosioides against cutaneous leishmaniasis in BALB/c mice, caused by Leishmania amazonensis. Forsch. Komplementmed. 2009, 16, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koffi, K.; Guyon, C.; Christine, R.; Jean-Pierre, C.; Komla, S.; Nicod, L. Chemical Composition and Cytotoxic Activity of Chenopodium ambrosioides L. Essential Oil from Togo. Bangladesh J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2009, 44, 138–141. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.N.; Li, X.X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.Y.; Yang, J.; Ma, D.-W. Evaluation of the genetic toxicity of essential oil from Chenopodium ambrosioides L.with TK mutation assay. Carcinog. Teratog. Mutagenesis 2014, 5, 378–381. [Google Scholar]
- Gadano, A.; Gurni, A.; López, P.; Ferraro, G.; Carballo, M.; Gadano, A.; Gurni, A.; López, P.; Ferraro, G.; Carballo, M. In vitro genotoxic evaluation of the medicinal plant Chenopodium ambrosioides L. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2002, 81, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.-Y.; Seol, D.-W. The role of mitochondria in apoptosis. BMB Rep. 2008, 41, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Green, D.R.; Reed, J.C. Mitochondria and Apoptosis. Science 1998, 281, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagrero-Nieves, L.; Bartley, J.P. Volatile Constituents from the Leaves of Chenopodium ambrosioides L. J. Essent. Oil Res. 1995, 7, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallal, A.; Benali, S.; Markouk, M.; Bekkouche, K.; Abdouni, M. Evaluation of the Analgesic and Antipyretic Activities of Chenopodium ambrosioides L. Asian J. Exp. Biol. Sci. 2010, 1, 189–192. [Google Scholar]
- Jardim, C.M.; Jham, G.N.; Dhingra, O.D.; Freire, M.M. Composition and Antifungal Activity of the Essential Oil of the Brazilian Chenopodium ambrosioides L. J. Chem. Ecol. 2008, 34, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Ma, D.-W. Progress Research of Chemical Constituents and Effects of Invasive Plant Chenopodium ambrosioides L. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2011, 39, 3532–3534. [Google Scholar]
- Hengartner, M.O. The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 407, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, S. Apoptosis induced by a death factor. Cell 1997, 88, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amanullah, A.; Upadhyay, A.; Chhangani, D.; Joshi, V.; Mishra, R.; Yamanaka, K.; Mishra, A. Proteasomal Dysfunction Induced By Diclofenac Engenders Apoptosis Through Mitochondrial Pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 1014–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wu, F.; Zhang, X.; Chai, Y.; Chen, D.; Yang, Y.; Xu, K.; Yin, J.; Li, R.; Shi, H.; et al. Valproate Attenuates Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced Apoptosis in SH-SY5Y Cells via the AKT/GSK3β Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Z.-X.; Yang, Y.-T.; Yu, S.; Li, Y.-Z.; Wang, W.-W.; Huang, J.; Xie, X.-F.; Xiong, L.; Lei, S.; Peng, C. Pogostone induces autophagy and apoptosis involving PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis in human colorectal carcinoma HCT116 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 202, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossy-Wetzel, E.; Newmeyer, D.D.; Green, D. Mitochondrial cytochrome c release in apoptosis occurs upstream of DEVD-specific caspase activation and independently of mitochondrial transmembrane depolarization. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, M.C.; Zong, W.-X.; Cheng, E.H.-Y.; Lindsten, T.; Panoutsakopoulou, V.; Ross, A.J.; Roth, K.A.; MacGregor, G.R.; Thompson, C.B.; Korsmeyer, S.J. Proapoptotic BAX and BAK: A Requisite Gateway to Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Death. Science 2001, 292, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tamm, I.; Wang, Y.; Sausville, E.; A Scudiero, D.; Vigna, N.; Oltersdorf, T.; Reed, J.C. IAP-family protein survivin inhibits caspase activity and apoptosis induced by Fas (CD95), Bax, caspases, and anticancer drugs. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 5315–5320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guan, L.Y.; Xu, C.M.; Pan, H.Z. Endoplasmic Reticulam Stress-induced Apoptosis. Prog. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 34, 1136–1141. [Google Scholar]
| Gene | Sequences |
|---|---|
| Cytochrome C | Forward: CCTTTGTGGTGTTGACCAGC |
| Reverse: CCATGGAGGTTTGGTCCAGT | |
| Bcl-2 | Forward: AGTGGGATGCGGGAGATGTGG |
| Reverse: TAGCGGCGGGAGAAGTCGTC | |
| Bax | Forward: GATTGCCGCCGTGGACACAG |
| Reverse: GAGCACTCCCGCCACAAAGATG | |
| Caspase-3 | Forward: AGATGTCGATGCAGCAAACCTCAG |
| Reverse: TGTCTCAATGCCACAGTCCAGTTC | |
| Caspase-9 | Forward: CTTCGTTTCTGCGAACTAACAGG |
| Reverse: GCACCACTGGGGTAAGGTTT | |
| Caspase-12 | Forward: TACAGCTCAGGAAATGGAGACA |
| Reverse: TCAATGGCTCAACACACATTCC | |
| β-actin | Forward: GGCACTCTTCCAGCCTTCCT |
| Reverse: GCACTGTGTTGGCGTACAGG |
| Concentrations (μg/mL) | Cell Population % | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| G0/G1 | S | G2/M | |
| Control | 49.43 ± 2.35 | 35.37 ± 2.71 | 11.96 ± 0.55 |
| 12.5 | 50.96 ± 1.33 | 26.25 ± 5.04 | 11.91 ± 2.21 |
| 25 | 47.57 ± 3.43 | 34.93 ± 2.60 | 14.88 ± 1.26 |
| 50 | 42.66 ± 3.25 | 37.41 ± 3.42 | 16.51 ± 3.39 |
| 100 | 31.06 ± 2.01 ** | 54.08 ± 3.78 ** | 11.67 ± 3.71 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.-Y.; Hao, J.-M.; Ren, Q.-R.; Li, H.-Y.; Wu, J.-S.; Zhu, X.-H.; Chen, J.-Y.; Wang, Y.-N.; Zhang, L.-S. Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis Induced by Chenopodium ambrosioides L. Essential Oil in Human Normal Liver Cell Line L02 via the Endogenous Mitochondrial Pathway Rather Than the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7469. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18147469
Wang X-Y, Hao J-M, Ren Q-R, Li H-Y, Wu J-S, Zhu X-H, Chen J-Y, Wang Y-N, Zhang L-S. Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis Induced by Chenopodium ambrosioides L. Essential Oil in Human Normal Liver Cell Line L02 via the Endogenous Mitochondrial Pathway Rather Than the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(14):7469. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18147469
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiao-Ying, Jun-Mei Hao, Qiu-Rong Ren, Hai-Ying Li, Jing-Song Wu, Xiao-Huan Zhu, Jin-Yao Chen, Ya-Nan Wang, and Li-Shi Zhang. 2021. "Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis Induced by Chenopodium ambrosioides L. Essential Oil in Human Normal Liver Cell Line L02 via the Endogenous Mitochondrial Pathway Rather Than the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 14: 7469. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18147469
APA StyleWang, X.-Y., Hao, J.-M., Ren, Q.-R., Li, H.-Y., Wu, J.-S., Zhu, X.-H., Chen, J.-Y., Wang, Y.-N., & Zhang, L.-S. (2021). Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis Induced by Chenopodium ambrosioides L. Essential Oil in Human Normal Liver Cell Line L02 via the Endogenous Mitochondrial Pathway Rather Than the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(14), 7469. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18147469





