Effects of Seven-Year Fertilization Reclamation on Bacterial Community in a Coal Mining Subsidence Area in Shanxi, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site Description
2.2. Experimental Treatments and Soil Sampling
2.3. Selected Soil Properties Analysis
2.4. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, Illumina MiSeq Sequencing, and Sequencing Data Processing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Properties
3.2. Soil Bacterial Abundance and Diversity
3.3. Soil Bacterial Taxa Community Composition
3.4. Relationship between Soil Properties and Bacterial Community Composition
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Reclamation on Soil Properties and Bacterial Community
4.2. Effects of Soil Properties on Bacterial Community Composition
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, Z.J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, F.W.; Bi, R.T.; Zhu, H.F.; Lv, C.J.; Yu, J. Effect of Underground Coal Mining on the Regional Soil Organic Carbon Pool in Farmland in a Mining Subsidence Area. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Quadros, P.D.; Zhalnina, K.; Davis-Richardson, A.G.; Drew, J.C.; Menezes, F.B.; de O. Camargo, F.A.; Triplett, E.W. Coal mining practices reduce the microbial biomass, richness and diversity of soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 98, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, A.; Yin, B. Modeling and analysis of mining subsidence disaster chains based on stochastic Petri nets. Nat. Hazards 2018, 92, 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Zhang, Y.X.; Ruan, M.Y.; Guo, J.; Chai, T.Y. Land Subsidence in a Coal Mining Area reduced Soil Fertility and Led to Soil Degradation in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, P.L.; Zhang, Y.X.; Hu, Z.Q.; Ma, K.; Wang, H.; Chai, T.Y. The response of soil bacterial communities to mining subsidence in the west China Aeolian sand area. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 121, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, X.; Tsolmon, B.; Chen, J.; Bao, Y. The influence of transplanted trees on soil microbial diversity in coal mine subsidence areas in the Loess Plateau of China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 21, e00877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guebert, M.D.; Gardner, T.W. Macropore flow on a reclaimed surface mine: Infiltration and hillslope hydrology. Geomorphology 2001, 39, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Li, Y.; Wei, Y.; Meng, H.S.; Cao, Y.Z.; Lead, J.R.; Hong, J.P. Effects of fertilization and reclamation time on soil bacterial communities in coal mining subsidence areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brussaard, L.; de Ruiter, P.C.; Brown, G.G. Soil biodiversity for agricultural sustainability. