Consumer Acceptance of Gene-Edited versus Genetically Modified Foods in Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Methods
4. Materials
4.1. Survey Overview
4.2. General Characteristics of the Respondents
5. Results
5.1. Part-Worth by an Attribute Level
5.2. Relative Importance by Attribute
5.3. Marginal Willingness to Pay by an Attribute Level
5.4. MWTP Variation Range for the Production Technology by Respondents’ Characteristics
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Association for the Advancement of Science. Statement by the AAAS Board of Directors on Labeling of Genetically Modified Foods. 20 October 2012. Available online: https://www.aaas.org/news/statement-aaas-board-directors-labeling-genetically-modified-foods (accessed on 20 March 2020).
- Shew, A.M.; Danforth, D.M.; Nalley, L.L.; Nayga, R.M.; Tsiboe, F.; Dixon, B.L. New Innovations in Agricultural Biotech: Consumer Acceptance of Topical RNAi in Rice Production. Food Control. 2017, 81, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shew, A.M.; Nalley, L.L.; Snell, H.A.; Nayga, R.M.; Dixon, B.L. CRISPR Versus GMOs: Public Acceptance and Valuation. Glob. Food Sec. 2018, 19, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Biosafety Clearing House. 2018 Major Statistics for Living Modified Organisms; KBCH: Daejeon, Korea, 2019; Available online: https://www.biosafety.or.kr/portal/index.do?pageid=f_08&bbscttPid=1372&bbsPid=5&totalCnt=&searchCode=A&searchText=&bbsPid=5&pageSize=15&pageNumber=1& (accessed on 20 March 2020).
- Ishii, T.; Araki, M. Consumer Acceptance of Food Crops Developed by Genome Editing. Plant Cell Rep. 2016, 35, 1507–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoph, I.B.; Roosen, J.; Bruhn, M. Willingness to Pay for Genetically Modified Food and Non-Food Products. In Proceedings of the American Agricultural Economics Association Annual Meeting, Long Beach, CA, USA, 23–26 July 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berning, J.; Campbell, B. Consumer Preference and Market Simulations of Food and Non-Food GMO Introductions. In Proceedings of the Southern Agricultural Economics Association 2017 Annual Meeting, Mobile, AL, USA, 4–7 February 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousu, M.; Hffian, W.E.; Shogren, J.F.; Tegene, A. Should the United States Regulate Mandatory Labeling for Genetically Modified Foods? Evidence from Experimental Auctions. In Economics Working Papers; Iowa State University: Ames, IA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhr, B.L.; Hayes, D.J.; Shogren, J.F.; Kliebenstein, J.B. Valuing Ambiguity: The Case of Genetically Engineered Growth Enhancers. J. Agric. Resour. Econ. 1995, 18, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccaletti, S.; Moro, D. Consumer Willingness-to-Pay for GM Food Products in Italy. Agrofórum 2000, 3, 259–267. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10355/377 (accessed on 20 March 2020).
- Baker, G.A.; Burnham, T.A. Consumer Response to Genetically Modified Foods: Market Segment Analysis and Implications for Producers and Policy Makers. J. Agric. Resour. Econ. 2001, 26, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chern, W.S.; Rickertsen, K.; Tsuboi, N.; Fu, T. Consumer Acceptance and Willingness to Pay for Genetically Modified Vegetable Oil and Salmon: A Multiple-Country Assessment. Ag. BioForum. 2003, 5, 105–112. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10355/303 (accessed on 20 March 2020).
- Kwon, O.S. Estimating the Willingness to Pay for the Non-GMO Agricultural Products: A Contingent Valuation Study. Korean J. Agric. Econ. 2003, 44, 111–131. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, O.S.; Kim, G.C. Valuing GMO and Non-GMO Agricultural Products and Experimental Auction Markets. Korean J. Agric. Econ. 2003, 44, 101–119. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Curtis, K.R.; McCluskey, J.J.; Wahl, T.I. Consumer Attitudes toward Genetically Modified Foods in Beijing, China. AgBioForum 2003, 5, 145–152. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/235912725_Consumer_attitudes_toward_genetically_modified_foods_in_Beijing_China (accessed on 20 March 2020).
