The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Vulnerable People Suffering from Depression: Two Studies on Adults in France
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study 1
2.1. Materials and Methods
2.1.1. Participants
2.1.2. Procedure
2.1.3. Statistical Analyses
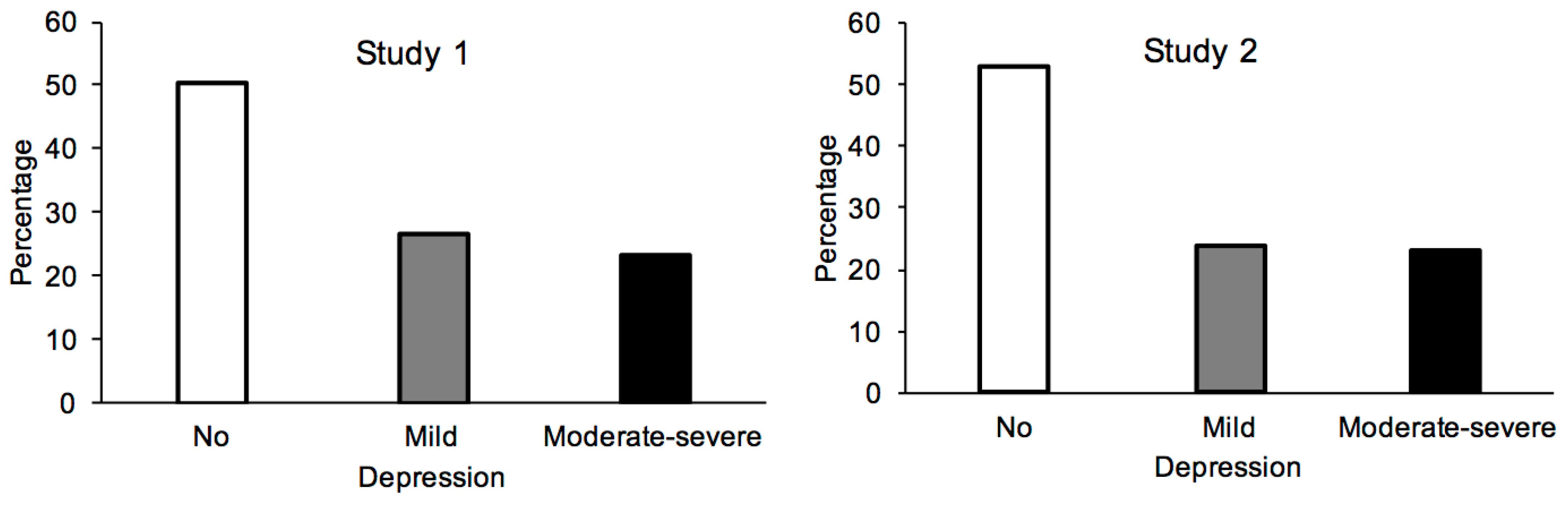
2.2. Results
3. Study 2
3.1. Methods
3.2. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Worth Health Organization. The World Health Report 2001, Mental Health: New Understanding, New Hope; WHO library: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Salari, N.; Hosseinian-Far, A.; Jalali, R.; Vaisi-Raygani, A.; Rasoulpoor, S.; Mohammadi, M.; Rasoulpoor, S.; Khaledi-Paveh, B. Prevalence of stress, anxiety, depression among the general population during the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Glob. Health 2020, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno-Notivol, J.; Gracia-García, P.; Olaya, B.; Lasheras, I.; López-Antón, R.; Santabárbara, J. Prevalence of depression during the COVID-19 outbreak: A meta-analysis of community-based studies. Int. J. Clin. Health Psychol. 2020, 21, 100196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’ Connor, R.; Wetherall, K.; Cleare, S.; McClelland, H.; Melson, A.; Niedzwiedz, C.; O’Carroll, R.; O’Connor, D.; Platt, S.; Scowcroft, E.; et al. Mental health and well-being during the COVID-19 pandemic: Longitudinal analyses of adults in the UK. Br. J. Psychiatry 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droit-Volet, S.; Gil, S.; Martinelli, N.; Andant, N.; Clinchamps, M.; Parreira, L.; Rouffiac, K.; Dambrun, M.; Huguet, P.; Dubuis, B.; et al. Time and Covid-19 stress in the lockdown situation: Time Free, Dying of Boredom and Sadness. PLoS ONE 2020, 5, e0236465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Pan, R.; Wan, X.; Tan, Y.; Xu, L.; McIntyre, R.; Choo, F.; Tran, B.; Ho, R.; Sharma, V.; et al. A longitudinal study on the mental health of general population during the COVID-19 epidemic in China. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 87, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazza, C.; Ricci, E.; Biondi, S.; Colasanti, M.; Ferracuti, S.; Napoli, C.; Roma, P. A nationwide survey of psychological distress among italian people during the COVID-19 pandemic: Immediate psychological responses and associated factors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, S.; Webster, R.; Smith, L.; Woodland, L.; Wessely, S.; Greenberg, N.; Rubin, G.J. The psychological impact of quarantine and how to reduce it: Rapid review of the evidence. Lancet 2020, 395, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawryluck, L.; Gold, W.L.; Robinson, S.; Pogorski, S.; Galea, S.; Styra, R. SARS control and psychological effects of quarantine, Toronto. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 354–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, R.S. The passage of time during the UK Covid-19 lockdown. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehm, J.; Kilian, C.; Ferreira-Borges, C.; Jernigan, D.; Monteiro, M.; Parry, C.D.H.; Sanchez, Z.M.; Manthey, J. Alcohol use in times of the COVID 19: Implications for monitoring and policy. Drug Alcohol Rev. 2020, 39, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.U.; Majid, A.; Judge, R.; Crook, P.; Nathwani, R.; Selvapatt, N.; Lovendoski, J.; Manousou, P.; Thursz, M.; Dhar, A.; et al. Effect of COVID-19 lockdown on alcohol consumption in patients with pre-existing alcohol use disorder. Lancet 2020, 5, 886–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballenger, J.C.; Davidson, J.R.T.; Lecrubier, Y.; Nutt, D.J.; Borkovec, T.D.; Rickels, K.; Stein, D.J.; Wittchen, H.U. Consensus statement on generalized anxiety disorder from the International Consensus Group on Depression and Anxiety. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2001, 62, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Santini, Z.I.; Koyanagi, A.; Tyrovolas, S.; Mason, C.; Haro, J.M. The association between social relationships and depression: A systematic review. J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 175, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivertsen, B.; Salo, P.; Mykletun, A.; Hysing, M.; Pallesen, S.; Krokstad, S.; Nordhus, I.H.; Overland, S. The