Estimation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Pollution in Mediterranean Sea from Volturno River, Southern Italy: Distribution, Risk Assessment and Loads
Abstract
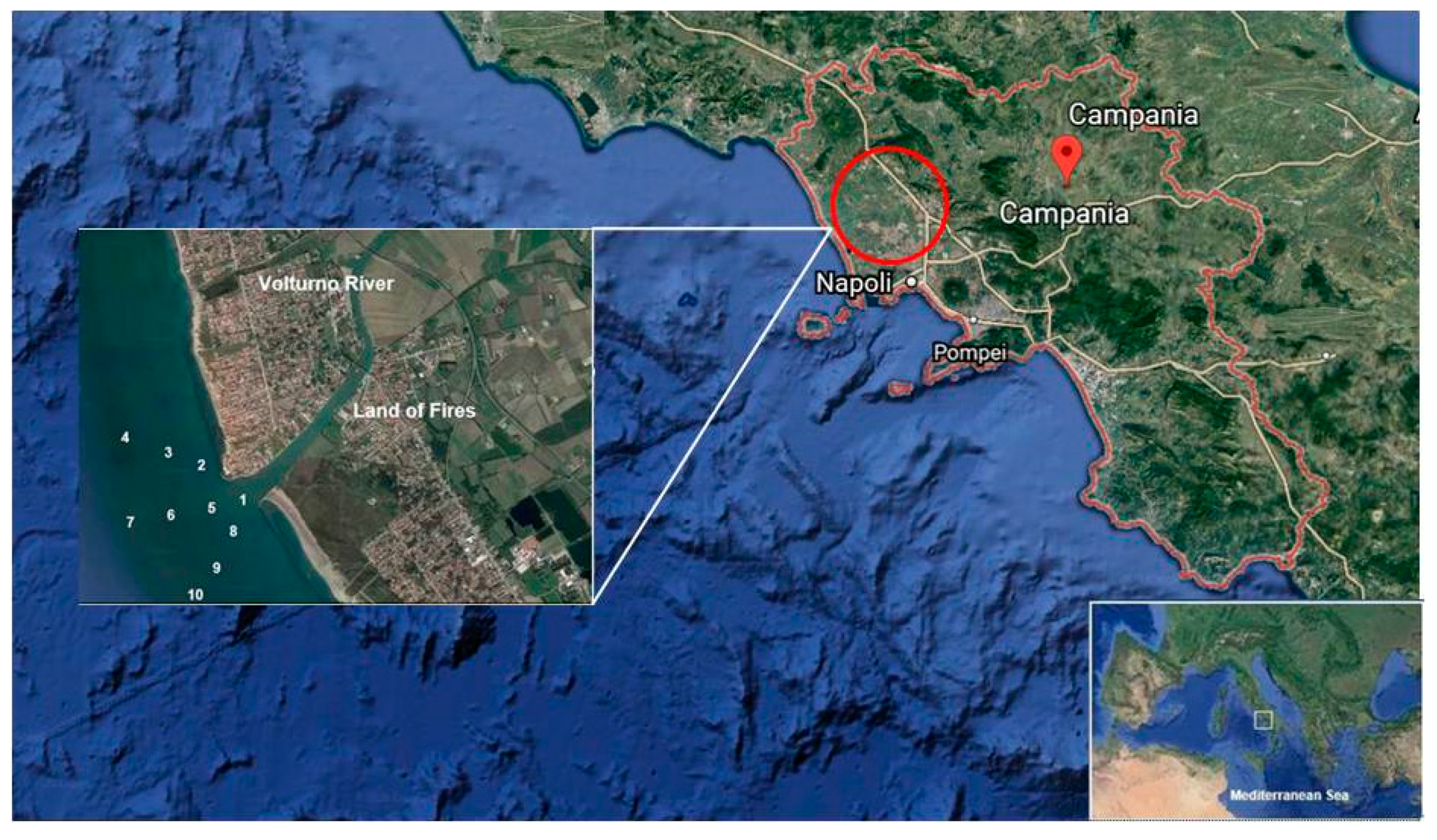
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Sample Cleanup and Analysis
2.3. Instrumental Analysis
2.4. Quality Assurance and Quality Control
2.5. Statistical Analysis and Calculation of PAHs Inputs
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. PAHs Concentrations in Water Samples
3.2. PAHs Concentrations in Suspended Particulate Matter
3.3. PAHs Concentrations in Sediments
3.4. PAHs Seasonal and Spatial Distribution in DP, SPM, and Sediment Samples
3.5. Source Identification
3.6. A Composite Indicator for Water Pollution
3.7. Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Consent for Publication
Abbrevations
References
- Qin, N.; He, W.; Kong, X.Z.; Liu, W.X.; He, Q.S.; Yang, B.; Ouyang, H.L.; Wang, Q.M.; Xu, F.L. Ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the water from a large Chinese lake based on multiple indicators. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 24, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duodu, G.O.; Ogogo, K.N.; Mummullage, S.; Harden, F.; Goonetilleke, A.; Ayoko, G.A. Source apportionment and risk assessment of PAHs in Brisbane River sediment, Australia. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 73, 784–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Liu, R.; Xu, F.; Shen, Z. Environmental risk assessments and spatial variations of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments in Yangtze River Estuary, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 100, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Singh, V.P.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, L.; Zeng, D.; Liu, D.; Zeng, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, L.; et al. Ecological and health risk assessment of PAHs, OCPs, and PCBs in Taihu Lake basin. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 92, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egres, G.; Hatje, V.; Miranda, D.A.; Gallucci, F.; Barros, F. Functional response of tropical estuarine benthic assemblages to perturbation by Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 96, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Fernández, B.; Viñas, L.; Franco-Hernández, M.; Bargiela, J. PAHs in the Ría de Arousa (NW Spain): A consideration of PAHs sources and abundance. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 95, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singare, P.U. Studies on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments of Mithi River near Mumbai, India: Assessment of sources, toxicity risk and biological impact. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarria-Villa, R.; Ocampo-Duque, W.; Paez, M.I.; Schuhmacher, M. Presence of PAHs in water and sediments of the Colombian Cauca River during heavy rain episodes, and implications for risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 540, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Beckingham, B.; Ruegner, H.; Li, Z.; Ma, L.; Schwientek, M.; Xie, H.; Zhao, J.; Grathwohl, P. Comparison of Sedimentary PAHs in the Rivers of Ammer (Germany) and Liangtan (China): Differences between Early- and Newly-Industrialized Countries. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, A.L.; Quintas, P.Y.; La Colla, N.S.; Arias, A.H.; Marcovecchio, J.E. Distribution, Sources, and Potential Ecotoxicological Risk of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Surface Sediments from Bahía Blanca Estuary, Argentina. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 69, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Ya, M.; Luo, H.; Hong, H. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers, organochlorine pesticides, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water from the Jiulong River Estuary, China: Levels, distributions, influencing factors, and risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 24, 8933–8945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumard, P.; Budzinski, H.; Michon, Q.; Garrigues, P.; Burgeot, T.; Bellocq, J. Origin and Bioavailability of PAHs in the Mediterranean Sea from Mussel and Sediment Records. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1998, 47, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunker, M.B.; Macdonald, R.W.; Vingarzan, R.; Mitchell, R.H.; Goyette, D.; Sylvestre, S. PAHs in the Fraser River basin: A critical appraisal of PAH ratios as indicators of PAH source and composition. Org. Geochem. 2002, 33, 489–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legambiente. Rapporto Ecomafia—I Numeri e le Storie Della Criminalità Ambientale Legambiente: Roma, Italy. 2007. Available online: http://www.amblav.it/download/0417_ecomafia_introduzione.pdf (accessed on 31 March 2020).