- Lusk, J.L. Effect of Cheap Talk on Consumer Willingness-to-Pay for Golden Rice. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2003, 85, 840–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusk, J.L.; Fox, J.A. Value Elicitation in Retail and Laboratory Environments. Econ. Lett. 2003, 79, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J. Consumer Acceptance and Willingness to Pay for Genetically Modified Rice in China: A Double Bounded Dichotomous Choice Contingent Valuation Survey Calibrated by Cheap Talk. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Arkansas, Fayetteville, AR, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmond, A.R.; McCluskey, J.J.; Yormirzoev, M.; Rogova, M.A. Russian Consumer Willingness to Pay for Genetically Modified Food. Food Policy 2018, 78, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Ribaya, B.; Areal, F.J. Is There an Opportunity for Product Differentiation between GM and non-GM Soya-Based Products in Argentina? Food Control. 2020, 109, 106895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusk, J.L.; House, L.O.; Valli, C.; Jaeger, S.R.; Moore, M.; Morrow, B.; Traill, W.B. Effect of Information About Benefits of Biotechnology on Consumer Acceptance of Genetically Modified Food: Evidence from Experimental Auctions in the United States, England, and France. Eur. Rev. Agric. Econ. 2004, 31, 179–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusk, J.L.; Jamal, M.; Kurlander, L.; Roucan, M.; Taulman, L. A Meta-Analysis of Genetically Modified Food Valuation Studies. J. Agric. Resour. Econ. 2005, 30, 28–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciriacy-Wantrup, S.V. Capital Returns from Soil-Conservation Practices. J. Farm Econ. 1947, 29, 1181–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, P.E.; Srinivasan, V. Conjoint Analysis in Consumer Research: Issues and Outlook. J. Con. Res. 1978, 5, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohm, P. Estimating Demand for Public Goods: An Experiment. Eur. Econ. Rev. 1972, 3, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lancaster, K.J. A New Approach to Consumer Theory. J. Pol. Econ. 1966, 74, 132–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadden, D. The Choice Theory Approach to Market Research. Mark. Sci. 1986, 5, 275–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voca Moran, F.F. Application of Choice-Based Conjoint Analysis to Determine Consumers’ Preferences and Willingness to Pay for Grass Fed Beef in The United States. Ph.D. Thesis, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2014. Available online: https://digitalcommons.lsu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=2685&context=gradschool_dissertations (accessed on 20 March 2020).
- Rao, V.R. Applied Conjoint Analysis, 2014th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 127–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujarati, D.N.; Porter, D.C. Basic Econometrics of Gujarati, 5th ed.; Park, W.G., Hong, S.P., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 650–675. [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen, B.; Goos, P.; Vandebroek, M. Models and Optimal Designs for Conjoint Choice Experiments Including a No-Choice Option. Int. J. Res. Mark. 2008, 25, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausman, J.; McFadden, D. Specification Tests for the Multinomial Logit Model. Econometrica 1984, 52, 1219–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eggers, F.; Sattler, H.; Teichert, T.; Völckner, F. Choice-Based Conjoint Analysis; Handbook of Market Research; Homburg, C., Klarmann, M., Vomberg, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navrud, S.; Bråten, K.G. Consumers’ Preferences for Green and Brown Electricity: A Choice Modeling Approach. Rev. Econ. Politiqe 2007, 117, 795–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadden, D. Conditional Logit Analysis of Qualitative Choice Behavior. In Frontiers in Econometrics; Zarembka, P., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1974; pp. 105–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, R. A Discrete Choice Experiment to Estimate Willingness to Pay for a Microfinance Product in Urban Romania. Master’s Thesis, Wageningen University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2015. Available online: https://edepot.wur.nl/348738 (accessed on 20 March 2020).