Bidirectional Association Between Depression and Insomnia. Psychosom. Med. 2012, 75, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rheenen, T.E.; Meyer, D.; Neill, E.; Phillipou, A.; Tan, E.J.; Toh, W.L.; Rossell, S. Mental health status of individuals with a mood-disorder during the COVID-19 pandemic in Australia: Initial results from the COLLATE project. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 275, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, A.T.; Ward, C.; Mendelson, M. Beck depression inventory (BDI). Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1961, 4, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, D.W. UCLA Loneliness Scale (Version 3): Reliability, validity, and factor structure. J. Pers. Assess. 1996, 26, 20–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery Rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fond, G.; Lancon, C.; Auquier, P.; Boyer, L. Prévalence de la dépression majeure en France en population générale et en populations spécifiques de 2000 à 2018: Une revue systématique de la littérature. La Presse Médicale 2019, 48, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipovic-Pierucci, A.; Samson, S.; Fagot, J.-P.; Fagot-Campagna, A. Estimating the prevalence of depression associated with healthcare use in France using administrative databases. BMC Psychiatry 2017, 17, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, G.Y.; Tam, W.W.; Lu, Y.; Ho, C.S.; Zhang, M.W.; Ho, R.C. Prevalence of depression in the community from 30 countries between 1994 and 2014. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özdin, S.; Bayrak Özdin, Ş. Levels and predictors of anxiety, depression and health anxiety during COVID-19 pandemic in Turkish society: The importance of gender. Int. J. Soc. Psychiatry 2020, 66, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirowsky, J.; Ross, C.E. Age and Depression. J. Health Soc. Behav. 1992, 33, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braunack-Mayer, A.; Tooher, R.; Collins, J.E.; Street, J.M.; Marshall, H. Understanding the school community’s response to school closures Canada during the H1N1 2009 influenza pandemic. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Bueno, R.; Calatayud, J.; Casaña, J.; Casajús, J.A.; Smith, L.; Tully, M.A.; Andersen, L.L.; López-Sanchez, G.F. COVID-19 Confinement and Health RiskBehaviors in Spain. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Bueno, R.; Calatayud, J.; Ezzatvar, Y.; Casajús, J.A.; Smith, L.; Andersen, L.L.; López-Sanchez, G.F. Association between current physical activity and current perceived anxiety and mood in the initial phase of COVID-19 Confinement. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.; Jacob, L.; Trott, M.; Yakkundi, A.; Butler, L.; Barnett, Y.; Armstrong, N.C.; McDermott, D.; Schuch, F.; Meyer, J.; et al. The association between sreen time and mental health during COVID-19: A corss sectional study. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 292, 113333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| No Depression | Mild Depression | Moderate-Severe Depression | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | Lockdown | Before | Lockdown | Before | Lockdown | |||||||
| M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | |
| Age | 45.68 | 15.67 | 40.31 | 15.81 | 32.98 | 13.30 | ||||||
| Education | 14.85 | 3.11 | 15.01 | 3.06 | 14.62 | 2.63 | ||||||
| poeple home | 2.71 | 1.27 | 2.67 | 1.24 | 2.79 | 1.30 | ||||||
| Living space (m2) | 108.15 | 57.39 | 104.33 | 57.2 | 97.82 | 60.53 | ||||||
| Affiliation | 0.88 | 0.62 | 1.08 | 0.68 | 0.92 | 0.57 | 1.11 | 0.596 | 1.07 | 0.74 | 1.30 | 0.80 |
| Compliance lockdown | 5.01 | 0.58 | 4.93 | 0.56 | 5.004 | 0.59 | ||||||
| Compliance gestures | 4.49 | 0.89 | 4.36 | 0.86 | 4.12 | 1.03 | ||||||
| Vulnerability perception | 1.61 | 0.96 | 1.68 | 0.99 | 1.81 | 1.09 | ||||||
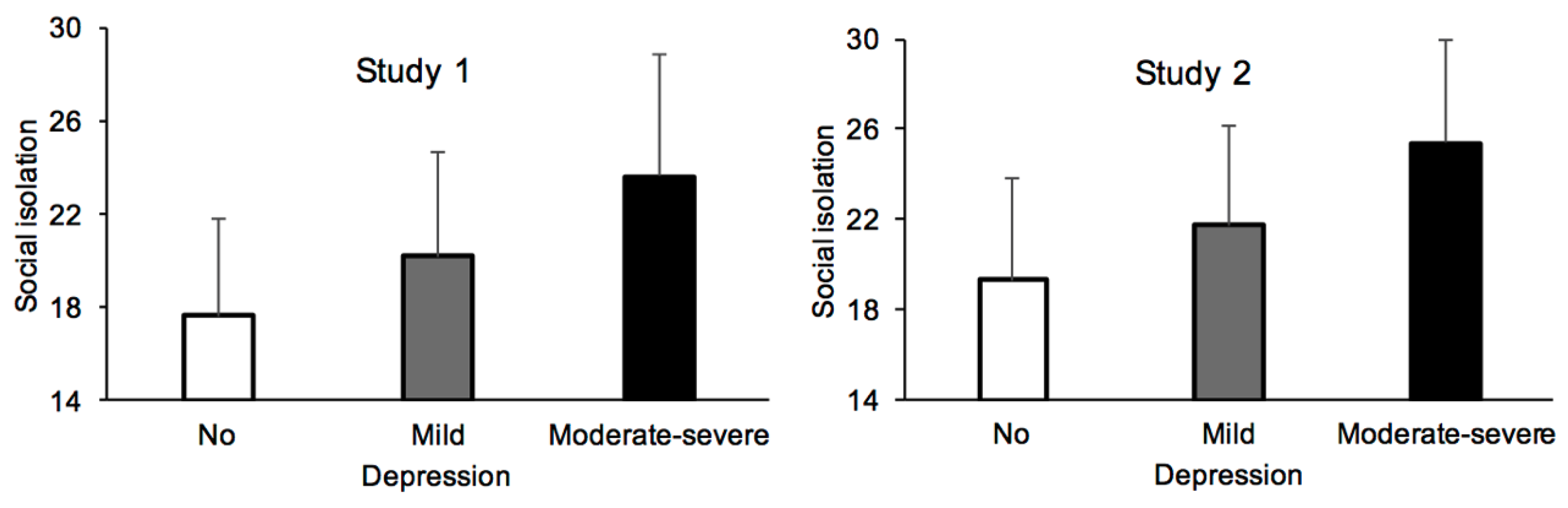
| Social isolation | 17.67 | 4.19 | 20.21 | 4.49 | 23.64 | 5.21 | ||||||
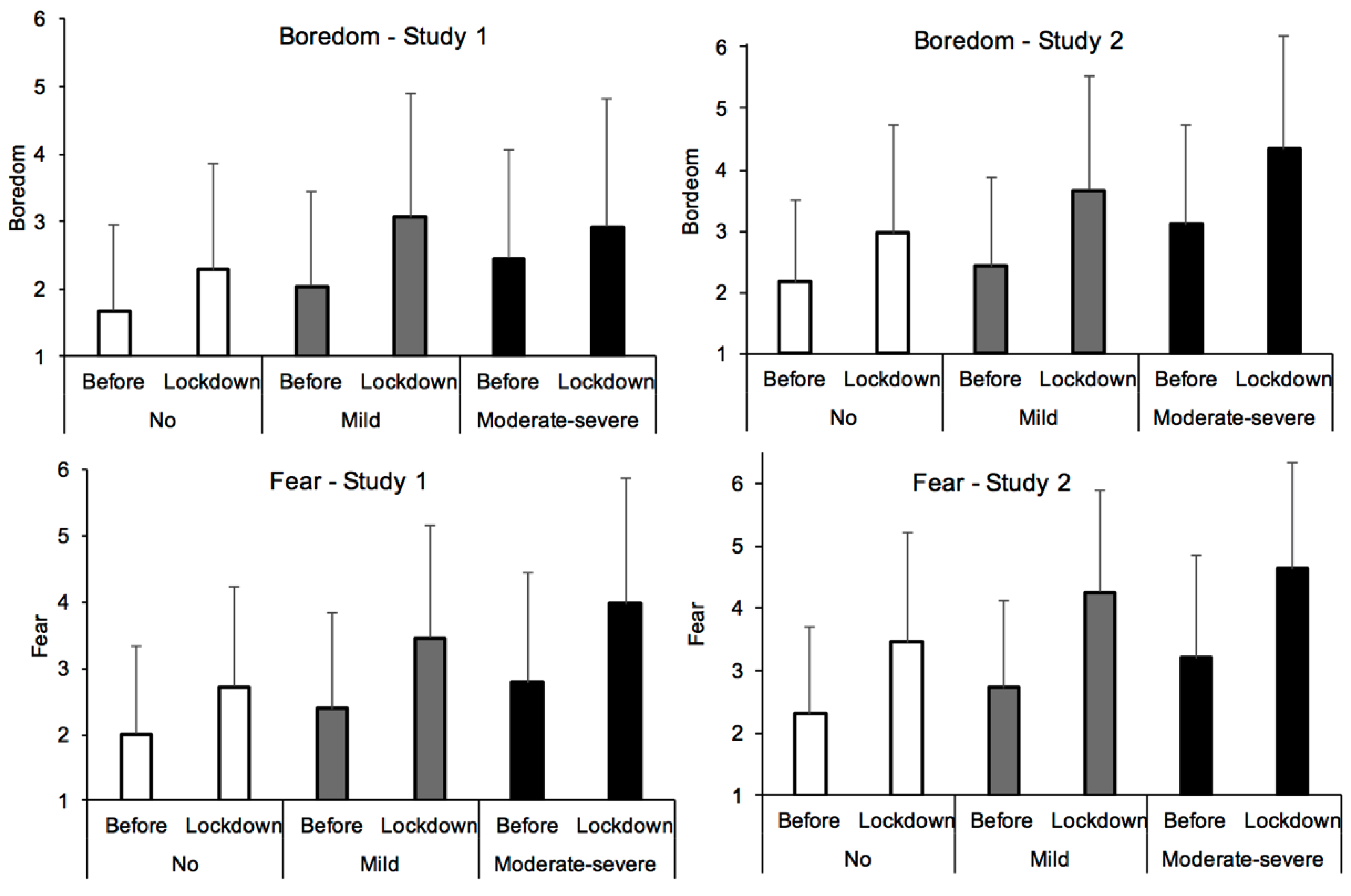
| Boredom | 1.68 | 1.28 | 2.29 | 1.56 | 2.04 | 1.41 | 3.07 | 1.81 | 2.45 | 1.61 | 4.14 | 2.03 |
| Anxiety | 2.56 | 1.60 | 2.76 | 1.55 | 3.35 | 1.71 | 3.71 | 1.68 | 4.25 | 1.79 | 4.90 | 1.77 |