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 121, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagg, C.; Bender, S.F.; Widmer, F.; Heijden, M. Soil biodiversity and soil community composition determine ecosystem multifunctionality. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5266–5270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trap, J.; Bonkowski, M.; Plassard, C.; Villenave, C.; Blanchart, E. Ecological importance of soil bacterivores for ecosystem functions. Plant Soil 2016, 398, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romaniuk, R.; Giuffré, L.; Costantini, A.; Nannipieri, P. Assessment of soil microbial diversity measurements as indicators of soil functioning in organic and conventional horticulture systems. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 1345–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.S.; Pandey, V.C.; Singh, D.P. Efficient soil microorganisms: A new dimension for sustainable agriculture and environmental development. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 140, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Qiao, J.; Zhu, Z.; Li, P.; Wu, L. Soil bacterial community responses to long-term fertilizer treatments in Paulownia plantations in subtropical China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 124, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.D.; Ingram, L.J.; Stahl, P.D. Influence of reclamation management practices on microbial biomass carbon and soil organic carbon accumulation in semiarid mined lands of Wyoming. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2008, 40, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangi, S.R.; Stahl, P.D.; Wick, A.F.; Ingram, L.J.; Buyer, J.S. Soil Microbial Community Recovery in Reclaimed Soils on a Surface Coal Mine Site. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriu, P.A.; Prescott, C.E.; Quideau, S.A.; Grayston, S.J. Impact of reclamation of surface-mined boreal forest soils on microbial community composition and function. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 2289–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Zhang, F.; Gale, W.J.; Wang, W.; Sang, W.; Yang, H. Effects of reclamation years on composition and diversity of soil bacterial communities in Northwest China. Can. J. Microbiol. 