- Halbrendt, C.K.; Wirth, I.W.; Waughn, G.F. Conjoint Analysis of the Mid-Atlantic Food-Fish Market for Farm-Raised Hybrid Striped Bass. South. J. Agric. Econ. 1991, 23, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, J.H.; Kim, B.S.; Joo, H.J. GMO Production and Distribution Status Analysis and GMO Labeling Cost/Benefit Analysis Research; Korea Rural Economic Institute: Naju, Korea, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. Labeling Standards for Genetically-Modified Foods, etc.; MFDS: Osong, Korea, 2017. Available online: https://members.wto.org/crnattachments/2018/TBT/KOR/18_4348_00_e.pdf (accessed on 2 March 2020).
- IDRE Stats-Statistical Consulting Web Resources. Available online: https://stats.idre.ucla.edu (accessed on 2 March 2020).
- Stanton, J.; Wirth, F.F.; Dao, Y. An Analysis of Consumers’ Preferences Between Locally Grown/Processed Food and Organic Food. Curr. Investig. Agric. Curr. Res. 2018, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manalo, A.B. Assessing the Importance of Apple Attributes: An Agricultural Application of Conjoint Analysis. Northeast. J. Agric. Resour. Econ. 1990, 19, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, W.S.; Lee, J.S.; Park, D.S. Local Food Movement and the Development of Food Service Industries. Korean Hosp. Tour. Acad. 2012, 21, 329–343. Available online: http://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiqoM2695_vAhWKd94KHUT1AJ8QFjABegQIAhAD&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.khta.re.kr%2Fdesign%2Fupload_file%2FBD1001%2F15c380e28e7a86179b3791c6430dc478_1868_1.pdf&usg=AOvVaw11-pACY3gV-_FTa2rzxCNJ (accessed on 20 March 2020).
- Yang, S.B. Analyzing the Relative Value of Food Labelling on Organic and Origin of Tofu. Korean J. Org. Agric. 2014, 22, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, C.H. EU, Overview of Agricultural Product Quality Policy and Geographic Labeling System; World Agricltural News; Korea Rural Economic Institute: Naju, Korea, 2007; Available online: https://repository.krei.re.kr/bitstream/2018.oak/18674/1/EU,%20%EB%86%8D%EC%82%B0%EB%AC%BC%ED%92%88%EC%A7%88%EC%A0%95%EC%B1%85%EA%B3%BC%20%EC%A7%80%EB%A6%AC%EC%A0%81%ED%91%9C%EC%8B%9C%EC%A0%9C%20%EA%B0%9C%EC%9A%94.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2020).
- Miles, S.; Hafner, C.; Bolhaar, S.; Mancebo, E.G.; Fernández-Rivas, M.; Knulst, A.; Hoffmann-Sommergruber, K. Attitudes Towards Genetically Modified Food with a Specific Consumer Benefit in Food Allergic Consumers and Non-Food Allergic Consumers. J. Risk Res. 2006, 9, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenbült, P.; de Vries, N.K.; Dreezens, E.; Martijn, C. Perceived Naturalness and Acceptance of Genetically Modified Food. Appetite 2005, 45, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Compared to | Study | Product | Country | Valuation Method | Price Premium for Non-GM (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GM 2 | Buhr, Hayes, Shogren, and Kliebenstein [9] | Pork sandwich | US | Auction | −15.44 | |