| Happiness | 5.49 | 1.13 | 5.14 | 1.18 | 5.01 | 1.20 | 4.40 | 1.22 | 4.23 | 1.56 | 4.50 | 1.46 |
| Fear | 2.01 | 1.32 | 2.72 | 1.51 | 2.39 | 1.46 | 3.46 | 1.70 | 2.79 | 1.66 | 3.98 | 1.89 |
| Anger | 2.31 | 1.56 | 2.48 | 1.66 | 2.80 | 1.74 | 3.22 | 1.80 | 3.14 | 1.70 | 4.01 | 1.85 |
| Low-Arousal | 4.13 | 1.54 | 4.44 | 1.48 | 3.84 | 1.57 | 3.90 | 1.59 | 3.22 | 1.55 | 3.03 | 1.54 |
| Sleep | 5.11 | 1.65 | 5.02 | 1.61 | 4.80 | 1.64 | 4.32 | 1.78 | 4.26 | 1.84 | 3.48 | 1.90 |
| Life rhythm | 5.53 | 1.62 | 5.16 | 1.69 | 5.40 | 1.64 | 4.54 | 1.82 | 4.94 | 1.90 | 3.65 | 2.00 |
| Acohol | 1.11 | 0.75 | 0.96 | 0.79 | 1.13 | 0.78 | 0.93 | 0.80 | 1.23 | 0.85 | 0.97 | 0.96 |
| sleeping pills-anxiolytics | 0.08 | 0.30 | 0.06 | 0.24 | 0.12 | 0.32 | 0.09 | 0.30 | 0.26 | 0.51 | 0.25 | 0.56 |
| Coffee/tea | 1.41 | 0.63 | 1.30 | 0.67 | 1.40 | 0.71 | 1.34 | 0.72 | 1.30 | 0.70 | 1.20 | 0.80 |
| Cigarette | 0.26 | 0.54 | 0.25 | 0.53 | 0.31 | 0.57 | 0.26 | 0.56 | 0.47 | 0.68 | 0.29 | 0.58 |
| Stimulant | 0.06 | 0.32 | 0.03 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.41 | 0.06 | 0.31 |
| Other substances | 0.07 | 0.33 | 0.04 | 0.25 | 0.14 | 0.48 | 0.10 | 0.43 | 0.30 | 0.67 | 0.20 | 0.64 |
| Group Comparison | Dependent Variable | Cohen’s d | ddl | t | p | Rank | q a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study 1 | |||||||
| Mod-Sev vs. No | Boredom | 0.60 | 859 | 8.13 | <0.001 | 1 | =0.050 |
| Mod-Sev vs. No | Life rhythm | 0.48 | 859 | 6.56 | <0.001 | 2 | =0.043 |
| Mod-Sev vs. No | Sleep | 0.47 | 859 | 6.37 | <0.001 | 3 | =0.036 |
| Mod-Sev vs. No | Other substances | 0.47 | 859 | 6.37 | <0.001 | 4 | =0.029 |
| Mod-Sev vs. No | Compliant gestures | 0.40 | 814 | 5.24 | <0.001 | 5 | =0.021 |
| Mod-Sev vs. Mild | Boredom | 0.33 | 583 | 3.97 | <0.001 | 6 | =0.014 |
| Mild vs. No | Boredom | 0.25 | 902 | 3.59 | <0.001 | 7 | =0.007 |
| Study 2 | |||||||
| Mod-Sev vs. No | Sleep | 0.78 | 790 | 10.14 | <0.001 | 1 | =0.005 |
| Mod-Sev vs. No | Life rhythm | 0.58 | 790 | 7.46 | <0.001 | 2 | =0.01 |
| Mild vs. No | Sleep | 0.457 | 796 | 5.97 | <0.001 | 3 | =0.15 |
| Mod-Sev vs. No | Affiliation | 0.35 | 790 | 4.49 | <0.001 | 4 | =0.02 |