- D’Alisa, G.; Armiero, M.; De Rosa, S.P. Rethink Campania’s toxic-waste scandal. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 509, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esposito, F.; Nardone, A.; Fasano, E.; Scognamiglio, G.; Esposito, D.; Agrelli, D.; Ottaiano, L.; Fagnano, M.; Adamo, P.; Beccaloni, E.; et al. A systematic risk characterization related to the dietary exposure of the population to potentially toxic elements through the ingestion of fruit and vegetables from a potentially contaminated area. A case study: The issue of the “Land of Fires” area in Campania region, Italy. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 1781–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senior, K.; Mazza, A. Italian “Triangle of death” linked to waste crisis. Lancet Oncol. 2004, 5, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isidori, M.; Lavorgna, M.; Nardelli, A.; Parrella, A. Integrated environmental assessment of Volturno River in South Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 327, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triassi, M.; Nardone, A.; Giovinetti, M.C.; De Rosa, E.; Canzanella, S.; Sarnacchiaro, P.; Montuori, P. Ecological risk and estimates of organophosphate pesticides loads into the Central Mediterranean Sea from Volturno River, the river of the “Land of Fires” area, southern Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 741–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, M.; Semprucci, F.; Vezzulli, L.; Balsamo, M.; Fabiano, M.; Albertelli, G. The use of nematodes in assessing ecological quality status in the Mediterranean coastal ecosystems. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, P.L.; Mait, K.; Bam, W. Fate of particle-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the river influenced continental margin of the northern Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 141, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.L.; Hong, H.; Zhang, Z.; Maskaoui, K.; Chen, W.J.W.R. Multi-phase distribution of organic micropollutants in Xiamen Harbour, China. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2132–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafilzadeh, F.; Shiva, A.H.; Malekpour, R. Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in water and sediments of the Kor River, Iran. Middle East J. Sci. Res. 2011, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, R. Characterization and distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in surface water and sediment from Qiantang River, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Dong, L.; Meng, X.; Li, Q.; Huang, Z.; Li, C.; Crittenden, J. Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydro-carbons and phthalic acid esters in water and surface sediment from the Three Gorges Reservoir. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 69, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montuori, P.; Triassi, M. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons loads into the Mediterranean Sea: Estimate of Sarno River inputs. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- USEPA (US Environmental Protection Agency). Regional Screening Levels for Chemical Contaminants at Superfund Sites. Regional Screening Table. User’s Guide. 2012. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2713671/ (accessed on 31 March 2020).
- UNEP/MAP. Guidelines for River (Including Estuaries) Pollution Monitoring Programme for the Mediterranean Region; MAP Technical Reports Series No. 151; UNEP/MAP: Athens, Greece, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Walling, D.E.; Webb, B.W. Estimating the discharge of contaminants to coastal waters by rivers: Some cautionary comments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1985, 16, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HELCOM. Second Baltic Sea Pollution Load Compilation; Baltic Sea Environment Proceedings No. 45; Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission: Helsinki, Finland, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Steen, R.J.C.A.; Van Der Vaart, J.; Hiep, M.; Van Hattum, A.; Cofino, W.; Brinkman, U. Gross fluxes and estuarine behaviour of pesticides in the Scheldt Estuary (1995–1997). Environ. Pollut. 2001, 115, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Gutiérrez, A.I.; Jover, E.; Bodineau, L.; Albaigés, J.; Bayona, J.M. Organic contaminant loads into the Western Mediterranean Sea: Estimate of Ebro River inputs. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montuori, P.; Aurino, S.; Nardone, A.; Cirillo, T.; Triassi, M. Spatial distribution and partitioning of organophosphates pesticide in water and sediment from Sarno River and Estuary, Southern Italy. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 8629–8642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montuori, P.; Aurino, S.; Garzonio, F.; Sarnacchiaro, P.; Polichetti, S.; Nardone, A.; Triassi, M. Estimates of Tiber River organophosphate pesticide loads to the Tyrrhenian Sea and ecological risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 559, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pearson, K. On lines and planes of closest fit to systems of points in space. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1901, 2, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hotelling, H. Analysis of a complex of statistical variables into principal components. J. Educ. Psychol. 1933, 24, 417–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman, L. Some necessary conditions for common-factor analysis. Psychometrika 1954, 19, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, H.F. The Application of Electronic Computers to Factor Analysis. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1960, 20, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeomans, K.A.; Golder, P.A. The Guttman-Kaiser Criterion as a Predictor of the Number of Common Factors. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. D 1982, 31, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, L.; Jeon, H.J.; Kim, Y.C.; Yang, S.H.; Choi, H.; Kim, T.O.; Lee, S.E. Monitoring polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon concentrations and distributions in rice paddy soils from Gyeonggi-do, Ulsan, and Pohang. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2019, 62, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edokpayi, J.N.; Odiyo, J.O.; Popoola, O.E.; Msagati, T.A.M. Determination and Distribution of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Rivers, Sediments and Wastewater Effluents in Vhembe District, South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zakaria, M.P.; Mahat, A.A. Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAHs) in sediments in the Langat Estuary. Coast. Mar. Sci. 2006, 30, 387–395. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, H.; Peng, P.; Huang, W.; Song, J. Distribution and loadings of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Xijiang River in Guangdong, South China. Chemosphere 2006, 64, 1401–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xia, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, R.; Voulvoulis, N. Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River, China. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 144, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.-L.; Liu, L.-Y.; Qi, H.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Song, W.-W.; Shen, J.-M.; Chen, Z.-L.; Ren, N.-Q.; Grabuski, J.; Zhang, Z.-F. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water, sediment and soil of the Songhua River Basin, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 8399–8409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeckel, C.; Monteith, D.T.; Llewellyn, N.R.; Henrys, P.A.; Pereira, M.G. Relationship between the Concentrations of Dissolved Organic Matter and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in a Typical U.K. Upland Stream. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siemers, A.-K.; Mänz, J.S.; Palm, W.-U.; Ruck, W.K. Development and application of a simultaneous SPE-method for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), alkylated PAHs, heterocyclic PAHs (NSO-HET) and phenols in aqueous samples from German Rivers and the North Sea. Chemosphere 2015, 122, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrolecco, L.; Ademollo, N.; Capri, S.; Pagnotta, R.; Polesello, S. Occurrence of priority hazardous PAHs in water, suspended particulate matter, sediment and common eels (Anguilla anguilla) in the urban stretch of the River Tiber (Italy). Chemosphere 2010, 81, 1386–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; He, M.; Yang, Z.; Lin, C.; Quan, X.; Men, B. Distribution, partitioning and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Daliao River water system in dry season, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 1379–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Qiu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J. Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface water from the upper reach of the Yellow River, Northwestern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 6950–6956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ding, J.; You, H. Spatial distribution and temporal trends of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in water and sediment from Songhua River, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2014, 36, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Wang, L.; Lei, K.; Nan, B. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water, suspended particulate matter and sediment from Daliao River estuary and the adjacent area, China. Chemosphere 2016, 149, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.; Verma, P.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, K.P. Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water and bed sediments of the Gomti River, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 172, 529–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, J.L.; Massone, C.G.; Valdés, M.; Vazquez, R.; Lima, L.A.; Olivares-Rieumont, S. Occurrence and Source Appraisal of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Surface Waters of the Almendares River, Cuba. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 69, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeniji, A.O.; Okoh, O.O.; Okoh, A.I. Levels of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Water and Sediment of Buffalo River Estuary, South Africa and Their Health Risk Assessment. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 76, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.H.; Wang, G.L.; Chai, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Feng, J. Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Henan Reach of the Yellow River, Middle China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2009, 72, 1614–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, A.S.; Szabó, J.; Vass, I. Occurrence and distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface water and sediments of the Danube River and its tributaries, Hungary. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2014, 49, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrojalbiz, N.; Dachs, J.; Ojeda, M.J.; Valle, M.C.; Castro-Jiménez, J.; Wollgast, J.; Ghiani, M.; Hanke, G.; Zaldivar, J.M. Biogeochemical and physical controls on concentrations of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water and plankton of the Mediterranean and Black Seas. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2011, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marrucci, A.; Marras, B.; Campisi, S.S.; Schintu, M. Using SPMDs to monitor the seawater concentrations of PAHs and PCBs in marine protected areas (Western Mediterranean). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 75, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.B.; Liu, C.W.; Kao, Y.H.; Jang, C.-S. Characterization and risk assessment of PAH-contaminated river sediment by using advanced multivariate methods. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 525, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Jin, H.; Ji, Z.; Li, D.; Kaw, H.Y.; Chen, J.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, T. PAES and PAHs in the surface sediments of the East China Sea: Occurrence, distribution and influence factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; Bu, Q.; Cao, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C.; He, X.; Yun, M. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Surface Water from Wuhai and Lingwu Sections of the Yellow River: Concentrations, Sources, and Ecological Risk. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minissi, S.; Caccese, D.; Passafiume, F.; Grella, A.; Ciccotti, E.; Rizzoni, M. Mutagenicity (micronucleus test in Vicia faba root tips), polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and heavy metal content of sediments collected in Tiber river and its tributaries within the urban area of Rome. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 1998, 420, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavalcante, R.M.; Sousa, F.W.; Nascimento, R.F.; Silveira, E.R.; Freire, G.S. The impact of urbanization on tropical mangroves (Fortaleza, Brazil): Evidence from PAH distribution in sediments. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 91, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanzari, F.; Syakti, A.D.; Asia, L.; Malleret, L.; Piram, A.; Mille, G.; Doumenq, P. Distributions and sources of persistent organic pollutants (aliphatic hydrocarbons, PAHs, PCBs and pesticides) in surface sediments of an industrialized urban river (Huveaune), France. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 478, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanzari, F.; Asia, L.; Syakti, A.D.; Piram, A.; Malleret, L.; Mille, G.; Doumenq, P. Distribution and risk assessment of hydrocarbons (aliphatic and PAHs), polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), and pesticides in surface sediments from an agricultural river (Durance) and an industrialized urban lagoon (Berre lagoon), France. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Shafy, H.I.; Mansour, M.S.M. A review on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Source, environmental impact, effect on human health and remediation. Egypt. J. Pet. 2016, 25, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; He, L.; Lu, Y.; Su, J.; Song, H.; Zeng, X.; Yu, Z. Distribution, source, and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface sediments from the Hun River, northeast China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Dong, H.; Zhang, D.; Han, B.; Zhu, C.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Ma, Q.; Li, X. Sources and ecological risk assessment of PAHs in surface sediments from Bohai Sea and northern part of the Yellow Sea, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 96, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobiszewski, M.; Namieśnik, J. PAH diagnostic ratios for the identification of pollution emission sources. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 162, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekpo, B.O.; Oyo-Ita, O.E.; Oros, D.R.; Simoneit, B.R.T. Distributions and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments from the Cross River estuary, S.E. Niger Delta, Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 184, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazza, A.; Piscitelli, P.; Falco, A.; Santoro, M.L.; Colangelo, M.; Imbriani, G.; Idolo, A.; De Donno, A.; Iannuzzi, L.; Colao, A. Heavy Environmental Pressure in Campania and Other Italian Regions: A Short Review of Available Evidence. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arienzo, M.; Albanese, S.; Lima, A.; Cannatelli, C.; Aliberti, F.; Cicotti, F.; Qi, S.; De Vivo, B. Assessment of the concentrations of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and organochlorine pesticides in soils from the Sarno River basin, Italy, and ecotoxicological survey by Daphnia magna. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wakeham, S.G.; Canuel, E.A. Biogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments of the San Joaquin River in California (USA), and current paradigms on their formation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 23, 10426–10442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, E.R.; MacDonald, D.D.; Smith, S.L.; Calder, E.D. Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environ. Manag. 1995, 19, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, D.D.; Carr, R.S.; Calder, F.D.; Long, E.R.; Ingersoll, C.G. Development and evaluation of sediment quality guidelines for Florida coastal waters. Ecotoxicology 1996, 5, 253–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleye, A.O.; Jin, H.; Di, Y.; Li, D.; Chen, J.; Ye, Y. Distribution and ecological risk of organic pollutants in the sediments and seafood of Yangtze Estuary and Hangzhou Bay, East China Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 1540–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Directive 2008/105/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on Environmental Quality Standards in the Field of Water policy, Amending and Subsequently Repealing Council Directives 82/176/EEC, 83/513/EEC, 84/156/ EEC, 84/491/EEC, 86/280/EEC and amending Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council. Off. J. Eur. Union 2008, 348, 84–97. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=celex%3A32008L0105 (accessed on 22 December 2020).