| Boccaletti and Moro [10] | Food | Italy | CVM 1 | 1.06 | ||
| Baker and Burnham [11] | Cornflakes | US | Conjoint (ranking) | 39.84 | ||
| Chern, Rickertsen, Tsuboi, and Fu [12] | Vegetable oil | US Norway Japan Taiwan | Conjoint (choice) | 56.00 62.00 36.50 19.00 | ||
| Kwon [13] | Tofu | Korea | CVM | 44.7~136 | ||
| Kwon and Kim [14] | Chocolate bar | Korea | Auction | 104.00 (student) 356.00 (housewife) | ||
| Li, Curtis, McCluskey, and Wahl [15] | Rice Soybean oil | China | CVM | −38.00 −16.30 | ||
| Lusk [16] | Golden rice | US | CVM | −19.54 | ||
| Lusk and Fox [17] | Beefsteak | US UK Germany France | Conjoint (choice) | 38.94 74.24 90.24 109.65 | ||
| Rousu, Hffian, Shogren, and Tegene [8] | Vegetable oil Corn chips Potato | US | Auction | 5.26 10.29 12.00 | ||
| Lusk, House, Valli, Jaeger, Moore, Morrow, and Traill [21] | Cookie | TX, US CA, US FL, US England France | Auction | 40.00 80.00 20.00 160.00 784.00 | ||
| Christoph, Roosen, and Bruhn [6] | French fries Potato paper | Germany | Conjoint (choice) | 106.32 3 91.23 4 −83.22 3 −1.00 4 | ||
| Jin [18] | Rice | China | CVM | 89.00 | ||
| Berning and Campbell [7] | Fresh tomato Tomato plants Geraniums Turf | US | Conjoint (ranking) | - | ||
| Delmond, McCluskey, Yormirzoev, and Rogova [19] | Bread | Russia | Conjoint (choice) | 197.00 | ||
| Martinez-Ribaya and Areal [20] | Soya-based product | Argentina | CVM | 50.00 | ||
| RNAi 5, GM | Shew, Danforth, Nalley, Nayga, Tsiboe, and Dixon [2] | Rice | US Canada Belgium France Australia | Field experiment | RNAi | GM |
| 152.40 87.60 - 98.40 84.80 | 251.20 179.40 173.20 267.00 159.00 | |||||
| GE 6, GM | Shew, Nalley, Snell, Nayga, and Dixon [3] | Rice | US Canada Belgium France Australia | Field experiment | GE | GM |
| 91.60 23.40 31.80 42.40 44.80 | 96.00 18.40 32.00 42.00 44.20 | |||||
| Description | N | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 100 | 50 |
| Female | 100 | 50 | |
| Age | 20 to 29 | 50 | 25 |
| 30 to 39 | 50 | 25 | |
| 40 to 49 | 50 | 25 | |
| 50 to 59 | 50 | 25 | |
| Final education level | High school graduation | 31 | 16 |
| University attending or graduation | 155 | 77 | |
| Graduate school or higher | 14 | 7 | |
| Attribute | Attribute Level | |
|---|---|---|
| Origin of raw material | Korea | |
| US | ||
| China | ||
| Production technology | Non-GM | |
| GM | ||
| GE | ||