| Mod-Sev vs. Mild | Life rhythm | 0.38 | 486 | 4.21 | <0.001 | 5 | =0.025 |
| Mod-Sev vs. Mild | Sleep | 0.34 | 486 | 3.77 | <0.001 | 6 | =0.03 |
| Mod-Sev vs. No | Living space | 0.25 | 789 | 3.24 | =0.001 | 7 | =0.035 |
| Mod-Sev vs. Mild | Affiliation | 0.27 | 486 | 2.94 | =0.003 | 8 | =0.04 |
| Mod-Sev vs. No | Age | 0.22 | 790 | 2.84 | =0.004 | 9 | =0.045 |
| Mild vs. No | Life rhythm | 0.21 | 796 | 2.79 | =0.01 | 10 | =0.05 |
| No Depression | Mild Depression | Moderate-Severe Depression | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | Lockdown | Before | Lockdown | Before | Lockdown | |||||||
| M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | |
| Age | 46.62 | 15.03 | 46.65 | 15.36 | 43.38 | 13.92 | ||||||
| Education | 13.26 | 2.95 | 12.91 | 2.76 | 12.88 | 2.85 | ||||||
| poeple home | 2.64 | 1.21 | 2.64 | 1.21 | 2.50 | 1.23 | ||||||
| Living space (m2) | 102.10 | 48.55 | 95.83 | 46.12 | 90.29 | 43.86 | ||||||
| Affiliation | 1.00 | 0.88 | 0.96 | 0.83 | 1.08 | 0.89 | 1.00 | 0.81 | 1.35 | 1.30 | 1.29 | 1.25 |
| Compliance lockdown | 4.49 | 0.89 | 4.36 | 0.86 | 4.12 | 1.03 | ||||||
| Compliance gestures | 4.51 | 0.94 | 4.47 | 0.97 | 4.05 | 1.07 | ||||||
| Vulnerability perception | 1.43 | 0.97 | 1.51 | 1.00 | 1.95 | 1.23 | ||||||
| Social isolation | 19.32 | 4.54 | 21.73 | 4.44 | 25.40 | 4.55 | ||||||
| Boredom | 2.17 | 1.32 | 2.97 | 1.75 | 2.43 | 1.44 | 3.66 | 1.87 | 3.11 | 1.61 | 4.34 | 1.84 |
| Anxiety | 2.80 | 1.49 | 3.36 | 1.66 | 3.43 | 1.48 | 4.34 | 1.60 | 4.00 | 1.60 | 4.78 | 1.60 |
| Happiness | 5.30 | 1.12 | 4.67 | 1.31 | 4.86 | 1.09 | 3.85 | 1.29 | 4.28 | 1.41 | 3.15 | 1.48 |
| Fear | 2.31 | 1.38 | 3.46 | 1.75 | 2.72 | 1.40 | 4.26 | 1.61 | 3.21 | 1.64 | 4.63 | 1.71 |
| Anger | 2.45 | 1.39 | 3.13 | 1.78 | 2.90 | 1.43 | 3.74 | 1.76 | 3.39 | 1.58 | 4.30 | 1.75 |
| Low-Arousal | 4.54 | 1.35 | 4.24 | 1.45 | 4.09 | 1.36 | 3.48 | 1.43 | 3.69 | 1.44 | 3.20 | 1.59 |
| Sleep | 4.98 | 1.60 | 4.75 | 1.64 | 4.57 | 1.61 | 3.81 | 1.67 | 4.02 | 1.77 | 3.37 | 1.73 |
| Life rhythm | 5.37 | 1.49 | 4.91 | 1.65 | 5.34 | 1.41 | 4.38 | 1.71 | 4.85 | 1.59 | 3.87 | 1.81 |