| Sampling Location | ΣPAHs | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site Number Identification | Site Characteristics | Site Location | Dissolved Phase (ng L−1) | Particulate Phase (ng L−1) (ng g−1 dry wt) | Sediments (ng g−1 dry wt) | ||||||
| Apr | Jul | Nov | Feb | Apr | Jul | Nov | Feb | Apr | |||
| 1 (river water) | Volturno River Source | 40°48′54.03″ N 14°36′45.36″ E | 919.8 | 1429.1 | 865.1 | 318.1 | 401.1 (49,334.1) | 257.1 (26,324.6) | 243.8 (21,499.3) | 444.9 (155,032) | 872.1 |
| 2 (sea water) | River Mouth at 500mt North | 40°46′42.73″ N 14°34′00.48″ E | 604.0 | 987.5 | 571.1 | 197.8 | 332.3 (35,892.9) | 221.8 (118,021.2) | 183.3 (5907.4) | 381.0 (3253.1) | 637.2 |
| 3 (sea water) | River Mouth at 500mt Central | 40°46′00.34″ N 14°33′10.68″ E | 726.9 | 1020.9 | 708.8 | 329.4 | 372.3 (94,015.7) | 225.1 (79,558.8) | 214.5 (68,758.0) | 400.9 (134,546) | 777.5 |
| 4 (sea water) | River Mouthat 500mt South | 40°43′42.62″ N 14°28′07.89″ E | 783.3 | 1246.2 | 813.3 | 332.4 | 387.9 (38,000.5) | 241.8 (226,017.2) | 225.0 (6516.6) | 417.2 (3902.2) | 822.2 |
| 5 (sea water) | River Mouth at 1000mt North | 40°43′40.11″ N 14°28′06.45″ E | 496.6 | 797.4 | 436.2 | 120.8 | 243.9 (32,792.5) | 194.3 (13,512.9) | 167.2 (12,661.5) | 267.7 (2644.7) | 514.1 |
| 6 (sea water) | River Mouth at 1000mt Central | 40°43′42.46″ N 14°28′05.03″ E | 627.3 | 923.6 | 548.9 | 248.1 | 328.7 (114,934.8) | 214.7 (71,336) | 193.2 (67,336.9) | 361.1 (118,028) | 686.5 |
| 7 (sea water) | River Mouth at 1000mt South | 40°43′45.09″ N 14°28′05.17″ E | 602.7 | 1111.2 | 611.5 | 262.1 | 361.7 (41,484.5) | 218.7 (14,888.4) | 185.7 (9221.1) | 351.7 (2946.8) | 640.1 |
| 8 (sea water) | River Mouth at 1500mt North | 40°43′35.68″ N 14°28′02.94″ E | 375.4 | 612.4 | 295.2 | 64.3 | 204.2 (20,348.5) | 179.0 (10,706.3) | 149.3 (7564.9) | 192.3 (60,683.0) | 434.8 |
| 9 (sea water) | River Mouth at 1500mt Central | 40°43′42.25″ N 14°27′59.97″ E | 482.8 | 831.7 | 445.3 | 174.9 | 268.6 (86,952.9) | 197.9 (66,193.6) | 169.5 (60,767.3) | 269.1 (91,871) | 560.4 |
| 10 (sea water) | River Mouth at 1500mt South | 40°43′49.26″ N 14°27′59.82″ E | 545.8 | 911.9 | 519.5 | 206.0 | 275.0 (97,525.2) | 194.1 (16,159.0) | 173.1 (4485.7) | 277.9 (97,859.7) | 646.3 |
| Area | References | Number PAHs | Range ∑PAHs | Mean ∑PAHs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water (ng L−1) | ||||
| Xijiang River, China | Deng et al. [43] | 15 | 21.7–138.0 | - |
| Yellow River, China | Li et al. [44] | 15 | 179.0–369.0 | 248.2 |
| Daliao River, China | Guo et al. [49] | 18 | 570.2–2318.6 | - |
| Henan Reach of Yellow River, China | Sun et al. [56] | 16 | 144.3–2361.0 | 662.0 |
| Songhua River, China | Ma et al. [45] | 15 | 14.0–161.0 | 33.9 |
| Yellow River, China | Zhao et al. [50] | 16 | 548.0–2598.0 | 1375.0 |
| Songhua River, China | Zhao et al. [51] | 16 | 163.5–2746.2 | 934.6 |
| Daliao River estuary, China | Zheng et al. [52] | 16 | 71.1–4255.4 | 748.8 |
| Gomti River, India | Malik et al. [53] | 16 | 60–84,210.0 | 10,330.0 |
| Cauca River, Colombia | Sarria-Villa et al. [8] | 12 | 52.1–12,888.2 | 2344.5 |
| Almendares River, Cuba | Santana et al. [54] | 14 | 836.0–15,811.0 | 2512.0 |
| Buffalo River Estuary, South Africa | Adeniji et al. [55] | 16 | ND-24,910 | - |
| Wyre River, England | Moeckel et al. [46] | 28 | 2.7–20.0 | - |
| Elbe and Weser Rivers, Germany | Siemers et al. [47] | 16 | 10.0–40.0 | - |