| Product price | Soybean oil (900 mL) | $2.5 (3000 won), $2.9 (3500 won), $3.3 (4000 won), $3.7 (4500 won), $4.1 (5000 won) |
| Cotton t-shirt (a specific SPA brand) | $4.2 (5000 won), $6.3 (7500 won), $8.4 (10,000 won), $10.5 (12,500 won), $12.6 (15,000 won) | |
| Alternative 1 | Alternative 2 | Alternative 3 |
|---|---|---|
 |  | No choice |
| (√) | ( ) | ( ) |
| Awareness | Yes | No | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Have you ever heard of GM technology? | 169 persons (85%) | 31 persons (15%) | ||
| Have you ever heard of GE technology? | 90 persons (45%) | 110 persons (55%) | ||
| Scientific Knowledge Level | Yes | No | Correct Answer | |
| Can a person’s genes change by eating GM soybeans? | 99 persons (59%) | 70 persons (41%) | No | |
| Are GM genes (DNA) left in a soybean oil made by heat-treating GM soybeans? | 120 persons (71%) | 49 persons (29%) | No | |
| Technology Safety | Both Are Safe | GE Is Safer | GM Is Safer | Both Are Unsafe |
| What do you think about the safety of GM and GE technology? | 26 persons (13%) | 103 persons (51%) | 14 persons (7%) | 57 persons (29%) |
| Sensitivity to Food Safety | Very Much So | Somewhat | Hardly | Not at all |
| Do you mainly buy foods made from organic/eco-friendly raw materials? | 21 persons (11%) | 97 persons (48%) | 75 persons (37%) | 7 persons (4%) |
| Other | Yes | No | I Do Not Know | Correct Answer |
| Among the domestic large food brands, is there a soybean oil made from domestic non-GM soybeans? | 69 persons (35%) | 36 persons (18%) | 95 persons (48%) | No |
| Attribute | Level | Part-Worth | Model 1 | Model 2 | Reference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soybean Oil | Cotton t-Shirt | Soybean Oil | Cotton t-Shirt | |||||
| Origin of raw material | Korea | 1.4719 *** (0.1139) | 0.9773 *** (0.1040) | 1.2924 *** (0.0966) | 0.9347 *** (0.0955) | China | ||
| US | 0.3838 *** (0.1005) | 0.2844 *** (0.0862) | 0.4090 *** (0.1162) | −0.0965 (0.0758) | ||||
| Production technology | GM | −1.3376 *** (0.0955) | −0.5866 *** (0.0872) | −1.0684 *** (0.0882) | −0.1620 * (0.0899) | non-GM | ||
| GE | −1.0907 *** (0.0898) | −0.9198 *** (0.0829) | −0.8999 *** (0.0952) | −0.8715 *** (0.0857) | ||||
| Product price | −0.00017 *** (0.00002) | −0.00005 *** (0.000007) | −0.0958 (0.1029) | −0.1123 (0.0756) | $2.5 $4.2 | |||
| −0.3090 *** (0.1051) | −0.4168 *** (0.1128) | |||||||
| −0.3538 *** (0.0778) | −0.7606 *** (0.1057) | |||||||
| −0.4722 *** (0.0799) | −0.9849 *** (0.1075) | |||||||
| Log-likelihood | −3753.911 | −3934.698 | −3848.223 | −3937.283 | ||||
| Wald test (p-value) | 636.424 *** (0.0000) | 386.367 *** (0.0000) | 501.9547 *** (0.0000) | 376.8171 *** (0.0000) | ||||