2018, 64, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kohler, J.; Caravaca, F.; Azcon, R.; Diaz, G.; Roldan, A. Suitability of the microbial community composition and function in a semiarid mine soil for assessing phytomanagement practices based on mycorrhizal inoculation and amendment addition. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 169, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, A.S.; Quideau, S.A. Long-term effects of organic amendments on the recovery of plant and soil microbial communities following disturbance in the Canadian boreal forest. Plant Soil 2012, 363, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mummey, D.L.; Stahl, P.D.; Buyer, J.S. Soil microbiological properties 20 years after surface mine reclamation: Spatial analysis of reclaimed and undisturbed sites. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmeades, D.C. The long-term effects of manures and fertilisers on soil productivity and quality: A review. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2003, 66, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torsvik, V.; Øvreås, L. Microbial diversity and function in soil: From genes to ecosystems. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2002, 5, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Jiang, X.; Ma, M.; Zhou, B.; Guan, D.; Zhao, B.; Zhou, J.; Cao, F.; Li, L.; Li, J. Effect of 35 years inorganic fertilizer and manure amendment on structure of bacterial and archaeal communities in black soil of northeast China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 105, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Xun, W.; Huang, T.; Zhang, G.; Gao, J.; Ran, W.; Li, D.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, R. Alteration of the soil bacterial community during parent material maturation driven by different fertilization treatments. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 96, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, E.; Ferreras, L.; Toresani, S. Soil bacterial functional diversity as influenced by organic amendment application. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1484–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, E.H.; Chung, R.S.; Tsai, Y.H. Effect of different application rates of organic fertilizer on soil enzyme activity and microbial population. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2007, 53, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Han, Z.; Bai, Z.; Zhuang, G.; Shim, H. Progress in decontamination by halophilic microorganisms in saline wastewater and soil. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Gu, T.; Wang, W.; Zhang, B.; Lin, X.; Huang, Q.; Shen, W. The effects of mineral fertilizer and organic manure on soil microbial community and diversity. Plant Soil 2010, 326, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Guan, D.W.; Zhou, B.K.; Zhao, B.S.; Ma, M.C.; Qin, J.; Jiang, X.; Chen, S.F.; Cao, F.M.; Shen, D.L.; et al. Influence of 34-years of fertilization on bacterial communities in an intensively cultivated black soil in northeast China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 90, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driessen, P.; Deckers, J.; Spaargaren, O.; Nachtergaele, F. Lecture Notes on the Major Soils of the World; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2001; pp. 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.Y.; Deng, Y.; Li, Q.; Lu, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, J.; He, Z. Shifts of functional gene representation in wheat rhizosphere microbial communities under elevated ozone. ISME J. 2013, 7, 660–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strickland, T.C.; Sollins, P. Improved Method for Separating Light and Heavy-Fraction Organic Material from Soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1987, 51, 1390–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J.M. Nitrogen Total. In Methods of Soil Analysis Part 3: Chemical Methods; SSSA Book Series, 5; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 1085–1122. [Google Scholar]
- Hedley, M.J.; Stewart, J.W.B. Method to measure microbial phosphate in soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1982, 14, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehlich, A. Mehlich 3 soil test extractant: A modification of Mehlich 2 extractant. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant. Anal. 1984, 15, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadrosh, D.W.; Ma, B.; Gajer, P.; Sengamalay, N.; Ott, S.; Brotman, R.M.; Ravel, J. An improved dual-indexing approach for multiplexed 16S rRNA gene sequencing on the Illumina MiSeq platform. Microbiome 2014, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lozupone, C.; Lladser, M.; Knights, D.; Stombaugh, J.; Knight, R. UniFrac: An effective distance metric for microbial community comparison. ISME J. 2011, 5, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheik, C.S.; Mitchell, T.W.; Rizvi, F.Z.; Rehman, Y.; Faisal, M.; Hasnain, S.; McInerney, M.J.; Krumholz, L.R. Exposure of soil microbial communities to chromium and arsenic alters their diversity and structure. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasch, C.; Huzurbazar, S.; Stahl, P. Measuring soil disturbance effects and assessing soil restoration success by examining distributions of soil properties. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2014, 76, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poncelet, D.; Cavender, N.; Cutright, T.; Senko, J. An assessment of microbial communities associated with surface mining-disturbed overburden. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 186, 1917–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, G.; Osman, S.; Vaishampayan, P.A.; Andersen, G.L.; Stetler, L.D.; Sani, R.K. Microbial diversity in uranium mining-impacted soils as revealed by high-density 16S microarray and clone library. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 59, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauber, C.L.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Pyrosequencing-based assessment of soil pH as a predictor of soil bacterial community structure at the continental scale. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 5111–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhan, J.; Sun, Q.Y. Development of microbial properties and enzyme activities in copper mine wasteland during natural restoration. Catena 2014, 116, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Chen, L.; Wen, H.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, T.; Gao, X. 454 Pyrosequencing Analysis of Bacterial Diversity Revealed by a Comparative Study of Soils from Mining Subsidence and Reclamation Areas. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 24, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kielak, A.; Pijl, A.S.; van Veen, J.A.; Kowalchuk, G.A. Phylogenetic diversity of Acidobacteria in a former agricultural soil. ISME J. 2009, 3, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, N.L.; Challacombe, J.F.; Janssen, P.H.; Henrissat, B.; Coutinho, P.M.; Wu, M.; Xie, G.; Haft, D.H.; Sait, M.; Badger, J.; et al. Three genomes from the phylum Acidobacteria provide insight into the lifestyles of these microorganisms in soils. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 2046–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.Y.; Wen, H.; Chen, L.; Yin, T. Succession of bacterial community structure and diversity in soil along a chronosequence of reclamation and re-vegetation on coal mine spoils in China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhuang, K.