| Danube River, Hungary | Nagy et al. [57] | 16 | 25.0–1208.0 | 122.6 |
| Tiber River, Italy | Patrolecco et al. [48] | 6 | 23.9–72.0 | 43.4 |
| Tiber River, Italy | Montuori et al. [34] | 17 | 1.75–607.48 | 90.46 |
| Sarno River, Italy | Montuori and Triassi [26] | 17 | 12.4–2321.1 | 739 |
| Xijiang River, China | Deng et al. [43] | 15 | 1.4–58.1 | 29.8 |
| Yellow River, China | Li et al. [44] | 13 | 54.0–155.0* | - |
| Daliao River, China | Guo et al. [49] | 18 | 151.0–28,483.8 | - |
| Henan Reach of Yellow River, China | Sun et al. [56] | 16 | 506.6–10,510.0* | 4100.0 * |
| Songhua River, China | Ma et al. [45] | 15 | 9.21–83.1 | 26.4 |
| Yellow River, China | Zhao et al. [50] | 16 | 1502.0–11,562.0* | 5591.0 * |
| Daliao River estuary, China | Zheng et al. [52] | 16 | 1969.9–11,612.2 | 4015.7 |
| Tiber River, Italy | Patrolecco et al. [48] | 6 | 37.6–353.0 | |
| Tiber River, Italy | Montuori et al. [34] | 17 | 4.53–473.39 | 111.51 |
| Sarno River, Italy | Montuori and Triassi [26] | 17 | 6.1–778.9 | - |
| Yellow River, China | Li et al. [44] | 13 | 31.0–133.0 | 76.8 |
| Daliao River, China | Guo et al. [49] | 18 | 102.9–3419.2 | - |
| Henan Reach of Yellow River, China | Sun et al. [56] | 16 | 16.4–1358.0 | 182.0 |
| Yellow River, China | Zhao et al. [50] | 16 | 181.0–1583.0 | 810.0 |
| Erjien River, Taiwan | Wang et al. [60] | 16 | 22.0–28,622.0 | 737.0 |
| East China Sea, China | Zhao et al. [61] | 16 | 57.5-364.5 | 166.2 |
| Yellow River Estuary, China | Liu et al. [62] | 15 | 89.5–208.0 | 140.5 |
| Tiber River, Italy | Minissi et al. [63] | 13 | 4.5–652.2 | - |
| Cocó and Ceará Rivers, Brazil | Cavalcante et al. [64] | 17 | 3.0–2234.8 | - |
| Cauca River, Colombia | Sarria-Villa et al. [8] | 12 | ND-3739.0 | 1028.0 |
| Buffalo River Estuary, South Africa | Adeniji et al. [55] | 16 | ND-7792 | - |
| Ammer River, Germany | Liu et al. [9] | 16 | 112.0–22,900.0 | 8770.0 |
| Danube River, Hungary | Nagy et al. [57] | 16 | 8.3–1202.5 | 170.0 |
| Huveaune River, France | Kanzari et al. [65] | 16 | 571.7–4234.9 | 1966.00 |
| Durance River, France | Kanzari et al. [66] | 16 | 57.0–1528.0 | - |
| Ría de Arousa, Spain | Peréz-Fernández et al. [6] | 35 | 45.0–7901.0 | - |
| Tiber River, Italy | Patrolecco et al. [48] | 6 | 157.8–271.6 | 215.2 |
| Tiber River, Italy | Montuori et al. [34] | 17 | 36.21–545.60 | 155.26 |
| Sarno River, Italy | Montuori and Triassi [26] | 17 | 5.5–678.6 | 266.9 |
| This study | DP | 17 | 64.3–1429.1 | 602.6 ± 319.3 |
| SPM | 143.3–444.9 | 264.7 ± 83.3 | ||
| Sediment | 434.8–872.1 | 659.1 ± 136.9 | ||
| − High Pollution + | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPM Specific Composite Indicator | 07-apr | 10-apr | 06-apr | 05-apr | 09-feb | 06-feb | 02-feb | 01-apr | 09-apr | 05-feb | 08-apr | 08-feb | 01-feb | |
| DP Specific Composite Indicator | 10-apr | 09-apr | 05-apr | 01-apr | 07-jul | 02-jul | 10-jul | 08-apr | 06-jul | 05-jul | 09-jul | 01-jul | 08-jul | |
| WP Composite Indicator | 07-apr | 09-jul | 06-apr | 01-jul | 10-apr | 05-feb | 08-jul | 05-apr | 08-feb | 01-feb | 01-apr | 09-apr | 08-apr | |
| − Medium Pollution + | ||||||||||||||
| SPM Specific Composite Indicator | 02-jul | 05-jul | 08-nov | 05-nov | 01-nov | 02-apr | 03-apr | 06-jul | 09-jul | 01-jul | 08-jul | 03-feb | 10-feb | 07-feb |