| Attribute | Soybean Oil | Cotton t-Shirt | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Importance (%) | Range | Importance (%) | |
| Origin of raw material | 1.29 | 46 | 0.93 | 34 |
| Production technology | 1.06 | 37 | 0.87 | 31 |
| Product price | 0.47 | 17 | 0.98 | 35 |
| Total | 2.82 | 100 | 2.78 | 100 |
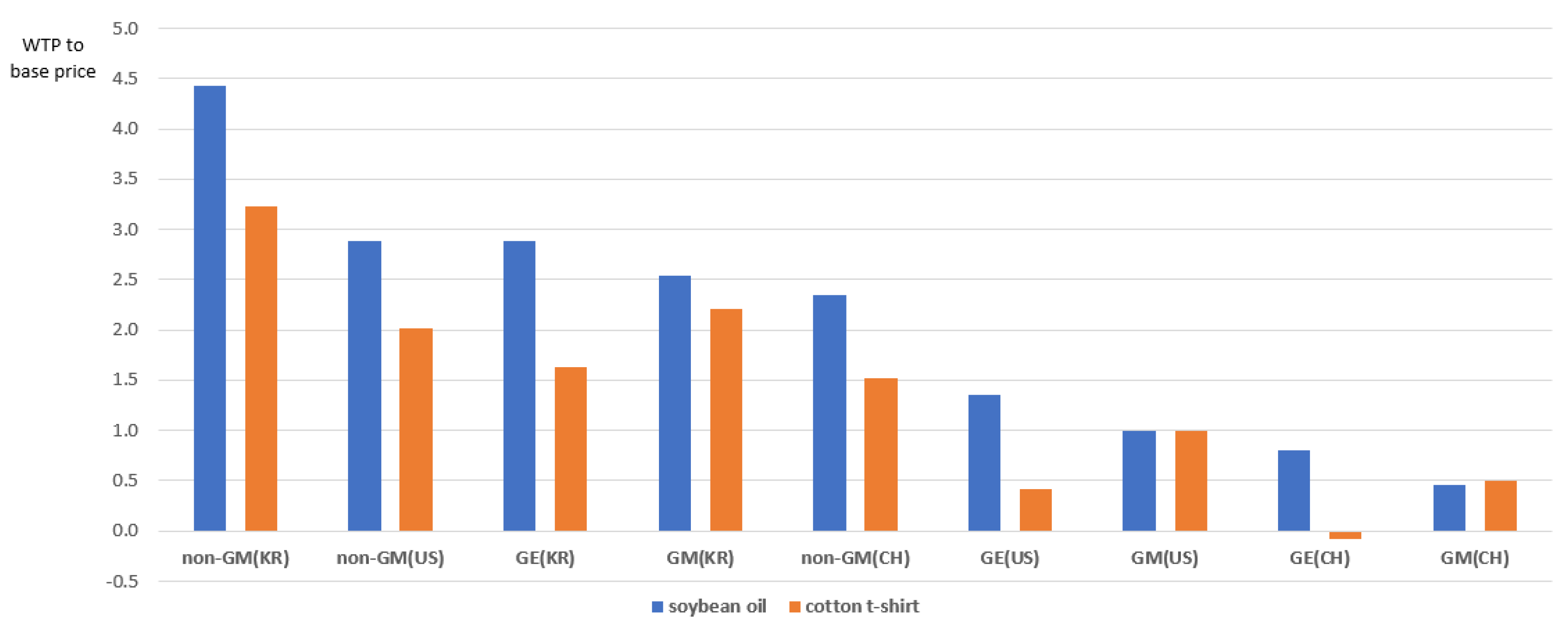
| Attribute | Level | MWTP (Won) | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soybean Oil (900 mL) | Cotton t-Shirt (A Specific SPA Brand) | |||
| Origin of raw material | Korea | 8315 *** (807) | 17,027 *** (1777) | China |
| US | 2168 ** (419) | 4956 *** (1231) | ||
| Production technology | GM | −7557 *** (1163) | −10,220 *** (2069) | Non-GM |
| GE | −6162 *** (1057) | −16,025 *** (2778) | ||
| Soybean Oil (900 mL) | Cotton t-Shirt (A Specific SPA Brand) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GM (Imported) | Non-GM (Korea) | Organic (Imported) | GM (Imported) | Non-GM (Korea) | Organic (Imported) | ||
| WTP | Choice-based conjoint analysis | - | 17,704 won | - | - | 32,291 won | - |
| 4.4 times | 3.2 times | ||||||
| CVM | - | 5500 won | - | - | 14,500 won | - | |
| 1.4 times | 1.5 times | ||||||
| Market price | 4000 won (base) | 32,000 won 1 | 11,000 won 2 | 10,000 won (base) | - | 20,000 won 3 | |
| 8 times | 2.8 times | 2 times | |||||
| Product | Production Technology | MWTP Variation Range (Won) | Reference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scientific Knowledge Level 1 | Sensitivity to Food Safety 2 | Sensitivity to Technology Safety 3 | Children’s Age 4 | |||
| Soybean oil | GM | 7594 | 3762 | 13,519 | 11,452 | Non-GM |
| GE | 1036 | 1645 | 6990 | 6131 | ||
| Cotton t-shirt | GM | 43,909 | 15,827 | - | - | |
| GE | 40,281 | 8711 | - | - | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Son, E.; Lim, S.S. Consumer Acceptance of Gene-Edited versus Genetically Modified Foods in Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3805. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18073805
Son E, Lim SS. Consumer Acceptance of Gene-Edited versus Genetically Modified Foods in Korea. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(7):3805. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18073805
Chicago/Turabian StyleSon, Eunae, and Song Soo Lim. 2021. "Consumer Acceptance of Gene-Edited versus Genetically Modified Foods in Korea" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 7: 3805. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18073805
APA StyleSon, E., & Lim, S. S. (2021). Consumer Acceptance of Gene-Edited versus Genetically Modified Foods in Korea. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(7), 3805. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18073805