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, X.; Xi, Y. Responses of microbial activity, abundance, and community in wheat soil after three years of heavy fertilization with manure-based compost and inorganic nitrogen. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 213, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayston, S.J.; Campbell, C.D.; Bardgett, R.D.; Mawdsley, J.L.; Clegg, C.D.; Ritz, K.; Griffiths, B.S.; Rodwell, J.S.; Edwards, S.J.; Davies, W.J.; et al. Assessing shifts in microbial community structure across a range of grasslands of differing management intensity using CLPP, PLFA and community DNA techniques. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2004, 25, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Chen, L.; Wen, H. Changes in the composition and diversity of bacterial communities 13 years after soil reclamation of abandoned mine land in eastern China. Ecol. Res. 2015, 30, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Yu, D.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, L.; Dai, L. The effects of forest type on soil microbial activity in Changbai Mountain, Northeast China. Ann. Forest Sci. 2016, 73, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Y.; Yu, L.F.; Zhang, J.C.; Yu, Y.C.; Deangelis, D.L. Relationship Between Vegetation Restoration and Soil Microbial Characteristics in Degraded Karst Regions: A Case Study. Pedosphere 2011, 21, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichel, R.; Radl, V.; Rosendahl, I.; Albert, A.; Amelung, W.; Schloter, M.; Sören, T.B. Soil microbial community responses to antibiotic-contaminated manure under different soil moisture regimes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 6487–6495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Wei, Q. Pyrosequencing technology reveals the impact of different manure doses on the bacterial community in apple rhizosphere soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2014, 78, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, I.M.; Goyne, K.W.; Kennedy, A.C.; Kremer, R.J.; McLain, J.; Williams, C.F. Antibiotic Effects on Microbial Community Characteristics in Soils under Conservation Management Practices. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 77, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francioli, D.; Schulz, E.; Lentendu, G.; Wubet, T.; Buscot, F.; Reitz, T. Mineral vs. Organic Amendments: Microbial Community Structure, Activity and Abundance of Agriculturally Relevant Microbes Are Driven by Long-Term Fertilization Strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, J.; Liu, C.