| DP Specific Composite Indicator | 10-nov | 06-nov | 08-feb | 01-feb | 02-nov | 09-nov | 04-jul | 05-nov | 02-apr | 06-apr | 07-apr | 03-jul | 08-nov | 01-nov |
| WP Composite Indicator | 03-feb | 05-nov | 10-feb | 07-feb | 10-jul | 08-nov | 02-apr | 02-jul | 01-nov | 05-jul | 09-feb | 02-feb | 06-feb | 06-jul |
| − Low Pollution + | ||||||||||||||
| SPM Specific Composite Indicator | 04-jul | 04-nov | 03-nov | 07-nov | 10-nov | 03-jul | 07-jul | 04-apr | 04-feb | 02-nov | 09-nov | 10-jul | 06-nov | |
| DP Specific Composite Indicator | 04-feb | 03-feb | 07-feb | 04-nov | 10-feb | 02-feb | 04-apr | 09-feb | 06-feb | 03-nov | 07-nov | 03-apr | 05-feb | |
| WP Composite Indicator | 04-nov | 03-nov | 07-nov | 04-feb | 04-jul | 04-apr | 10-nov | 03-jul | 02-nov | 09-nov | 06-nov | 07-jul | 03-apr | |
| PAHs | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nap | Acy | Ace | Flu | Phe | An | Fl | Pyr | BaA | Chr | BbF | BkF | BaP | DahA | BghiP | InP | ∑PAHs | |
| TEL a | 34.6 | 5.87 | 6.71 | 21.2 | 86.7 | 46.9 | 113 | 153 | 74.8 | 108 | - | - | 88.8 | 6.22 | - | - | 1684 |
| Samples percentage over the TEL | 30 | 100 | 100 | 30 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 80 | 100 | 0 | ||||
| PEL a | 391 | 128 | 88.9 | 144 | 544 | 245 | 1494 | 1398 | 693 | 846 | - | - | 763 | 135 | - | - | 16,770 |
| Samples percentage over the PEL | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | ||||
| ERL a | 160 | 44 | 16 | 19 | 240 | 85 | 600 | 665 | 261 | 384 | - | - | 430 | 63.4 | - | - | 4022 |
| Samples percentage over the ERL | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | ||||
| ERM a | 2100 | 640 | 500 | 540 | 1500 | 1100 | 5100 | 2600 | 1600 | 2800 | - | - | 1600 | 260 | - | - | 44,792 |
| Samples percentage over the ERM | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montuori, P.; De Rosa, E.; Di Duca, F.; Provvisiero, D.P.; Sarnacchiaro, P.; Nardone, A.; Triassi, M. Estimation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Pollution in Mediterranean Sea from Volturno River, Southern Italy: Distribution, Risk Assessment and Loads. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18041383
Montuori P, De Rosa E, Di Duca F, Provvisiero DP, Sarnacchiaro P, Nardone A, Triassi M. Estimation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Pollution in Mediterranean Sea from Volturno River, Southern Italy: Distribution, Risk Assessment and Loads. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(4):1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18041383
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontuori, Paolo, Elvira De Rosa, Fabiana Di Duca, Donatella Paola Provvisiero, Pasquale Sarnacchiaro, Antonio Nardone, and Maria Triassi. 2021. "Estimation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Pollution in Mediterranean Sea from Volturno River, Southern Italy: Distribution, Risk Assessment and Loads" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 4: 1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18041383
APA StyleMontuori, P., De Rosa, E., Di Duca, F., Provvisiero, D. P., Sarnacchiaro, P., Nardone, A., & Triassi, M. (2021). Estimation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Pollution in Mediterranean Sea from Volturno River, Southern Italy: Distribution, Risk Assessment and Loads. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(4), 1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18041383