| Acohol | 1.02 | 0.74 | 0.93 | 0.80 | 1.09 | 0.75 | 0.97 | 0.87 | 1.05 | 0.80 | 1.00 | 0.88 |
| sleeping pills-anxiolytics | 0.14 | 0.47 | 0.16 | 0.51 | 0.26 | 0.66 | 0.28 | 0.72 | 0.53 | 0.87 | 0.60 | 0.97 |
| Coffee/tea | 1.84 | 0.87 | 1.76 | 0.89 | 1.78 | 0.79 | 1.79 | 0.86 | 1.85 | 0.94 | 1.84 | 1.00 |
| Cigarette | 0.47 | 0.90 | 0.47 | 0.92 | 0.45 | 0.90 | 0.45 | 0.92 | 0.80 | 1.07 | 0.79 | 1.13 |
| Stimulant | 0.09 | 0.37 | 0.09 | 0.40 | 0.13 | 0.42 | 0.11 | 0.41 | 0.30 | 0.67 | 0.28 | 0.69 |
| Other substances | 0.07 | 0.35 | 0.06 | 0.35 | 0.07 | 0.32 | 0.09 | 0.41 | 0.19 | 0.55 | 0.22 | 0.65 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martinelli, N.; Gil, S.; Chevalère, J.; Belletier, C.; Dezecache, G.; Huguet, P.; Droit-Volet, S. The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Vulnerable People Suffering from Depression: Two Studies on Adults in France. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3250. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18063250
Martinelli N, Gil S, Chevalère J, Belletier C, Dezecache G, Huguet P, Droit-Volet S. The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Vulnerable People Suffering from Depression: Two Studies on Adults in France. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(6):3250. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18063250
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartinelli, Natalia, Sandrine Gil, Johann Chevalère, Clément Belletier, Guillaume Dezecache, Pascal Huguet, and Sylvie Droit-Volet. 2021. "The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Vulnerable People Suffering from Depression: Two Studies on Adults in France" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 6: 3250. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18063250
APA StyleMartinelli, N., Gil, S., Chevalère, J., Belletier, C., Dezecache, G., Huguet, P., & Droit-Volet, S. (2021). The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Vulnerable People Suffering from Depression: Two Studies on Adults in France. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(6), 3250. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18063250