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Ye, Z.; Fang, C. Long-term changes in topsoil chemical properties under centuries of cultivation after reclamation of coastal wetlands in the Yangtze Estuary, China. Soil Tillage Res. 2012, 123, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.G.; Li, X.; Mander, Ü.; He, Y.L.; Jia, Y.; Ma, Z.G.; Guo, W.Y.; Xin, Z.J. Effect of reclamation time and land use on soil properties in Changjiang River Estuary, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2011, 21, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, M.; Frey, B.; Mayer, J.; Mäder, P.; Widmer, F. Distinct soil microbial diversity under long-term organic and conventional farming. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1177–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, R.; Zhang, X.X.; Guo, X.; Wang, D.; Chu, H. Bacterial diversity in soils subjected to long-term chemical fertilization can be more stably maintained with the addition of livestock manure than wheat straw. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 88, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Liu, X.; Ling, S.; Lin, X.; Chu, H. Nitrogen fertilization directly affects soil bacterial diversity and indirectly affects bacterial community composition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 92, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, H.; He, X.; Thomas, B.Z.; Lupwayi, N.; Hao, X.; Thomas, M.; Shi, X. Fertilization Shapes Bacterial Community Structure by Alteration of Soil pH. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, X. pH is the primary determinant of the bacterial community structure in agricultural soils impacted by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollution. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rousk, J.; Baath, E.; Brookes, P.C.; Lauber, C.L.; Lozupone, C.; Caporaso, J.G.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Soil bacterial and fungal communities across a pH gradient in an arable soil. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheoran, V.; Sheoran, A.; Poonia, P. Soil Reclamation of Abandoned Mine Land by Revegetation: A Review. Int. J. Soil Sediment Water 2010, 3, 13. [Google Scholar]
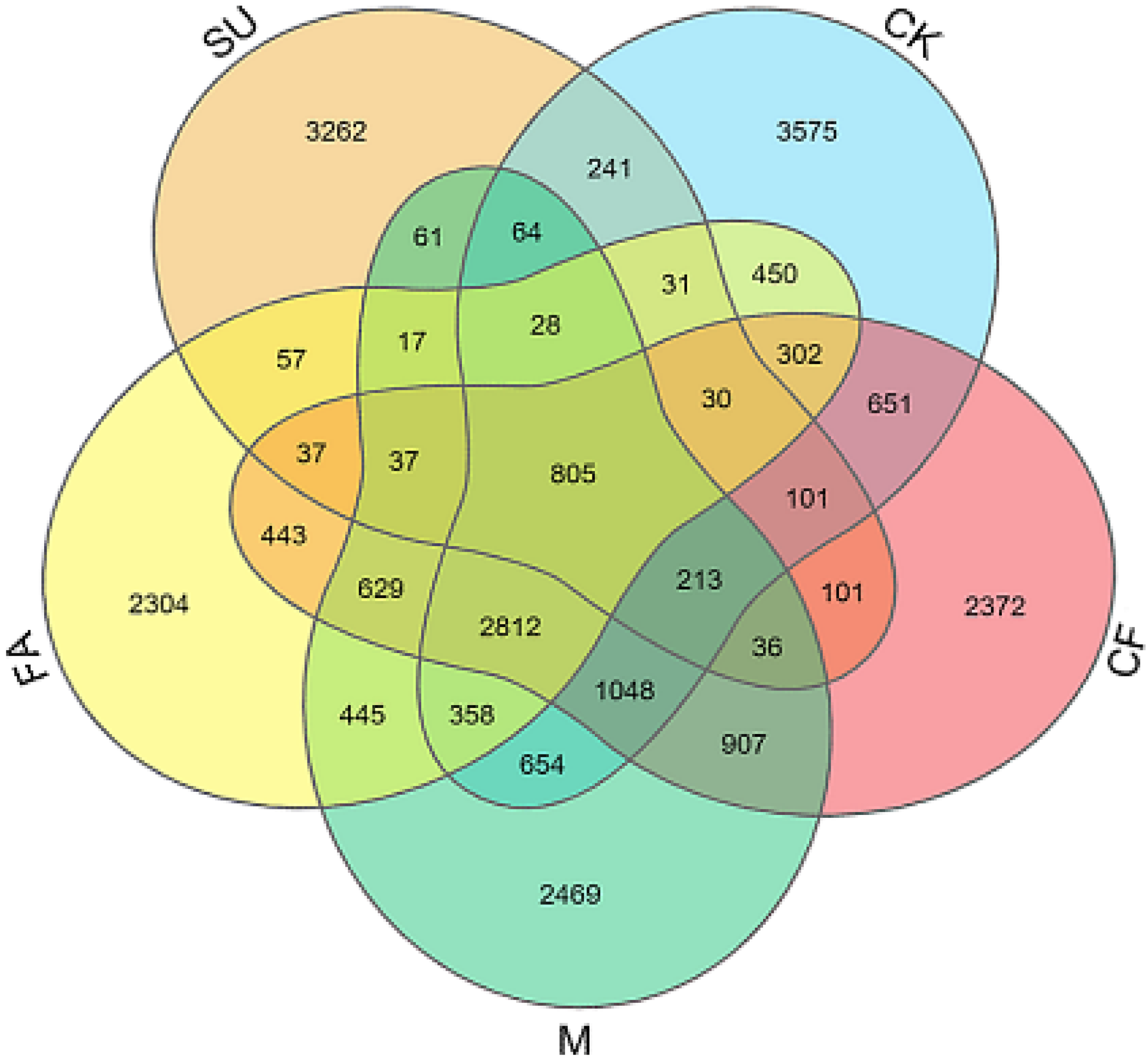
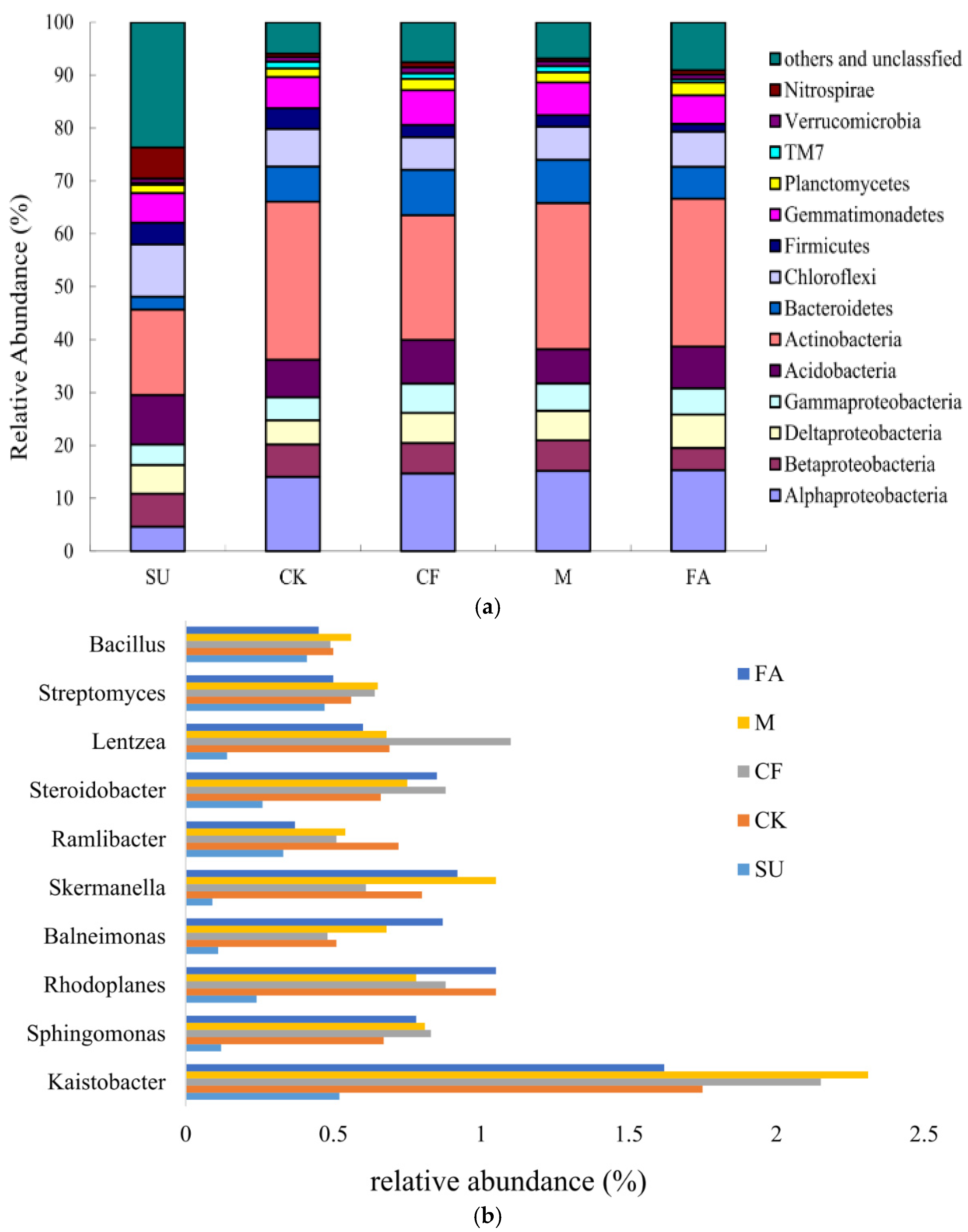
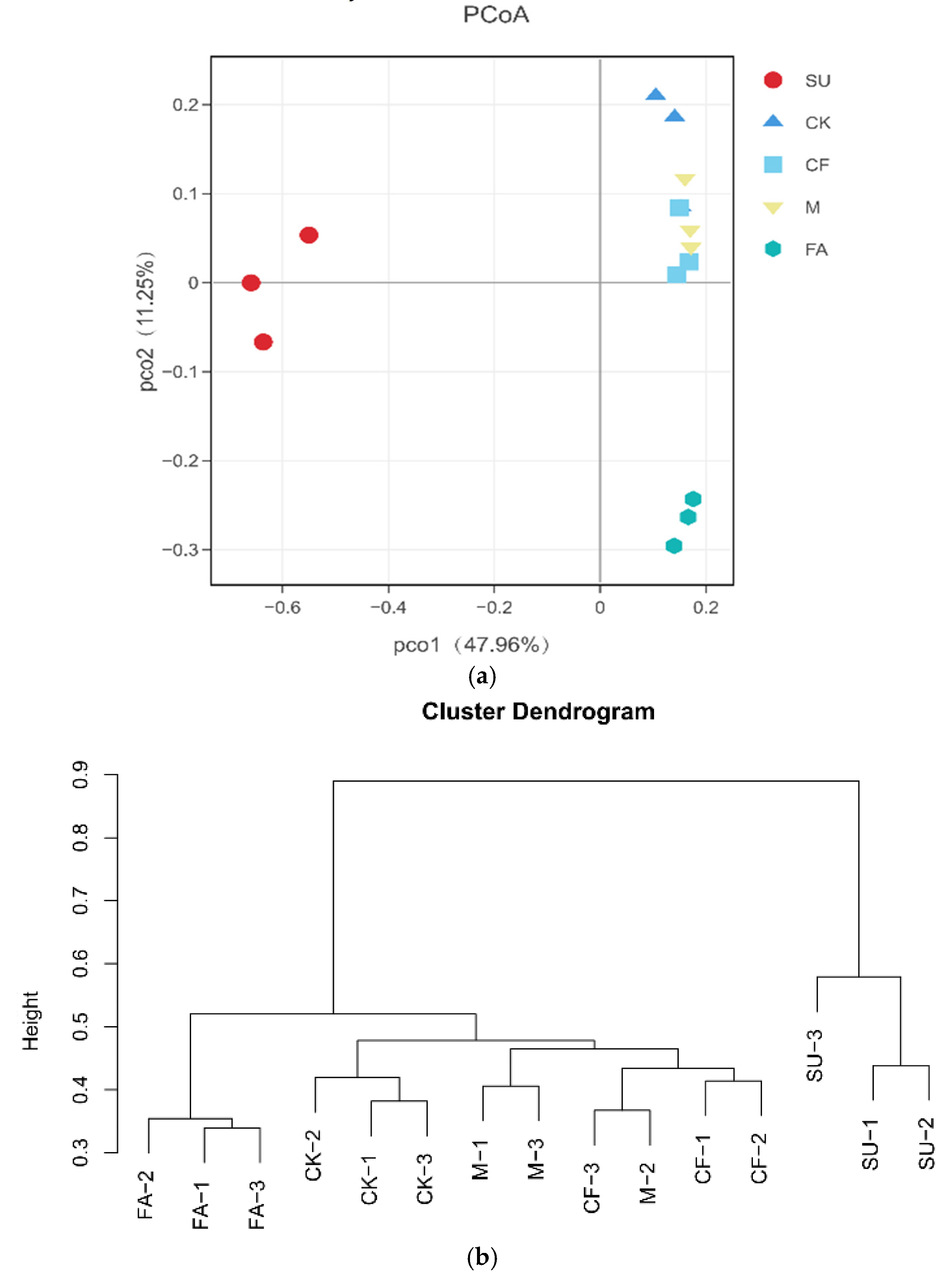
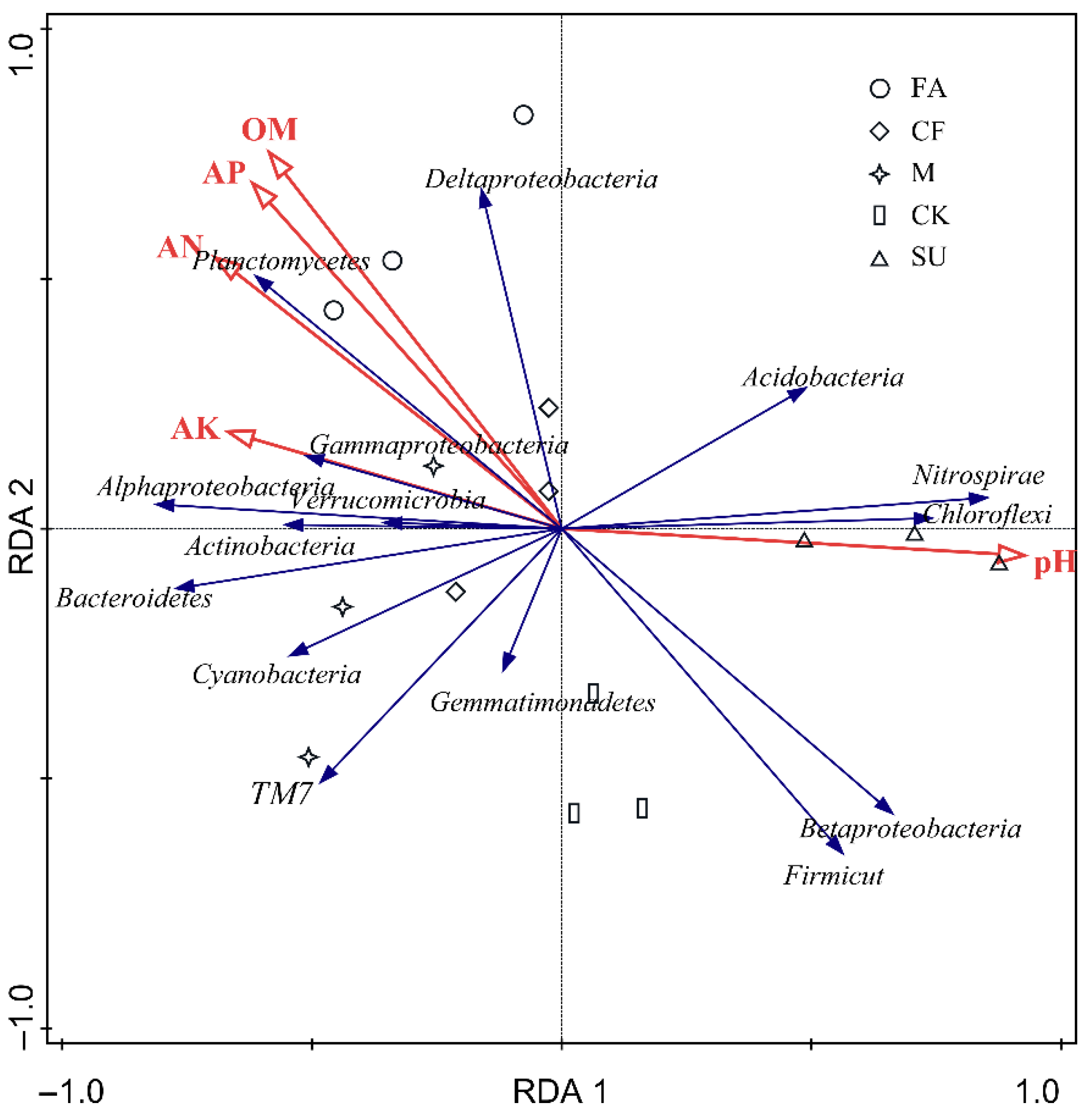
| Treatments | pH | SOM (g∙kg−1) | AN (mg∙kg−1) | AP (mg∙kg−1) | AK (mg∙kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SU | 8.06 ± 0.06 a | 9.74 ± 0.28 e | 16.51 ± 0.58 e | 3.18 ± 0.12 c | 123.30 ± 4.61 b |
| CK | 7.91 ± 0.03 b | 11.37 ± 0.59 d | 24.68 ± 1.01 d | 4.65 ± 0.31 c | 135.30 ± 2.31 b |
| CF | 7.84 ± 0.02 bc | 14.06 ± 0.46 c | 27.13 ± 1.46 c | 17.75 ± 1.54 b | 233.57 ± 15.32 a |
| M | 7.76 ± 0.02 c | 18.15 ± 0.51 b | 35.60 ± 0.68 b | 19.46 ± 1.47 b | 236.36 ± 19.58 a |
| FA | 7.85 ± 0.03 bc | 26.64 ± 0.40 a | 48.59 ± 2.33 a | 35.60 ± 0.68 a | 201.7 ± 15.78 a |
| Treatments | Sobs | Coverage | Richness and Diversity Indices | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chao1 | ACE | Shannon | |||
| SU | 3672 ± 195 b | 0.97 ± 0.01 a | 4455 ± 323 c | 4358 ± 319 c | 10.02 ± 0.24 d |
| CK | 10803 ± 106 a | 0.96 ± 0.02 a | 13864 ± 174 b | 14078 ± 242 b | 11.37 ± 0.05 c |
| CF | 11021 ± 731 a | 0.94 ± 0.01 ab | 15190 ± 463 a | 15621 ± 413 a | 11.60 ± 0.05 b |
| M | 11030 ± 337 a | 0.95 ± 0.00 a | 15330 ± 216 a | 15845 ± 170 a | 11.39 ± 0.12 c |
| FA | 9772 ± 288 a | 0.91 ± 0.02 b | 14430 ± 313 a | 14988 ± 302 a | 11.77 ± 0.04 a |
| Pearson | Sobs | Chao1 | ACE | Shannon |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | −0.768 ** | −0.826 ** | −0.824 ** | −0.745 ** |
| SOM | 0.399 | 0.545 * | 0.564 * | 0.616 * |
| AN | 0.463 | 0.572 * | 0.647 ** | 0.559 * |
| AP | 0.377 | 0.606 * | 0.659 ** | 0. 623 * |
| AK | 0.508 | 0.644 ** | 0.656 ** | 0.409 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Li, T.; Meng, H.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hong, J. Effects of Seven-Year Fertilization Reclamation on Bacterial Community in a Coal Mining Subsidence Area in Shanxi, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12504. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312504
Li L, Li T, Meng H, Xie Y, Zhang J, Hong J. Effects of Seven-Year Fertilization Reclamation on Bacterial Community in a Coal Mining Subsidence Area in Shanxi, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(23):12504. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312504
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Li, Tingliang Li, Huisheng Meng, Yinghe Xie, Jie Zhang, and Jianping Hong. 2021. "Effects of Seven-Year Fertilization Reclamation on Bacterial Community in a Coal Mining Subsidence Area in Shanxi, China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 23: 12504. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312504
APA StyleLi, L., Li, T., Meng, H., Xie, Y., Zhang, J., & Hong, J. (2021). Effects of Seven-Year Fertilization Reclamation on Bacterial Community in a Coal Mining Subsidence Area in Shanxi, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(23), 12504. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312504





